Abstract
Case-based learning (CBL) is a teaching method centered on active student learning that can overcome the limitations of traditional teaching methods used in undergraduate medical education. The aim of this systematic review was to compare the effectiveness of CBL against other teaching methodologies in terms of academic performance and perceptions (intra-individual, interpeer and student–faculty) of undergraduate medical students. Literature searches were performed using PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science databases up to 28 April 2021. We included studies that quantitatively compared the academic performance and perception outcomes of CBL against other teaching methodologies in undergraduate medical students. The risk of bias was judged using the RoBANS tool and certainty of evidence using the GRADE framework. Meta-analyses were conducted using a random-effects model and reported as standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Of a total of 4470 records, 41 studies comprising 7667 undergraduate medical students fulfilled the eligibility criteria and were included in our systematic review. The CBL group was superior to the other teaching method groups in terms of academic performance measured by exam scores (SMD = 2.37, 95% CI 1.25–3.49, large effect, very low certainty) and interest and motivation (SMD = 0.79, 95% CI 0.13–1.44, moderate effect, very low certainty). Other academic performance or perception outcomes were not statistically different between CBL and other teaching methods when considering the pooled effect. Still, they were often superior in the CBL group for specific subgroups. CBL showed superior academic performance (especially compared to didactic lectures and tutorial-based teaching) and interest and motivation compared to other teaching methods used with undergraduate medical students. However, the certainty of evidence was very low and further studies are warranted before a stronger and more definitive conclusion can be drawn.
1. Introduction
An undergraduate medical degree presents a demanding academic challenge and should be taught using an effective method that facilitates learning. The medical curriculum should be designed and developed with the aim of meeting the learning needs of a medical student [1,2,3,4,5,6] based on predefined core learning objectives, outcomes and competencies [7,8,9]. Preclinical medical education has shifted over the past few decades, with teaching strategies going beyond the syllabic content and focusing also on the learning experience and the skills needed to manage clinical cases (e.g., rational and clinical thinking, decision making and problem solving) [10,11]. As medical teaching moves towards a competency-based curriculum with a focus on student performance, teaching methodologies that are student-centered and based on objectives and learning outcomes are becoming more important and increasingly popular.
There are many teaching methods that have been implemented worldwide within medical education, but the traditional method using didactic lectures is probably still the most commonly implemented [12,13]. Didactic lectures consist of the active transmission of theoretical knowledge by the teacher, while the student plays a (mostly) passive role based on listening, annotation and acceptance of the content presented by the teacher. Didactic lectures are more commonly implemented in first-year and second-year at the medical undergraduate course to provide a baseline foundation of information for subsequent years. However, this method has received much criticism in the literature [14,15,16], especially due to its passive nature [17] (knowledge is transmitted by and from the teacher and passively received by the students) as a teacher-centered strategy. While didactic lectures allow to communicate a large quantity of information [16,18,19,20], they rely on the students’ attention span [21] and their ability to memorize this large amount of knowledge [22], which is limited due to the poor performance of short-term and long-term memory for lectures over 20 min [23,24,25], the overload of information communicated and the lack of dynamic interaction between the student and the teacher [11,13,18,26]. More importantly, despite the benefits of lecture-style teaching, didactic lectures in undergraduate medical teaching have been questioned due to the lack of important clinical critical thinking and reasoning skills, a key factor in a medical education curriculum and in any medical career. Aiming to overcome the limitations of didactic lectures, more interactive teaching methods have been investigated and implemented, including case-based learning (CBL), team-based learning (TBL), problem-based learning (PBL), human patient simulation (HPS) and tutorial-based method (Box 1). The introduction of these student-oriented teaching methodologies into the preclinical medical curriculum grants a chief benefit of promoting clinical decision-making and problem-solving skills at an early stage of medical training [27].
Box 1. Common teaching methods in undergraduate medical university teaching.
Didatic lectures usually involve face-to-face interaction between teachers and students in a classroom (although online formats are becoming less uncommon); however, while the teacher has a active role, students play a more passive role. The teacher (who is competent in the field) orally deliveres theoretical knowledge in a systematic and organized fashion—supported by slideshows, videos or demonstration—to a class of students, while the students are focused on listening, annotation and acceptance of the content presented by the teacher. Although students have a passive role, there is usually room for some active participation in question and answer periods.
Independent readings is a teaching method that relies on the active role of students in independent study of a specific subject. Students are provided selected and focussed reading materials that they should read and study to understand the assigned subject and develop basic and specific knowledge into the topic. While teachers provide selected reading materials, students are encouraged to complement their study with independent active research using relevant information and different resources (scientific articles, books, etc).
CBL engages students in discussion of specific scenarios that resemble real-world clinical cases. Students are provided with clinical vignettes containing detailed information about a clinical case and should gradually make decisions, propose solutions and identify key characteristics about the condition of the clinical case. This is a student-centered method, where students have a more active role in resolving clinical cases and teachers play a more passive facilitating role in challenging and guiding students. CBL involves an intense interaction and discussion within groups of students that are tasked to collaboratively apply and build up knowledge to propose solutions for how to manage the assigned clinical cases. The teacher guides the discussion of topics identified by the students, but also focuses on the learning outcomes that were stipulated previously to the CBL sessions.
TBL engages students in an active learning strategy that provides students with opportunities to apply conceptual knowledge through a sequence of activities that includes individual work, team work and immediate feedback. This method employs a testing component that evaluates students’ knowledge individually and after group collaboration (a common testing tool is the Readiness Assurance Test (RAT)). TBL begins with preclass preparation of students using selected resources or active searching. At the beginning of the class, students’ knowledge is tested individually (iRAT) and then in teams (tRAT). After testing, the teacher provides immediate feedback and clarification of team responses. Teams of students are then engaged in clinical problem-solving activities that are concluded with a class reflection on the take-home messages of the session. Similarly to the CBL method, the TBL stimulates active interpeer collaboration.
PBL engages students in problem-solving activities as the vehicle to promote student self-directed learning within small groups. PBL places the students in the central and leading role during the classroom process. The aim of the group sessions is to identify a problem or scenario, define and discuss the key concepts and identify learning objectives, followed by independent or group study and research to be discussed in subsequent sessions. This method enables students to develop a hypothesis and search for learning needs that can help them to better understand the problem and meet the predetermined learning objectives. Similarly to CBL and TBL, PBL relies on a student-centered teaching strategy using small groups. The same principles of critical and analytical thinking are focused in PBL. However, while CBL and TBL are usually implemented during short(er) timeframes, PBL is commonly implemented over the entire semesters within large classes of students. Moreover, PBL is conducted with the support of nondirective tutors, implying that students have a more independent and autonomous role in self-study, research, discussion and cooperation, thus shifting the focus of teaching to an autonomous learning process.
Tutorial-based method follows a similar strategy to PBL, where groups of students are guided by a tutor. Similarly to the previous methods (CBL, TBL and PBL), the tutorial method is an active learning strategy that is student-centered. The term “tutorial” is often used within PBL, which may generate some confusion as to the differences between the two methods. While the tutorial sessions in PBL are focused on resolving the assigned problems, the tutorial-based method can involve an array of different activities that may combine more or less student-centered strategies (as compared to CBL, TBL and PBL).
HPS involves scenario-based learning through a “simulation” format that is intended to re-create real clinical scenarios. The simulation can be based on high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality systems or computer-based simulations to mimic clinical scenarios in a controlled and safe environment, while providing real-time and physiologically accurate feedback. The simulations mirror human disease states in a realistic setting and allow students to engage with the simulations to apply their acquired knowledge to resolve a clinical scenario without risk of harm to real patients. The simulation-based method provides students with low-stakes (controlled and safe) opportunities to improve their clinical skills using a hands-on approach while shaping their decision-making and problem-solving skills according to feedback provided by the simulation.
CBL is a teaching method that can be defined as a form of inquiry-based learning that integrates structured and guided learning [11]. It is both a student-centered (active learning) and patient-centered (clinical cases) method [28,29,30,31]. Although several pedagogical models [32,33] can interplay in CBL, it mainly follows a constructivist model [11,32,34] (similarly to other student-centered methods) that focuses on the active role of students in creating their own knowledge by engaging with clinical cases. CBL relies on discussing clinical cases (real or hypothetical) that aim to simulate a real medical scenario and has particular relevance for medical teaching. Within the scope of medical education, the goal of CBL is to prepare medical students for their future clinical practice by challenging them with realistic clinical cases wherein they are expected to apply their theoretical background knowledge (previously acquired during preparatory classes) to clinical practice (authentic clinical cases) [11]. It promotes a more active learning style and allows the students to develop critical thinking, analytical and reasoning skills to solve clinical cases [35,36,37]. The teacher (facilitator) provides detailed information about the clinical case (vignettes) and stimulates a gradual discussion of the case among small groups of students [38,39,40,41,42]. Based on the clinical vignettes, the student has to carry out an active search for evidence-based knowledge on the topic and share their ideas with their peers on how they propose to make clinical decisions, which solutions they suggest to manage the case and to identify key characteristics of the condition being discussed [35,43,44,45]. Guidelines and examples on how to prepare, structure and implement group-based CBL (including lesson plans and case studies) in undergraduate medical teaching can be found elsewhere [20,27,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. At the end of the class, the clinical case is usually summarized and discussed with the teacher to consolidate key messages and the most relevant findings [54,55]. CBL is thus a versatile method in which the teacher has a less active role and should focus on guiding the students to find solutions to their queries [29,43,47,56,57,58,59] and introducing the discussion of key learning outcomes [18,22].
