Abstract
In the era of educational digital transformation, integrating information and communication technology (ICT) into school administration aligns with the goals of promoting personalized learning, equity, and teaching quality. This study examines how ICT reshapes management practices, addresses challenges, and achieves educational objectives. To explore ICT’s impact on school administration (2009–2024), we conducted a systematic scoping review of four databases (Web of Science, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and IEEE Xplore) following the PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Retrieved studies were screened, analyzed, and synthesized to identify key trends and challenges. The results show that ICT significantly improves administrative efficiency. Automated systems streamline routine tasks, allowing administrators to allocate more time to strategic planning. It enables data-driven decision-making. By analyzing large datasets, ICT helps identify trends in student performance and resource utilization, facilitating accurate forecasting and better resource allocation. Moreover, ICT strengthens stakeholder communication. Online platforms enable instant interaction among teachers, students, and parents, increasing the transparency and responsiveness of school administration. However, there are challenges. Data privacy concerns can erode trust, as student and staff data collection and use may lead to breaches. Infrastructure deficiencies, such as unreliable internet and outdated equipment, impede implementation. The digital divide exacerbates inequality, with under-resourced schools struggling to utilize ICT fully. ICT is vital in educational administration. Its integration requires a strategic approach. This study offers insights for optimizing educational management via ICT and highlights the need for equitable technological advancement to create an inclusive, high-quality educational system.
1. Introduction
In the digital era, ICT has become a cornerstone of modern educational management, reshaping how schools operate and interact with their stakeholders (Bharti et al., 2024). Educational institutions worldwide are increasingly adopting ICT solutions to address the growing complexity of administrative tasks, improve decision-making processes, and enhance stakeholder communication (Saif et al., 2022). From primary schools to higher education, ICT integration has emerged as a transformative force in educational administration, offering innovative solutions to longstanding managerial challenges (Baharuldin et al., 2019; Krishnaveni & Meenakumari, 2010).
The 2010s marked a turning point with the proliferation of cloud computing, Big Data analytics, and mobile technologies (Yang et al., 2017). These developments enabled more sophisticated data-driven decision-making capabilities, allowing administrators to access real-time information and analytics across multiple platforms (Ambasht, 2023). The rise of AI and machine learning (ML) further accelerated innovation, offering predictive analytics that optimize resource allocation (Nama et al., 2023; Xu & Wang, 2025a, 2025b). Today, schools are leveraging advanced ICT tools such as blockchain for secure record-keeping, virtual and augmented reality for enhanced training experiences, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices for smart campus management (Swargiary, 2024). The journey of ICT in educational administration began with basic computerization efforts in the 1980s, primarily focusing on administrative tasks such as record-keeping and payroll management (Haruna & Abdullahi, 2022). Early systems were often standalone and lacked integration, resulting in fragmented data silos. However, with the advent of the internet and advancements in networking technologies, schools began to adopt more sophisticated ICT solutions by the late 1990s and early 2000s (Kozma & Isaacs, 2011). This period saw the emergence of student information systems (SIS) (El-Bakry et al., 2009), learning management systems (LMS) (Cheng & Yuen, 2018), and financial management platforms (Yan, 2022) that began to connect previously disparate administrative functions.
The integration of ICT in educational administration has transformed several core functions, each contributing to more efficient and effective educational management. One of the most immediate benefits of ICT implementation is the significant enhancement of administrative efficiency (Qureshi & Qazi Abro, 2016). The automation of routine tasks such as attendance tracking, report generation, and exam scheduling has freed up administrative staff to focus on more strategic initiatives (Tayong, 2023). For example, cloud-based platforms such as Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 enable real-time collaboration among staff members, reducing document versioning issues and improving response times (Elmroth et al., 2017). Workflow automation tools have further streamlined operations, allowing for automatic task assignment and progress tracking (Adepoju et al., 2022). ICT systems have revolutionized the way schools approach decision-making by providing comprehensive, data-driven insights (Alsbou & Alsaraireh, 2024). Learning analytics platforms can track student progress in real-time, identifying at-risk students and enabling timely intervention (Ravichandran, 2024). Financial management systems provide detailed expenditure tracking and predictive budgeting tools, helping administrators make informed resource allocation decisions (Mohzana, 2024). Strategic planning tools leverage historical data and predictive algorithms to forecast enrollment trends, facility needs, and staffing requirements (Kalusivalingam et al., 2020). Effective communication is critical for successful school administration, and ICT has significantly enhanced this aspect (Oyedemi, 2015). Parent-teacher communication platforms such as ClassDojo and Remind facilitate real-time updates between educators and families (Wyne et al., 2021). SIS often includes parent portals where guardians can access grades, attendance records, and important announcements (Dries, 2014). Social media and school websites serve as important information dissemination tools, while mobile apps provide push notifications for emergencies and important events (Cox & McLeod, 2014). These technologies have created more transparent and responsive communication channels between schools and their communities. While primarily focused on administration, ICT also supports teaching and learning functions that indirectly benefit administration. LMSs such as Moodle and Canvas streamline course administration while enhancing the learning experience. Student information systems provide valuable data to teachers for individualized instruction and progress monitoring (Sohail et al., 2025). Special educational management systems help administrators coordinate support services for students with disabilities (Blackwell & Lilly, 2022). These interconnected systems create a more cohesive educational ecosystem that benefits both administrators and educators.
The adoption of ICT in educational administration has led to several transformative changes. First is business simplification. ICT eliminates manual processes, reducing paperwork and administrative burdens (Nielsen, 2016). Automated systems ensure greater accuracy in record-keeping and reporting, minimizing human error (Pancholi et al., 2025). Digital workflows ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory requirements. Second, it is resource optimization. Advanced analytics enable more efficient allocation of human, financial, and physical resources (Adesina et al., 2024). Predictive maintenance systems for school facilities reduce downtime and repair costs. Energy management systems optimize utility consumption, leading to cost savings (Saleem et al., 2023). Furthermore, accountability can be strengthened. ICT systems provide transparent tracking of administrative processes, enhancing accountability at all levels (Kuriyan et al., 2011).
With the continuous development of ICT, new trends and technologies are expected to further change educational management. These technologies can mainly be classified into the following categories. First of all, AI, including machine learning and deep learning, has demonstrated powerful effects in applications in many fields (Xu et al., 2023; Xu & Wang, 2025a, 2025b). Researchers apply ML algorithms to analyze student data and predict academic performance and recommend intervention measures (Y. Luo, 2023). Chatbots can handle daily administrative inquiries, allowing employees to free up time to complete more complex tasks (Lee et al., 2019). The AI-driven course scheduling system optimizes the class schedule and teachers’ homework (Taye et al., 2023). The second is blockchain technology. The secure and immutable records of blockchain technology support credential verification and transcript sharing (Han et al., 2018). Smart contracts automate administrative processes such as fee payment and scholarship payment (Nguyen-Hoang et al., 2024). The blockchain voting system enhances the transparency of school governance. There is also IoT-based smart classroom technology to monitor environmental conditions and equipment (Burunkaya & Duraklar, 2022). Smart cards track students’ attendance rates and campus activities. IoT devices facilitate remote monitoring of school facilities and equipment (Dixon & Abuzneid, 2020). Finally, there are VR and AR. These technologies enhance teachers’ professional development plans through immersive training experiences. Virtual campus tours have improved the recruitment process, and AR applications support maintenance operations and asset management (Khatri, 2024).
