Abstract
Prompted by participation gaps in the tech industry, this study explores the relationship between recent college graduates’ college experiences and their perceptions of their tech work environments. Using survey data from 15 research universities across the U.S., the findings suggest that gender and racial/ethnic identity influence the likelihood of viewing the field of computing as inclusive. Participants who were computing majors or felt a strong sense of belonging within the computing community were more likely to view the computing career environment positively. Notably, positive predictors of perceptions of an inclusive tech work environment, including majoring in computing as an undergraduate and feeling connected within computing, directly related to early career professionals’ undergraduate experiences. This study’s implications are relevant to various higher education stakeholders, including STEM department leaders, career development staff, and student affairs staff focused on fostering a strong pipeline from computing undergraduate programs to computing careers.
1. Introduction
One of the functions of higher education is to prepare graduates to enter the workforce and contribute their expertise to their chosen field (Chan, 2016). This is especially true in fields such as computing, where there are critical shortages of individuals who hold degrees in computer science and related fields. Indeed, the Department of Labor Statistics’ employment projections suggest there will be approximately 4.7 million computing-related jobs in the United States by the year 2030 but only about 20% of these jobs could be filled by U.S. computing graduates (NCWIT, 2022). There is a particular need to retain women and people of color1 who earn computing degrees in technology fields. Women make up only 22.6% of the high-tech workforce, even as they make up nearly half (47.3%) of the total American workforce (U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, 2024). Even more concerning, women’s representation in the tech workforce has not increased in the past two decades (U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, 2024). When we consider women of color in the high-tech workforce, disparities persist:
Black and Hispanic/Latina women each make up only 2% of the high-tech workforce, despite Black women making up 6% and Hispanic/Latina women making up 8% of the U.S. workforce (U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, 2024).
While similar gender disparities exist at the undergraduate level—women earned only 21% of computing bachelor’s degrees awarded in 2019 (National Center for Education Statistics, 2020)—retaining recent graduates in the field is a major contributor to participation gaps in the technology workforce. Some research indicates that approximately 15% of women who earn degrees in engineering and computing never hold a job in their field (Fouad & Singh, 2012). Further, a staggering 56% of women employed in the technology sector leave their organizations by the mid-career point (i.e., approximately 10 years after college graduation; Hewlett et al., 2014). This “quit rate” for women is more than double that of men in technology roles (Hewlett et al., 2014).
The existing literature suggests that the transition period from college to career is essential for job satisfaction and retention for recent college graduates in science and technology fields as they navigate social and cultural aspects of the workplace (Lutz & Paretti, 2021). Yet, little research focuses on recent college graduates’ transition to the workforce in computing fields, with some emphasis on women’s experiences but little work focusing on the experiences of people of color or the intersectional experiences of women of color. To retain more college graduates in the tech workforce, particularly those who have been historically minoritized in the field, there is a need to increase our knowledge about the factors that shape recent graduates’ perceptions of the field of computing. To this end, this study draws on a national survey of recent college graduates who hold full-time jobs in the field of computing to explore their identity and belonging within computing, their experiences in their computing jobs, and how these factors relate to their perception of the field of computing’s degree of inclusivity.
2. Literature Review
Most college students seek employment after graduation; indeed, 86% of 25- to 34-year-olds with a bachelor’s degree or higher were employed in 2021 (National Center for Education Statistics, 2022). Yet the experience of searching for and transitioning to a post-college job is not universal. There are key differences in students’ job-seeking behaviors (i.e., method of search, search quality, and search intensity) as well as gender and racial/ethnic differences that shape their employment success and quality (Mau & Kopischke, 2001; van Hooft et al., 2021). Once employed, recent graduates are likely to encounter a markedly different environment. That is, in most college and university settings, the institution provides myriad resources for students’ personal, professional, and academic development (Lutz & Paretti, 2021). This may be limited in the work environment, since most organizations are profit- or mission-driven (Lutz & Paretti, 2021). Further, employees are often expected to complete tasks that are not necessarily related to their interests nor are they intended to advance their intellectual or professional growth (Hu & Wolniak, 2013; Lutz & Paretti, 2021). In short, recent college graduates face steep learning curves and a difficult transition to the workforce that may shape their early career experiences and their sense that their field is welcoming. This may be particularly true for those entering STEM workplaces (Lutz & Paretti, 2021; Xu, 2017). Further, the challenges inherent in moving through the college to career transition may be exacerbated for women, women of color, and people of color in STEM fields, where there are known concerns relating to structural supports for those holding marginalized identities (Barker, 2009; Margolis & Fisher, 2002; Margolis et al., 2008; Strayhorn, 2012; Williams et al., 2022).
2.1. Early Career Experiences in STEM and Computing
There is a growing body of literature that focuses on explanations for the gender gaps in the tech workforce. Sassler et al. (2017) examined gender gaps in STEM degree recipients’ first jobs. They reported that most of the gender gap in STEM occupations overall was explained by women’s underrepresentation in computer science and engineering majors, but that a large share of gender gaps in the STEM workforce remained unexplained by their data. Further, Main and Schimpf (2017) conducted a literature synthesis on explanations for gendered participation gaps in computing fields and identified 14 studies that focused on post-baccalaureate employment. Their review identified several key themes in the explanations for gender gaps in the tech workforce, including conflicts between work and family responsibilities (e.g., Armstrong et al., 2007; Riemenschneider et al., 2006; Wardell et al., 2006), the professional culture within computing domains (e.g., Guzman & Stanton, 2008; Wardell et al., 2006), gendered value orientations (e.g., Trauth, 2002, 2006; Trauth et al., 2004), and women’s restricted access to mentoring and networking resources (e.g., Trauth et al., 2008; Wardell et al., 2006; Windeler & Riemenschneider, 2013).
Relatively few empirical studies have investigated the broader early career experiences of recent college graduates working in computing fields. Existing work demonstrates that students whose major is congruent with their career (e.g., a STEM major in a STEM career) tend to have better earnings and job satisfaction than those whose major and career are incongruent (Xu, 2017). Further, women, women of color, and people of color face gender and racial pay gaps in STEM fields (Hu & Wolniak, 2013; Sterling et al., 2020; Zhang, 2008) and these inequities are present from the point of transition from college to career within STEM disciplines (Xu, 2017).
