Abstract
Parental engagement is of interest to teachers, school leaders, researchers, and policy makers as a key driver of pupil outcomes. Existing evidence suggests that parental engagement with learning in the home is most effective, but English schools often prioritise school-based events. However, the move to home-learning due to COVID-19 required parents and teachers to play different roles in relation to learning and in relation to each other. Little is known about how this has affected teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement. This mixed-methods, longitudinal case study examined whether teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement changed during COVID-19. Data was gathered from teachers at one large English primary school using interviews (n = 9) and questionnaires (n = 16). Data from before and after the school closures was compared. Teachers reported that parental engagement had become increasingly digital, flexible, and wellbeing-focussed during the school closures. However, teachers were pessimistic about the likelihood of retaining any benefits and their future plans remained focussed on school-based parental engagement events. Whilst school closures resulted in a temporary positive shift towards partnerships and family-centric parental engagement, teachers now need time and training to embed these changes. Without this, some of the potential benefits of the home-learning period may be lost.
1. Introduction
Parental engagement is an umbrella term which encompasses “any parental attitudes, behaviours, style, or activities that occur within or outside the school setting to support children’s academic and/or behavioural success” [1] (p. 2). It is often used interchangeably with the terms ‘parent involvement’, ‘parent participation’ and ‘family-school partnerships’ [2]. Parental engagement was chosen as our preferred term because it is widely recognised in the English school context. Parental engagement has attracted significant attention from researchers, policymakers and practitioners alike because it has been linked to improvements in behaviour [3], attendance [4], self-regulation [5], and multiple measures of academic achievement [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Over a student’s school career, strong parental engagement equates to 2–3 years of additional learning [12]. For primary school pupils, parental engagement may be more impactful than socioeconomic status [13] or school quality [14]. However, not all forms of parental engagement are equally effective. There is growing consensus that effective parental engagement tends to be family-centric and rooted in the home [14,15,16,17,18]. By contrast, school-based parental engagement (such as attending information session or volunteering in school) does not consistently raise attainment [19,20,21]. As a result, school leaders should aim to support parental engagement with learning beyond the school gates [22].
Despite the weight of evidence supporting a move away from school-centric definitions of parental engagement [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21], before the COVID-19 pandemic teachers appeared to “only value those efforts by parents that take place within the physical confines of the school” [23] (p. 251). Teachers tended to view parental engagement as parents supporting the school, which risks alienating some parents, including those who have had negative school experiences or do not speak English confidently [24,25]. This suggests that teachers and school leaders may not have been using the most effective conceptualisation of parental engagement and may therefore have been misdirecting time and resources. This apparent mismatch, between the definitions supported by research and those being used by practitioners in English schools, may be attributable to a lack of training. Just 10% of UK teachers have received any training in relation to parental engagement [26].
The COVID-19 pandemic is likely to have affected teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement. Parents and teachers were required to play different roles in relation to learning and in relation to each other, with children around the world learning from home for months at a time [27]. In England, schools were ordered to close from 20 March 2020, with most pupils not returning until September 2020. Mass school closures in England returned in January 2021, with schools reopening from 8 March 2021. During the school closures, children were expected to continue their learning remotely. Almost all pupils in England were provided with asynchronous remote learning tasks by their teachers (e.g., pre-recorded videos, online activities, or worksheets), with approximately half of pupils also receiving online real-time teaching [28]. Schools in England maintained communication with parents via emails or texts (86%), the school website (80%), phone or video calls (69%) and home visits (47%) [29]. To date, little research attention has been paid to how teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement may have been affected by the unprecedented school closures during COVID-19.
These periods of home-learning were challenging for parents and teachers alike. In the context of the COVID-19 school closures, home-learning was usually defined in relation to the completion of formal schoolwork, either online or offline [30]. However, we also acknowledge the informal learning that took place at home during this time [31]. In a study of over 21,000 Portuguese parents, reported difficulties included juggling home-learning with remote working (24%), tiredness and mental health (20%), lack of time (16%), lack of knowledge (13%), and balancing the needs of several children (9%) [32]. Meanwhile, a survey of over 7500 German parents found that parental stress had a negative impact on parents’ ability to engage with their children’s education at home [33]. In Saudi Arabia too, parents were forced to play new roles in relation to learning, but most did not enjoy the teaching role forced on them during the COVID-19 school closures [34]. For teachers, uncertainty and burnout had a negative impact on mental health and wellbeing during the pandemic [35]. Even experienced teachers suddenly found themselves feeling technologically and pedagogically unprepared for online teaching [36,37].
However, some benefits have also been identified. Evidence from Italy suggests that fathers may have taken on more educational responsibility during home-learning [38], though this may have varied between countries, with teachers in Israel reporting low engagement from fathers during the school closures [39]. It has also been suggested that the COVID-19 pandemic enabled more authentic parent-teacher partnerships, with both sides gaining knowledge of the others’ realities [40]. Large-scale survey evidence from China suggests that parental engagement was positively correlated with students’ engagement during remote learning [41]. Consistent with the pre-pandemic evidence, the correlation between parental engagement and pupil outcomes was stronger when parental engagement was measured in relation to parent-child communication compared to parent-teacher communication. Meanwhile, surveys of teachers, parents, and pupils in Norway have indicated that parental engagement with learning increased during periods of home-learning [42]. Across all year groups, parents reported increased knowledge of their children’s learning, with over half feeling better-equipped to support with schoolwork in future. Most parents and teachers reported that the parent-teacher relationship was strengthened by increased communication and that their digital skills had improved. School leaders indicated that the use of technology and increased communication with parents were things they intended to maintain beyond the pandemic. Similarly, teachers in the USA identified an increased sense of agency and increased recognition of their role in empowering parents [43]. However, none of these studies collected longitudinal data.
Longitudinal studies of families in England revealed that parents spent an average of 2.2 h per day assisting with home-schooling (e.g., English and Maths activities) and a similar amount of time each day on other parent-child activities (e.g., playing games or painting together) during the COVID-19 school closures [31]. However, there was substantial variation, with parents of primary-aged children spending nearly 2 h more than those with secondary-aged children. This primary/secondary school divide is consistent with the perceptions of 1800 teachers surveyed by Lucas et al. [29]. They found that 56% of primary school teachers reported strong parental engagement with learning during the first set of English school closures, compared to 48% of secondary teachers. This continues pre-pandemic trends whereby parents of secondary school children tend to have less engagement with their children’s learning and with the school [14]. This has been attributed to a combination of factors including children becoming more independent, the curriculum becoming increasingly difficult, having different teachers for each subject, and fewer informal opportunities for parent-teacher interactions [44].
As we continue with post-COVID-19 pandemic recovery, the World Bank has emphasised the need to “build back better”, including “education systems that enable children to learn continuously both in schools and at home” [45] (p. 33). Thus, COVID-19 has provided an opportunity to refocus the ‘what, how, and where of learning’ [46]. In particular, the dramatic reconfiguration of the parent-learning and parent-teacher relationships during the COVID-19 school closures could present an opportunity to capitalise on the increased engagement with learning in the home [38,40,42]. Pre-pandemic evidence suggests that teachers were overly focused on school-based parental engagement [23,24,25], despite evidence that refocussing on home-based parental engagement would be more effective [14,15,16,17,18,19]. It is possible that the extended periods of home learning may have helped to shift teachers towards more family-centric ways of conceptualising parental engagement. Spear et al.’s exploratory mixed method study in England found that teachers’ perceptions of expectations of parental engagement during the school closures focused on ‘parental participation in schooling’ [47]. Teachers expected parents to facilitate, supervise, and participate in the learning activities they set. However, this study was not able to compare with teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement prior to COVID-19 and did not ask interviewees about their future ambitions for parental engagement in light of the period of home learning.