CBL engages students in linking the classroom-based theory of basic science and principles of clinical management [29,30,40,60,61] into their clinical practice [30,62,63]. Its role is to guide learning through clinical cases, which is of particular relevance for medical education as the medical profession is highly involved in managing patient cases. Although CBL stimulates all the learning domains under the revised Bloom’s taxonomy [64], it has a major focus on the “evaluate” and “create” domains, which are less focused in the more traditional teaching method (didactic lectures). These domains play a major role in the learning process of medical students as they prepare them for the clinical demands of their careers as well as stimulating skills that are important for their competency and performance. CBL provides students with opportunities to formulate diagnoses and delineate possible management solutions [65], as well as to understand how underlying mechanisms can relate to the diagnosis and treatment of illness [66]. Students engage in these case-based and problem-solving activities with support and feedback from their peers and experts (teachers) [67]. The preparation and discussion of clinical cases helps students to create more effective clinical thinking habits [68]. Similarly to other student-centered teaching methods (TBL, PBL and HPS, among others), CBL encourages students to autonomously develop skills in problem-solving and decision-making as well as critical and analytical thinking [69,70,71]. These skills are of utmost importance to medical students and will play a major role when translating knowledge into clinical practice. Although not all CBL activities must be carried out in groups, it is most commonly implemented in small groups, thereby promoting active and interpeer collaboration [63,72], which are valuable components of medical practice. As compared to PBL, the CBL method is more structured and more closely guided using predefined learning outcomes that are obtained through an inquiry-based approach [73].
Although the CBL teaching method has been implemented in the undergraduate medical degree programs of several universities, and notwithstanding the theoretical advantages already identified, the comparison of its effectiveness compared to other teaching methods has not been quantitatively systematized in the literature. A previous systematic review [11] critically analyzed CBL interventions in medical education, but searches were only performed up to 2010 and new studies have been published since then. Moreover, this previous systematic review did not provide a focused summary nor a quantitative systematization of available findings, which is needed to investigate whether the theoretical advantages are consistently seen and reproducible throughout scientific studies. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to systematize the available information on CBL and fill the current knowledge gap in the literature. Our specific objective was to compare CBL against other teaching methods in terms of academic performance and perceptions (intra-individual, interpeer and student–faculty) of undergraduate medical students. The main research question was whether CBL would improve academic performance in undergraduate medical students as compared to other teaching methods, especially those that are teacher-centered (e.g., didactic lectures).
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines [74].
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria were set according to the Participants, Interventions, Comparators, Outcomes and Study Design (PICOS) framework. Due to the lack of access to translation services, we only included studies written in English, Portuguese and Spanish.
2.1.1. Participants
We considered studies that included medical degree undergraduate students. Studies that included students from other health-allied science courses (dental medicine, nursing, veterinary medicine, psychology, physiotherapy) or those outside the health-allied field were excluded. Studies that incorporated participants in postgraduate training—such as physicians or residents—were also excluded.
2.1.2. Interventions
We included all studies that implemented the CBL teaching method as an intervention group. There are many broad definitions of the term CBL and there is no clear and widely accepted definition of CBL. We defined CBL as a teaching method centered on presenting and discussing realistic clinical cases with a group of students who play an active role in their own learning. However, it was not always clear what definition the studies used for CBL and we looked for varying definitions that studies used that could fit within the abovementioned definition. Studies that combined CBL with other complementary methods—such as PBL, TBL, Flipped Classroom (FC), digital clinical support platforms or WhatsApp group messaging—were also included. Studies that only used the PBL method as an intervention group without a main component of CBL were excluded from this systematic review, as were studies in which the CBL method was applied outside the university context.
2.1.3. Comparators
All studies that compared CBL with other teaching methods in medical education were considered for inclusion: didactic lectures, HPS, PBL, TBL, tutorial-based method, independent readings, lectures with tutorial sessions and unspecified teaching methods. While we allowed unspecified teaching methods as a comparison group (for overall analyses), we excluded them during sensitivity analyses.
2.1.4. Outcomes
The outcomes considered for inclusion in this systematic review were (i) academic performance determined through exam evaluation and (ii) perceptions about CBL (intra-individual, interpeer, student–faculty and other relevant perceptions. All outcomes had to be provided with quantitative data analysis to be included in the analysis.
2.1.5. Study Design
We included studies that employed study designs that allowed the comparison of CBL with other teaching methodologies: randomized or quasi-randomized studies, nonrandomized cohort studies, case–control studies, crossover and cross-sectional studies. While exclusively qualitative studies (e.g., only based on structured interviews) were excluded, we allowed qualitative and mixed-methods studies that quantified results.
2.2. Search Strategy
We undertook a comprehensive search on PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science databases to identify studies that compared CBL against other teaching methodologies in terms of academic performance and/or perceptions of CBL among undergraduate medical students. The search strategy was applied from database inception up until 28 April 2021 (Table S1). The reference lists of reviews that were relevant to this topic and studies that satisfied the eligibility criteria were manually searched for other potentially eligible studies not identified via the database searches.
2.3. Study Selection
All records resulting from database searches were exported to the “Mendeley Desktop” (Elsevier Solutions), where duplicate studies were automatically removed and confirmed through a manual search. Two authors (D.M., R.A.) independently examined all titles and abstracts found to identify potentially relevant studies for inclusion. Relevant studies were read in full to determine whether they met the eligibility criteria. Disagreements were resolved by consensus.
2.4. Data Collection and Extraction
All data were extracted from the included studies by one author (D.M.) and rechecked by another two authors (R.A., J.A.). Data were collected in an Excel file and organized into different subsections: characteristics of the study (citation, year of study, country in which the study was carried out, study design, curricular area and curricular year), characteristics of the population (total sample and divided by CBL and comparison(s) group(s), and sample number for each curricular year) and the outcome measures comparing CBL with other teaching methods. Teaching methodologies were characterized according to models, strategies and methods [75]. Outcome measures were grouped according to clusters of measures: “academic performance”, “intra-individual student perceptions”, “interpeer perceptions”, “student–faculty perceptions” and “other perceptions”.
2.5. Data Management
Means and standard deviations were extracted for each outcome measure. When it was not possible to extract the standard deviation, the methods suggested by the Cochrane Handbook [34] were employed to impute the standard deviation using the standard error or the confidence interval associated with the statistical significance value (p value) between the two groups (experimental and control). In cases where the mean and standard deviation values were represented in figures, WebPlotDigitizer software [35] was used to extract these values.
For the quantitative synthesis, when a study presented more than one outcome measure within the same cluster of measures, the metric that best represented the outcome being evaluated was prioritized. For example, if a study reported final and other intermediate academic performance exam results, the final academic performance exam was prioritized. When the same study presented several evaluation timepoints, including groups within the same population of students, the sample size of each group was divided by the number of evaluations for each timepoint/evaluation, thus avoiding overlapping and over-representation of the same population in the analysis. Similarly, for crossover studies where the sample size was overlapped for both groups, the sample size for each group was divided in half. In studies that had more than one comparison group, the sample size of the CBL or control group (the one being compared twice) was proportionally divided by the sample size of the other comparison groups.
2.6. Risk of Bias
Two authors (R.A., J.A.) judged the risk of bias using the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for Non-randomized Studies (RoBANS) tool [76]. The RoBANS is a validated tool used to assess the risk of bias in nonrandomized studies, comprising six domains of bias, including the selection of participants, confounding variables, measurement of exposure, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data and selective outcome reporting. Each domain is judged as low risk, high risk or unclear risk of bias. There is no specific tool to appraise the risk of bias in medical education studies. We decided to use the RoBANS tool, which evaluates several key domains of risk of bias, and adapted the judgment criteria to the topic being studied (Table S2).
