Abstract
Interest in instructional leadership has grown dramatically in Asia since 2010. This systematic state-of-the-art review analyzed the evolution of analytical models, research methods, and findings in Asian studies of instructional leadership that employed the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale (PIMRS). The authors applied content analysis to 349 Asian instructional leadership studies sourced from multiple digital databases. The publication of Asia-based studies of instructional leadership increased from 47 before 2011 to 257 in the subsequent 15 years. Our analysis of 302 quantitative and mixed methods studies found that Asian scholars have primarily employed univariate and direct effects models in their instructional leadership studies, a limitation for knowledge advancement. At the same time, the use of advanced multivariate analytical models increased from 2.1% of the literature before 2011 to 23.3% in the subsequent period. Analysis of 20 “state-of-the-art studies” found a consistent pattern of significant mediated and direct effects of instructional leadership on teacher attitudes and practices. Moreover, several well-designed studies found that a school’s cultural context moderated the effects of instructional leadership on teaching and learning. Findings from the state-of-the-art review highlight the relationship between analytical models, variable selection, and research methods in studies that advance knowledge.
1. Introduction
American scholars dominated research publication in educational leadership and management (EDLM) during the 20th century (Hallinger & Kovačević, 2019). However, over the past 15 years, Asian scholars have rapidly increased their share of EDLM publications (Hallinger et al., 2020). These trends also describe research on instructional leadership, which has expanded worldwide, as well as in Asia, over the past two decades (Gümüş et al., 2018; Hallinger et al., 2020). Numerous research reviews have highlighted the role that the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale (PIMRS) has played in research on instructional leadership (e.g., Alanoglu, 2022; Harris et al., 2019; Ng et al., 2015; Ng, 2019; Robinson et al., 2008).
The PIMRS (Hallinger, 1983; Hallinger & Murphy, 1985) was developed in response to the need for stronger conceptual models and research instruments for studying the effects of school leadership on teaching and learning (Bossert et al., 1982; Bridges, 1967, 1982; Erickson, 1979). During the three decades following publication of the PIMRS, scholars, primarily in the United States (USA), began using this instrument in studies of principal instructional leadership (Hallinger, 2011; Hallinger et al., 2020; Robinson et al., 2008).
In 2011, Hallinger identified a PIMRS literature comprising 130 doctoral dissertations, six journal articles, and three conference papers. American scholars were the primary contributors of these studies (91%), with only 16 other documents authored in seven Asian societies. This finding highlighted instructional leadership’s limited traction outside the USA. The review further concluded that “the conceptual frameworks and methodologies used by these doctoral students were, on the whole, inadequate for the task of contributing to either the theoretical or the practical knowledge base in this field” (Hallinger, 2011, p. 272). This challenged the field to improve the quality of future research on instructional leadership.
During the ensuing 15 years, research reviews have highlighted the increased production of instructional leadership studies worldwide (e.g., Alanoglu, 2022; Gümüş et al., 2018; Hallinger et al., 2020; Ng, 2019). This is especially evident in Asia, where researchers and policymakers were increasingly interested in exploring instructional leadership’s potential for supporting education reforms (Ng et al., 2015; Pan et al., 2017; Samichan et al., 2021; Walker & Hallinger, 2015; Walker & Qian, 2022). This led scholars to review instructional leadership research conducted in individual Asian societies. These “national research reviews” examined instructional leadership in Malaysia (Harris et al., 2019), Singapore (Ng et al., 2015), Taiwan (Pan et al., 2015), China (Qian et al., 2017; Walker & Qian, 2022), Vietnam (Hallinger et al., 2015), Iran (Hosseingholizadeh et al., 2021), and Turkey (Gümüş et al., 2021).
Nonetheless, no reviews have synthesized the Asian literature on instructional leadership. Consequently, scholars lack perspective on this rapidly emerging knowledge base’s scale, geographic scope, and research quality. Practitioners lack insights into findings on the enactment of instructional leadership across Asian societies. These research gaps were addressed in this article, which synthesized conceptual, methodological, and substantive trends in the Asian instructional leadership literature.
The timeliness of reviewing Asian research on instructional leadership is grounded in broader EDLM research trends. Scholars have emphasized the need for EDLM to build a more geographically diverse knowledge base (Dimmock & Walker, 2000; Hallinger & Kovačević, 2019; Hallinger & Leithwood, 1996; Wong & Cheng, 1995). This recommendation is based on evidence that school leadership practices are shaped by cultural and institutional features of the school context (Bajunid, 1996; Clarke & O’Donoghue, 2017; Hallinger et al., 2018; Hallinger & Leithwood, 1996). Although Asia is culturally diverse, the composite societies share a tendency toward high power distance in social relations and centralized bureaucratic education structures compared with Anglo-American societies (Dimmock & Walker, 2000; Hallinger et al., 2018). The following research questions guided this review.
- How has Asian research on instructional leadership evolved in terms of publication trajectory and geographic scope over the past 40 years?
- What analytical models have guided Asian research on instructional leadership?
- What analytical models and research methods have been used in state-of-the-art Asian studies of instructional leadership?
- What research findings can be synthesized from state-of-the-art studies of instructional leadership in Asia?
The review focused on 349 Asian studies of instructional leadership conducted through the end of 2024. The authors employed content analysis on the full corpus of studies to address the first research question. Content analysis was then applied to a subset of 302 quantitative and mixed methods studies to address the second research question. Finally, the researchers synthesized data extracted from a subset of 20 “state-of-the-art studies” for the third and fourth research questions.
The significance of the review lies in three domains. First, the review of Asian studies extends prior societal-level reviews of Asian research on instructional leadership (Gümüş et al., 2021; Harris et al., 2019; Ng et al., 2015; Ng, 2019; Pan et al., 2015). Second, the conceptual and methodological findings from the review provide scholars with specific guidance concerning analytical models, methods, and lines of inquiry that should improve the quality of future research. Third, although the state-of-the-art review was limited to only 20 studies, the findings point toward potentially useful research trends that can be tested in future studies and have specific implications for practice.
2. Conceptual Framework
This review examined instructional leadership research that employed the PIMRS conceptual framework and instrument. Notably, while the PIMRS instrument has been widely used for data collection in quantitative and mixed methods research, other qualitative studies have relied on the underlying PIMRS conceptual framework to generate interview questions for data collection (see Figure 1). Thus, in this section, we will briefly present the PIMRS conceptual framework (see also Hallinger & Murphy, 1985; Hallinger & Wang, 2015).
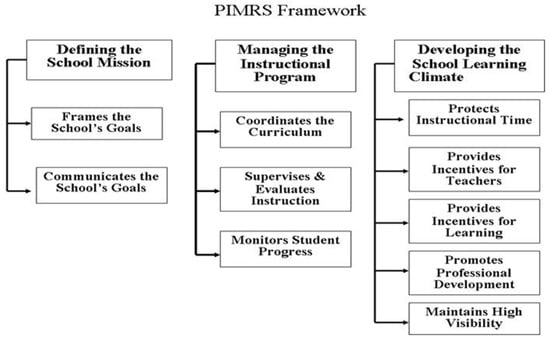
Figure 1.
PIMRS conceptual framework (From Hallinger, 2011, p. 276).
2.1. The PIMRS Framework
Other sources have described the PIMRS conceptual framework in detail (see Hallinger & Wang, 2015). In brief, the PIMRS conceptual framework consists of three broad dimensions: Defines the School Mission, Manages the Instructional Program, and Promotes a Positive School Learning Climate. These three dimensions are further broken out into 10 composite job functions (see Figure 1).
