Abstract
Problem-oriented pedagogies have emerged as strategic way for universities to respond to an international higher education agenda that increasingly prioritises innovative, student-centred learning, and the cultivation of both civic and employability competences. Alongside this pedagogic shift is a policy-driven emphasis on monitoring teaching and learning for quality assurance purposes. This article aims to untangle the ways problem- and inquiry-based pedagogies are currently evaluated in universities, and thus consider how ‘quality’ implementation, and the effects of this suite of pedagogic approaches, might be better understood, practised, and measured. Taking a systematic approach to the review of the literature, the article maps evaluation methods that assess the effectiveness of problem-oriented and inquiry-based pedagogies implemented in university settings. The key findings include that evaluation methods in the field (i) prioritise qualification-related outcomes, (ii) are limited in scale and scope, and (iii) often function as demonstrations of performativity rather than as part of an ongoing improvement cycle. The article argues that evaluations that take a multi-method approach from the perspective of a range of stakeholders, with an exploration of civic and social competences in addition to employability outcomes, would significantly strengthen the field.
1. Introduction
Current policy for European universities emphasises innovation in learning and teaching, with a strong focus on quality assurance for continuous improvement. The Bologna Process is a central component of this policy reform agenda, which seeks to ensure European universities and colleges are competitive in an international market [1]. The European Commission states that there is a “strong need for flexible, innovative learning approaches and delivery methods to improve quality and relevance while expanding student numbers” [2]. The emphasis is on implementing an inclusive educational approach that develops competencies in critical thinking, creative processes and respectful collaboration, enabling students to become both economically independent and civically engaged [3]. These policies are responses to societal change, particularly informed by “unemployment and social inequality to migration-related issues and a rise in political polarisation, radicalisation and violent extremism” [4]. Higher education is positioned as part of the solution to these social complexities, with a ‘decisive’ role to play in improving economic and social conditions. This constitutes a unique opportunity to consider how university education can challenge students to “think about and engage with complex global issues and others in their world” [5] as they gain their employment qualification.
In this context, problem-oriented approaches to learning have emerged as an innovative pedagogic response, one that aligns with and enacts these policy priorities. Inquiry-centred pedagogies, including problem-, project-, and inquiry-based approaches, involve students in a collaborative investigation of complex issues or situations. While there exists a range of problem-based ‘constellations’, consisting of differing foci in relation to knowledge-development, learning emphasis, and facilitation method, all begin with a problematic scenario to facilitate learning and stimulate knowledge development (see, [6]). Problem-Based Learning (PBL) approaches begin from multidisciplinary, complex authentic problems and prioritise the construction of knowledge through active and collaborative student work in groups [7]. PBL reflects an understanding that knowledge is not stagnant, but rather “an activity, a process of finding out” [8] (original emphasis, p. 4). This makes it particularly suitable in the development of transferrable ‘21st Century’ skills [9], which include oral and written communication, critical thinking, self-management, teamwork skills, and innovation (see, [10]). At best, students are motivated to inquire actively into a problematic situation, resulting in an “academic experience where authentic learning environments assist students to develop employer-prized graduate capabilities, e.g. metacognition, networking, time management, collaborative skills” [11]. Due to these strengths, problem-based and inquiry approaches have strategic value in a current university climate that prioritises these outcomes.
Parallel to this, an ongoing focus on quality assurance emphasises the need to monitor teaching and learning, measure learning outcomes, and demonstrate performativity. Quality assurance practices meet the twin purposes of enhancement and accountability, and include all activities that contribute to continuous improvement cycles [12]. The logic of educational quality is increasingly inseparable from the logic of accountability [13], with a political prioritisation of measures of learning gain [14]. While logics of performativity, individualism, efficiency, and the market inform the interest in metrics to capture performance [13,15,16], it is questionable whether meaningful learning or teaching quality can be measured in this way [14] (p. 2). Peters [17] (p. 6) argues that “the system [of quantitative measures] has perverse effects not least on university faculty and students, skewing knowledge in favor of the calculable, the visible, and the viral.” Despite this, the appetite for measures and measurement continues to influence all stakeholders in education, shaping the practices of educators [15,16]. Within this context, teaching and learning research has become part of this measurement regime, an aspect of demonstrating both internal and external legitimacy and accountability.
Quality research into the effects of problem-oriented pedagogies has the potential to provide insight into the efficacy of the method. However, the majority of evaluations in the field focus on medicine and engineering disciplines, where the pedagogy is used extensively. This review therefore aimed to map how problem-oriented pedagogies in university and college settings are evaluated and measured in disciplines other than medicine or engineering. While acknowledging that the included disciplines are in no way homogenous, this constraint increased the feasibility of the review. The limited scope also allowed for a consideration of the ways problem-based approaches are implemented in disciplines where they may not be commonly accepted practice. In addition, the review sought to consolidate the effects of the problem-oriented or inquiry-based approaches most commonly evaluated or measured, and consider which evaluation methods best represent exemplary high-quality research design in assessing problem-oriented pedagogies. These aims guided the systematic review presented here.
