Exploring Students’ Learning Experience and Engagement in Asynchronous Learning Using the Community of Inquiry Framework through Educational Design Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Theoretical Framework
1.2. Research Purpose and Questions
- RQ1: What are students’ perceptions of the asynchronous lectures developed based on the CoI framework for different applied science courses?
- RQ2: What are students’ perceptions of engagement in the asynchronous lectures developed based on the CoI framework?
- RQ3: What design features are important for designing asynchronous lectures that are perceived positively and engage students?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Participants
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Data Collection
3. Results
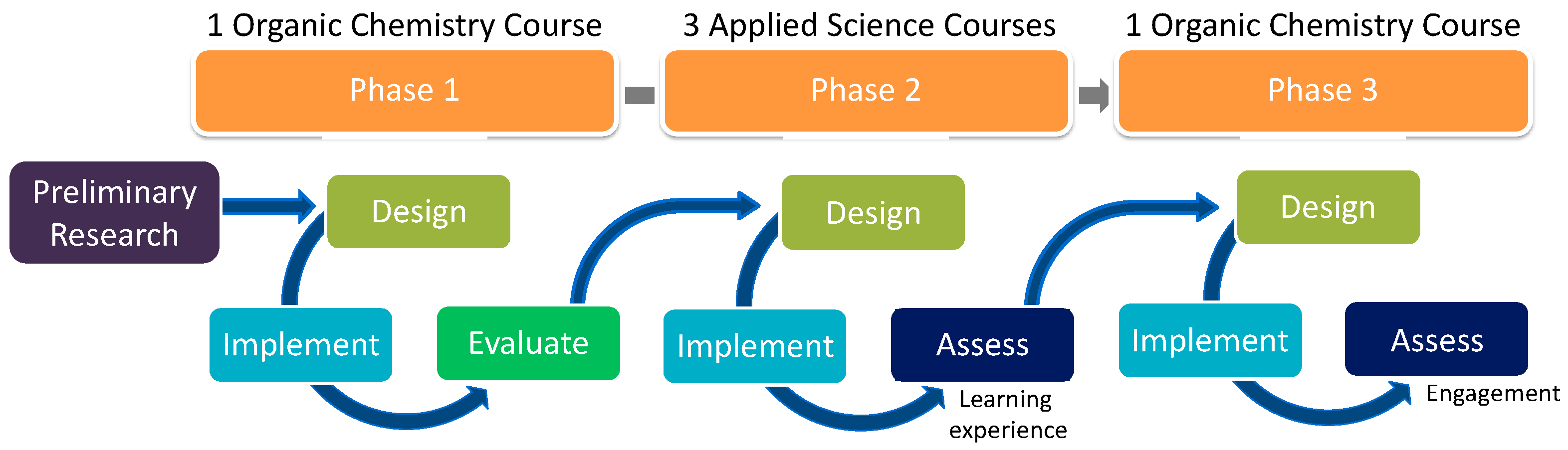
3.1. Phase 1—Prototyping the Design Features
3.2. Phase 2—Applicability of the Design Features
3.3. Phase 3—Student Engagement and Design Features
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, C. Review on Blended Learning: Identifying the Key Themes and Categories. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2017, 7, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Times Higher Education Blended Learning Is Here to Stay, But Which Aspects of Digital Teaching Will Universities Keep? Available online: https://www.timeshighereducation.com/hub/blackboard/p/blended-learning-here-stay-which-aspects-digital-teaching-will-universities-keep (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Ministry of Education Blended Learning to Enhance Schooling Experience and Further Develop Students into Self-Directed Learners. Available online: https://www.moe.gov.sg/news/press-releases/20201229-blended-learning-to-enhance-schooling-experience-and-further-develop-students-into-self-directed-learners (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Hrastinski, S. What Do We Mean by Blended Learning? TechTrends 2019, 63, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, B. The Flipped Classroom: Online Instruction at Home Frees Class Time for Learning. Educ. Next 2012, 12, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cormier, C.; Voisard, B. Flipped Classroom in Organic Chemistry Has Significant Effect on Students’ Grades. Front. ICT 2018, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.J.M.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Togo, K.A.; Chew, J.Y.; Lam, Y.; Fung, F.M. Supporting Social and Learning Presence in the Revised Community of Inquiry Framework for Hybrid Learning. J. Chem. Educ. 2022, 99, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasna, I.W.; Putri, P.A.W. Improving the Quality of Online Chemistry Learning—A Systematic Literature Review. In Improving Assessment and Evaluation Strategies on Online Learning; Routledge: London, UK, 2022; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, P. The Banking Model of Education. In Critical Issues in Education: An Anthology of Readings; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, R.; Dembo, M. The Relationship Between Self-Regulation and Online Learning in a Blended Learning Context. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2004, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, L.; Lan, W.Y.; To, Y.M.; Paton, V.O.; Lai, S.-L. Measuring Self-Regulation in Online and Blended Learning Environments. Internet High. Educ. 2009, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-H. Developing Web-Based Assessment Strategies for Facilitating Junior High School Students to Perform Self-Regulated Learning in an e-Learning Environment. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, G.; Ahmad, R.; Ives, B. Web-Based Virtual Learning Environments: A Research Framework and a Preliminary Assessment of Effectiveness in Basic IT Skills Training. MIS Q. 2001, 25, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, D.R.; Anderson, T.; Archer, W. Critical Inquiry in a Text-Based Environment: Computer Conferencing in Higher Education. Internet High. Educ. 1999, 2, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, D.R.; Vaughan, N.D. Blended Learning in Higher Education; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780787987701. [Google Scholar]