While significant progress has been made in ICT adoption, the research landscape remains fragmented. Most studies concentrate on specific technologies such as LMS (Guo & Xie, 2021; Weng & Tang, 2014) or data analytics platforms (Yu, 2023; Zhou & Li, 2024). There is limited comparative analysis across different ICT solutions. Research is heavily concentrated in developed countries, with China dominating the field (S. Cao, 2016; Wang, 2021; Zhou & Li, 2024). There is a paucity of comprehensive reviews that examine ICT’s impact across all administrative functions. Existing reviews often focus narrowly on specific technologies or applications, missing the broader picture. Many studies suffer from small sample sizes, lack of control groups, or insufficient longitudinal data. The dominance of case studies and single-institution analyses limits the generalizability of findings. The impact of newer technologies such as blockchain, VR/AR, and IoT remains largely unexplored in the context of school administration. Their potential benefits and challenges require more systematic examination.
This study explores the multifaceted impact of ICT on school administration through a systematic scoping review, focusing on its applications, benefits, and challenges across diverse educational contexts. The primary objective of this study is to systematically map and synthesize existing research on ICT in school administration, focusing on its applications, impacts, and challenges. Specifically, it aims to: identify global publication trends in ICT-based school administration research; categorize and analyze different research designs and methodologies employed; examine the range and implementation of ICT tools in various administrative areas; investigate the evaluation metrics used to assess ICT’s impact; and synthesize key findings, benefits, and persistent challenges.
To achieve these objectives, this study addresses the following research questions:
- (1)
- What are the temporal and geographic patterns in ICT research related to school administration?
- (2)
- What research methodologies and designs have been most commonly used?
- (3)
- Which ICT tools are most prevalent, and how are they implemented in different administrative contexts?
- (4)
- What evaluation frameworks and indicators are used to measure ICT’s impact?
- (5)
- What are the documented benefits, limitations, and implementation challenges of ICT in school administration?
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
This systematic scoping review’s reports follow the guidelines of the PRISMA-ScR, which stands for the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (Moher et al., 2010). In this study, the relevant literature was screened from four databases: Web of Science, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and IEEE Xplore. These databases were strategically selected to encompass multidisciplinary perspectives on educational technology, with Web of Science covering education and management sciences, Scopus providing wider global coverage of all types of academic publications, ScienceDirect indexing authoritative journals in computer science and educational engineering, and IEEE Xplore focusing on cutting-edge ICT research. The search date was 10 June 2025, and the search terms included “information and communication technology,” “technology,” “educational administration,” “school administration,” “higher education administration,” and “education management.”, etc. (see Table 1). PRISMA-ScR checklist, see Appendix A.

Table 1.
Selected databases and search formats.
2.2. Data Selection and Extraction
All retrieved records were imported into EndNote 21 software for deduplication and initial screening. Two independent reviewers (authors TL and YL) assessed the titles and abstracts of articles against predefined inclusion criteria, with discrepancies resolved through discussion or arbitration by a third reviewer (author PP). To maintain focus on empirically grounded studies demonstrating practical impacts, the inclusion criteria required that studies: (1) examined ICT integration in educational administration, particularly involving digital tools or AI application, to ensure this study directly aligns with our research objective of understanding technology’s role in administrative practice, not just in pedagogy or learning; (2) investigated the practical effects of technology on management efficiency, decision-making, or administrative processes to focus the review on functional outcomes relevant to institutional performance and school governance; (3) reported measurable outcomes related to ICT implementation to ensure the findings are actionable and grounded in real-world observations; (4) were original journal articles to ensure methodological transparency and research integrity. Conference papers are not generally considered authoritative sources in management and education, so they were excluded; and (5) were published in English. Conversely, studies were excluded if they: (1) applied technology outside educational contexts; (2) focused solely on theoretical frameworks without empirical validation; (3) addressed administrative tasks unrelated to efficiency improvements (e.g., recruitment and hiring); (4) Conference papers were excluded because they often lack the rigorous peer-review process and comprehensive methodological detail typically found in peer-reviewed journals, which are critical for synthesizing high-confidence evidence in a scoping review. However, we acknowledge that some conference proceedings are respected in ICT and education research; these were excluded primarily because of inconsistent availability of full-text data and the prioritization of peer-reviewed sources for methodological consistency; or (5) were not written in English. These criteria, summarized in Table 2, ensured the review’s relevance to its objective of synthesizing practical insights into ICT applications in school administration (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
2.3. Data Charting and Critical Appraisal of Included Studies
A standardized data extraction form was developed based on the Joanna Briggs Institute guidelines (Peters et al., 2020) and refined through pilot testing with five articles representing diverse geographic regions and publication years. The final form captured detailed information, including authorship, publication year, country of origin, research design, thematic focus, sample characteristics, administrative functions addressed, types of ICT tools employed, implementation strategies, evaluation metrics, key findings, and identified limitations. Two reviewers (authors TL and YL) independently extracted data from the 19 included studies, with disagreements resolved via a third reviewer (author PP) adjudication to ensure consistency in interpreting complex methodologies and outcome measures.
To ensure the reliability and validity of the synthesized evidence, all included studies underwent a critical appraisal of their methodological quality. We employed the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) (Hong, 2018), version 2018, a validated instrument for assessing the quality of diverse study designs (quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods) in systematic and scoping reviews. The MMAT evaluates five criteria: (1) appropriateness of the research question, (2) appropriateness of this study design to address the question, (3) adequacy of data collection methods, (4) consideration of confounding factors or biases (for quantitative studies) or rigor of data analysis (for qualitative studies), and (5) validity of findings (e.g., alignment between data, analysis, and conclusions).
2.4. Collating, Summarizing, and Reporting the Results
Extracted data were systematically analyzed using descriptive statistics to characterize the sample of included studies. The results were presented descriptively with supplementary graphs and charts to enhance clarity, followed by narrative synthesis to address the review’s specific research questions. The findings were collectively validated by the research team to ensure accuracy and coherence in interpreting patterns across the literature.
3. Results
As shown in Figure 1, a total of 2982 articles were retrieved through the systematic search. After removing duplicate entries using EndNote software, 2064 articles remained. Two reviewers independently screened the article titles and abstracts to exclude 1863 articles that were not directly related to the research topic, as well as three non-English articles. The two reviewers then conducted a thorough assessment of the remaining 193 articles, which resulted in the exclusion of a further 174 articles. The reason for exclusion was that the topic did not match the focus of this study, which was mainly concerned with financial support for education, entrepreneurship education development, and the application of the OSEM theory in science education. In order to identify potentially relevant studies that may have been missed, this study conducted some backward tracking searches on the literature to be included. The results showed that no new articles in the searched databases met the inclusion criteria under the backward tracking strategy. Ultimately, 19 articles were identified for inclusion in the scoping review for this systematic scoping review (see Table 3).
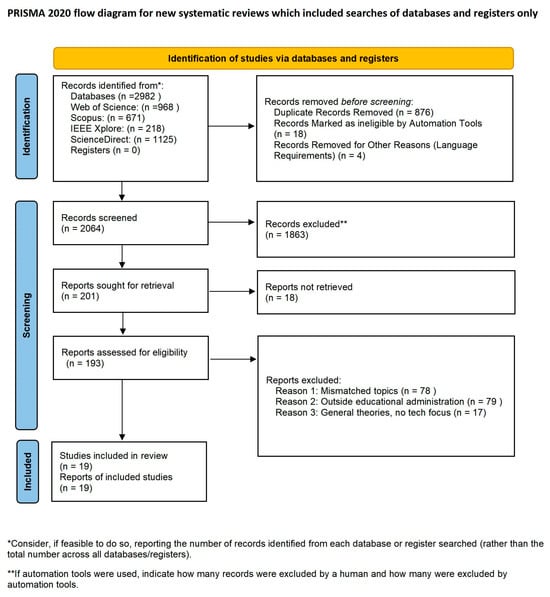
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart.

