Abstract
Nanotechnology is an interdisciplinary field that promises to reshape many spheres of our lives. One core activity in nanotechnology is the synthesis of nanoparticles. Here, we introduce a research-based activity centered on the use of zein, the main constitutive protein in maize, as a raw material for the synthesis of nanoparticles. In the context of the contingency imposed by COVID-19, this experimental activity was designed to be independent of a central laboratory. Therefore, it was enabled by a portable heating do-it-yourself (DIY) device that the students assembled in their own home. We describe the implementation of this activity as part of a graduate-level seminar series, and share our observations. We assessed the students’ knowledge on seven topics related to nanotechnology, do-it-yourself devices, and protein synthesis. The students appeared to perceive that their degree of knowledge had advanced (on average) in all the learning topics; the students stated that their degree of knowledge in the topics of assembly of devices and protein structure had advanced the most. The results of this assessment suggest that this simple, hands-on, research-based activity effectively engaged students in a learning process that allowed them to integrate knowledge while exercising their experimental skills. In addition, we show that these types of activities are suitable for implementation even in circumstances of restricted access to laboratory facilities, such as the ones recently experienced during the pandemic.
1. Introduction
Today, nanotechnology is one of the most active fields of research. The use of nanoparticles promises to drastically reshape many aspects of our daily life [1,2,3], including the way we manufacture superior and/or smart materials [4,5,6,7], and the manner in which we prevent, diagnose, or treat our diseases [1,8]. The fabrication of nanoparticles—particles that possess at least one dimension in the nanoscale (i.e., under 100 nm) [9]—is a core activity in nanotechnology [10,11,12,13].
Exposing science and engineering students to the fabrication of nanoparticles is an obvious strategy for introducing them to nanotechnology [14,15,16]. However, most methodologies for the fabrication of nanoparticles require conditions (i.e., high temperatures, high pressures, hazardous reagents) that limit their implementation in a regular classroom and even in a conventional chemistry laboratory [17].
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a severe restriction of access to laboratories in many countries around the globe, and made exposing students to real, hands-on experimental activities related to nanotechnology an even greater challenge. In this context, we designed a simple research-based activity centered on the fabrication of protein-based nanoparticles, which the students could conduct in their own homes.
We selected zein, the main constitutive protein in maize [18,19], as the main raw material. Zein possesses several attributes that make it attractive for nanoparticle synthesis. One is that it is a relatively inexpensive and widely available material that can be easily dissolved in conventional and low-risk solvents, such as ethanol [20], isopropanol [21], and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) [22]. Zein itself is very safe; indeed, it is a GRAS (generally recognized as safe) reagent with wide uses in adhesive [23], food [24,25], and pharmaceutical formulations [26,27]. Zein is also a friendly material from a fabrication perspective [20,28,29,30,31].
The fabrication of zein nanoparticles is also attractive from the point of view of its simplicity and safety for the students. Many different methods have been proposed for the fabrication of zein-based nanoparticles [32,33,34,35,36,37], and several involve the use of inexpensive, non-hazardous, and readily accessible reagents (ethanol, isopropanol, and glycerol) and simple procedures that can be implemented even at home.
Here, we designed and implemented a research-based activity that was amenable to implementation in very basic laboratory settings or even at home during the pandemic. In this hands-on activity, students fabricated zein nanoparticles using different methodologies that they selected. Furthermore, we present a semi-quantitative assessment of the effect of this intervention on the learning of concepts relevant to a graduate course in nanobiotechnology.
This proof-of-concept pilot study illustrates the implementation of a cost-effective and minimum-risk experimental activity that enables the fabrication of nanoparticles in any laboratory setting or even at home. We believe that this is also a good example of the implementation of research-based learning during the pandemic times.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Logistics of the Research-Based Activity
We developed a laboratory/home research-based activity centered on the fabrication of zein nanoparticles. This activity was implemented in a graduate course setting, during a period of contingency and social distancing caused by the pandemic, in the fall semester in 2021. A total of sixteen graduate students participated in the activity. The students were divided into 6 teams of 2 or 3 members each. Each team was asked to propose and implement a method for the synthesis of zein nanoparticles that could be executed at home.