2.7. Data Synthesis
We employed quantitative synthesis methods to allow a head-to-head comparison between CBL and the other teaching methodologies. For the quantitative syntheses, we conducted a meta-analysis using Rstudio 3.3.1 software (Rstudio, Boston, MA, USA) and the “devtools”, “meta” and “metafor” packages. Meta-analysis was performed when at least three studies/entries reported the same outcome measure (i.e., within the same cluster) comparing a CBL group with any other teaching methodology. Outcomes that were not reported in a minimum of three studies and/or not homogenously evaluated across studies were excluded from the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis framework provided a head-to-head comparison between CBL and other teaching methods (didactic lectures, TBL, PBL, HPS and tutorial method) for each available outcome. The main analyses were stratified according to the different outcome measures for all curriculum areas. Then, subgroup analyses were conducted according to the curriculum area to investigate the effect size for each outcome within each area.
The random-effects model (Sidik–Jonkman estimator with Hartung–Knapp adjustment [77]) was used to attenuate the variations in the methodology and evaluation methods across studies and within the same outcome measures (methodological heterogeneity). This model is appropriate when there is considerable methodological heterogeneity and/or between-study heterogeneity in the true effects. The impact of statistical heterogeneity was established using the I2 and interpreted as unimportant (<50%), moderate (50–75%) or high (>75%) [78]. Quantitative syntheses were expressed as the standardized mean differences (SMDs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI). The magnitude of the SMDs were interpreted as high (≥0.8), moderate (0.5 to 0.79) or weak (0.2 to 0.49) [79].
Sensitivity analyses were performed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity and analyze their influence on the pooled statistical heterogeneity and pooled effect size. Sensitivity analyses involved rerunning the main analyses, but removing studies with characteristics that could influence the results: (i) studies that had an outlier effect (the 95% CI of the study did not cross the 95% CI of the pooled effect); (ii) studies with a crossover design; (iii) studies in which the experimental group differed from traditional CBL (e.g., with an added component to CBL); (iv) studies in which academic performance was assessed for a focused topic (e.g., diabetes) or did not reflect overall (final) academic performance. We also conducted two additional sensitivity analyses comparing the results of CBL against didactic lectures and against the tutorial method (the only comparison groups with enough studies for single-method analyses). A minimum of two studies had to remain after exclusions in order to perform the sensitivity analysis.
The risk of publication bias was statistically analyzed using the Egger’s test [80] and by inspecting the funnel plots when the meta-analysis included 10 or more studies. However, it should be noted that publication bias should not be automatically inferred, as many other causes can explain funnel plot asymmetry [81,82,83]. Trim-and-fill analysis [84] was also performed to verify whether there was an adjustment in the effect size (SMD) when correcting for the risk of publication bias.
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
Two authors (R.A., C.V.) judged the certainty of evidence, which was summarized using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach [85]. Certainty of evidence was graded as high, moderate, low or very low certainty. Certainty was downgraded if there were concerns related to risk of bias, inconsistency, imprecision, indirectness or risk of publication bias. When the meta-analysis included fewer than 10 studies, risk of publication bias was not considered for downgrading the certainty of evidence.
3. Results
3.1. Search Results and Study Characteristics
Database and manual searches yielded 4470 records. After screening the titles and abstracts, 239 studies were selected for full-text analysis, of which 41 studies met the eligibility criteria and were included in the systematic review [13,18,20,27,37,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,55,69,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112]. The reasons for excluding the remaining 198 studies are reported in the PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 1).
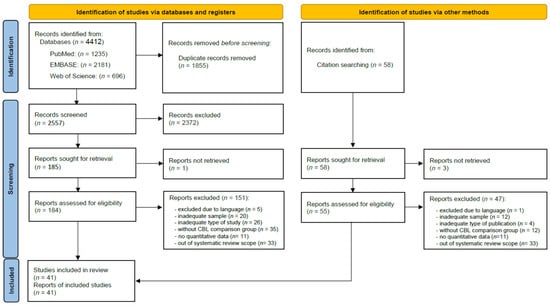
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram for searches and study selection.
The majority of the included studies were published within the last 10 years (36 out of 41 studies). Geographical distribution showed that studies were mostly conducted on the Asian continent (27 studies), followed by the North American continent (10 studies), and with only a few conducted on the European continent (4 studies).
There were 11 studies with a crossover design, 10 studies with a cross-sectional design (post), 16 studies with a pre–post design and 4 with an intermediate–post design (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies, study populations and outcome measures.
3.2. Risk of Bias
All but one of the studies [51] were judged to have a high risk of bias in at least one domain (Figure 2). Around half of the studies (k = 21, 51%) were judged to have a high risk of selection bias due to patient selection, and more than half (k = 26, 63%) due to uncontrolled confounding variables. Nearly all studies (k = 37, 90%) were judged to have a high risk of performance bias due to measurement of exposure. Most studies were judged to have either high (k = 26, 63%) or unclear (k = 13, 32%) risk of detection bias. High risk of attrition bias was identified in nearly half of the studies (k = 19, 46%). No study was judged to have a low risk of selective reporting bias, with 29% (k = 12) of studies being judged to have a high risk and the remaining 71% (k = 29) an unclear risk.

Figure 2.
Risk of bias judgement: (a) study-level; (b) overall summary of all included studies. * The total number of students evaluated in the study was not clear.
3.3. Population Characteristics
A total of 7332 undergraduate medical students were included (Table 1), of which 3168 were from the preclinical (1st to 3rd year) and 3880 from the clinical years (4th to 6th year). The curriculum year was impossible to distinguish for 199 students (between the 3rd and 4th year) and another 62 students (between the 3rd and 6th year).
3.4. Characteristics of CBL and Other Teaching Methodologies
There were 41 studies implementing CBL, 29 studies implementing didactic lectures, 3 studies implementing TBL, 4 studies implementing PBL, 1 study implementing HPS, 5 studies implementing the tutorial method and 1 study implementing independent readings. The characterization of these teaching methodologies according to their models, strategies and methods is described in Table S3.
There were 4639 students in the CBL groups and 3938 students in non-CBL comparison groups (Table 1). The comparison groups were taught using different teaching methods: 1547 students were in didactic lectures groups, 335 students in tutorial-based method groups, 745 students in unspecified teaching method groups, 97 students in independent readings groups, 73 students in TBL groups, 50 students in HPS groups, 27 students in groups receiving lectures with tutorial sessions and 64 students in PBL groups.
The most common curriculum areas investigated were biochemistry (7 studies), microbiology (5 studies), pharmacology (4 studies) and emergency medicine, general surgery, internal medicine, immunology and physiology (3 studies each).
3.5. Comparison of CBL against Other Teaching Methodologies
The outcomes were clustered into the same domains and grouped into academic performance and perceptions. Of the 45 different outcomes collected, 6 outcomes (13.3%) were related to academic performance and 39 outcomes (86.7%) to the different perceptions (Table S4). Within the academic performance domain, 30 studies reported exam scores, 3 studies reported objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) scores and the remaining four outcomes were reported in only 1 study. Perceptions were grouped into four domains, of which the intra-individual student perceptions were the most commonly reported (13 studies). Other perceptions included interpeer (6 studies), student–faculty (8 studies) and other perceptions (5 studies).
3.5.1. Academic Performance
Within the academic performance domain, only two outcomes—exam scores (k = 40) and OSCE scores (k = 3)—were eligible for meta-analysis. The forest plots are shown in Figure S5. The CBL group showed superior academic performance (exam scores) compared to other teaching methodology groups (SMD = 2.37, 95% CI 1.25 to 3.49; large effect, very low certainty). Subgroup analysis showed that the effect size was larger for the otorhinolaryngology subgroup (SMD = 11.78, 95% CI 9.65 to 13.92; large effect). Conversely, there were no significant differences between CBL and other teaching methodologies for the general surgery, microbiology, endocrinology, pharmacology, physiology and molecular biology/biochemistry/genetic medicine subgroups (Table 2). The impact of heterogeneity was high (94%) and significant for the pooled effect and the subgroup analysis, except for the otorhinolaryngology and general surgery subgroups. The funnel plot showed asymmetric effect sizes (Figure S6), and there was a potential risk of publication bias (Egger’s test, t = 5.37, p < 0.001). The trim-and-fill analysis (11 entries added) did not impact the degree of heterogeneity (Figure S6), but the effect size was no longer significant when corrected for publication bias (SMD = 0.66, 95% CI −0.77 to 2.10). Sensitivity analyses revealed that the impact of heterogeneity remained significant except when excluding studies with an outlier effect. In all sensitivity analyses, the effect size remained large and significant. When compared in isolation with didactic lectures or the tutorial method, CBL remained significantly superior (Table S7). On the other hand, academic performance measured using OSCE scores was not significantly different between CBL and other teaching methodologies (Table 2).

Table 2.
