Techno-Pedagogical Approaches and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study Based on LMS Log Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background: LMS Integration and the Rise of Data-Driven Education
1.2. Towards Interpretable and Instructor-Centred Learning Analytics
1.3. From Data to Interpretation: Study Structure
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Population and Sample
2.3. Research Ethics
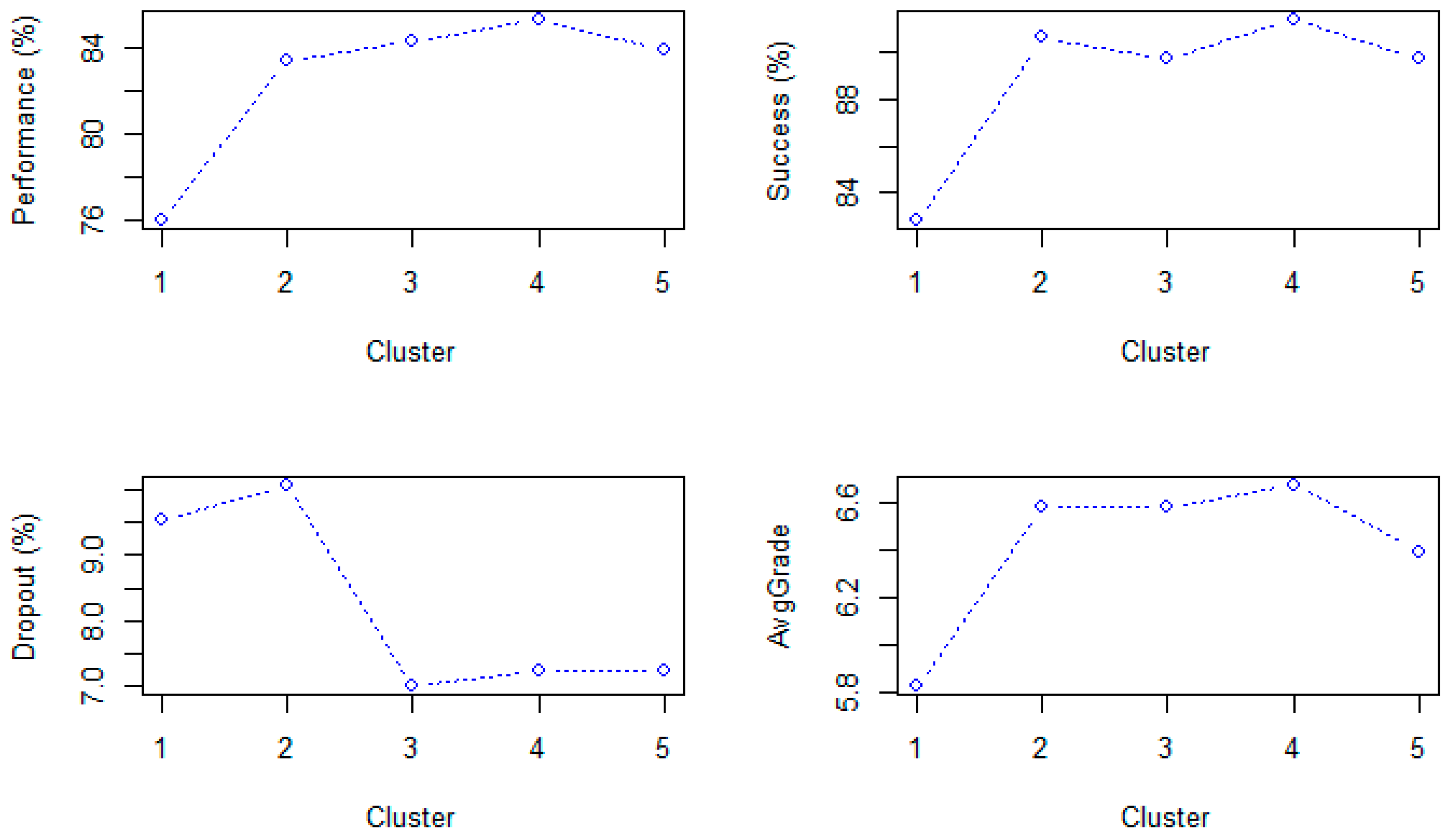
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akpen, C. N., Asaolu, S., Atobatele, S., Okagbue, H., & Sampson, S. (2024). Impact of online learning on student’s performance and engagement: A systematic review. Discover Education 3, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, M. A., & Allinjawi, A. A. (2025). Determining patterns of instructors’ usage of blackboard features using a clustering technique. Journal of King Abdulaziz University: Computing and Information Technology Sciences, 14(1), 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, J., Rienties, B., & Divjak, B. (2025, March 3–7). Decoding learning design decisions: A cluster analysis of 12,749 teaching and learning activities. 15th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK ‘25) (pp. 407–417), Dublin, Ireland. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tameemi, R. A. N., Johnson, C., Gitay, R., Abdel-Salam, A.-S. G., Hazaa, K. A., BenSaid, A., & Romanowski, M. H. (2023). Determinants of poor academic performance among undergraduate students—A systematic literature review. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 4, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avello Martínez, R., Fernández-Álvarez, D., & Gómez Rodríguez, V. G. (2023). Moodle logs analytics: An open web application to monitor student activity. Universidad y Sociedad, 15(4), 715–721. Available online: https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/4030 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Basantes-Andrade, A., Casillas-Martín, S., Cabezas-González, M., Naranjo-Toro, M., & Guerra-Reyes, F. (2022). Standards of teacher digital competence in higher education: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 14(21), 13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M., Bedenlier, S., Marín, V. I., & Händel, M. (2021). Emergency remote teaching in higher education: Mapping the first global online semester. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(1), 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, R., & Movahedazarhouligh, S. (2018). Successful stories and conflicts: A literature review on the effectiveness of flipped learning in higher education. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34(4), 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chytas, K., Tsolakidis, A., Triperina, E., & Skourlas, C. (2022). Educational data mining in the academic setting: Employing the data produced by blended learning to ameliorate the learning process. Data Technologies and Applications, 57(3), 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón Artacho, E., Martínez, T. S., Ortega Martín, J. L., Marín Marín, J. A., & Gómez García, G. (2020). Teacher