To facilitate the synthesis process, an experimental kit was provided to each team; the kits were assembled at the university and sent to students at different locations in Monterrey NL (México) using urban delivery services (Rappifavor or Uber). Each kit contained a commercial on-off W1209 12 V DC thermal controller (from MakerHawk, Amazon.com, accessed 15 August 2021; USA), a 12 V round and flexible heating plate (from Icstation, 12 V, 13 W, 70 mm, round polyamide; Amazon.com, accessed 15 August 2021; USA), a 12 V and 1 A power adapter from AC 100–240 V to DC 12 V (e.g., N/X 12 V adapter; Amazon.com, accessed 15 August 2021; USA), and a 50 mL glass jar with a metallic lid (from Amazon.com.mx, accessed 15 August 2021; Mexico). The students also received 10 g of zein in powder form (Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 200 mL of ethanol. This basic kit was intended to provide the means for controlled heating of zein suspensions/solutions, thereby enabling the fabrication of zein particles in any locale.
Students received directions on how to assemble the do-it-yourself heater using the materials provided. We also held Zoom sessions with the students to provide them with a step-by-step demonstration of how to assemble the do-it-yourself (DIY) heating system with the materials contained within the kit. These sessions were recorded and made available to the students.
Figure 1 shows different aspects of the assembly of the controlled DIY heaters. A schematic of the heater is shown in Figure 1A. Students were allowed to include alternative solvents in their experimental design/strategy; some teams used isopropanol or acetone [38] as alternative zein solvents. Figure 1C shows a schematic indicating how the heating element (heating resistance), the thermal controller, and the 12 V power adapter should be connected. In brief, the positive and the negative cables from the 12V power adapter were to be connected to the third and the fourth ports, respectively, in the thermal controller. The wires from the heating element did not have polarity, and were to be connected to the first and the fourth ports of the controller. A bridge wire was then to be connected between the second and the third ports of the controller. Figure 1D shows an assembled incubator that was used in one of our students’ apartments. When used for heating, the glass container was to be filled with the solvent (most students used ethanol), and the thermocouple of the thermal controller was to be fully inserted into the solvent.
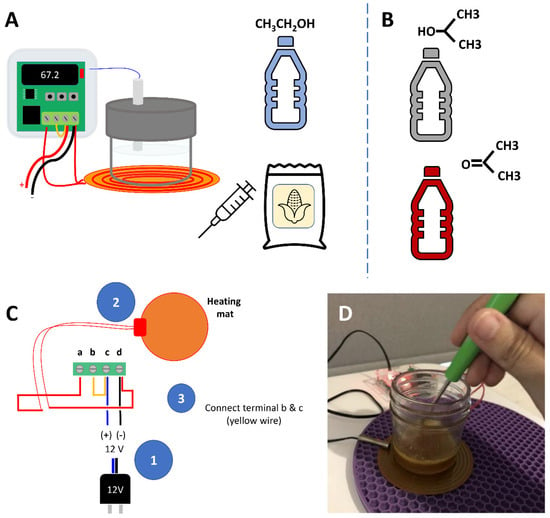
Figure 1.
Experimental resources. (A) Students received a kit containing all the components needed to assemble a controlled heater at home. This kit also included 200 mL of ethanol and 10 g of zein in powder form. (B) Some teams of students used isopropanol or acetone as alternative or additional solvents for zein. (C) Schematic showing how to wire the thermal controller, the heating element, and the 12 V adapter to build a do-it-yourself heater for zein solutions. (D) Actual image of the thermal heater.
2.2. Group of Students
Each team was instructed (i) to assemble their DIY heating system; (ii) to investigate methods of fabrication of zein nanoparticles in the scientific literature; (iii) to select one or two methods of fabrication, focusing on simplicity, safety, and availability of reagents; (iv) to conduct experiments on the fabrication of zein nanoparticles using at least one of the selected methods; (v) to characterize the produced nanoparticles (or nanoparticle suspensions) as much as possible using simple procedures and resources (i.e., using photo-documentation of the dispersion at different time points and image analysis to asses color variations); and (vi) to document their experiments and observations in a free-format technical report and as a short (i.e., less than 5 min) video.