The best source of data on recent graduates’ experiences would come from tech companies themselves. While many conduct climate surveys of their own employees, they do not publish or share this proprietary information. In fact, it is only recently that some tech companies have begun to share data on the demographics of their technical workforce (AnitaB.org, 2022). However, two organizations have surveyed individuals working in tech fields with a goal of understanding differences in workplace experience for women and women of color. AnitaB.org surveys Grace Hopper Celebration attendees, their social media followers, and subscribers of their newsletter each year as part of their Technical Equity Experience Survey (AnitaB.org, 2021), which provides some information on technologists’ perceptions of their field. Over 1400 individuals working in the field of tech responded to their survey; 30% of these respondents were in an entry-level tech role. Due to the nature of their recruitment pool, nearly all (96%) of their respondents were women. Their survey reports that practically all women respondents experienced discrimination and/or harassment while working in tech, yet approximately 64% reported feeling a sense of belonging in the workplace and, on a scale of 1 (very dissatisfied) to 10 (very satisfied), respondents’ average job satisfaction rating was 7.3. Although this report is not representative of the broader computing workforce, it demonstrates a need to better understand how workplace experiences shape employees’ perceptions of working in computing and how these experiences and perceptions may vary by gender and race/ethnicity. The Center for WorkLife Law at the University of California College of the Law, San Francisco also conducted a smaller survey (n = 214) of individuals working in tech workplaces, though these individuals did not necessarily fall into entry-level roles. Still, their findings highlight the intersectional nature of workplace experiences, as women of color who responded to their survey reported higher levels of bias in the workplace than did White women (Williams et al., 2022).
Additionally, research has explored how college students develop and sustain interest in a computing career that may be relevant to their early career experiences in computing. As noted above, many students who earn technical degrees do not go on to hold jobs in the field (Fouad & Singh, 2012). This may be due to students’ declining interest in a computing career throughout college; a recent study of students who took introductory computer science courses showed there were more students planning to leave the computing career pipeline than there were students planning to join it two years after taking the course (George et al., 2022). Further, women across racial/ethnic groups showed greater declines in interest than men, while Asian students were more likely than their White and Black peers to sustain their interest in a computing career (George et al., 2022). College students’ interests in a computing career are shaped by several factors, including their family backgrounds and career values (Barker, 2009; George et al., 2022; Lehman et al., 2016), experiences with computing in college (George et al., 2022), social relationships in computing (Ross et al., 2020), and sense of belonging and identity (Blaney & Stout, 2017; Cheryan et al., 2009; George et al., 2022; Stormes, 2023). More information is needed about whether these same factors continue to be important in how those newly employed in computing perceive the field and their place in it.
2.2. Sense of Belonging and Computing Identity
Sense of belonging is intrinsically linked with students’ computing identity, or the extent that one sees themselves as a computing person (Rodriguez & Lehman, 2017), as sense of belonging is a core component of computing identity (Lunn et al., 2021; Taheri et al., 2018). Computing identity and sense of belonging seem particularly important to sustaining interest in computing, as they not only predict interest in a computing career but also are key to persistence and retention (Aschbacher et al., 2010; Blaney & Stout, 2017; Cheryan et al., 2009; George et al., 2022; Hausmann et al., 2007; Perez et al., 2014; Stormes, 2023; Strayhorn, 2018; Taheri et al., 2018). Further, sense of belonging has been correlated with women technologists’ comfort in asking for a promotion and their intention to stay at their current company for at least a year (AnitaB.org, 2021). Hence, both computing identity and sense of belonging are key points of interest in the present study, as we seek to understand the early career experiences of individuals working in the field of computing and how these experiences shape their perceptions of it. However, the research on sense of belonging in computing has been largely limited to educational spaces; there is a need to understand how sense of belonging evolves as individuals transition to the workforce.
2.3. Perceptions of the Computing Field
Though there is some research on the career experiences of women working for tech companies and how they relate to women’s intentions to stay at their current workplace (AnitaB.org, 2021), we identified no work that considered how employees in the tech work force perceived the field more broadly. This is essential because women and people of color are leaving the field altogether, and not just their particular employer. Hence, empirical work is needed to understand how newly graduated employees are experiencing their computing workplaces and how this shapes their perceptions of the field.
3. Study Objectives
Despite knowledge that the college to career transition is a time of considerable stress for many recent college graduates, there is limited research on their career transitions and early career experiences, and there is almost no work focused on the unique experiences of individuals transitioning to careers in the field of computing. While scholars have investigated the career aspirations, as well as the sense of belonging and identity, of computing students in higher education, there is a need to extend our knowledge of how these factors may change as individuals enter the computing workforce, particularly for those who have been historically minoritized in computing spaces. Our study investigates how recent college graduates navigate the transition from college to a career in computing and how their perceptions of workplace inclusivity may evolve. Given the persistent participation gaps in computing fields, we emphasize differences in perceptions by gender and race/ethnicity. To this end, we ask the following research questions:
- How do recent college graduates working full-time in computing fields perceive their belonging and identity in computing? How does this vary by gender and/or race/ethnicity?
- How do recent college graduates working in computing fields perceive the inclusivity of their work environments? How do their perceptions vary by gender and/or race/ethnicity?
- How do the background characteristics, college experiences, and work environments of recent college graduates working in computing fields predict their perception that the general environment in computing careers is inclusive of women, people of color, and women of color?
4. Conceptual Framework
Given this study’s focus on recent college graduates’ transitions into computing careers and their perceptions of their work environments, we draw on Carlone and Johnson’s (2007) Science Identity Model alongside an extension of Lent et al.’s (1994) Social Cognitive Career Theory (SCCT), referred to as a Social Cognitive Model of Career Self-Management (CSM) (Lent & Brown, 2013), to provide relevant theoretical grounding for this work. It is important to note the intention in using these two seemingly disparate works in tandem. Carlone and Johnson’s work centers science identity and is typically cited in work that focuses on the development of this identity within higher education spaces (e.g., Espinosa, 2011; Ong et al., 2011). Using this work to frame the current study underscores the extent to which students’ self-perceptions (related to the study’s independent variable of belonging and identity) have the potential to shape their perceptions of inclusivity in their tech workplaces, the study’s key dependent variable. Moreover, pairing this model with Lent and Brown’s work, which focuses on the transition from a collegiate setting to a corporate setting, allows the overall conceptual framework guiding this study to highlight the continued importance of collegiate experiences (i.e., science identity formation) even as students become full-time professionals. The following sections provide an overview of each theory along with a discussion of its application to the study.
4.1. Science Identity Model
Carlone and Johnson (2007) point to three key arguments that support a focus on identity in the context of STEM education research. These arguments include using identity as an analytic tool to understand participation in STEM and centering identity as a means of viewing STEM as a community into which individuals are socialized. Their model extends standard notions of identity such as race or gender to consider what it might mean for someone to consider themself a “science person.” The Science Identity Model depicts three overlapping dimensions of competence, performance, and recognition, all of which are predicated on the assumption that these dimensions are necessarily influenced by racial, ethnic, and gender identities.