training in lifelong learning—The importance of digital competence in the encouragement of teaching innovation. Sustainability, 12(7), 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R. L., Rockinson-Szapkiw, A. J., & Cook, V. S. (2020). Community college faculty perceptions of the quality MattersTM rubric. Online Learning, 24(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llauró, A., Fonseca, D., Villegas, E., Aláez, M., & Romero, S. (2024). Improvement of academic analytics processes through the identification of the main variables affecting early dropout of first-year students in technical degrees. A case study. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 9(1), 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, L., Heathcote, E., & Dawson, S. (2013). Informing pedagogical action: Aligning learning analytics with learning design. American Behavioral Scientist, 57(10), 1439–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P., & Siemens, G. (2011). Penetrating the fog: Analytics in learning and education. EDUCAUSE Review, 46(5), 30–40. Available online: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2011/9/penetrating-the-fog-analytics-in-learning-and-education (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Lowenthal, P., & Hodges, C. (2015). In search of quality: Using quality matters to analyze the quality of massive, open, online courses (MOOCs). The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 16(5), 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaroska, K., & Giannakos, M. (2019). Learning analytics for learning design: A systematic literature review of analytics-driven design to enhance learning. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 12(4), 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhiça, R., Santos, A., & Cravino, J. (2022, June 22–25). The use of artificial intelligence in learning management systems in the context of higher education: Systematic literature review. 17th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI) (pp. 1–6), Madrid, Spain. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena-Sánchez, R., López-Nozal, C., Ji, Y. P., Pardo-Aguilar, C., & Arnaiz-González, Á. (2022). UBUMonitor: An open-source desktop application for visual e-learning analysis with moodle. Electronics, 11(6), 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K., Horikoshi, I., Majumdar, R., & Ogata, H. (2023, December 4–8). Visualization of instructional patterns from daily teaching log data. International Conference on Computers in Education, Matsue, Japan. Available online: https://library.apsce.net/index.php/ICCE/article/view/4733 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Nurmalitasari, Awang Long, Z., & Faizuddin Mohd Noor, M. (2023). Factors influencing dropout students in higher education. Education Research International, 2023(1), 7704142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochukut, S., Hernedez-Leo, D., Oboko, R. O., & Miriti, E. K. (2024). Alignment of learning design with learning analytics: Case of MOODLE blended learning course in higher education. In Lecture notes in networks and systems (Vol. 1171, pp. 201–210). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouariach, F. Z., Nejjari, A., Ouariach, S., & Khaldi, M. (2024). Place of forums in online communication through an LMS platform. World Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology and Sciences, 11(1), 096–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z., Biegley, L., Taylor, A., & Zheng, H. (2024). A systematic review of learning analytics: Incorporated instructional interventions on learning management systems. Journal of Learning Analytics, 11(2), 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, D., & Pozzi, F. (2015). Learning analytics to support teachers’ decision-making. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(6), 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, B. V., Zarco, C., & Cordón, O. (2023). Mapping the situation of educational technologies in the spanish university system using social network analysis and visualization. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 8(2), 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanta, C., Botturi, L., Goodyear, P., Guàrdia, L., & Koole, M. (2020). Online university teaching during and after the COVID-19 crisis: Refocusing teacher presence and learning activity. Postdigital Science and Education, 2, 923–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueras, L. M., Verdú, M. J., Castro, J. D., & Verdú, E. (2019). Clustering analysis for automatic certification of LMS strategies in a university virtual campus. IEEE Access, 7, 137680–137690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueras Santos, L. M., Verdú Pérez, M. J., & Castellanos Nieves, D. (2025). Analíticas académicas y análisis de aulas virtuales. Un estudio en los tiempos post-Covid19. In M. Area-Moreira, J. Valverde-Berrocoso, & B. Rubia-Avi (Eds.), Transformación digital de la enseñanza universitaria. Analíticas académicas y escenarios de futuro (pp. 99–115). Octaedro. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, M. Á., Santana-Mancilla, P. C., & Anido-Rifón, L. E. (2025). Machine learning and generative ai in learning analytics for higher education: A systematic review of models, trends, and challenges. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C., & Ventura, S. (2020). Educational data mining and learning analytics: An updated survey. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 10(3), e1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T., Sondergaard, R., Ives, C., Han, A., & Graf, S. (2025). Enhancing access to educational data for educators and learning designers: Staged evaluation of the academic analytics tool. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 30, 1371–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, M., Maier, R., Berger, S., Kastorff, T., & Stegmann, K. (2024). Learning activities in technology-enhanced learning: A systematic review of meta-analyses and second-order meta-analysis in higher education. Learning and Individual Differences, 112, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M., & Shaalan, K. (2025). Unlocking the power of machine learning in E-learning: A comprehensive review of predictive models for student performance and engagement. Education and Information