Instructional Design Models for Pervasive Learning Environment: Bridging Formal and Informal Learning in Collaborative Social Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
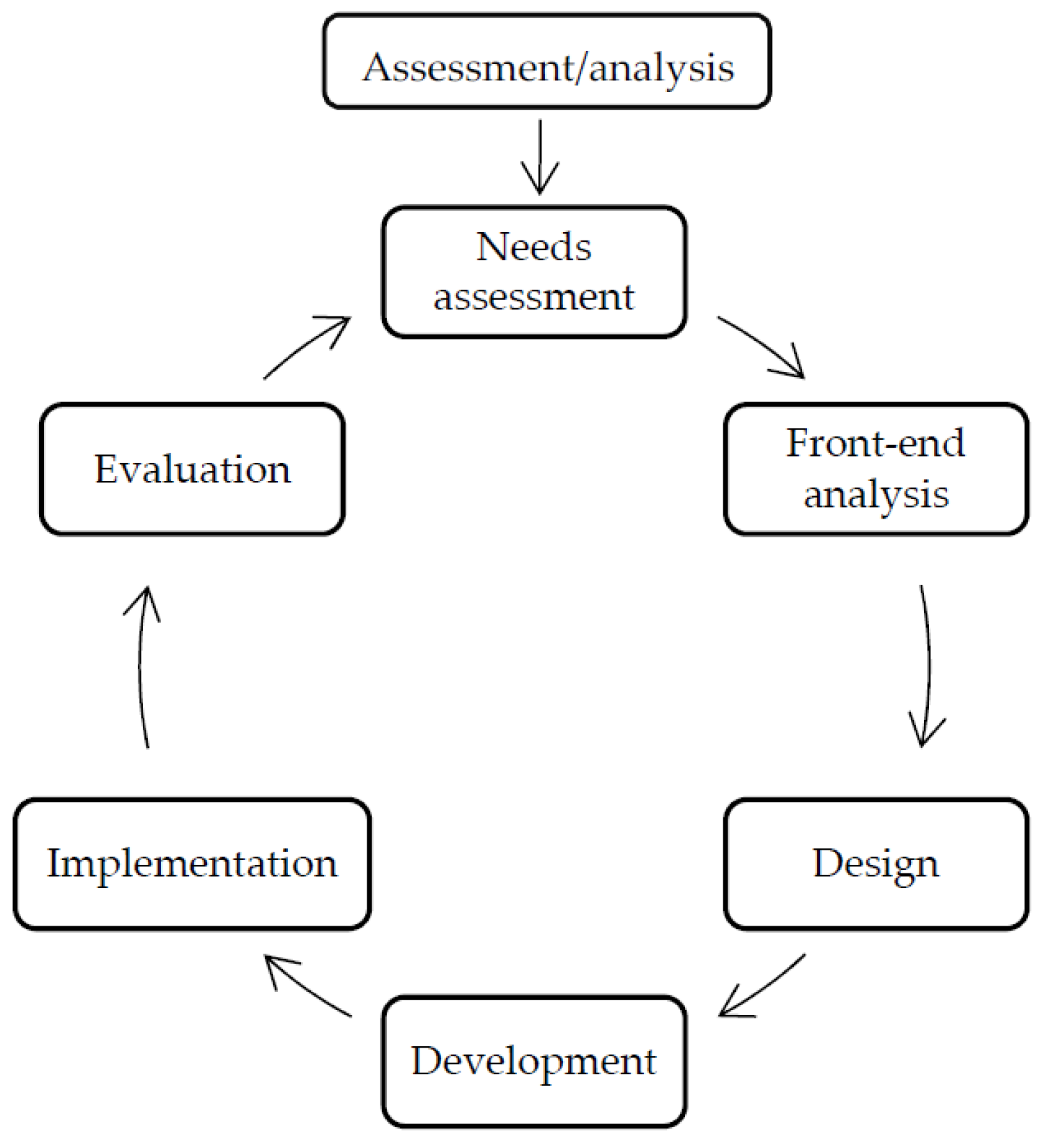
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Model Development
2.4. Product Validation and Trial
2.5. Instrument
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design of Pervasive Learning Model Based on Formal and Informal Collaborative Social Learning in the Course of Learning Material Development
3.2. Final Product
- Learning Activity 1: Introduction to the course
- Learning Activity 2: Position of teaching materials in learning system.
- Learning Activity 3: Basic concepts of teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 4: Types and characteristics of teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 5: Identification of teaching material content.
- Learning Activity 6: Principles of teaching material design.
- Learning Activity 7: Phases for developing teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 8: Mid-semester exam.
- Learning Activity 9: Development of printed/visual teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 10: Development of audio teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 11: Development of video teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 12: Development of multimedia teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 13: Development of electronic/online modules (e-modules/online)
- module/LMS.
- Learning Activity 14: Development of digital student worksheets.
- Learning Activity 15: Evaluation of teaching materials.
- Learning Activity 16: Final semester exam.
3.3. Product Validity
- (1)
- Beginning with a clear outline of learning objectives, students should achieve before presenting the material.
- (2)
- Enriching the material with updates, including the study of artificial intelligence (AI) applications in learning.
- (3)
- Developing content to support student higher-order thinking skills (HOTS).