Quantitative synthesis of the comparison of CBL and other teaching methodologies.
3.5.2. Intra-Individual Student Perceptions
Five outcomes within the intra-individual student perceptions category were eligible for meta-analysis. The outcome “interest and motivation” was significantly superior in the CBL group (SMD = 0.79, 95% CI 0.13 to 1.44; moderate effect, very low certainty). The remaining four outcomes were not significantly different between CBL and other teaching methodology groups when considering the pooled effect (very low certainty). Subgroup analyses showed a significantly superior effect of CBL for most curricular areas. The impact of heterogeneity was generally high (61% to 96%) and significant, and usually remained unchanged after sensitivity analyses. The effect size did not change with sensitivity analyses, except for the “interest and motivation” outcome, which was no longer significant after removing studies with heterogenous CBL or control groups, but remained significant when removing studies with a crossover design. Forest plots are shown in Figure S5.
3.5.3. Interpeer Perceptions
Only one outcome assessed interpeer perceptions and was eligible for meta-analysis. The CBL and control groups were not statistically different for the “interpeer interaction in team work” outcome (very low certainty). However, the effect size was significantly superior in the CBL groups for all subgroups except for the immunology curriculum area (Table 2). The impact of heterogeneity and effect size remained unchanged after sensitivity analyses (Table S6). Forest plots are shown in Figure S5.
4. Discussion
4.1. Is CBL Effective for Undergraduate Medical Teaching?
Our systematic review with meta-analysis showed that there is a very low certainty of evidence that CBL is significantly superior to other teaching methodologies (especially when compared to didactic lectures or tutorial method) in improving academic performance measured by exam scores. Although a similar significant effect should have been seen in OSCE scores, which reflect clinical cases in real-world scenarios, the meta-analysis of this outcome only accounted for two studies and may thus be unrepresentative.
CBL was also significantly superior at enhancing student interest and motivation. Interestingly, other important student-centered features related to CBL, such as critical thinking and self-learning, were not significantly different in the groups exposed to other teaching methodologies. However, subgroup analysis showed that the CBL group scored significantly higher in critical thinking for all curriculum areas and within all included studies, suggesting that these skills may be improved when using CBL. During the implementation of CBL—as a teaching method oriented towards inquiry and critical thinking—there are different epistemological and theoretical approaches (such as constructivism, cognitivism and behaviorism) [11,32,33,34,114,115] that can interplay to promote and enhance the skills of decision-making, problem-solving and critical and analytical thinking. A constructivist approach is foundational to CBL because it emphasizes the active role of students in creating their own knowledge (discovery learning) while engaging with clinical cases and thus building their own understanding of medical concepts and procedures. Within a constructivist approach, CBL can be seen as more effective at developing critical thinking skills than didactic lectures as it allows students to make connections between what they have learned and real-world scenarios. Social constructivism is also at play during group-based CBL where construction of knowledge occurs through social interaction and communication while working together and discussing the clinical cases. CBL can incorporate elements of cognitivism by developing the cognitive abilities of students by requesting them to process and apply clinical information for them to diagnose and suggest appropriate treatments for the assigned clinical case. For this purpose, students apply their existing cognitive models (mental representations of knowledge) to understand the clinical information presented—which may include recognizing patterns in the patient’s symptoms or drawing connections between the patient’s medical history and their current condition—and thus forming hypotheses about potential diagnoses and treatments. While working through the case, students may refine or expand their existing cognitive models as they learn new information and gain new insights into their decision-making process. By working with real-life clinical cases and applying their knowledge to new situations, students are able to build their own understanding of medical concepts, rather than simply memorizing information. CBL can also be seen through the lens of behaviorism theory (to a lesser extent than didactic lectures), as learning occurs as a result of the students’ response to clinical cases and can be observed and measured by changes in their behavior. By receiving feedback on their performance when making clinical decisions, students are able to understand the consequences of their behavior and adjust it accordingly. Repeated exposure to different realistic clinical cases and feedback can help students to reinforce and strengthen their critical thinking skills. These theoretical learning approaches can blend in CBL, combining into a dynamic process of connectivism and interbehaviorism wherein students’ understanding of clinical cases is shaped by connecting internal (previous experiences and knowledge) and external factors (active construction of meaning that takes place during CBL). By engaging with clinical cases, students are able to actively construct their own understanding of clinical cases while also being influenced by the feedback they receive from their peers and teachers. An experiential learning approach can also be considered as, during the constructivist process, students go through a process of experience, reflection and action (especially if using real patient cases) and can reflect on their own experiences and feedback received. These approaches play a role during CBL, but are also common in other student-centered methods as PBL, TBL and HPS, which promote critical thinking and other related reasoning skills. These features will play a critical role in the students’ future careers as medical doctors as they implement and interpret new knowledge to solve real clinical cases, which is often focused CBL [35,36,45,116,117,118,119].
Our findings underpin an important and relevant effect of CBL and suggest that this teaching method can be successfully implemented in undergraduate medical curricula. These findings should, however, be interpreted with caution. The certainty of evidence was very low for all outcomes due to several limiting factors, including risk of bias, inconsistency, imprecision and indirectness. Both main and subgroup analyses displayed a high impact of heterogeneity for most outcomes, even after sensitivity analysis to exclude studies with potentially confounding factors related to study design and teaching methodologies. However, it should be noted that no meta-analysis showed a tendency or a significant effect for other teaching methodologies compared to CBL. There may have been different potential confounding factors that could not be controlled or analyzed in our sensitivity analyses and that might have influenced the development of important student-centered skills such as self-learning and critical thinking. These student-centered skills, besides being inherently influenced by intra-individual student characteristics (either behavioral, motivational or psychological) [115,120], can be confounded by external factors. Although we excluded studies where the CBL method was applied outside the university context, students might have developed or enhanced these skills by attending extracurricular courses outside the intended curricula or even through previous experience with other teaching methods (e.g., PBL) that might have provided some advantages in developing critical thinking skills. However, such instances were not reported in most of the included studies and could not be controlled or accounted for in our analyses. The socioeconomic and educational factors of the family of origin are also known to influence students’ personal and professional development and performance [121,122,123,124], which may have confounded our results; however, these factors could also not be controlled or accounted for in our analyses. Lastly, the characteristics, profile and charisma of teachers and the strategies they used to implement CBL (or any of the other teaching methods) may have exerted an important influence on the experience of learning and ultimately affected the students’ academic performance and their experience and perceptions of CBL and other teaching methods.
CBL (and other student-centered teaching methods) have not come to completely supersede the traditional method of teaching. Didactic lectures still have a place in medical education as they convey a large amount of basic knowledge to large student classes in a simple and time-efficient fashion. This teaching method may be more suitable for the basic years of medical curriculum where the teacher needs to transmit a huge amount of basic and fundamental information that students must acquire and which will be foundational in later years. This early exposure to fundamental knowledge will allow to enhance the assimilation of knowledge through the discussion of cases [125]. Moreover, teaching methods do not need to be implemented in a standalone fashion, but can rather be combined to allow the advantages of each method to complement other methods. Didactic lectures can thus be combined and complemented with one or more active teaching methods (CBL, TBL, PBL, etc.) to promote students’ autonomy and responsibility in learning while promoting valuable real-world cognitive skills such as problem-solving, decision-making and rational and clinical thinking. This hybrid strategy can be implemented in many different ways that may fit the faculty goals—e.g., using Flipped Classrooms [126,127]—and this can be done as early as the preclinical years [27].
4.2. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CBL?
Theoretical knowledge is important for any medical professional, but it is also crucial to establish a teaching program that can provide future doctors with other intersocial and clinical skills necessary for the practice of medicine. CBL provides a teaching method that relies on students taking an active role to discuss and resolve clinical cases. This teaching method stimulates students to develop their clinical judgement, which will help them to incorporate this clinical knowledge during their medical careers, resulting in better clinical diagnostic decisions and treatment planning. Adequate clinical decisions can have a relevant socioeconomic impact on patients and the healthcare system by avoiding unnecessary complementary diagnostic testing and inadequate treatments. CBL may result in better economic perception, allowing them to understand how their decisions will financially impact their patients and the healthcare system, and can thus promote the financial responsibility required for clinical decision-making [39,103]. Although the effect size was not significantly higher in CBL groups for critical thinking, all studies showed a significant and large effect size compared to the control groups, suggesting that critical thinking can be enhanced with CBL.
CBL results in enhanced interest and motivation among medical students, as shown by our meta-analysis. The higher interest and motivation in the dynamic learning process of CBL allows students to be more focused during lectures, thus maximizing their learning potential and resulting in higher class attendance [98,128]. Higher interest and motivation should reflect higher satisfaction with the teaching method. Although the pooled effect was not significant for self-learning and satisfaction outcomes, several subgroups showed a significantly superior effect size for the CBL group, suggesting that satisfaction with the teaching method can be improved with CBL.