The three dimensions of the model balance the understanding of identity as a concept that is simultaneously internally held and externally confirmed. The model’s competence dimension refers to the cultivation of a deep knowledge base within a chosen scientific field (i.e., computing, for the purposes of the present study), whereas the performance dimension centers on the ability to communicate and demonstrate relevant scientific knowledge. The recognition dimension refers to a student’s self-perception of being a “science person” and having this perception affirmed by meaningful others in the field (e.g., professors, internship supervisors, etc.). Taken together someone with a strong science identity would rate highly (and receive high ratings from meaningful others) on all three of these dimensions.
This model informed the variable selection process for this study’s descriptive research questions. In addition to considering early career professionals’ racial, ethnic, and gender identities, this model underscored the importance of items such as “I see myself as a computing person” (i.e., the recognition dimension) and “I see myself as a leader in computing” (i.e., the competence dimension). Further, the overarching framing of the field of computing as a community into which early career professionals must gain both professional and social entry guided the development of this study’s research questions to focus on sense of belonging and perceptions of inclusivity.
4.2. Social Cognitive Model of Career Self-Management (CSM)
Lent et al.’s (1994) SCCT provides a comprehensive view of career trajectories by framing a person’s background characteristics as influencing their learning environment, which in turn influences expectations for self-efficacy and outcomes. The model identifies personal characteristics and experiences (referred to as person inputs and background contextual affordances, respectively) as initial drivers of career development. These are then combined with learning experiences that inform goals, actions, and outcomes.
As an extension of this model, CSM maintains this framing with key nuances. Most importantly, whereas SCCT was designed to address questions of career content, CSM is instead conceived as a mechanism through which to understand career processes. For the purposes of this study, the process is understood to be that of transitioning to a new job upon graduating from college. The CSM also emphasizes the influence of self-efficacy in shaping outcome expectations, thereby serving as a key point of convergence between this model and the Science Identity Model. While several studies have previously applied SCCT to understanding computing students (George et al., 2022; Lent et al., 2008, 2011; Sax et al., 2017), the focus of this study presents a valuable opportunity to use the CSM extension of this theory. Figure 1 shows this study’s adapted CSM model.
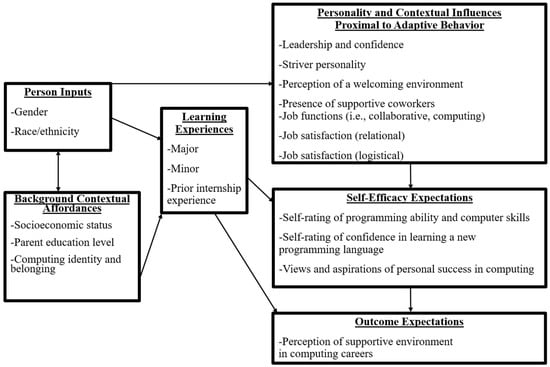
Figure 1.
Adapted CSM model.
5. Methods
5.1. Data and Sample
This study uses data from a longitudinal survey of undergraduate students in introductory computing courses at 15 universities across the U.S. that participated in the Building, Recruiting, and Inclusion for Diversity (BRAID) initiative. These institutions committed to working to diversify their undergraduate computing majors. Alongside this program, the BRAID research team studied two cohorts of undergraduate students: those enrolled in introductory computing courses during the 2015–2016 and 2016–2017 academic years, respectively. Then, the BRAID research team administered annual follow-up surveys to track baseline respondents through college and into graduate school and early careers. This study relies on data from the most recent BRAID follow-up survey in 2020. While prior BRAID follow-up surveys examined students’ persistence in computing majors and career and graduate school aspirations, the 2020 survey—four to five years after the introductory computing courses—captured the early career experiences of thousands of young adults across the U.S.
We restricted our study sample (n = 845) to those in both cohorts who responded to the 2020 survey, had graduated from college, and were working full-time in a computing field. Approximately 65% of respondents identified as men and 35% identified as women. The racial/ethnic breakdown of our sample is as follows: 40% White, Caucasian, or European American; 34% Asian or Asian American; 5% Black or African American, 9% Hispanic or Latina/o/x; 12% Indigenous, Middle Eastern, Multiracial, or Other. See Table 1 for detailed sample demographics.

Table 1.
Profile of Recent Graduates in a Computing Career (n = 845).
5.2. Measures
The dependent variable (DV) for the inferential model is a composite measure of the perception that the environment in computing careers is inclusive of women, people of color, and women of color. Although the dependent variable was based on Likert-type items, it was treated as approximately continuous in the regression analysis due to its multi-item composition and high internal consistency (See Table 3; Cronbach’s alpha = 0.939).
Independent variables for the descriptive analyses were selected with guidance of Carlone and Johnson’s (2007) Science Identity Model. Appendix A includes the full list of variables and their coding schemes. In the inferential model, 24 independent variables (IVs) were selected and organized in accordance with CSM (Lent & Brown, 2013). As guided by CSM, independent variables included person inputs and background contextual affordances, including gender, race/ethnicity, computer major or minor, and number of computing-related internships. To disaggregate participants’ racial/ethnic identities as much as possible, we created dichotomous variables to include racial/ethnic groups as separate predictors in the regression model to the extent possible given the sample sizes of each racial/ethnic group (i.e., binary variables were included in the regression model for the following races/ethnicities: Black/African American, Hispanic/Latinx, and Asian/Asian American, with White serving as the reference group).
The remaining independent variables are composite measures our team developed by conducting exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis to reduce the overall number of predictors and increase the parsimoniousness of the final model. The threshold for reliability was set at a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.65, and variables were only considered valid for inclusion in a factor if they loaded at 0.40 or higher, consistent with recommendations for exploratory research involving diverse constructs (Taber, 2018). While some scales approached this threshold, we prioritized conceptual breadth over strict internal consistency to capture the multifaceted nature of early career experiences. See Table 2 for descriptives of all independent variables included in the regression model. Descriptions of all composite variables are included in Table 3.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics on key characteristics.

Table 3.
Factor loadings for all composite variables.
