Life Satisfaction of International Students: (How) Do Study Demands, Institutional, and Individual Resources Matter?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Study Demands-Resources Model
1.2. The Acculturation Framework
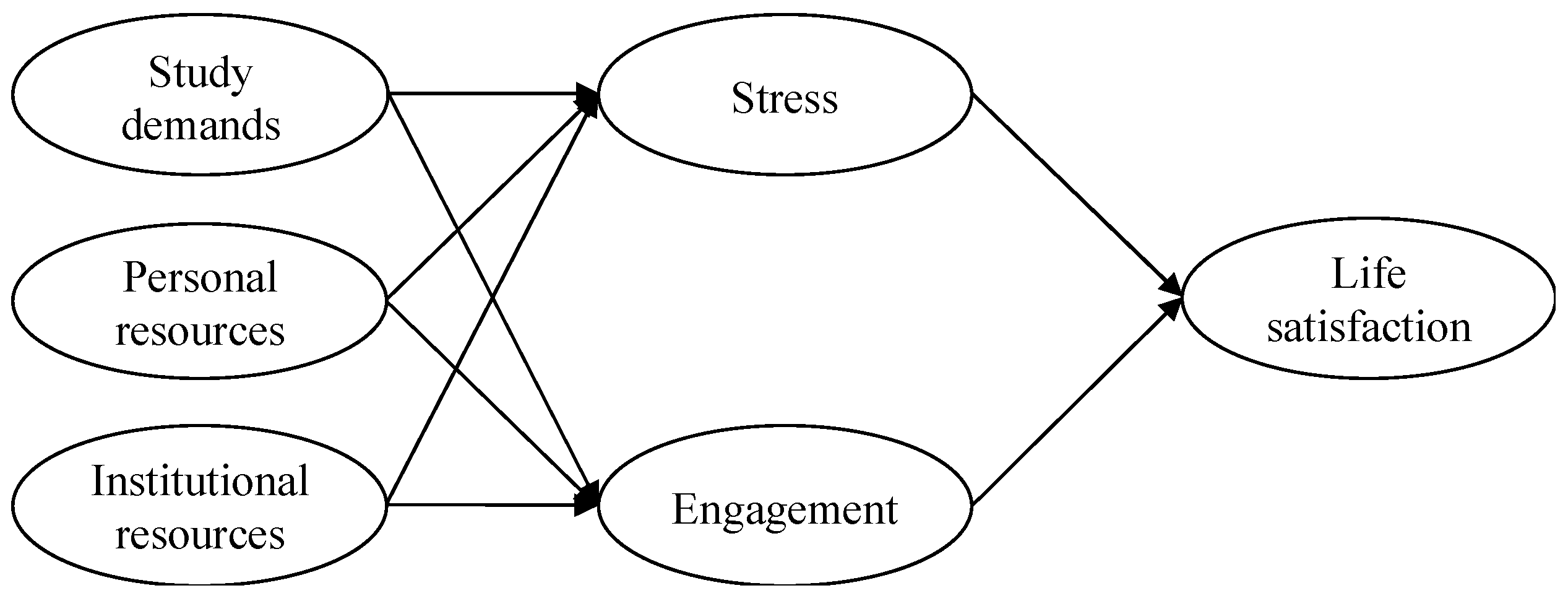
1.3. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
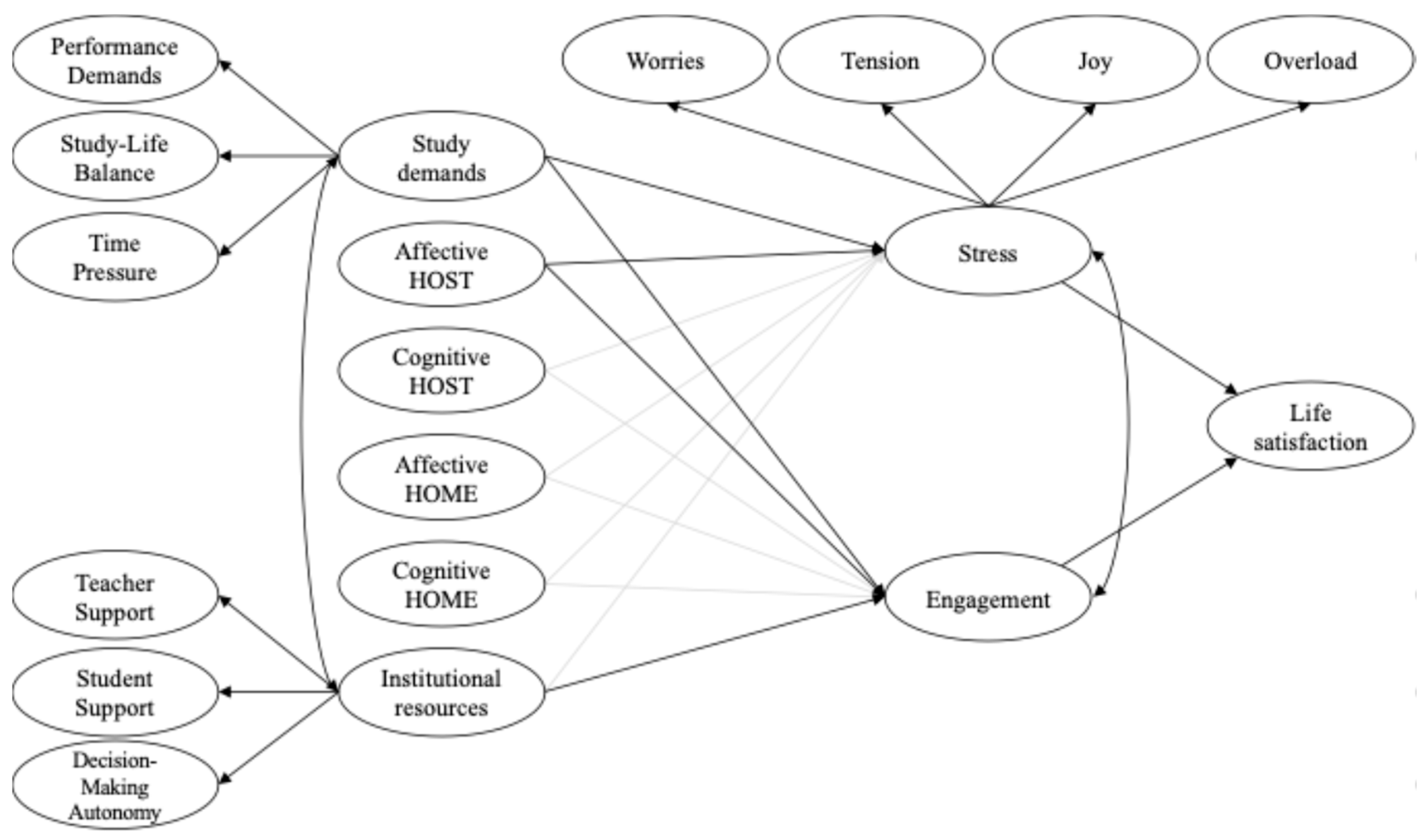
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Analytical Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analyses
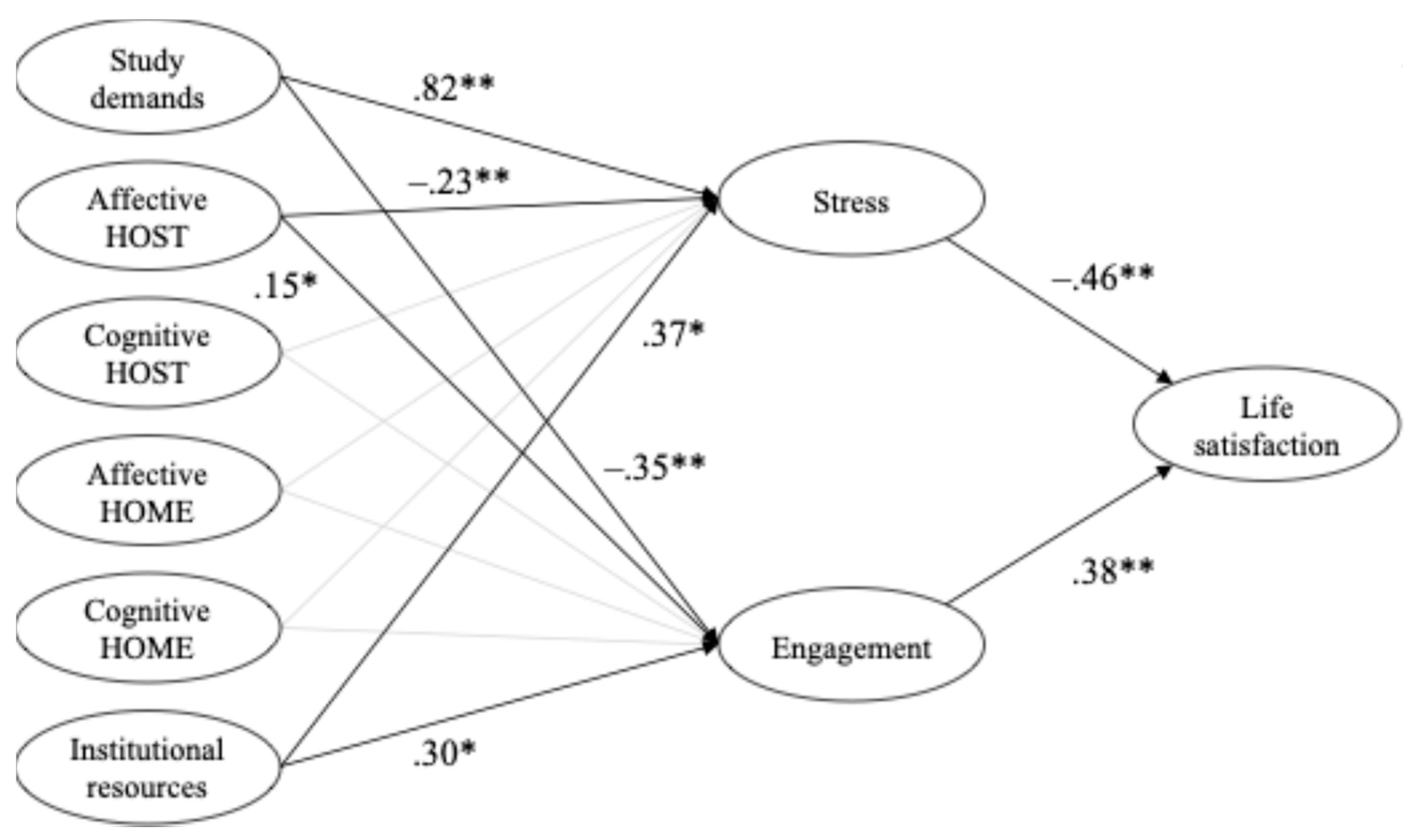
3.2. Structural Equation Modeling
4. Discussion
Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD-R model | Study demands-resources model |
| JD-R model | Job demands-resources model |
| PSQ | Perceived Stress Questionnaire |
| SEM | Structural equation modeling |
| HOST | Orientation towards the host culture |
| HOME | Orientation towards the culture of origin |
References
- Alharbi, E. S., & Smith, A. P. (2018). Review of the literature on stress and wellbeing of international students in English-speaking countries. International Education Studies, 11(6), 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanvermez, Y., Karyotaki, E., Cuijpers, P., Ciharova, M., Bruffaerts, R., Kessler, R. C., Klein, A. M., Wiers, R. W., & de Wit, L. M. (2023). Sources of stress among domestic and international students: A cross-sectional study of university students in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Anxiety, Stress, & Coping, 37(4), 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, B., & Wilding, J. M. (2004). The relation of depression and anxiety to life-stress and achievement in students. British Journal of Psychology, 95, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antaramian, S., & Lee, J. (2017). The importance of very high life satisfaction for students’ academic success. Cogent Education, 4(1), 1307622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends-Tóth, J., van de Vijver, F. J. R., & Poortinga, Y. H. (2006). The influence of method factors on the relation between attitudes and self-reported behaviors in the assessment of acculturation. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 22(1), 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalar, A. (2020). Student exchange: The first step toward international collaboration. In A. AI-Youbi, A. Zahed, & W. Tierney (Eds.), Successful global collaborations in higher education institutions. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A. B., Demerouti, E., & Sanz-Vergel, A. (2023). Job demands–resources theory: Ten years later. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 10, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A. B., & Mostert, K. (2024). Study demands-Resources theory: Understanding student well-being in higher education. Educational Psychology Review, 36(3), 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerkens, M., Souto-Otero, M., Wit, H. D., & Huisman, J. (2016). Similar students and different countries? An analysis of the barriers and drivers for Erasmus participation in seven countries. Journal of Studies in International Education, 20(2), 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J. W. (2006). Stress perspectives on acculturation. In D. Sam, & J. Berry (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of acculturation psychology (Cambridge handbooks in psychology, pp. 43–57). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J. W., Phinney, J. S., Sam, D. L., & Vedder, P. (2006). Immigrant youth. Acculturation, identity, and adaptation. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 55(3), 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewick, B., Koutsopoulou, G., Miles, J., Slaa, E., & Barkham, M. (2010). Changes in undergraduate students’ psychological well-being as they progress through university. Studies in Higher Education, 35(6), 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C. M., Gibbons, J. L., & Hughes, H. M. (2013). Acculturation clusters and life satisfaction. Acta de Investigación Psicológica, 3(2), 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C., & Meng, Q. (2022). A systematic review of predictors of international students’ cross-cultural adjustment in China: Current knowledge and agenda for future research. Asia Pacific Education Review, 23(1), 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.-Y. (2015). Internationalisation of higher education: Proposed framework on international students’ satisfaction. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities, 23, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cruwys, T., Ng, N. W. K., Haslam, S. A., & Haslam, C. (2021). Identity continuity protects academic performance, retention, and life satisfaction among international students. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 70(3), 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D. E., & Lecik, M. D. (2010). The overseas immersion setting as contextual variable in adult SLA: Learner behaviors associated with language gain to level-3 proficiency in Russian. Russian Language Journal, 60, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Nachreiner, F., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2001). The job demand-resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(3), 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demes, K. A., & Geeraert, N. (2014). Measures matter: Adaptation, cultural distance, and acculturation orientation revisited. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 45(1), 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD) & Deutsches Zentrum für Hochschul- und Wissenschaftsforschung (DZHW). (2025). Wissenschaft weltoffen kompakt 2025: Daten und Fakten zur Internationalität von Studium und Forschung in Deutschland und weltweit. Available online: https://www.wissenschaft-weltoffen.de/content/uploads/2025/04/WWO_Kompakt_DT_barrierefrei.