Perception of learning efficacy is frequently cited as superior in the CBL groups compared to the traditional teaching method groups [11,90,97,129]. Although this outcome could not be included in our meta-analysis, this may have been reflected in the CBL group achieving significantly higher exam scores.
CBL can also improve bilateral perceptions of this teaching method between students and faculty. Teachers often report that during the discussion of clinical cases, they feel the students are closer, more active and confident in the classes [31,91,130,131,132,133]. This may be attributed to the way CBL is implemented, relying on open questions [11,31,94,134], which leaves the students more comfortable and confident to participate in the clinical discussion [27,109,132,134]. Our meta-analysis could not analyze these theoretical advantages due to the scarcity of studies that evaluated student–faculty perceptions and the heterogenous methods applied by studies that collected these outcomes.
Interpeer collaboration in team work is also an important advantage of CBL. CBL encourages students to share their ideas and knowledge to discuss and resolve clinical cases [41,90,129]. CBL fosters peer interaction, a fundamental skill needed for future medical doctors to work in multidisciplinary teams. Although the pooled effect size of interpeer interaction in team work was not significantly different in our meta-analysis, all but one subgroup showed that this outcome was significantly superior in the CBL groups.
As with any teaching method, CBL is not free of disadvantages. The potential need for more time allotted for classes can be a disadvantage of the CBL teaching method. The time allotted for classes depends on the facilitator profile and how CBL is implemented, but it can be continuously adjusted in response to students’ feedback to provide a more successful implementation and performance [135,136]. Our meta-analysis showed no differences in the time allotted for classes between CBL and didactic lectures. Academic burden outside classes can also be an important disadvantage of CBL. While CBL enhances students’ time management [73,129,137], it can also demand more time from students to prepare for classes [136,138] and result in insufficient time for students to rest between classes [139,140,141]. These factors can increase stress levels of students and decrease their academic performance [37]. There were not enough studies that evaluated the burden of time consumed before and after classes, and we were not able to perform a meta-analysis on the academic burden. This theoretical disadvantage showed conflicting results across the included studies and the true influence of CBL on out-of-class stress levels remains elusive. While a few studies [92,112] reported no differences in the academic burden or preclass workload, another study [20] even reported less free time consumed in the CBL group. Conversely, another study [37] reported increased stress levels from lack of relaxation and sleeping time in the CBL group, but their outcomes were confounded by the more condensed schedule of the CBL group (reduction by four weeks of the academic semester) compared to the didactic lectures group, which may have resulted in less time to relax and rest during a shorter semester.
4.3. Unanswered Questions and Future Directions
There is a clear need for further studies on this topic with homogeneous research methods that provide extractable and quantifiable data to allow more robust findings to be achieved in future systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Most available comparative studies compare CBL to didactic lectures, but it is important to extend future research to compare other teaching methods that are less represented in our systematic review (TBL, HPS, PBL, tutorial method and independent readings). When there are enough studies comparing these different teaching methods, it will be possible to make a more direct comparison through a network meta-analysis and identify the most effective teaching method(s) for undergraduate medical students.
Future studies should include different stages of the medical curriculum, as the studies included in our systematic review did not cover all curricular areas. It is also important to conduct long-term studies comparing exposure to different teaching methods throughout the undergraduate medical curriculum (from the basic components to the clinics) to understand which methods enhance long-term knowledge retention and improve clinical and interpersonal skills. These long-term studies will help researchers to understand how the maturity of students plays a role in the providing adequate teaching methods and in which curricular year(s) CBL can yield higher efficacy. Our systematic review included studies from different regions of the world, but European and African countries were under-represented. It is important to have data from the other global regions because different countries can represent varying cultural and educational contexts. We encourage future studies on CBL to be conducted within European and African educational contexts.
Although exam scores have an unquestionable impact on students’ academic paths, the perceptions of the teaching method also play an important role. The influence of these perceptions should be evaluated at several timepoints that may be related to CBL—such as in the preparation for classes, during classes and in studying for exams—along with how these perceptions impact the active participation of students and their understanding of the educational content. Our systematic review included only studies that objectively quantified the students’ perceptions, but there is also a significant body of literature that analyzes these perceptions in a qualitative fashion [40,142,143,144,145,146,147]. Future studies should focus on a mixed-methods approach to combine quantitative and qualitative analysis and reach a deeper understanding of the impact of perception on CBL efficacy and effectiveness.
The assessment of the teachers’ perspective was often overlooked in the included studies. It is crucial to understand how facilitators feel about their less active role in CBL, their tolerance and receptivity to CBL and their vulnerability when discussing clinical cases that may go beyond their specialization, clinical skills and experience. Indeed, some teachers have reported that they felt insecure when transitioning to CBL [47]. These factors can influence the facilitator’s own identity and should also be considered in future studies. There is only limited evidence of the perceptions of teachers in regards to the CBL method. Faculty teaching CBL have reported that a CBL program can be time-intensive [47,49], especially concerning the burden associated with the preparation of clinical cases and classes [148] and coordinating with other facilitator(s) [47]. Notwithstanding, faculty often reported positive feedback [148,149] and welcomed CBL as a complement to conventional methods [150], as it could help them to achieve their objectives [62].
There are some more unanswered questions. Further research should focus on how the clinical cases presented in CBL can impact the efficacy of learning: (i) structured vs. unstructured clinical cases; (ii) use of multimedia (e.g., avatars) or case simulations (with dummies or actors) to complement the clinical vignettes; (iii) adequate duration of classes; and (iv) the benefits of theoretical presentation of the topic (e.g., didactic lectures) before and after the discussion of cases to complement and reinforce the acquired knowledge.
4.4. Limitations
There are some limitations related to the systematic review process. The poor uniformity in the descriptions of CBL across the studies in the literature may have led us to miss some potentially relevant studies during the database searches.
There were also some limitations that were inherent to the original studies. The scarcity of studies that compared CBL with other teaching methodologies (other than didactic lectures) limited the stratification of meta-analysis. The definition of control interventions was also heterogenous due to the available studies, but we made several sensitivity analyses to account for this confounder. This limitation precluded a head-to-head comparison between CBL and each of the other teaching methodologies. However, a head-to-head comparison between CBL and didactic lectures was possible and is reported in our sensitivity analyses.
Although the CBL is well established and commonly used, was often described using broad pedagogical concepts [11]—i.e., CBL interventions were heterogeneous in terms of conceptual and practical perspectives—which were inherent to each study purpose and specific aim. The poor definition of methods and implementation of CBL and the other teaching methodologies contributed to the difficulty in homogenizing meta-analysis groups, and we thus had to group CBL under a broader umbrella concept of CBL; future studies should allow for a stricter definition of CBL and for the grouping CBL into more homogenous subgroups.
The heterogeneity in how outcomes were collected and the lack of objective quantification of outcome data also precluded us from conducting further meta-analyses on other outcomes that would have been relevant to our systematic review. The variation in how outcomes were collected and the definition and implementation of the teaching methodologies may explain some of the heterogeneity we found, even despite the sensitivity analyses we performed.
The heterogeneity in the included populations, especially related to the curriculum years and areas, may have also led to heterogeneity in the meta-analysis. The imprecision of the reporting of sample sizes (occasionally reported as intervals) decreased the accuracy of the sample size determination; in these cases, where the sample size was reported as a range, we selected the largest sample size.
Studies in medical education are often of a pre–post design which is not ideal for control of all extraneous/confounder factors; this limitation was reflected in a high risk of selection bias.
5. Conclusions
The CBL teaching method significantly enhanced academic performance and improved interest and motivation in undergraduate medical students compared to other teaching methods (especially when compared to didactic lectures or the tutorial method). However, the certainty of evidence was very low and further studies are warranted before a stronger and more definitive conclusion can be drawn. Nonetheless, CBL seems to be superior to or as good as other teaching methods and may be successfully implemented for undergraduate medical students.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/educsci13030238/s1, Table S1—Database search strategy for each database included; Table S2—Risk of bias appraisal criteria defined according to Risk of Bias Assessmenttool for Non-randomized Studies (RoBANS) tool; Table S3—Characterization of teaching methodologies according to their models and strategies. Table S4—Scoping summary of outcome measures; Figure S1—Forest plots of included meta-analyses; Figure S1.1—Forest plot comparing exam scores between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.2—Forest plot comparing OSCE (objective structured clinical examination) scores between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.3—Forest plot comparing self-learning between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.4—Forest plot comparing critical thinking between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.5—Forest plot comparing satisfaction with teaching method between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.6—Forest plot comparing time allotted for classes between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.7—Forest plot comparing interest and motivation between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S1.8—Forest plot comparing interpeer interaction in teamwork between CBL and other teaching methodologies; Figure S2—Funnel plots of included meta-analyses; Figure S2.1—Funnel plot of exam score outcomes; Figure S2.2—Trim-and-fill funnel plot of exam score outcomes; Table S5—Sensitivity analyses of each eligible outcome.