Technologies, 30, 19027–19050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghir, N., Adadi, A., & Lahmer, M. (2023). Recent advances in predictive learning analytics: A decade systematic review (2012–2022). Education and Information Technologies, 28(7), 8299–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa Alonso, J. J., de Castro Fernández, J. P., & Regueras Santos, L. M. (2025). Configuraciones tecnopedagógicas en aulas virtuales y rendimiento académico: Un análisis comparativo a partir de analíticas de aprendizaje. In M. Area-Moreira, J. Valverde-Berrocoso, & B. Rubia-Avi (Eds.), Transformación digital de la enseñanza universitaria. Analíticas académicas y escenarios de futuro (pp. 117–142). Octaedro. [Google Scholar]
- Tempelaar, D. T., Rienties, B., & Giesbers, B. (2015). In search for the most informative data for feedback generation: Learning analytics in a data-rich context. Computers in Human Behavior, 47, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinjić, D., & Nordén, A. (2024). Crisis-driven digitalization and academic success across disciplines. PLoS ONE, 19(2), e0293588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torstrick, R., & Finke, J. (2025). Using technology to support success: Assessing value using strategic academic research and development. Education Sciences, 15(5), 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, O., Hatakka, M., Bälter, O., & Mavroudi, A. (2018). The current landscape of learning analytics in higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 89, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelock-Wainwright, A., Tsai, Y.-S., Lyons, K., Kaliff, S., Bryant, M., Ryan, K., & Gaševic, D. (2020, March 23–27). Disciplinary differences in blended learning design: A network analytic study. 10th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK ‘20) (pp. 579–588), Frankfurt, Germany. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, T. T., Gibson, C., & Rankin, S. (2015). Defining and measuring academic success. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation, 20(1), 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | % of Courses | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Assign | 61.4% | numAssigns, averageWordsIntro, numGroupAssigns |
| AssignFeedback | 25.1% | numAssignFeedbacks, averageWordsComment |
| Feedback | 6.8% | numFeedbacks, averageWordsIntro, averageWordsPost |
| Folder | 35.8% | numFolders, averageWordsIntro, allReviewFolders |
| Forum | 98.7% | numForums, diffTypesForums, averageWordsIntro, TeacherDiscuss, perStudentDiscuss, TeacherPosts, perStudentPosts |
| Glossary | 2.2% | numGlossaries, averageWordsIntro, diffTypesGlossaries |
| Label | 39.0% | numLabels, averageWordsIntro |
| Module | 99.7% | numModules, diffTypesModules |
| Pages | 14.3% | numPages, averageWordsIntro, averageWordsContent, allReviewPages |
| Quiz | 18.1% | numQuizzes, averageWordsIntro, averageQuestionQuiz, numAllQuestions, averageDiffTypesQuestions, averageWordsQuestions, averageWordsFeedbacks |
| Resources | 83.6% | numFiles, averageWordsIntro |
| Scales | 3.9% | numScales, averageWordsDescription, diffTypesScales |
| Url | 44.2% | numUrls, averageWordsIntro, numUniqueUrls |