- Garrison, D.R.; Anderson, T.; Archer, W. The First Decade of the Community of Inquiry Framework: A Retrospective. Internet High. Educ. 2010, 13, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Gurvitch, R. Online Education Research Adopting the Community of Inquiry Framework: A Systematic Review. Quest 2020, 72, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, Z.; Garrison, D.R. The Development of a Community of Inquiry over Time in an Online Course: Understanding the Progression and Integration of Social, Cognitive and Teaching Presence. J. Asynchronous Learn. Netw. 2008, 12, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, P.; Bidjerano, T. Community of Inquiry as a Theoretical Framework to Foster “Epistemic Engagement” and “Cognitive Presence” in Online Education. Comput. Educ. 2009, 52, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilis, S.; Yıldırım, Z. Investigation of Community of Inquiry Framework in Regard to Self-Regulation, Metacognition and Motivation. Comput. Educ. 2018, 126, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaugh, J.B.; Cleveland-Innes, M.; Diaz, S.R.; Garrison, D.R.; Ice, P.; Richardson, J.C.; Swan, K.P. Developing a Community of Inquiry Instrument: Testing a Measure of the Community of Inquiry Framework Using a Multi-Institutional Sample. Internet High. Educ. 2008, 11, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Exploring Blended Learning Experiences through the Community of Inquiry Framework. Lang. Learn. Technol. 2020, 24, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Yuan, C.-H. Blended Learning Performance Influence Mechanism Based on Community of Inquiry. Asia Pac. J. Educ. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, K.P.; Richardson, J.C.; Ice, P.; Garrison, D.R.; Cleveland-Innes, M.; Arbaugh, J. Ben Validating a Measurement Tool of Presence in Online Communities of Inquiry. Available online: https://www.e-mentor.edu.pl/artykul/index/numer/24/id/543. (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Díaz, S.R.; Swan, K.; Ice, P.; Kupczynski, L. Student Ratings of the Importance of Survey Items, Multiplicative Factor Analysis, and the Validity of the Community of Inquiry Survey. Internet High. Educ. 2010, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaugh, J.B.; Bangert, A.; Cleveland-Innes, M. Subject Matter Effects and the Community of Inquiry (CoI) Framework: An Exploratory Study. Internet High. Educ. 2010, 13, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, J.J.; Christenson, S.L.; Furlong, M.J. Student Engagement with School: Critical Conceptual and Methodological Issues of the Construct. Psychol. Sch. 2008, 45, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M. Theory of Transactional Distance. In Theoretical Principles of Distance Education; Keegan, D., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1997; pp. 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, A. Disrupting to Driving: Exploring Upper Primary Teachers’ Perspectives on Student Engagement. Teach. Teach. 2020, 26, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flener-Lovitt, C.; Bailey, K.; Han, R. Using Structured Teams to Develop Social Presence in Asynchronous Chemistry Courses. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 2519–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Dobosz, D.; Jeng, A.; Azevedo, R.F.L.; Bosch, N.; Ray, C.; Perry, M. Ask for Help: Online Help-Seeking and Help-Giving as Indicators of Cognitive and Social Presence for Students Underrepresented in Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.W.J.; Ng, Y.N. Effect of Research-Based Blended Learning with Scrum Methodology on Learners’ Perception and Motivation in a Laboratory Course. J. Chem. Educ. 2022, 99, 4102–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonji, G.; Hammoudi Halat, D.; Mourad, N.; Sonji, N.; Mehyou, Z.; Rahal, M. Pharmacy Students’ Perceptions and Satisfaction with Blended Instruction in Quantitative Chemical Analysis Course. Pharm. Educ. 2023, 23, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, H.; Omer, U.; Nazar, Z.; Husband, A. A Study to Investigate the Impact of a Blended Learning Teaching Approach to Teach Pharmacy Law. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2019, 27, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.W.J.; Ng, Y.N. Students’ Perceptions of Asynchronous Lectures Via the Community of Inquiry Framework and Its Relationship with Learning Performance. J. Chem. Educ. 2024, 101, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, T. Educational Design Research: An Introduction. In Educational Design Research—Part A: An Introduction; Plomp, T., Nieveen, N., Eds.; SLO: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 10–51. [Google Scholar]