The PIMRS instrument was developed as a behaviorally anchored rating scale that aligns with the PIMRS conceptual framework (Hallinger, 1983; Hallinger & Murphy, 1985). There are 50-item Teacher, Principal, and Supervisor Forms of the PIMRS, as well as a 22-item Teacher Short Form. These have been periodically updated and validated in multiple national contexts (Hallinger & Wang, 2015).
2.2. Analytical Models Used in Quantitative Studies of School Leadership
Since the 1980s and 1990s, scholars have highlighted the relationship between analytical models, research methods, and the efficacy of the research results (Bridges, 1982; Heck & Hallinger, 1999, 2005; Leithwood, 2005; Pitner, 1988; Pitner & Hocevar, 1987). The conceptual framework that guided the primary data analyses in this review identified 11 “analytical models” used in studying school leadership effects (see Figure 2).
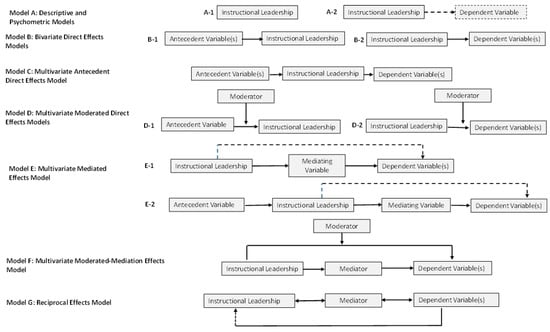
Figure 2.
Conceptual framework of analytical models for studying instructional leadership. Note: dashed arrows indicate a possible relationship examined within the model.
Analytical models frame variable relationships in studies investigating forces that shape school leadership’s enactment and effects. The models vary in order of complexity from univariate models (Model A) to bivariate direct effects models (Model B) to multivariate models (Models C, D, E, F, and G). The multivariate models are distinguished by how variables are conceptualized to influence one another, i.e., either directly or through mediation, moderation, or reciprocity. Variations on this framework were used in prior reviews of educational leadership research (Hallinger, 2011; Hallinger & Heck, 1996; Pitner, 1988).
The sequencing of analytical models within this conceptual framework (i.e., A to G) assumes that they vary in their capacity to capture the complexity of leadership processes. Thus, for example, Model A-1 studies are typically limited to describing perceptions of instructional leadership held by teachers and/or principals. However, these studies neither offer insight into how leadership is shaped by the school context nor how leadership influences the school.
Direct effects studies (i.e., Models B and C) begin to explore the antecedents and effects of leadership. However, they have been criticized for oversimplifying leader-follower relationships and leaving critical questions about the mechanisms through which effects are achieved (Bridges, 1982; Heck & Hallinger, 1999, 2005; Pitner & Hocevar, 1987). For example, Pitner and Hocevar (1987) demonstrated empirically the advantages of multifactor over two-factor models. Hallinger and Heck (1996) concluded that two decades of “direct effects studies” had failed to identify a significant relationship between school leadership and student achievement due to theoretical limitations of the prevailing analytical models (i.e., Models B and C). They asserted that opening up the “black box” of leadership effects required advanced multivariate models capable of exploring mediated, moderated, and reciprocal variable relationships (i.e., Models D, E, F, and G).
Our review employed this conceptual framework in two ways. First, we applied the framework to the quantitative and mixed-methods studies identified in the review. This analysis yielded insight into the analytical models that have guided Asian research on instructional leadership. Then, the framework was used to identify 20 state-of-the-art studies of instructional leadership for further analysis.
3. Materials and Methods
This article followed guidelines for systematic “state-of-the-art” research reviews (García-Peñalvo, 2022). Barry et al. (2022) asserted that “SotA literature reviews provide a time-based overview of the current state of knowledge about a phenomenon and suggest directions for future research” (p. 659). The foci of this state-of-the-art review included documenting the evolution of instructional leadership in Asia, identifying the analytical models that have guided Asian studies, and synthesizing conceptual, methodological features, and substantive findings from a subset of 20 state-of-the-art (SOTA) studies.
3.1. Document Identification
The document search was conducted in two stages. In the first stage, the authors searched the Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar, and ProQuest digital databases to identify all studies that included the PIMRS model or instrument. The decision to focus on PIMRS studies was based on prior reviews, which had identified this as the most frequently employed model and instrument used in studying instructional leadership in Asia (Cansoy & Polatcan, 2018; Gümüş et al., 2018; Gümüş et al., 2021; Hallinger et al., 2020). Moreover, although reviews limited to a particular analytical model and/or instrument may sacrifice the sample size, they can offer greater consistency in data analysis and interpretation.
The keyword string, PIMRS OR Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale, was used in the basic search mode in Google Scholar and the ProQuest dissertation database. The exact keyword string was entered into the “title, keywords, or abstract” fields in the Web of Science and Scopus. The search was conducted iteratively over multiple years. New titles were added to an Excel spreadsheet, and PDF files were downloaded when relevant documents became available.
The final search was conducted on 30 January 2025, but was limited to documents published through the end of 2024. The Excel file contained reference information for 936 journal articles, doctoral dissertations, master’s theses, books, book chapters, and technical reports. The authors included all document types in the review to obtain a broad perspective on the Asian PIMRS literature.
The search and exclusion process was guided by the PRISMA 2020 (Page et al., 2021) guidelines (see Figure 3). Excel’s conditional formatting function identified 35 duplicate documents that were excluded.
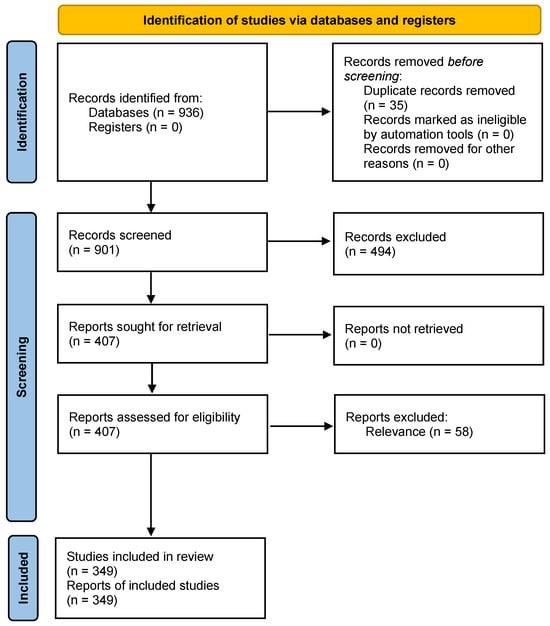
Figure 3.
PRISMA chart for identification of documents (Source: Page et al., 2021).
Next, we limited the database to empirical studies conducted in Asia and conceptual or review papers authored by Asian scholars. Asia was defined as all countries and territories extending from Turkey in the West to Fiji in the East and China in the North to Indonesia in the South. At this stage, the 901 documents were coded for geographical source and document type (i.e., empirical, conceptual, review). We employed the country where the data were collected for empirical studies, regardless of where the authors were located. For conceptual and review documents, codes for the geographical source of the research were based on the first author’s affiliation. Next, the list was sorted by country, and 494 non-Asian documents were deleted from the spreadsheet (see Figure 3).
Next, we read abstracts of the remaining 407 documents to assess each study’s relevance to the review. The authors used Google Translate and ChatGPT 4.0 software to translate 80 Malay, Indonesian, Turkish, Chinese, Persian, and Thai language documents into English. This screening for relevance resulted in the exclusion of 58 documents where the PIMRS was mentioned but not used in the research. The final dataset consisted of 349 mixed PIMRS-related documents authored in Asian societies.