Table 3.
Overview of study characteristics.
3.1. Characteristics of Studies
The publication trend of the 19 included studies demonstrates a gradual yet uneven increase in scholarly attention over time, with a notable uptick during the period of digital acceleration triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. Between 2009 and 2013, research activity was minimal, with only two publications (in 2009 and 2010) and a gap in output until 2014. From 2014 to 2017, the number of studies grew steadily, reaching a peak in 2021 when three studies were published—likely influenced by the intensified emphasis on digital transformation in education during the pandemic. After 2021, the research momentum continued with a relatively stable output, suggesting sustained academic interest in the integration of advanced technologies in school administration (see Figure 2).
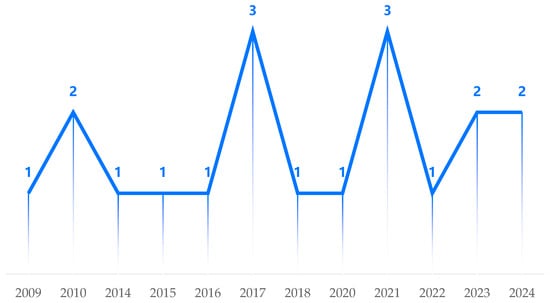
Figure 2.
Annual number of publications.
In terms of geographical distribution, the studies reflect a broad global interest in ICT integration. China leads the field with ten publications, signaling its strong commitment to educational technology research. Reflecting a notable over-representation compared with other regions. This concentration aligns with China’s national policies, prioritizing educational technology integration allocated substantial funding for ICT infrastructure in schools nationwide. Several other Asian countries—such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, and Pakistan—also contribute to this growing body of literature, indicating a region-wide investment in advancing digital solutions for educational contexts (see Figure 3).
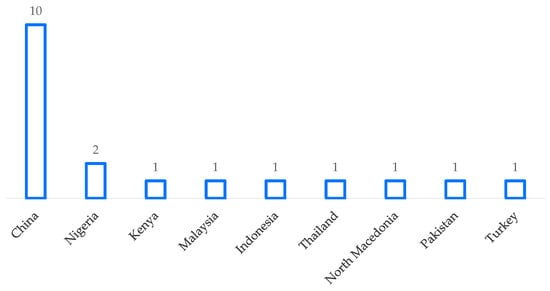
Figure 3.
Distribution of 19 articles by country.
3.2. Study Types
Upon reviewing the 19 studies, empirical and applied methods were the most common, each appearing four times. Empirical studies rely on real-world data collection and analysis, providing practical insights into how technology is applied in school administration. Applied studies focus on the practical implementation and evaluation of technological solutions in educational contexts, demonstrating a strong emphasis on real-world applicability. Experimental methods were used in three studies, involving controlled settings to test specific hypotheses about the impact of technology, thereby providing rigorous evidence of causal relationships. Survey methods were employed in two studies, useful for gathering data from a wide range of respondents, such as school administrators, teachers, and students, to understand their perceptions and experiences with technology in school administration. Each of the remaining methodologies—quantitative, theoretical, descriptive, and case study—appeared once. Quantitative studies use numerical data and statistical analysis to measure the impact of technology. Theoretical studies aim to develop or test theories related to the application of technology in school administration. Descriptive studies provide a detailed account of a particular phenomenon or situation, while case studies offer an in-depth analysis of a single case or a small number of cases to understand the complex interactions between technology and school administration (see Figure 4).
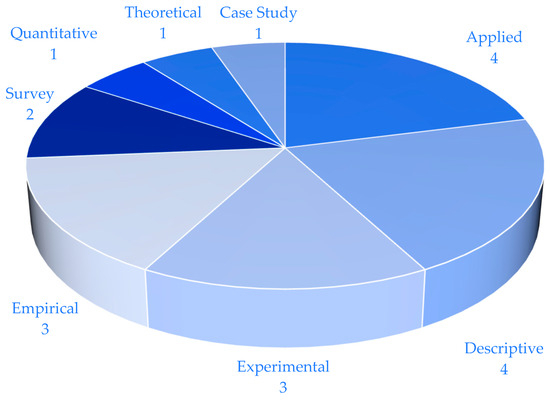
Figure 4.
Study types.
3.3. Research Themes
The included studies highlight several key applications of technology in school administration. Data analytics and optimization, including Big Data, AI, and data mining, were the most common focus, appearing in seven studies. These technologies enable schools to process large amounts of data, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. For example, they can be used for student performance prediction, resource allocation optimization, and teaching quality assessment. Information systems such as EMIS, MIS, and RFID were explored in five studies. These systems help in managing educational data across different levels of the institution, improving accuracy in tasks such as attendance tracking and asset management. Other themes included communication technologies, teaching quality and management optimization, and strategic planning and leadership. These studies demonstrate diverse but practical applications in enhancing administrative functions, from improving stakeholder interaction to supporting long-term institutional development (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Research themes.
3.4. Sample Types
The nineteen studies primarily focus on higher education, with nine studies examining universities, colleges, and vocational institutions, all of which fall under higher education. Higher education institutions often have more resources and a greater need for efficient administrative systems, making them an attractive focus for research. Primary education is represented in four studies, involving both public and private primary school administrators. These studies are important as they address the unique challenges and opportunities in managing primary schools, such as dealing with younger students and smaller budgets. Secondary education appears in three studies, with a focus on Catholic and public school administrators. The relatively small number of studies on secondary education may be due to the complexity of the educational system at this level, which includes multiple grade levels and diverse student populations. Notably, the total accounts for sixteen studies, indicating a gap of three studies. These remaining three studies likely focus on other educational levels or cross-level comparisons, highlighting a need for more detailed categorization in future research to capture the full scope of sample types. This distribution shows a continued emphasis on higher education, while primary education receives increased attention and secondary education maintains a similar focus compared with previous research, indicating a potential area for future expansion in primary and secondary education studies (see Table 5).

Table 5.
Sample types.
3.5. Technology Types
The most commonly addressed area in the studies is teaching management, appearing in nine studies, indicating its central role in technology application in school administration. These technologies include learning management systems, online course platforms, and teacher evaluation tools, which streamline teaching processes, improve student engagement, and enhance educational quality. Student management remains the second most frequent focus, appearing in five studies, reflecting expanded research on enrollment, attendance tracking, and academic progress monitoring through digital systems. Administrative management is explored in four studies, demonstrating growing interest in holistic administrative efficiency. Emerging areas such as cybersecurity and hybrid learning platforms are introduced in two studies, while community communication, library management, and financial/personnel management appear less frequently, with one study each (see Figure 5).
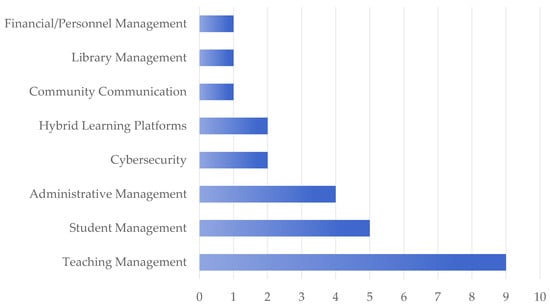
Figure 5.
Technology implementation and evaluation.