5.3. Analyses
We addressed the first two (descriptive) research questions using three-way crosstabulations with z-tests with the Bonferroni correction. This allowed us to assess significant differences in early computing career experiences and perceptions by gender and race/ethnicity in how the sample perceived their belonging and identity in computing (research question one) and in their perception of inclusivity in computing work environments (research question two). In the tables reporting these crosstabs, note that bold values indicate significant differences between men and women within each racial/ethnic group (the higher value is bolded). Superscripts indicate significant differences between graduates of the same gender but different racial/ethnic identities (White, Caucasian, or European American = W, Asian or Asian American = A, Black or African American = B, Hispanic or Latina/o/x = L, and Indigenous, Middle Eastern, Multiracial, or Other = O).
To address research question three, which examined the factors that predict participants’ perception that the general environment in computing careers is inclusive of women, people of color, and women of color, we ran an Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) linear regression model. Before running the regression, we examined a correlation matrix using Pearson correlation coefficients and determined that none of the independent variables were highly correlated (greater than r = 0.5), which might present issues relating to multicollinearity. To further assess multicollinearity among predictors, we calculated Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs). All VIFs were below the commonly accepted threshold of 5, ranging from 1.01 to 2.97, indicating no significant multicollinearity.
6. Findings
6.1. Research Question One
This study first investigated how recent college graduates working full-time in computing fields perceive their belonging and identity in computing (see Table 4). We then further examined how these perceptions vary by gender and/or race/ethnicity. Most participants responded positively on these measures, indicating they generally felt a sense of belonging and identity in computing. More than half of participants agreed with the statements “I see myself as a computing person” and “I feel like I belong in computing.” However, there were notable gender differences with regard to these perceptions. Overall, men consistently reported higher belonging and identity in computing than women. For example, 87% and 81% of men agreed with “I see myself as a computing person” and “I feel like I belong in computing”, respectively, compared to only 70% and 60% of women. Further, 36% of women agreed that they “feel like an outsider in the computing community,” compared to only 19% of men. Finally, 48% of women reported feeling “welcomed in the computing community,” compared to 72% of men. These gender-based differences also emerged within racial/ethnic groups. For instance, 17% of Black women reported seeing themselves as leaders in computing compared to 46% of Black men. Similarly, only 33% of Latina women agreed with “Computing is a big part of who I am,” compared to 62% of Latino men. Finally, 48% of Asian or Asian American women reported feeling welcomed in the computing community compared to 70% of Asian or Asian American men.

Table 4.
Recent graduates’ perceptions of their belonging and identity in computing by gender and racial/ethnic identity, percent rating “Agree” or “Strongly Agree” (n = 845).
When examining responses from respondents of the same gender (i.e., among men or among women) but across racial/ethnic groups, we found significant differences in perceptions of belonging and identity in computing. For example, over 22% of Black women agreed they had an unfair supervisor/manager compared to only 3% of White women. Asian or Asian American men reported significantly lower belonging in computing (75%) than White men (87%).
6.2. Research Question Two
The second research question examined how recent college graduates working in computing fields perceive the inclusivity of their working environments as well as how these perceptions vary by gender and/or race/ethnicity (see Table 5). Generally, participants reported inclusive work environments in computing fields. For example, nearly 60% of participants agreed there is a supportive environment for women in computing careers and 56% of participants agreed there is a supportive environment for people of color in computing careers. However, despite these supportive environments, over 90% of participants strongly agreed there is a competitive environment in computing careers.

Table 5.
Recent graduates’ perceptions of a supportive work environment in computing by gender and racial/ethnic identity, percent rating “Agree” or “Strongly Agree” (n = 845).
While we did not observe any racial/ethnic differences in participants’ perceptions of the inclusivity of their working environments, there were many significant differences by gender. Overall, the results suggest that women working in computing fields hold a more critical view of the environment in computing careers compared to their male counterparts. For example, 65% of men reported a supportive environment for women in computing careers compared to only 49% of women. Similarly, 58% of men compared to only 34% of women reported a supportive environment for women of color in computing careers. Given that women generally reported less inclusive work environments, it follows that a higher proportion of women than men (48% vs. 40%) reported that people who succeed in computing tend to fit a certain stereotype.
These findings held when examining differences by gender within racial/ethnic groups (e.g., White, Asian/Asian American, Black/African American, and Hispanic or Latinx), such that men generally reported more inclusive work environments in computing careers than women. For example, 64% of Latino men reported a supportive environment for women of color in computing careers compared to only 38% of Latina women. Similarly, 63% of Asian or Asian American men reported a supportive environment for people of color in computing careers compared to only 47% of Asian or Asian American women.
6.3. Research Question Three
The third research question examined how the background characteristics, college experiences, and work environments of recent college graduates in computing fields predict their perception that the general environment in computing careers is inclusive of women, people of color, and women of color. After conducting OLS linear regression, the resulting model indicated six statistically significant predictors. Overall, the model predicted 28.7% of the variance in recent graduates’ perception of computing as inclusive. See Table 6 for a summary of the final OLS regression model.

Table 6.
Summary of OLS regression predicting perception of inclusivity in computing careers.
The following were positive predictors, meaning they were associated with perceiving a more inclusive environment in computing careers for the three groups specified above: computing identity and belonging, computing major, and a perception of the work environment as welcoming. Across all significant predictors, perceiving a welcoming work environment was the strongest predictor of perceiving general inclusivity in computing careers. Moreover, it is noteworthy that two of the three positive predictors (i.e., feeling connected to the computing community and majoring in computing) related to identities and experiences largely cultivated during students’ undergraduate experiences, further underscoring the utility of the decision to undergird the Social Cognitive Model of Career Self-Management with the Science Identity Model. As discussed in more detail below, these findings suggest the crucial role that undergraduate academic environments can play in shaping students’ later perceptions of their chosen career field.
The three negative predictors associated with perceiving the general environment in computing careers as less inclusive were identifying as a woman, prioritizing an inclusive work environment in the job search process, and reporting satisfaction with supervisor or manager (i.e., those who reported higher satisfaction with their manager were less likely to view the field of computing as inclusive). The relationship between identifying as a woman and holding a view of the field of computing as less inclusive reflects the previously discussed findings from the descriptive analyses: women are more likely than men to report experiencing exclusion or isolation in computing spaces, which may signal a lack of inclusivity in the computing work environment. Though they may seem somewhat counterintuitive, the other negative predictors point to the challenges of navigating the college-to-career transition, as students’ job search process may lead to a mismatch between the expectations and realities of their role as well as their experiences with their manager and their company overall. These findings will be discussed fully below.