3.2. Data Analysis
Content analysis represented this review’s main data analysis approach (Stemler, 2000). First, we defined explicit data categories corresponding to the aims of the research questions (e.g., publication types, analytical models, research methods, sampling, statistical methods, and variables). Coded data were entered into the master spreadsheet for each document as it was read.
Given the size of the database, coding proceeded over several years, with multiple research assistants contributing. Finally, the lead researchers rechecked the coding of all documents and resolved discrepancies. The final document list was saved in an Excel spreadsheet comprising 349 rows and 38 columns of data (i.e., 13,000+ cells). These data were analyzed in Excel to address the first research question (i.e., growth trajectory and geographic distribution).
For the second research question, we sorted the 302 quantitative and mixed methods studies by the analytical model that guided the research. Two studies employed multiple models in different data analyses (n = 304).
The third and fourth research questions investigated conceptual and methodological features and substantive findings extracted from 20 “state-of-the-art (SOTA) studies”. Identification of the SOTA studies proceeded in several steps. First, the authors sorted the documents based on their analytical models (i.e., A-G). We assumed that a study’s potential for knowledge production was significantly influenced by its analytical model. We limited eligibility for the SOTA analysis to studies that employed “advanced multivariate models” (i.e., Models D, E, F, and G). When executed with theoretically justified variable selection and robust methods, studies that use these analytical models offer greater potential for contributing to knowledge than Models A-C (Hallinger & Heck, 1996; Heck & Hallinger, 1999, 2005; Pitner, 1988; Pitner & Hocevar, 1987). After this step, 59 studies remained.
In the next step, we evaluated the methodological quality of the 59 studies using a rubric adapted from Petticrew and Roberts (2006). Their rubric contains three methodological dimensions (i.e., research sample, variables and measures, and data analysis) and six specific criteria (see Table 1). The “research sample” criterion differentiated studies based on sampling methods (e.g., convenience, stratified non-random, random) and sample size (i.e., small, moderate, large). Sample size was particularly relevant since the quantitative tests used in multivariate studies often require larger samples (e.g., SEM). The sample size varied from a low of 34 teachers to a high of 4300 within the pool of 58 potential SOTA studies.

Table 1.
Methodological quality assessment criteria.
Variables and measures were evaluated for conceptual clarity and theoretical justification. In addition, we examined the sequencing of variables within the analytical models (Hallinger & Heck, 2011). For example, several studies (e.g., Jalapang & Raman, 2020) employed the teachers’ years of experience (i.e., respondents) as a moderator of instructional leadership effects on teacher attitudes and practices. This was assigned fewer points than studies that employed moderators that, in our opinion, held more theoretical and practical significance (e.g., teacher collegiality, professional learning community, urban/rural, and cultural dimensions).
Finally, we evaluated the data analyses conducted in the studies. Studies varied, for example, on the extent of information provided on the reliability and validity of measures. While some studies reported the results of reliability and factor analyses, others either relied on results from prior studies or omitted this information altogether.
Statistical tests were rated to determine their suitability for analyzing the data collected in the study. This did not always align with the test’s sophistication. For example, Guo and Lu (2018) received full points on this criterion despite relying on paired sample t-tests. Their test selection was deemed suitable for testing their hypotheses. In contrast, it was considered a weakness if a study used SEM but failed to employ multi-level analysis when the data were collected at the individual and collective levels.
Two researchers independently evaluated and coded the studies on the six criteria using a 3-point scale (1, 0.5, or 0). Cohen’s Kappa test was used to determine the inter-rater reliability of the results (Wahyuni et al., 2021). The results were: Sample Criterion: Cohen’s Kappa 0.88; Variable Criterion: Cohen’s Kappa 0.85; Data Analysis Criterion: Cohen’s Kappa 0.91.
The 20 top-rated studies were then selected for the SOTA review. A new worksheet containing the coded data associated with the 20 SOTA studies was created. Then, seven additional columns of data were added to this worksheet: citations, overall findings, findings on each type of variable (i.e., antecedent, moderator, mediator, dependent), and research implications. We re-read the 20 SOTA studies and entered the relevant data into the worksheet. Correlations, R2, effect sizes, and significance levels were extracted from the SOTA studies and included in the Excel worksheet.
The data associated with the 20 SOTA studies were then synthesized to identify trends related to their methodological features and findings. The analyses generated data displayed in two tables. The first focused on methodological characteristics of the SOTA studies, and the second on their findings.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Analysis of the Asian PIMRS Knowledge Base
The Asian PIMRS corpus grew significantly from 54 documents published before 2011 to 305 documents published during the succeeding 15 years. The discrepancy between this result and Hallinger’s in 2011 (i.e., 16), was due to our inclusion of master’s theses, conference papers, books, chapters, and journal articles. Moreover, numerous documents unavailable in 2010 were digitized and indexed during the succeeding 15 years.
The review corpus comprised 230 journal articles, 57 master theses, 44 doctoral dissertations, 14 conference papers, three book chapters, and one book (not tabled). It was noted that only eight of the 230 journal articles were published before 2011. The 349 PIMRS studies were heavily weighted toward empirical studies (90%). There was a reasonable proportion of reviews (7%), but relatively few conceptual papers (3%).
The Asian corpus of PIMRS research also became more geographically diverse over time. While Hallinger (2011) reported contributions from seven Asian nations and territories, by 2024, studies had been conducted in 31 nations. This research has been led by researchers from Malaysia (n = 150), Turkey (n = 33), Indonesia (n = 21), China (n = 19), Philippines (n = 18), Thailand (n = 17), and Pakistan (n = 15).
4.2. Analytical Models Used in Asian Instructional Leadership Research
Analysis of the analytical models used in this corpus of studies offers insights into the research aims of Asian scholars and the region’s EDLM research capacity. The research documents comprised 315 empirical studies, 11 conceptual papers, and 23 research reviews (not tabled). Among the empirical studies, 266 used quantitative methods, 36 mixed methods, and 13 qualitative methods. The data analyses conducted for this review were limited to the quantitative and mixed methods studies (n = 302 studies). The other 46 articles were compiled to obtain a broader perspective on the nature of the Asian knowledge base (i.e., the first research question).
From 1987 to 2010, Models A-1, B, and C were used in all but one of the Asian studies (Ponnusamy, 2010). These descriptive (A-1) and direct effects (B and C) models have previously acknowledged limitations for unpacking the complexity of leadership interactions. It was, however, noted that 34 of these studies employed mixed methods (not tabled). This suggests the possibility of more significant contributions to knowledge by elaborating on quantitative results through qualitative analysis (Barnes et al., 2010).
After 2010, the rapidly growing literature featured expanded use of advanced multivariate models (see Table 1). Although Models A, B, and C continued to predominate in the post-2010 research (i.e., 76.7%), 60 studies employed advanced multivariate models (see Table 2). The increased adoption of Models D, E, and F in Asian research suggests more ambitious research aims and increasing research capacity during recent years. The studies using advanced analytical models were authored in Malaysia (n = 20), Turkey (n = 10), China (n = 7), Indonesia (n = 5), Oman (n = 3), Iran (n = 4), Pakistan (n = 3), Iran (n = 3), India (n = 2), Philippines (n = 2), Israel (n = 1), and Saudi Arabia (n = 1).

Table 2.
Longitudinal analysis of analytical models used in PIMRS studies in Asia (n = 302).
Model A-1 studies (n = 56) typically employed descriptive statistics to profile principals on the PIMRS’ instructional leadership dimensions and/or functions (see Figure 1). In some studies, this was presented as a purely quantitative analysis (n = 37), while other employed mixed methods (n = 19). Authors often framed Model A-1 studies as investigations of a particular type of school (e.g., high achieving, low achieving, or private school). However, small school samples and the lack of comparison groups limited the knowledge contribution of studies using this descriptive model.
