Teaching Mathematics with Technology: TPACK and Effective Teaching Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- In what ways did secondary mathematics teacher candidates show evidence of growth in TPACK and the use of effective mathematics teaching practices during the student teaching year?
- To what degree did TPACK correlate with the use of effective mathematics teaching practices?
Importance
2. Background Literature
2.1. Mathematics Knowledge for Teaching and the Use of Technology
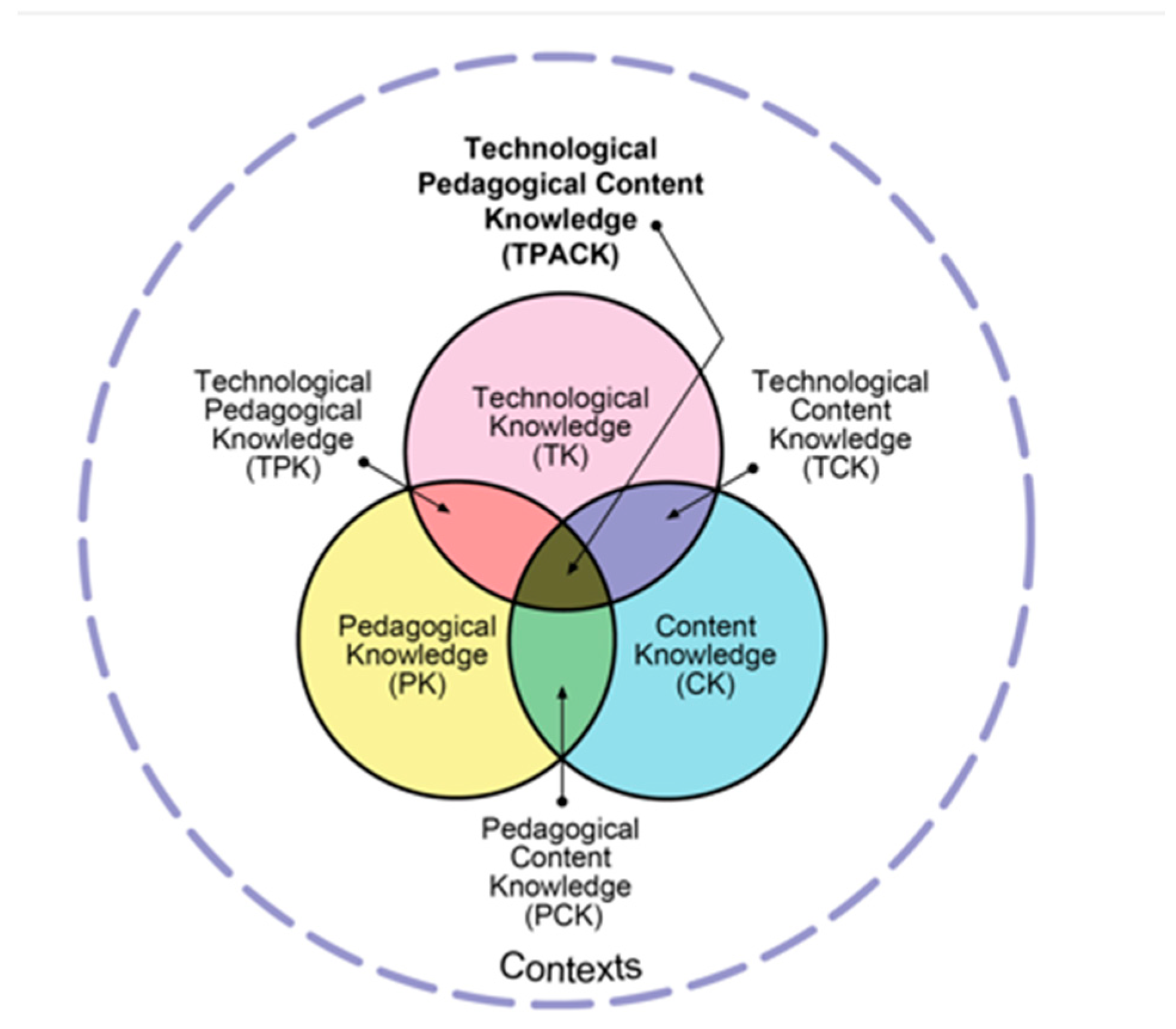
2.2. The TPACK Framework
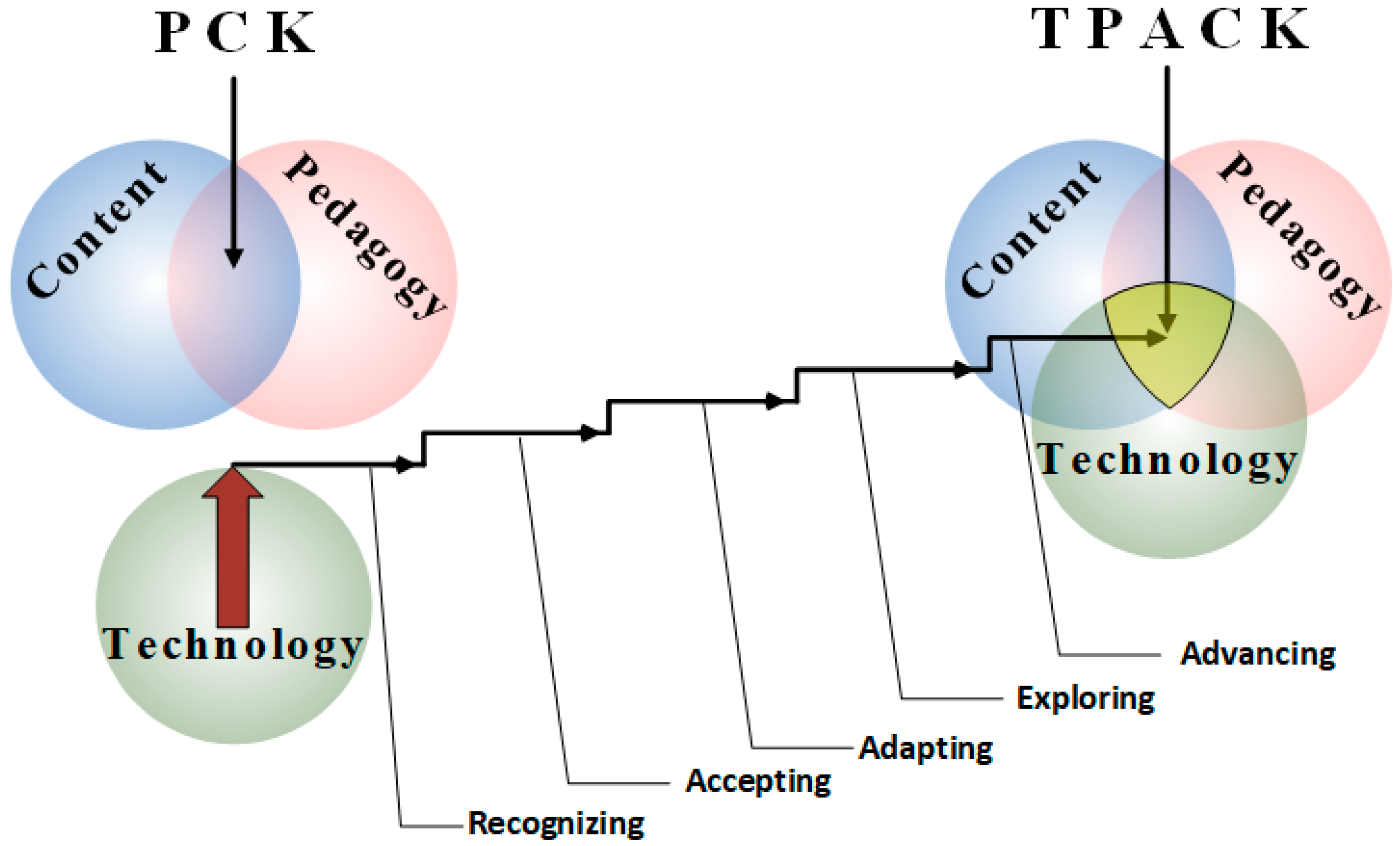
2.3. The PrimeD Framework
3. Methods
3.1. Sample
3.2. Measures
3.3. Procedures
3.4. Analytic Methods
- How has participation in this project changed your relationship with your (apprentice/mentor/cooperating teacher/student teacher)?