Unlike previous studies, our study presents comparable data gathered before and after the COVID-19 school closures. This study examines whether and how parental engagement changed during the COVID-19 school closures, with a particular emphasis on whether teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement have shifted to encompass learning beyond the school gates, and on whether any such changes are likely to persist. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first study to explore this possibility, which could have far-reaching consequences for theory and practice. A mixed-methods, longitudinal case study design was used to investigate the following research questions (RQ):
- RQ1:
- From teachers’ perspectives, how was parental engagement different during the COVID-19 school closures?
- RQ2:
- Have teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement changed following those periods of home-learning?
- RQ3:
- Are there likely to be any lasting effects on the theory or practice of parental engagement?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
The research questions required comparable data about teachers’ views of parental engagement, before and after the COVID-19 school closures. In 2019, before the COVID-19 pandemic, we had collected data relating to teachers’ views of parental engagement at one large English primary school as part of a wider project [48]. Returning to the same school after the COVID-19 school closures provided an opportunity to collect directly comparable data, thus creating a longitudinal case study. Case studies are particularly useful when the research aims to study “contemporary phenomena within their real-life context” [49] (p. 73). Clearly, the study of parental engagement during a pandemic involves investigating a contemporary phenomenon and there is strong evidence that parental engagement is context-dependent [50,51]. A case study design was therefore seen to be more appropriate than attempting to combine data across different schools. The longitudinal element refers to the study of change using data gathered at two different time points—before the COVID-19 school closures (July 2019) and after those closures (July 2021).
Whilst case studies are most commonly associated with qualitative methods, this case study utilised a mixed methods approach. Quantitative data was gathered using questionnaires, allowing us to ask the same participants, the same questions, phrased in exactly the same way across the two time points. Thus, producing directly comparable data that could be used to examine changes over time. However, quantitative methods may fail to capture unexpected phenomena occurring, because they focus on testing existing theories [52]. This was a concern due to the unprecedented changes to schooling that took place during COVID-19. The extended periods of home learning may have altered the parent-learning and parent-teacher relationships in unanticipated ways. We therefore used interviews to incorporate a qualitative strand of inquiry, taking an inductive approach to allow new categories and theories to emerge [53]. An overview of the research design is presented in Figure 1. The following sections describe the development of the data collection instruments in detail.
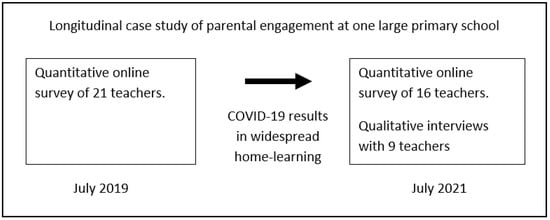
Figure 1.
An overview of the research design.
2.2. Survey Design
The original 2019 questionnaire consisted of eight questions. The current study was designed to follow up on a subset of these questions in greater detail. As such, three questions from the 2019 survey were reproduced word-for-word to allow for longitudinal comparison, for example, “What barriers do you see to higher levels of parental engagement in the future? Please tick all that apply”. This question was asked at both time points, along with eleven response options identified from the literature, including “other—please specify” and “none—I don’t see any barriers to increasing parental engagement”. The 2021 survey also contained eleven new questions designed to probe the effects of COVID-19, for example, “What—if any—benefits have there been to parental engagement as a result of home learning? Please tick all that apply”. Again, response options from the literature were provided but respondents were also free to select “other—please specify” or “none”.
The survey consisted mostly of closed questions (Likert scales and multiple choice) to facilitate direct comparisons. However, one of the replicated questions used at both time points was open-ended. Participants were asked “In your own words, please explain as fully as possible what you think is meant by ‘parental engagement’. Please include examples of what you think strong parental engagement looks like”. It was deemed essential that parental engagement definitions were captured in participants’ own words because providing multiple choice options would have limited the possible outcomes and risked guiding participants towards particular definitions [54]. The full 2021 questionnaire can be viewed as part of the codebook linked in the data availability statement.
2.3. Interview Design
This study used qualitative, semi-structured interviews. They had a structured opening and closing [55], and a semi-structured main section. The semi-structured design meant that questions were carefully pre-prepared as part of the interview guide, but those questions could be deployed flexibly during the interviews to ensure the interviewer could pursue emerging themes [56]. It was also important to enable probing follow-up questions that could be used to clarify any ambiguous statements made by participants, thus providing a more trustworthy start point for analysis [56].
The first half of the interview was designed to triangulate with the survey questions and provided an opportunity to probe the participants’ reasons for giving particular responses [57]. For example, interviewees were asked to give an open response to statements such as “supporting parents is an important part of a teacher’s job”. The same statements were used in the quantitative survey, with participants asked to respond on 1–5 Likert scale, but asking during the interviews produced rich explanations of participants’ reasoning. This serves to validate the findings and support interpretation of the quantitative data. The second part of the interview was designed to extend the findings by exploring new and emerging categories related to the pandemic. Examples of these types of questions include “tell me about how you approached parental engagement during the school closures,” and “did that differ from your approach before the pandemic?”.
To test and refine the interview guide, three pilot interviews were conducted with primary school teachers at other schools. The first pilot interview lasted 50 min which was considered too long given the time pressures faced by teachers in England [58]. Several questions were therefore removed. The second pilot interview ran more smoothly but still lasted 45 min. In response, the third pilot interviewee was sent an overview of the questions and all of the consent information in advance. This resulted in a productive interview covering all the key areas in sufficient depth in approximately 35 min.
2.4. Procedures
The online questionnaire was constructed in Qualtrics. The link was distributed to teachers as a standing item on the school’s daily electronic staff briefing. Response rate was maximised by offering anonymity, allowing participants to complete the questionnaire at their convenience, and sending reminders [59].
The interviews were conducted online via Microsoft Teams due to the ongoing impact of COVID-19. The interviews lasted between 22 and 42 min. They were recorded, with the consent of participants, and later transcribed. All interviews took the form of a conversation between professionals, because the interviewer and interviewees had shared reference points as teachers familiar with the school’s context. Due to the challenging nature of data collection in the context of the ongoing pandemic, some pragmatic decisions had to be taken during data collection. Positive tests for COVID-19 frequently resulted in teachers needing to cancel interviews at short notice. Two teachers, who were unable to reschedule, therefore answered the interview questions via email. For all participants, member-checking was used to ensure that the final transcripts represented their views fairly [60]. Following their interview, each participant was emailed their transcript and invited to check, clarify, or expand on anything they had said. None of the participants opted to make changes.
2.5. Ethics
This study received ethical approval from the Department of Education Studies ethics committee at the University of Warwick. Informed consent was gained in writing from the headteacher and all participants. None of the questions covered sensitive topics, but participants could stop data collection at any time. The questionnaire was fully anonymous from the outset and identifiable information was removed from the interview data during transcription. The school has also been given the pseudonym ‘Redhill’ to ensure the privacy of the staff, pupils, parents, and local community.