The hands-on activity was implemented in a graduate-level Nanobiotechnology course. This course is taught once per year to students enrolled in graduate programs offered by Tecnologico de Monterrey. Both masters-level and doctoral students attend this course. Typically, most of these students were enrolled in the graduate programs in Nanotechnology or Biotechnology.
However, the course was also open to any graduate program offered by Tecnológico de Monterrey. The course was identified as “national,” which means that was transmitted from one university campus and could be taken remotely (i.e., by Zoom) by students at other university campuses. During the semester of implementation (i.e., the fall semester in 2021), all students attended this course remotely due to the pandemic contingency. In general, the course was attended by a highly diverse group of students in terms of academic backgrounds and professional interests. A total of sixteen students were registered in this offering of the course; 50% of them were enrolled in doctoral programs. In terms of area of study, 50% of the students were registered in the Nanotechnology graduate program and the other 50% came from the Biotechnology program. In this session of the course, 24% of the students were females and all students were Latino Americans.
2.3. Quantitative Assessment of Learnings
We used a simple survey to evaluate the familiarity of the students with seven different concepts or elements related to the activity (i.e., the general types of nanoparticles; the general types of methods used to fabricate nanoparticles; methods to specifically fabricate zein nanoparticles; methods to characterize nanoparticles; and the structure of a protein, a heating resistor, and a thermal controller) (Supplementary Materials File S1).
This survey contained 7 figures, each illustrating one of the learning concepts or topics related to the activity. Below each figure, the students were asked to state their familiarity with each concept/element on a scale from 1 (the lowest degree of knowledge) to 10 (the highest degree of knowledge). Students were asked to describe each figure where their stated degree of knowledge was equal to or higher than 7. The survey was applied using Google forms before and after implementation of the research-based activity.
3. Results
3.1. Fabrication Strategies Adopted by Students
We designed this research-based activity as an open experimental challenge with minimum scaffolding. The students were free to decide on a suitable strategy for fabricating zein nanoparticles, favoring simplicity, safety, and availability of reagents and other resources. The students also debated and decided on the best way to characterize the produced nanoparticles. Therefore, we anticipated that a wide diversity of approaches would be explored by the students, with some expected concurrences.
An expected and induced commonality was the use of the DIY heating system that the students successfully assembled. Most teams used ethanol as a solvent. This was anticipated, as ethanol is the solvent most frequently used to dissolve zein for diverse applications, including casting [39], electrospinning [40], foaming [28], and printing [20]. Some students chose to use isopropanol and acetone as alternative solvents. Students selected different strategies to produce nanoparticles. During the period of implementation (four weeks), most students had limited access to the laboratories at the university. Consequently, most students conducted the process of synthesis of nanoparticles entirely at home (as instructed). However, some teams gained access to laboratories, and decided to assist the process of fabrication using equipment, such as high-speed stirring (e.g., using lab sonicators, vortexing devices, high-speed lab homogenizers, or laboratory stirrers), to disperse and dissolve the zein in ethanol–water solutions, or to later precipitate zein nanoparticles by adding water in high-agitation environments. One team included lyophilization in its experimental strategy.
The students also used different experimental strategies to characterize the zein nanoparticles obtained. One team produced zein nanoparticles under four different experimental conditions: the use of ethanol or isopropanol and two temperature levels. After fabrication, the stability [41] of the nanoparticle suspensions was evaluated using a simple image analysis approach. The students captured images of the suspensions (under controlled light conditions against a black background; Figure 2A) and then used open-source software (Image J) to determine the progression of intensities (on a scale of 0 to 250) of the suspensions with time.
