Abstract
This study explores graduate students’ perceptions of and experiences with digital governance in higher education, using data from semi-structured interviews with thirty participants. A qualitative research design guided the investigation, addressing six research questions related to the definition, roles, effectiveness, required skills, challenges, and opportunities of digital governance. The findings reveal varying levels of familiarity with digital governance, often linked to concepts of e-government and efficient decision-making. However, many participants lacked a deep understanding of the term. Key roles of digital governance identified include improved data management, enhanced transparency, and increased inclusivity in decision-making processes. The study also highlights significant challenges, such as inadequate infrastructure, inconsistent implementation, and a lack of formal training in digital governance. Despite these barriers, digital governance offers practical benefits, including streamlined administrative processes, better accessibility, and improved research outcomes. Participants emphasized the importance of digital skills education but noted that weak infrastructure and limited curricular integration hinder skill development. Opportunities identified include greater efficiency, expanded access to education, and better support for marginalized groups. The study concludes with recommendations for a holistic approach, combining education reform, infrastructure improvement, and stakeholder collaboration to optimize the benefits of digital governance in higher education. These insights provide valuable guidance for policymakers and educators seeking to enhance digital governance in academic institutions.
1. Introduction
The 21st century has brought unprecedented social, cultural, and technological changes reshaping societal structures, with universities at the forefront of this transformation. These institutions face mounting pressure to adapt to technological advancements, navigate new regulatory frameworks, and establish robust foundations for digital transformation to realize their full potential. As scientific, economic, social, and cultural relations continue to expand and evolve, inter-university relationships have grown increasingly important (Maringe & Foskett, 2010). The success of these institutions in the digital era hinges on their ability to adapt and innovate, particularly in terms of digital competence and maturity—how effectively they can implement and manage digitalization processes.
In this regard, digital competence refers to knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behaviours that enable individuals to use digital technologies confidently, critically, and responsibly for learning, work, communication, and social participation (Zhao et al., 2021).
Aldhaen (2024) stated that it includes accessing, evaluating, and managing digital information, creating and sharing digital content, engaging in online collaboration, ensuring digital safety and well-being, and adapting to emerging technologies in an ever-changing digital environment. In the context of the knowledge society, digital competence is essential for transforming information into actionable knowledge and fostering innovation and informed decision-making. Universities must develop innovative strategies, cultivate specialized expertise, and restructure organizational frameworks to succeed in this digital landscape. Public institutions, in particular, are developing digital applications to meet growing citizen demands and provide targeted digital services (Westerberg, 2021). This evolution has given rise to digital governance, which emphasizes the electronic dimension of governance while building upon traditional sound governance principles. Digital governance aims to transfer information to digital environments, making it universally accessible, thereby enhancing democratic freedoms and facilitating broader participation in decision-making processes (Nath, 2016).
The emergence of digital governance parallels the development of the digital state—a model that effectively utilizes technological tools without competing with traditional state structures. Instead, it addresses traditional governance shortcomings and fills gaps while evolving alongside information technologies (Dede, 2024). In the university context, governance encompasses the systems and structures that determine institutional values, decision-making processes, and resource allocation. It shapes how universities operate internally and connects with various stakeholders, including government bodies, businesses, and the broader community (Edwards, 2001). Graduate students play a crucial role in this evolving landscape in universities. As they develop their professional identities during their studies, they are positioned as future academic staff contributing to local and global changes (Kovalcikiene & Buksnyte-Marmiene, 2015). Their future responsibilities will include preparing and training the qualified workforce for national development. As university missions and values evolve, so does graduate students’ role, necessitating new approaches to institutional practices and partnerships (Arslan, 2013; Holen et al., 2020). Student representation in university governance is not merely about engagement—it is fundamental to inclusive decision-making. While most institutions report student participation at higher institutional levels, representation varies significantly across departments and in specific areas such as teaching, learning, social issues, and staffing (Haque & Sultana, 2021; Luescher-Mamashela, 2013). Kuh (2009) defines student engagement as the level of interest, motivation, and active participation students demonstrate in their learning and the academic and social activities of their educational experience. Student engagement is strongly linked to positive outcomes such as academic success, personal development, and overall satisfaction with the learning process. Digital governance is key in enhancing student engagement by providing students and academic staff with quicker, more accessible services, allowing them to make more informed decisions (Alowyd, 2024). This underscores the importance of involving students more comprehensively in governance processes at the university level.
Current research has primarily focused on the digitalization of higher education and digital governance from an academic perspective in Turkey (Cam & Eke, 2022; Gullu, 2021; Yavuz et al., 2023). However, a notable lack of studies examining graduate student participation in digital governance makes this research particularly valuable in the Turkish context. Digital governance refers to digital decision-making processes within higher education institutions and their broader impacts.
This study aims to explore graduate students’ perceptions and definitions of digital governance at the university level. It focuses on understanding how they define digital governance, their knowledge of the concept, and their views on its role in institutional decision-making.
While much of the existing research concentrates on academics and other university stakeholders, this study highlights the often-overlooked perspectives of graduate students. By addressing this gap, the study seeks to provide valuable insights into graduate students’ awareness of digital governance and identify opportunities for enhancing its integration within higher education institutions. To fill this research gap, the study investigates graduate student engagement and viewpoints on digital governance in higher education through several research questions.