2.6. Context
Redhill is a large, state-maintained English primary school with pupils aged 5–11. The school has 21 class teachers and seven senior leaders who are not class-based. It was rated ‘good’ during its most recent inspection. It is located in an inner-city part of the West Midlands ranked among the 10% most deprived wards in England [61]. The average income is less than £14,700, compared to £18,700 nationally. Consequently, over 45% of Redhill’s pupils are eligible for Pupil Premium Funding, compared to a national average of 17% [62]. The school’s location and high Pupil Premium percentage make it a particularly interesting case because parental engagement with home-learning during lockdown was reportedly lowest in the West Midlands, and in schools with high levels of Pupil Premium [29].
Around half of residents are from minority ethnic groups, which is more than double the national average (19%) [63]. Consequently, the schools’ pupils have diverse ethnic backgrounds. The largest groups within the school are Pakistani, White British and Romani. More than half of Redhill’s pupils speak English as an additional language. This contextual information is important because parental engagement correlates with socioeconomic status [64,65,66] and families from ethic-minority groups may experience different barriers to parental engagement [67,68].
2.7. Participants
All of the teachers and school leaders at Redhill were invited to complete the questionnaire. Table 1 provides an overview of survey respondents and response rates at both time points. The attrition between the two timepoints is typical of a longitudinal study [69,70]. Consequently, small samples are extremely common in longitudinal studies involving teachers and published examples use as few as one [52]. In the current study, retention was affected by COVID-related staff absences and teacher turnover. Despite this, the response rates remained high. Cook et al.’s meta-analysis found a mean response rate of less than 40% in published studies utilising online surveys [71]. Moreover, combining the survey data with other sources within a case study creates a research design that can cope with there being more factors of interest than there are data points [49].

Table 1.
An overview of survey participants.
Interview invitations were offered to all teachers and school leaders at Redhill. Nine qualitative interviews were conducted (seven live video calls and two via email). Whilst there are no rules about how many interviews should be conducted, a rigorous study should clearly articulate why the number of interviews conducted was considered to be enough [60]. Figure 2 shows that the number of new codes emerging from each interview decreased over time, reaching zero by the ninth interview. Whilst this does not guarantee that no new codes would have been found in subsequent interviews, it suggests that nine interviews approached data saturation [72]. This was therefore an adequate number of interviews and an appropriate place to stop given the time and resource constraints. The interview participants represented the full spectrum of experience, from Early Career Teacher (ECT) to senior leaders with over 25 years of experience (see Table 2).
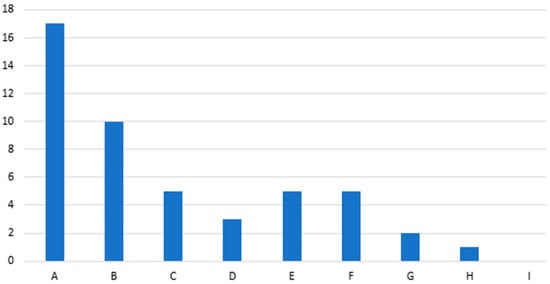
Figure 2.
The number of new codes emerging from each interview.

Table 2.
An overview of interview participants.
2.8. Data Analyis Procedures
The data from both surveys (2019 and 2021) were combined into a single dataset, with timepoint added as a dummy variable. The free-text survey question asking teachers to define parental engagement in their own words was converted into a categorical variable using procedures previously established by the authors [48]. This involved using Goodall and Montgomery’s continuum to code each response as level 1, 2 or 3 (see Table 3) to enable the 2019 and 2021 data to be directly compared [73]. Each response was independently coded by two people. The codes assigned were consistent for 30/37 responses (81%). Where different codes were assigned, the two raters reached an agreement through discussion with reference to the original definitions. The numeric levels then formed part of the final dataset.

Table 3.
An overview of how teachers’ free-text survey responses were assigned a numerical code.
Analysis of the interview data followed the general inductive approach comprising the following stages: (1) Preparing—transcribing, formatting, and repeated close reading of the data; (2) Coding—cycles of identifying and applying detailed codes to segments of text; (3) Categorising—revising and refining of codes into more general categories; (4) Theorising—considering how categories link together [53]. Coding was undertaken using Nvivo. Initially, every sentence was coded according to its content. Where it referred to multiple topics, it was given multiple codes. Each time a new code was identified, we revisited the other transcripts to test whether the new code helped to make sense of the rest of the data. A total of 48 codes were produced at this stage (see Table 4 for examples). Next, categories were developed by examining the contents of each code and identifying broader themes (see Table 5). This process resulted in 11 final categories. Some of these categories had distinct boundaries, for example benefits of home-learning and barriers to increased engagement. For others, there was significant overlap, resulting in several ways of categorising the same quotes. For example, I found that types of parental engagement could be usefully sorted by location (home vs. school vs. community vs. online), or approach (proactive vs. reactive), or purpose (academic vs. wellbeing), or focus (general vs. targeted). To choose just one of these classifications would be to fail to adequately capture the complexity of the phenomenon.

Table 4.
Examples of initial codes assigned to each segment of text during inductive analysis of the interview transcripts.

Table 5.
An example of how codes were refined to make sense of data across multiple transcripts before being grouped into broader categories. All of these codes were grouped under an overarching category labelled ‘the parent-teacher relationship’.
Theorising—considering how the categories link together—is the final stage of general inductive analysis [53]. In this study, the quantitative and qualitative strands of inquiry are drawn together in the results section to address each research question in turn. The aim here is to demonstrate that the understanding of the phenomena gained from one method, has been substantially enhanced by having data from a second method [74]. Where possible, participants’ own words are used to allow readers to assess the validity of assertions drawn from the quotes [75].
3. Results
3.1. RQ1: How Was Parental Engagement Different during the COVID-19 School Closures?
During the survey, teachers were asked what impact the school closures had on parental engagement at Redhill. The responses were mixed, with 31% of teachers saying the level of parental engagement had decreased, 38% suggesting no change, and 31% feeling it had increased. The divergent responses may be related to whether respondents were primarily thinking about home-based parental engagement (which presumably increased) or school-based parental involvement (which presumably decreased). It is clear from both the survey and the interviews, that there was increased reliance on digital parent-teacher communication during the COVID-19 school closures. The survey data shows that phone calls (85%) and electronic messaging (92%) were found to be effective by the vast majority of teachers at Redhill. The interview data corroborates this and adds depth to our understanding of how these technologies were used. Phone calls were made to all parents on a fortnightly basis to check-in on the families’ wellbeing and offer support. Meanwhile 1:1 electronic messages were used to communicate with pupils and parents about work. Where families did not have access to the necessary technology, the school provided it. This was seen as part of a wider trend, as explained by the class teacher below.
“It’s become a lot more electronic. We were already headed that way with ParentPay and texting parents, but it’s evolved… I think right now, everything is completely electronic; Dojo, text messages, web links, websites all that sort of stuff. Interviewer: Is digital the future of parental engagement? Absolutely. Undoubtedly. It has to be doesn’t it. From an environmental perspective but also an ease perspective.”(Transcript E)
The interview data also enabled participants to express nuance that was not present in the quantitative data. For example, whilst in the survey 85% of teachers perceived phone calls to be effective, during the interviews teachers explained that there was no appetite to retain them moving forward. For some teachers, phone calls were a source of anxiety. Others felt that face-to-face communication was more authentic and less prone to misunderstandings.