- In what ways has the PrimeD project influenced your beliefs/thinking about teaching mathematics?
- 2a.
- Would you recommend that other mathematics teachers get involved in a project such as this one?
- How has participation in this project changed your approach to teaching mathematics?
- 3a.
- To what degree has this project changed how you teaching mathematics?
- 3b.
- Please share an example of one mathematics concept and/or teaching practice that changed in your teaching as a result of PrimeD.
- In what ways did participation in this project lead to better mathematics learning for your students?
- 4a.
- Describe any changes in student achievement on mathematics quizzes and tests.
- 4b.
- Describe any changes in your students’ persistence in problem solving activities.
- 4c.
- Describe any changes in your students’ engagement in class activities. (make sure this is addressed)
- How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted this project—thinking about your teaching, student learning, your participation in this project?
- In what ways has this project changed this teacher preparation program? (If you feel this has not already been addressed).
4. Results
4.1. Comparisons between Growth in TPACK and MCOP2
4.2. Focus Groups
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
7. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Curriculum and Evaluation Standards for School Mathematics; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Principles and Standards of School Mathematics; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Principles to Actions: Ensuring Mathematical Success for All; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, H.C.; Rowan, B.; Ball, D.L. Effects of Teachers’ Mathematical Knowledge for Teaching on Student Achievement. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2005, 42, 371–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Academy of Sciences; National Academy of Engineering; National Academies, Institute of Medicine. Rising above the Gathering Storm, Revisited: Rapidly Approaching Category 5; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Available online: http://www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=12999 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- National Research Council. Rising above the Gathering Storm: Energizing and Employing America for a Brighter Economic Future; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Preparing Teachers: Building Evidence for Sound Policy; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J. Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge: A Framework for Teacher Knowledge. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2006, 108, 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, M.L. Preparing teachers to teach science and mathematics with technology: Developing a technology pedagogical content knowledge. Teach. Teach. Educ. An. Int. J. Res. Stud. 2005, 21, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyublinskaya, I.; Tournaki, N. The Effects of Teacher Content Authoring on TPACK and on Student Achievement inAlgebra: Research on Instruction with the TI-Nspire™ Handheld. In Educational Technology, Teacher Knowledge, and Classroom Impact: A Research Handbook on Frameworks and Approaches; Ronau, R.N., Rakes, C.R., Niess, M.L., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 295–322. [Google Scholar]
- Saderholm, J.; Ronau, R.N.; Rakes, C.R.; Bush, S.B.; Mohr-Schroeder, M. The critical role of a well-articulated, coherent design in professional development: An evaluation of a state-wide two-week program for mathematics and science teachers. Prof. Dev. Educ. 2017, 43, 789–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakes, C.R.; Bush, S.B.; Mohr-Schroeder, M.J.; Ronau, R.N.; Saderholm, J. Making teacher PD effective using the PrimeD framework. N. Engl. Math. J. 2017, 50, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Catalyzing Change in Middle School Mathematics: Initiating Critical Conversations; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, J.; Livers, S.D.; Zelkowski, J. Mathematics Classroom Observation Protocol for Practices: Descriptors Manual. Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2015. Available online: http://jgleason.people.ua.edu/uploads/3/8/3/4/38349129/mcop2_descriptors.