Author Contributions
All authors were involved in the conceptualization of the systematic review. D.M. and R.A. were involved in the database searches and data extraction. D.M., R.A. and C.V. performed the data synthesis (meta-analysis), organization and reporting. R.A. and J.A. judged the risk of bias of the studies included in the systematic review. R.A. and C.V. judged the certainty of recommendation using GRADE. J.A., P.C. and J.E.-M. guided and provided advice during all steps of the development of the systematic review, as well as providing critical revision of manuscript content. All authors contributed to drafting and approving the final manuscript prior to submission to the peer-reviewed journal. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare there are no conflict of interest.
References
- Armstrong, E.G.; Mackey, M.; Spear, S.J. Medical education as a process management problem. Acad. Med. 2004, 79, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korin, T.L.; Reznich, C.B.; Shin, J.Y. A “gold standard” for designing Web sites for clerkships’ online syllabi. Acad. Med. 2001, 76, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.S.; Yu, Y.R.; Yeh, A.C.; Newman, L.R.; Arky, R.; Roberts, D.H. Musculoskeletal preclinical medical school education: Meeting an underserved need. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Willett, K.M. Maintaining standards in surgical training: How effective is the accreditation by the Specialist Advisory Committee in the United Kingdom? J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundine, K.; Buckley, R.; Hutchison, C.; Lockyer, J. Communication skills training in orthopaedics. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, D.; Rowley, D.I.; Sher, J.L. Assessment of performance in orthopaedic training. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, A.; Ross, M. The Tuning Project for Medicine—Learning outcomes for undergraduate medical education in Europe. Med. Teach. 2007, 29, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.M. Approaches to curriculum planning. Med. Educ. 1986, 20, 458–466. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Cate, O.; Chen, H.C.; Hoff, R.G.; Peters, H.; Bok, H.; van der Schaaf, M. Curriculum development for the workplace using Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs): AMEE Guide No. 99. Med. Teach. 2015, 37, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, L.; Spooner, C.; Tjosvold, L.; Oswald, A. Problem-based learning in pre-clinical medical education: 22 years of outcome research. Med. Teach. 2010, 32, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thistlethwaite, J.E.; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay, D. The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 23. Med. Teach. 2012, 34, e421–e444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omelicheva, M.Y.; Avdeyeva, O. Teaching with Lecture or Debate? Testing the Effectiveness of Traditional versus Active Learning Methods of Instruction. PS Political Sci. Politics 2008, 41, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciraj, A.M.; Vinod, P.; Ramnarayan, K. Enhancing active learning in microbiology through case based learning: Experiences from an Indian medical school. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2010, 53, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidet, P.; Morgan, R.O.; O’Malley, K.; Moran, B.J.; Richards, B.F. A controlled trial of active versus passive learning strategies in a large group setting. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2004, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downar, J.; McNaughton, N.; Abdelhalim, T.; Wong, N.; Lapointe-Shaw, L.; Seccareccia, D.; Miller, K.; Dev, S.; Ridley, J.; Lee, C.; et al. Standardized patient simulation versus didactic teaching alone for improving residents’ communication skills when discussing goals of care and resuscitation: A randomized controlled trial. Palliat. Med. 2017, 31, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; King, A.; Soman, S.; Lischuk, A.; Schneider, B.; Walor, D.; Bramwit, M.; Amorosa, J.K. Medical students’ preferences in radiology education a comparison between the Socratic and didactic methods utilizing powerpoint features in radiology education. Acad. Radiol. 2011, 18, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, F. Medical education: Capitalizing on the lecture method. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendan, J.C.; Silver, M.; Ben-David, K. Changing the student clerkship from traditional lectures to small group case-based sessions benefits the student and the faculty. J. Surg. Educ. 2011, 68, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, S.J.; Stephenson, D.; Troy, J. Higher education students’ attitudes to student-centred learning: Beyond ‘educational bulimia’? Stud. High Educ. 2003, 28, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, L.; Deng, W.; Zhu, J.; Su, A.; Zhang, Y. The effectiveness of the combined problem-based learning (PBL) and case-based learning (CBL) teaching method in the clinical practical teaching of thyroid disease. BMC Med. Educ. 2020, 20, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.V.; Haughton, E.; Van Eyk, D. Increasing Endurance by Building Fluency: Precision Teaching Attention Span. Teach. Except. Child. 1990, 22, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zuo, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Zou, Y.; Liang, D. Comparison between flipped classroom and lecture-based classroom in ophthalmology clerkship. Med. Educ. Online 2017, 22, 1395679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, H.; Ketteridge, S.; Marshall, S. A Handbook for Teaching and Learning in Higher Education: Enhancing Academic Practice; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hempel, D.; Stenger, T.; Campo Dell’ Orto, M.; Stenger, D.; Seibel, A.; Röhrig, S.; Heringer, F.; Walcher, F.; Breitkreutz, R. Analysis of trainees’ memory after classroom presentations of didactical ultrasound courses. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2014, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.S.; Robinson, S.; Alberts, P. Students pay attention! Combating the vigilance decrement to improve learning during lectures. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2009, 10, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyke, P.; Jamrozik, K.; Plant, A.J. A randomized trial of a problem-based learning approach for teaching epidemiology. Acad. Med. 2001, 76, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Waliany, S.; Caceres, W.; Merrell, S.B.; Thadaney, S.; Johnstone, N.; Osterberg, L. Preclinical curriculum of prospective case-based teaching with faculty-and student-blinded approach. BMC Med. Educ. 2019, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutyak, J.P.; Lebeau, R.B.; Spotnitz, A.J.; O’Donnell, A.M.; Mehne, P.R. Role of case structure and prior experience in a case-based surgical clerkship. Am. J. Surg. 1996, 172, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.P.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hong, C.Y. Innovative” Case-Based Integrated Teaching” in an undergraduate medical curriculum: Development and teachers’ and students’ responses. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2008, 37, 952. [Google Scholar]
- Demarco, R.; Hayward, L.; Lynch, M. Nursing students’ experiences with and strategic approaches to case-based instruction: A replication and comparison study between two disciplines. J. Nurs. Educ. 2002, 41, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.S. Increased student self-confidence in clinical reasoning skills associated with case-based learning (CBL). J. Vet. Med. Educ. 2006, 33, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Newby, T.J. Behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism: Comparing critical features from an instructional design perspective. Perform. Improv. Q. 1993, 6, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, L.D. Demystifying instructional innovation: The case of teaching with case studies. J. Sch. Teach. Learn. 2013, 13, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, B. Teaching for engagement: Part 1--Constructivist principles, case-based teaching, and active learning. Coll. Q. 2015, 18, n2. [Google Scholar]
- van Gog, T.; Ericsson, K.A.; Rikers, R.M.J.P.; Paas, F. Instructional design for advanced learners: Establishing connections between the theoretical frameworks of cognitive load and deliberate practice. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2005, 53, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Merriënboer, J.J.G.; Sweller, J. Cognitive Load Theory and Complex Learning: Recent Developments and Future Directions. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2005, 17, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.A.; Karimi, A.A.; Alboloushi, N.A.; Al-Omari, Q.D.; AlSairafi, F.J.; Qudeimat, M.A. Stress Level of Dental and Medical Students: Comparison of Effects of a Subject-Based Curriculum versus a Case-Based Integrated Curriculum. J. Dent. Educ. 2017, 81, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.F.; Li, C.Z.; Shang, S.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Zhou, G. Practising case-based learning in oral medicine for dental students in China. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 2013, 17, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.M.; Collazo, R.A.; Athauda, G.; Obeso, V.T.; Toonkel, R.L. Taking CBL to the Lecture Hall: A Comparison of Outcomes Between Traditional Small Group CBL and a Novel Large Group Team-Based CBL Teaching Method. Med. Sci. Educ. 2019, 30, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, C.M.; Voss, J.; Thomas Aretz, H. Case method teaching: An effective approach to integrate the basic and clinical sciences in the preclinical medical curriculum. Med. Teach. 2009, 31, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B. Case based learning—A review of the literature: Is there scope for this educational paradigm in prehospital education? Emerg. Med. J. 2005, 22, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Sangle, D. Comparative Study of Case Based Learning (CBL) with Didactic Lectures as a Teaching–Learning (TL) Method for Improvement of Ethical Skills of M. Sc. Pharmaceutical Medicine Students. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2013, 6, 912–915. [Google Scholar]