3.6. Technology Type, Realization Methods, and Assessment Indicators
Most of the studies focused on data analytics and AI algorithms, highlighting the importance of data-driven decision-making. Communication tools such as WhatsApp and Google Drive are widely used for collaboration, while data mining aids in educational management optimization. RFID technology is applied in attendance and asset tracking, and other technologies, such as software platforms, basic tools, and cloud computing, support administrative functions. Software development and applications were the most commonly used in the included articles, with nine instances, including custom platforms and communication tools such as WhatsApp and Google Drive. Data processing and analytics were used in seven studies, focusing on Big Data analytics, feature extraction, and predictive modeling. Hardware and cloud services, such as RFID infrastructure and cloud storage, were used in five studies. Research methods, including surveys and pilot studies, appeared in four studies. Emerging technologies such as cybersecurity frameworks and hybrid learning systems were introduced in two studies, while blockchain for secure record-keeping was applied in one study (see Table 6).

Table 6.
Technology types and their context.
3.7. Findings and Limitations
The studies demonstrate that technology integration in school administration leads to improved teaching quality as measured by assessment scores or student feedback, and decision-making. Advanced tools, including data warehouse systems, artificial intelligence algorithms, and data mining techniques, show high predictive accuracy, optimizing resource allocation and performance evaluation. ICT platforms enhance teaching outcomes, student engagement, and personalized learning, while RFID systems and online communication tools (e.g., WhatsApp and Google Drive) streamline administrative workflows. Leadership strategies leveraging technology further strengthen institutional effectiveness. However, limitations persist: research predominantly focuses on higher education, with insufficient attention to primary and secondary schools. Key challenges include data privacy concerns in AI-driven assessment, infrastructure gaps in under-resourced institutions, and limited teacher training in emerging technologies. Most studies concentrate on specific contexts (e.g., China, vocational schools), reducing generalizability. Future research should address diverse educational levels, develop cost-effective solutions for resource-limited settings, and establish ethical guidelines for data-driven decision-making in education.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings and Results of Studies
The integration of technology into school administration has demonstrated context-dependent impacts on management efficiency, teaching quality, and decision-making (Ashraf, 2024). AI and data mining applications demonstrate transformative potential in administrative tasks ranging from attendance tracking to resource allocation (Y. Luo & Wang, 2024; Y. T. Luo et al., 2025); their effectiveness is contingent on institutional readiness. For instance, Eremie and Agi (2020) highlighted that attendance tracking systems improved efficiency in contexts with stable internet infrastructure and trained staff, but failed in under-resourced schools where technical support was lacking. Teacher training programs significantly influence the effectiveness of digital platforms in classroom settings—for example, personalized learning environments succeeded only when teachers were adequately trained to interpret data-driven insights and adapt instruction (Peng et al., 2019). Attendance tracking has become more accurate and efficient, reducing the time and effort required for manual record-keeping (Siew et al., 2023). Performance evaluation has also been enhanced, providing more objective and data-based insights into students’ and teachers’ performance. ICT-integrated platforms have had a positive impact on teaching outcomes and personalized learning support. They have created a more interactive and engaging learning environment for students, allowing for customized learning paths based on individual needs. Communication tools such as WhatsApp and Google Drive improved stakeholder collaboration in settings with low digital literacy barriers (Maitra et al., 2024), but their impact was limited in communities with fragmented connectivity or resistance to digital engagement. These tools have reduced administrative workloads by streamlining communication channels and facilitating the sharing of information.
These findings suggest that reported improvements (e.g., “teaching quality improved,” “stakeholder collaboration enhanced”) are not inherent to the tools themselves, but rather emerge from synergies between technology features, implementation strategies, and local contextual factors (e.g., infrastructure, training, cultural attitudes toward digital tools). For example, while Big Data analytics enabled more objective performance evaluations (Kamble & Gunasekaran, 2020), their success depended on institutions’ ability to address data privacy concerns and ensure algorithmic transparency—factors that were often overlooked in studies reporting “positive outcomes” without detailing these mechanisms (Wörle, 2024). When comparing different educational levels, resource availability and institutional support structures vary markedly between educational levels, with universities typically possessing stronger technological foundations. They often have well-developed infrastructure, a more highly trained staff, and greater flexibility in curriculum design. For example, in higher education, data-driven teaching quality assessment tools can be more easily integrated into existing systems, and teachers are more likely to have the skills to use them (Kurilovas, 2020). In contrast, primary education faces unique challenges. Primary school students have different learning needs and abilities, and teachers may need more training to use ICT tools effectively for personalized learning (Blyznyuk et al., 2025). Moreover, primary schools may have limited budgets and less access to advanced technical support, which can hinder the successful implementation of some ICT solutions (Eickelmann, 2011).
In terms of the comparison between developed and developing countries, developed countries usually have better infrastructure, higher levels of digital literacy, and more financial resources for educational technology (Addo, 2001). They can invest in cutting-edge ICT tools and provide comprehensive training for teachers and administrators (Khan et al., 2024). For example, in developed countries, schools are more likely to have high-speed internet, advanced hardware, and well-established data management systems (Iqbal & Qureshi, 2012). In developing countries, infrastructure deficiencies, such as unreliable electricity and limited internet access, are major barriers to ICT integration (Salam et al., 2018). Additionally, there may be a lack of trained personnel to support the use of new technologies, and financial constraints can limit the ability to purchase and maintain ICT equipment (Bingimlas, 2009). However, some developing countries have shown innovative approaches to overcome these challenges, such as leveraging mobile technology in areas with limited internet connectivity (Asabere, 2013).
Based on the analysis of 19 studies, these challenges vary by context. For example, data privacy concerns were highlighted in six studies, while scalability issues and infrastructure deficiencies. The research focus is skewed towards higher education, with nine studies concentrating on this level, while primary education and secondary education are neglected. There is also a lack of longitudinal studies, with most research being short-term. This suggests that primary and secondary education are underrepresented in research on ICT integration. While higher education institutions typically have more resources and infrastructure to support digital transformation, it is equally important to understand how these technologies work in resource-constrained or exam-driven environments, such as K-12 education settings. While higher education institutions often have more resources for ICT integration, future research should prioritize investigating cost-effective, context-appropriate solutions tailored specifically for K-12 environments (e.g., primary and secondary schools) where infrastructure limitations and exam-driven curricula present unique challenges (Göktaş et al., 2008). Furthermore, the paucity of longitudinal research limits our understanding of the ongoing impact of ICT on management practices and educational outcomes. The lack of long-term data makes it difficult to assess whether observed benefits are temporary or indicative of lasting change.
4.2. The Application of Technologies in Different Administrative Areas
In the realm of teaching quality management, the combination of information control theory and Buchberger’s algorithm has provided a data-driven, quantitative management mechanism for teaching quality assessment (Gjoko & Rezarta, 2023). This mechanism has strengthened the monitoring and incentive effects in the teaching process. By accurately analyzing data, it has improved the objectivity and reliability of assessment, overcoming the limitations of traditional qualitative assessment. ICT’s role in teaching quality management extends beyond assessment optimization. It is central to improving the accuracy and fairness of educational outcomes, ensuring that all students are evaluated based on objective criteria. The educational platform constructed using Big Data and collaborative filtering algorithms has significantly enhanced the precision of teaching resource recommendation and the personalized level of resource allocation (Sakuliampaiboon et al., 2015). This platform captures real-time changes in interests and uses support vector machines to classify resources. As a result, it optimizes the allocation and deployment efficiency of teaching resources, demonstrating the potential of data-driven management in achieving personalized teaching resource allocation and enhancing teaching effectiveness.
Systems based on data warehousing and integrated learning have provided strong support for educational decision-making in student management (Zhou & Li, 2024). By integrating multi-dimensional data and performing cluster analysis, these systems can accurately identify the characteristics of different student groups. This enables the provision of personalized education services, improving the efficiency and accuracy of student management. It also reflects the great value of technology in the rational allocation of educational resources and personalized support. In education administration, RFID has been used to improve the efficiency and safety of campus management through automatic identification of students and staff (Gjoko & Rezarta, 2023). EMIS has optimized data integration and management efficiency, which is particularly significant for schools in remote areas (Gjoko & Rezarta, 2023). The success of these tools was not universal but tied to alignment with specific administrative needs and local capacities. For example, EMIS platforms worked well in remote areas (Gjoko & Rezarta, 2023) because they addressed critical gaps in data accessibility, whereas in well-resourced urban schools, their impact was less pronounced because of redundant existing systems.