RQ1: How do you define the concept of digital governance? What prior knowledge do you have about digital governance?
RQ2: What role do you think digital governance plays in higher education institutions? What do you think about the contribution of digital tools to decision-making processes?
RQ3: Do you think universities are sufficient in digital governance? How can digital governance processes be used more effectively?
RQ4: How do you think your master’s and doctoral education developed digital governance awareness or knowledge?
RQ5: What skills and competencies should be offered to students or academics regarding digital governance? Were these skills sufficiently imparted during your education?
RQ6: What are the biggest challenges encountered in digital governance processes, and what are your suggestions for overcoming these challenges? Additionally, what opportunities do you think digital governance provides, and how does it offer benefits in terms of efficiency and inclusivity?
2. Digital Governance in Higher Education
Various international organizations have defined governance by highlighting complementary dimensions. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP, 1997) describes governance as the foundation for collective decision-making and action toward development, emphasizing participation, accountability, transparency, and inclusiveness. The OECD (2021) underscores the need for responsive and equitable institutions prioritizing human well-being, positioning good governance as essential for addressing complex social, economic, and environmental challenges. The World Bank (2022) defines governance as exercising authority through accountable leadership, effective policy implementation, and mutual respect between citizens and institutions, creating a stable and predictable environment. In organizational contexts, governance refers to how institutions are directed and managed through established structures. Edwards (2001) notes that while there is no single model for good governance, it consistently involves accountability, transparency, and effectiveness. With the rise of digital technologies, governance has expanded beyond traditional IT roles to become a core element of institutional and societal functioning (Westerberg, 2021). This shift transitions from centralized control to more inclusive, multi-stakeholder decision-making processes (Dede, 2024).
Turkey has made significant strides in digital transformation, particularly in higher education. The integration of digital governance has improved administrative efficiency, accessibility, and international competitiveness. Key platforms such as CoHE Atlas and the e-CoHE System streamline data access and communication between universities and the Council of Higher Education (CoHE, 2023). This transformation is obvious in the evolution of CoHE’s governance model. Kayıkcı (2018) highlights that Turkey’s traditional hierarchical structure has shifted toward a more network-based model. Before 2000, governance involved a simple triangle between CoHE, universities, and their direct stakeholders. After 2000, the system expanded to include international organizations, student mobility, and industry partnerships, reflecting a more complex and interconnected governance landscape.
Figure 1 illustrates the structure of Turkey’s higher education landscape before the 2000s, highlighting the central role of the CoHE. At this time, universities operated under a more centralized framework, with CoHE exerting significant influence over academic policies, university governance, and institutional operations. The structure shown in Figure 1 reflects the relatively straightforward organization of universities, where interactions primarily occurred between CoHE, universities, students, and academics, with limited external collaboration or influence. Students and academics were integral to the university environment, yet their roles and contributions were guided mainly by CoHE’s regulations, fostering a somewhat rigid academic system. This setup contrasts with the more diversified and dynamic higher education landscape in later years, shaped by globalization, increased autonomy, and various stakeholders’ involvement in university affairs.
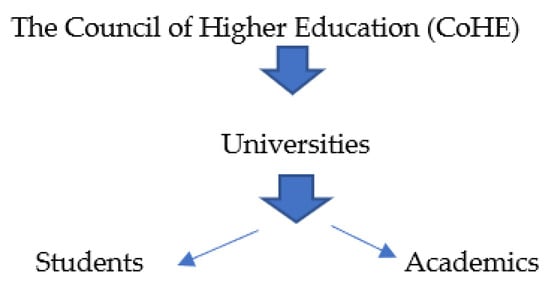
Figure 1.
Before the 2000s.
Figure 2 shows that before the 2000s, CoHE primarily acted as a policymaker working with universities, students, and academics. After 2000, the governance structure expanded to include international organizations, student mobility, industry, and the business sector. Programs like Erasmus strengthened the role of the European Commission in shaping higher education policy (European Commission, 2023). This shift reflects a global trend where digital technologies are transforming governance into higher education. Digital governance enables more transparent, efficient, and participatory decision-making, reshaping how institutions interact with stakeholders. Universities today face complex challenges, funding pressures, global competition, and the need for internationalization (Hayter et al., 2018; Lehmann & Stockinger, 2019). As Leja (2024) notes, governance increasingly balances economic demands with social responsibilities. Westerberg (2021) explains that E-governance supports this balance by promoting democratic values, effective service delivery, and inclusive participation. This marks a fundamental shift from traditional administration to a more dynamic, digitally driven governance model.
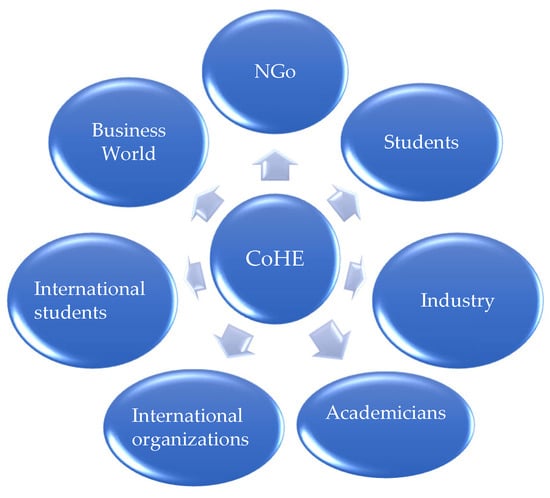
Figure 2.