- Daher, A.M.; Singh, H.J.; Kutty, M.K. Differentiating case-based learning from problem-based learning after a two-day introductory workshop on case-based learning. Australas. Med. J. 2017, 10, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.F. Case-Based Learning and its Application in Medical and Health-Care Fields: A Review of Worldwide Literature. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 2016, 3, JMECD-S20377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, H.S. A taxonomy of problem-based learning methods. Med. Educ. 1986, 20, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diggele, C.; Burgess, A.; Mellis, C. Planning, preparing and structuring a small group teaching session. BMC Med. Educ. 2020, 20, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordquist, J.; Sundberg, K.; Johansson, L.; Sandelin, K.; Nordenström, J. Case-based learning in surgery: Lessons learned. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, D.; Sinnathurai, S.; Haunhorst, S.; Seibel, A.; Michels, G.; Heringer, F.; Recker, F.; Breitkreutz, R. Influence of case-based e-learning on students’ performance in point-of-care ultrasound courses: A randomized trial. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 23, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamkar, A.V.; Burdick, W.; Morahan, P.; Yemul, V.Y.; Sarmukadum; Singh, G. Proposed model of case based learning for training undergraduate medical student in surgery. Indian J. Surg. 2007, 69, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.P.; Shah, T.; Seth, S.; Pandit, N.; Shah, G.V. Case based learning: A method for better understanding of biochemistry in medical students. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1576–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.R.; Fernandez, R.; Kouyoumjian, S.R.; Jones, K.A.; Compton, S. A randomized comparison trial of case-based learning versus human patient simulation in medical student education. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2007, 14, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, B.; Ertl, S.; Wong, G.; Wadowski, P.P.; Löffler-Stastka, H. Does case-based blended-learning expedite the transfer of declarative knowledge to procedural knowledge in practice? BMC Med. Educ. 2019, 19, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, M.H.; Newell, A.D.; Fotos, J.; Germaine, P.; Gilpin, J.W.; Lewis, K.; Stein, M.W.; Straus, C.; Sepulveda, K.A. Multisite Implementation of Radiology-TEACHES (Technology-Enhanced Appropriateness Criteria Home for Education Simulation). J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, E.C.; Osheroff, N.; Pettepher, C.C.; Cutrer, W.B.; Carnahan, R.H. Using Small Case-Based Learning Groups as a Setting for Teaching Medical Students How to Provide and Receive Peer Feedback. Med. Sci. Educ. 2017, 27, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, R. Impact of case-based lectures on students’ performance in vascular physiology module. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2014, 38, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, P.; Patel, M.; Johnson, E.; Weiss, M. Active learning and student-centered pedagogy improve student attitudes and performance in introductory biology. CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2009, 8, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, R.M.; Gaba, D.M. The role of debriefing in simulation-based learning. Simul. Healthc. 2007, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maudsley, G. Roles and responsibilities of the problem based learning tutor in the undergraduate medical curriculum. BMJ 1999, 318, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savery, J. Overview of Problem-based Learning: Definitions and Distinctions. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Learn. 2006, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, D.J.; Domer, F.R. Utility of the case-method approach for the integration of clinical and basic science in surgical education. J. Cancer Educ. 2002, 17, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Blewett, E.L.; Kisamore, J.L. Evaluation of an interactive, case-based review session in teaching medical microbiology. BMC Med. Educ. 2009, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.; Chia, K.S.; Jeyaratnam, J.; Chia, S.E.; Singh, J. Case studies in occupational medicine for medical undergraduate training. Occup. Med. 1995, 45, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, S.R.; Gonzalez, L.S. Instruction in professional issues using a cooperative learning, case study approach. Commun. Disord. Q. 2006, 27, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.S.; Airasian, P.; Cruikshank, K.; Mayer, R.; Pintrich, P.; Raths, J. A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives; Pearson: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.M.; Helberg, S.B. Chart-based, case-based learning. S. Dak. Med. 2007, 60, 391, 393, 395, 397, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, K.J. Beyond multiple-choice questions: Using case-based learning patient questions to assess clinical reasoning. Med. Educ. 2006, 40, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutyak, J.P.; Lebeau, R.B.; O’Donnell, A.M. Unstructured cases in case-based learning benefit students with primary care career preferences. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 175, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.; Ryall, M.A.; Corrigan, G. Case-based learning: Developing patient- and student-centred learning. Med. Educ. 2007, 41, 508–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiga, S.; Adiga, U. Problem based learning—An approach to learning pharmacology in medical school. Biomed. Res. 2010, 21, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, F.E.; Hendricson, W.D. A case-based learning model in orthodontics. J. Dent. Educ. 1994, 58, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholl, T.A.; Lou, K. A model for small-group problem-based learning in a large class facilitated by one instructor. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2012, 76, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, B.J.; Baines, A.T.; McVey, M.; Thompson, J.T.; Wilkins, H. A case-based approach increases student learning outcomes and comprehension of cellular respiration concepts. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2007, 35, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Wilkes, M.; Stevenson, F.; Nguyen, T.; Slavin, S. Comparing problem-based learning with case-based learning: Effects of a major curricular shift at two institutions. Acad. Med. 2007, 82, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Education, S. Instructional Approaches: A Framework for Professional Practice; Saskatchewan: Regina, SK, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.J.; Sheen, S.S.; Hahn, S.; Jang, B.H.; Son, H.J. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IntHout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Borm, G.F. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke, J. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Experts’ views are still needed. BMJ 1998, 316, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doleman, B.; Freeman, S.C.; Lund, J.N.; Williams, J.P.; Sutton, A.J. Funnel plots may show asymmetry in the absence of publication bias with continuous outcomes dependent on baseline risk: Presentation of a new publication bias test. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Schmid, C.H.; Olkin, I. The case of the misleading funnel plot. BMJ 2006, 333, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, G.W. Handbook for Grading the Quality of Evidence and the Strength of Recommendations: Using the GRADE Approach; GRADE Working Group: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alimoglu, M.K.; Sarac, D.B.; Alparslan, D.; Karakas, A.A.; Altintas, L. An observation tool for instructor and student behaviors to measure in-class learner engagement: A validation study. Med. Educ. Online 2014, 19, 24037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Bhardwaj, N.; Mahdi, F.; Srivastava, J.P.; Gupta, U. Integrated teaching program using case-based learning. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2015, 5, S24–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, G.A.; Behling, K.C.; Lopez, O.J. Evaluation of the role of incentive structure on student participation and performance in active learning strategies: A comparison of case-based and team-based learning. Med. Teach. 2018, 40, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Qiang, H.; Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Z. Application of PBL combining CBL in otorhinolaryngological teaching. Biomed. Res. 2017, S703–S705. [Google Scholar]
- Diwan, J.S.; Sanghavi, S.J.; Shah, C.J.; Shah, A.M. Comparison of case-based learning and traditional lectures in physiology among first year undergraduate medical students. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 7, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortun, J.; Morales, A.C.; Tempest, H.G. Introduction and evaluation of case-based learning in the first foundational course of an undergraduate medical curriculum. J. Biol. Educ. 2017, 51, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Garg, B.; Sood, N. Introduction of case-based learning aided by WhatsApp messenger in pathology teaching for medical students. J. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 66, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, W.F.; Ferguson, K.J.; Sipe, C.S.; Sorosky, J. Attitudes of faculty and students toward case-based learning in the third-year obstetrics and gynecology clerkship. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2005, 192, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Azam, N.; Shafi, M.; Majeed, S.; Ali, S. Perceptions of undergraduate medical students regarding case based learning and tutorial format. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2015, 65, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, K.B.; Nilawar, A.N.; Thorat, A.P. Effect of case based learning in understanding clinical biochemistry. Int. J. Biomed. Adv. Res. 2014, 5, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, S.K.; Marathe, P.A.; Patel, T.C.; Shetty, Y.C.; Rege, N.N. Introduction of case based teaching to impart rational pharmacotherapy skills in undergraduate medical students. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Rehncy, J.; Kahal, K.S.; Singh, J.; Sharma, V.; Matreja, P.S.; Grewal, H. Case-Based Learning as an Effective Tool in Teaching Pharmacology to Undergraduate Medical Students in a Large Group Setting. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 2020, 7, 2382120520920640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.F.; Chiu, N.T.; Li, C.Y. Value of case-based learning in a nuclear medicine clerkship. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2013, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Cao, M. Comparison of student perception and performance between case-based learning and lecture-based learning in a clinical laboratory immunology course. Med. Lab. 2016, 40, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, J.A.; Toonkel, R.L.; Athauda, G. Large Group Case-Based Learning (TB-CBL) Is an Effective Method for Teaching Cancer Chemotherapy to Medical Students. Med. Sci. Educ. 2018, 28, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaldo, L.G.; Herskovic, L.P. Teaching of clinical reasoning to medical students using prototypical clinical cases. Rev. Med. Chile 2013, 141, 823–830. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaiah, B.; Gowda, V.; Jeyachristy, S.; Maung, T. Motivating First year medical students to learn biochemistry by Case based learning. Int. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 5, 461–464. [Google Scholar]