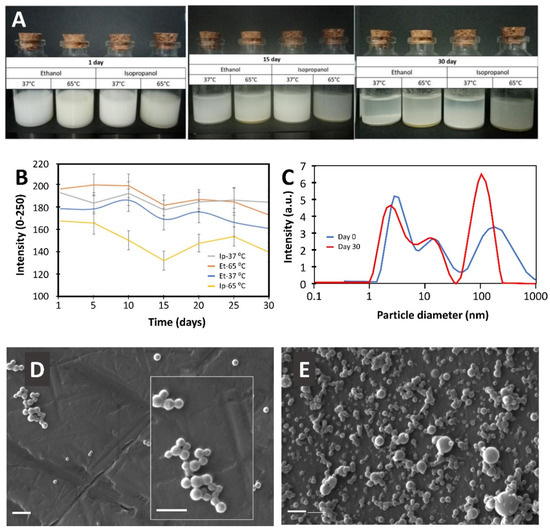
Figure 2.
Representative results of the characterization of the zein nanoparticles produced by the students. (A) Images show the evolution of the stability of suspensions of zein nanoparticles produced under four different experimental conditions: 100 mg of zein were dissolved in 3 mL of either 66% ethanol or 66% isopropanol at either 37 or 67 °C [25], and precipitated in 5 mL of water under vigorous agitation in an electric milk frother. (B) The stability of these nanoparticle suspensions was also investigated quantitatively using image analysis. (C) Alternatively, other teams used diffraction light scattering (DLS) to determine the nanoparticle size distribution of suspensions of zein nanoparticles immediately after synthesis (blue line) and after 30 days of storage at room temperature (red line). In this case, zein nanoparticles were prepared by dissolving 500 mg of zein in 7.5 mL of 70% ethanol at 65 °C and then adding this zein solution to 40 mL of distilled water under agitation at 15,000 RPM in a homogenizer. (D,E) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of zein nanoparticles synthetized by our students by (D) dropwise addition of zein solution (250 mg of zein in 5 mL of ethanol) into the anti-solvent (distilled water) under mixing at 200 RPM, or (E) quick addition of anti-solvent to the same zein solution under mixing at high speed (20,000 RPM) using a homogenizer. The inset in (D) shows a close-up. Scale bar: 100 nm.
As nanoparticles precipitated, the color of the suspensions shifted from lighter tones (high intensities) to darker tones (low intensities). The students were able to follow the color intensity of these suspensions for 30 days, and they determined that the nanoparticles fabricated in isopropanol at 37 °C were the most stable (Figure 2B). This example of their results illustrates that the students engaged in a real research-based learning experience that can be implemented even at home. Most teams of students used the available laboratory facilities to characterize their particles. For example, several teams used dynamic light scattering (DSL) to characterize the particle size distribution of their nanoparticles. Figure 2C shows a set of results from one of the teams. This team successfully fabricated zein nanoparticles by dissolving zein in 70 % ethanol at 65 °C and then precipitating the nanoparticles by adding water while agitating at high speed with a laboratory homogenizer operated at 15,000 RPM. The students compared the particle size distributions, as measured by dynamic light scattering, immediately after preparation and 30 days later. The students observed a shift in the particle size distribution (toward larger particle sizes) during the 30-day experiment. In their reports, they discussed that this change in the particle sizes is probably associated with particle aggregation. This example of results suggests that the students were able to articulate coherent research strategies to fabricate and to characterize nanoparticles, and that they effectively learned new concepts that were not covered in class. Remarkably, our students obtained particle sizes and z-potentials that were in the range of those reported in the recent literature related to the synthesis of zein nanoparticles by solvent/anti-solvent precipitation (Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of different methods to fabricate zein nanoparticles.
3.2. Qualitative Assessment of Learnings
The fabrication of nanoparticles is frequently perceived by students as a cumbersome and challenging process that requires the use of a well-equipped chemistry lab and some level of technical expertise. One of our design objectives was therefore to communicate that nanoparticle fabrication does not need to be highly complex and that nanotechnology can be practiced anywhere, including at home. A further aim was to expose our students to the concept of assembling simple devices to enable real experiments. A third objective was to favor the exploration of simple methods for characterization of nanoparticles through this research-based activity.