2. Method: A Systematic Literature Review
A “good literature review presents a critical synthesis of research articles, identifies knowledge, highlights gaps, and provides guidance, eventually offering a new perspective” [18] (p. 3). The research presented here works with a systematic literature review method to identify, appraise, and assemble existing empirical evaluations of problem-oriented pedagogies in higher education. When reviewing research literature, a quality review is systematic, explicit, comprehensive, and reproducible, with transparent descriptions and justifications of the review process, allowing other researchers to replicate the review and objectively decide whether the conclusions drawn are valid and reliable [19]. A mapping review takes a systematic approach to the literature search, mapping out and categorising existing literature to identify commonalities and gaps that can then inform subsequent primary research [20]. The analysis notes the study design and key features of existing research projects, describes the quantity and quality of the literature base, and compiles these, often in a graphic format [20]. This methodical process of synthesising research allows researchers to discern the effectiveness of interventions, identify knowledge gaps that require further study, as well as note the consistencies and variances in the field.
2.1. Search Methods
The scope of the review was deliberately constrained to ensure its feasibility. To respond to the research questions, two databases were selected: Education Research Complete and ERIC. Search terms to limit responses to those focused on the pedagogical approach included: “problem-oriented project learning”, “problem based learning” OR “problem-based learning” OR “PBL”, “inquiry based learning” OR “inquiry learning”. In addition, NOT medic* OR engineer* was added, to narrow the results returned. Results were further qualified with the addition “higher education” in the Education Research Complete database, and by selecting the “Higher Education” descriptor in ERIC. In both databases the results were limited to peer-reviewed entries. To ensure the review reflected currency in the field, the date range was restricted to studies published within the last five years (2015–2019). Following these methods, 259 articles were identified in the initial searches (see, Figure 1). Through the screening process described below, 48 were identified for inclusion in this review.
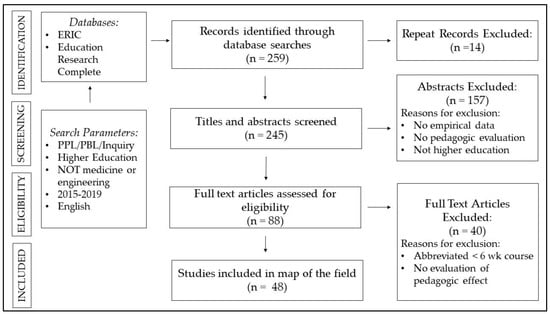
Figure 1.
Flowchart of systematic review process.
2.2. Screening Criteria
The titles and abstracts of the search results were appraised according to specific inclusion and exclusion criteria (see, Table 1). In making judgements on the inclusion and exclusion of articles according to their pedagogic alignment, I considered three key aspects. Whether termed problem-based learning, inquiry-based learning, or project-based learning, this study included exemplars of pedagogic practice that:

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the systematic review (informed by [19]).
- Began with a complex situation, ‘wicked’ problem, or authentic challenge;
- Necessitated groupwork as an integral aspect of the learning design;
- Were sustained over the course of a semester (twelve to sixteen weeks).
Each study was evaluated qualitatively, with an aim of identifying a pedagogic alignment with the key principles of problem-oriented pedagogies. Articles that were conceptual, philosophical, theoretical, or descriptive were excluded, as they did not evaluate enacted pedagogy through the use of empirical data. Despite the search terms, some articles represented research conducted in school settings and these too were excluded.
2.3. Analysis
In consolidating the evaluation foci of the studies, three dimensions of education proved useful for categorising what are considered important effects or outcomes of problem-oriented pedagogies. Biesta [15,16] articulates qualification, socialisation and subjectification as three entwined purposes and functions of educational systems. These are complex and interrelated concepts, where the qualification function provides students with “knowledge, skills and understandings” but also with “dispositions and forms of judgement” relevant to particular ‘doings’, such as future professional work [15] (p. 20). Rather than simply learning about teamwork skills or communication competences, the socialisation function “has to do with the many ways in which, through education, we become part of particular social, cultural and political ‘orders’” [15] (p. 20), both implicitly and explicitly. This is interrogated further in the subjectification function, where education’s impact on individuation is explored, particularly the possibilities for students to become independent of dominant political, social or cultural orders. Drawing on Freire (1970) and Giroux (1981), among others, Biesta [15] argues that, “any education worthy of its name should always contribute to processes of subjectification that allow those educated to become more autonomous and independent in their thinking and acting” (original emphasis, p. 21). While these purposes have the potential to work synergistically, it is also possible that there may exist conflicts and tensions. For this reason, the intersections and relations between the three are perhaps most important (and most interesting) to identify and explore. In categorising the effects the studies paid attention to, the review first identified the evaluation area or areas in each study. Common themes were then noted, including, for example, when studies evaluated students’ capability with content knowledge, employability competences, or group dynamics. The three purposes–functions [15,16] then became an organising device with which to consolidate and explore these as a suite, and through which I could situate my qualitative decisions as a researcher working independently. Two domains made up the qualification function; the first related to knowledge development and knowledge-related processes focused on understanding and evaluating content, while the second referred to more general skills—those ’doings’ deemed necessary for professional work. Usually, the classification of these evaluation effects was straightforward. Studies that measured academic achievement and application characterised the first stream, while evaluations of generic employability competences were categorised as skills, relevant to the second. Studies with a socialisation focus explored interactions between staff and students, or student groups, often uncovering the (sometimes subtle) interplay of power and position. Thus, they were classified as analyses of the ways university pedagogy—often unintentionally—functions to position students (and staff) within broader social, cultural and political orders. A focus on developing and evaluating student wellbeing was categorised as an aspect of subjectification. This was based on the emphasis on the development of self-efficacy and self-awareness at a personal, rather than professional, level, meaning it therefore contributed to individual autonomy. The results of this analysis are illustrated further in the presentation of the evaluation foci (see, Section 3.3).