Model A-2 studies (n = 9) comprised psychometric studies of translated versions of the PIMRS in different national contexts. Hallinger and Wang (2015) presented comprehensive reliability and validity data from international PIMRS studies conducted through 2012. Localized validation studies were subsequently carried out in China (Antoniou & Lu, 2018; Guo et al., 2018), Malaysia (Aziz et al., 2014; Basah & Abdul Razak, 2023; Thien, 2022), Iran (Yousefi et al., 2021), Korea (Park & Lee, 2007), and Turkey (Bellibaş et al., 2016). Although these psychometric studies supported the reliability and validity of the PIMRS, two points deserve mention.
First, factor analyses sometimes suggested constructs that differed somewhat from the framework presented in Figure 1. Second, the highly centralized education hierarchies in Asian societies tend to delegate less responsibility to school leaders for curriculum coordination than is assumed in the PIMRS model. Therefore, in some instances, this job function was either revised or eliminated from the scale (e.g., Bellibaş et al., 2016). The 9 Model A-2 studies were published in journal articles, six of which featured in Scopus Q1 and Q2 journals.
Model B studies examined the “direct effects” of an antecedent variable on instructional leadership (Model B-1; n = 50) or of instructional leadership on an outcome variable (Model B-2; n = 108). Model C studies (n = 21) also investigated the “direct effects” but included both antecedents and outcomes of instructional leadership (see Figure 1). Thus, Model C is the entry point into multivariate models that seek to account for the complexity in leadership practice.
Nonetheless, Model B-2 and C studies frequently suffered from theoretical and methodological limitations when investigating instructional leadership effects on student achievement (n = 22 studies). Highly cited research reviews have concurred that the effects of school leadership on student achievement are mediated by teacher attitudes, teacher practices, and school culture/climate (Hallinger & Heck, 1996; Leithwood et al., 2020; Liebowitz & Porter, 2019; Robinson et al., 2008; Witziers et al., 2003). Thus, as suggested earlier, Model B-2 and C studies oversimplify this relationship and typically yield insignificant results.
Studies grounded in these models can make useful contributions when the theoretical relationships among the variables are well justified. This was the case, for example, in some Model B and C studies that examined the direct effects of instructional leadership on teacher attitudes, instructional practices. teacher professional learning, and school climate/culture. Although 60% of the Model B and C studies were published in journals, less than 20% of the journals were indexed in Scopus (not tabled).
The capability to delve into the complexity of school leadership processes was more frequently apparent in studies that included moderating variables (Model D), mediating variables (Model E), or both (Model F). Although Model D studies were scarce (n = 8), they represent a significant advance due to their ability to examine the influence of one variable on the relationship between two other variables (e.g., Jalapang & Raman, 2020; Mannan, 2017; Thien & Adams, 2024).
For example, in a Model D-1 study, Guo and Lu (2018) investigated how the cultural norm of power distance in Chinese society accounted for differences in teacher and principal perceptions (i.e., role set) of the principals’ instructional leadership practices. In a Model D-2 study, Chen and Rong (2023) examined how the collective norm of teacher collegiality moderated the relationship between instructional leadership and teacher self-efficacy. This approach is more robust than the antecedent effects approach adopted in Models B and C.
Model E studies offer greater leverage than Models B-2 and C when studying leadership effects due to their potential for unpacking complex relationships. Model E-1 studies (n = 43) examined how the effects of instructional leadership on an outcome variable (e.g., instructional practice or student achievement) were mediated by an intervening variable such as teacher self-efficacy or teacher professional learning (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024a; Hammad et al., 2024). Model E-2 studies (n = 6) employed a similar approach but included an antecedent measure such as gender, school type, or principal self-efficacy (e.g., Bhutto et al., 2023; Bozkuş et al., 2024; Hallinger et al., 2018; Lim, 2016; Liu & Hallinger, 2018). As noted, mediated models are considered mandatory in school leadership studies where the dependent variable is student achievement (Hallinger & Heck, 1996; Heck & Hallinger, 1999, 2005). For example, in a Model E-2 study, Bozkuş et al. (2024) investigated how teacher trust and self-efficacy mediated the effects of instructional leadership on student learning.
Model F, moderated mediation studies (n = 4), represent the cutting-edge among non-experimental research designs for studying school leadership processes. Model F studies have significant potential for knowledge contribution when properly designed and executed. However, investigating “interaction effects” through this model is technically challenging, requiring larger sample sizes and more sophisticated statistical tests. All four Model F studies were published in Scopus Q1 journals during the past four years (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Bellibaş et al., 2021; Liu & Hallinger, 2021; Özdemir et al., 2023).
4.3. Analysis of State-of-the-Art PIMRS Studies from Asia
Next, we synthesized the 20 state-of-the-art (SOTA) studies to address the third and fourth research questions. First, we analyzed the methodological characteristics of the studies (see Table 3). Then, we analyzed their research foci and synthesized patterns in their results (see Table 4). This SOTA analysis aimed to illustrate the connections between conceptual models, research methods, and findings.

Table 3.
Methodological features of Asian state-of-the-art studies of instructional leadership 1 (n = 20).

Table 4.
Synthesis of foci and findings in Asian state-of-the-art studies of instructional leadership (n = 20).
4.3.1. Methodological Characteristics of the State-of-the-Art Studies
The SOTA studies used quantitative methods to analyze multivariate relationships between instructional leadership and related school factors. All but two of the SOTA studies were published as journal articles (Kavitha, 2024; Mannan, 2017). Five studies were sourced from Turkey and China, four from Malaysia, two from Oman, two from Iran, and one from Pakistan and India. The subset of SOTA studies included representation from Models D-1 (n = 1), D-2 (n = 3), E-1 (n = 11), E-2 (n = 3), and F (n = 4). Surprisingly, several E-2 studies that received full marks on the model criterion suffered from variable selection and methodological limitations.
As indicated in Table 3, the studies investigated instructional leadership in primary, middle, and high schools. This is of interest due to the long-standing belief that the school organization’s size and complexity shape principals’ instructional leadership practices. Scholars and practitioners have frequently asserted that the principal can engage in more active instructional leadership in primary schools than in high schools, where staff size and department structures imply a need for more significant delegation to middle-level leaders.
Regarding methodological characteristics, convenience and non-random sampling were the most commonly employed sampling strategies. Although random sampling is the preferred approach for generalizability, data access is challenging for large-scale studies. Indeed, these studies collected data from an average of 77 schools (min = 1/max = 230) and 1106 teachers (min = 186/max = 4300). Large sample sizes are especially critical when using multivariate models comprising four, five, and six variables, often at multiple data levels. Moreover, the statistical tests required for studying mediated and moderated relationships (e.g., SEM and MSEM) place an even greater premium on sample size (Aguinis et al., 2005; Cohen, 1988).
The “target role” was the principal, and teachers’ ratings of the principals’ instructional leadership were employed in all 20 studies. In some studies (e.g., Liu & Hallinger, 2018), however, data were also collected from principals concerning an attitude (e.g., leader self-efficacy) or a practice (e.g., time management). The 20 studies used established scales and conducted tests of reliability and validity (e.g., content, convergent, discriminant). Multivariate data analyses examined complex relationships between instructional leadership and other variables. Structural equation modeling and bootstrapping were frequently used to test mediated relationships. This analysis of the methodological characteristics of the SOTA studies sets the stage for synthesizing their research foci and findings.