After the 2000s. Source: (Kayıkcı, 2018).
3. Graduate Students’ Engagement and University Governance
Digital competence is a critical factor in student engagement, especially highlighted during the pandemic, when digital skills became essential for effective teaching and learning (Aldhaen, 2024). Student participation in higher education governance involves using their skills and contributions in decision-making. It also reflects students’ expectations, values, and beliefs, which evolve during their academic journey (Haque & Sultana, 2021). This participation extends beyond administrative frameworks, requiring a holistic approach integrating academic excellence, social responsibility, and economic sustainability. To address these challenges, universities must adopt innovative management practices encouraging inclusive participation and enhancing accountability while aiming for long-term sustainability (Meijer, 2015). Effective governance relies on three pillars: transparency, participation, and accountability, which have been amplified through e-governance. This digital transformation has streamlined operations, facilitating real-time stakeholder engagement and enabling universities to offer personalized services to their communities (Alowyd, 2024).
Student engagement, a key focus in higher education, involves behavioral, emotional, and cognitive components (Fredricks et al., 2004). Trowler (2010) sees it as a strategic partnership between students and institutions, where both invest resources to improve student outcomes and institutional effectiveness, creating a cycle of continuous improvement. Integrating students into governance fosters inclusive academic environments (Menon, 2022). It gives students a democratic decision-making experience and allows universities to adjust based on stakeholder feedback, improving educational quality and relevance. Modern universities use e-consultation platforms that enable meaningful student participation in policy formation, curriculum development, and campus life decisions. These platforms go beyond traditional feedback methods, allowing students to shape policies on key issues like sustainability and student welfare (Luna-Reyes, 2017). By combining digital tools with participatory governance, universities can create dynamic learning environments that meet stakeholder needs while maintaining academic rigor (UNESCO, 2020). This approach redefines how higher education operates in the digital age, fostering continuous improvement and shared responsibility for institutional success.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Research Design
This study employs a qualitative descriptive research design to explore graduate students’ perceptions and experiences of digital governance in higher education. The objective is to provide a detailed and comprehensive account of how students understand and engage with digital governance within their academic environments, based on their lived experiences. As Patton (2014) suggests, this approach allows researchers to uncover the meanings that participants attribute to their experiences, offering valuable insights that may not be immediately apparent. The focus here is on describing students’ lived experiences concerning digital governance, without the intention of statistical generalization. This qualitative method provides a nuanced understanding of complex social and institutional phenomena, allowing for a richer exploration of the subject matter (Creswell, 2014; Yıldırım & Şimşek, 2018).
4.2. Participants of the Study
This study employed criterion sampling, a purposive technique for selecting participants based on predefined characteristics. According to Patton (2014), this method ensures that participants meet specific criteria set by the researcher or based on existing frameworks. In this research, the participants were 30 graduate students (master’s and doctoral) enrolled at a public university in Turkey during the 2024–2025 academic year. Two main criteria were used for selection: (1) voluntary participation and (2) current enrollment in a graduate-level program. This approach ensured that the participants could provide relevant and meaningful insights into the research topic. Table 1 outlines the demographic characteristics of the participants, offering a comprehensive overview of the study group. The study explored how graduate students define and perceive digital governance in higher education, focusing on their conceptual understanding, prior knowledge, and opinions about its role in institutional decision-making. Participants were not provided a formal definition or digital governance framework before data collection. This choice intentionally captured authentic, unprompted perspectives, reflecting their natural understanding of the concept. By doing so, the study aims to provide contextually grounded insights into the level of awareness regarding digital governance among future academic professionals. The findings may inform educational policies and curriculum development, particularly in enhancing digital governance competencies in higher education, as graduate students are expected to play active roles in institutional governance in the near future.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of participants.
As seen in Table 1, the participant group in this study consists of 30 individuals, predominantly female (n = 18, 60%) compared to male participants (n = 12, 40%). Participants are diverse in age, ranging from 22 to 46, with a notable concentration of those in their early 20s and 40s. Academic levels vary, with the majority pursuing doctoral degrees (n = 18) and the remainder engaged in master’s studies (n = 12). The study fields covered a broad spectrum, including Primary Education, English Language, History, Science, Mathematics, ICT, Geography, and Social Sciences. There is a higher proportion of students specializing in English Language and Primary Education, particularly at the Ph.D. level. This composition suggests a sample encompassing early-career and more mature students, possibly reflecting different educational or professional trajectories. The presence of both master’s and Ph.D. students may provide insights into other perspectives on academic and professional development within varied educational disciplines.
4.2.1. Data Collection and Analysis
To collect data, the researcher developed a semi-structured interview form and conducted interviews with graduate students both face-to-face and via e-mail. Prior appointments were made with the participants to ensure that the interviews did not interfere with their class schedules. Interviews were held at mutually convenient times and were conducted voluntarily. All responses were meticulously documented in written form.
The researcher conducting this study is a graduate of the university where the research was carried out but holds no current academic, administrative, or personal affiliations with the institution or the participants. This absence of prior relationships helped minimize potential power dynamics or biases that could have influenced the data collection process. Acknowledging the inherent subjectivity in qualitative research, the researcher prioritized open-ended questioning to allow participants to express their experiences in their own words. All procedures were conducted following the ethical approval obtained from the institutional ethics committee.