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Catalyzing Change in High School Mathematics: Initiating Critical Conversations; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eli, J.A.; Mohr-Schroeder, M.J.; Lee, C.W. Mathematical Connections and Their Relationship to Mathematics Knowledge for Teaching Geometry. Sch. Sci. Math. 2013, 113, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conference Board of Mathematical Sciences (CBMS). The Mathematical Education of Teachers; ERIC No. ED457030; Conference Board of Mathematical Sciences (CBMS): Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fennema, E.; Franke, M.L. Teachers’ knowledge and its impact. In Handbook of Research on Mathematics Teaching and Learning: A Project of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics; Macmillan: Reston, VA, USA, 1992; pp. 147–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L. Knowing and Teaching Elementary Mathematics: Teachers’ Understanding of Fundamental Mathematics in China and the United States; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Niess, M.L.; Roschelle, J. Transforming Teachers’ Knowledge for Teaching Mathematics with Technologies through Online Knowledge-Building Communities. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the North American Chapter of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education, Greenville, SC, USA; 2018. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED606569.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Roshelle, J.; Leinwand, S. Improving student achievement by systematically integrating effective technology. NCSM J. Math. Educ. Leadersh. 2011, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.-S.; Sharma, P. A Systemic Plan of Technology Integration. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2006, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, C.R.; Burgoyne, N.; Cantrell, P.P.; Smith, L.M.; Clair, L.S.; Harris, R. TPACK Development in Science Teaching: Measuring the TPACK Confidence of Inservice Science Teachers. TechTrends 2009, 53, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.K.F.; Churchill, D. Exploring the characteristics of an optimal design of digital materials for concept learning in mathematics. Comput. Educ. 2015, 82, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakes, C.R.; Valentine, J.; McGatha, M.C.; Ronau, R.N. Methods of instructional improvement in algebra: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2010, 80, 372–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakes, C.R.; Ronau, R.N.; Bush, S.B.; Driskell, S.O.; Niess, M.L.; Pugalee, D.K. Mathematics achievement and orientation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of education technology. Educ. Res. Rev. 2020, 31, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skemp, R.R. Relational understanding and instrumental understanding. Math. Teach. Middle Sch. 2006, 12, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, S.; Stites, M. Preschool teachers’ views on distance learning during COVID-19. In Contemporary Perspectives in Early Childhood Education; Saracho, O., Ed.; Information Age Publishing: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, in press.
- Arcueno, G.; Arga, H.; Manalili, T.A.; Garcia, J.A. TPACK and ERT: Understanding teacher decisions and challenges with integrating technology in planning lessons and instruction. In DLSU Research Congress 2021; De La Salle University: Manila, Philippines, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Niess, M.L. Teacher Knowledge for Teaching with Technology: A TPACK Lens. In Educational Technology, Teacher Knowledge, and Classroom Impact: A Research Handbook on Frameworks and Approaches; Ronau, R.N., Rakes, C.R., Niess, M.L., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, L.S. Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educ. Res. 1986, 15, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, M.J.; Mishra, P. What is technological pedagogical content knowledge? Contemp. Issues Technol. Teach. Educ. 2009, 9, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niess, M.L.; Ronau, R.N.; Shafer, K.G.; Driskell, S.O.; Harper, S.R.; Johnston, C.J.; Browning, C.; Özgün-Koca, S.A.; Kersaint, G. Mathematics Teacher TPACK Standards and Development Model. Contemp. Issues Technol. Teach. Educ. 2009, 9, 4–24. [Google Scholar]
- Darling-Hammond, L. Teaching as a Profession: Lessons in Teacher Preparation and Professional Development. Phi. Delta Kappan 2005, 87, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, M.; Bocala, C.; Deckman, S.L.; Dickstein-Staub, S. Caricature and Hyperbole in Preservice Teacher Professional Development for Diversity. Urban. Educ. 2016, 51, 629–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, S.B.; Cook, K.L.; Ronau, R.N.; Mohr-Schroeder, M.J.; Rakes, C.R.; Saderholm, J. Structuring Integrated STEM Education Professional Development: Challenges Revealed and Insights Gained from a Cross-Case Synthesis. J. Res. Sci. Math. Educ. 2020, 24, 26–55. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1255599.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Rakes, C.R.; Saderholm, J.; Bush, S.B.; Mohr-Schroeder, M.J.; Ronau, R.N.; Stites, M. Structuring secondary mathematics teacher preparation through a professional development framework. Under Review.