4.3.2. Synthesis of Research Foci and Findings from State-of-the-Art PIMRS Studies of Instructional Leadership in Asia
Given the non-random selection of SOTA studies and the diversity of their research foci, our goal in this section was not to conduct a meta-analysis of research findings. Instead, we sought to synthesize patterns in their analytical models, variables studied, and findings.
We begin this synthesis of research foci and findings with the end in mind: the dependent variables selected for study in these investigations. Bridges (1982) asserted four decades ago that EDLM researchers should study school administrators’ impact on teacher practices and student learning. These studies heeded his call (see Table 4).
Thirteen SOTA studies examined the relationship between instructional leadership and teacher practices (e.g., instruction n = 5; teacher professional learning n = 6), and one on student achievement outcomes (Kavitha, 2024). Five SOTA studies framed a teacher’s attitude (i.e., self-efficacy, collective efficacy, commitment) as the dependent variable, and one investigated leadership effects on student engagement. However, it should be noted that these variable trends were influenced by the weights assigned during variable evaluation. Thus, the dependent variables in the pool of 59 potential SOTA studies included 15 that examined leadership effects on student achievement and 21 on teacher attitudes.
When analyzing the studies, we found that framing variable relationships was as important as the outcome measure. For example, research suggests positive teacher attitudes are critical to school effectiveness and improvement. However, Leithwood et al. (2020) demonstrated that “teacher emotions” primarily impact student learning through practices associated with what they termed “rational path” (e.g., instruction, academic press). This suggests that teacher attitudes “mediate” the efforts of school leaders to improve teaching and learning.
This was reflected in the SOTA studies, which frequently employed teacher attitudes (trust, agency self-efficacy, commitment, and enthusiasm) as mediators of leadership effects on instruction (n = 4), teacher learning (n = 5), and student achievement (n = 1). Moreover, collaborative teacher practices (e.g., professional learning, shared practices, collegiality, and collaboration) were framed as moderators (Chen & Rong, 2023) and mediators (e.g., Bellibaş et al., 2021; Dorukbaşi & Cansoy, 2024; Hammad et al., 2024) of instructional leadership effects on instruction (see Table 4).
Further examination of the data in Table 4 illustrates potentially important patterns concerning the relationship between analytical models, methods, and results. More specifically, four studies found that the effects of instructional leadership on the dependent measure (e.g., instruction) were “fully mediated” by teacher attitudes (e.g., Bellibaş et al., 2022; Hammad et al., 2024; Özdemir et al., 2023), a teacher practice (e.g., Bellibaş et al., 2021; Hammad et al., 2024), or school culture (Khan, 2022). Full mediation suggests that the effects of leadership on the outcome were gained through the interaction of instructional leadership and the mediator.
Additionally, 13 SOTA studies found that the relationship between instructional leadership and the dependent variables was “partially mediated by a teacher attitude or practice. This finding implies that both “direct” and “indirect” effects were detected in the relationship between instructional leadership and the study’s outcome variable (e.g., Al-Mahdy et al., 2024a; Hallinger et al., 2018; Liu & Hallinger, 2018; Ma & Marion, 2021; Thien & Liu, 2024). Several studies found that “moderating variables” (e.g., teacher collegiality, power distance, transformational leadership) significantly influenced the relationship between instructional leadership and other school-level factors (e.g., Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Bellibaş et al., 2021; Chen & Rong, 2023; Liu & Hallinger, 2021; Özdemir et al., 2023).
National culture (i.e., power distance) represents another significant variable highlighted in Table 4. For decades, the dominance of EDLM research by Anglo-American scholars meant that the cultural context of schooling received virtually no attention from scholars (Dimmock & Walker, 2000; Hallinger & Leithwood, 1996; Wong & Cheng, 1995). However, over the past 25 years, Asia’s scholars, in particular, have studied how the cultural and institutional context shapes the enactment of school leadership (e.g., Hallinger & Truong, 2016; Truong & Hallinger, 2017; Walker & Hallinger, 2015). This was reflected in SOTA studies conducted in China, Oman, and Turkey, which incorporated power distance as a “moderator” of teacher perceptions (Guo & Lu, 2018) and practices (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Bellibaş et al., 2021; Liu & Hallinger, 2021; Özdemir et al., 2023). These studies confirmed that power distance shaped teacher perceptions and instructional leadership enactment. Moreover, the Model F studies found that this “moderation effect” carried over into instructional leadership effects on teacher attitudes and practices.
5. Discussion
This review synthesized conceptual, methodological, and substantive patterns in Asian studies using the PIMRS instrument. In this section, we highlight limitations, interpret the main findings, and suggest implications for future research.
5.1. Limitations
First, although this article employed systematic review methods, we did not undertake a meta-analytic synthesis of findings. While the review analyzed substantive findings from 20 state-of-the-art studies, the purpose was to show connections between analytical models, methods, and findings rather than to draw firm substantive conclusions.
Second, although we sought to make the procedures for identifying the SOTA studies transparent, other researchers might choose different criteria. That could result in studies with somewhat different characteristics and findings. Nonetheless, we believe the key findings from the SOTA studies would remain relevant even if their composition somewhat varied.
Third, this review focused on quantitative studies. This does not discount the potential contribution of qualitative studies (Gümüş et al., 2021). However, assessing their contribution in Asia was not our priority given the small number of qualitative studies and potential paradigmatic conflicts.
Finally, the database extracted for this review was limited to Asian studies that employed the PIMRS model and/or instrument. While other research instruments have been used in Asian studies of instructional leadership (Lai & Lien, 2025; Li et al., 2016; Piyaman et al., 2017), studies using the PIMRS account for the largest portion of this literature (Hallinger et al., 2020).
5.2. Interpretation of the Findings
These results provide a window into the evolution of instructional leadership scholarship in Asia over the past five decades. The most obvious indicators of scholarly development were the rapid growth of published studies and the increasing geographic diversity of this literature. There was a 500% increase in the publication of Asian studies over the past 15 years, during which the sources of this research expanded from eight to 32 nations.
The latter trend suggests a relationship between education policy reforms adopted in Asian societies and the research foci of EDLM scholars. This was particularly evident in Malaysia, a positive outlier accounting for 150 of the PIMRS publications (i.e., 43% of the Asian corpus). This unexpectedly high level of Malaysian knowledge production was linked to education policies adopted during the 2010s that prioritized instructional leadership in the role of Malaysian principals (Harris et al., 2019; Ismail et al., 2020; Samichan et al., 2021). The increased relevance of instructional leadership was reflected in the research foci adopted by Malaysian graduate students and lecturers.
It was unsurprising to find that empirical studies dominated the corpus of PIMRS research. Nonetheless, the scarcity of conceptual papers suggests future opportunities for analyses that conceptualize instructional leadership enactment in Asian societies (Hallinger et al., 2015; Lai & Lien, 2025; Samichan et al., 2021; Hallinger et al., 2017; Walker & Qian, 2022). These conceptual efforts should seek to unpack how contextual features (e.g., culture, autonomy, size, policy directions) of Asian societies shape the enactment of instructional leadership (Hallinger et al., 2018; Qian et al., 2017; Hallinger et al., 2017).
Our analysis of analytical models offers a unique perspective on the evolution of Asian EDLM research. For example, it was noted that only one empirical study conducted before 2011 employed an advanced multivariate model (i.e., Model D, E, or F). In contrast, 59 studies in the post-2010 corpus (22.9%) employed an advanced analytical model, thereby suggesting increased regional research capacity. Nonetheless, the broader trend of relying on less robust models suggests continued room for capacity development.