7. Limitations
This study addresses questions related to recent college graduates’ perceptions of inclusivity in their tech workplaces. The study’s results make valuable contributions to the literature that examines how higher education institutions can broaden participation in computing, from the classroom to careers, particularly among women and people of color. Alongside these contributions, there are some limitations that nuance the ways in which these findings should be understood. First, the sample sizes necessitated aggregating across some racial/ethnic groups. Given the notable findings among racial groups, particularly among Asian and Asian American college graduates, future research should aim to further disaggregate these groups so as to gain a more focused understanding of their unique experiences. Additionally, although we have longitudinal data on many of the study participants, using multiple timepoints for this study would have significantly reduced our analytical sample, which would have further limited our ability to study individuals from minoritized groups. Therefore, this study uses a single timepoint (the fall 2020 follow-up survey). This leads to some “chicken or the egg” uncertainties, especially about the role of measures like computing identity or belonging. Given our conceptual framework, we have largely focused on the role of colleges and universities in strengthening computing identity and belonging, but we recognize that students’ experiences prior to college also shape this and other psychosocial traits (e.g., striver personality). Related to the timing of the survey, fall of 2020 was a tumultuous time globally, as the world was still immersed in the COVID-19 pandemic and there was heightened attention on racial justice. Both of these and other factors may have shaped how respondents perceived inclusivity and belonging. Further, recent college graduates in this study all attended institutions that had made an expressed commitment to broadening participation in computing. Hence, majoring in computing at a BRAID institution may have especially primed them to view computing careers as inclusive. Future work should draw from broader institutional samples. Finally, this study broadly defined a career in computing. Future studies should consider narrowly focusing on a specific functional area (e.g., coders) or a specific type of work environment (e.g., small start-ups) to better understand how perceptions of inclusivity can vary within more narrowly defined environments.
8. Discussion and Implications
This study investigated the early career experiences of recent college graduates working full-time in computing fields and the relationship between these experiences and their perception of the field of computing as inclusive, emphasizing their sense of belonging and computing identity. In the following sections, we discuss these findings in conversation with the extant literature and our conceptual frameworks, drawing conclusions about the study’s implications for research and practices.
8.1. Computing Identity and Belongingness Among New Computing Professionals
Our findings underscore the need to continue developing an understanding of how identity shapes participation in computing. Carlone and Johnson’s (2007) work is often used to point to ways that undergraduate students can be socialized into STEM. The findings from this study suggest that early career professionals similarly need to have tangible markers of their belongingness in their chosen field. Indeed, we found that one’s computing identity and belonging was a significant positive predictor of participants’ perception of the field as inclusive. Previous research has routinely found that sense of belonging is a key predictor of various outcomes related to an individual’s success in computing, particularly retention in the field (Aschbacher et al., 2010; Blaney & Stout, 2017; Cheryan et al., 2009; George et al., 2022; Hausmann et al., 2007; Perez et al., 2014; Stormes, 2023; Strayhorn, 2018; Taheri et al., 2018). This finding builds from that body of work and makes clear the connection between the individual’s own sense of fit in the field and their larger view of the field as a whole. In other words, this finding suggests that, when a person sees themselves as a computing person and feels a sense of fit in the field, they are more likely to believe the field is inclusive, but the opposite is also true, such that negative experiences not only impact an individual’s own experience in computing but also their overall view of the field.
Gender and Racial/Ethnic Differences
Our analyses revealed widespread gender and racial/ethnic differences across all dimensions of our study. We note that women rate themselves significantly lower than men on their sense of belonging and computing identity, and they are more likely than men to report negative experiences in their workplace. Further, we found that identifying as a woman was a negative predictor of viewing the overall field of computing as inclusive. This study extends what is known about sense of belonging among undergraduate computing students—women tend to come to computing courses with lower computing belonging than men and this gap widens over time (Sax et al., 2018)—and highlights how gender gaps in computing identity and belonging persist from college into career and have longer-term implications for individuals’ view of the field of computing.
Further, this study underscores the need to examine individuals’ computing experiences intersectionally. For instance, White and Asian/Asian American men are often aggregated into a single “majority” group, even as Asian and Asian American technologists have varying experiences in computing and face systemic and exclusionary barriers in the field (Tari et al., 2021). This study highlights the importance of disaggregating groups as much as possible in analyses, as Asian and Asian American men reported significantly lower sense of belonging than their White male peers. This finding reminds us that while academic identities (e.g., Carlone and Johnson’s Science Identity) play a key role in shaping perceptions, social identities such as gender and race also powerfully influence how early college graduates make sense of their place within the tech field.
Indeed, it is important that we disentangle our understanding of “representation” from the experiences of people in computing. This is particularly true for women of color who hold multiple marginalized identities and navigate systemic barriers founded on racist and sexist practices in computing (Ong et al., 2011; Rankin & Thomas, 2020). The Black women in our study reported having an unfair manager at significantly higher rates than did White women. These findings echo the results of AnitaB.org’s (2021) Technical Equity Experience Survey, which unveiled a number of ways in which Black women working in computing have negative experiences in the workforce, ranging from reporting the lowest sense of belonging of women in any racial/ethnic group to being the most likely of women from any racial/ethnic group to report feeling unsafe on their work teams. Indeed, gendered racism influences Black women’s ability to persist in computing and shapes their early career experiences (Rankin & Thomas, 2020); more intersectional research is needed that highlights the lived experiences of Black women in computing, as well as the experiences of those from other oft-overlooked marginalized groups.
8.2. The Role of Colleges in Recent Graduates’ Career Transitions
The respondents in our sample were all college graduates within one or two years of graduation who held full-time jobs in the field of computing. As suggested by CSM (Lent & Brown, 2013), our study demonstrates the importance of college experiences in shaping their transitions to the workforce and their early career experiences. In alignment with previous work suggesting that congruence between one’s major and career promotes job satisfaction (Xu, 2017), we found that majoring in computing in college was a positive predictor of viewing the field as inclusive. Drawing on SCCT/CSM (Lent & Brown, 2013) and Science Identity Theory (Carlone & Johnson, 2007), we hypothesize that this finding relates to the socialization process graduates who majored in computing might have experienced in college. Indeed, previous work found that participating in computing organizations in college predicted college students’ computing career aspirations (George et al., 2022); relatedly, a prior study indicated that having social relationships in college positively predicted CS career intentions for Black women (Ross et al., 2020). Computing departments can leverage these opportunities to prepare students for the college-to-career transition by embedding identity-and-belonging work into the curriculum, infusing career readiness initiatives into all levels of the program, and formalizing alumni mentoring programs to create near–peer support for students’ transition to their first professional role.