- (4)
- Prompting the “offering constructive ideas” phase to be more concrete by adding a real action plan in line with social collaborative learning and current educational trends, such as problem-based learning (PBL) and project-based learning (PjBL).
- (5)
- Incorporating features to facilitate interaction between lecturers and students in each activity.
- (6)
- Ensuring the relevance of classroom learning to daily life and the professional world.
- (1)
- Offering diverse learning sources and multimedia to accommodate different student preferences and learning styles.
- (2)
- Increasing the number of informal learning activities by including a wider variety of practitioners and experts.
- (3)
- Providing open access features to enable students to search for additional references, allowing students to compare materials on the platform.
- (4)
- Adding a tutoring service feature for interaction between teachers and students.
- (5)
- Including a feature for tracking student learning progress.
- (6)
- Adding a “display ongoing score” menu for students to monitor learning progress.
- (1)
- The use of LMS and various features, such as forums, chats, and quizzes, greatly supported collaborative learning.
- (2)
- More learning activities outside the classroom using case methods were suggested to apply knowledge in different contexts.
- (3)
- P-learning material presentation was highly structured and easy to understand, facilitating independent learning.
- (4)
- Learning became more flexible as the course could be accessed anytime and anywhere.
- (5)
- Assignments were clearly described, aiding completion.
- (6)
- Group assignments stimulated students to exchange experiences, complement each other, and collaborate.
- (7)
- Group projects allowed students to apply the learned theories and knowledge learned, and
- (8)
- This course was user-friendly.
- (1)
- Provide a brief overview of the learning plan, including objectives, resources, and activities for each stage.
- (2)
- Adding practical applications of AI in teaching materials development.
- (3)
- HOTS assignments were introduced, requiring critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity through case studies and team-based projects.
- (4)
- Additional chat features and online discussion forums were added to facilitate interaction between lecturers and students.
- (5)
- A variety of media elements and learning resources, such as text, images, sound, animation, video, and multimedia, were incorporated.
- (6)
- Expert and practitioner-sharing activities were added.
- (7)
- Experience points (XP) and progress bar features were introduced in the P-learning courses.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations
- (1)
- The developed learning model should be implemented among student groups at universities enrolled in courses focused on teaching material development.
- (2)
- For students using this learning model for the first time, lecturers should guide the use despite being designed to offer flexible learning opportunities.
- (3)
- The model design should be disseminated through various channels, such as academic seminars organized by universities, training sessions on developing learning media, collaboration with educational institutions, and other forums to ensure wider adoption and usage, particularly in teaching materials studies.
- (4)
- Efforts to enhance pervasive learning should focus on optimizing the variety of presentation methods.
- (5)
- Further research should be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of this model in enhancing student creativity and innovation skills. This was critical for the twenty-first century using classroom action and experimental research on a broader range of participants.
7. Limitations
- (1)
- The application required the use of a computer or mobile device.
- (2)
- Adequate internet access was necessary.
- (3)
- The model was limited to teaching material development content.
- (4)
- Students as the subjects of this research only come from state and private universities in Indonesia.
- (5)
- Effectiveness testing was not conducted.
- (6)
- The evaluation in this research did not extend to the impact evaluation stage (long term).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
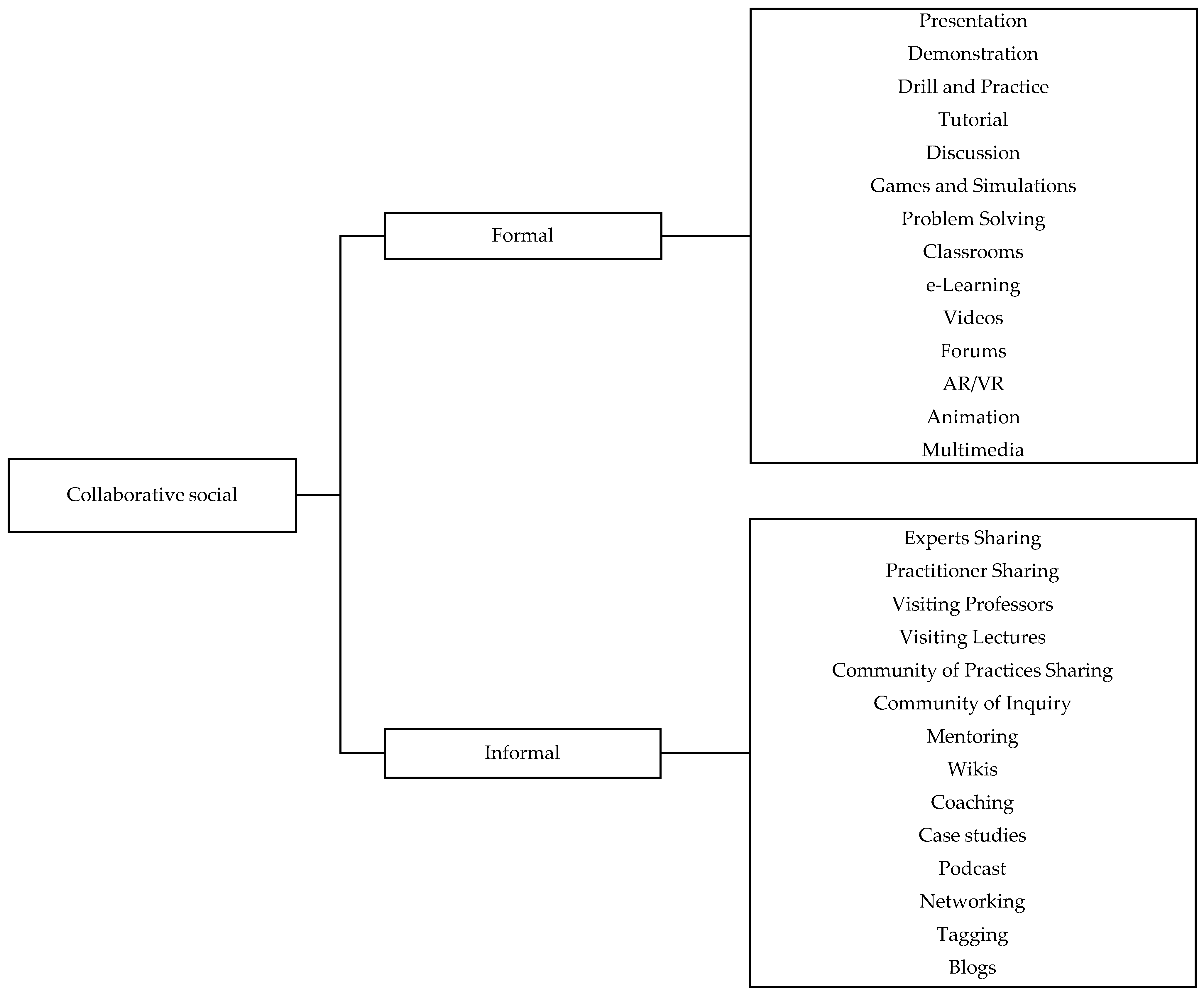
| Presentations | : | Method of expressing ideas, concepts, and feelings in front of students by one or more lecturers by including a script of teaching materials or not. |
| Demonstrations | : | Method used to show a process or how an object works related to the subject matter. |