These studies paid greater attention to instructional leadership effects than to the antecedents that influence its enactment. For example, relatively few studies examined how the institutional context of schools (e.g., school size, level, autonomy) shaped instructional leadership practices. Theoretical and practical discourse suggests that principals must consider these contextual features of schools when enacting their instructional leadership role. Even fewer (n = 4) investigated how cultural norms (e.g., power distance) influence the enactment and effects of instructional leadership (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Guo & Lu, 2018; Liu & Hallinger, 2021; Özdemir et al., 2023). Nonetheless, significant findings concerning the impact of power distance on leader-follower relationships suggest this is a fertile topic for future research. Similar recommendations apply to studying personal antecedents, such as leader gender, self-efficacy, and emotional intelligence (see Leithwood, 2023).
As we have elaborated, moderation models (Models D and F) also offer a distinct advantage over direct effects studies due to their ability to explore the influence of one factor on the relationship between other variables. Thus, for example, an antecedent study of the relationship between gender and instructional leadership (i.e., Model B-1 or C) is only able to establish whether there is a significant relationship between the variables. A moderation effects study (i.e., Models D or F) could assess whether the moderating variable (e.g., gender) is associated with the effects of instructional leadership on a mediating or dependent variable.
We believe that the findings from our SOTA review are important for several reasons. First, the high quality of the SOTA studies offers greater confidence that the findings are robust and meaningful. Second, this analysis demonstrated the fruits of aligning analytical models, variable selection and ordering, and research methods when designing empirical studies. Indeed, we argue that the consistently significant findings of positive leadership effects were made possible by the researchers’ sophisticated analytical models and robust methods.
The SOTA studies also highlighted the importance of selecting and ordering variables based on theory and prior research findings. The findings suggested that instructional leaders who stimulate positive teacher attitudes (e.g., self-efficacy, commitment, trust, and agency) create conditions that support teacher professional learning (Hosseingholizadeh et al., 2023; Karacabey et al., 2022; Liu & Hallinger, 2018, 2021) and instructional quality (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Bellibaş et al., 2021; Hammad et al., 2024; Özdemir et al., 2023). Accordingly, we suggest that teacher attitudes (e.g., self-efficacy, commitment, agency, collective efficacy) should be framed as mediators of instructional leadership effects on “rational path” variables (i.e., professional learning, teaching quality, and academic press). This has implications for future research, which we address in the closing section of this article.
5.3. Implications
The first implication arises from the increasingly widespread use of the PIMRS model and instrument in Asian societies. Although psychometric studies have been conducted in nine Asian nations, additional psychometric studies of translated versions of the PIMRS are warranted in countries where the instrument is frequently used (e.g., Indonesia, Philippines, Pakistan, Arab societies). The published studies cited in this review provide models for validation studies (e.g., Hallinger & Wang, 2015; Thien, 2022).
Moreover, it is time to update the earlier meta-analyses of validation studies (Hallinger & Wang, 2015). Numerous studies have reported comprehensive reliability and confirmatory factor analysis results that can be synthesized in a meta-analysis. In particular, this synthesis should identify dimensions of instructional leadership that the current model and instrument may not address, such as parental and community engagement, and the use of digital technologies in teaching and learning. Additionally, there is a need to craft indigenous models of instructional leadership (Hallinger & Walker, 2017; Hallinger et al., 2016; Qian et al., 2017; Rauf et al., 2025; Walker & Qian, 2022).
A second implication concerns studies of instructional leadership and student achievement. Twenty-three studies in our database employed direct effects models (i.e., Model B or C) to study this relationship. Thus, we reprise Hallinger and Heck’s (1996) conclusion that advanced multivariate effects models should be used to investigate school leadership effects on student learning (i.e., Models E, F, and G). The most suitable mediators to include in these studies are teacher practices (e.g., instruction, professional learning, shared practice, professional learning community) and school climate or culture.
The relationship between instructional leadership and teacher attitudes represented this literature’s most frequently studied topic. Scholars have begun synthesizing these results (e.g., Alanoglu, 2022; Karakose et al., 2024). Future instructional leadership studies will preferably analyze teacher attitudes as mediators and moderators (e.g., Models D, E, and F) rather than as the dependent variable. When graduate students undertake studies informed by direct effects models (e.g., Model B or C), mixed methods are recommended to compensate for the less robust quantitative analysis.
Fourth, given the wide range of teacher attitudes studied, meta-analyses should examine the relationship between instructional leadership and specific attitudes (e.g., self-efficacy, commitment, job satisfaction). Then, multi-factor meta-analysis can synthesize findings for variable combinations with sufficient studies (e.g., instructional leadership, teacher attitudes, and professional learning; instructional leadership, teacher attitudes, and instructional practices; gender, instructional leadership, and teacher attitudes). Scholars have begun to unpack these relationships, but more must be done (e.g., Alanoglu, 2022; Hallinger et al., 2016; Karakose et al., 2025).
Finally, the SOTA analyses highlighted a set of advanced multivariate studies that examined power distance as a moderator of instructional leadership perceptions and practices (Al-Mahdy et al., 2024b; Guo & Lu, 2018; Liu & Hallinger, 2021; Özdemir et al., 2023). The significant findings reported in these studies highlight one of the potentially important contributions the region’s research can make to the EDLM field. Therefore, we recommend that future research extend this line of inquiry through quantitative and mixed methods studies that employ Models D and F.
6. Conclusions
This review examined the rapidly growing knowledge base on instructional leadership in Asia. We conclude that research quality, though improving, has not kept pace with the rate of growth in publications. Our synthesis of features and findings of 20 state-of-the-art studies yielded clear recommendations to support the design of research studies capable of advancing the Asian knowledge base in the next decade.