After data collection, qualitative content analysis was employed to interpret and derive meaning from the textual data systematically. As Creswell (2014) explains, content analysis aims to uncover underlying themes and patterns in participants’ narratives. During the analysis phase, a second independent researcher was involved to ensure credibility and minimize personal bias. Both researchers worked collaboratively, discussing and agreeing upon codes and themes to enhance the trustworthiness of the findings. The content analysis followed a three-stage inductive process as described by McMillan and Schumacher (2010):
Initial Coding: The raw data were carefully examined and broken down into meaningful units, each coded to reflect key ideas and emerging insights.
Categorization: Related codes were grouped into broader categories for a more structured and nuanced understanding of the data.
Theme Development: These categories were then synthesized into overarching themes, revealing deeper patterns and interrelationships across participant responses.
In line with the inductive approach (Sandelowski, 2000), codes and themes were not derived from predefined categories or theoretical frameworks but emerged directly from the data. This data-driven process allowed the researchers to remain close to participants’ authentic voices and lived experiences. Both researchers coded the data independently and then engaged in discussions to reach an inter-rater agreement. To enhance the validity and transparency of the findings, direct quotations from participants were included to illustrate each theme, accompanied by summary tables. These verbatim excerpts supported thematic interpretations. Additionally, the frequency of each code’s occurrence was reported to add a quantitative dimension to the qualitative data, offering greater insight into the prevalence and significance of the identified themes.
4.2.2. Findings
This section presents the findings from the participant’s responses to the semi-structured interview questions, followed by each result based on the responses of the thirty participants from the six research questions raised in this study. The respondents, who were current university graduate students, were presented with themes, sub-themes, and codes.
RQ1.
How do you define the concept of digital governance? What prior knowledge do you have about digital governance?
Table 2 presents the views of graduate students regarding this question. It also gives the subthemes, codes, and number of participants created for the graduate students theme under this topic.

Table 2.
The concept of digital governance.
Table 2 reveals two main themes: the definition and scope of digital governance and awareness and familiarity with digital governance. Within the first theme, definition and scope of digital governance, 18 participants identified e-government as a key component, describing digital governance as using digital technologies in governance processes. Additionally, 12 participants mentioned that digital governance aims to enhance decision-making speed and efficiency through digital means. The second theme, awareness and familiarity with digital governance, indicates that 20 participants had no prior scientific knowledge of the concept and were unfamiliar with it. Seven participants expressed a basic understanding of digital governance and the digital tools and systems used in governance. In comparison, three participants noted that this interview was their first encounter with the concept. This data highlights varying levels of familiarity, suggesting a need for further education on digital governance in this demographic. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
This is the first time I have encountered it (P2). I define it as ensuring digital networking within institutions (P16). I am unfamiliar with the concept (P28). From the name, I would guess that it refers to methods developed by the state to facilitate tasks in various institutions and save time by using information technology. Applications like e-government, MHRS, and e-nabız could be examples of this (P16).
Digital governance is how the public and private sectors utilize digital technologies to manage decision-making, service delivery, and interaction processes (P5). This concept emerges by integrating information technologies into governance processes, highlighting transparency, participation, efficiency, and accountability. It facilitates citizens’ access to public services through digital platforms. For instance, e-government applications and digital service portals are examples of such governance (P30).
RQ2.
What role do you think digital governance plays in higher education institutions? What do you think about the contribution of digital tools to decision-making processes?
Table 3 presents the participants’ role in digital governance. These responses are grouped under three main themes.

Table 3.
Role of digital governance.
Table 3 presents an analysis of the role of digital governance across three primary themes: digital data and information management, impact on efficiency and decision-making, and digital governance in institutions and networks. Digital data and information management is a central theme, focusing on how governance adapts to technological advancements. Managing and organizing digital data, such as photos, videos, and documents, and ensuring data are stored and classified effectively is essential for efficient governance, as emphasized by 28 participants. Additionally, 12 participants stated that data management practices within digital governance play an important role by promoting network-based organizational management, further supporting collaborative digital ecosystems. A total of 15 participants stated that digital tools also enhance transparency and accessibility in governance, streamlining decision-making processes, increasing management efficiency, saving time, and improving overall decision quality. Impact on efficiency and decision-making illustrates how digital governance empowers organizations to make more informed decisions by leveraging data-driven insights. A total of 10 participants defined data and analytics as enabling precise, evidence-based decision-making, improving outcomes, and responding to stakeholder needs effectively. Furthermore, digital tools support inclusive governance by democratizing decision-making processes. A total of 5 participants stated that this inclusivity broadens access to participation in governance, allowing diverse stakeholders to contribute to decision-making. Also, 23 participants stated that digital governance in institutions and networks highlights integrating digital technologies to enhance communication and coordination within and across organizations. By facilitating inter-network communication, digital governance enables institutions to manage processes more effectively, share information seamlessly, and collaborate across networks to address complex governance challenges. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
There could be a possibility of making biased or unbiased decisions. For this reason, there should be proper and competent governance (P10). Digital governance plays an essential role in higher education institutions. Nowadays, many of our tasks are handled through digital platforms. In this sense, coordination between students and teachers can be highly effective (P28).