There were blurred instances that complicated the categorisation. Capabilities such as collaboration and intercultural competence seemingly spanned both qualification and socialisation functions. Similarly, competencies such as reflection and self-regulation might have been equally relevant in the subjectification category, as pedagogic effects that contribute to independent thought and action. When this uncertainty occurred, I returned to the research, seeking the rationale articulated in the article. Almost invariably, the processes, skills, and understandings found at the intersections of the functions were described as related to future employment potential, qualification competence, or professional identity development. This decided the classification. As such, while certain foci evaluated in the studies may relate to more than one function, if that remained implicit, as incidental outcomes left to chance rather than deliberately cultivated or purposefully assessed, it was not included in the final categorisation.
3. Results
This section maps the suite of articles identified for critical review. First, the articles are categorised according to the methodological approach and methods used in the evaluation. Second, the scope and scale of the evaluations is presented, considering the number of participants, courses, and institutions involved in each study. Third, the evaluation foci are explored, working with the areas of qualification, socialisation, and subjectification [15,16].
3.1. Methodological Approaches and Common Methods
The field ranges between quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods approaches (see, Table 2). It was not uncommon that the methodological approach was tacit, rather than explicitly articulated, and therefore, at times, this categorisation was deduced from the methods used and/or the data presented.

Table 2.
Methodological approach taken in evaluations of problem-oriented pedagogies.
The most common methods used in the field include self-report data, primarily from student participants (through surveys, questionnaires, reflections, and interviews) (see, Table 3). This reiterates a similar finding reported in an earlier literature review of 61 qualitative studies in the field, which concluded that, “the majority were self-report, participant perception designs” [18] (p. 20). The difficulty with an over-reliance on self-report data is that “what people say they do, what they say they prefer and what they say they think cannot be automatically assumed to reflect the truth” [21] (p. 203).

Table 3.
Methods Employed in Evaluating Problem-Oriented Pedagogies.
While a multi-method approach is common among the studies (only 13 of the 48 studies use a single data collection tool), only ten work with multiple stakeholder groups to triangulate students’ perceptions and achievement with additional views. Student and staff participants are included in seven studies [46,50,51,56,59,62,69]. Combinations of students and alumni [45], students and external partners [63] and students, staff and external partners [38] are less common, despite the potential opportunity this provides to compare effects from a range of viewpoints.
Fourteen studies make use of academic achievement data. At times, researchers test content knowledge using pre-and post-tests [30,31,43,44], an exam [27], a recall test [26] or multiple-choice exams [46]. Others use student grades [28,34,36,51,52] and/or assessment pieces, such as essays, reports and problem solutions [27,34,40,42]. In contrast, the assessment of generic (‘21st Century’) proficiencies is predominantly achieved by student self-perception reports, rather than by the kind of performance-based assessment worthwhile in the field [10].
3.2. Scale and Scope
Of the identified studies, the majority—29 of the 48 studies—focus on evaluating a single course within one institution (see Table 4). While 12 of these consider multiple cohorts of students, 17 of the studies present data from one cohort only. Many of the studies implement problem-based approaches as an innovative intervention. This makes the possibility of studies working longitudinally with the same cohort of students over time more difficult, since they reflect a ‘single module’ approach [70], rather than an embedded, institution-wide pedagogy. This is a significant gap in the literature, given the number of studies that indicate the influence pedagogical unfamiliarity has on achievement and experience. Students may experience emotions of worry and irritation when studying PBL for the first time [49], and students new to the approach need scaffolding into the learning method [33,68]. As students progress through multiple iterations of problem-oriented learning, it appears to become less of a ‘culture shock’ [71], with results indicating that academic results increase [27], group functioning improves [44,47], and critical reflection is enhanced [60]. This indicates an opportunity for future pedagogical implementations and evaluations to consider sustained patterns and impacts when students have multiple, progressive encounters with problem-oriented learning.

Table 4.
Scope of evaluations of problem-oriented pedagogies.
The number of participants varies widely, from in-depth cases studies of two students [53] to surveys of 714 students [26]. This reflects the variety of methodological approaches; 28 of the studies have fewer than 100 participants, while 20 have 101 or greater (see, Table 5). A significant number of studies have fewer than 50 contributors (23 studies), which includes 15 reports of research with fewer than 20 participants. Small-scale qualitative studies demonstrated rigour, through working with clear theoretical frameworks and models for analysing and interpreting data with strong methodological framing (e.g., [53,60,67]). Larger scale quantitative and mixed-method studies demonstrated quality through triangulating data from multiple sources, articulating clearly the pedagogical foundation, and transparently presenting the strengths and limitations evident in the findings (e.g., [34,43,46]).

Table 5.
Scale of the Evaluations by Number of Participants.