4.3. Advantages and Limitations of Technologies in School Administration
Analytical tools enable administrators to identify patterns in student performance and institutional operations. It allows for the analysis of large datasets to identify trends related to student performance and resource allocation (Zhou & Li, 2024; Zhu, 2024). Predictive analytics can forecast issues such as student dropout rates, enabling early intervention. It also supports personalized learning, which has been shown to improve educational outcomes (Yin & He, 2022). However, data privacy concerns are a major drawback. The collection and storage of large amounts of student data raises questions about how this information is being used and protected. The complexity and cost of implementation can be prohibitive, especially for resource-constrained institutions. Additionally, an over-reliance on quantitative data may overlook the humanistic aspects of education, such as the emotional and social development of students. Inaccurate or incomplete data in Big Data analysis can lead to incorrect predictions about student performance, affecting resource allocation decisions (Bai et al., 2021). RFID enhances operational efficiency by automating tasks such as attendance tracking and access control (Akpınar & Kaptan, 2010). It also supports contactless transactions, streamlining processes such as payments. Despite these benefits, RFID has high initial costs, which can be a barrier to adoption. Privacy concerns, including continuous surveillance and potential security vulnerabilities, also limit its widespread use. Compatibility issues between RFID systems and existing hardware/software in some schools have led to additional upgrade and maintenance costs (Kitkowska et al., 2024). ICT is crucial for communication within educational institutions. It facilitates tasks such as registration, scheduling, and fee management (Nagar et al., 2018). It also supports professional development by providing teachers with tools to improve their practices. However, the digital divide and high infrastructure costs hinder effective ICT integration. Ongoing investment in staff training is necessary to ensure that teachers and administrators can use the technology effectively. The rapid emergence of new communication tools has made it challenging for teachers and administrators to stay updated, leading to underutilization of ICT potential due to a lack of training (Habibu, 2012). AI, such as large language models, offers the potential to automate routine administrative tasks and provide predictive insights, improving decision-making and academic performance (Zhou & Li, 2024; Zhu, 2024). However, its high development and operational costs, along with concerns over algorithmic bias and the limited effectiveness of some AI applications in education, present barriers to widespread adoption (Y. Luo et al., 2025). The advantages and limitations of technologies in school administration are complex and multifaceted.
4.4. Overcoming Barriers to Technology Integration in Education
In the process of integrating technology into education, overcoming the digital divide, technological skills gap, and resistance to change is key to achieving equity and inclusion. Perceived complexity is often a major barrier to technology adoption. If the technology is perceived to be difficult to use, the initial rollout may need to rely on coercive measures. However, as technology improves and users become more familiar with it, its complexity becomes less of a barrier. To overcome this, user-centered design is crucial. Tools should be developed with the end-user in mind, making them easy to understand and operate (Chen et al., 2020). Mobile-based learning platforms can provide access to educational resources in areas with limited internet connectivity (Mahenge & Mwangoka, 2014).
Technology knowledge gaps significantly affect the effectiveness of educational technology integration. The technological competence of teachers and administrators directly determines the level of technology utilization in teaching and management. Therefore, it is crucial to strengthen relevant technological training (Gjoko & Rezarta, 2023). Professional development programs should be implemented to enhance the skills of educators and administrators, enabling them to make the most of the available technological tools. Unequal distribution of resources further exacerbates the digital divide. Equitable access to technology resources and support is necessary to bridge this gap (Sakuliampaiboon et al., 2015). Investment in infrastructure, such as providing reliable internet access and up-to-date hardware, is essential. Additionally, software and digital content should be accessible to all students and teachers. Data privacy and security issues are becoming increasingly prominent. Educational institutions need to strictly comply with laws and regulations to ensure the protection of student data and avoid privacy leakage or misuse (Zhou & Li, 2024). Clear policies and procedures should be established to safeguard sensitive information.
When comparing primary and higher education, higher education institutions may have more in-house expertise and resources to address the technological skills gap through professional development programs. In contrast, primary schools may rely more on external support and face more challenges in providing comprehensive training. Regarding developed and developing countries, developed countries can leverage their financial resources and advanced infrastructure to overcome the digital divide more effectively (Rice, 2003). They can invest in high-speed internet, provide digital devices to students and teachers, and offer training programs (Garlinska et al., 2023). Developing countries, on the other hand, may need to adopt more cost-effective solutions, such as using mobile technology or leveraging international aid and partnerships, to bridge the gap.
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) provide valuable frameworks for understanding technology adoption (Granić & Marangunić, 2019; Lewis et al., 2013). TAM and UTAUT highlight that perceived usefulness, ease of use, and social influence are critical factors shaping technology acceptance in educational contexts. Both TAM and UTAUT are well-established theories in the fields of ICT and educational technology. However, there are relatively few studies examining the application of these technologies in the retrieved articles. Recently, some research in the field of educational technology has increasingly utilized related theoretical frameworks (Al-Emran et al., 2018; Chan et al., 2023; Yildiz Durak, 2019), suggesting that researchers should more frequently incorporate relevant theoretical support into their investigations of ICT in school management.
4.5. Limitations
In this systematic scoping review, despite a thorough search and selection process, several limitations exist. The reliance on published peer-reviewed articles may have led to the exclusion of the relevant gray literature or studies that used non-traditional approaches to explore the role of technology in school management. The gray literature, such as reports from non-profit organizations and theses, may contain valuable insights that are not represented in traditional journals. The rapid evolution of technology means that some research findings may quickly become outdated. Furthermore, to ensure consistency and quality of the evidence base, we included only peer-reviewed journal articles and explicitly excluded conference papers. Because this review focuses on educational administration research, peer-reviewed journal articles are often viewed as the primary and most rigorous publication platform for empirical research. This disciplinary characteristic determined our decision not to include conference papers in this review; however, in fields such as computer science and information systems, conference papers are equally important academically. New technologies and applications are emerging at a fast pace, and the review may not fully capture the latest trends and developments. This necessitates continually updating the review to ensure that it remains relevant and up-to-date. The current review lies in the limited generalizability of many included studies, which predominantly originate from single-institution contexts, with a notable concentration from China. This over-representation raises concerns about the cross-national transferability of the findings. When considering cross-national transferability, factors such as cultural differences, economic development levels, and educational systems play crucial roles. Developed countries may have more advanced technological infrastructures and higher levels of digital literacy among both teachers and students. These contextual limitations mean that the conclusions drawn from the included studies should be interpreted with caution. Future research should aim to include a more diverse range of institutions and countries to enhance the generalizability of findings.
Future research should prioritize the practical needs of schools in resource-constrained settings by conducting in-depth fieldwork and case studies to systematically examine the unique barriers and feasible pathways for ICT implementation in these contexts. Subsequent investigations ought to direct particular attention to the distinct challenges encountered by marginalized groups—including rural and ethnic minority communities—during educational digital transformation. Exploring technology adaptation strategies under low-bandwidth conditions and devising differentiated approaches for cultivating teachers’ digital competencies. Moreover, research designs should intentionally incorporate the perspectives of these underrepresented populations, employing cross-regional comparative analyses to uncover the mechanisms underlying variations in technology application effectiveness across diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Such efforts are essential for generating robust evidence to inform the development of more inclusive educational technology policies.