We designed and implemented a simple survey to assess the level of knowledge of our students on seven concepts (Table 2) related to the research-based activity described here. The survey was administered to the students via Google forms (Supplementary Materials, File S1).

Table 2.
Learning topics evaluation in the survey.
Notably, we implemented this research-based activity in a course that was designed as a seminar series (related to nanobiotechnology research), where invited speakers presented different topics of interest to the students every week. Brief introductory lectures preceded each seminar. However, the students were not exposed to the seven concepts explored in the survey in the formal lectures.
Figure 3 summarizes the results of the survey. Figure 3A presents the average degrees of knowledge on each of the seven learning topics covered in the survey. Students declared themselves to be poorly knowledgeable (~5) on learning aspects 4 and 7, which are related to electro-mechanical devices (the heating element [HTE]) and assembling do-it-yourself (DIY) devices. This result was anticipated, as only a small fraction of the students (less than 30%) had any professional background in mechanical sciences or mechatronics. The students also declared limited knowledge (~6) on the topic of protein structure. In the context of a seminar series open to graduate students of diverse backgrounds, only a fraction of our students was expected to have mastered biological concepts (SPT). In this group, only 40% of the students had a professional background in biology.
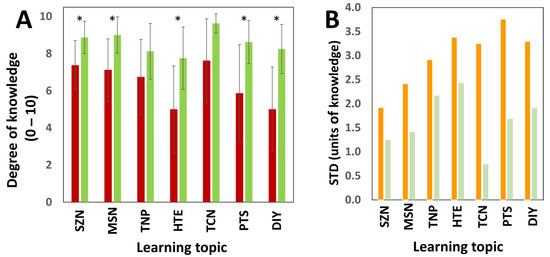
Figure 3.
Comparison of the degree of knowledge before and after a research-based activity centered on the synthesis of zein nanoparticles. (A) Degree of knowledge of the students before (red bars) and after (green bars) participating in a research-based activity centered on the synthesis of zein nanoparticles. The asterisks (*) indicate statistically significant differences in paired comparison t-tests (p value < 0.05). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals calculated in paired samples. (B) Standard deviations of the level of student knowledge on seven different learning topics, as surveyed before (orange bars) and after (light green bars) participating in the research-based activity.
In general, before participating in the research-based activity, the students declared only moderate levels of knowledge (averages between 6.75 and 7.62) about the rest of the learning topics, which were more directly related to nanotechnology (Figure 3A, red bars). The degree of knowledge of the students on all the learning topics increased after participating in the research-based activity. In 5 of the 7 learning topics, the students’ degree of knowledge was significantly higher after they participated in the activity than before. These topics included methods of synthesis of nanoparticles, synthesis of zein nanoparticles, methods of fabrication of nanoparticles, protein structure, heating elements, and assembly of DIY devices. In all these topics, the students declared high degrees of knowledge, with scores between 8.12 and 8.87. The degree of knowledge on the remaining topics (types of nanoparticles and characterization of nanoparticles) was also higher (but not significantly higher) after the activity than before. Indeed, on these two topics, students declared a very high degree of knowledge, equal to or above 9, after participating in the activity.
Notably, we observed a wide variability in the level of knowledge of the students for all the learning topics surveyed before their participation in the research-based activity. Figure 3B shows the value of the standard deviations corresponding to the levels of knowledge on the different learning topics, as surveyed before and after the activity. The results of the survey suggest that student participation in the activity reduced the variability of the degree of knowledge on all the learning topics. Indeed, the standard deviation of the degree of knowledge on the topics related to the assembly of electro-mechanical devices (HTE and DIY) was reduced by more than two units. This suggests that the research-based activity effectively contributed to homogenize the students’ degree of knowledge on all the learning topics, and particularly in those that the students initially perceived as the least familiar.
Figure 4 presents an analysis of the gain of knowledge by our students on the 7 learning topics explored by the survey.