- Palappallil, D.S.; Sankar, H.K.; Retnayyan, A.; Radhakrishnan, S. Effectiveness of case-based learning, task-based learning, and didactic lectures on teaching personal drug concept among medical undergraduates. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Bhowmick, K.; Sadhu, M. Efficacy of case based learning as an adjunct to traditional teaching learning methods in Physiology. South-East Asian J. Med. Educ. 2013, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Karadesai, S. To Determine the Effectiveness of Case Based Tutorials As Compared To Traditional Tutorials in Microbiology. Natl. J. Integr. Res. Med. 2016, 7, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, S.J.; Jacob, T.M.; Sathyendra, S. Vertical integration of basic science in final year of medical education. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2016, 6, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, B.; Ajay, G.A.; Gupta, A. Case based versus didactic lecture for effective learning biochemistry in first MBBS. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2017, 4, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Surapaneni, K. The effect of integrated teaching with case based learning (CBL) in the biochemistry of undergraduate medical curriculum. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2010, 5, 3058–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Tathe, S.S.; Singh, A. Case based lectures versus conventional lectures for teaching medical microbiology to undergraduate students. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2014, 6, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Vedi, N.; Dulloo, P. Students’ perception and learning on case based teaching in anatomy and physiology: An e-learning approach. J. Adv. Med. Educ. Prof. 2021, 9, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vora, M.B.; Shah, C.J. Case-based learning in pharmacology: Moving from teaching to learning. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2015, 5, S21–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y. Flipped classroom combined with case-based learning is an effective teaching modality in nephrology clerkship. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiga, U.; Adiga, S. Case based learning in biochemistry. Int. J. Pharm. Biosci. 2011, 2, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner, J.L.; Cox, M.T.; González-Calero, P.A. Case-based reasoning-inspired approaches to education. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2005, 20, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.A.; Qazi, W.; Yousufi, S.Q. The influence of psychological, motivational, and behavioral factors on university students’ achievements: The mediating effect of academic adjustment. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2021, 13, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricson, W.D. Changes in educational methodologies in predoctoral dental education: Finding the perfect intersection. J. Dent. Educ. 2012, 76, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Petersen, D.J.; Soriano, R.; Friedman, E.; Bensinger, L.D. Training Tomorrow’s Teachers Today: A national medical student teaching and leadership retreat. Med. Teach. 2007, 29, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, H.S.; Tamblyn, R.M. Problem-Based Learning: An Approach to Medical Education; Springer Publishing Company: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.G. Assumptions underlying self-directed learning may be false. Med. Educ. 2000, 34, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Donoso-González, M.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J. Analysis of perceptual, psychological, and behavioral factors that affect the academic performance of education university students. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 238, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.P.; Chen, C.H.; Su, T.P.; Shih, W.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hou, S.M. The association between parental socioeconomic status (SES) and medical students’ personal and professional development. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2007, 36, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpole, M. Emerging from the pipeline: African American students, socioeconomic status, and college experiences and outcomes. Res. High. Educ. J. 2008, 49, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooter, R.; Erdmann, J.B.; Gonnella, J.S.; Callahan, C.A.; Hojat, M.; Xu, G. Economic diversity in medical education: The relationship between students’ family income and academic performance, career choice, and student debt. Eval. Health Prof. 2004, 27, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Kahlon, N.; Agarwal, P.; Dixit, S. Relationship between Student’s Family Socio-economic Status, Gap Year/years after Schooling and Self-concept: A Cross-Sectional Study among Medical Students. Int. Physiol. J. 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorey, K.; Lamoria, M.; Singh, Y.; Naik, S.C. Introduction of Case Based Learning (CBL) in First Year Mbbs and Its Comparison with Tutorial as a Teaching Learning Tool; Semantic Scholar: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.; Wiesbauer, F. The flipped classroom in medical education: A new standard in teaching. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2022, 42, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçayır, G.; Akçayır, M. The flipped classroom: A review of its advantages and challenges. Comput. Educ. 2018, 126, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Cook, K. Attendance and achievement in problem-based learning: The value of scaffolding. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2012, 6, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Khan, R.A.; Yasmeen, R.; Ahsan, N.U. How Case Based Learning Promotes Deep Learning In Preclinical Years Of Medical Students? J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2020, 32, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Matar, E.; Roberts, C.; Haq, I.; Wynter, L.; Singer, J.; Kalman, E.; Bleasel, J. Scaffolding medical student knowledge and skills: Team-based learning (TBL) and case-based learning (CBL). BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, D.K.; Averbach, R.E.; Fryer, G.E., Jr. Student preference for a case-based vs. lecture instructional format. J. Dent. Educ. 1991, 55, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peplow, P.V. Self-directed learning in anatomy: Incorporation of case-based studies into a conventional medical curriculum. Med. Educ. 1990, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.N.; Buckley, P. An evaluation of case-based teaching: Evidence for continuing benefit and realization of aims. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2004, 28, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamede, S.; van Gog, T.; Sampaio, A.M.; de Faria, R.M.; Maria, J.P.; Schmidt, H.G. How can students’ diagnostic competence benefit most from practice with clinical cases? The effects of structured reflection on future diagnosis of the same and novel diseases. Acad. Med. 2014, 89, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Katsikitis, M. The ‘expert’ in problem-based and case-based learning: Necessary or not? Med. Ed. 2001, 35, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.; Healy, M.; McCutcheon, M.; O’Callaghan, S. Adapting Case-Based Teaching to Large Class Settings: An Action Research Approach. Account. Educ. 2011, 20, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauer, G.F.; Forrester, S.D.; Shuman, C.; Sanderson, M.W. Comparison of student performance after lecture-based and case-based/problem-based teaching in a large group. J. Vet. Med. Educ. 2008, 35, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiat, P.N.; Kwong, Y.T. The flipped classroom experience. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 27th Conference on Software Engineering Education and Training (CSEE&T), Klagenfurt, Austria, 23–25 April 2014; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pöhlmann, K.; Jonas, I.; Ruf, S.; Harzer, W. Stress, burnout and health in the clinical period of dental education. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 2005, 9, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedky, N.A. Perceived Sources of Stress among Junior & Mid-Senior Egyptian Dental Students. Int. J. Health Sci. 2012, 6, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, R.S.; Adams, J.S.; Simeon, D.; Persad, S. Sources of stress and psychological disturbance among dental students in the West Indies. J. Dent. Educ. 2002, 66, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoulas, A.; Forty, E.; Hoskins, M.; Walters, J.; Riley, S. A case-based medical curriculum for the 21st century: The use of innovative approaches in designing and developing a case on mental health. Med. Teach. 2017, 39, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Shankar, N. Students’ perceptions about the use of case based learning during dissections in an Indian medical college. Eur. J. Anat. 2017, 21, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg, S.B.; Deutsch, S.; Bellissimo, J.; Elkowitz, D.E.; Stern, J.N.; Lucito, R. Integration of leadership training into a problem/case-based learning program for first-and second-year medical students. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 2018, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; López-Novoa, J.M. Teaching integrative physiology using the quantitative circulatory physiology model and case discussion method: Evaluation of the learning experience. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2008, 32, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, S.; Bobby, Z.; Ananthanarayanan, P.; Radhika, M.; Kavitha, M.; Prashanth, T. Case based learning versus problem based learning: A direct comparison from first year medical students perspective. Med. Educ. 2011, 2, WMC001976. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, J.K.; Begum, S.; Goud, M.B.; Zaki, B. Comparison of didactic lectures and case-based learning in an undergraduate biochemistry course at RAK Medical and Health Sciences University, UAE. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2016, 5, 3212–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.T.; Krackov, S.K. The use of small group case-based exercises in human gross anatomy: A method for introducing active learning in a traditional course format. Clin. Anat. 1994, 7, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufert, J.; Wiebe, R.; Schwartz, K.; Labine, L.; Lutfiyya, Z.M.; Pearse, C. End-of-life ethics and disability: Differing perspectives on case-based teaching. Med. Health Care Philos. 2010, 13, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, S.; Hörnlein, A.; Tony, H.P.; Kraemer, D.; Oberück, S.; Betz, C.; Puppe, F.; Kneitz, C. Assessment of a case-based training system (d3web.Train) in rheumatology. Rheumatol. Int. 2006, 26, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).