Despite these limitations, the review highlights the multifaceted impact of technology on school management. It emphasizes the need for ongoing research to address emerging challenges and ethical considerations in the field. This contributes to the existing body of knowledge by providing targeted strategies for future research and understanding the dynamic interplay between technology and administrative practices for educational policymakers.
5. Conclusions
This systematic scoping review highlights that ICT integration significantly enhances school administration across operational efficiency, decision-making, and stakeholder communication. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven analytics, RFID systems, and EMIS platforms have optimized resource management and data-driven decisions, while ICT platforms have improved collaboration. However, limitations such as uneven technology adoption across educational levels, digital divide risks, and data privacy concerns persist, with underrepresentation of primary/secondary education in research. Future efforts should prioritize investigating implementation strategies tailored to primary and secondary education settings, where evidence remains limited. Focus on cost-effective solutions for under-resourced institutions, ethical data governance standards, and longitudinal studies to assess long-term impacts. This underscores ICT’s potential while addressing implementation challenges for sustainable educational management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L. and Y.T.L.; methodology, T.L.; software, Y.T.L.; validation, T.L.; formal analysis, T.L.; investigation, T.L.; resources, T.L.; data curation, Y.T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.; writing—review and editing, P.C.-I.P.; visualization, T.L.; supervision, P.C.-I.P. and H.Y.K.; project administration, P.C.-I.P.; funding acquisition, P.C.-I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Macao Polytechnic University research grant, grant number RP/FCA-10/2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable. No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist.
Table A1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist.
| Section | Item | Prisma-ScR Checklist Item | Reported on Page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a scoping review. | Cover page |
| Abstract | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary that includes (as applicable): background, objectives, eligibility criteria, sources of evidence, charting methods, results, and conclusions that relate to the review questions and objectives. | 1 |
| Introduction | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known. Explain why the review questions/objectives lend themselves to a scoping review approach. | 2–3 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of the questions and objectives being addressed with reference to their key elements (e.g., population or participants, concepts, and context) or other relevant key elements used to conceptualize the review questions and/or objectives. | 4 |
| Methods | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate whether a review protocol exists; state if and where it can be accessed (e.g., a Web address); and if available, provide registration information, including the registration number. | 4 |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify characteristics of the sources of evidence used as eligibility criteria (e.g., years considered, language, and publication status), and provide a rationale. | 4–5 |
| Information sources * | 7 | Describe all information sources in the search (e.g., databases with dates of coverage and contact with authors to identify additional sources), as well as the date the most recent search was executed. | 5 |
| Search | 8 | Present the full electronic search strategy for at least 1 database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated. | 5 |
| Selection of sources of evidence † | 9 | State the process for selecting sources of evidence (i.e., screening and eligibility) included in the scoping review. | 5–6 |
| Data charting process ‡ | 10 | Describe the methods of charting data from the included sources of evidence (e.g., calibrated forms or forms that have been tested by the team before their use, and whether data charting was performed independently or in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators. | 5–6 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought and any assumptions and simplifications made. | 5–6 |
| Critical appraisal of individual sources of evidence § | 12 | If conducted, provide a rationale for conducting a critical appraisal of included sources of evidence; describe the methods used and how this information was used in any data synthesis (if appropriate). | 5–6 |
| Synthesis of results | 13 | Describe the methods of handling and summarizing the data that were charted. | 5–6 |
| Results | |||
| Selection of sources of evidence | 14 | Give the number of sources of evidence screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally using a flow diagram. | 6–7 |
| Characteristics of sources of evidence | 15 | For each source of evidence, present characteristics for which data were charted and provide the citations. | 8–12 |
| Critical appraisal within sources of evidence | 16 | If conducted, present data on critical appraisal of included sources of evidence (see item 12). | 13–17 |
| Results of individual sources of evidence | 17 | For each included source of evidence, present the relevant data that were charted that relate to the review questions and objectives. | 13–17 |
| Synthesis of results | 18 | Summarize and/or present the charting results as they relate to the review questions and objectives. | 18 |
| Discussion | |||
| Summary of evidence | 19 | Summarize the main results (including an overview of concepts, themes, and types of evidence available), link to the review questions and objectives, and consider the relevance to key groups. | 18–21 |
| Limitations | 20 | Discuss the limitations of the scoping review process. | 21 |
| Conclusions | 21 | Provide a general interpretation of the results with respect to the review questions and objectives, as well as potential implications and/or next steps. | 22 |
| Funding | |||
| Funding | 22 | Describe sources of funding for the included sources of evidence, as well as sources of funding for the scoping review. Describe the role of the funders of the scoping review. | Not applicable |
JBI = Joanna Briggs Institute; PRISMA-ScR = Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews. * Where sources of evidence (see second footnote) are compiled from, such as bibliographic databases, social media platforms, and Web sites. † A more inclusive/heterogeneous term used to account for the different types of evidence or data sources (e.g., quantitative and/or qualitative research, expert opinion, and policy documents) that may be eligible in a scoping review as opposed to only studies. This is not to be confused with information sources (see first footnote). ‡ The frameworks by Arksey and O’Malley (6) and Levac and colleagues (7) and the JBI guidance (4, 5) refer to the process of data extraction in a scoping review as data charting. § The process of systematically examining research evidence to assess its validity, results, and relevance before using it to inform a decision. This term is used for items 12 and 19 instead of “risk of bias” (which is more applicable to systematic reviews of interventions) to include and acknowledge the various sources of evidence that may be used in a scoping review (e.g., quantitative and/or qualitative research, expert opinion, and policy document).