“Face-to-face is most effective because if you’re sending messages over ClassDojo or phone calls then your point doesn’t always come across. It’s easy to take something one way when actually something else was meant… Bin phone calls!”(Transcript C)
“I don’t like phone calls. Being able to talk properly encourages conversation. You can read body language and stuff. You can see whether they’re ready to finish a conversation or not… I didn’t enjoy anything about the phone calls.”(Transcript E)
“They were hard work. But then that was the only type of communication we had… So I’m not buzzing to make phone calls again.”(Transcript I)
Digital communication also allowed senior leaders to track teacher-parent engagement systematically. Interviewees described how spreadsheets were used to check whether each individual family had been spoken to each week. Where there had been no communication, senior leaders tried other methods, including home visits, to ensure that every family was safe and well. This is a significant change to pre-COVID parental engagement and was seen as an improvement by senior leaders. The survey results suggest that increased parent-teacher communication brought improvements including; parents’ understanding of the curriculum, teachers’ understanding of parents’ situations, and the overall parent-teacher relationship (see Figure 3). All of these benefits were also identified by interviewees along with some additional suggestions.
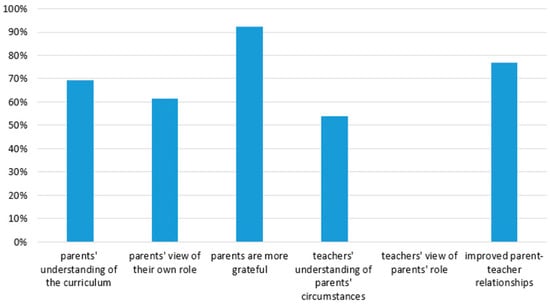
Figure 3.
Reported benefits of home-learning during the COVID-19 school closures.
“Parents now know more than ever what their child can and can’t do… Then when the teacher is saying these things, the parents can appreciate where they’re coming from. I think it will make a big difference.”(Transcript B)
“Parents have a much better understanding of the curriculum and learning taking place. They have also seen the feedback given from teachers more.”(Transcript G)
At the same time, some teachers in the interviews suggested there was a risk of ‘over-engagement’ as instantaneous digital communication between parents and teachers risked overwhelming both parties. It was also suggested that while digital channels could improve parent-teacher communication, they might actually hinder parent-child communication. The suggestion here is that direct, digital communication may be quicker and easier for most parents and teachers, but that it might inadvertently cut the child out of those communications.
“We’ve got to be careful that we don’t over-engage. Parents will need that time to cut off.”(Transcript B)
“A lot of the staff are just sick of it. With the phone calls. I think they need a break from parents. They’ve got a bit overwhelmed.”(Transcript C)
“I think a lot of parents still want to physically take something out their children’s bag. And I can see that. Because if you’re emptying their bag, you take it out, you talk to you children about what you’ve found. But then with a text message… I perhaps wouldn’t look until later when it’s quieter.”(Transcript E)
Another theme that emerged, was the increasingly individualised approach taken by teachers during the school closures, closely connected with staff being more proactive. Where engagement with the school was low, staff were flexible in making alternative arrangements including home visits and delivering physical packs of work. Teachers appeared to be increasingly aware of the need to adapt to the specific needs of the parents and community.
“It is evidence based, but then also, you need to know your own community as well… it needs to work with who you’ve got.”(Transcript F)
“Not everything will work for everyone—support for each family can look very different.”(Transcript G)
At the same time, there was a clear shift in the focus of communications. The wellbeing of children and parents seemed to be at the heart of many of the parent-teacher interactions during the school closures. For some teachers this was a positive experience. However, others felt out of their depth suddenly being expected to deliver wellbeing support rather than the academic support they are trained to provide.
“It’s the partnership between school and parents. Not just with the academic side of things, but with all the personal, social and health.”(Transcript A)
“When we first went into lockdown, it sounds ridiculous, but we were no longer just about learning, we about caring for everybody.”(Transcript H)
“In a couple of cases it was almost getting to the point of social calls rather than teachers calls. Being asked to sort out psychological and emotional problems… Stuff like that I was almost helpless with.”(Transcript E)
Finally, whilst the survey asked teachers about their experiences during ‘the school closures’, teachers in the interviews were quick to distinguish between the two periods of school closures. The extracts below suggest that there was no time to plan out the approach to parental engagement during the first period of school closures. By contrast, the approach during the second period appears to have been more structured, with clearer expectations and more success.
“The first school closure—March to September—it was very ad hoc. Just speaking to parents through dojo when they contacted us… But then the second lockdown from January was a lot different.”(Transcript E)
“Well it’s two parts really… In March when schools were first closed schools didn’t have a clue what they were doing… We had to reply to messages but it was very low key… When school were shut again in January that was on a more intense basis.”(Transcript I)
3.2. RQ2: Have Teachers’ Perceptions of Parental Engagement Changed Following the COVID-19 Pandemic?
In 2019, just 19% of teachers at Redhill conceptualised parental engagement in relation to learning in the home or community. The 2021 data shows that this had risen to 44% post pandemic (see Table 6). Whilst the sample size is not big enough to confirm statistical significance, the interview data suggests a similar increased focus on learning beyond the school gates. Home-learning appeared to have refocussed their attention on children’s learning as the end-goal for parental engagement. Several senior leaders spontaneously spoke of their realisation that many past school-based events had no clear purpose.

Table 6.
An overview of the levels assigned to the parental engagement definitions provided by survey respondents at each timepoint.
“Parents need to know how to help their children at home… It’s been a big wake up call for how important it is to have those home links and if you’ve got families where historically you’ve said well they’re hard to reach, well you can’t afford to do that anymore.”(Transcript A)
“[Pre-COVID] it was very much just bums on seats. How many people can we get in… We probably wouldn’t have admitted it at the time, but I feel, it was all about the numbers. But over time we’ve been trying to shift that to more purposeful engagement.”(Transcript H)
We also examined whether there were changes in how teachers viewed parents. In response to the survey, over 50% of teachers said that they felt they understood parents’ circumstances better due to the school closures. This was echoed by the interview data, with a particular focus on how this had forced staff to challenge their own assumptions.
“With lockdown, the staff here made all sorts of assumptions… ultimately you can’t make assumptions because there were people that we thought would be doing nothing—and they weren’t engaging with the online Maths or English—but my goodness did those parents work hard with them. They cooked, they sewed, they baked, they went on bike rides… things that I would argue are just as important.”(Transcript F)
“I became very aware of some of the challenges parents were facing… I was also surprised by some parents’ response to the remote learning. For example, one higher ability child who did very little home learning and a lower ability child who produced work every day.”(Transcript G)
Moreover, for many teachers, home-learning appeared to reinforce their dual role as parents themselves. The fact that many teachers are parents is frequently absent from studies of parental engagement, but the extracts below suggest that parent teachers were frequently using their experiences as parents.