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49(1), 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federal Statistical Office—Destatis. (2020). Bildung und kultur: Studierende an hochschulen. sommersemester 2020. (Fachserie 11—Bildung und Kultur 4.1.). Available online: https://www.statistischebibliothek.de/mir/servlets/MCRFileNodeServlet/DEHeft_derivate_00061732/2110410207314_fuer_Bibliothek.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Fliege, H., Rose, M., Arck, P., Levenstein, S., & Klapp, B. F. (2001). Validierung des “perceived stress questionnaire” (PSQ) an einer deutschen Stichprobe. Diagnostica, 47(3), 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislieri, C., Sanseverino, D., Dolce, V., Spagnoli, P., Manuti, A., Ingusci, E., & Addabbo, T. (2023). Emotional exhaustion and engagement in higher education students during a crisis, lessons learned from COVID-19 experience in Italian universities. Social Sciences, 12(2), 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groccia, J. E. (2018). What is student engagement? Teaching and Learning, 154, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, J., Gusy, B., Lesener, T., Sudheimer, S., & Willige, J. (2018). Gesundheit Studierender in Deutschland 2017. In Ein Kooperationsprojekt zwischen dem Deutschen Zentrum für Hochschul- und Wissenschaftsforschung, der Freien Universität Berlin und der Techniker Krankenkasse. Freie Universität Berlin. [Google Scholar]
- Gusy, B., & Lohmann, K. (2011). Gesundheit im Studium: Dokumentation der Instrumente (Schriftenreihe des AB Public Health: Prävention und psychosoziale Gesundheitsforschung Nr. 01/P11). Freie Universität Berlin. [Google Scholar]
- Gusy, B., Wörfel, F., & Lohmann, K. (2016). Erschöpfung und Engagement im Studium: Eine Anwendung des Job Demands-Resources Modells. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitspsychologie, 24(1), 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E., Kuhlee, D., & Porsch, R. (2021). Institutionelle und individuelle Einflussfaktoren des Belastungserlebens von Lehramtsstudierenden in der Corona-Pandemie. In C. Reintjes, R. Porsch, & G. im Brahm (Hrsg.), Das Bildungssystem in Zeiten der Krise: Empirische Befunde, Konsequenzen und Potentiale für das Lehren und Lernen (S. 221–238). Waxmann. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, E., Kuhlee, D., Zimmermann, J., & Serrano-Sánchez, J. (2024). Belastungserleben und Lebenszufriedenheit Studierender unter pandemischen und postpandemischen Studienbedingungen–individuelle und strukturelle Differenzen. In Y. Hofmann (Hrsg.), Die psycho-soziale Situation von Studierenden in der (post-)pandemischen Zeit. Stand der Forschung und Impulse aus der Praxis (S. 128–146). UniversitätsVerlagWebler. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrecht, L. (2019). Studienerfolg von berufsbegleitend studierenden: Entwicklung und validierung eines erklärungsmodells. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Hofhuis, J., Hanke, K., & Rutten, T. (2019). Social network sites and acculturation of international sojourners in the Netherlands: The mediating role of psychological alienation and online social support. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 69, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-t., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. (2023). IBM SPSS statistics for windows (version 29.0) [Computer Software]. IBM Corp. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of International Education. (2023). Open Doors data: International students: Enrollment trends. Available online: https://opendoorsdata.org/data/international-students/enrollment-trends/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Janke, S., & Glöckner-Rist, A. (2012). Deutsche version der satisfaction with life scale (SWLS). Zusammenstellung Sozialwissenschaftlicher Items und Skalen (ZIS). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. S. K., & Abreu, J. M. (2001). Acculturation measurement: Theory, current instruments, and future directions. In J. G. Ponterotto, J. M. Casas, L. A. Suzuki, & C. M. Alexander (Eds.), Handbook of multicultural counseling (2nd ed., pp. 394–424). Sage Publications, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Y. (2006). From ethnic to interethnic: The case for identity adaptation and transformation. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 25(3), 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J. (2012). Student mobility and internationalization: Trends and tribulations. Research in Comparative and International Education, 7(1), 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G. D., Kinzie, J., Schuh, J. H., & Whitt, E. J. (2005). Assessing conditions to enhance educational effectiveness: Inventory for student engagement and success. Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, R. S., Beal, D. J., & Tesluk, P. E. (2000). A comparison of approaches to forming composite measures in structural equation models. Organizational Research Methods, 3(2), 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcombe, W., Ryan, T., & Baik, C. (2023). Are international students relatively resilient? Comparing international and domestic students’ levels of self-compassion, mental health and wellbeing. Higher Education Research & Development, 43(2), 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. (2014). The relationship between student engagement and academic performance: Is it a myth or reality? The Journal of Educational Research, 107(3), 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiner, D. J. (2024). SoSci survey (version 3.5.01) [Computer software]. Available online: https://www.soscisurvey.de (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Lesener, T., Gusy, B., & Wolter, C. (2018). The job demands-resources model: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal studies. Work & Stress, 33(1), 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesener, T., Pleiss, L. S., Gusy, B., & Wolter, C. (2020). The study demands-resources framework: An empirical introduction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levent, F. (2016). The economic impacts of international