At the same time, this finding raises the question as to how those who enter a computing career without having majored in computing fare; this is especially important because historically marginalized individuals tend to develop interests in computing later such that they may take their first computing course at the end of their college career (Lehman et al., 2020) or come to the field after completing a computing internship, rather than a computing degree (Lehman et al., 2023). Hence, colleges and universities play a key role in preparing their graduates for the transition to their career in computing, regardless of major. Career offices can serve as important intermediaries between students and future employers by facilitating internships and supporting students in their job search.
Related to the job search process, we found that those who prioritized an inclusive work environment in their job search were less likely to view the field as inclusive, thereby supporting the prior literature which ties job search behaviors to an individual’s job satisfaction (Mau & Kopischke, 2001; van Hooft et al., 2021). Indeed, college students are likely to meet barriers and unmet expectations in their career transition, particularly for women, women of color, and people of color (AnitaB.org, 2021; Lutz & Paretti, 2021; Xu, 2017). Hence, campuses may need to support their students in processing these experiences and advocating for themselves. Further, colleges and universities hold privileged spaces in society and can often use their influence to effect change—we offer that colleges and universities can advocate for change with tech employers. At the same time, tech employers hold the responsibility to interrogate the negative experiences recent graduates face as they assume roles in the tech workforce and to seek to address structural and systemic barriers that may be driving them.
8.3. Computing Workplaces as Inclusive Spaces
Above all, the findings from our study assert the importance of a workplace in shaping an individual’s view of the field as a whole: the strongest predictor of recent graduates’ views of computing as an inclusive field was a welcoming environment in their current workplace. Indeed, when tech companies hire recent graduates, this job may well be their first exposure to a career in computing. As the differences between a college and workplace environment are palpable (Lutz & Paretti, 2021), employers should not take that power lightly. At the undergraduate level, research on best practices to broaden participation in undergraduate computer science underscores the importance of students’ introductory courses serving as many individuals’ first encounter with computing (Lazowska et al., 2013). Our findings suggest that an individual’s first job in the field plays a similarly important role. Relatedly, our study found an inverse relationship between recent graduates’ satisfaction with their supervisor/manager and their view of the field (i.e., those who were more satisfied with their supervisor were less likely to view computing as inclusive). Though counterintuitive, it connects to previous findings that suggest that college students who had mentors who discussed career options were less likely to aspire to a computing career (George et al., 2022). We arrive at a similar conclusion as George and her colleagues to explain the phenomenon in the present study: it is possible that recent graduates are seeking out their supervisor for support when experiencing challenging circumstances at the company more broadly. Alternatively, it is possible that supervisors are sharing stories about their own or others’ negative experiences in computing. Hence, more research is needed to clarify the role of supervision in new employees’ transition to the computing workforce.
As tech companies seek to recruit and retain more women, women of color, and people of color in their companies, particularly in technical roles (AnitaB.org, 2022), the findings from this study emphasize the need to increase support for employees new to the field. Given that recent college graduates will have participated in programs and initiatives that intentionally centered and supported their identities in STEM (e.g., student organizations, conferences such as the Grace Hopper Celebration, etc.), early career computing professionals should be provided with similar opportunities to engage during their initial transition into their new roles. This may look like mentoring and training programs both for new hires as well as for current employees to increase individuals’ computing identity and belonging and promote a welcoming environment. Further, employers should seek to identify and implement policies that promote workplace inclusivity, knowing that their employees’ perceptions of their workplace will translate to their view of the field writ large. CSM (Lent & Brown, 2013) emphasizes the cyclic nature of career decision-making. Early career professionals will continually reevaluate their belongingness in the field, and retaining diverse talent requires providing intentional and ongoing support.
9. Conclusions
While higher education institutions are charged with equipping their graduates with the skills and knowledge to thrive in the workplace, the findings from this study highlight the ways that undergraduate experiences can also shape students’ longer term career trajectories. Alongside their gender and racial identities, the identity of being a “computing person” is crucially important to early career professionals’ ability to thrive in the workplace. Computing departments play a key role in helping develop these identities through the ways that faculty interact with their students as well as the opportunities afforded to students through student organizations. As these students transition into the workplace as early career professionals, it is important to continue emphasizing the ways in which the field of computing not only needs, but also explicitly values, diversity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.J.L. and S.S.; methodology, K.J.L. and T.R.; software, K.J.L.; validation, K.J.L., T.R. and S.S.; formal analysis, K.J.L. and T.R.; investigation, K.J.L., T.R. and S.S.; resources, K.J.L.; data curation, K.J.L., T.R. and S.S.; writing—original draft K.J.L., T.R. and S.S.; writing—review and editing, K.J.L. and S.S.; visualization, K.J.L. and S.S.; supervision, K.J.L.; project administration, K.J.L.; funding acquisition, K.J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation grant number 1525737. The APC was fully waived.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was approved by the Institutional Review Board of UCLA (approval code: IRB-15-1164; approval date: 18 August 2015).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because they are part of an ongoing study. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the Momentum staff at momentum@ucla.edu.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Variable Definitions and Coding Scheme
| Variable | Definition/Coding Scheme |
| Dependent Variable | |
| Perception of a supportive environment in computing careers | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Person Inputs (Block 1) | |
| Gender | Dichotomous: 0 = Man; 1 = Woman |
| Race/Ethnicity (Aggregated Groupings) | 1 = White, Caucasian, or European American; 2 = Asian or Asian American; 3 = Black or African American; 4 = Hispanic or Latina/o; 5 = Arab, Middle Eastern, or Persian; 6 = Indigenous, Multiracial, or Other |
| Asian Race/Ethnicity (ref. group: White) | Dummy coded: 0 = Not Asian or American; 1 = Asian or Asian American |
| Black Race/Ethnicity (ref. group: White) | Dummy coded: 0 = Not Black or African American; 1 = Black or African American |
| Latinx Race/Ethnicity (ref. group: White) | Dummy coded: 0 = Not Hispanic or Latina/o; 1 = Hispanic or Latina/o |
| Background Contextual Influences (Block 2) | |
| Socioeconomic status | 1 = Poor; 2 = Below Average; 3 = Average; 4 = Above Average; 5 = Wealthy |
| Parental education level | 1 = High school or less; 2 = Some college or associate’s degree; 3 = Bachelor’s degree; 4 = Graduate/Professional Degree |
| Computing Identity and Belonging | Five-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Learning Experiences (Block 3) | |
| Major | 0 = Non-computing major; 1 = Computing major |
| Minor | 0 = Non-computing minor; 1 = Computing minor |
| Prior internship experience | 1 = I have not participated in a computing-related internship or co-op; 2 = 1 computing-related internship or co-op; 3 = 2 computing-related internships or co-ops; 4 = 3 computing-related internships or co-ops; 5 = More than 3 computing-related internships or co-ops |
