Digitalization of Higher Education: Students’ Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses
2.1.1. Digitalization of HEIs
2.1.2. The State of Education Digitalization in HEIs
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample and Procedure
2.2.2. Measures
2.2.3. Research Design and Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Implications for Practice
5.3. Limitations
5.4. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agerwal, V., Verma, P., & Ferrigno, G. (2025). Education 5.0 challenges and sustainable development goals in emerging economies: A mixed-method approach. Technology in Society, 81, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, R., & Sharma, V. (2018). Smart education with artificial intelligence-based determination of learning styles. Procedia Computer Science, 132, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T., Stull, A., Hsu, T., & Hegarty, M. (2015). Constrained interactivity for relating multiple representations in science: When virtual is better than real. Computers & Education, 81, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R. (1956). The three R’s plus: What today’s schools are trying to do and why. University of Minnesota Press. [Google Scholar]
- Chaika, O. (2024). Bridging the gap: Traditional vs. modern education (A value-based approach for multiculturalism). In F. Gomez Paloma (Ed.), Lifelong learning—Education for the future world. IntechOpen. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. (2024). Exploring the application scenarios and issues facing metaverse technology in education. Interactive Learning Environments, 32(5), 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillakuri, B., & Mahanandia, R. (2018). Generation Z entering the workforce: The need for sustainable strategies in maximizing their talent. Human Resource Management International Digest, 26(4), 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D., & Vartiainen, T. (2022). Digital strategy in information systems: A literature review and an educational solution based on problem-based learning. Journal of Information Systems Education, 33(3), 261–282. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/jise/vol33/iss3/6 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Dawley, L., & Dede, C. (2014). Situated learning in virtual worlds and immersive simulations. In J. M. Spector, M. D. Merrill, J. Elen, & M. J. Bishop (Eds.), Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (p. 723). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, K. (2021). Smart education framework. Smart Learning Environments, 8(1), 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabagh, H. A. (2021). Adaptive e-learning environment based on learning styles and its impact on development students’ engagement. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(1), 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Center for The Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP). (2024). Recently implemented action plan ANDI to transform digital education. National new on VET. Available online: https://www.cedefop.europa.eu/en/news/slovenia-recently-implemented-action-plan-andi-transform-digital-education (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- European Commission (EC) (2024). 