Author Contributions
P.H. conceptualized the review, managed data collection and analysis, and wrote the text. S.L. and P.N.A. contributed to data collection and curation. P.N.A. assisted in the evaluation of studies. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
As a review of secondary studies, no ethical approval was required.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The database employed in this review can be accessed at: dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28605221.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aguinis, H., Beaty, J. C., Boik, R. J., & Pierce, C. A. (2005). Effect size and power in assessing moderating effects of categorical variables using multiple regression: A 30-year review. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(1), 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanoglu, M. (2022). The role of instructional leadership in increasing teacher self-efficacy: A meta-analytic review. Asia Pacific Education Review, 23(2), 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahdy, Y. F. H., Hallinger, P., Emam, M., Hammad, W., Alabri, K. M., & Al-Harthi, K. (2024a). Supporting teacher professional learning in Oman: The effects of principal leadership, teacher trust, and teacher agency. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 52(2), 395–416. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mahdy, Y. F. H., Hallinger, P., Omara, E., & Emam, M. (2024b). Exploring how power distance influences principal instructional leadership effects on teacher agency and classroom instruction in Oman: A moderated-mediation analysis. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 52(4), 878–900. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, P., & Lu, M. (2018). Evaluating the measuring properties of the principal instructional management rating scale in the Chinese educational system: Implications for measuring school leadership. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 46(4), 624–641. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, N. A. B., Foo, S. F., Hassan, A., & Asimiran, S. (2014). Instructional leadership: Validity and reliability of PIMRS 22-item instrument. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(23), 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bajunid, I. A. (1996). Preliminary explorations of indigenous perspectives of educational management: The evolving Malaysian experience. Journal of Educational Administration, 34(5), 50–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C. A., Camburn, E., Sanders, B. R., & Sebastian, J. (2010). Developing instructional leaders: Using mixed methods to explore the black box of planned change in principals’ professional practice. Educational Administration Quarterly, 46(2), 241–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E. S., Merkebu, J., & Varpio, L. (2022). Understanding state-of-the-art literature reviews. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 14(6), 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basah, A. A., & Abdul Razak, A. Z. B. (2023). Exploring instructional leadership practises items among headmasters in public primary schools: An exploratory factor analysis. Malaysian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities (MJSSH), 8(9), e002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellibaş, M. S., Bulut, O., Hallinger, P., & Wang, W. C. (2016). Developing a validated instructional leadership profile of Turkish primary school principals. International Journal of Educational Research, 75, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellibaş, M. Ş., Kılınç, A. Ç., & Polatcan, M. (2021). The moderation role of transformational leadership in the effect of instructional leadership on teacher professional learning and instructional practice: An integrated leadership perspective. Educational Administration Quarterly, 57(5), 776–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellibaş, M. Ş., Polatcan, M., & Kılınç, A. Ç. (2022). Linking instructional leadership to teacher practices: The mediating effect of shared practice and agency in learning effectiveness. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 50(5), 812–831. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutto, S., Mydin, A. A., Malik, K. H., Rind, G. M., & Tiwari, V. (2023). The impact of workplace spirituality on teachers’ critical thinking: Mediating role of instructional leadership and knowledge management. Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Management, 11(4), 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bossert, S. T., Dwyer, D. C., Rowan, B., & Lee, G. V. (1982). The instructional management role of the principal. Educational Administration Quarterly, 18(3), 34–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkuş, K., Güngör, T. A., & Öztürk, H. K. (2024). Predictive factors of student achievement: The role of instructional leadership, organizational trust, and teacher self-efficacy. GESJ: Education Science and Psychology, 3(72), 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, E. M. (1967). Instructional leadership: A concept re-examined. Journal of Educational Administration, 5(2), 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, E. M. (1982). Research on the school administrator: The state of the art, 1967–19801. Educational Administration Quarterly, 18(3), 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansoy, R., & Polatcan, M. (2018). Examination of instructional leadership research in Turkey. International Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 10(1), 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., & Rong, J. (2023). The moderating role of teacher collegiality in the relationship between instructional leadership and teacher self-efficacy. SAGE Open, 13(4), 21582440231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S., & O’donoghue, T. (2017). Educational leadership and context: A rendering of an inseparable relationship. British Journal of Educational Studies, 65(2), 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock, C., & Walker, A. (2000). Globalisation and societal culture: Redefining schooling and school leadership in the twenty-first century. Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, 30(3), 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorukbaşi, E., & Cansoy, R. (2024). Examining the mediating role of teacher professional learning between perceived instructional leadership and teacher instructional practices. European Journal of Education, 59, e12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, D. A. (1979). Research on educational administration: The state-of-the-art. Educational Researcher, 8(3), 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peñalvo, F. J. (2022). Developing robust state-of-the-art reports: Systematic literature reviews. Education in the Knowledge Society, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W., & Lu, J. (2018). Assessing instructional leadership from two mindsets in China: Power distance as a moderator. Educational Assessment, Evaluation and Accountability, 30(4), 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W., Lu, J., & Qian, H. (2018). Principal instructional leadership: Chinese PIMRS development and validation. Chinese Education & Society, 51(5), 337–358. [Google Scholar]
- Gümüş, S., Bellibaş, M. S., Esen, M., & Gümüş, E. (2018). A systematic review of studies on leadership models in educational research from 1980 to 2014. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 46(1), 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gümüş, S., Hallinger, P., Cansoy, R., & Bellibaş, M. Ş. (2021). Instructional leadership in a centralized and competitive educational system: A qualitative meta-synthesis of research from Turkey. Journal of Educational Administration, 59(6), 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P. (1983). Assessing the instructional management behavior of principals [Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Stanford University (United States)]. [Google Scholar]
- Hallinger, P. (2011). A review of three decades of doctoral studies using the principal instructional management rating scale: A lens on methodological progress in educational leadership. Educational Administration Quarterly, 47(2), 271–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., Gümüş, S., & Bellibaş, M. Ş. (2020). ‘Are principals instructional leaders yet?’ A science map of the knowledge base on instructional leadership, 1940–2018. Scientometrics, 122(3), 1629–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Heck, R. H. (1996). Reassessing the principal’s role in school effectiveness: A review of empirical research, 1980–1995. Educational Administration Quarterly, 32(1), 5–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Heck, R. H. (2011). Conceptual and methodological issues in studying school leadership effects as a reciprocal process. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 22(2), 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., Hosseingholizadeh, R., Hashemi, N., & Kouhsari, M. (2018). Do beliefs make a difference? Exploring how principal self-efficacy and instructional leadership impact teacher efficacy and commitment in Iran. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 46(5), 800–819. [Google Scholar]
- Hallinger, P., & Kovačević, J. (2019). A bibliometric review of research on educational administration: Science mapping the literature, 1960 to 2018. Review of Educational Research, 89(3), 335–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Leithwood, K. (1996). Culture and educational administration: A case of finding out what you don’t know you don’t know. Journal of Educational Administration, 34(5), 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., Li, D., & Wang, W. C. (2016). Gender differences in instructional leadership: A meta-analytic review of studies using the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale. Educational Administration Quarterly, 52(4), 567–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Murphy, J. (1985). Assessing the instructional management behavior of principals. The Elementary School Journal, 86(2), 217–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Truong, T. (2016). “Above must be above, and below must be below”: Enactment of relational school leadership in Vietnam. Asia Pacific Education Review, 17(4), 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Walker, A. (2017). Leading learning in Asia–emerging empirical insights from five societies. Journal of Educational Administration, 55(2), 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., Walker, A., Nguyen, D. T. H., Truong, T., & Nguyen, T. T. (2017). Perspectives on principal instructional leadership in Vietnam: A preliminary model. Journal of Educational Administration, 55(2), 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., Walker, A., & Trung, G. T. (2015). Making sense of images of fact and fiction: A critical review of the knowledge base for school leadership in Vietnam. Journal of Educational Administration, 53(4), 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P., & Wang, W. C. (2015). Assessing instructional leadership with the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale. Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, W., Hilal, Y. Y., & Bellibaş, M. Ş. (2024). Exploring the link between principal instructional leadership and differentiated instruction in an understudied context: The role of teacher collaboration and self-efficacy. International Journal of Educational Management, 38(4), 1184–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A., Jones, M., Adams, D., & Cheah, K. (2019). Instructional leadership in Malaysia: A review of the contemporary literature. School Leadership & Management, 39(1), 76–95. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, R., & Hallinger, P. (1999). Conceptual models, methodology, and methods for studying school leadership. In K. Leithwood, & P. Hallinger (Eds.), The 2nd handbook of research in educational administration (pp. 141–162). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, R. H., & Hallinger, P. (2005). The study of educational leadership and management: Where does the field stand today? Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 33(2), 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseingholizadeh, R., Amrahi, A., & El-Farr, H. (2023). Instructional leadership, and teacher’s collective efficacy, commitment, and professional learning in primary schools: A mediation model. Professional Development in Education, 49(3), 518–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseingholizadeh, R., Sharif, A., & Taghizadeh Kerman, N. (2021). A systematic review of conceptual models and methodologies in research on school principals in Iran. Journal of Educational Administration, 59(5), 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S. N., Muhammad, S., Omar, M. N., & Raman, A. (2020). The great challenge of Malaysian school leaders’ instructional leadership: Can it affect teachers’ functional competency across 21st century education? Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(6), 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalapang, I., & Raman, A. (2020). Effect of instructional leadership, principal efficacy, teacher efficacy and school climate on students’ academic achievements. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 9(3), 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacabey, M. F., Bellibaş, M. Ş., & Adams, D. (2022). Principal leadership and teacher professional learning in Turkish schools: Examining the mediating effects of collective teacher efficacy and teacher trust. Educational Studies, 48(2), 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakose, T., Gurr, D., Tülübaş, T., & Kanadlı, S. (2025). What factors mediate the relationship between leadership for learning and teacher professional development? Evidence from meta-analytic structural equation modelling. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 17411432241308461. [Google Scholar]
- Karakose, T., Kardas, A., Kanadlı, S., Tülübaş, T., & Yildirim, B. (2024). How collective efficacy mediates the association between principal instructional leadership and teacher self-efficacy: Findings from a meta-analytic structural equation modeling (MASEM) study. Behavioral Sciences, 14(2), 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, K. (2024). Role of principal’s instructional leadership and teacher efficacy in secondary school performance: A case study of CBSE schools in Bengaluru [Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Dayananda Sagar University (India)]. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z. (2022). Examining the mediating role of school culture in the relationship between heads’ instructional leadership and students’ engagement at secondary level in Punjab, Pakistan. Bulletin of Education and Research, 44(2), 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H. C., & Lien, H. Y. (2025). Instructional leadership scale for high school principals: Development and validation. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 53(3), 484–498. [Google Scholar]
- Leithwood, K. (2005). Understanding successful principal leadership: Progress on a broken front. Journal of Educational Administration, 43(6), 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithwood, K. (2023). The personal resources of successful leaders: A narrative review. Education Sciences, 13(9), 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithwood, K., Sun, J., & Schumacker, R. (2020). How school leadership influences student learning: A test of “The four paths model”. Educational Administration Quarterly, 56(4), 570–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Hallinger, P., & Ko, J. (2016). Principal leadership and school capacity effects on teacher learning in Hong Kong. International Journal of Educational Management, 30(1), 76–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebowitz, D. D., & Porter, L. (2019). The effect of principal behaviors on student, teacher, and school outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 89(5), 785–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S. H. (2016). Amalan kepimpinan instruksional, budaya organisasi dan organisasi pembelajaran di sekolah berprestasi tinggi Malaysia (The relationship between instructional leadership, organizational culture and learning organization in high performing schools in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan dan Kepimpinan Pendidikan, 30(2), 1–19. (In Malaysian). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S., & Hallinger, P. (2018). Principal instructional leadership, teacher self-efficacy, and teacher professional learning in China: Testing a mediated-effects model. Educational Administration Quarterly, 54(4), 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., & Hallinger, P. (2021). Unpacking the effects of culture on school leadership and teacher learning in China. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 49(2), 214–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X., & Marion, R. (2021). Exploring how instructional leadership affects teacher efficacy: A multilevel analysis. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 49(1), 188–207. [Google Scholar]
- Mannan, F. (2017). The relationship between women principal instructional leadership practices, teacher organizational commitment and teacher professional community practice in secondary schools in Kuala Lumpur [Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Malaya (Malaysia)]. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, D. F. S. (2019). Instructional leadership. Instructional leadership and leadership for learning in schools. In T. Townsend (Ed.), Understanding theories of leading (pp. 15–48). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, D. F. S., Nguyen, T. D., Wong, K. S. B., & Choy, K. W. W. (2015). Instructional leadership practices in Singapore. School Leadership & Management, 35(4), 388–407. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, N., Kılınç, A. Ç., & Turan, S. (2023). Instructional leadership, power distance, teacher enthusiasm, and differentiated instruction in Turkey: Testing a multilevel moderated mediation model. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 43(3), 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., & Chou, R. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H. L. W., Nyeu, F. Y., & Chen, J. S. (2015). Principal instructional leadership in Taiwan: Lessons from two decades of research. Journal of Educational Administration, 53(4), 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H. L. W., Nyeu, F. Y., & Cheng, S. H. (2017). Leading school for learning: Principal practices in Taiwan. Journal of Educational Administration, 55(2), 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. K., & Lee, S. E. (2007). A study on the construct validity for the scale of instructional leadership of principals. Open Education Research, 15(2), 51–70. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2006). Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Blackwell Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitner, N. J. (1988). The study of administrator effects and effectiveness. In N. Boyan (Ed.), Handbook of research in educational administration (pp. 106–132). Longman. [Google Scholar]
- Pitner, N. J., & Hocevar, D. (1987). An empirical comparison of two-factor versus multifactor theories of principal leadership: Implications for the evaluation of school principals. Journal of Personnel Evaluation in Education, 1, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyaman, P., Hallinger, P., & Viseshsiri, P. (2017). Addressing the achievement gap: Exploring principal leadership and teacher professional learning in urban and rural primary schools in Thailand. Journal of Educational Administration, 55(6), 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, P. (2010). The relationship of instructional leadership, teachers’ organizational commitment and students’ achievement in small schools [Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Universiti Sains Malaysia (Malaysia)]. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H., Walker, A., & Li, X. (2017). The West wind vs the East wind: Instructional leadership model in China. Journal of Educational Administration, 55(2), 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A., Waqar, Y., Aslam, M., & Muhammad, Y. (2025). Rethinking instructional leadership in Pakistan’s elite schools: A call for indigenous leadership models. Journal for Social Science Archives, 3(1), 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, V. M., Lloyd, C. A., & Rowe, K. J. (2008). The impact of leadership on student outcomes: An analysis of the differential effects of leadership types. Educational Administration Quarterly, 44(5), 635–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samichan, A., Awang, M., & Beram, S. (2021). Perbandingan model kepimpinan instruksional: Persepsi barat dan Malaysia (A comparison of instructional leadership models: The Western and Malaysian perception). Management Research Journal, 10, 94–105. (In Malaysian). [Google Scholar]
- Stemler, S. (2000). An overview of content analysis. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation, 7(1), 17. [Google Scholar]
- Thien, L. M. (2022). Psychometric analysis of a Malay language version of the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 50(4), 711–733. [Google Scholar]
- Thien, L. M., & Adams, D. (2024). Investigating the relationships between principal instructional leadership and teachers’affective commitment through collective teacher efficacy in Malaysian rural and urban primary schools. MOJEM: Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Management, 12(2), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, L. M., Darmawan, I. N., & Adams, D. (2023). (Re) Investigating the pathways between instructional leadership, collective teacher efficacy, and teacher commitment: A multilevel analysis. International Journal of Educational Management, 37(4), 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, L. M., & Liu, P. (2024). Linear and nonlinear relationships between instructional leadership and teacher professional learning through teacher self-efficacy as a mediator: A partial least squares analysis. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T. D., & Hallinger, P. (2017). Exploring cultural context and school leadership: Conceptualizing an indigenous model of có uy school leadership in Vietnam. International Journal of Leadership in Education, 20(5), 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, L. D., Gumela, G., & Maulana, H. (2021). Interrater reliability: Comparison of essay tests and scoring rubrics. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1933(1), 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A., & Hallinger, P. (2015). A synthesis of reviews of research on principal leadership in East Asia. Journal of Educational Administration, 53(4), 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A., & Qian, H. (2022). Developing a model of instructional leadership in China. Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, 52(1), 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witziers, B., Bosker, R. J., & Krüger, M. L. (2003). Educational leadership and student achievement: The elusive search for an association. Educational Administration Quarterly, 39(3), 398–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K. C., & Cheng, K. M. (1995). Educational leadership and change: An international perspective (Vol. 1). Hong Kong University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, A., Zahed Bablan, A., & Moeinikia, M. (2021). Investigating the psychometric properties of Principals’ Instructional Management Rating Scale (PIMRS-22). School Administration, 9(1), 358–337. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).