| Drills and practice | : | Learning method that focuses on repetition and practice to strengthen certain skills or knowledge. |
| Tutorials | : | Learning method that includes direct and personal interaction between tutors and students, usually in small groups or one-on-one. This method aims to provide more in-depth and personal guidance, customized to the needs of individual students to improve understanding and skills. |
| Discussions | : | Learning method that includes active interaction between participants to exchange information, ideas, and views on a particular topic. |
| Games and simulations | : | Method used to model, analyze, and solve problems through real-world representations in the form of games or simulations. |
| Problem-solving | : | The process of systematically identifying and solving problems includes several phases designed to understand the problem, find possible solutions, and implement those solutions. |
| Classrooms | : | Classroom teaching methods with various strategies used by educators to deliver subject matter, facilitate learning, and increase student engagement. |
| e-Learning | : | An educational method that uses electronic and digital technology to provide and support teaching and learning. It allows students and instructors to interact, access learning materials, and conduct educational activities through the Internet or other electronic devices. |
| Videos | : | A method of learning and communication that utilizes video media as the primary tool. This method is used to communicate information, teach skills, or entertain through visuals and audio. |
| Forums | : | An online platform where students can interact, discuss, and share information on a variety of topics. Forums usually consist of several subforums, each focused on a specific topic. Students can create posts, reply to other people’s posts, and participate in current discussions. |
| AR/VR | : | Technologies are changing how interaction is conducted with the digital and physical world. AR is a technology that adds digital elements, such as images, sounds, or text to the real world. VR is a technology that completely replaces the real world with a virtual world generated by a computer. |
| Animations | : | A tool or method that uses animation to deliver educational material. This animation can be in the form of moving images, animated videos, or interactive simulations designed to help students understand complex concepts or processes more easily and enjoyably. |
| Multimedia | : | The use of various types of media, such as text, images, audio, video, animation, and interactivity, to deliver learning materials. The main objective is to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of the teaching and learning process by providing multiple ways to understand and absorb information. |
| Experts sharing | : | The process by which experts in a particular field share knowledge, experience, and skills with others. This can be carried out through various methods, such as presentations, seminars, webinars, podcasts, articles, videos, and online discussions. |
| Practitioner sharing | : | A method for sharing knowledge, ideas, experiences, or skills from an individual, department, organization, agency, or company. This method can improve course knowledge, think about teaching strategies in different ways, and learn new ideas to try in the classroom. The type of collaborative activity also increases innovation in the classroom and builds self-confidence. |
| Visiting professors | : | Professors who visit a university or college to teach, give lectures, or conduct research on a topic that the host deems valuable. |
| Visiting lectures | : | Lectures include external speakers who visit a university or college. The speakers can be practitioners, authorities, or experts in a particular field to expand the knowledge and insight of lecturers and students by bringing new perspectives and outside experiences. |
| Community of practices sharing | : | A group of individuals with a common interest or profession who come together to engage in collective learning, knowledge sharing, and networking. |
| Community of inquiry | : | A group of individuals engaged in the process of empirical or conceptual investigation into a problem. |
| Mentoring | : | The process by which someone with more experience helps others learn new knowledge. |
| Wikis | : | A website (or other collection of hypertext documents) that allows users to add to or edit the content of the site. The term can also refer to collaborative software used to create websites. |