- Driskell, S.O.; Bush, S.B.; Ronau, R.N.; Niess, M.L.; Rakes, C.R.; Pugalee, D.K. Mathematics Education Technology Professional Development: Changes over Several Decades. In Handbook of Research on Transforming Mathematics Teacher Education in the Digital Age; Niess, M.L., Driskell, S.O., Hollebrands, K., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, S.B.; Cook, K.L.; Ronau, R.N.; Rakes, C.R.; Mohr-Schroeder, M.J.; Saderholm, J. A highly structured collaborative STEAM program: Enacting a professional development framework. J. Res. STEM Educ. 2018, 2, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, A.S.; Gomez, L.M.; Grunow, A. Getting Ideas into Action: Building Networked Improvement Communities in Education. Carnegie Perspectives; Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bryk, A.S.; Gomez, L.M.; Grunow, A.; LeMahieu, P.G. Learning to Improve: How America’s Schools Can Get Better at Getting Better; Harvard Education Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, W.G.; Gobstein, H. Generating a Networked Improvement Community to Improve Secondary Mathematics Teacher Preparation: Network Leadership, Organization, and Operation. J. Teach. Educ. 2015, 66, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, D.; Bryk, A.S.; Muhich, J.; Hausman, H.; Morales, L. Practical Measurement; Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching: Stanford, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.carnegiefoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/Practical_Measurement.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Desimone, L.M. Improving Impact Studies of Teachers’ Professional Development: Toward Better Conceptualizations and Measures. Educ. Res. 2009, 38, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loucks-Horsley, S.; Hewson, P.W.; Love, N.; Stiles, K.E. Designing Professional Development for Teachers of Science and Mathematics; Corwin Press: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, L.S. Theory, Practice, and the Education of Professionals. Elem. Sch. J. 1998, 98, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shulman, L.S.; Wilson, S.M. The Wisdom of Practice: Essays on Teaching, Learning, and Learning to Teach; Jossey-Bass: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough, D.B.; Shulha, L.M.; Hopson, R.K.; Caruthers, F.A. The Program Evaluation Standards: A Guide for Evaluators and Evaluation Users, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shadish, W.R.; Cook, T.D.; Campbell, D.T. Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference; Houghton Mifflin: Elkridge, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, J.; Livers, S.; Zelkowski, J. Mathematics Classroom Observation Protocol for Practices (MCOP2): A validation study. Investig. Math. Learn. 2017, 9, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplon-Schilis, A.; Lyublinskaya, I. Analysis of differences in the levels of TPACK: Unpacking performance indicators in the TPACK Levels Rubric. In American Educational Research Association; Virtual: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makel, M.C.; Hodges, J.; Cook, B.G.; Plucker, J.A. Both Questionable and Open Research Practices are Prevalent in Education Research. Educ. Res. 2021, 50, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.E.; Thompson, B.J.; Hess, S.A.; Knox, S.; Williams, E.N.; Ladany, N. Consensual Qualitative Research: An Update. J. Couns. Psychol. 2005, 52, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gainsburg, J. Why new mathematics teachers do or don’t use practices emphasized in their credential program. J. Math. Teach. Educ. 2012, 15, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, A.; Apthorp, H. (Eds.) Classroom Instruction that Works. Research Report, 2nd ed.; MCREL International: Denver, CO, USA; Available online: https://www.mcrel.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/McREL-research-report_Nov2010_Classroom-Instruction-that-Works_Second-Edition.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Dick, T.P.; Hollebrands, K.F. Focus in High School Mathematics: Technology to Support Reasoning and Sense Making; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Hollebrands, K.F. Technology tools to support mathematics teaching. In Focus in High. School Mathematics: Technology to Support Reasoning and Sense Making; Dick, T.P., Hollebrands, K.F., Eds.; National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Roschelle, J.; Shechtman, N.; Tatar, D.; Hegedus, S.; Hopkins, B.; Empson, S.; Knudsen, J.; Gallagher, L.P. Integration of technology, curriculum, and professional development for advancing middle school mathematics: Three large-scale studies. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2011, 47, 833–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| University | Number of TCs in Cohort | Number of TCs in Sample | Reasons for Sample Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 18 | 1 | District limitations on video recording. |