3.3. Evaluation Foci
A consideration of what is evaluated in the suite of articles provides an insight into which outcomes are most frequently sought and prioritised in the field1. As previously discussed, these are consolidated using Biesta’s [15,16] three purposes and functions of education: qualification, socialisation, and subjectification. Predominantly, the studies prioritise educational effects related to students’ qualification knowledges, skills and competences (see, Table 6). In the first qualification stream (Academic Achievement & Processes, see Table 2), 24 studies were found to focus on students’ academic development and application of content knowledge. This included the measurement of academic achievement (e.g., [26,27,43]) or applied problem-solving skills (e.g., [28,42,58]), which exemplified a focus on the development of knowledge and understanding for qualification purposes. In the second (Employability Competences), 17 studies evaluated generic employability-relevant competences (variably labelled as ‘soft’ skills [58,63], ‘transversal’ competences [45], and transferable skills [25]) such as creativity, information literacy, and critical thinking. These were articulated as essential skills (‘doings’) for students’ future employment.

Table 6.
Evaluation foci by Category.
The evaluation of the socialisation function of problem-oriented learning generally considered group dynamics, through analyses of beliefs, behaviours, and discourse. The 19 studies investigated the subtle and implicit ways that power, ideology, and culture shape collaborative problem-oriented group work. These reflected both staff–student and student peer group interactions, including the effects of teacher beliefs and behaviours [26,37,47,54], silence [59] or age differences [64] within group interaction.
Of the 48 articles, only 15 attend to evaluation priorities outside of academic outcomes [37,38,50,54,55,56,57,59,61,62,64,65,66,67,68]. Mostly, these concentrate on the socialisation effects listed above. Very few have a specific focus on subjectification effects, either in pedagogic implementation or evaluation (with the two inherently interrelated). In their explicit emphasis on civic engagement when working with an inquiry approach, and in their prioritisation of socialisation and subjectification outcomes, Carlise et al. [38] and Werder et al. [50] are notable exceptions in the field. These studies work with participatory research methods, multiple stakeholders, and an explicit commitment to empower students to exercise individual agency within prevailing social structures. As such, they illustrate and evaluate what is pedagogically possible at the intersection of qualification, socialisation, and subjectification education functions.
4. Discussion
The systematic review aimed to map how evaluations of problem-oriented pedagogies are conducted outside of medicine and engineering, identify what is most commonly evaluated, and ascertain those approaches that exemplify high-quality research design. Through the mapping process, three key limitations within the field were identified as areas to consider in conducting future research. Currently, the field focuses on a narrow suite of qualification outcomes, is often limited in scale and scope, and regularly demonstrates performativity, rather than an aim to facilitate continuous improvement in teaching and learning. Each of these will be discussed, along with the limitations of the review and areas for possible future research.
4.1. Prioritisation of Qualification Outcomes
The suite of studies overwhelmingly favours educational effects and outcomes related to students’ qualification for employment purposes. This appears to reflect prevailing neoliberal ideologies, where there is an emphasis on evidence, outputs, competencies, and impact and an instrumental understanding of teaching ‘effectiveness’ [15,72]. Although the capacity of problem-oriented pedagogies to enhance socialisation and personal development is often noted, the evaluations reviewed here rarely evaluate the full suite of outcomes possible. Even when outcomes are assessed that might be identified as contributing to socialisation (teamwork, communication, collaboration), these are aligned with (and subsumed by) instrumental aims to facilitate future employment. This is perhaps no coincidence, since current university contexts privilege measures of performativity, student employability and employment figures as key metrics for demonstrating the success of the institution (such as in the Times Higher Education Global University Employability Ranking). These construct education “as a commodity to be sold” [72] (p. 8).
Pedagogic outcomes can extend beyond students and the bounds of the university. Universities face an increasing imperative to demonstrate civic engagement and public benefit [2,73]. Problem-oriented pedagogies often work in partnership with community partners, meaning that involvement with university staff and students will impact their organisations. However, in the studies reviewed, while ten implemented an inquiry pedagogy with community partners [25,29,34,38,45,48,50,58,63,69], the perspectives of external organisations or employers are rarely sought. Only two—[38] and [63]—offer rare examples where external partner perspectives are included. The view that pedagogic effects might extend to, and exist within, the broader community is, as yet, underrepresented in the field, and hence offers an opportunity for future research.
Another relevant factor relevant is the ease of measuring academic outcomes as indicators of pedagogic impact, rather than evaluating dispositions of active citizenship or personal agency. However, what is easy to measure does not always reflect what it is most important to measure [74]. This reiterates Biesta’s assertion that that being clear about the rationale for measurement is essential, since educational evaluation is an engagement with values: it speaks to the question of “whether we are indeed measuring what we value, or whether we are just measuring what we (can) measure” [15] (p. 13). While qualification is a key purpose and function of education, it seems that, within this suite of studies, it supersedes the additional possibilities inherent within inquiry pedagogy as a way of enacting multiple functions of education. Even when the effects evaluated have the potential to align with socialisation or subjectification aims, these are often articulated as instrumental qualities of employable graduates, rather than contributing to broader goals to improve and enhance society or quality of life.
4.2. Limitations in Scale and Scope
Despite the methodological prioritisation of qualification attributes deemed necessary for future employment, the field reflects an overarching narrowness of both scale and scope. While there is an implicit assumption that inquiry pedagogies will develop students’ knowledge and competences, the majority do not investigate this empirically beyond (i) the bounds of a single course, or (ii) the perceptions of students. While sixteen of the studies take a comparative approach, either comparing cohorts pre- and post- the introduction of a problem-based approach [27,42,52], comparing multiple pedagogic methods [22,24,28,30,31,33,35,43,44,46], or comparing multiple universities [54,56], more than half of the studies consider a single subject. As Laursen and colleagues [43] similarly conclude, there is a “shortage in the literature of comparative and multi-institution studies” (p. 170). This is potentially influenced by the reality that problem-oriented pedagogies appear to be rarely implemented as an institution-wide curriculum philosophy integrated throughout the institution (see, [70]). Instead, the pedagogy is rather used an ‘innovative’ single-subject intervention, complicating the opportunities for a comparative approach. This singular approach means that some studies act as an (instrumental) illustration of impact or improvement, in order to justify the implementation of an inquiry approach to teaching.