student mobility in the globalization process. Journal of Human Sciences, 13(3), 3853–3870. Available online: https://www.j-humansciences.com/ojs/index.php/IJHS/article/view/3877 (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Little, T. D., Cunningham, W. A., Shahar, G., & Widaman, K. F. (2002). To parcel or not to parcel: Exploring the question, weighing the merits. Structural Equation Modeling, 9(2), 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lörz, M., & Krawietz, M. (2011). Internationale mobilität und soziale selektivität: Ausmaß, mechanismen und entwicklung herkunftsspezischer unterschiede zwischen 1990 und 2005. Kölner Zeitschrift für Soziologie und Sozialpsychologie, 63(2), 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J., & Jamieson-Drake, D. (2015). Predictors of study abroad intent, participation, and college outcomes. Research in Higher Education, 56(1), 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I. M., Youssef-Morgan, C. M., Chambel, M. J., & Marques-Pinto, A. (2019). Antecedents of academic performance of university students: Academic engagement and psychological capital resources. Educational Psychology, 39(8), 1047–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEPS. (2013). Startkohorte 4: Klasse 9 (SC4) wellen 1 und 2 erhebungsinstrumente (SUFVersion 1.1.0). Available online: https://www.neps-data.de/Portals/0/NEPS/Datenzentrum/Forschungsdaten/SC4/1-1-0/SC4_1-1-0_Q_w1-2_de.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- OECD. (2023). International student mobility (indicator). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A., Chang, L., & Fang, Y. (2015). International student mobility trends 2015: An economic perspective. World Education News & Reviews. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2571491 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Petersdotter, L., Niehoff, E., & Freund, P. A. (2017). International experience makes a difference: Effects of studying abroad on students’ self-efficacy. Personality and Individual Differences, 107, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, J. S. (1992). The multigroup ethnic identity measure: A new scale for use with diverse groups. Journal of Adolescent Research, 7(2), 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuß, J. S., Zimmermann, J., & Jonkmann, K. (2025). Intersectional perspectives on the university belonging of international STEM students. Social Psychology of Education, 28, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumpe, I. E., & Jonkmann, K. (2025). Study demands and resources in distance education—Their associations with engagement, emotional exhaustion, and academic success. Education Sciences, 15(6), 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, J. C., Arthaud-Day, M. L., Mooney, C. H., Near, J. P., Baldwin, T. T., Bommer, W. H., & Rubin, R. S. (2005). Life satisfaction and student performance. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 4(4), 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, Y. (2012). Lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. Journal of Statistical Software, 48(2), 1–36. Available online: http://www.jstatsoft.org/v48/i02/ (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sam, D. L., & Berry, J. W. (2010). Acculturation: When individuals and groups of different cultural backgrounds meet. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5(4), 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawir, E. (2013). Internationalisation of higher education curriculum: The contribution of international students. Globalisation, Societies and Education, 11(3), 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W. B., & Bakker, A. B. (2003). Test manual for the Utrecht work engagement scale [Unpublished manuscript]. Utrecht University. Available online: https://www.wilmarschaufeli.nl/tests/#engagement (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Serrano-Sánchez, J., Zimmermann, J., & Jonkmann, K. (2021a). Thrilling travel or lonesome long haul? Loneliness and acculturation behavior of adolescents studying abroad. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Sánchez, J., Zimmermann, J., & Jonkmann, K. (2021b). When in Rome… A longitudinal investigation on the predictors and development of student sojourners’ host cultural behavioral engagement. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 83, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Sánchez, J., Zimmermann, J., & Jonkmann, K. (2022). Personality, behavioral engagement, and psychological adaptation of high school students abroad: A longitudinal perspective on between- and within-person dynamics. European Journal of Personality, 38(1), 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. A., & Khawaja, N. G. (2011). A review of the acculturation experiences of international students. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 35(6), 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkman, D. J., Eidelman, S., & Blanchar, J. C. (2016). Multicultural experiences reduce prejudice through personality shifts in openness to experience. European Journal of Social Psychology, 46(7), 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrant, M. A. (2010). A conceptual framework for exploring the role of studies abroad in nurturing global citizenship. Journal of Studies in International Education, 14, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taušováa, J., Bendera, M., Dimitrova, R., & Vijver, F. V. D. (2019). The role of perceived cultural distance, personal growth initiative, language proficiencies, and tridimensional acculturation orientations for psychological adjustment among international students. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 69, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonsing, K. N. (2014). Acculturation and adaptation of first- and second-generation South Asians in Hong Kong. International Journal of Social Welfare, 23(4), 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadyaya, K., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2013). Development of school engagement in association with academic success and well-being in varying social contexts: A review of empirical research. European Psychologist, 18(2), 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, C., Rodríguez, C., & Arias-Gundín, O. (2018). Coping, academic engagement and performance in university students. Higher Education Research & Development, 37(7), 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C., & Geeraert, N. (2016). Advancing acculturation theory and research: The acculturation process in its ecological context. Current Opinion in Psychology, 8, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, S., & Huisman, J. (2011). Student recruitment at international branch campuses. Can they compete in the global market? Journal of Studies in International Education, 15(3), 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J., Falk, S., Thies, T., Yildirim, H. H., Kercher, J., & Pineda, J. (2021a). Spezifische problemlagen und studienerfolg internationaler Studierender. In M. Neugebauer, H.-D. Daniel, & U. Wolter (Eds.), Studienerfolg und Studienabbruch (pp. 179–202). Springer VS. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J., Greischel, H., & Jonkmann, K. (2021b). The development of multicultural effectiveness in international student mobility. Higher Education, 82, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J., Greischel, H., Jonkmann, K., & Neyer, F. J. (2021c). Growth all along the road? Personality development and international contacts of (in)experienced sojourners. European Journal of Personality, 35(4), 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J., Preuß, J. S., & Jonkmann, K. (2024). Proactive personality and international student mobility: Patterns of self-selection and development. Personality and Individual Differences, 219, 112501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J., & Serrano-Sánchez, J. (2023). Subjektives Wohlbefinden internationaler Studierender in Deutschland im Studienverlauf und zu Beginn der Corona-Pandemie. DAAD Forschung kompakt. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| M (SD) | α | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Life satisfaction | 4.37 (1.35) | .87 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | Stress | 2.52 (0.56) | .91 | −.51 *** | |||||||||||
| 3 | Engagement | 2.82 (0.61) | .80 | .43 *** | −.28 *** | ||||||||||
| 4 | Performance demands | 2.08 (0.65) | .80 | −.35 *** | .37 *** | −.47 *** | |||||||||
| 5 | Study-life balance | 2.38 (0.64) | .84 | −.38 *** | .44 *** | −.42 *** | .54 *** | ||||||||
| 6 | Time pressure | 2.56 (0.75) | .78 | −.20 *** | .46 *** | −.14 ** | .39 *** | .47 *** | |||||||
| 7 | Teacher support | 2.93 (0.67) | .81 | .20 *** | −.20 *** | .36 *** | −.39 *** | −.16 *** | −.40 *** | ||||||
| 8 | Student support | 2.75 (0.72) | .77 | .21 *** | −.18 *** | .32 *** | −.29 *** | −.11 * | −.32 *** | .41 *** | |||||