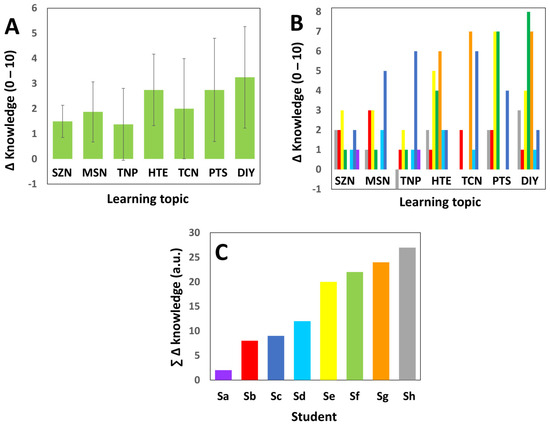
Figure 4.
Assessment of gain of knowledge generated by a research-based activity centered in the synthesis of zein nanoparticles. (A) The average gain of knowledge of the students after participating in a research-based activity centered on the synthesis of zein nanoparticles. Error bars indicate standard deviations calculated in paired samples. (B) The gain of knowledge of each student (indicated by the color bars) in each one of the learning topics assessed by the survey. (C) Analysis of the sum of gains of knowledge of each student. Colors are consistent between panels (B,C).
Figure 4A shows the average gain of knowledge on each learning topic after participating in the hands-on activity. The students appeared to perceive that their degree of knowledge had advanced (on average) in all the learning topics. In particular, the students expressed the opinion that their degree of knowledge in the topics of assembly of devices (DIY and HTE) and protein structure (PTS) had advanced the most.
On those fronts of knowledge, the students had felt the least comfortable before the research-based activity. Figure 4B shows the gain of knowledge of each individual student (the responses of different students are represented in different color bars), and therefore describes the actual distribution of the perceptions of the students regarding their learning. Figure 4C shows the sum of gains of knowledge of each student across the different topics examined in the survey. The graphical analysis in Figure 4B,C also reveals interesting information regarding the gains in knowledge of individual students and the distribution of the gains of knowledge on each learning topic. For example, 50% of the students expressed that their gain in knowledge across all the learning topics was high (see yellow, light blue, dark blue, and grey bars in Figure 4B,C). By contrast, one student expressed gaining only two units of knowledge across all the learning topics (Figure 4C).
4. Conclusions
We developed and implemented a research-based activity centered on the fabrication of nanoparticles from zein, the main constitutive protein in maize. This experimental activity was designed to have minimum scaffolding to engage students in a realistic research experience. We assessed the gain in knowledge in our students in seven learning topics that included aspects related to nanotechnology, assembling of simple devices, and concepts related to protein structure. This simple hands-on activity made effective and substantial contributions to the gain of knowledge in our students. This proof-of-concept implementation of a research-based activity suggests that simple experimental activities can greatly enhance the learning experiences of students. Moreover, we found that these types of activities are suitable for implementation even in circumstances of restricted access to laboratory facilities, such as the ones recently experienced during the pandemic.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/educsci12050307/s1, File S1: Evaluation survey.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; methodology, M.M.A., L.d.C.F.-C., S.C.P.-G. and G.T.-d.S.; software, L.d.C.F.-C.; validation, M.M.A. and S.C.P.-G.; formal analysis, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; investigation, G.T.-d.S., L.d.C.F.-C., S.C.P.-G., and M.M.A.; resources, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; data curation, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.A.; writing—review and editing, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; visualization, M.M.A.; supervision, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; project administration, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S.; funding acquisition, M.M.A. and G.T.-d.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of NOVUS (Grant number: ID-916). The authors acknowledge the support of the Institute for the Future of Education, Tecnológico de Monterrey, México, in the production of this work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee for the Novus Initiative at Tecnológico de Monterrey (Novus ID-916, 15 December 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy concerns.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the experimental support of members of the Alvarez-Trujillo Lab at Tecnológico de Monterrey. The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Fondo de Publicaciones del Tecnológico de Monterrey. L.d.C.F.-C and S.C.P.-G. acknowledge doctoral scholarships awarded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT). The authors acknowledge the experimental contribution of Carolina Ramírez Martínez, Saúl Antonio Hernández Martínez, Alberto Fernández del Castillo, Pamela Viaña, and Sergio Rodríguez.