- van den Akker, J. Principles and Methods of Development Research. In Design Methodology and Developmental Research in Education and Training; van den Akker, J., Nieveen, N., Branch, R., Gustafson, K., Plomp, T., Eds.; Kluwer: Alphen am Rhein, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Blumenfeld, P.C.; Paris, A.H. School Engagement: Potential of the Concept, State of the Evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 2004, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.E.; Gay, L.R. Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Applications, 11th ed.; Pearson Education Ltd.: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, J.J.; Christenson, S.L.; Kim, D.; Reschly, A.L. Measuring Cognitive and Psychological Engagement: Validation of the Student Engagement Instrument. J. Sch. Psychol. 2006, 44, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, J. How Students Create Motivationally Supportive Learning Environments for Themselves: The Concept of Agentic Engagement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 105, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, E.A.; Kindermann, T.A.; Furrer, C.J. A Motivational Perspective on Engagement and Disaffection. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2009, 69, 493–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, C.A. Advancing Achievement Goal Theory: Using Goal Structures and Goal Orientations to Predict Students’ Motivation, Cognition, and Achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 96, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.G. Editorial: Three Types of Interaction. Am. J. Distance Educ. 1989, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenman, M.V.J.; Van Hout-Wolters, B.H.A.M.; Afflerbach, P. Metacognition and Learning: Conceptual and Methodological Considerations. Metacognition Learn. 2006, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phase | Sample Size | Diploma Programme | Course |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44 | Diploma in Medicinal Chemistry | Organic Chemistry |
| 2 | 65 | Diploma in Applied Chemistry | Analytical Chemistry |
| Diploma in Pharmaceutical Science | Pharmacy Practice | ||
| Diploma in Pharmaceutical Science | Pharmacotherapy I | ||
| 3 | 64 | Diploma in Applied Chemistry | Organic Chemistry |
| CoI Presence | Code | Survey Item | Mean a (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive presence (CP) | CP1 | Problems posed increased my interest in course issues. | 3.18 (0.69) |
| CP2 | Course activities piqued my curiosity. | 3.36 (0.69) | |
| CP3 | I felt motivated to explore content related questions. | 3.27 (0.66) | |
| CP4 | I utilized a variety of information sources to explore problems posed in this course. | 3.36 (0.57) | |
| CP5 | Brainstorming and finding relevant information helped me resolve content related questions. | 3.41 (0.62) | |
| CP6 | Online discussions were valuable in helping me appreciate different perspectives. | 3.20 (0.67) | |
| CP7 | Combining new information helped me answer questions raised in course activities. | 3.25 (0.61) | |
| CP8 | Learning activities helped me construct explanations/solutions. | 3.50 (0.55) | |
| CP9 | Reflection on course content and discussions helped me understand fundamental concepts in this class. | 3.55 (0.50) | |
| CP10 | I can describe ways to test and apply the knowledge created in this course. | 3.27 (0.50) | |
| CP11 | I have developed solutions to course problems that can be applied in practice. | 3.30 (0.51) | |
| CP12 | I can apply the knowledge created in this course to my work or other non-class related activities. | 3.45 (0.55) | |
| Social presence (SP) | SP1 | Getting to know other course participants gave me a sense of belonging in the course. | 3.20 (0.73) |