| Coaching | : | The process of coaching individuals, groups, or organizations to achieve optimal performance. This process is carried out in a planned, orderly, and directed manner to improve knowledge, attitudes, and skills in handling assigned responsibilities as well as overcoming obstacles and barriers. |
| Case studies | : | The process of investigating or examining in depth, in detail, and in detail a particular event that occurs. |
| Podcast | : | Audio content is specifically designed for learning purposes that focuses on delivering information, knowledge, and insights relevant to a particular topic. |
| Networking | : | A method that uses networks as a supporting tool in the teaching and learning process. |
| Tagging | : | The process of labeling or marking content that is related to certain keywords or topics. |
| Blogs | : | A teaching strategy or method that uses blogs as the main tool or platform for delivering learning materials, interacting with students, and facilitating online learning. |
References
- Deguchi, A.; Hirai, C.; Matsuoka, H.; Nakano, T.; Oshima, K.; Tai, M.; Tani, S. What is society 5.0. In Society 5.0; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieser, J.C.T.; Hilty, L.M. Conceptualizing the impact of information and communication technology on individual time and energy use. Telemat. Inform. 2020, 49, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R. The Globotics Upheaval: Globalization, Robotics, and the Future of Work; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aquilani, B.; Piccarozzi, M.; Abbate, T.; Codini, A. The role of open innovation and value co-creation in the challenging transition from industry 4.0 to society 5.0: Toward a theoretical framework. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.C.; Wechsler, S.M. Creativity and innovation: Skills for the 21st century | Criatividade e inovação: Competências para o século XXI. Estud. Psicol. Camp. 2018, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledow, R.; Frese, M. A Dialectic Perspective on Innovation: Conflicting Demands, Multiple Pathways, and Ambidexterity University of Amsterdam. Perspective 2009, 2, 305–337. [Google Scholar]
- Cropley, D.H.; Kaufman, J.C.; Cropley, A.J. Measuring creativity for innovation management. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2011, 6, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.; Madgavkar, A. The world at work: Matching skills and jobs in Asia. Prospects 2014, 44, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards-Schachter, M.; García-Granero, A.; Sánchez-Barrioluengo, M.; Quesada-Pineda, H.; Amara, N. Disentangling competences: Interrelationships on creativity, innovation and entrepreneurship. Think. Skills Creat. 2015, 16, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, L.E.; Perez, P.J.; Morillas, F.G. Higher education and the development of competencies for innovation in the workplace. Manag. Decis. 2012, 50, 1634–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, M.; Arifin, Z.; Mutohhari, F.; Nurtanto, M. Competency of Digital Technology: The Maturity Levels of Teachers and Students in Vocational Education in Indonesia. J. Educ. Technol. 2021, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, S. Pre-service education for primary school English teachers in Indonesia: Policy implications. Asia Pac. J. Educ. 2016, 36, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S. Online Learning: A Panacea in the Time of COVID-19 Crisis. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 2020, 49, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Kusumaningrum, B.; Yulia, Y.; Widodo, S.A. Challenges During the Pandemic: Use of E-Learning in Mathematics Learning in Higher Education. Infin. J. 2020, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusnilita, N. The Impact of Online Learning: Student’s Views. Eternal Engl. Teach. J. 2020, 11, 393297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susiani, K.; Dharsana, I.K.; Suartama, I.K.; Suranata, K.; Yasa, I.N. Student Motivation and Independent Learning in Social Studies, English, and Math: The Impact of the Classroom Environment. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2022, 5, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, M.; Amirullah, A.; Safiah, I.; Ridha, S.; Suartama, I.K. Development of the CPOL design to improve the ability to develop teaching materials. Cypriot J. Educ. Sci. 2022, 17, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M. Online learning amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Students perspectives. J. Pedagog. Res. 2020, 1, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tight, M. Reflection: An assessment and critique of a pervasive trend in higher education. Eur. J. High. Educ. 2024, 14, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjällander, S.; Åkerfeldt, A.; Mannila, L.; Parnes, P. Makerspaces Across Settings: Didactic Design for Programming in Formal and Informal Teacher Education in the Nordic Countries. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2018, 34, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayildurai, R.; Karthik, K.; Ashokkumar, R.; Daniel, S. Teaching Methodologies for Engaging Generation Z Learners: Strategies, Challenges, and Implications. In Transforming Education for the 21st Century-Innovative Teaching Approaches; OrangeBooks Publication: Bhilai, India, 2024; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- Pontefract, D. Flat Army: Creating a Connected and Engaged Organization; Elevate Publishing: Boise, ID, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, T.; Ehmke, T. Informal and formal lesson planning in school internships: Practices among pre-service teachers. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2023, 132, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.G.L.; Evans, M.A.; Carey, C.; Schnittka, C.G. Youth appropriation of social media for collaborative and facilitated design-based learning. Comput. Human. Behav. 2015, 50, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeow, K.Y.-H. Enhancing Student Thinking Through Collaborative Learning; ERIC Clearinghouse on Reading, English, and Communication, Indiana University: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Suartama, I.K.; Triwahyuni, E.; Suranata, K. Mastering knowledge construction skills through a context-aware ubiquitous learning model based on the case method and team-based projects. Int. J. Educ. Pract. 2024, 12, 1094–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Mildenberger, T. Facilitating flexible learning by replacing classroom time with an online learning environment: A systematic review of blended learning in higher education. Educ. Res. Rev. 2021, 34, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suartama, I.K.; Sudarma, I.K.; Sudatha, I.G.W.; Sukmana, A.I.W.I.Y.; Susiani, K. Student engagement and academic achievement: The effect of gamification on case and project-based online learning. J. Educ. Learn. 2024, 18, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, S.; Schwemmle, M. Teaching university students through technology-mediated experiential learning: Educators’ perspectives and roles. Comput. Educ. 2023, 207, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.A.; Watson, S.; Watson, W. Learning Technology Models that Support Personalization within Blended Learning Environments in Higher Education. TechTrends 2021, 65, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M. Transforming Universities with Digital Distance Education: The Future of Formal Learning; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, A.L.; Klein, J.D. Facilitating informal learning at work. TechTrends 2020, 64, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, P.; Boratto, L.; Carta, S.; Fenu, G. UP SCHOOL: Introduction of Pervasive Learning Technologies to Enhance Classic Educational Models. Bull. IEEE Tech. Comm. Learn. Technol. 2015, 17, 10–13. Available online: http://tc.computer.org/tclt/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2018/01/Garau.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Kay, J. Grand Challenges for Pervasive Technology to Transform Pervasive Education. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2022, 21, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, D.; Bogdanović, Z.; Petrović, L.; Mitrović, S.; Labus, A. Empowering learning process in secondary education using pervasive technologies. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 31, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, R.C.; Klein, J.D. Design and Development Research; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Richey, R.C. Validating instruction design and development models. In Innovations in Instructional Technology: Essays in Honor of M. David Merrill; Spector, J.M., Wiley, D.A., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.W.; Owens, D.L. Multimedia Based Instructional Design: Computer Based Training Web Based Training Distance Broadcast Training, Performance Based Solutions, 2nd ed.; Pfeiffer: San Fransisco, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Suartama, I.K.; Setyosari, P.; Sulthoni, S.; Ulfa, S. Development of Ubiquitous Learning Environment Based on Moodle Learning Management System. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. IJIM 2020, 14, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.F.; Hess, R.D. Instructional Software: Principles and Perspectives for Design and Use; Wadsworth Publishing Company: Belmont, TN, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Debattista, M. A comprehensive rubric for instructional design in e-learning. Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol. 2018, 35, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.; Timulak, L. Essentials of Descriptive-Interpretive Qualitative Research: A Generic Approach; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sukardjo. Evaluasi Pembelajaran: Buku Pegangan Kuliah [Learning Evaluation: Lecture Handbook]; PPs Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: Sleman, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schusler, T.M.; Decker, D.J.; Pfeffer, M.J. Social learning for collaborative natural resource management. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2003, 16, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvani, A.; Fini, A.; Pettenati, M.; Sarti, L.; Masseti, M. Design of Collaborative Learning Environments: Bridging the gap between CSCL theories and Open Source Platforms. J. E-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 2006, 2, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, P.; Guercio, A.; Stanganelli, L.; Arndt, T. Maresca Experiences in Collaborative Learning. J. E-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 2014, 10, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijon, M.; Nordmo, I.; Tieva, Å.; Troelsen, R. Formal learning spaces in Higher Education—A systematic review. Teach. High. Educ. 2024, 29, 1460–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degner, M.; Moser, S.; Lewalter, D. Digital media in institutional informal learning places: A systematic literature review. Comput. Educ. Open 2022, 3, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decius, J.; Hein, J. Motivated to learn? Investigating the link of achievement goals and informal workplace learning of lecturers in higher education. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 2024, 35, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallán, J.G.; Diaz-Vicario, A.; Barrera-Corominas, A.; Duran-Bellonch, M. Teachers’ informal learning and organizational learning in Spain. J. Workplace Learn. 2022, 34, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, R. The Problem of Expertise in Knowledge Societies. Minerva 2017, 55, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. Practice Partnerships in Education: Benefits for Researchers and Practitioners. Alta. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 67, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho-Filho, M.A.; Tio, R.A.; Steinert, Y. Twelve tips for implementing a community of practice for faculty development. Med. Teach. 2020, 42, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalavra, E.; Papanikolaou, K. A wiki-based framework for collaborative learning design in teacher education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 6407–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, L. Podcasts in higher education: Teacher enthusiasm increases students’ excitement, interest, enjoyment, and learning motivation. Educ. Stud. 2021, 47, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Arribas, R.; Herrero-Gutiérrez, F.J.; Frutos-Esteban, F.J. Podcasting: The Radio of Generation Z in Spain. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjaya, D.B.; Suartama, I.K.; Suastika, I.N. The Effect of the Conflict Resolution Learning Model and Portfolio Assessment on the Students’ Learning Outcomes of Civic Education. Int. J. Instr. 2022, 15, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Koehler, A.A. Online case-based discussions: Examining coverage of the afforded problem space. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2014, 62, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Bozic, C.; Gretter, S.; Nauman, E. Benefits and challenges of implementing case-based instruction: A student perspective. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2015, 31, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Aravind, B.R.; Bhuvaneswari, G. Utilizing Blogs on ESL learners’ vocabulary learning through social constructivist theory: A descriptive study. MethodsX 2023, 10, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.; Pachler, N. Online people tagging: Social (mobile) network (ing) services and work-based learning. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 43, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, T.; Antonczak, L. Implementing a mobile social media framework for designing creative pedagogies. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Dennen, V.P.; Mei, L. Influential factors for mobile learning acceptance among Chinese users. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2017, 65, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suartama, I.K.; Triwahyuni, E.; Suranata, K. Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.D.; Brant-Ribeiro, T.; Mendonça, I.E.S.; Mendes, M.M.; Dorça, F.A.; Cattelan, R.G. Social and collaborative interactions for educational content enrichment in ULEs. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Suartama, I.K.; Setyosari, P.; Ulfa, S.; Yunus, M.; Sugiani, K.A. Ubiquitous Learning vs. Electronic Learning: A Comparative Study on Learning Activeness and Learning Achievement of Students with Different Self-Regulated Learning. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2021, 16, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
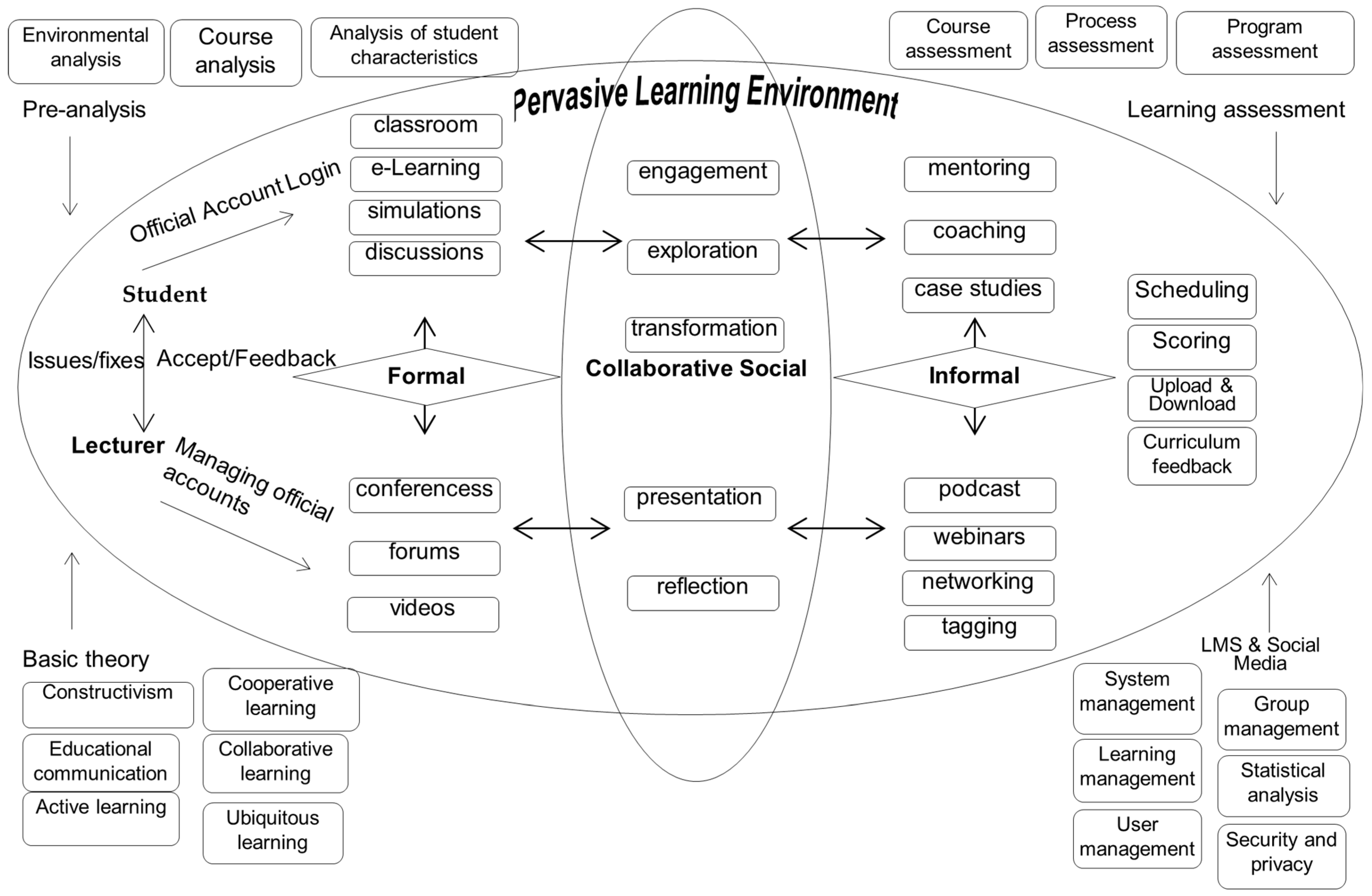
| No. | Phases | Activity | Targeted Results and Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Analysis |
|
|
| 2. | Design |
|
|
| 3. | Development | Creating PLE system, this phase consists of:
|
|
| 4. | Implementation | Organizing/implementing/trialing pervasive learning model designs oriented toward formal and informal collaborative social learning in the subject of developing teaching materials. | Trial results report. |
| 5. | Evaluation | Conducting student evaluations and product revisions. | Product feasibility document. |
| Aspects Assessed | Indicators | |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Aspect |
|
|
| Material Aspect |
|
|
| Language Aspect |
|
|
| Main Standards | Specific Standards | |
|---|---|---|
| Course opening |
|
|
| Instructional resources for teaching and learning |
|
|
| Interaction and community |
|
|
| Learner support |
|
|
| Technology design |
|
|
| Course closing |
|
|
| Assessment of learning |
|
|
| Instructional design cycle |
|
|
| Value/Category | Score | |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | Calculation | |
| Very good | X > + 1.80 Sbi | X > 4.21 |
| Good | + 0.60 Sdi < X ≤ + 1.80 Sdi | 3.40 < X ≤ 4.21 |
| Quite good | − 0.60 Sdi < X ≤ + 0.60 Sdi | 2.60 < X ≤ 3.40 |
| Not good | − 1.80 Sdi < X ≤ − 0.60 Sdi | 1.79 < X ≤ 2.60 |
| Bad | X ≤ − 1.80 Sdi | X ≤ 1.79 |
| Phase | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | : | Students answer the trigger questions about the material or topic to be examined. |
| Exploration | : | Students explore initial ideas by examining learning material connection. |
| Transformation | : | Students analyze, synthesize, and discuss the material or topic being examined and connect the material or topic being explored to daily living. |
| Presentation | : | Students present the results. |
| Reflection | : | Students prepare the results summary of the analysis, identifying strengths and weaknesses, as well as offering constructive ideas. |
| Topic | Type of Teaching Materials | Pervasive Learning Environment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collaborative Social Learning Syntax | Formal | Informal | ||
| Position of teaching materials in learning system | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Question and answer in Classrooms | |
| Exploration | Study learning material link at P-learning | |||
| Transformation | Case examination | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Basic concepts of teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Presentation | |
| Exploration | Discussion forum | |||
| Transformation | Problem-solving | |||
| Presentation | Videos | |||
| Reflection | Sharing/tagging in social media | |||
| Types and characteristics of teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) Multimedia (exe) | Engagement | Demonstration | |
| Exploration | Experts sharing | |||
| Transformation | Case method | |||
| Presentation | Podcast | |||
| Reflection | Wikis | |||
| Identification of teaching material content | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Question and answer in Classrooms | |
| Exploration | Study learning material link at P-learning | |||
| Transformation | Case examine | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Principles of teaching material design | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Presentation | |
| Exploration | Problem-solving | |||
| Transformation | Case examine | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Wikis | |||