| Personality (Block 4) | |
| Leadership and Confidence | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Striver Personality | Two-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Contextual Influences (Block 5) | |
| Prioritizing Inclusive Work Environment | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Colleague Support | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Collaborative Job Functions | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Computing Job Functions | Two-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Welcoming Job Environment | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Personal Value in Job Environment | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Job Satisfaction with Organizational Values | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Job Satisfaction with Salary and Benefits | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Job Satisfaction with Appreciation and Promotions | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Job Satisfaction with Supervisor or Manager | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Self-Efficacy Expectations (Block 6) | |
| Computing Self-Concept | Four-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Success in Computing | Three-item factor scale (Table 3) |
| Outcome Expectations (Block 7) | |
| Perception of a supportive environment in computing careers | See above (DV) |
Note
| 1 | A variety of terms are common in the STEM literature to describe individuals from historically excluded racial/ethnic groups. This paper focuses on how experiences vary between individuals in different racial/ethnic groups, with a particular emphasis on the field of computing’s inclusivity of individuals who identify as Asian/Asian American, Black/African American, Hispanic/Latina/o/x, Indigenous/Native People, Middle Eastern, and/or Multiracial. The survey from which these data were drawn used the phrase “People of Color” to reference this group and that term is central to the dependent variable used in this study. Hence, we use that phrase to reference this group in the aggregate, while recognizing its limitations. As described in our analyses, we disaggregated these groups to the extent possible to focus on the unique experiences of individuals from specific racial/ethnic groups. |
References
- AnitaB.org. (2021, May). Technical equity experience survey: The field of technology continues to fail women, Non-binary people: Experiences and impacts worst when viewed intersectionally. AnitaB.org. Available online: https://legacy.anitab.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Anita-B-TechEES-2022-Report-FINAL-1.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- AnitaB.org. (2022). Top companies for women technologists: Key findings & insights report. AnitaB.org. Available online: https://anitab.org/research-and-impact/top-companies/2022-results/ (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Armstrong, D. J., Riemenschneider, C. K., Allen, M. W., & Reid, M. F. (2007). Advancement, voluntary turnover, and women in IT: A cognitive study of work–family conflict. Information Management, 44(2), 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aschbacher, P. R., Li, E., & Roth, E. J. (2010). Is science me? High school students’ identities, participation and aspirations in science, engineering, and medicine. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 47(5), 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L. (2009). Student and faculty perceptions of undergraduate research experiences in computing. ACM Transactions on Computing Education, 9(1), 5:1–5:28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, J. M., & Stout, J. G. (2017, March 8–11). Examining the relationship between introductory computing course experiences, Self-efficacy, and belonging among first-generation college women. 2017 ACM SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (pp. 69–74), Seattle, WA, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlone, H. B., & Johnson, A. (2007). Understanding the science experiences of successful women of color: Science identity as an analytic lens. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 44(8), 1187–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R. Y. (2016). Understanding the purpose of higher education: An analysis of the economic and social benefits for completing a college degree. Journal of Education Policy, Planning and Administration, 6(5), 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cheryan, S., Plaut, V. C., Davies, P. G., & Steele, C. M. (2009). Ambient belonging: How stereotypical cues impact gender participation in computer science. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, L. (2011). Pipelines and pathways: Women of color in undergraduate STEM majors and the college experiences that contribute to persistence. Harvard Educational Review, 81(2), 209–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, N. A., & Singh, R. (2012). Stemming the tide: Why women leave engineering. University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. Available online: https://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/NSF_Stemming%20the%20Tide%20Why%20Women%20Leave%20Engineering.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- George, K. L., Sax, L. J., Wofford, A. M., & Sundar, S. (2022). The tech trajectory: Examining the role of college environments in shaping students’ interest in computing careers. Research in Higher Education, 63(5), 871–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, I. R., & Stanton, J. M. (2008). Women’s adaptation to the IT culture. Women’s Studies, 37(3), 202–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, L. R. M., Schofield, J. W., & Woods, R. L. (2007). Sense of belonging as a predictor of intentions to persist among African American and White first-year college students. Research in Higher Education, 48(7), 803–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S. A., Sherbin, L., Dieudonné, F., Fargnoli, C., & Fredman, C. (2014). Athena factor 2.0: Accelerating female talent in science, engineering & technology. Center for Talent Innovation. Available online: https://coqual.org/reports/athena-factor-2-0-accelerating-female-talent-in-science-engineering-technology/ (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Hu, S., & Wolniak, G. C. (2013). College student engagement and early career earnings: Differences by gender, race/ethnicity, and academic preparation. The Review of Higher Education, 36(2), 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazowska, E., Reges, S., Martin, H., & Eney, C. (2013). Broadening participation: The why and the how. Computer, 46(3), 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lehman, K. J., Sax, L. J., & Zimmerman, H. B. (2016). Women planning to major in computer science: Who are they and what makes them unique? Computer Science Education, 26(4), 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, K. J., Stormes, K., Smith, K., & Lapan, J. (2023, April 13–16). Exploring participation in computing internships among undergraduates in non-computing majors. American Education Research Association Annual Meeting 2023, Chicago, IL, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, K. J., Wofford, A. M., Sendowski, M., Newhouse, K. N., & Sax, L. J. (2020, March 11–14). Better late than never: Exploring students’ pathways to computing in later stages of college. 51st ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (pp. 1075–1081), Portland, OR, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Lent, R. W., & Brown, S. D. (2013). Social cognitive model of career self-management: Toward a unifying view of adaptive career behavior across the life span. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 60, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lent, R. W., Brown, S. D., & Hackett, G. (1994). Toward a unifying social cognitive theory of career and academic interest, choice, and performance. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 45(1), 79–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lent, R. W., Nota, L., Soresi, S., Ginevra, M. C., Duffy, R. D., & Brown, S. D. (2011). Predicting the job and life satisfaction of Italian teachers: Test of a social cognitive model. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 79(1), 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lent, R. W., Sheu, H.-B., Singley, D., Schmidt, J. A., Schmidt, L. C., & Gloster, C. S. (2008). Longitudinal relations of self-efficacy to outcome expectations, interests, and major choice goals in engineering students. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 73(2), 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, S., Ross, M., Hazari, Z., Weiss, M. A., Georgiopoulos, M., & Christensen, K. (2021). How do educational experiences predict computing identity? ACM Transactions on Computing Education, 22(2), 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, B., & Paretti, M. C. (2021). Exploring the social and cultural dimensions of learning for recent engineering graduates during the school-to-work transition. Engineering Studies, 13(2), 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, J. B., & Schimpf, C. (2017). The underrepresentation of women in computing fields: A synthesis of literature using a life course perspective. IEEE Transactions on Education, 60(4), 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, J., Estrella, R., Goode, J., Holme, J. J., & Nao, K. (2008). Stuck in the shallow end. MIT Press. Available online: https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262514040/stuck-in-the-shallow-end/ (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Margolis, J., & Fisher, A. (2002). Unlocking the clubhouse: The Carnegie Mellon experience. ACM SIGCSE Bulletin, 34(2), 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, W. C., & Kopischke, A. (2001). Job search methods, job search outcomes, and job satisfaction of college graduates: A comparison of race and sex. Journal of Employment Counseling, 38(3), 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Education Statistics. (2020). Digest of education statistics. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/digest/d20/tables/dt20_322.50.asp (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- National Center for Education Statistics. (2022). Employment and unemployment rates by educational attainment. Condition of education. U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/coe/indicator/cbc (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- NCWIT. (2022). By the numbers. National Center for Women & Information Technology. Available online: https://ncwit.org/resource/bythenumbers/ (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Ong, M., Wright, C., Espinosa, L., & Orfield, G. (2011). Inside the double bind: A synthesis of empirical research on undergraduate and graduate women of color in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Harvard Educational Review, 81(2), 172–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, T., Cromley, J. G., & Kaplan, A. (2014). The role of identity development, values, and costs in college STEM retention. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, Y. A., & Thomas, J. O. (2020, March 11–14). The intersectional experiences of black women in computing. 51st ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (pp. 199–205), Portland, OR, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemenschneider, C. K., Armstrong, D. J., Allen, M. W., & Reid, M. F. (2006). Barriers facing women in the IT workforce. DATABASE Advances in Information Systems, 37(4), 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S. L., & Lehman, K. (2017). Developing the next generation of diverse computer scientists: The need for enhanced, intersectional computing identity theory. Computer Science Education, 27(3–4), 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M., Hazari, Z., Sonnert, G., & Sadler, P. (2020). The intersection of being black and being a woman: Examining the effect of social computing relationships on computer science career choice. ACM Transactions on Computing Education, 20(2), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassler, S., Glass, J., Levitte, Y., & Michelmore, K. M. (2017). The missing women in STEM? Assessing gender differentials in the factors associated with transition to first jobs. Social Science Research, 63, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sax, L. J., Blaney, J. M., Lehman, K. J., Rodriguez, S. L., George, K. L., & Zavala, C. (2018). Sense of belonging in computing: The role of introductory courses for women and underrepresented minority students. Social Sciences, 7(8), 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, L. J., Lehman, K. J., Jacobs, J. A., Kanny, M. A., Lim, G., Monje-Paulson, L., & Zimmerman, H. B. (2017). Anatomy of an enduring gender gap: The evolution of women’s participation in computer science. The Journal of Higher Education, 88(2), 258–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, A. D., Thompson, M. E., Wang, S., Kusimo, A., Gilmartin, S., & Sheppard, S. (2020). The confidence gap predicts the gender pay gap among STEM graduates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 117(48), 30303–30308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stormes, K. (2023). Compiling a computing identity: A byte of self-efficacy, belonging, and other predictive factors [Unpublished Doctoral dissertation, University of California Los Angeles]. [Google Scholar]
- Strayhorn, T. L. (2012). College students’ sense of belonging (1st ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayhorn, T. L. (2018). College students’ sense of belonging (2nd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, K. S. (2018). The use of Cronbach’s alpha when developing and reporting research instruments in science education. Research in Science Education, 48(6), 1273–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M., Ross, M., Hazari, Z., Weiss, M., Georgiopoulos, M., Christensen, K., Solis, T., Garcia, A., & Chari, D. (2018, October 3–6). A structural equation model analysis of computing identity sub-constructs and student academic persistence. 2018 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1–7), San Jose, CA, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, M., Hua, V., Ng, L., & Annabi, H. (2021). How Asian women’s intersecting identities impact experiences in introductory computing courses. In K. Toeppe, H. Yan, & S. K. W. Chu (Eds.), Diversity, divergence, dialogue (Vol. 12645, pp. 603–617). Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauth, E. M. (2002). Odd girl out: An individual differences perspective on women in the IT profession. Information Technology & People, 15(2), 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauth, E. M. (2006). Theorizing gender and information technology research using the individual differences theory of gender and IT. In The encyclopedia of gender and information technology (pp. 1154–1159). Idea Group. [Google Scholar]
- Trauth, E. M., Quesenberry, J. L., & Morgan, A. J. (2004). Understanding the under representation of women in IT: Toward a theory of individual differences. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGMIS conference on computers and people research (pp. 114–119). Association for Computing Machinery. [Google Scholar]
- Trauth, E. M., Quesenberry, J. L., & Yeo, B. (2008). Environmental influences on gender in the IT workforce. ACM SIGMIS Database, 39(1), 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. (2024). High tech, low inclusion: Diversity in the high tech workforce and sector, 2014–2022. Available online: https://www.eeoc.gov/sites/default/files/2024-09/20240910_Diversity%20in%20the%20High%20Tech%20Workforce%20and%20Sector%202014-2022.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- van Hooft, E. A. J., Kammeyer-Mueller, J. D., Wanberg, C. R., Kanfer, R., & Basbug, G. (2021). Job search and employment success: A quantitative review and future research agenda. Journal of Applied Psychology, 106(5), 674–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardell, M., Sawyer, S., Mitory, J., & Reagor, S. (2006). Gender and IT professionals in the United States: A survey of college graduates. Journal of Social and Economic Relations at Work, 16(3), 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J., Korn, R., & Ghani, A. (2022). Pinning down the jellyfish: The workplace experiences of women of color in tech. The Center for Worklife Law, University of California Hastings Law. [Google Scholar]
- Windeler, J. B., & Riemenschneider, C. (2013). Organizational commitment of IT workers: Leader support and differences across gender and race. In Proceedings of the annual conference on computers and people research (pp. 3–14). Association for Computing Machinery. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. J. (2017). Attrition of women in STEM: Examining job/major congruence in the career choices of college graduates. Journal of Career Development, 44(1), 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. (2008). Gender and racial gaps in earnings among recent college graduates. The Review of Higher Education, 32(1), 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).