References
- Addo, H. (2001). Utilizing information and communication technology for education and development: Issues and challenges for developing countries. IFLA Journal, 27(3), 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, A. H., Austin-Gabriel, B., Eweje, A., & Collins, A. (2022). Framework for automating multi-team workflows to maximize operational efficiency and minimize redundant data handling. IRE Journals, 5(9), 663–664. [Google Scholar]
- Adesina, A. A., Iyelolu, T. V., & Paul, P. O. (2024). Optimizing business processes with advanced analytics: Techniques for efficiency and productivity improvement. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 22(3), 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afariogun, A., & Nwaozor, A. O. (2023). Management and administration of education through information and communication technology. Journal of Agriculture and Food Sciences, 21(2), 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Akpınar, S., & Kaptan, H. (2010). Computer aided school administration system using RFID technology. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2(2), 4392–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., & Kamaludin, A. (2018). Technology acceptance model in M-learning context: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 125, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsbou, M. K. K., & Alsaraireh, R. E. A. I. (2024, April 18–19). Data-driven decision-making in education: Leveraging AI for school improvement. 2024 International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Communication Systems (ICKECS), Chikkaballapur, India. [Google Scholar]
- Ambasht, A. (2023). Real-time data integration and analytics: Empowering data-driven decision making. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology, 71(7), 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabere, N. Y. (2013). Benefits and challenges of mobile learning implementation: Story of developing nations. International Journal of Computer Applications, 73(1), 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S. R. (2024). The role of artificial intelligence in enhancing managerial decision-making in education. International Journal of Advanced Social Sciences Research, 1(1), 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Baharuldin, Z., Jamaluddin, S., & Shaharom, M. S. N. (2019). The role of school administrative support and primary school teachers’ ICT literacy to integrate ICT into the classrooms in Pahang, Malaysia. International Online Journal of Educational Leadership, 3(1), 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X., Zhang, F., Li, J., Guo, T., Aziz, A., Jin, A., & Xia, F. (2021). Educational big data: Predictions, applications and challenges. Big Data Research, 26, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, R., Pomal, K., Ahmed, M., & Singh, C. B. (2024). Transformative impact of ICT on education: Leveraging technology and communication to enhance teaching and learning. Feedback International Journal of Communication, 1(3), 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingimlas, K. A. (2009). Barriers to the successful integration of ICT in teaching and learning environments: A review of the literature. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 5(3), 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, W. H., & Lilly, J. D. (2022). Applying organizational theory to special education case management. Journal of Special Education Leadership, 35(1), 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blyznyuk, O., Kachak, T., Blyznyuk, T., & Nazaruk, S. K. (2025). Quality education in the digital age: Adapting to 21st century primary school learners. Journal of Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University, 12(1), 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burunkaya, M., & Duraklar, K. (2022). Design and implementation of an IoT-based smart classroom incubator. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F., & Peng, X. (2020, June 13–14). Research on the innovation mechanism model of education management under the background of artificial intelligence technology. 2020 5th International Conference on Smart Grid and Electrical Automation (ICSGEA), Zhangjiajie, China. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S. (2016, August 13–14). Study on application of computer technology in education management. 2016 4th International Education, Economics, Social Science, Arts, Sports and Management Engineering Conference (IEESASM 2016), Yinchuan, China. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K. I., Pang, P. C.-I., & Wei, W. (2023, November 28–December 1). Exploring the factors and moderators influencing the use of radar visualisation of student performance from parents’ perspective. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Auckland, New Zealand. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M., & Yuen, A. H. K. (2018). Student continuance of learning management system use: A longitudinal exploration. Computers & Education, 120, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D., & McLeod, S. (2014). Social media strategies for school principals. Nassp Bulletin, 98(1), 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J., & Abuzneid, A.-S. (2020, December 16–18). An NFC based student attendance tracking/monitoring system using an IoT approach. 2020 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Dries, S. D. (2014). The influence of parent portal access on student efficacy and parental involvement [Doctoral dissertation, Seton Hall University]. Seton Hall University Dissertations and Theses (ETDs). Available online: https://scholarship.shu.edu/dissertations/2076 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Eickelmann, B. (2011). Supportive and hindering factors to a sustainable implementation of ICT in schools. Journal for Educational Research Online, 3(1), 75–103. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bakry, H. M., Mastorakis, N., Mastorakis, N., Mladenov, V., Bojkovic, Z., Kartalopoulos, S., & Simian, D. (2009, January 10–12). E-learning and management information systems for E-universities. 3rd WSEAS International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications (CEA’09), Ningbo, China. [Google Scholar]
- Elmroth, E., Elastisys, A., Leitner, P., Schulte, S., & Venugopal, S. (2017). Connecting fog and cloud computing. IEEE Cloud Computing, 4(2), 22–25. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7912269 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Eremie, I., & Agi, U. K. (2020). Information and Communication Technology (ICT) skills and efficient management of educational resources in public secondary schools. Journal of the International Society for Teacher Education, 24(1), 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Garlinska, M., Osial, M., Proniewska, K., & Pregowska, A. (2023). The influence of emerging technologies on distance education. Electronics, 12(7), 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjoko, S., & Rezarta, Z.-H. (2023). Perceived benefits and post-adoption usage of education management information system. Library Hi Tech, 41(4), 1063–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Göktaş, Y., Yıldırım, Z., & Yıldırım, S. (2008). The keys for ICT integration in K-12 education: Teachers’ perceptions and usage. Hacettepe Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 34(34), 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Granić, A., & Marangunić, N. (2019). Technology acceptance model in educational context: A systematic literature review. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(5), 2572–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S., & Xie, B. (2021, January 16–17). An education management assessment model based on information control theory. 2021 13th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Beihai, China. [Google Scholar]
- Habibu, T. (2012). A study of difficulties faced by teachers in using ICT in classroom teaching-learning in technical and higher educational Institutions in Uganda [Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Technical and Vocational Education (TVE), Islamic University]. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M., Li, Z., He, J., Wu, D., Xie, Y., & Baba, A. (2018, October 3–6). A novel blockchain-based education records verification solution. 19th Annual SIG Conference on Information Technology Education, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Haruna, L., & Abdullahi, I. (2022). Role of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) for record keeping in school management and administration for effective teaching and learning. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Applied Science, 7(4), 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, F., Alam, G. M., & Siraj, S. (2010). Information and communication technology for participatory based decision-making-E-management for administrative efficiency in Higher Education. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 5(4), 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Q. N. (2018). Revision of the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT): A mixed methods study. McGill University. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S., & Qureshi, I. A. (2012). M-learning adoption: A perspective from a developing country. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 13(3), 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalusivalingam, A. K., Sharma, A., Patel, N., & Singh, V. (2020). Optimizing workforce planning with AI: Leveraging machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics for enhanced decision-making. International Journal of AI and ML, 1(3), 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, S. S., & Gunasekaran, A. (2020). Big data-driven supply chain performance measurement system: A review and framework for implementation. International Journal of Production Research, 58(1), 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. A., Hussain, T., Al Siyabi, M., Al Shibli, A., Hussain, S., & Pillai, J. R. (2024). Challenges and prospects of cutting-edge technology in education. In Studies on education, science, and technology 2024 (p. 104). International Society for Technology, Education and Science (ISTES). [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, S. K. (2024). Higher education in the digital era: Exploring the transformative effects of technological advancements on higher education. International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology (IJARSCT), 4(2), 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kitkowska, A., Brodén, K., & Abdullah, L. (2024). The requirements, benefits, and barriers of iot solutions to support well-being in elementary schools. IEEE Access, 12, 144965–144981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, R. B., & Isaacs, S. (2011). Transforming education: The power of ICT policies. Unesco. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaveni, R., & Meenakumari, J. (2010). Usage of ICT for information administration in higher education Institutions–A study. International Journal of Environmental Science And Development, 1(3), 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilovas, E. (2020). On data-driven decision-making for quality education. Computers in Human Behavior, 107, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyan, R., Bailur, S., Gigler, S., & Park, K. R. (2011). Technologies for transparency and accountability: Implications for ICT policy and Implementation. Open Development Technology Alliance, World Bank. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K., Jo, J., Kim, J., & Kang, Y. (2019, July 26–31). Can chatbots help reduce the workload of administrative officers? Implementing and deploying FAQ chatbot service in a university. International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Orlando, FL, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, C. C., Fretwell, C. E., Ryan, J., & Parham, J. B. (2013). Faculty use of established and emerging technologies in higher education: A unified theory of acceptance and use of technology perspective. International Journal of Higher Education, 2(2), 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. (2023, September 8–10). Identifying factors influencing China junior high students’ cognitive ability through educational data mining: Utilizing LASSO, random forest, and XGBoost. 