2030 digital decade—Report on the state of the digital decade 2024. Available online: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/report-state-digital-decade-2024 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Fernández, A., Gómez, B., Binjaku, K., & Kajo Meçe, E. (2023). Digital transformation initiatives in higher education institutions: A multivocal literature review. Education and Information Technologies, 28(10), 12351–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, I., & Luiz, J. (2024). Exploring gender differences in Gen Z students’ attribution of obstacles influencing their academic and professional success. The International Journal of Management Education, 22(2), 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, E., Rogach, O., & Ryabova, T. (2020). Digitalization of education in modern scientific discourse: New trends and risks analysis. European Journal of Contemporary Education, 9(2), 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanouli, D., Murphy, C., & Gardner, J. (2024). Teachers’ perceptions of the effectiveness of Ict-competence training. Computers & Education, 43(1–2), 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, T. (2019). The concept of a university: Theory, practice, and society. Danish Yearbook of Philosophy, 52(1), 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J. (2008). Innovative technologies for education and learning: Education and knowledge-oriented applications of blogs, wikis, podcasts, and more. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies (IJWLTT), 3(3), 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A., Jacovina, M., Russell, D., & Soto, C. (2016). Challenges and solutions when using technologies in the classroom. In S. A. Crossley, & D. S. McNamara (Eds.), Adaptive educational technologies for literacy instruction (pp. 13–29). Routledge. ISBN 9781315647500. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, N., & Salaz, A. M. (2019). Exploring the reasons why university students prefer print over digital texts: An Australian perspective. Journal of the Australian Library and Information Association, 68(2), 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacka, E., & Wong, T. C. (2021). Examining the impact of digital technologies on students’ higher education outcomes: The case of the virtual learning environment and social media. Studies in Higher Education, 46(8), 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J., & Bower, M. (2019). How is the use of technology in education evaluated? A systematic review. Computers & Education, 133, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J. E., & Tar, U. A. (2018). Factors that influence teachers’ adoption and integration of Ict in teaching/learning process. Educational Media International, 55(1), 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Managi, S., Lindner, R., & Stevens, C. (2021). Technology policy for the sustainable development goals: From the global to the local level. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 162, 120410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R., & Moreno, R. (2003). Nine ways to reduce cognitive load in multimedia learning. Educational Psychologist, 38(1), 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertala, P. (2020). Paradoxes of participation in the digitalization of education: A narrative account. Learning, Media and Technology, 45(2), 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J., Dickson-Deane, C., & Galyen, C. (2011). E-learning, online learning, and distance learning environments: Are they the same? The Internet and Higher Education, 14(2), 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R., & Mayer, R. (2007). Interactive multimodal learning environments. Educational Psychology Review, 19(3), 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelko, Z., Peleckienė, V., Peleckis, K., Peleckis, K. K., Lapinskienė, G., & Potocan, V. (2022). Generation Z and ethicality of advancement in the workplace: A study of Slovenia and Lithuania. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 23(2), 482–506. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:248654639 (accessed on 1 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- OECD. (2021). OECD digital education outlook 2021: Pushing the frontiers with artificial intelligence, blockchain and robots. OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. (2023). Country digital education ecosystems and governance: A companion to digital education outlook 2023. OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanov, D., Henrik, F., & Netland, T. (2023). Digital transformation: A review and research agenda. European Management Journal, 41(6), 821–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R., & Nagasubramani, P. (2018). Impact of modern technology in education. Journal of Applied and Advanced Research, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M. F., & Ortiz, K. R. (2021). Evaluating digital instructional materials for K-12 online and blended learning. TechTrends, 65(6), 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblin, P. N., Schunn, C., & McKenney, S. (2018). What are critical features of science curriculum materials that impact student and teacher outcomes? Science Education, 102, 260–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P. (2020). Barriers to adopting emerging technologies in education. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 22(4), 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, C., Nguyen, F., Sweller, J., & Baddeley, M. (2006). Efficiency in learning: Evidence-based guidelines to manage cognitive load. Performance Improvement, 45, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secundo, G., Ndou, V., Del Vecchio, P., & De Pascale, G. (2020). Sustainable development, intellectual capital and technology policies: A structured literature review and future research agenda. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 153, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemiller, C., & Grace, M. (2018). Generation Z goes to college. Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn, N. (2011). Education and technology: Key issues and debates. Continuum International Publishing Group. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V., & Thurman, A. (2019). How many ways can we define online learning? A systematic literature. review of definitions of online learning (1988–2018). American Journal of Distance Education, 33(4), 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweller, J., van Merriënboer, J. J. G., & Paas, F. (2019). Cognitive architecture and instructional design: 20 years later. Educational Psychology Review, 31(2), 261–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, M., & Alvi, S. (2019). Edtech Inc.: Selling, automating and globalizing higher education in the digital age. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Timotheou, S., Miliou, O., Dimitriadis, Y., Sobrino, S. V., Giannoutsou, N., Cachia, R., Monés, A. M., & Ioannou, A. (2022). Impacts of digital technologies on education and factors influencing schools’ digital capacity and transformation: A literature review. Education and Information Technologies, 28(6), 6695–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. (2012). International standard classification of education ISCED 2011. UNESCO Institute for Statistics. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO-IITE, COL & BNU. (2022). Smart education strategies for teaching and learning: Critical analytical framework and case studies. UNESCO IITE. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations (UN). (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld/publication (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- United States Department of Education (USDE). (2015). Future ready learning: Reimagining the role of technology in education. 2016 national technology education plan. United States Department of Education. Available online: https://tech.ed.gov/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Wang, C., Chen, X., Yu, T., Liu, Y., & Jing, Y. (2024). Education reform and change driven by digital technology: A bibliometric study from a global perspective. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfart, O., & Wagner, I. (2023). Teachers’ Role in Digitalizing education: An umbrella review. Educational Technology Research and Development, 71(2), 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoav, B., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Basham, J., & Yang, S. (2020). Understanding the implementation of personalized learning: A research synthesis. Educational Research Review, 31, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z., Yu, M.-H., & Riezebos, P. (2016). A research framework of smart education. Smart Learning Environments, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, R. D., Liu, D., Sampson, D., Mandic, S., You, S., Huang, Y., & Huang, R. (2023). Smart education in China and Central & Eastern European countries. Springer. [Google Scholar]
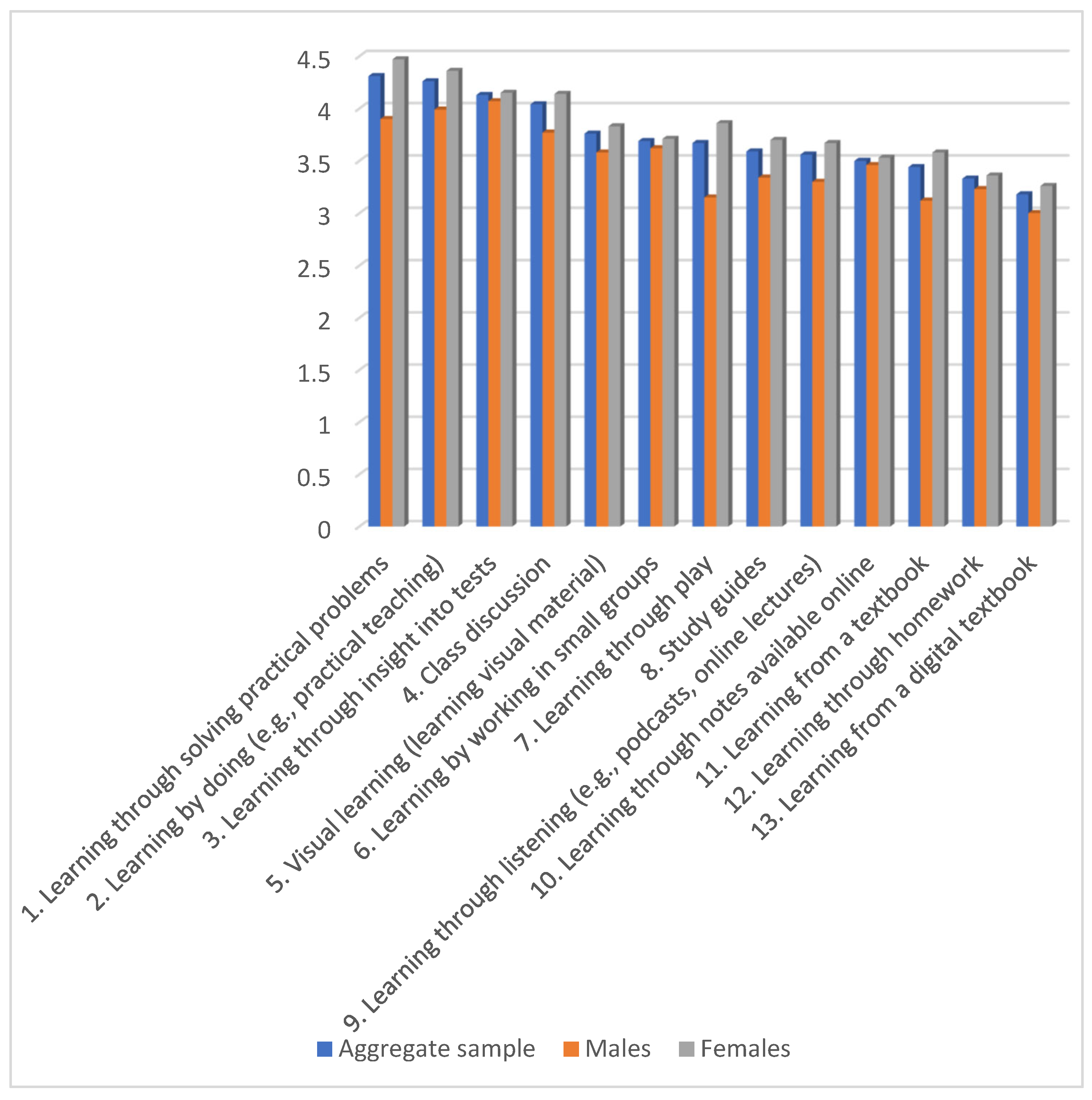
| Teaching Method | Aggregate Sample | Males | Females | Corrected t-Statistics a | p-Values | Corrected p-Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |||||
| 1. Learning through solving practical problems | 4.31 | 0.73 | 3.90 | 0.87 | 4.47 | 0.60 | 5.12 | <0.001 | 0.013 | −0.82 |
| 2. Learning by doing (e.g., practical teaching) | 4.26 | 0.85 | 3.99 | 1.07 | 4.36 | 0.72 | 2.77 | 0.024 | 0.312 | −0.44 |
| 3. Learning through insight into tests | 4.13 | 0.85 | 4.07 | 0.83 | 4.15 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.538 | 1 | −0.10 |
| 4. Class discussion | 4.04 | 0.93 | 3.77 | 1.14 | 4.14 | 0.82 | 2.50 | 0.038 | 1 | −0.39 |
| 5. Visual learning (learning visual material) | 3.76 | 0.87 | 3.58 | 0.89 | 3.83 | 0.87 | 1.79 | 0.092 | 1 | −0.28 |
| 6. Learning by working in small groups | 3.69 | 1.00 | 3.62 | 0.99 | 3.71 | 1.02 | 0.56 | 0.585 | 1 | −0.09 |
| 7. Learning through play | 3.67 | 1.09 | 3.15 | 1.21 | 3.86 | 0.98 | 4.23 | <0.001 | 0.013 | −0.68 |
| 8. Study guides | 3.59 | 0.91 | 3.34 | 0.85 | 3.70 | 0.92 | 2.50 | 0.015 | 0.195 | −0.40 |