It saves time, helps make more accurate decisions, and supports more confident decision-making processes (P23). The use of digital resources provides savings in both time and space. I think it is possible for groups of people who cannot meet in person to come together using digital tools, and online tools can be used to manage and track tasks. This shows that participants can join the process from wherever they are, which provides a significant advantage for both managers (P13).
RQ3.
Do you think universities are sufficient in digital governance? How can digital governance processes be used more effectively?
Table 4 presents the effectiveness of digital governance. These responses are grouped under three main themes.

Table 4.
Effectiveness of digital governance.
Table 4 reveals key challenges and needs in the digital governance of higher education institutions, highlighting three critical areas. First, there is an urgent need for increased investments to address inadequate infrastructure, limited internet access, and insufficient technological resources, which 26 participants emphasized. These deficiencies are further exacerbated by disparities in digital governance across universities, leading to unequal access and implementation. Second, the training, awareness, and capacity-building theme underscores the necessity of equipping faculty, staff, and students with the digital skills required to use modern tools effectively. However, uneven digital governance across institutions remains a barrier to widespread adoption and skill enhancement, a concern of 19 participants. Finally, technological integration and the use of digital tools demand strategic improvements, such as enhanced data management and interdisciplinary collaboration. This theme, highlighted by 15 participants, stresses the importance of coordinated planning and partnerships among universities to ensure the effective use of digital technologies. Addressing these interconnected challenges is essential for fostering equitable and efficient digital governance in higher education. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
Universities have great potential in digital governance, but in general, they have not yet fully realized this potential. While some universities have made significant progress in digital transformation processes, many higher education institutions face challenges in using digital governance tools more comprehensively and effectively (P9). To use digital governance processes more effectively, universities should increase infrastructure investments, develop digital awareness, and adopt data-driven decision-making processes. Additionally, involving students and academics more through participatory and transparent digital governance models can make the university’s digital transformation more inclusive. This way, universities can increase their academic and administrative performance and contribute more to society (P17).
No, it is insufficient because I think there is a lack of internet and adequate cognitive and technological infrastructure (P3). Compared to other countries, more extensive and accessible research can be conducted (P6). It needs further development. Interaction should be increased (P17). I think it could be better (P5). No, it is not sufficient. The necessary infrastructure work, training, and in-service education can make it more effective (11). I think more education and opportunities could be provided, but I do not think it is sufficient (14).
RQ4.
How do you think your master’s and doctoral education developed your digital governance awareness or knowledge?
Table 5 presents the awareness of digital governance. These responses are grouped under three main themes.

Table 5.
Awareness of digital governance.
Table 5 reveals significant insights into digital governance’s practical application and benefits in higher education, emphasizing its transformative potential in three key areas. First, the use of digital platforms in education, highlighted by 24 participants, demonstrates how digital governance enhances the efficient management of educational resources and administrative tasks, streamlining operations across institutions. Second, the benefits of digital governance in the academic environment, identified by 21 participants, include improved accessibility to information and academic resources, which saves time and boosts overall efficiency in academic processes. Finally, the development of research and access skills, emphasized by 18 participants, underscores the role of digital tools in advancing research quality by enabling better data management and access to essential resources. Together, these findings highlight the multifaceted value of digital governance in fostering efficiency, accessibility, and innovation within the academic landscape. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
Since I am in the early stages of my master’s program, I have not yet gained significant awareness (P1). I do not think it has changed much (P12). The more research we do on the literature, the more it positively impacts our knowledge base (P23). Mainly in literature reviews, using many applications has contributed significantly to my development. I have greatly benefited from digital tools in my research during this process. They help me achieve results and increase my knowledge (P8).
Due to my work in the field and teaching, I effectively use web tools. I do not think my master’s and doctoral studies have contributed significantly to this process, but tools like Microsoft Teams are essential for tracking it and improving speed (P6). As a master’s student, my professors can provide us with the course schedule, resources, and guidance on becoming more successful through digital communication (P27). A considerable library now fits into a small computer, making accessing information and management easier. For example, it was tough to reach a dean or rector physically, but thanks to digital governance, I can now be just an email away. The same applies to the government; for instance, with CİMER, you can reach even the highest authorities (P30).
RQ5.
What skills and competencies should be offered to students or academics regarding digital governance? Were these skills sufficiently imparted during your education?
Table 6 presents the skills of digital governance. These responses are grouped under three main themes.

Table 6.
Skills of digital governance.
Table 6 reveals the essential skills and challenges associated with digital governance in higher education, focusing on the perspectives of students and academics. The most critical theme, identified by 30 participants, underscores the importance of digital literacy, particularly skills related to analyzing data and making informed decisions, a cornerstone of effective digital governance. Furthermore, 28 participants emphasized the positive impact of education in equipping them with valuable digital governance skills, indicating that formal education has played a significant role in fostering these competencies. However, challenges persist, as highlighted by 26 participants, who noted barriers such as insufficient infrastructure and the limited integration of digital tools within the education system. These shortcomings have forced some individuals to acquire digital governance skills independently or through non-formal means. Addressing these gaps in infrastructure and curriculum integration is vital to ensuring that all students and academics are adequately prepared for the demands of digital governance. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
Training on this topic can be provided (P8). It was not imparted. If it had been imparted, I would have learned it myself (P19). Competencies suitable for the current era should be imparted (P16). More training and seminars should be held. However, the most important thing is to create a solid digital infrastructure. I do not think it contributed much to me during my education (P10). I think there should be training sessions with helpful information from competent people to help us manage the process better. We should receive training on practical activities to apply and use in the process (P22).