Of 48 investigations, most discuss the efficacy of the method for preparing students for future employment. However, as previously discussed, the perspectives of employers are non-existent in the field, with few examples that include graduate voices (there are a few exceptions to the rule, see [39,45,48]). This is particularly problematic due to the delay that can occur between educational experiences and impact [72]. In Dewey’s [75] (p. 80) sense, educational experiences are continuously reconstructed and have value “in their use to increase the meaning of the things with which we have actively to do at the present time.” For these reasons, future studies that longitudinally investigate the impacts of the pedagogy would benefit the field and support an improved understanding of the efficacy of the educational approach. Diversifying the perspectives included in evaluations is an additional way the scope of further research may be strengthened.
4.3. Accountability and Enhancement?
Quality assurance processes ideally monitor teaching and learning with an aim to jointly ensure a commitment to pedagogic improvement and professional accountability. There is, however, an implicit prioritisation in the field of demonstrations of performativity. Rather than working explicitly as part of an ongoing reflexive pedagogic improvement cycle, most studies focus on illustrating the way that the teaching approach implemented in a singular course (and, at times, by particular teacher/s), were able to contribute to improvements in select student employability outcomes. Neoliberal ideologies value and prioritise demonstrations of impact, frequently removed from meaningful, holistic and complex integrated pedagogic concepts [72]. As Biesta [15] notes, this technicist focus on effects has resulted in an instrumental value for educational pathways that ‘assure’ those outcomes deemed most desirable (such as generic, transferable skills and 21st Century competencies). Demonstrating this kind of performativity within teaching practice has become (a potentially problematic) part of the pathway to promotion and tenure [72].
While publications in the field of teaching and learning can function as demonstrations of scholarship (despite how problematic it may be to equate publication through peer review to scholarship, see [72]), in neoliberal contexts, publication outputs have become metrics for universities to create an identity and a global reputation, adding to the pressure for academics to publish [17]. This influence seems to underpin the field; a significant number of published studies lack an explicit methodological or theoretical orientation, and often demonstrate a confusion between pedagogic strategies and educational research methods. Despite calls for the involvement of students in the evaluation of teaching (e.g. ‘students as partners’ [76,77] or ‘students as co-inquirers’ [50,78]), the overarching tendency in the suite of studies instead co-opt student voices in directed ways in order to justify teaching practice. Participatory methods of evaluating students’ experience and perceptions are limited. Due to these factors, few studies articulate how strengths that were identified might be amplified in future practice or how identified areas for improvement might be targeted in the next iteration of teaching.
4.4. Limitations and Further Research
This review has not consolidated the findings of the studies, for the primary reason that, although the studies meet common criteria (inquiry practice that begins with a complex problem, is conducted in groups and is sustained over the course of a semester), there remains disparity. As elaborated in the work of Savin-Baden [6], there exists a range of ‘constellations’ in the implementation of problem-based learning. In some cases in this study, students work with challenges that are developed and assigned by the teacher, while some reflect genuine, ‘real-life’ challenges from external organisational partners; in others, the students negotiate problems relevant to their interests in response to a theme or topic. Within a semester-long course, some student groups may work with a single problem in a sustained engagement, whereas, in others, they conduct multiple short-term problem cycles (over one day or a week). While group interaction is consistently a facet of the learning, group formations vary in number and composition, and at times are deliberately constructed and assigned by supervisors to ensure heterogeneity.
At times, the implementation takes a ‘hybrid’ approach, where traditional lectures complement students’ research and students must attend problem-based tutorials each week where the supervisor was present, others have flexible arrangements for student supervision. Some courses offer a highly structured approach with regular workshops, accountability mechanisms, and ongoing supervision and some provide significant scaffolding to support students in their self-directed learning (including lists of relevant articles, cases, and websites). This complicates the process of drawing general conclusions regarding the efficacy of the pedagogic method, and also illustrates the need for further longitudinal research that works with multiple courses or institutional-level evaluations. In addition, a limitation of this study is that the research was conducted by a single reviewer, and, while the systematic process is an objective procedural one, in practice, research “shifts over time as you find things out” in a non-linear and recursive way [79] (p. 21). For this reason, conclusions have been guided by the literature review questions and themes identified in the literature.
The findings indicate that there is much opportunity for future research. In particular, there is a need for evaluations that consider the socialisation and subjectification effects of participation in problem-oriented learning processes. An emergent possibility within the field includes the use of narrative reflections to evaluate beyond-qualification outcomes. Ten of the studies work with reflections (see, Table 3) which offer insight into the ways students’ understanding transforms over the course of their participation, often alluding to socialisation and subjectification outcomes. While Podeschi [63] codes and quantifies the specific professional skills described as significant in students’ written reflections, Korpi et al. [60] thematically analyse reflections within student portfolios to identify the evolution of critical reflection, understandings of peer group work, and creative learning processes. These are found to indicate students’ emergent agency within the method over time. Similarly, in another study, students described in reflective journals their transformed understanding of their ability to contribute to and affect university decision-making and the broader community [50]. These reflective responses “consistently demonstrate the transformational impact of the co-inquiry process and the program’s development of tolerance, collaboration, and self-confidence” [50] (p. 9). The use of rubrics [46] or multiple raters [44] to evaluate narratives can improve the reliability and validity of reflections as research data able to assess educational effects.