| SP2 | Online or web-based communication is an excellent medium for social interaction. | 2.93 (0.50) | |
| SP3 | I felt comfortable conversing through the online medium. | 3.41 (0.58) | |
| SP4 | I felt comfortable participating in the course discussions. | 3.27 (0.59) | |
| SP5 | I felt comfortable interacting with other course participants. | 3.30 (0.51) | |
| SP6 | I felt comfortable disagreeing with other course participants while still maintaining a sense of trust. | 3.09 (0.71) | |
| SP7 | I felt that my point of view was acknowledged by other course participants. | 3.20 (0.63) | |
| SP8 | Online discussions help me to develop a sense of collaboration. | 3.32 (0.67) | |
| Teaching presence (TP) | TP1 | The instructor clearly communicated important course topics. | 3.77 (0.42) |
| TP2 | The instructor provided clear instructions on how to participate in course learning activities. | 3.73 (0.50) | |
| TP3 | The instructor clearly communicated important due dates/time frames for learning activities. | 3.68 (0.47) | |
| TP4 | The instructor was helpful in guiding the class towards understanding course topics in a way that helped me clarify my thinking. | 3.70 (0.51) | |
| TP5 | The instructor helped to keep course participants engaged and participating in the course learning activities. | 3.75 (0.49) | |
| TP6 | The instructor helped keep the course participants on task in a way that helped me to learn. | 3.80 (0.41) | |
| TP7 | The instructor encouraged course participants to explore new concepts in this course. | 3.61 (0.54) | |
| TP8 | Instructor actions reinforced the development of a sense of community among course participants. | 3.55 (0.63) | |
| TP9 | The instructor provided feedback that helped me understand my strengths and weaknesses relative to the course’s goals and objectives. | 3.50 (0.63) | |
| TP10 | The instructor provided feedback in a timely fashion. | 3.57 (0.62) |
| Mean a (SD) | |
|---|---|
| Cognitive presence | 3.34 (0.48) |
| Social presence | 3.22 (0.45) |
| Teaching presence | 3.67 (0.43) |
| Learning experience | 3.41 b (0.39) |
| CoI Presence | Item Code | Mean a (SD) | Mean b (SD) | LE Mean c (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teaching presence (TP) | TP1 | 3.62 (0.49) | 3.53 (0.67) | 3.31 (0.71) |
| TP2 | 3.55 (0.61) | |||
| TP3 | 3.74 (0.44) | |||
| TP4 | 3.66 (0.57) | |||
| TP5 | 3.57 (0.61) | |||
| TP6 | 3.57 (0.73) | |||
| TP7 | 3.42 (0.86) | |||
| TP8 | 3.35 (0.84) | |||
| TP9 | 3.43 (0.75) | |||
| TP10 | 3.42 (0.81) | |||
| Social presence (SP) | SP1 | 3.29 (0.80) | 3.15 (0.80) | |
| SP2 | 2.95 (0.99) | |||
| SP3 | 3.14 (0.88) | |||
| SP4 | 3.15 (0.71) | |||
| SP5 | 3.34 (0.69) | |||
| SP6 | 3.11 (0.79) | |||
| SP7 | 3.20 (0.77) | |||
| SP8 | 3.02 (0.78) | |||
| Cognitive presence (CP) | CP1 | 3.14 (0.68) | 3.26 (0.66) | |
| CP2 | 3.15 (0.75) | |||
| CP3 | 3.09 (0.70) | |||
| CP4 | 3.22 (0.70) | |||
| CP5 | 3.40 (0.63) | |||
| CP6 | 3.22 (0.70) | |||
| CP7 | 3.34 (0.69) | |||
| CP8 | 3.42 (0.61) | |||
| CP9 | 3.38 (0.55) | |||
| CP10 | 3.29 (0.63) | |||
| CP11 | 3.31 (0.58) | |||
| CP12 | 3.18 (0.68) |
| Engagement | Survey Item | Mean a (SD) | Mean b (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral engagement (BE) | I tried hard to do well in this module. | 3.58 (0.50) | 3.52 (0.43) |
| In this module, I worked as hard as I could. | 3.53 (0.56) | ||
| I attempted the questions in the e-learning lecture. | 3.52 (0.69) | ||
| I paid attention to the e-lecture. | 3.48 (0.53) | ||
| When I studied for this module, I listened very carefully to the e-lectures. | 3.47 (0.62) | ||
| Emotional engagement (EE) | When I study for this module, I felt good. | 2.83 (0.75) | 3.18 (0.51) |
| When I worked on a question during the e-lecture, I am more interested in the content. | 3.03 (0.78) | ||
| The e-lecture and the activities (questions/drag-and-drop interaction) were fun. | 3.33 (0.64) | ||
| I enjoyed learning new things. | 3.31 (0.69) | ||
| When I worked on a question during the e-lecture, I feel more involved in learning. | 3.41 (0.66) | ||
| Cognitive engagement (CE) | I was engaged with the topic while going through the e-lectures. | 3.19 (0.66) | 3.17 (0.45) |