| 9 | Decision-making autonomy | 2.84 (0.68) | .81 | .23 *** | −.23 *** | .39 *** | −.46 *** | −.17 *** | −.47 *** | .50 *** | .31 *** | ||||
| 10 | Affective HOST | 3.12 (0.84) | .88 | .29 *** | −.29 *** | .29 *** | −.21 *** | −.06 | −.22 *** | .15 ** | .20 *** | .14 ** | |||
| 11 | Cognitive HOST | 3.92 (0.77) | .78 | .09 * | −.10 * | .21 *** | −.13 ** | .00 | −.13 ** | .06 | .10 * | .06 | .46 *** | ||
| 12 | Affective HOME | 3.36 (0.98) | .89 | .09 | −.03 | .12 * | −.11 * | .06 | −.14 ** | .07 | .15 ** | .05 | −.04 | .11 * | |
| 13 | Cognitive HOME | 2.89 (0.88) | .78 | .02 | .01 | .05 | .00 | .06 | −.10 * | −.04 | .06 | .05 | −.07 | .13 ** | .59 *** |
| β | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Life Satisfaction | |||
| Stress | −.46 | ** | <.001 |
| Engagement | .38 | ** | <.001 |
| Gender (male) | −.15 | ** | <.001 |
| Age | −.02 | .570 | |
| Stress | |||
| Study demands | .82 | ** | <.001 |
| Institutional resources | .37 | * | .027 |
| Affective HOST | −.23 | ** | .002 |
| Cognitive HOST | .11 | .141 | |
| Affective HOME | −.04 | .698 | |
| Cognitive HOME | .07 | .484 | |
| Gender (male) | −.06 | .235 | |
| Age | .08 | .067 | |
| Engagement | |||
| Study demands | −.35 | ** | .004 |
| Institutional resources | .30 | * | .014 |
| Affective HOST | .15 | * | .022 |
| Cognitive HOST | .08 | .275 | |
| Affective HOME | .03 | .709 | |
| Cognitive HOME | .03 | .760 | |
| Gender (male) | .03 | .530 | |
| Age | .08 | .119 | |
| Study demands | |||
| Gender (male) | −.13 | * | .013 |
| Age | −.03 | .589 | |
| Institutional resources | |||
| Gender (male) | .03 | .565 | |
| Age | −.02 | .685 | |
| Affective HOST | |||
| Gender (male) | .09 | .071 | |
| Age | −.18 | ** | .001 |
| Cognitive HOST | |||
| Gender (male) | .16 | ** | .002 |
| Age | .04 | .412 | |
| Affective HOME | |||
| Gender (male) | −.03 | .489 | |
| Age | −.08 | .105 | |
| Cognitive HOME | |||
| Gender (male) | .11 | * | .031 |
| Age | .09 | .071 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Sánchez, J.; Zimmermann, J.; Hahn, E.; Kuhlee, D. Life Satisfaction of International Students: (How) Do Study Demands, Institutional, and Individual Resources Matter? Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070918
Serrano-Sánchez J, Zimmermann J, Hahn E, Kuhlee D. Life Satisfaction of International Students: (How) Do Study Demands, Institutional, and Individual Resources Matter? Education Sciences. 2025; 15(7):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070918
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Sánchez, Juan, Julia Zimmermann, Edgar Hahn, and Dina Kuhlee. 2025. "Life Satisfaction of International Students: (How) Do Study Demands, Institutional, and Individual Resources Matter?" Education Sciences 15, no. 7: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070918
APA StyleSerrano-Sánchez, J., Zimmermann, J., Hahn, E., & Kuhlee, D. (2025). Life Satisfaction of International Students: (How) Do Study Demands, Institutional, and Individual Resources Matter? Education Sciences, 15(7), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070918