“Some parents have to work. They haven’t got the time. Like me really, my kids have all these wonderful things going on in school and I can’t go because I have to be here.”(Transcript B)
“Dojo, text messages, web links, websites all that sort of stuff is what’s worked best for me as a parent and a teacher”(Transcript E)
“For some teachers, being at home with their own children… We had staff saying ‘I haven’t got a clue! They’re doing GCSE whatever-it-is. I don’t know how to do it!’ And it’s like ok, this is how some of our parents feel.”(Transcript F)
Despite this, none of the survey respondents reported viewing parents’ role in education differently as a result of home-learning. This was consistent with the qualitative data whereby none of the interviewees felt that there had been any change in how they or their colleagues viewed the role of parents moving forward.
“There’s not been much change… Some teachers like it, some really despise it.”(Transcript C)
Meanwhile, many teachers continued to adopt a deficit model of other parents when asked about the barriers to parental engagement (see Figure 4). Over half of survey respondents suggested that parents not caring about their children’s education was a barrier. This was an increase from 2019. The biggest changes between the 2019 and 2021 data were increases in teachers worried about parents’ skills, and teachers that felt not enough staff spoke other languages. The increase in concern around parents’ skills is unsurprising because during home-learning parents were expected to provide more direct academic support than in 2019. However, the change in teachers’ perceptions of the language barrier is interesting. In 2019, the majority of teachers thought that not enough parents spoke English, but most did not feel that more staff needed to speak children’s home languages. This suggested that teachers perceived it to be the responsibility of parents to overcome the language barrier. Encouragingly, the 2021 data suggests that school staff now share responsibility for this. This may be due teachers finding themselves unable to proactively communicate with some parents during school closures.
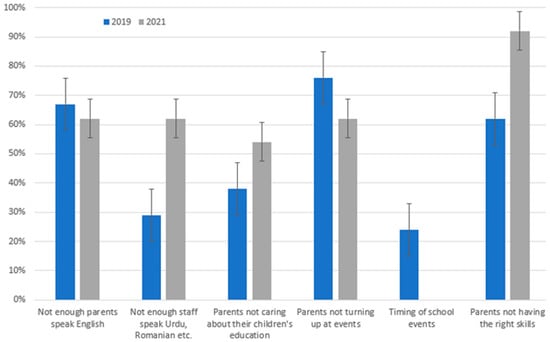
Figure 4.
Barriers to parental engagement, as perceived by teachers before and after school closures.
“There’s only one translator in the school, in terms of Romanian. But I’ve got six Romanian children in my classroom. Plus all the other classrooms. So it’s really hard to break down that barrier currently.”(Transcript C)
3.3. RQ3: Are There Likely to Be Any Lasting Effects of the COVID-19 School Closures on Parental Engagement?
Turning to post-COVID aspirations, 100% of survey respondents agreed that schools should do more to support learning interactions between parents and children outside of school (for example, at home and in the community) and 92% agreed that how parents engage with their children at home has a bigger impact than whether they attend events in school. Despite this, when asked to indicate whether the school’s priority should be to support parental engagement with learning in school (54%), in the community (31%), or at home (15%), the majority of respondents chose the school. This may have reflected concerns around staff time, with 69% indicating that this was a barrier to more effective parental engagement. In the interviews, many teachers identified the potential for the period of home-learning to act as a springboard for reimagining and enhancing parental engagement.
“It’s about harvesting and maintaining that… keeping the best bits and building. I think we’re at a crucial point. This is a golden opportunity to do something a little bit different.”(Transcript B)
“I think [parents] probably realised at that point they needed to work with their children to move them forward. But now they’re back in school, will that continue? I think that’s something that we need to look into”(Transcript A)
However, there was a strong pessimistic undertone to most of the interviews when it came to the likelihood of capitalising on this opportunity. Teachers were concerned that ongoing restrictions, lack of time, and lack of training were resulting in a reluctant slide back to pre-COVID approaches. This was consistent with the survey data in which less than half of respondents agreed that teachers had the skills and training to facilitate parental engagement.
“The sad thing is we’re losing it… Class teachers haven’t got time to respond to all those messages like they could before… we are losing what we built. Not because we wanted to, but because we couldn’t… we’ve come back and just tried to get back on with the job of teaching… I think now we’ve gone back to the same-old-same-old… teachers just haven’t had the capacity.”(Transcript H)
“The important thing is that this is not forgotten. Because these things can happen and you can all have the best of intentions… but it drains away.”(Transcript B)
“We’ve definitely changed in term of our thinking of what we want parental engagement to look like, but it hasn’t actually happened. Partly because we haven’t been able to with COVID restrictions, but also, I think the bigger thing for me, is that we need to invest more time and money into it… with parental engagement we just expect teachers and leaders to know how to do it… that has to happen before real change can take effect.”(Transcript F)
“Planning more would eliminate barriers because you can pre-empt them… but as a teacher you have a limited amount of time and if you do want more time that means you’re taking it out of the teaching itself.”(Transcript I)
Finally, several teachers referred to wider political pressures and sensitivities affecting parental engagement moving forward. These included cuts to external services, pressure to secure results quickly, and the sensitivities involved in trying to influence parents’ choices.
“With the introduction of things like children’s centres and Sure Start programs, there was a move to try and engage parents at a much earlier stage… But I think with funding cuts that’s gone.”(Transcript F)
“The reality is that we have targets and we’re focused on getting certain numbers in certain areas… we’re afraid to shift that focus to parental engagement and invest the time in it because we know we won’t get the results just like that *clicks fingers*… I don’t think any of us really believe that’s the right way to do it, but that’s the system we’re caught in.”(Transcript H)
“On one hand it’s paternalistic, isn’t it? It’s saying I, or we, or the education sector, perceive that this thing is important or valuable and the right way to do it… I’m a little bit uncomfortable with that because we have different cultural norms and expectations… who is to say what the best way is.”(Transcript F)
4. Discussion
This study used rich mixed methods data to compare teachers’ perceptions of parental engagement pre- and post- the periods of home learning. The data suggests that the school closures should not be treated as a single event because teachers’ approaches changed over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. By the second period, teachers were using an increasingly digital, flexible, wellbeing-focussed approach to parental engagement. Despite this, approximately half of teachers in this study continued to deploy deficit models of parents and to view parental engagement in terms of school-based activities. Teachers were not optimistic about retaining benefits of home-learning in relation to parental engagement. In the following sections, these findings are discussed in relation to the wider literature and broader context.
4.1. How Was Parental Engagement Different during the COVID-19 School Closures?
Teachers at Redhill identified many of the same changes as the parents in previous studies. For example, most felt that parents had gained curriculum knowledge, greater appreciation for teachers, and parent-teacher relationships were stronger [42]. Unsurprisingly, there was also increased reliance on digital communication [35,36]. Consistent with Bubb and Jones, school leaders saw this as positive and were keen to build on this in the future [42]. The interview data suggests that in doing so, school leaders may need to be wary of unintended consequences including the risk of over-engagement and inadvertently removing children from the conversations. From a theoretical perspective, the rapid increase in digital parent-teacher communication, virtual events, and online initiatives, suggest that ‘online’ may need to be added as a potential location in models of parental engagement. This is absent in most existing models where the emphasis in on home versus school versus community as sites for parental engagement e.g., [14,73,76].
Also of importance to the research community, is the finding that the two periods of school closures were seen by teachers as entirely distinct. Redhill’s approach to parents and learning differed drastically between the two lockdowns. This potential difference is not reflected in many other published studies e.g., [28,31,32,77]. This finding is vital because it suggests that researchers, school leaders and policy makers must be cautious in drawing wider inferences about home learning from studies of the first period alone.