| I put in a lot of effort when I study for this module. | 3.39 (0.66) | ||
| Online learning has improved my learning significantly. | 2.67 (0.78) | ||
| Online learning gives me more time to solve problems and learn at my own pace. | 3.42 (0.64) |
| CoI Presence | CoI Categories | Design Features |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching presence (TP) | Instructional management | Educators arrange the asynchronous lecture content, incorporating a collapsible menu to propose the learning sequence and enable students to monitor their progress in learning (program control). More adept students have the option to learn according to their preferred sequence (learner control). |
| Building understanding | Educators oversee and support the discussion platform, employing interactive activities such as drag-and-drop exercises to actively involve less participative students. | |
| Direct instruction | Educators produce video recordings, segmenting them into concise intervals of 15–20 min per video. These recordings feature voiceover explanations of concepts, supplemented with annotations as needed. | |
| Social presence (SP) | Emotional expression | While this category may not be explicitly featured in the asynchronous lectures, it has the potential to be incorporated into the discussion platform. |
| Open communication | Educators need to establish a secure learning environment, particularly within the discussion platform. All students and teachers should follow general rules and maintain positive online etiquette, characterized by mutual respect and encouraging tones. | |
| Group cohesion | The discussion platform, such as Padlet, is integrated to facilitate interactions between students, and between students and teachers. | |
| Cognitive presence (CP) | Triggering event | At the commencement of the asynchronous lecture, a trigger, such as a brief video or image related to the topic, is incorporated. This trigger serves to captivate students’ attention, pique interest, and evoke a sense of curiosity about the subject, encouraging them to delve deeper into the topic. |
| Exploration | Supplementary resources sourced from the internet are integrated to offer students alternatives for gaining a better understanding and seeking clarification. This inclusion also enables them to broaden their knowledge of the topic. | |
| Integration | After each video, straightforward interactive activities like drag-and-drop, matching, and multiple-choice questions are provided to assist students in consolidating their learning. These activities aim to help students integrate information and knowledge into a cohesive understanding of the concept. | |
| Resolution | At the conclusion of each sub-topic, questions are posed to enable students to apply the concepts they have learned. Students are encouraged to independently attempt these questions before referring to video presentations featuring worked solutions accompanied by voiceover explanations. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ang, J.W.J.; Ng, Y.N.; Lee, L.H.-W.; Yong, J.Y. Exploring Students’ Learning Experience and Engagement in Asynchronous Learning Using the Community of Inquiry Framework through Educational Design Research. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030215
Ang JWJ, Ng YN, Lee LH-W, Yong JY. Exploring Students’ Learning Experience and Engagement in Asynchronous Learning Using the Community of Inquiry Framework through Educational Design Research. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(3):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030215
Chicago/Turabian StyleAng, Jayden Wei Jie, Yin Ni Ng, Lynette Hui-Wen Lee, and Jia Ying Yong. 2024. "Exploring Students’ Learning Experience and Engagement in Asynchronous Learning Using the Community of Inquiry Framework through Educational Design Research" Education Sciences 14, no. 3: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030215
APA StyleAng, J. W. J., Ng, Y. N., Lee, L. H.-W., & Yong, J. Y. (2024). Exploring Students’ Learning Experience and Engagement in Asynchronous Learning Using the Community of Inquiry Framework through Educational Design Research. Education Sciences, 14(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030215