Data analysis, digital communication, project management, cybersecurity, and critical thinking skills should be developed. I will gain these skills in my ongoing education (P27). Most importantly, reaching the most distant individual or information or managing an organization significantly benefits students and academics. Of course, some skills have been gained (P28). Academics and students should be able to effectively use digital tools, translate their knowledge into practice, and understand cybersecurity. They should also be able to communicate and interact with other stakeholders, so their social skills and sense of responsibility are also necessary. Some courses in my doctoral education increased my awareness and achievements in this area (P12).
RQ6.
What are the biggest challenges encountered in digital governance processes, and what are your suggestions for overcoming these challenges? Additionally, what opportunities do you think digital governance provides, and how does it benefit in terms of efficiency and inclusivity?
Table 7 presents the opportunities and challenges of digital governance. These responses are grouped under four main themes.

Table 7.
Opportunities and challenges of digital governance.
Table 7 comprehensively analyzes digital governance’s challenges, opportunities, and benefits in higher education. The most pressing challenges, noted by 30 participants, include a lack of formal education in digital governance, inadequate knowledge and skills, infrastructure deficiencies, limited access to technology, cybersecurity concerns, resource insufficiencies, and resistance to change. Addressing these barriers requires a multifaceted approach, as highlighted by 27 participants, who emphasized the importance of service-based education, including targeted training programs, technological investments, strategic infrastructure planning, and awareness initiatives to foster open communication and adaptability. On the positive side, opportunities in digital governance, recognized by 28 participants, include enhanced efficiency, inclusivity, transparency in decision-making, and the provision of personalized and accessible educational services. Furthermore, the benefits of efficiency and inclusivity, identified by 30 participants, demonstrate how digital governance facilitates faster access to information, empowers individuals through digital tools, supports disadvantaged groups, and enables effective remote management. Together, these findings highlight the transformative potential of digital governance while emphasizing the need for strategic action to overcome challenges and maximize its benefits. Some participants in the research expressed their views as follows:
Challenges in digital governance processes may include cost insufficiency and lack of hardware (P1). The biggest challenge is insufficient knowledge, and expanding inclusivity while increasing efficiency is crucial (P10). Limited access to the internet and network administrators are restrictive factors. The opportunities include efficiently conducting research and acquiring competencies in digital environments. In terms of efficiency, it will positively affect the reliability and scope of research (P3). With the internet going down and not always having devices available to access, aside from a phone, we can search and get help on any topic we need (P15).
Lack of knowledge leads to an inability to use digital tools effectively. Digital tools can simplify our lives in many ways (P12). Infrastructure problems and various restrictions limit access to information. However, this allows us to finish our work more quickly and easily (P5). Security concerns, lack of self-efficacy, and resource insufficiency are challenges (P14). The biggest problem is the lack of internet resources, especially for people living in remote areas like villages. The second most significant issue is the inadequate use of technology. Unfortunately, there are still severe deficiencies in this regard. As for the benefits, I think it is essential because it allows access from anywhere and under any condition, enables remote management of processes, and increases the efficiency of these processes (P9).
5. Discussion
The findings of this study provide a comprehensive understanding of graduate students’ perceptions of digital governance in higher education, emphasizing its definition, roles, challenges, and opportunities. Through the analysis of responses, several key insights emerge that contribute to the ongoing discourse on integrating digital governance in educational institutions. The findings highlight four primary thematic areas: conceptual understanding, institutional effectiveness, skill development, and implementation challenges.
Firstly, the study reveals varying levels of awareness of digital governance among graduate students. Some participants defined digital governance as using digital technologies in governance processes, while others highlighted its potential to enhance decision-making efficiency. This disparity suggests a gap in knowledge and familiarity with the concept. Many students were unfamiliar with or encountered digital governance for the first time, indicating that it is not sufficiently addressed in academic curricula or orientation programs. This finding is consistent with previous research, which points to a general lack of understanding of digital governance in higher education despite its growing role in administrative functions (Alowyd, 2024). The gap in familiarity underscores the need for educational interventions to introduce and explain digital governance early in students’ academic careers.
The second research question explored the role of digital governance in higher education, with digital data and information management emerging as a central theme. Participants noted that digital governance allows for more efficient data organization and storage, streamlining administrative processes. This finding reflects the increasing importance of data-driven decision-making in higher education, as 10 participants emphasized the role of data analytics in improving decisions. Additionally, digital governance significantly enables the electronic storage and sharing of documents, thus contributing to environmental sustainability and accelerating access to information (Gobble, 2018).
Furthermore, the study suggests that digital tools can significantly improve the efficiency of governance processes. Participants highlighted benefits such as time savings, easier communication, and better coordination, particularly in remote or decentralized settings. These findings align with literature emphasizing how digital governance enhances administrative efficiency by streamlining tasks and enabling more agile decision-making. Linkov et al. (2018) note that digital governance is especially critical during crises, where swift and accurate decision-making is essential. Digital platforms and communication tools help universities manage crises effectively by supporting quick and reliable decision-making.