4th International Conference on Modern Education and Information Management (ICMEIM 2023), Wuhan, China. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y., Liu, T., Pang, P. C.-I., McKay, D., Chen, Z., Buchanan, G., & Chang, S. (2025). Enhanced bloom’s educational taxonomy for fostering information literacy in the era of large language models. arXiv, arXiv:2503.19434. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y., & Wang, Z. (2024, March 18–20). Feature mining algorithm for student academic prediction based on interpretable deep neural network. 2024 12th International Conference on Information and Education Technology (ICIET), Yamaguchi, Japan. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. T., Liu, T., Pang, P. C.-I., Wang, Z., & Chan, K. I. (2025). Exploring information interaction preferences in an LLM-assisted learning environment with a topic modeling framework. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahenge, M. P., & Mwangoka, J. W. (2014). Mobile-based system for cost-effective e-learning contents delivery in resource and bandwidth constrained learning environments. Knowledge Management & E-Learning, 6(4), 449. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, C., Rowley, J., & Miyake, E. (2024). Benefits and barriers of using WhatsApp in eye health communication in deprived settings in India. In Technology innovation for sustainable development of healthcare and disaster management (pp. 179–201). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Menjo, D. K., & Boit, J. M. (2010). The challenges of using information communication technology (ICT) in school administration in Kenya. Journal of African Studies in Educational Management and Leadership, 1(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & Group, P. (2010). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. International Journal of Surgery, 8(5), 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohzana, M. (2024). Data analysis and predictions in education financial management for effective budget planning. At-Tasyrih: Jurnal pendidikan dan hukum Islam, 10(2), 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Nagar, M. A. K., Rahoo, L. A., Rehman, H. A., & Arshad, S. (2018, November 22–23). Education management information systems in the primary schools of sindh a case study of hyderabad division. 2018 IEEE 5th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), Bangkok, Thailand. [Google Scholar]
- Nama, P., Pattanayak, S., & Meka, H. S. (2023). AI-driven innovations in cloud computing: Transforming scalability, resource management, and predictive analytics in distributed systems. International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science, 5(12), 4165. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Hoang, T.-A., Hoang, N. C., Hua, P. T., Thi, M.-T. N., Ta, T.-T., Nguyen, T., Tan-Vo, K., Dinh, N.-T., & Nguyen, H.-T. (2024). Advancing scholarship management: A blockchain-enhanced platform with privacy-secure identities and AI-driven recommendations. IEEE Access, 12, 168060–168090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M. M. (2016). The potential and evidence of ict-based cost and burden reduction in public administration and public service delivery–workshop report. WSIS-World Summit on the Information Society. [Google Scholar]
- Oboegbulem, A., & Ugwu, R. N. (2013). The Place of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) in the administration of secondary schools in south eastern states of Nigeria. Online Submission, 3(4), 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Oyedemi, O. A. (2015, July 1–3). ICT and effective school management: Administrators’ perspective. World Congress on Engineering, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi, P. D., Patel, S. B., Patel, S. J., Patel, J. N., & Darji, D. A. (2025). Performance optimization in records management artificial intelligence-driven strategies. In Artificial intelligence in records and information management (pp. 393–424). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H., Ma, S., & Spector, J. M. (2019). Personalized adaptive learning: An emerging pedagogical approach enabled by a smart learning environment. Smart Learning Environments, 6(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M. D., Marnie, C., Tricco, A. C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., McInerney, P., Godfrey, C. M., & Khalil, H. (2020). Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 18(10), 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z., & Huo, H.-Y. (2009, December 13–14). Application of PCFA in assessing operation environment of computer security in education management. 2009 Second International Conference on Education Technology and Training, Sanya, China. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, Z. H., & Qazi Abro, M. (2016). Efficient use of ICT in administration. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, IV(10), 540–550. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, K. (2024). Identifying learning difficulties at an early stage in education with the help of artificial intelligence models and predictive analytics. International Research Journal of Multidisciplinary Scope (IRJMS), 5(4), 1455–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M. F. (2003). Information and communication technologies and the global digital divide: Technology transfer, development, and least developing countries. Comparative Technology Transfer and Society, 1(1), 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, S. M., Ansarullah, S. I., Ben Othman, M. T., Alshmrany, S., Shafiq, M., & Hamam, H. (2022). Impact of ICT in modernizing the global education industry to yield better academic outreach. Sustainability, 14(11), 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuliampaiboon, C., Songkhla, J. N., & Sujiva, S. (2015). Strategies of information communication and technology integration by benchmarking for primary school in Catholic (Layman) School administration club bangkok arch diocese for students’ 21st century skill. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, S., Zeng, J., Pathan, Z. H., Latif, Z., & Shaheen, A. (2018). Impediments to the integration of ICT in public schools of contemporary societies: A review of literature. Journal of Information Processing Systems, 14(1), 252–269. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M. U., Shakir, M., Usman, M. R., Bajwa, M. H. T., Shabbir, N., Shams Ghahfarokhi, P., & Daniel, K. (2023). Integrating smart energy management system with internet of things and cloud computing for efficient demand side management in smart grids. Energies, 16(12), 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, E. S. K., Chong, Z. Y., Sze, S. N., & Hardi, R. (2023). Streamlining attendance management in education: A web-based system combining facial recognition and QR code technology. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 33(2), 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A., Yousaf, M., Idrees, M., & Mushtaq, A. (2025). Integrating technology and self-regulation strategies to enhance learning outcomes: A dual-analysis approach. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swargiary, K. (2024). ICT revolutionizing education. Google. [Google Scholar]
- Taye, G., Sharma, S., Shah, P., & Nuriye, Y. G. (2023, October 10–12). Exploring the role of artificial intelligence in class scheduling and management: A comprehensive survey and review. 2023 International Conference on Computer Science and Emerging Technologies (CSET), Bangalore, India. [Google Scholar]
- Tayong, A. A. (2023). New optimization/automation models for HEI managerial work: Grading, registering attendance, examination scheduling, archiving, and timetabling. Journal of Tianjin University Science and Technology, 56, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-l. (2021, March 5–8). Research on the core technology of education big data based on data mining. 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Big Data Analytics (ICBDA), Xiamen, China. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, C.-H., & Tang, Y. (2014). The relationship between technology leadership strategies and effectiveness of school administration: An empirical study. Computers & Education, 76, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiyono, B. B., Indreswari, H., & Prastiawan, A. (2021, June 25–27). The use of communication technology in establishing community relationships applied by school administration staff, in relation to their education level and age. 2021 3rd International Conference on Computer Communication and the Internet (ICCCI), Nagoya, Japan. [Google Scholar]
- Wörle, F. T. (2024). Negative feedback loops and self-fulfilling prophecies: Sociotechnical assessment of unfairness in predictive algorithms [Master’s thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München]. [Google Scholar]
- Wyne, M. F., Hunter, M., Moran, J., & Patil, B. (2021). Parent-Teacher Portal (PTP): A communication tool. In Advances in software engineering, education, and e-learning (pp. 351–361). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J., Jiang, Y., Yuan, B., Li, S., & Song, T. (2023, November 28–30). Automated scoring of clinical patient notes using advanced nlp and pseudo labeling. 2023 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), Dalian, China. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J., & Wang, Y. (2025a, July 15–17). Enhancing healthcare recommendation systems with multimodal LLMs-based MOE architecture. 5th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning (CONF SPML 2025), Hohhot, China. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J., & Wang, Y. (2025b, March 14–16). FMT: A multimodal pneumonia detection model based on stacking MOE framework. 2025 8th International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), Hawaii, HI, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R. (2022). Analysis on the construction of digital sharing service platform for school-enterprise cooperation financial management. International Journal of Educational Economy and Management, 2(1), 36. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C., Huang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, K., & Hu, F. (2017). Big data and cloud computing: Innovation opportunities and challenges. International Journal of Digital Earth, 10(1), 13–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz Durak, H. (2019). Examining the acceptance and use of online social networks by preservice teachers within the context of unified theory of acceptance and use of technology model. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 31(1), 173–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J., & He, X. (2022, September 2–3). Research on the application of computer artificial intelligence recognition technology in the education management system. 2022 International Conference on Education, Network and Information Technology (ICENIT), Liverpool, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y. (2023, October 27–29). Consttuction and optimization of higher education management system based on data mining technology. 2023 7th International Symposium on Computer Science and Intelligent Control (ISCSIC), Nanjing, China. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J., & Li, X. (2024). Application of big data in college student education management based on data warehouse technology and integrated learning. International Journal of e-Collaboration (IJeC), 20(1), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. (2024). Analysis of the innovation path of university education management informatization in the era of big data. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).