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mostafavi, E.; Soltantabar, P.; Webster, T.J. Nanotechnology and Picotechnology: A New Arena for Translational Medicine. Biomater. In Biomaterials in Translational Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Deng, H.; Hwang, H.M. The Current Application of Nanotechnology in Food and Agriculture. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, T.; Lowry, G.V.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N.; Brambilla, D.; Dutcher, J.R.; Gilbertson, L.M.; Giraldo, J.P.; Kinsella, J.M.; Landry, M.P.; et al. Technology Readiness and Overcoming Barriers to Sustainably Implement Nanotechnology-Enabled Plant Agriculture. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lee, V.E.; Liu, R.; Priestley, R.D. Responsive Polymers as Smart Nanomaterials Enable Diverse Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2019, 10, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolívar-Monsalve, E.J.; Alvarez, M.M.; Hosseini, S.; Espinosa-Hernandez, M.A.; Ceballos-González, C.F.; Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Shin, S.R.; Cecen, B.; Hassan, S.; Di Maio, E.; et al. Engineering Bioactive Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical Applications: A Review with Emphasis on Tissue Engineering and Controlled Release. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4447–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Mehdi, M.; Siyal, S.H.; Wassan, R.K.; Hashemikia, S.; Sarwar, M.N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kim, I.S. Conductive and Antibacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Decorated with Copper Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Wearable Devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Hussain, S.; Mehdi, M.; Khatri, M.; Ullah, S.; Khatri, Z.; Van Langenhove, L.; Kim, I.S. Introducing Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Water-Free Dyeing Medium for Poly (1,4-CYclohexane Dimethylene Isosorbide Terephthalate) PICT Nanofibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.M.; Aizenberg, J.; Analoui, M.; Andrews, A.M.; Bisker, G.; Boyden, E.S.; Kamm, R.D.; Karp, J.M.; Mooney, D.J.; Oklu, R.; et al. Emerging Trends in Micro- and Nanoscale Technologies in Medicine: From Basic Discoveries to Translation. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5195–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modena, M.M.; Rühle, B.; Burg, T.P.; Wuttke, S. Nanoparticle Characterization: What to Measure? Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; et al. “Gold Rush” in Modern Science: Fabrication Strategies and Typical Advanced Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Sensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 359, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini-nassab, R.; Pouryosef Miandoab, M.; Şaşmaz, M. Microfluidic Synthesis, Control, and Sensing of Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tian, T.; Zhou, R.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Shi, S.; Li, Q.; Xie, X.; et al. Design, Fabrication and Applications of Tetrahedral DNA Nanostructure-Based Multifunctional Complexes in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Treatment. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2728–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Singh, S.K.; Arya, S.K.; Kundu, S.C.; Kapoor, S. Protein Nanoparticles: Promising Platforms for Drug Delivery Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3939–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larm, N.E.; Essner, J.B.; Thon, J.A.; Bhawawet, N.; Adhikari, L.; St. Angelo, S.K.; Baker, G.A. Single Laboratory Experiment Integrating the Synthesis, Optical Characterization, and Nanocatalytic Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaris, Z.N.; Freitas, D.N.; Mac, K.; Gerner, K.T.; Nameth, C.; Wheeler, K.E. Nanoparticle Synthesis, Characterization, and Ecotoxicity: A Research-Based Set of Laboratory Experiments for a General Chemistry Course. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.M.; Bärtsch, A.; Stark, W.J.; Grass, R.N. Safe One-Pot Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Lemon Juice for a Hands-On Experience of Nanotechnology. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.; Hebert, D.; Kelly, J.A. Sweet Nanochemistry: A Fast, Reliable Alternative Synthesis of Yellow Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles Using Benign Reagents. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 92, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The Industrial Protein from Corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.Y. Basic Study of Corn Protein, Zein, as a Biomaterial in Tissue Engineering, Surface Morphology and Biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4691–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Negrete, J.A.; Aceves-Colin, A.E.; Rivera-Flores, D.C.; Díaz-Armas, G.G.; Mertgen, A.S.; Trinidad-Calderón, P.A.; Olmos-Cordero, J.M.; Gómez-López, E.G.; Pérez-Carrillo, E.