| Phases in developing teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Question and answer in Classrooms | |
| Exploration | Study learning material link at P-learning | |||
| Transformation | Case examine | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Evaluation of teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Presentation | |
| Exploration | Study learning material link at P-learning | |||
| Transformation | Case examine | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Development of printed or visual teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Expert sharing | |
| Exploration | Practitioner sharing | |||
| Transformation | Team-based project | |||
| Presentation | Videos | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Development of audio teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Demonstration | |
| Exploration | Practitioner sharing | |||
| Transformation | Coaching | |||
| Presentation | Podcast | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Development of video teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Demonstration | |
| Exploration | Practitioner sharing | |||
| Transformation | Coaching Team-based project | |||
| Presentation | Videos | |||
| Reflection | Sharing/tagging in social media | |||
| Development of multimedia teaching materials | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Demonstration | |
| Exploration | Practitioner sharing | |||
| Transformation | Coaching Team-based project | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Sharing/tagging in social media | |||
| Development of electronic/online modules (e-modules/online modules/LMS) | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Demonstration | |
| Exploration | Practitioner sharing | |||
| Transformation | Mentoring Community of inquiry | |||
| Presentation | Videos | |||
| Reflection | Blogs | |||
| Development of digital student worksheets | Document (pdf) Presentation (ppt) Video (mp4) | Engagement | Question and answer in Classrooms | |
| Exploration | Visiting professors | |||
| Transformation | Mentoring Community of inquiry | |||
| Presentation | Community of practices sharing | |||
| Reflection | Sharing/tagging in social media | |||
| Assessment Aspects | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Aspect | 4.33 | Very good |
| Material Aspect | 4.29 | Very good |
| Language Aspect | 4.35 | Very good |
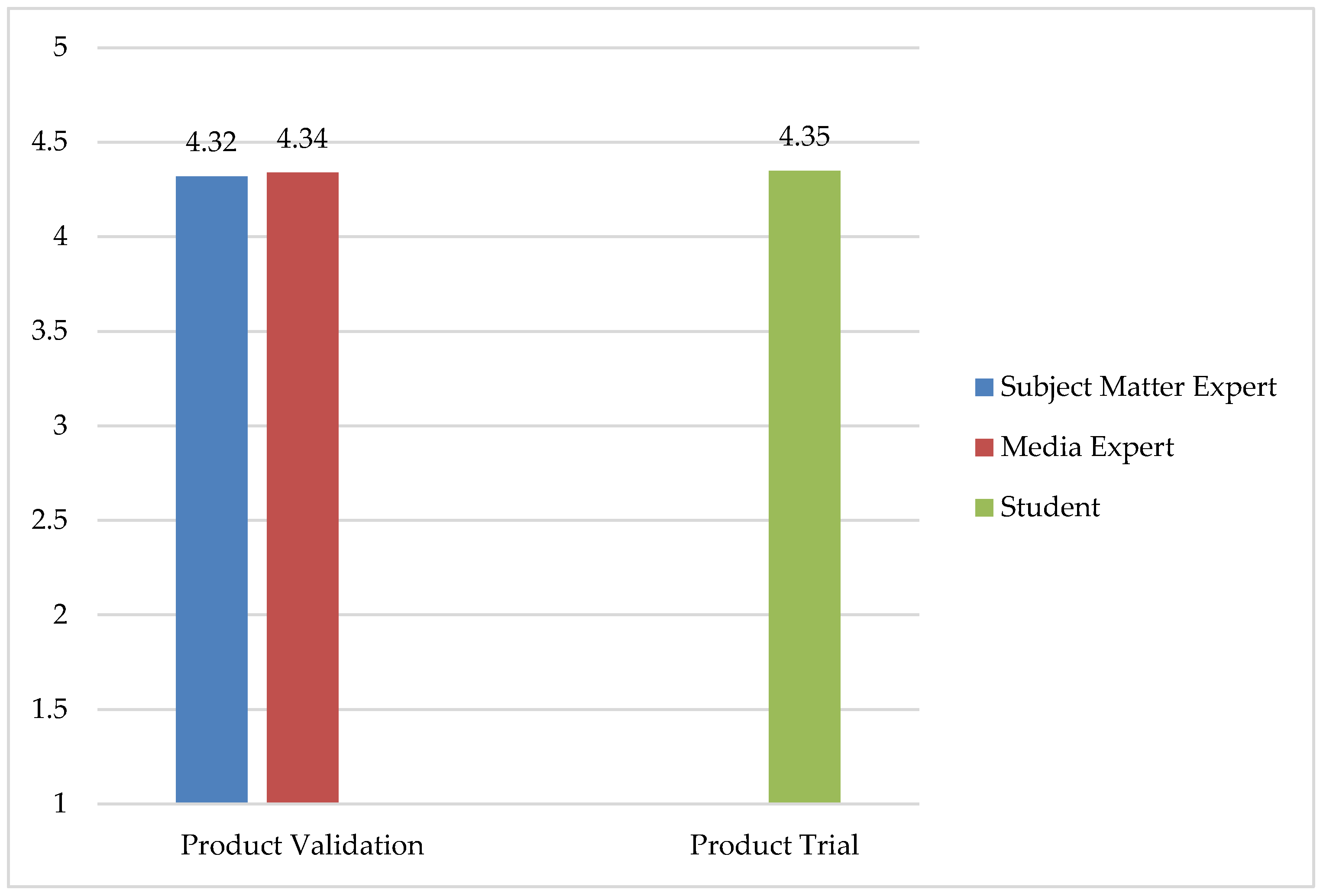
| Overall Average Score | 4.32 | Very good |
| Assessment Aspects | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Opening | 4.40 | Very good |
| Learning resources | 4.36 | Very good |
| Interaction and communication | 4.31 | Very good |
| Student/learner support | 4.30 | Very good |
| Technology design | 4.37 | Very good |
| Course closing | 4.28 | Very good |
| Assessment | 4.30 | Very good |
| Learning cycle | 4.42 | Very good |
| Overall Average Score | 4.34 | Very good |
| Assessment Aspects | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Material Aspect | 4.32 | Very good |
| Learning Aspect | 4.38 | Very good |
| Language Aspect | 4.38 | Very good |
| Opening | 4.40 | Very good |
| Learning resources | 4.35 | Very good |
| Interaction and communication | 4.38 | Very good |
| Student/learner support | 4.32 | Very good |
| Technology design | 4.29 | Very good |
| Course closing | 4.39 | Very good |
| Assessment | 4.39 | Very good |
| Learning cycle | 4.34 | Very good |
| Overall Average Score | 4.35 | Very good |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suartama, I.K.; Yasa, I.N.; Triwahyuni, E. Instructional Design Models for Pervasive Learning Environment: Bridging Formal and Informal Learning in Collaborative Social Learning. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14121405
Suartama IK, Yasa IN, Triwahyuni E. Instructional Design Models for Pervasive Learning Environment: Bridging Formal and Informal Learning in Collaborative Social Learning. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14121405
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuartama, I Kadek, I Nyoman Yasa, and Eges Triwahyuni. 2024. "Instructional Design Models for Pervasive Learning Environment: Bridging Formal and Informal Learning in Collaborative Social Learning" Education Sciences 14, no. 12: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14121405
APA StyleSuartama, I. K., Yasa, I. N., & Triwahyuni, E. (2024). Instructional Design Models for Pervasive Learning Environment: Bridging Formal and Informal Learning in Collaborative Social Learning. Education Sciences, 14(12), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14121405