This study also found that teachers’ approaches to parental engagement during COVID-19 school closures were more individualised and proactive than before the pandemic. This suggests that teachers recognised that parents were facing different barriers to engagement, whilst before the pandemic, many schools treated parents as a homogeneous group [68]. Finally, parental engagement during COVID-19 included a greater focus on wellbeing. This may have contributed to creating stronger parent-teacher relationships, but some teachers felt out of their depth and unprepared to deal with wellbeing issues. Generally, teachers and senior leaders felt that this focus on wellbeing was positive but that it should ordinarily fall outside of a class teachers’ responsibilities [78].
4.2. Have Teachers’ Perceptions of Parental Engagement Changed Following the COVID-19 School Closures?
Based on their survey of parents, Bubb and Jones concluded that parental engagement had increased during the school closures [42]. By contrast, teachers in this study were equally likely to say that it had decreased. This may be related to differing conceptualisations of parental engagement. For those who view it as learning in the home and/or parent-teacher communication it is likely to have increased. For those who view it in relation to parents attending school-based events it will have decreased during the school closures. One motivation for conducting this study was to investigate the possibility that the period of home-learning might have counteracted teachers’ pre-COVID tendency towards less effective, school-centric types of parental engagement [23,24,25,48]. The survey results showed a large increase in the percentage of teachers conceptualising parental engagement in relation to parent-child learning beyond the school gates (from 19% to 44%). However, this means that more than half of teachers made no reference to home when asked to define and exemplify strong parental engagement, despite 8 months of home-learning. This suggests that teachers’ focus on school-based parental engagement is deeply ingrained. Further evidence of this was provided by the interviews where only one teacher referred to informal parent-child activities (such as gardening, painting, or cooking together) despite evidence that parents in England were spending over 2 h per day on these sorts of activities during the pandemic [31]. Consistent with previous studies, teachers appeared to be focused almost exclusively on how much formal English and Maths had been completed [29,47].
Consistent with Soltero-Gonzalez and Gillanders [40], the interview data in this study provides some evidence that increased communication between teachers and parents has helped to challenge some of the assumptions that teachers held about parents. However, the barriers identified by teachers in the survey suggests that the deficit model continues to persist, with half of teachers identifying parents not caring as a barrier. This is consistent with pre-pandemic findings [48] and suggests a continuing need for training that targets teachers attitudes towards parental engagement [79]. On a more positive note, experiences during the pandemic appear to have led teachers to take some responsibility for removing the language barrier. In 2019 teachers at Redhill saw it as parents’ responsibility to speak English, but in the post-lockdown survey there was increased recognition that the school needed more staff that spoke other languages. As in Crozier et al. [80], parent-teacher communication was hindered by a lack of interpreters.
Finally, the theme of teachers as parents was unexpected and requires more attention. Teachers repeatedly and spontaneously referred to their own experiences as parents when discussing parental engagement. This is not a discussion that we have come across in the parental engagement literature where parents and teachers are usually presented as distinct—and even opposing—categories e.g., [28,31,32]. Further research is needed to understand how these identities interact to influence and inform the perspectives of teachers who are also parents.
4.3. Are There Likely to Be Any Lasting Effects of the COVID-19 School Closures on Parental Engagement?
There is currently an emphasis in research and policy on ‘building back better’ after the COVID-19 pandemic [45]. We have a unique opportunity to ensure that pupils benefit from the increased engagement with learning in the home and the strengthening of relationship between teachers and parents [46]. However, teachers in this study were pessimistic about the likelihood of retaining many of the positive changes. Pre-pandemic issues related to a lack of parental engagement training [26,50,79] and significant teacher workloads [58] have not been addressed. Concerningly for policymakers, even Early Career Teachers trained under the new Initial Teacher Training framework [81] reported receiving no training in relation to parental engagement. Teachers in this study were clear that effective change is unlikely to happen without a concerted efforts to give teachers the training and time needed to plan for parental engagement more effectively. Furthermore, senior leaders in this study felt constrained by pressure to secure results quickly and funding cuts to external services. These are long-standing systematic issues [82,83] and discussions of parental engagement must acknowledge them or risk ‘absolving the system’ by making parents responsible for overcoming them [84].
4.4. Limitations and Suggestions for Further Research
Caution should be exercised in drawing generalisations from this study because it relies on a small sample of teachers, from one school. As a case study, the aim was to generate detailed insight into a complex phenomenon by focusing on a specific context. Detailed contextual information about the chosen school is provided to allow readers to assess the extent to which the findings may be relevant to their own context. Yet, the case study method was able to generate new ideas that can now be tested with larger samples moving forward. For example, the idea that digital communication might benefit parent-teacher forms of engagement, but harm parent-child forms of engagement is not one that we have seen articulated elsewhere. Physical letters or certificates spark learning conversations between parents and children [85], but electronic versions may not have the same effect if parents open texts/emails/instant messages at work or after children have gone to bed. Similarly, children play an important role in parent-teacher meetings [86], but they may not be present if parent-teacher conversations move online. The potential impacts require further empirical research and theoretical consideration in future. The findings of the current study also suggest that that the dual identities of teachers who are parents could be a fruitful line of enquiry, as this is a surprising omission in much of the parental engagement literature. Larger samples in future could also allow for comparison between the perceptions of primary and secondary teachers, given the differences observed between parental engagement in these age groups before [14,44] and during [29] school closures. Finally, parents’ views were not sought in this study. Several studies have examined parents’ role during the COVID-19 pandemic [31,32,41,43,77], but future research should assess whether this has affected parents’ role construction in relation to parental engagement moving forward. This should include exploration of gender differences given mothers did more of the home learning during school closures [31,34].
Internal validity or “the extent to which the findings accurately represent the phenomenon under investigation” must also be considered [87] (p. 82). Respondents’ accuracy can present a significant threat to the internal validity of survey data [88]. This can be impacted by question wording [89], so technical vocabulary and ambiguous terms were avoided during the design of the questionnaire and tested during piloting. Despite the steps taken, there remains a reliance on self-report. Whilst most published studies rely on self-report, memory failures and social desirability effects can affect the accuracy of self-reported data [90]. In this study, the questions were designed to focus on recent events to limit the reliance of recall and social desirability effects were unlikely with an anonymous questionnaire [91].