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.J.; et al. Three-Dimensional Printing Using a Maize Protein: Zein-Based Inks in Biomedical Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3964–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, R.; Liu, J. Effects of Different Concentrations of Ethanol and Isopropanol on Physicochemical Properties of Zein-Based Films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Ren, Q.; Huang, F.; Yan, Y. Fabrication of Polysaccharide-Stabilized Zein Nanoparticles by Flash Nanoprecipitation for Doxorubicin Sustained Release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Water-Resistant Zein-Based Adhesives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7668–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. Zein and Zein -Based Nano-Materials for Food and Nutrition Applications: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Froiio, F.; Salvatici, M.C.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Characterization and Refinement of Zein-Based Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, A.; Tabibiazar, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Shi, B. Zein-CMC-PEG Multiple Nanocolloidal Systems as a Novel Approach for Nutra-Pharmaceutical Applications. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; Curti, P.S.; Meniqueti, A.B.; Martins, A.F.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22438–22470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Santiago, G.T.; Portales-Cabrera, C.G.; Portillo-Lara, R.; Araiz-Hernández, D.; Del Barone, M.C.; García-López, E.; De Gante, C.R.; De Los Angeles De Santiago-Miramontes, M.; Segoviano-Ramírez, J.C.; García-Lara, S.; et al. Supercritical CO2 Foaming of Thermoplastic Materials Derived from Maize: Proof-of- Concept Use in Mammalian Cell Culture Applications. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimna, C.; Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. Novel Zein-based Multilayer Wound Dressing Membranes with Controlled Release of Gentamicin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.M.; Torres-Giner, S.; Vicente, A.A.; Cerqueira, M.A. Electrohydrodynamic Processing for the Production of Zein-Based Microstructures and Nanostructures. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, M.; Khatri, Z.; El-Ghazali, S.; Hussain, N.; Qureshi, U.A.; Kobayashi, S.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, I.S. Zein Nanofibers via Deep Eutectic Solvent Electrospinning: Tunable Morphology with Super Hydrophilic Properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoli, M.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara, M.C.; Monteiro, R.A.; Carvalho, L.B.; Oliveira, J.L.; Fraceto, L.F. Enzyme Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Bioinsecticides: An Emerging Approach for Uses in Crop Protection. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Arunkumar, P.; Prasad, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Reddy, B.P.K.; De, A.; Srivastava, R. Facile Synthesis of Plasmonic Zein Nanoshells for Imaging-Guided Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, C.J.; Kaur, R.; Singh, K.; Bakshi, M.S. Temperature Induced Phase Transition in Fluorescence Active Zein Nanoparticles. Can. J. Chem. 2021, 99, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Qi, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhong, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Guan, Y.; et al. Size-Controlled Fabrication of Zein Nano/Microparticles by Modified Anti-Solvent Precipitation with/without Sodium Caseinate. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, R.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Zhang, B. Preparation and Characterization of Zein/Carboxymethyl Dextrin Nanoparticles to Encapsulate Curcumin: Physicochemical Stability, Antioxidant Activity and Controlled Release Properties. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, I.; Campardelli, R.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E. Zein/Luteolin Microparticles Formation Using a Supercritical Fluids Assisted Technique. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisharat, L.; Berardi, A.; Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Casettari, L.; Cespi, M.; AlKhatib, H.S.; Palmieri, G.F. Aggregation of Zein in Aqueous Ethanol Dispersions: Effect on Cast Film Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, S.C.; Benaut, P.; Laget, S.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F. Optimization of Electrospinning Parameters for the Production of Zein Microstructures for Food and Biomedical Applications. Micron. 2022, 152, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Haes, A.J. What Does Nanoparticle Stability Mean? J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 16495–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).