The study also identified several challenges that hinder fully realizing digital governance’s potential in higher education. Common barriers included infrastructure problems such as inadequate internet access, insufficient technological resources, and security concerns. These issues are especially prevalent in developing countries or remote areas, where digital infrastructure is often underdeveloped. Additionally, the lack of formal education and training in digital governance was a significant issue, with many students and academics not adequately equipped to navigate and contribute to governance processes. This gap in education highlights the need for targeted training and digital literacy programs to bridge the divide and ensure that all stakeholders can engage effectively with digital governance (Rapanta et al., 2021).
Despite these challenges, participants identified significant opportunities that digital governance offers. Increased efficiency, faster access to information, and improved decision-making were among the primary benefits mentioned. Digital tools also promote inclusivity, allowing marginalized or distant groups to participate more easily in academic and administrative processes. These advantages align with other studies showing how digital governance can democratize access to higher education and services, fostering more equitable educational environments (Aldhaen, 2023). Moreover, digital governance empowers students and faculty to interact more effectively and manage academic and administrative tasks, thus adapting to the evolving demands of modern education.
Participants suggested strategies to address the identified challenges, including increased investment in digital infrastructure, enhanced training for students and staff, and strategic planning to integrate digital tools across university systems. Many emphasized the importance of building a robust digital infrastructure and offering continuous education and awareness programs. Aldhaen (2023) defined the development of digital governance curricula and prioritized digital literacy as a cornerstone of academic development.
As Luna-Reyes (2017) notes, uneven access to digital platforms creates a digital divide that excludes specific demographics from governance processes. Additional challenges, such as cybersecurity concerns, resistance to change, and resource insufficiency, complicate the situation. Additionally, Luescher-Mamashela (2013) identified that structural challenges include the transient nature of student roles, tokenization of student representative bodies, insufficient access to relevant information, and time constraints due to academic responsibilities.
A notable finding is the disparity in stakeholder participation in governance processes, particularly in comparison to European universities. While digital platforms have the potential to act as virtual public spaces that encourage broader participation (Luna-Reyes, 2017), student involvement often remains superficial—limited to attendance rather than active engagement in decision-making (Li & Zhao, 2020). This limitation is especially evident among research assistants, administrative staff, and students, while faculty members tend to have stronger representation on governing boards (Nagaraja, 2016). This disparity underscores the need to democratize governance through more inclusive digital solutions. In developing countries, although students participate in governance, their involvement is often informal and lacks a structured framework. Universities often fail to recognize or institutionalize these contributions (Haque & Sultana, 2021).
The study also highlights that graduate education plays a mixed role in developing students’ awareness and knowledge of digital governance. While some students reported limited exposure or awareness due to the early stages of their studies, others pointed to the positive influence of digital tools on their academic activities. This reflects a broader trend where digital governance plays an indirect role in academic environments, with digital tools often being more about personal or departmental adaptation rather than institution-wide strategic implementation.
Finally, regarding necessary competencies, the study found that digital literacy and data analysis skills are essential for students and academics. Although participants recognized the importance of these skills, many felt that their educational experiences did not adequately prepare them for the demands of digital governance. This gap highlights the need for universities to integrate practical digital governance skills into their curricula, ensuring that students and faculty can confidently engage with and contribute to digital governance processes.
6. Conclusions
This study provides valuable insights into graduate students’ perceptions of digital governance in higher education, revealing a gap in awareness and understanding despite its increasing importance. While students recognize the potential of digital governance to enhance efficiency, decision-making, and inclusivity, challenges such as infrastructure limitations, lack of formal education, and security concerns hinder its full implementation. The study highlights the need for universities to integrate digital governance into curricula and invest in digital infrastructure and training to prepare students for a digitalized academic environment better. Future research should explore broader perspectives, including faculty and administrative staff, and compare different regions to understand varying implementations of digital governance. Additionally, longitudinal studies could track changes in student engagement with digital governance over time while investigating the effectiveness of digital literacy programs. Limitations of the study include a small sample size, a focus on perceptions rather than actual implementations, and the absence of institutional perspectives. These findings call for further exploration of how digital governance can be optimized and integrated into higher education to improve efficiency, inclusivity, and engagement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D. and H.A.; methodology, M.D. and H.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D. and H.A.; writing—review and editing, M.D. and H.A.; visualization, M.D.; supervision, H.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Social and Human Sciences Ethics Committee of Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Turkey (Decision Date: 21 March 2025; Decision No: 23/80).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the original researcher upon reasonable request. Data may be shared upon obtaining the necessary permission from the re-searcher.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aldhaen, E. (2023). Education skills for digital age toward sustainable development—Analysis and future directions. Development and Learning in Organizations, 37(3), 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhaen, E. (2024). The influence of digital competence of academicians on students’ engagement at university level: Moderating effect of the pandemic outbreak. Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal Incorporating Journal of Global Competitiveness, 34(1), 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowyd, J. (2024). E-governance applications and their importance for universities. Eurasian Business & Economics Journal, 37(1), 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, H. (2013). Effectiveness of board of trustees in university governance. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 13(9), 1165–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Cam, S., & Eke, E. (2022). University employees’ perceptions of digitalization in management: A qualitative study. Süleyman Demirel University Visionary Journal, 13(30), 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Higher Education (CoHE). (2023). University monitoring and assessment general report 2023. YÖK. Available online: https://www.yok.gov.tr (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (Pearson, new international edition, 4th ed.). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Dede, A. (2024). Digital communication, digital citizenship, digital governance, and CİMER. Abant Journal of Social Sciences, 24(1), 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M. (2001, November 1). University governance: A mapping and some issues. Lifelong Learning Network National Conference, Canberra, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. (2023). Erasmus+ programme guide. Available online: https://erasmus-plus.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobble, M. M. (2018). Digitalization, digitization, and innovation. Research-Technology Management, 61(4), 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullu, O. (2021). Digitalization in higher education [Master’s thesis, Marmara University]. Available online: https://www.proquest.com (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Haque, M. S., & Sultana, M. (2021). Higher education governance and student participation. In A. Farazmand (Ed.), Global encyclopedia of public administration, public policy, and governance. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayter, C. S., Nelson, A. J., Zayed, S., & O’Connor, A. (2018). Conceptualizing academic entrepreneurship ecosystems: A review, analysis, and extension of the literature. Journal of Technology Transfer, 43, 1039–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holen, R., Ashwin, P., Maassen, P., & Stensaker, B. (2020). Student partnership: Exploring the dynamics in and between different conceptualizations. Studies in Higher Education, 46(12), 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayıkcı, S. (2018). The applicability of governance in public institutions: The case of the council of higher education. Ombudsman Academic, 1, 163–181. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/645122 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kovalcikiene, K., & Buksnyte-Marmiene, L. (2015). Towards an understanding of doctoral students’ professional identity complexity. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 191, 2693–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G. D. (2009). What student affairs professionals need to know about student engagement. Journal of College Student Development, 50, 683–706. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ868898 (accessed on 1 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E. E., & Stockinger, S. A. (2019). Entrepreneurship in higher education: The impact of competition-based policy programs exemplified by the German excellence initiative. Higher Education Quarterly, 73(1), 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leja, K. W. (2024). Student participation in the governance of university alliances: A case study of student participation at a European university, Una Europa [Master’s thesis, Tampere University]. Available online: https://trepo.tuni.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/158698/LejaKarol.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Li, X., & Zhao, G. (2020). Democratic involvement in higher education: A study of Chinese student E-participation in university governance. Higher Education Policy, 33(1), 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I., Trump, B. D., Poinsatte-Jones, K., & Florin, M.-V. (2018). Governance strategies for a sustainable digital world. Sustainability, 10(2), 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luescher-Mamashela, T. M. (2013). Student representation in university decision making: Good reasons, a new lens? Studies in Higher Education, 38(10), 1442–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Reyes, L. F. (2017). Opportunities and challenges for digital governance in a world of digital participation. Information Polity, 22(2–3), 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringe, F., & Foskett, N. (2010). Introduction: Globalization and universities. In Globalization and internationalization in higher education: Theoretical, strategic and management perspectives (pp. 1–13). Continuum International Publishing Group. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, J. H., & Schumacher, S. (2010). Research in education: Evidence-based inquiry (MyEducationLab series). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, A. (2015). E-governance innovation: Barriers and strategies. Government Information Quarterly, 32(2), 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M. E. (2022). Perceptions of stakeholders on the problems facing higher education: Implications for university governance and student engagement. Student Engagement in Higher Education Journal, 4(1), 70–87. Available online: https://sehej.raise-network.com/raise/article/view/1049 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Nagaraja, K. (2016). E-governance in India: Issues and challenges. IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance, 7(5), 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, V. (2016). Digital governance models: Moving towards good governance in developing countries. Available online: http://www.digitalgovernance.org (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- OECD. (2021). The digital transformation of education systems. OECD Publishing. Available online: https://digital-education-outlook.oecd.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Patton, M. Q. (2014). Qualitative research and evaluation methods (4th ed.). Sage Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Rapanta, C., Botturi, L., Goodyear, P., Guardia, L., & Koole, M. (2021). Balancing technology, pedagogy and the new normal: Post-pandemic challenges for higher education. Postdigital Science and Education, 3(3), 715–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandelowski, M. (2000). Whatever happened to qualitative description? Research in Nursing & Health, 23(4), 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowler, V. (2010). Student engagement literature review. Higher Education Academy. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322342119_Student_Engagement_Literature_Review (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- UNDP. (1997). Governance for sustainable human development: A UNDP policy document. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/492551?v=pdf (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- UNESCO. (2020). COVID-19 and the digital transformation in education. UNESCO Publishing. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000374309 (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Westerberg, S. (2021). Public IT governance for digital transformation: A grounded theory approach for model development. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1585926/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- World Bank. (2022). Bridging the digital divide in Turkey. The World Bank. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/099800307152412262/pdf/IDU136626fc5100dc1403d182371253d10b5db00.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Yavuz, M., Kayalı, B., & Karaman, S. (2023). An investigation of digital transformation activities of higher education in Türkiye. Participatory Educational Research, 10(4), 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, A., & Simsek, H. (2018). Qualitative research methods in the social sciences (11th ed.). Seçkin Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y., Llorente, A. M. P., & Gómez, M. C. S. (2021). Digital competence in higher education research: A systematic literature review. Computers and Education, 168, 104–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).