5. Conclusions
Teachers in this study identified some benefits to the periods of home-learning, including stronger parent-teacher relationships as a result of a more individualised and wellbeing-focused approach to parental engagement during this time. There was clear appetite to use the experiences of home-learning as a springboard to rethink and revitalise parental engagement, but teachers generally perceived that they were reluctantly falling back into pre-pandemic routines due to lack of time and training. If these issues are not addressed urgently, we risk losing the opportunity to use the unprecedented periods of home learning to generate sustainable improvements in parental engagement with learning. Teachers in this study also continued to conceptualise parental engagement in relation to school-based activities despite eight months of home learning. Researchers and policy makers must clearly communicate the evidence-base for parental engagement with learning, versus parent involvement with schools, to ensure that the most effective forms of parental engagement are being promoted by schools. Without this, time and resources will continue to be disproportionately spent on school-centric activities, which are often ineffective. It is hoped that providing a richer understanding of how teachers’ views of parental engagement changed following COVID-19 at one school, might act as a springboard for wider research in this area. Finally, the rapid rise of digital home-school communication following the COVID-19 pandemic suggests that theoretical models can no longer afford to overlook online spaces as important sites of parental engagement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.J.; Methodology, C.J. and O.P.; Formal analysis, C.J.; Data curation, C.J.; Writing—original draft, C.J.; Writing—review & editing, C.J. and O.P.; Supervision, O.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
C.J. is supported by an ESRC studentship (award number ES/P000711/1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was reviewed and approved by the ethics board of the Department of Education Studies at the University of Warwick (14 June 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data Availability Statement
To enable others to inspect, reproduce, and extend our analysis the survey dataset and codebook are deposited at 10.6084/m9.figshare.15179031 and the full interview transcripts and interview guide are deposited at 10.6084/m9.figshare.22957121.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to the headteacher, senior leaders and class teachers at Redhill school, who generously gave their time to participate in this research. We would also like to thank Andrew Fell for their work as second reviewer categorising the open-text responses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Abdul-Adil, J.K.; Farmer, A.D. Inner-City African American Parental Involvement in Elementary Schools: Getting beyond Urban legends of Apathy. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2006, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, G. Parent involvement in children’s education: Implications of a new parent involvement framework for teacher education in Australia. In Teacher Education: Local and Global; Cooper, M., Ed.; Griffith University: Nathan, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, S.; Epstein, J. Improving Student Behaviour and Discipline with Family and Community Involvement; John Hopkins University: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, S. Improving Student Attendance with School, Family, and Community Partnerships. J. Educ. Res. 2007, 100, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, M.; Merz, E.C.; Repka, K.R.; Landers, C.; Noble, K.G.; Duch, H. Parent Involvement in the Getting Ready for School Intervention Is Associated with Changes in School Readiness Skills. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorard, S.; See, B.; Davies, P. The Impact of Attitudes and Aspirations on Educational Attainment and Participation; Joseph Rowntree Foundation: York, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jeynes, W. A Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Different Types of Parental Involvement Programs for Urban Students. Urban Educ. 2012, 47, 706–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, W. Relational Aspects of Parental Involvement to Support Educational Outcomes: Parental Communication, Expectations, and Participation for Student Success; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wilder, S. Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educ. Rev. 2014, 66, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, E.; Simpkins, S.; Kreider, H.; Weiss, H. Family Involvement in School and Low-Income Children’s Literacy: Longitudinal Associations between and within Families. J. Educ. Psychol. 2006, 98, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénéchal, M.; LeFevre, J.-A. Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: A five-year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 2002, 73, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J. Visible Learning; a Synthesis of over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jasso, J. African American and Non-hispanic White Parental Involvement in the Education of Elementary School-Aged Children; Syracuse University: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Desforges, C.; Abouchaar, A. The Impact of Parental Involvement, Parental Support and Family Education on Pupil Achievement and Adjustment: A Literature Review; Department for Education and Skills: London, UK, 2003.
- Lehrl, S.; Evangelou, M.; Sammons, P. The home learning environment and its role in shaping children’s educational development. Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 2020, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammons, P.; Toth, K.; Sylva, K.; Melhuish, E.; Siraj, I.; Taggart, B. The long-term role of the home learning environment in shaping students’ academic attainment in secondary school. J. Child. Serv. 2015, 10, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylva, K.; Siraj-Blatchford, I.; Taggart, B. Assessing Quality in the Early Years: Early Childhood Environment Rating Scale; Stoke on Trent: Trentham, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Erion, J. Parent Tutoring: A Meta-Analysis. Educ. Treat. Child. 2006, 29, 79–106. [Google Scholar]
- Okpala, C.; Okpala, A.; Smith, F. Parental involvement, instructional expenditures, family socioeconomic attributes, and student achievement. J. Educ. Res. 2001, 95, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Goodall, J. Engaging Parents in Raising Achievement. Do Parents Know They Matter? DfCSF: London, UK, 2007.
- Axford, N.; Berry, V.; Lloyd, J.; Moore, D.; Rogers, M.; Hurst, A.; Blockley, K.; Durkin, H.; Minton, J. How Can Schools Support Parents’ Engagement in Their Children’s Learning? Evidence from Research and Practice; Education Endowment Foundation: London, UK, 2019; Available online: https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/education-evidence/evidence-reviews/parental-engagement (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Goodall, J. Ofsted’s judgement of parental engagement: A justification of its place in leadership and management. Manag. Educ. 2015, 29, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, P.; Miguel, N.; East, J. Changing directions: Participatory action research as a parent involvement strategy. Educ. Action Res. 2009, 17, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Goodall, J. Do Parents Know They Matter? Engaging All Parents in Learning. Educ. Res. 2008, 50, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.J.; Minke, K.M. Parent Involvement in Education: Toward an Understanding of Parents’ Decision Making. J. Educ. Res. 2007, 100, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Education Endowment Foundation. Working with Parents to Support Children’s Learning; EEF: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/tools/guidance-reports/working-with-parents-to-support-childrens-learning/ (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- UNESCO. Education: From Disruption to Recovery. 2021. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse#schoolclosures (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Eivers, E.; Worth, J.; Ghosh, A. Home Learning during COVID-19: Findings from the Understanding Society Longitudinal Study; NFER: Slough, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.; Nelson, J.; Sims, D. Schools’ Responses to COVID-19: Pupil Engagement in Remote Learning; NFER: Slough, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, A.; Cattan, S.; Costa Dias, M.; Farquharson, C.; Kraftman, L.; Krutikova, S.; Phimister, A.; Sevilla, L. Learning during the Lockdown: Real-Time Data on Children’s Experiences during Home Learning; Institute for Fiscal Studies: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Villadsen, A.; Conti, G.; Fitzsimons, E. Parental Involvement in Home Schooling and Developmental Play during Lockdown: Initial Findings from the COVID-19 Survey in Five National Longitudinal Studies; UCL IoE: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.M.; Cunha, R.S.; Silva, M.C.A.; Carvalho, M.; Vital, M.L. Parental Involvement during Pandemic Times: Challenges and Opportunities. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, E.; Cohen, F.; Wolf, K.; Burghardt, L.; Anders, Y. Changes in Parents’ Home Learning Activities with Their Children during the COVID-19 Lockdown—The Role of Parental Stress, Parents’ Self-Efficacy and Social Support. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 682540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, M. Parental Involvement in Children’s Online Education During COVID-19; A Phenomenological Study in Saudi Arabia. Early Child. Educ. J. 2023, 51, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, J.; Buttimer, C.J.; Coleman, D.; Colwell, R.D.; Faruqi, F.; Larke, L.R. What’s Lost, What’s Left, What’s Next: Lessons learned from the Lived Experiences of Teachers during the 2020 Novel Coronavirus Pandemic. EdArXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pang, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z. “What if… it never ends?”: Examining challenges in primary teachers’ experience during the wholly online teaching. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 114, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, K. Online Education in Early Primary Years: Teachers’ Practices and Experiences during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiavacchi, L.; Piccoli, L.; Pieroni, L. Fathers matter: Intrahousehold responsibilities and children’s wellbeing during the COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2021, 42, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabi, M.; Cohen-Ynon, G. Parental Involvement in Elementary Schools during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Teachers’ Challenges and Crises. J. Educ. Learn. 2022, 11, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltero-Gonzalez, L.; Gillanders, C. Rethinking Home-School Partnerships: Lessons Learned from Latinx Parents of Young Children During the COVID-19 Era. Early Child. Educ. J. 2021, 49, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, M.; Li, S. Students’ affective engagement, parental involvement, and teacher support in emergency remote teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from a cross-sectional survey in China. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022, 54, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, S.; Jones, M. Learning from the COVID-19 home-schooling experience: Listening to pupils, parents/carers and teachers. Improv. Sch. 2020, 23, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layne, D.A. Rural Title I School Teachers’ and Parents’ Perspectives on Parent Involvement at Home during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ph.D. Thesis, Walden University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2022. Available online: http://0-search.proquest.com.pugwash.lib.warwick.ac.uk/dissertations-theses/rural-title-i-school-teachers-parents/docview/2640409665/se-2 (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- DeSpain, S.N.; Conderman, G.; Gerzel-Short, L. Fostering Family Engagement in Middle and Secondary Schools. Clear. House 2018, 91, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.P.; Hasan, A.; Goldemberg, D.; Iqbal, S.A.; Geven, K. Simulating the Potential Impacts of COVID-19 School Closures on Schooling and Learning Outcomes; Policy Research Working Paper 9284; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/2b6bde96-8b1c-5fde-91e9-256504fb7590/content (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Zhao, Y. COVID-19 as a catalyst for educational change. Prospects 2020, 49, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.; Parkin, J.; van Steen, T.; Goodall, J. Fostering “parental participation in schooling”: Primary school teachers’ insights from the COVID-19 school closures. Educ. Rev. 2021, 75, 932–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Palikara, O. How do parents and school staff conceptualize parental engagement? A primary school case study. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 990204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R. Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 4th ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Goodall, J.; Vorhaus, J. Review of Best Practice in Parental Engagement; DfE: London, UK, 2011.