In addition, there is potential in the use of participatory research methods. Policy in Europe recommends that students are included within internal university quality assurance practices [12]. Photovoice is a participatory research method where participants have the opportunity to speak directly with policy and decision makers to communicate the kinds of effects that have significance and meaning for them [80,81]. With a photovoice methodology, students have the agency to illustrate and narrate their experiences, to critically situate their views in relation to a broader suite of responses, co-analyse data, and communicate with teaching staff and administrators. The Most Significant Change (MSC) technique [82] similarly allows students to narrate and critically co-evaluate educational effects, positioning them as partners in the research process (see, [76]). With a future focus, participatory methods are especially suited to learning about and improving processes, rather than singularly demonstrating accountability [83]. As such, these represent a promising way of enhancing evaluation practice to engage with qualification, socialisation and subjectification, and the intersections between the three. Further development of methods and metrics that can capture the development of student agency, a critical civic consciousness, or students’ orientations to, and dispositions for, equitable social action would also expand the field.
5. Conclusions
Problem-based pedagogies are often purposefully implemented in order to enhance academic learning and contribute to generic competences deemed essential for students’ employability. This systematic review has synthesised current evaluations of these pedagogic enactments outside the fields of medicine and engineering. As discussed, the findings presented here include that the suite of studies generally prioritise qualification-related outcomes, are limited in scale and scope, and often foreground teaching performativity. While the influence of neoliberal priorities seems to influence the field, quality evaluations demonstrated several key characteristics valuable when designing future research. These include a clear articulation of the pedagogical foundations, theoretical orientations, and research aims of the study, with clarity regarding the distinctions between them, coupled with and an orientation towards iterative educational improvement. In addition, a robust and explicit methodology; the use of multiple methods, cohorts, stakeholders and/or institutions with comparison of data sets; and a consideration of socialisation and subjectification effects in addition to qualification outcomes distinguish quality studies within the suite of inquiry approaches.
Evaluations that imagine and evaluate pedagogic outcomes beyond the university, for example those experienced by partner organisations and communities, would significantly strengthen the field. This kind of approach may benefit from engagement with students, graduates and community partners around the rich outcomes possible in problem-oriented work—beyond employable, technicist professional competences. If the ultimate goal is improved social cohesion, this requires more than implementing an innovative pedagogy while still positioning students as individuals who strategically accumulate capital for future work. The evaluation methods used to provide insight into the efficacy of the method and its effects have the potential to enhance and value the substantial possibilities for civic awareness and subjectification inherent in the pedagogy.
Notes
1: In consolidating the evaluation foci, I have excluded those foci unrelated to student learning outcomes, such as satisfaction [25,34,36,51], perception of the learning environment [22,27] or student experience [42].
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to my colleagues and research group members associated with the RUC Centre for Research on Problem-oriented Project Learning for continued discussions regarding problem-oriented pedagogies and the effects of higher education learning that could (or should) be measurable and measured. I also acknowledge with gratitude the insight of Donna Goldie, Simon Warren, and the peer reviewers who provided feedback on earlier versions of the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- The Bologna Process and the European Higher Education Area. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/education/policies/higher-education/bologna-process-and-european-higher-education-area_en (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- About Higher Education Policy. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/education/policies/higher-education/relevant-and-high-quality-higher-education_en (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Development of Skills. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/education/policies/european-policy-cooperation/development-skills_en (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Education Higher Education Area. Paris Communiqué. Available online: http://www.ehea.info/Upload/document/ministerial_declarations/EHEAParis2018_Communique_final_952771.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Benham Rennick, J. Learning that makes a difference: Pedagogy and practice for learning abroad. Teach. Learn. Inq. 2015, 3, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin-Badin, M. Using problem-based learning: New constellations for the 21st Century. J. Excell. Coll. Teach. 2014, 25, 1–24. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/42594749.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Andersen, A.S.; Kjeldsen, T.H. Theoretical Foundations of PPL at Roskilde University. In The Roskilde Model: Problem-Oriented Learning and Project Work; Andersen, A.S., Heilesen, S.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Savin-Badin, M. Problem-Based Learning in Higher Education: Untold Stories; The Society for Research into Higher Education & Open University Press: Buckingham, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yusofa, K.M.; Hassan, S.A.H.S.; Jamaludina, M.Z.; Harun, N.F. Cooperative Problem-based Learning (CPBL): Framework for Integrating Cooperative Learning and Problem-based Learning. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 56, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavelson, R.; Zlatkin-Troitschanskaia, O.; Mariño, J. International performance assessment of learning in higher education (iPAL): Research and development. In Assessment of Learning Outcomes in Higher Education: Cross National Comparisons and Perspectives; Zlatkin-Troitschanskaia, O., Toepper, M., Pant, H.A., Lautenbach, C., Kuhn, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Firn, J. ‘Capping off’ the development of graduate capabilities in the final semester unit for biological science students: Review and recommendations. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2015, 12, 1–16. Available online: http://ro.uow.edu.au/jutlp/vol12/iss3/3 (accessed on 11 August 2018).
- Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area (ESG). Available online: https://enqa.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/ESG_2015.pdf. (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Manatos, M.; Rosa, M.; Sarrico, C. The perceptions of quality management by universities’ internal stakeholders: Support, adaptation or resistance? In The University as a Critical Institution; Deem, R., Eggins, H., Eds.; Sense Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, C.; Howson, C.K.; Forsythe, A. Making sense of learning gain in higher education. High. Educ. Pedagog. 2018, 3, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesta, G. Good Education in an Age of Measurement: Ethics, Politics, Democracy; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Biesta, G. Good Education in an age of measurement: On the Need to Reconnect with the Question of Purpose in Education. Educ. Assess. Evaluat. Account. 2009, 21, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M. Global university rankings: Metrics, performance, governance. Educ. Philos. Theory 2019, 51, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Bridges, S. Qualitative research in PBL in health sciences education: A review. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2016, 10, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, A. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, A.; Papaioannou, D.; Sutton, A. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Denscombe, M. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects, 3rd ed.; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alt, D. Assessing the contribution of a constructivist learning environment to academic self-efficacy in higher education. Learn. Environ. Res. 2015, 18, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.S.; Wulf-Andersen, T.; Heilesen, S.B. The evolution of the Roskilde model in Denmark. Counc. Undergrad. Res. Q. 2015, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Brassler, M.; Dettmers, J. How to enhance interdisciplinary competence—Interdisciplinary problem-based learning versus interdisciplinary project-based learning. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2017, 11, 12. Available online: https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1686 (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Carvalho, A. The impact of PBL on transferable skills development in management education. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2016, 53, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, E.; Yew, E.; Schmidt, H. To what extent do tutor-related behaviours influence student learning in PBL? Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2015, 20, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujinuma, R.; Wendling, L. Repeating knowledge application practice to improve student performance in a large, introductory science course. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2015, 37, 2906–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, E.; Enrique-Mirón, C.; González-García, J.; Fernández-Carballo, D. Problem-based learning in prenursing courses. Nurse Educ. 2016, 41, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Goodman, F. Well-being, leadership, and positive organizational scholarship: A case study of project-based learning in higher education. J. Leadersh. Educ. 2015, 14, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. The influence of problem-based learning on learning effectiveness in students’ of varying learning abilities within physical education. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2019, 56, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbıçakçı, Ş.; Gezer, N.; Bilik, Ö. Comparison of effects of training programs for final year nursing students in Turkey: Differences in self-efficacy with regard to information literacy. Nurse Educ. Today 2015, 35, e73–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piercey, V.; Militzer, E. An inquiry-based quantitative reasoning course for business students. Primus Probl. Resour. Issues Math. Undergrad. Stud. 2017, 27, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santicola, C. Academic controversy in macroeconomics: An active and collaborative method to increase student learning. Am. J. Bus. Educ. 2015, 8, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, L.; Jerez, O.; Hasbún, B.; Pizarro, V.; Valenzuela, G.; Orsini, C. Closing the gap between business undergraduate education and the organisational environment: A Chilean case study applying experiential learning theory. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2018, 55, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardimci, F.; Bektaş, M.; Özkütük, N.; Muslu, G.; Gerçeker, G.; Başbakkal, Z. A study of the relationship between the study process, motivation resources, and motivation problems of nursing students in different educational systems. Nurse Educ. Today 2017, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra-Gómez, J.; Román-Martínez, I.; Gómez-Miranda, M. Measuring the impact of inquiry-based learning on outcomes and student satisfaction. Assess. Evaluat. High. Educ. 2015, 40, 1050–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assen, J.; Meijers, F.; Otting, H.; Poell, R. Explaining discrepancies between teacher beliefs and teacher interventions in a problem-based learning environment: A mixed methods study. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2016, 60, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, S.; Gourd, K.; Rajkhan, S.; Nitta, K. Assessing the Impact of Community-Based Learning on Students: The Community Based Learning Impact Scale (CBLIS). J. Serv. Learn. High. Educ. 2017, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cremers, P. Student-framed inquiry in a multidisciplinary bachelor course at a Dutch university of applied sciences. Counc. Undergrad. Res. Q. 2017, 37, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, J.; Jackson, P.; Murray, M. Transforming undergraduate biology learning with inquiry-based instruction. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2018, 30, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttel, H.; Gnaur, D. If PBL is the answer, then what is the problem? J. Probl. Based Learn. High. Educ. 2017, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.; McLoughlin, E.; Finlayson, O. Analysing student written solutions to investigate if problem-solving processes are evident throughout. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2016, 38, 1766–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, S.; Hassi, M.; Hough, S. Implementation and outcomes of inquiry-based learning in mathematics content courses for pre-service teachers. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 47, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, Z. Comparative effect of project-based learning and electronic project-based learning on the development and sustained development of English idiom knowledge. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2018, 30, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossano, S.; Meerman, A.; Kesting, T.; Baaken, T. The Relevance of Problem-based Learning for Policy Development in University-Business Cooperation. Eur. J. Educ. 2016, 51, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdà, B.; Alsina, Á. Knowledge-transfer and self-directed methodologies in university students’ learning. Reflective Pract. 2018, 19, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, L.; Ayyıldız, Y. The Views of Undergraduates about Problem-based Learning Applications in a Biochemistry Course. J. Biol. Educ. 2015, 49, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.; Depasquale, J. Connecting curriculum, capabilities and careers. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2016, 17, 738–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, J.; Rasi, P. Integrating Web 2.0 Technologies into Face-to-Face PBL to Support Producing, Storing, and Sharing Content in a Higher Education Course. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2017, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Werder, C.; Thibou, S.; Simkins, S.; Hornsby, K.; Legg, K.; Franklin, T. Co-inquiry with students: When shared questions lead the way. Teach. Learn. Inq. 2016, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wijnen, M.; Loyens, S.; Smeets, G.; Kroeze, M.; Van der Molen, H. Students’ and teachers’ experiences with the implementation of problem-based learning at a university law school. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S. The problem of constructive misalignment in international business education: A three-stage integrated approach to enhancing teaching and learning. J. Teach. Int. Bus. 2016, 27, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anthony, G.; Hunter, J.; Hunter, R. Prospective teachers development of adaptive expertise. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2015, 49, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulls, M.; Magon, J.K.; Shore, B. The distinction between inquiry-based instruction and non-inquiry-based instruction in higher education: A case study of what happens as inquiry in 16 education courses in three universities. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2015, 51, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, R.; Koch, T.; Messing, H. Understanding the prospect of success in professional training: An ethnography into the assessment of problem-based learning. Ethnogr. Educ. 2019, 14, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G. A poststructuralist view on student’s project groups: Possibilities and limitations. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2016, 15, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, G.; Wiggins, S.; Anderson, T. The discursive construction of group cohesion in problem-based learning tutorials. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2016, 15, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, R.B.; Kimmel, C.; Robertson, D.; Mortimer, M. International field experiences promote professional development for sustainability leaders. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2016, 17, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Students’ silence and identity in small group interactions. Educ. Stud. 2017, 43, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpi, H.; Peltokallio, L.; Piirainen, A. Problem-Based Learning in Professional Studies from the Physiotherapy Students’ Perspective. Interdisc. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2018, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Henning, T. Getting started with PBL—A reflection. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2017, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliver, K.; Oesterreich, H.; Aranda, R.; Archeleta, J.; Blazer, C.; de la Cruz, K.; Martinez, D.; McConnell, J.; Osta, M.; Parks, L.; et al. ‘The sweetness of struggle’: Innovation in physical education teacher education through student-centered inquiry as curriculum in a physical education methods course. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2015, 20, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podeschi, R.; Building, I.S. Professionals through a Real-World Client Project in a Database Application Development Course. Inf. Syst. Educ. J. 2016, 14, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, L. Age difference and face-saving in an inter-generational problem-based learning group. J. Furth. High. Educ. 2016, 40, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.; Harris, A.; Burton, R. Saving face: Managing rapport in a Problem-Based Learning group. Active Learn. High. Educ. 2015, 16, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosander, M.; Chiriac, E. The purpose of tutorial groups: Social influence and the group as means and objective. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2016, 15, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryberg, T.; Davidsen, J.; Hodgson, V. Understanding nomadic collaborative learning groups. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2018, 49, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, P. Fostering student engagement: Creative problem-solving in small group facilitations. Collect. Essays Learn. Teach. 2015, 8, 153–164. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1069715.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2019). [CrossRef]
- Thorsted, A.C.; Bing, R.G.; Kristensen, M. Play as mediator for knowledge-creation in Problem Based Learning. J. Probl. Based Learn. High. Educ. 2015, 3, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Savin-Baden, M. Disciplinary differences or modes of curriculum practice? Who promised to deliver what in problem-based learning? Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2003, 31, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Feehily, R. Problem-based learning and international commercial dispute resolution in the Indian Ocean. Law Teach. 2018, 52, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshier, R. Why is the scholarship of teaching and learning such a hard sell? High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2009, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truly Civic: Strengthening the Connection Between Universities and their Places. The Final Report of the UPP Foundation Civic University Commission. Available online: https://upp-foundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Civic-University-Commission-Final-Report.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Unterhalter, E. Negative capability? Measuring the unmeasurable in education. Comp. Educ. 2017, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, J. Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Acton, R. Innovative Learning Spaces in Higher Education: Perception, Pedagogic Practice and Place. Ph.D. Thesis, James Cook University, Townsville, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kahu, E.; Nelson, K. Student engagement in the educational interface: Understanding the mechanisms of student success. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2018, 37, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A. Students as co-inquirers in Australian higher education: Opportunities and challenges. Teach. Learn. Inq. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A. The Future of Knowing. “Brunch with Books” Sponsored by the University of Chicago Alumni Association and the University of Chicago Library. 2009. Available online: http://home.uchicago.edu/aabbott/Papers/futurek.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2019).
- Sutton-Brown, C. Photovoice: A methodological guide. Photogr. Cult. 2014, 7, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Burris, M.A. Photovoice: Concept, methodology, and use for participatory needs assessment. Health Educ. Behav. 1997, 24, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.; Dart, J. The ‘Most Significant Change’ (MSC) Technique: A Guide to its Use. 2005. Available online: https://www.kepa.fi/tiedostot/most-significant-change-guide.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2013).
- Acton, R.; Riddle, M.; Sellers, W. A review of post-occupancy evaluation tools, 203-221. In School Space and Its Occupation: The Conceptualisation and Evaluation of New Generation Learning Spaces; Alterator, S., Deed, C., Eds.; Brill Sense Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).