| Wiki | 3.1% | numWikis, averageWordsIntro, diffTypesWikis |
| Workshop | 2.0% | numWorkshops, averageWordsIntro, averageWordsSubmissionInstruct, averageWordsAssessmentInstruct, diffGradingStrategies, averageWordsFeedbackAuthors, averageWordsDescripRubric, averageNumLevels, averageWordsRubric |
| Chat | 1.9% | numChats, averageWordsIntro, numMessagesChat |
| Videotool | 29.4% | numSyncVideo, numAsyncPresent, numInteractiveContent |
| Other | 5.5% | numOrganizationalTools, numEquivAssigns, numOtherMaterials |
| Element | Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|
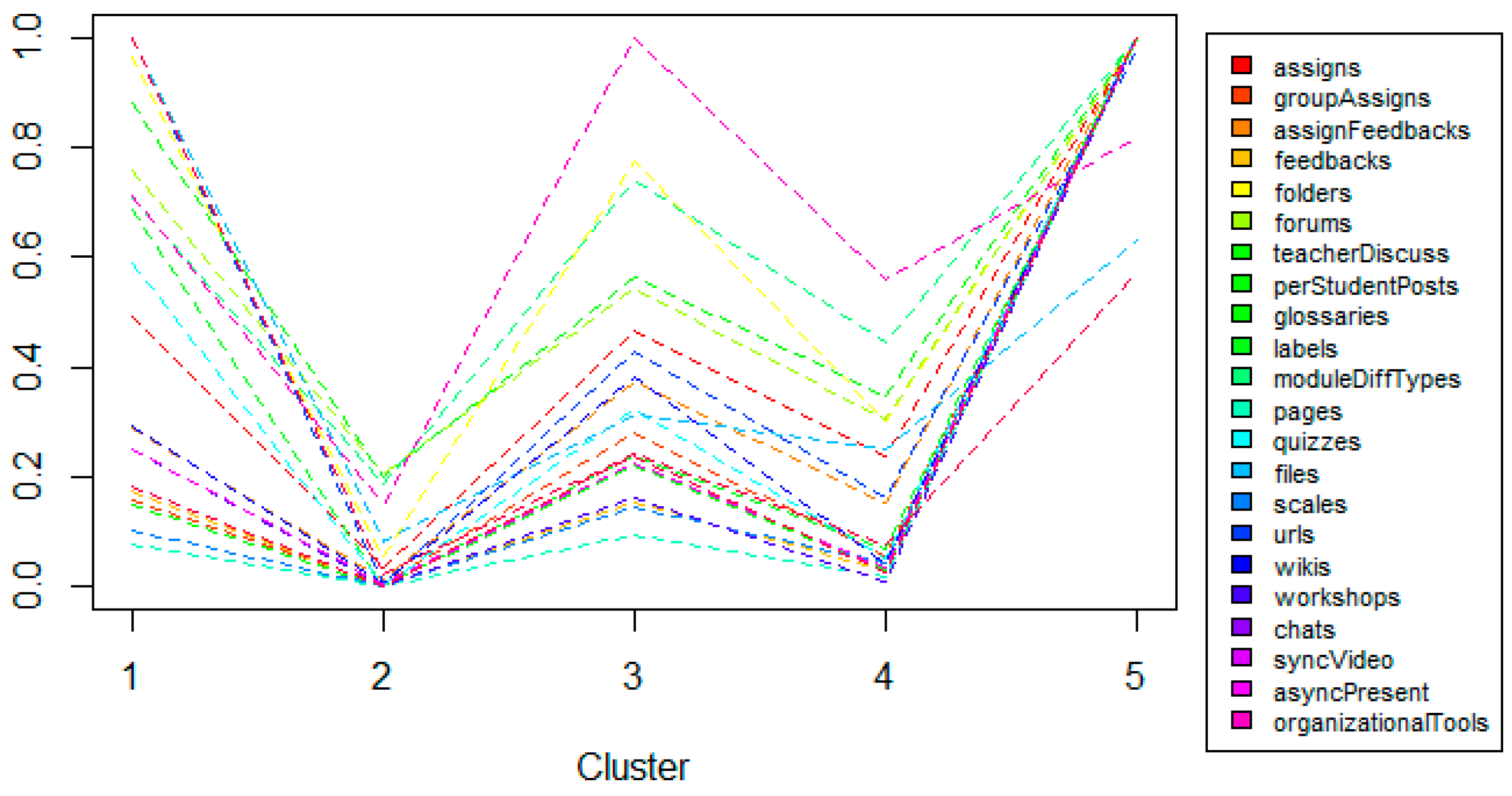
| Assign | assigns, groupassigns | Number of assigns and group assigns |
| AssignFeedback | assignfeedbacks | Number of feedbacks to students’ assigns |
| Feedback | feedbacks | Number of feedbacks (surveys) |
| Folder | folders | Number of folders |
| Forum | forums, teacherdiscuss, perstudentposts | Number of forums, discussions (initiated by teacher) and students’ posts |
| Glossary | glossaries | Number of glossaries |
| Label | labels | Number of labels |
| Module | moduledifftypes | Number of different types of modules |
| Pages | pages | Number of pages |
| Quiz | quizzes | Number of quizzes |
| Resources | files | Number of files |
| Scales | scales | Number of evaluation scales |
| Url | urls | Number of links |
| Wiki | wikis | Number of wikis |
| Workshop | workshops | Number of workshops |
| Chat | chats | Number of chats |
| Videotool | syncvideo, asyncpresent | Number of videoconferences (synchronous) and recorded presentations (asynchronous) |
| Other | organizationaltools | Number of organisational elements |
| Cluster | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | 6% | Innovation based on audiovisual resources |
| Cluster 2 | 35% | Traditional model with low use of virtual campus |
| Cluster 3 | 19% | Traditional model with participative use |
| Cluster 4 | 37% | Repository (uploading resources and collecting assigns) |
| Cluster 5 | 3% | Advanced innovation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Regueras, L.M.; Verdú, M.J.; de Castro, J.P.; Álvarez-Álvarez, S. Techno-Pedagogical Approaches and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study Based on LMS Log Data. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111533
Regueras LM, Verdú MJ, de Castro JP, Álvarez-Álvarez S. Techno-Pedagogical Approaches and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study Based on LMS Log Data. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111533
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegueras, Luisa M., María J. Verdú, Juan P. de Castro, and Susana Álvarez-Álvarez. 2025. "Techno-Pedagogical Approaches and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study Based on LMS Log Data" Education Sciences 15, no. 11: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111533
APA StyleRegueras, L. M., Verdú, M. J., de Castro, J. P., & Álvarez-Álvarez, S. (2025). Techno-Pedagogical Approaches and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study Based on LMS Log Data. Education Sciences, 15(11), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111533