- Ofsted. School and Parents; Ofsted: London, UK, 2011.
- Beck, C.; Kosnik, C.; Rosales, E. Longitudinal Study of Teachers. Oxf. Res. Encycl. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R. A General Inductive Approach for Analyzing Qualitative Evaluation Data. Am. J. Eval. 2006, 27, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillham, B. Developing a Questionnaire, 2nd ed.; Continuum: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, S.; Kvale, S. Interviews: Learning the Craft of Qualitative Research Interviewing, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kvale, S. Interviews: An Introduction to Qualitative Research Interviewing; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, W. Triangulation in Social Research: Qualitative and Quantitative methods can really be mixed. In Developments in Sociology; Holborn, M., Ed.; Causeway Press: Ormskirk, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Department for Education. Teacher Workload Survey 2019; Department for Education: London, UK, 2019.
- Saleh, A.; Bista, K. Examining Factors Impacting Online Survey Response Rates in Educational Research: Perceptions of Graduate Students. J. Multi-Discip. Eval. 2017, 13, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, V. Criteria for evaluating qualitative research. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 2017, 28, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office for National Statistics. The English Indices of Deprivation 2015; Department for Communities and Local Government: London, UK, 2015.
- Office for National Statistics. Schools, Pupils and Their Characteristics. 2020. Available online: https://explore-education-statistics.service.gov.uk/find-statistics/school-pupils-and-their-characteristics/2019-20 (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Office for National Statistics. Census: Find Facts and Figures about Areas in England and Wales. 2021. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/visualisations/areas (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Sacker, A.; Schoon, I.; Bartley, M. Social inequality in educational achievement and psychosocial adjustment throughout childhood: Magnitude and mechanisms. Soc. Sci. Med. 2002, 55, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.; Mayer, E.; Kreider, H.; Vaughan, M.; Dearing, E.; Hencke, R.; Pinto, K. Making it work: Low income working mothers’ involvement in their children’s education. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2003, 40, 879–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; McGuire, K. They’d already made their minds up’: Understanding the impact of stigma on parental engagement. Br. J. Sociol. Educ. 2021, 42, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhopal, K.; Gundara, J.; Jones, C.; Owen, C. Working towards Inclusive Education: Aspects of Good Practice for Gypsy Traveller Pupils; Department for Education and Employment: London, UK, 2000.
- Crozier, G.; Davies, J. Hard to reach parents or hard to reach schools? A discussion of home–school relations, with particular reference to Bangladeshi and Pakistani parents. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2007, 33, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, S. Longitudinal Research, 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ruspini, E. Introduction to Longitudinal Research; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, C.; Heath, F.; Thompson, R.L. A Meta-Analysis of Response Rates in Web- or Internet-Based Surveys. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2000, 60, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, G.; Bunce, A.; Johnson, L. How Many Interviews Are Enough?: An Experiment with Data Saturation and Variability. Field Methods 2006, 18, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, J.; Montgomery, C. Parental involvement to parental engagement: A continuum. Educ. Rev. 2014, 66, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, A. Barriers to Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Research. J. Mix. Methods Res. 2007, 1, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldh, A.C.; Årestedt, L.; Berterö, C. Quotations in Qualitative Studies: Reflections on Constituents, Custom, and Purpose. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J. Building bridges of home, school, and community: The importance of design. J. Educ. Stud. Placed Risk 2001, 6, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenelle-Tereshchu, D. ‘Homeschooling’ and the COVID-19 Crisis: The Insights of Parents on Curriculum and Remote Learning. Interchange 2021, 52, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCuaig, L.; Rossi, T.; Enright, E.; Shelley, K. Schools, student health and family welfare: Exploring teachers’ work as boundary spanners. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2019, 45, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushor, D.; Amendt, T. Leading an examination of beliefs and assumptions about parents. Sch. Leadersh. Manag. 2018, 38, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, G.; Davies, J.; Szymanski, K. Education, identity and Roma families: Teachers’ perspectives and engagement with INSETRom training. Intercult. Educ. 2009, 20, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department for Education. ITT Core Content Framework; Department for Education: London, UK, 2019.
- Miller, P.W. Exploring School Leadership in England and the Caribbean: New Insights from a Comparative Approach; Bloomsbury: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Torjesen, I. Austerity cuts are eroding benefits of Sure Start children’s centres. BMJ 2016, 352, i335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, J. Parental engagement and deficit discourses: Absolving the system and solving parents. Educ. Rev. 2021, 73, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, L. Involving parents through school letters: Mothers, fathers and teachers negotiating children’s education and rearing. Ethnogr. Educ. 2007, 2, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, G. Reconstructing Parents’ Meetings in Primary Schools: The Teacher as Expert, the Parent as Advocate and the Pupil as Self-Advocate. Cent. Educ. Policy Stud. J. 2012, 2, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T. Authenticity in Research: Reliability, Validity and Triangulation. In Research Methods in Educational Leadership and Management, 3rd ed.; Briggs, A.R.J., Coleman, M., Morrison, M., Eds.; Sage: London, UK, 2012; pp. 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Manion, L. Research Methods in Education; Routledge: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.; Woolner, P. Developing and Using Questionnaires. In Research Methods in Educational Leadership and Management, 3rd ed.; Briggs, A.R.J., Coleman, M., Morrison, M., Eds.; Sage: London, UK, 2012; pp. 266–280. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, K.; Ahmed, B.; Choi, J.; Gutierrez-Osuna, R. Consistency and Validity of Self-reporting Scores in Stress Measurement Surveys. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook, A.L.; Krosnick, J.A. Social Desirability Bias in Voter Turnout Reports. Public Opin. Q. 2010, 74, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).