| 9. Learning through listening (e.g., podcasts, online lectures) | 3.56 | 1.08 | 3.30 | 1.14 | 3.67 | 1.05 | 2.15 | 0.034 | 1 | −0.35 |
| 10. Learning through notes available online | 3.50 | 1.04 | 3.46 | 1.00 | 3.53 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 0.668 | 1 | −0.07 |
| 11. Learning from a textbook | 3.44 | 0.95 | 3.12 | 0.98 | 3.58 | 0.91 | 3.09 | 0.003 | 0.039 | −0.50 |
| 12. Learning through homework | 3.33 | 1.10 | 3.23 | 1.20 | 3.36 | 1.05 | 0.74 | 0.442 | 1 | −0.13 |
| 13. Learning from a digital textbook | 3.18 | 0.99 | 3.00 | 0.98 | 3.26 | 0.99 | 1.65 | 0.103 | 1 | −0.27 |
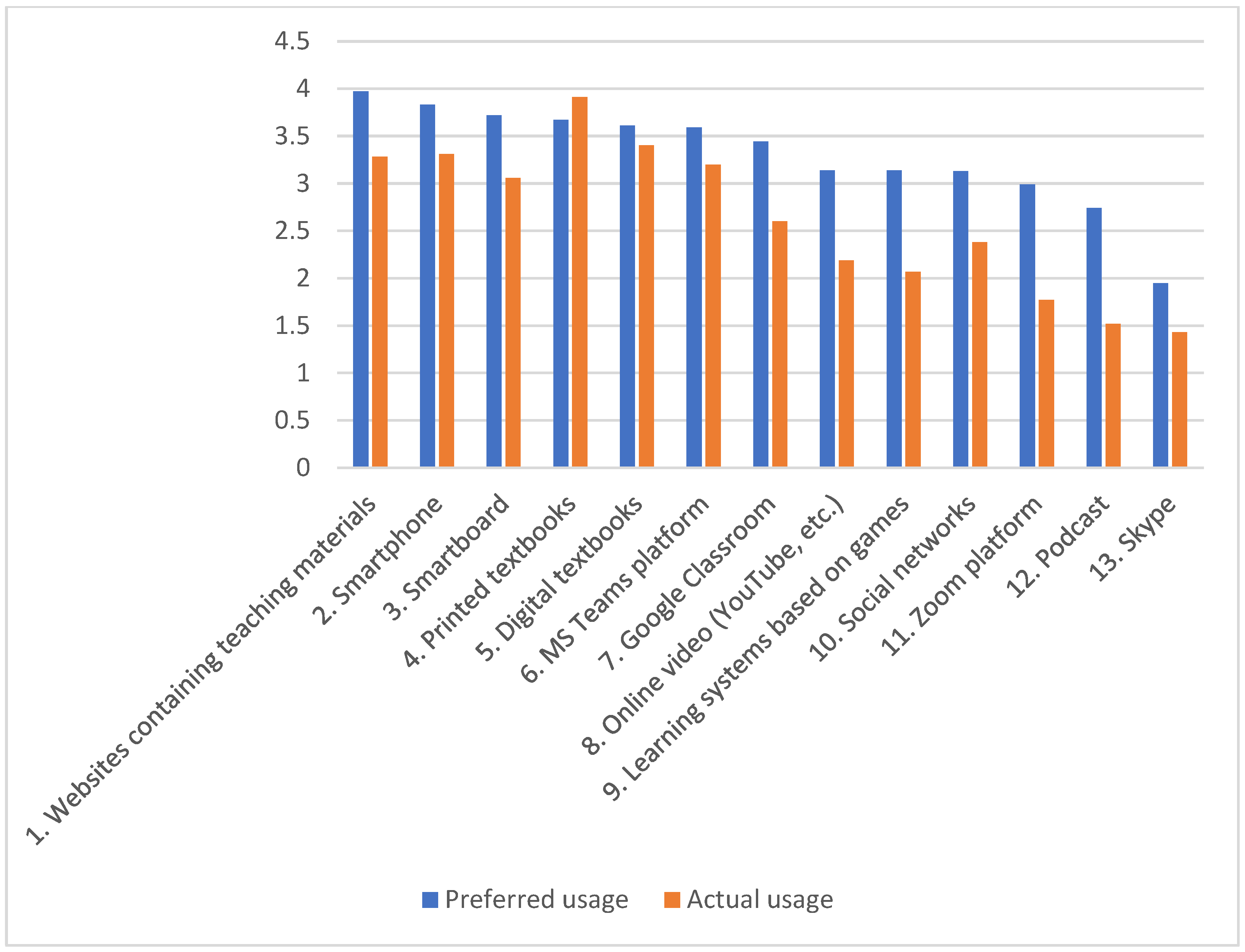
| Teaching Method | Preferred Usage | Actual Usage | Paired Differences | t-Test b | p-Value | Corrected p-Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |||||
| 1. Websites containing teaching materials | 3.97 | 0.84 | 3.28 | 1.22 | 0.69 | 1.36 | 6.86 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.51 |
| 2. Smartphone | 3.83 | 0.99 | 3.31 | 1.14 | 0.52 | 1.15 | 6.13 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.45 |
| 3. Smartboard | 3.72 | 1.07 | 3.06 | 1.44 | 0.66 | 1.38 | 6.64 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.48 |
| 4. Printed textbooks a | 3.69 | 1.02 | 3.91 | 1.03 | −0.22 | 1.35 | −2.22 | 0.028 | 0.364 | −0.16 |
| 5. Digital textbooks | 3.61 | 1.01 | 3.40 | 1.10 | 0.21 | 1.35 | 2.12 | 0.036 | 0.468 | 0.16 |
| 6. MS Teams platform | 3.59 | 1.03 | 3.20 | 1.11 | 0.38 | 1.25 | 4.21 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.31 |
| 7. Google Classroom | 3.44 | 1.19 | 2.60 | 1.40 | 0.84 | 1.43 | 8.07 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.59 |
| 8. Online video (YouTube, etc.) | 3.14 | 1.05 | 2.19 | 1.09 | 0.95 | 1.34 | 9.74 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.71 |
| 9. Learning systems based on games | 3.14 | 1.08 | 2.07 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 1.23 | 11.84 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.87 |
| 10. Social networks | 3.13 | 1.09 | 2.38 | 1.30 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 7.74 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.57 |
| 11. Zoom platform | 2.99 | 1.18 | 1.77 | 1.08 | 1.22 | 1.40 | 11.98 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.87 |
| 12. Podcast | 2.74 | 1.19 | 1.52 | 0.95 | 1.21 | 1.32 | 12.49 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.92 |
| 13. Skype | 1.95 | 1.09 | 1.43 | 0.96 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 7.20 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potocan, V.; Nedelko, Z.; Rosi, M. Digitalization of Higher Education: Students’ Perspectives. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070847
Potocan V, Nedelko Z, Rosi M. Digitalization of Higher Education: Students’ Perspectives. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(7):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070847
Chicago/Turabian StylePotocan, Vojko, Zlatko Nedelko, and Maja Rosi. 2025. "Digitalization of Higher Education: Students’ Perspectives" Education Sciences 15, no. 7: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070847
APA StylePotocan, V., Nedelko, Z., & Rosi, M. (2025). Digitalization of Higher Education: Students’ Perspectives. Education Sciences, 15(7), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070847









