Exploring the Effects of a Problem-Posing Intervention with Students at Risk for Mathematics and Writing Difficulties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual-Model-Based Problem-Solving Approach
3. Problem Posing
4. Writing Theory and the Role of Working Memory
5. Scaffolded Writing Support
6. Purpose of the Study
- What is the relationship between the problem-posing intervention and the word problem performance (i.e., problem solving and problem posing)?
- What is the relationship between the problem-posing intervention and the sentence-writing conventions in the problem-posing response performance (i.e., total words written, words spelled correctly, and correct writing sequences)?
7. Method
7.1. Participants
7.2. Setting and Interventionists
7.3. Materials
7.4. Design and Procedures
7.5. Baseline
7.6. Intervention
7.7. Maintenance
7.8. Dependent Measures
8. Data Analysis
8.1. Implementation Procedure Fidelity
8.2. Inter-Rater Agreement
8.3. Social Validity
9. Results
9.1. Word Problem Performance
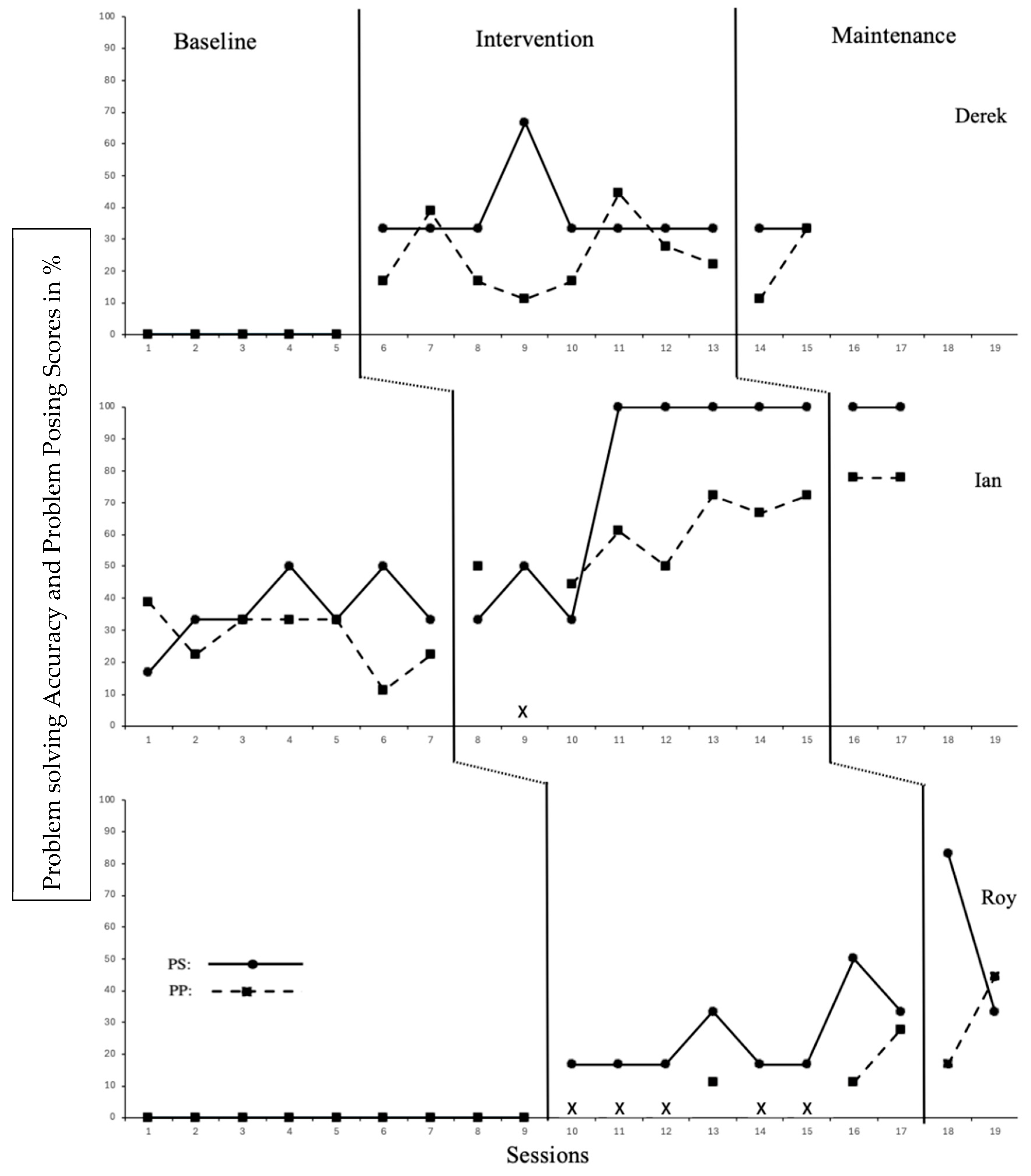
9.2. Sentence-Writing Conventions in Problem-Posing Response Performance

9.3. Social Validity Results
10. Discussion
11. Limitations
Implications for Practice and Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, A. A., Jung, P. G., Poch, A. L., Brandes, D., Shin, J., Lembke, E. S., & McMaster, K. L. (2020). Technical adequacy of curriculum-based measures in writing in grades 1–3. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 36(6), 563–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, T. P., & Alloway, R. G. (2010). Investigating the predictive roles of working memory and IQ in academic attainment. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 106(1), 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, T. L., Powell, S. R., & King, S. G. (2024). Mathematics-writing synthesis: Kindergarten through Grade 12 mathematics-writing outcomes and instructional methods. In Reading and writing (pp. 1–43). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R. D., Nagy, W., & Carlisle, J. (2010). Growth in phonological, orthographic, and morphological awareness in grades 1 to 6. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 39(2), 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berninger, V. W., & Amtmann, D. (2003). Preventing written expression disabilities through early and continuing assessment and intervention for handwriting and/or spelling problems: Research into practice. In H. L. Swanson, K. Harris, & S. Graham (Eds.), Handbook of research on learning disabilities (pp. 345–363). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Berninger, V. W., Vaughan, K., Abbott, R. D., Begay, K., Coleman, K. B., Curtin, G., Hawkins, J. M., & Graham, S. (2002). Teaching spelling and composition alone and together: Implications for the simple view of writing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(2), 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V. W., & Winn, W. (2006). Implications of advancements in brain research and technology for writing development, writing instruction, and educational evolution. In C. Mac Arthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (pp. 96–114). Guilford. [Google Scholar]
- Bevan, D., & Capraro, M. M. (2021). Posing creative problems: A study of elementary students’ mathematics understanding. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 16(3), em0654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, A., Capraro, R. M., & Capraro, M. M. (2013). Integrating writing into mathematics classroom to increase students’ problem solving skills. International Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 5(2), 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, A., Polo-Blanco, I., Van Vaerenbergh, S., Fernández-Cobos, R., & González-López, M. J. (2024). Strategies for solving multiplicative problems using a conceptual model-based problem-solving approach. A case study with a student with autism spectrum disorder. ZDM–Mathematics Education, 56(6), 1239–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J. (2003). Singaporean students’ mathematical thinking in problem solving and problem posing: An exploratory study. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 34(5), 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J., & Hwang, S. (2002). Generalized and generative thinking in U.S. and Chinese students’ mathematical problem solving and problem posing. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 21(4), 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J., Moyer, J. C., Wang, N., Hwang, S., Nie, B., & Garber, T. (2013). Mathematical problem posing as a measure of curricular effect on students’ learning. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 83(1), 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, T. M., Firmender, J. M., Cahill, J., Cardetti, F., Choppin, J. M., Cohen, J., Cole, S., Colonnese, M. W., Copley, J., DiCicco, M., Dieckmann, J., Dorl, J., Gavin, M. K., Hebert, M. A., Karp, K. S., LaBella, E., Moschkovich, J. N., Moylan, K., Olinghouse, N. G., … Zawodniak, R. (2016). Types of and purposes for elementary mathematical writing: Task force recommendations. Available online: https://mathwriting.education.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/1454/2016/04/Types_of_and_Purposes_for_Elementary_Mathematical_Writing_for_Web-2.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Datchuk, S. M., & Kubina, R. M. (2013). A review of teaching sentence-level writing skills to students with writing difficulties and learning disabilities. Remedial and Special Education, 34(3), 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datchuk, S. M., & Rodgers, D. B. (2019). Text writing within simple sentences: A writing fluency intervention for students with high–incidence disabilities. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 34(1), 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deno, S. L. (2003). Curriculum-based measures: Development and perspectives. Assessment for Effective Intervention, 28(3–4), 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, W. B., & Roe, C. J. (2010). Using sentence frames to develop academic vocabulary for English learners. The Reading Teacher, 64(2), 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., & Malone, A. S. (2017a). The taxonomy of intervention intensity. Teaching Exceptional Children, 50(1), 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Seethaler, P. M., & Barnes, M. A. (2020). Addressing the role of working memory in mathematical word-problem solving when designing intervention for struggling learners. ZDM, 52, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L. S., Malone, A. S., Schumacher, R. F., Namkung, J., & Wang, A. (2017b). Fraction intervention for students with mathematics difficulties: Lessons learned from five randomized controlled trials. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 50(6), 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S., Bollinger, A., Booth Olson, C., D’Aoust, C., MacArthur, C., McCutchen, D., & Olinghouse, N. (2012a). Teaching elementary school students to be effective writers: A practice guide (NCEE 2012-4058). What Works Clearinghouse. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Available online: https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/practiceguide/17 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2000). The role of self-regulation and transcription skills in writing and writing development. Educational Psychologist, 35(1), 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2003). Students with learning disabilities and the process of writing: A meta-analysis of SRSD studies. In H. L. Swanson, K. R. Harris, & S. Graham (Eds.), Handbook of learning disabilities (pp. 323–344). The Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, S., & Hebert, M. (2011). Writing to read: A meta-analysis of the impact of writing and writing instruction on reading. Harvard Educational Review, 81(4), 710–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S., McKeown, D., Kiuhara, S., & Harris, K. R. (2012b). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104(4), 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99, 445–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, C. C., Gagnon, J. C., Jossi, M. H., Ulrich, T. G., & Myers, J. A. (2018). Priming mathematics word problem structures in a rural elementary classroom. Rural Special Education Quarterly, 37(3), 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, D. J., Kiuhara, S. A., & Levin, J. R. (2019). A metacognitive intervention for teaching fractions to students with or at-risk for learning disabilities in mathematics. ZDM Mathematics Education, 51(4), 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K. R., Graham, S., Aitken, A. A., Barkel, A., Houston, J., & Ray, A. (2017). Teaching spelling, writing, and reading for writing: Powerful evidence-based practices. Teaching Exceptional Children, 49(4), 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, M. A., Powell, S. R., Bohaty, J., & Roehling, J. (2019). Piloting a mathematics–writing intervention with late elementary students at–risk for learning difficulties. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 34(3), 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, M. A., Shanahan Bazis, P., & Santangelo, T. (2023). Addressing the needs of students who struggle with literacy. In Z. A. Philippakos, & S. Graham (Eds.), Writing and reading connections: Building research and practice (pp. 289–310). The Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, E. M., Lee, J. Y., Cook, M. J., & Riccomini, P. J. (2019). Exploratory study of a self-regulation mathematical writing strategy: Proof-of-concept. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 17(2), 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaiah, T., Howard, D., & Olinghouse, N. (2019). Writer’s checklist: A procedural support for struggling writers. The Reading Teacher, 73(1), 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitendra, A. K., Rodriguez, M., Kanive, R., Huang, J. P., Church, C., Corroy, K. A., & Zaslofsky, A. (2013). Impact of small-group tutoring interventions on the mathematical problem solving and achievement of third-grade students with mathematics difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 36(1), 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C. H. (2005). Single-case designs for educational research. Allyn & Bacon. [Google Scholar]
- Kratochwill, T. R., Hitchcock, J., Horner, R. H., Levin, J. R., Odom, S. L., Rindskopf, D. M., & Shadish, W. R. (2010). Single-case designs technical documentation. What Works Clearinghouse. Available online: https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/ReferenceResources/wwc_scd.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Ledford, J. R., & Gast, D. L. (2024). Single case research methodology: Applications in special education and behavioral sciences (4th ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q., & Xin, Y. P. (2023). A synthesis of mathematical word problem-solving instructions for English learners with learning disabilities in mathematics. Review of Education, 11(2), e3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X., & Xin, Y. P. (2024). Teaching mathematics word problem solving to students with autism spectrum disorder. The Journal of Special Education, 58(1), 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutchen, D. (2000). Knowledge, processing, and working memory: Implications for a theory of writing. Educational Psychologist, 35(1), 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, J. M., Peng, P., & Goodrich, M. J. (2024). The relation between mathematics anxiety and mathematics competence for students with versus without mathematics learning difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 48(2), 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R. I., Vannest, K. J., Davis, J. L., & Sauber, S. B. (2011). Combining nonoverlap and trend for single-case research: Tau-U. Behavior Therapy, 42, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, S. R., Berry, K. A., & Barnes, M. A. (2020). The role of pre-algebraic reasoning within a word-problem intervention for third-grade students with mathematics difficulty. ZDM, 52(1), 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchey, K. D., McMaster, K. L., Al Otaiba, S., Puranik, C. S., Kim, Y.-S. G., Parker, D. C., & Ortiz, M. (2016). Indicators of fluent writing in beginning writers. In K. D. Cummings, & Y. Petscher (Eds.), The fluency construct: Curriculum-based measurement concepts and applications (pp. 21–66). Springer Science + Business Media. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, M., Gersib, J., Powell, S. R., Shen, Z., King, S. G., Akther, S. S., Arsenault, T. L., Bos, S. E., Lariviere, D. O., & Lin, X. (2024). A meta-analysis of mathematics interventions: Examining the impacts of intervention characteristics. Educational Psychology Review, 36(1), 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, E., & Ellerton, N. F. (1996). A framework for research into students’ problem posing in school mathematics. In P. C. Clarkson (Ed.), Technology in mathematics education (pp. 518–525). Mathematics Education Research Group of Australasia. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, H. L., & Beebe-Frankenberger, M. (2004). The relationship between working memory and mathematical problem solving in children at risk and not at risk for serious math difficulties. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(3), 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H. L., Harris, K. R., & Graham, S. (2013). Handbook of learning disabilities (2nd ed.). Guilford. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, H. L., Moran, A., Lussier, C., & Fung, W. (2014). The effect of explicit and direct generative strategy training and working memory on word problem-solving accuracy in children at risk for math difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 37(2), 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troia, G. A. (2009). Self-regulation and the writing process: Enhancing the performance of students with language and learning difficulties. Perspectives on Language Learning and Education, 16(1), 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Lopez-Reyna, N., & Kim, S. (2023). Word problem solving interventions for English learners at elementary grade levels: A review of the literature. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 21(2), 111–131. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y. P. (2008). The effect of schema-based instruction in solving mathematics word problems: An emphasis on prealgebraic conceptualization of multiplicative relations. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 39(5), 526–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y. P. (2012). Conceptual model-based problem solving: Teach students with learning difficulties to solve math problems. Sense Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y. P., Kim, S. J., Lei, Q., Liu, B. Y., Wei, S., Kastberg, S. E., & Chen, Y. V. (2023). The effect of model-based problem solving on the performance of students who are struggling in mathematics. The Journal of Special Education, 57(3), 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y. P., Kim, S. J., Lei, Q., Wei, S., Liu, B., Wang, W., Kastberg, S. E., Chen, Y., Xuan, Y., & Richardson, S. E. (2020). The effect of computer-assisted conceptual model-based intervention program on mathematics problem-solving performance of at-risk English learners. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 36(2), 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y. P., Tzur, R., Hord, C., Liu, J., Park, J. Y., & Si, L. (2017). An intelligent tutor-assisted mathematics intervention program for students with learning difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 40(1), 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., & Xin, Y. P. (2022). Teaching problem posing to students with learning disabilities. Learning Disability Quarterly, 45(4), 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D., Xin, Y. P., Harris, K., & Ding, Y. (2014). Improving multiplication strategic development in children with math difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 37(1), 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Participant | Gender | Ethnicity | Age | Grade | Disability Diagnosis | TOMA %ile Rank | WIAT %ile Rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | CO | ML | WP | SB | ||||||
| Ian | M | White | 8 years 11 months | 3rd | at risk for MWD | 16 | 75 | 9 | 5 | 16 |
| Roy | M | White | 10 years 5 months | 3rd | at risk for MWD | <1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | 2 |
| Derek | M | African American | 9 years 6 months | 3rd | at risk for MWD | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | <1 |
| Mathematical expression “2 × 3 = y” | |
| For the first quantity “2” | |
| 2 points | Students explicitly included the concept of “number of groups” in the problem and constructed a complete sentence. Example: “There are 2 bags of apples”, where “2 bags of apples” represents the “number of groups.” |
| 1 point | Students included the number and/or a word indicating groups but did not include a complete description of the group objects. Example: “There are 2.” or “There are 2 bags.” |
| 0 point | No response is provided. |
| For the second quantity “3” | |
| 2 points | Students explicitly included the “number of items in each group” in the problem and constructed a complete sentence. Example: “Each bag has 3 apples”, where “each” indicates the concept of “unit” and “3 apples” specifies the “number of items” in each group. |
| 1 point | Students included a number and/or a term indicating grouping but omitted the word “each” or description of items. Examples: “Each bag has 3.” or “There are 3 apples.” |
| 0 point | No response is provided. |
| For the last quantity “y” | |
| 2 points | Students formulated a complete and relevant question that includes the term “How many” and indicates the concept of “total”. Example: “How many apples are there in total?” or “How many apples do I have?” |
| 1 point | Students formulated a question but lacked full clarity or completeness. Examples: “How many are there?” or “How many do I have?” |
| 0 point | No response is provided. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Shanahan Bazis, P.; Lei, Q. Exploring the Effects of a Problem-Posing Intervention with Students at Risk for Mathematics and Writing Difficulties. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060780
Wang J, Shanahan Bazis P, Lei Q. Exploring the Effects of a Problem-Posing Intervention with Students at Risk for Mathematics and Writing Difficulties. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060780
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Pamela Shanahan Bazis, and Qingli Lei. 2025. "Exploring the Effects of a Problem-Posing Intervention with Students at Risk for Mathematics and Writing Difficulties" Education Sciences 15, no. 6: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060780
APA StyleWang, J., Shanahan Bazis, P., & Lei, Q. (2025). Exploring the Effects of a Problem-Posing Intervention with Students at Risk for Mathematics and Writing Difficulties. Education Sciences, 15(6), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060780