| B | 13 | 11 | Technical issues with recording video. |
| C | 6 | 5 | District limitations on video recording. |
| D | 3 | 0 | Spring to fall student teaching. |
| Total | 40 | 17 |
| Instrument | Variable | Time | Min | Mean | SD | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPACK | Overarching Concept | Pre | 1.0 | 1.82 | 0.585 | 3.0 |
| Post | 1.0 | 1.91 | 0.566 | 3.5 | ||
| Knowledge of Students | Pre | 1.0 | 1.85 | 0.552 | 3.0 | |
| Post | 1.0 | 2.00 | 0.468 | 3.0 | ||
| Knowledge of Curriculum | Pre | 0.5 | 1.77 | 0.731 | 3.0 | |
| Post | 1.0 | 1.97 | 0.838 | 3.5 | ||
| Instructional Strategies | Pre | 0.5 | 1.91 | 0.795 | 3.5 | |
| Post | 1.5 | 2.15 | 0.552 | 3.5 | ||
| Overall Mean | Pre | 0.8 | 1.84 | 0.622 | 3.0 | |
| Post | 1.1 | 2.01 | 0.556 | 3.4 | ||
| MCOP2 | Student Engagement | Pre | 0.0 | 1.12 | 0.750 | 2.7 |
| Post | 0.7 | 1.68 | 0.572 | 2.7 | ||
| Teacher Facilitation | Pre | 0.2 | 1.03 | 0.573 | 2.2 | |
| Post | 0.6 | 1.45 | 0.563 | 2.6 | ||
| Overall Mean | Pre | 0.1 | 1.10 | 0.645 | 2.4 | |
| Post | 0.7 | 1.57 | 0.539 | 2.5 |
| Variable | No. Items | Points Possible | Mean Difference (Post–Pre) | SD | t (df = 16) | p (2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPACK | ||||||
| Overarching Concept | 1 | 5 | 0.088 | 0.618 | 0.588 | 0.565 |
| Knowledge of Students | 1 | 5 | 0.147 | 0.460 | 1.319 | 0.206 |
| Knowledge of Curriculum | 1 | 5 | 0.206 | 0.730 | 1.163 | 0.262 |
| Instructional Strategies | 1 | 5 | 0.235 | 0.773 | 1.255 | 0.227 |
| Overall Mean | 4 | 5 | 0.169 | 0.532 | 1.311 | 0.209 |
| MCOP2 | ||||||
| Student Engagement | 9 | 3 | 0.562 | 0.959 | 2.416 * | 0.028 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 9 | 3 | 0.418 | 0.773 | 2.230 * | 0.040 |
| Overall Mean | 16 a | 3 | 0.474 | 0.845 | 2.314 * | 0.034 |
| TPACK Variables | MCOP2 Variables | Pearson Correlation | p | LO95 | HI95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overarching Concept | Student Engagement | 0.104 | 0.692 | 0.557 | 0.397 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.053 | 0.841 | 0.520 | 0.439 | |
| Total | 0.106 | 0.687 | 0.558 | 0.395 | |
| Knowledge of Students | Student Engagement | 0.247 | 0.340 | 0.650 | 0.265 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.224 | 0.387 | 0.636 | 0.287 | |
| Overall | 0.271 | 0.292 | 0.665 | 0.241 | |
| Knowledge of Curriculum | Student Engagement | 0.108 | 0.680 | 0.559 | 0.393 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.220 | 0.395 | 0.634 | 0.291 | |
| Overall | 0.185 | 0.476 | 0.611 | 0.324 | |
| Instructional Strategies | Student Engagement | 0.039 | 0.881 | 0.510 | 0.450 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.182 | 0.485 | 0.609 | 0.327 | |
| Overall | 0.137 | 0.600 | 0.580 | 0.368 | |
| Overall | Student Engagement | 0.129 | 0.623 | 0.574 | 0.375 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.189 | 0.469 | 0.614 | 0.321 | |
| Overall | 0.188 | 0.471 | 0.613 | 0.322 |
| TPACK Variable | MCOP2 Variable | Pearson Correlation | p | LO95 | HI95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overarching Concept | Student Engagement | −0.065 | 0.803 | −0.528 | 0.430 |
| Teacher Facilitation | −0.140 | 0.592 | −0.579 | 0.369 | |
| Overall | −0.089 | 0.735 | −0.544 | 0.412 | |
| Knowledge of Students | Student Engagement | −0.026 | 0.921 | −0.500 | 0.461 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.031 | 0.906 | −0.457 | 0.503 | |
| Overall | 0.010 | 0.969 | −0.473 | 0.488 | |
| Knowledge of Curriculum | Student Engagement | 0.295 | 0.250 | −0.225 | 0.675 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.115 | 0.661 | −0.390 | 0.562 | |
| Overall | 0.234 | 0.366 | −0.285 | 0.638 | |
| Instructional Strategies | Student Engagement | 0.368 | 0.146 | −0.148 | 0.715 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.121 | 0.643 | −0.385 | 0.566 | |
| Overall | 0.279 | 0.278 | −0.241 | 0.665 | |
| Overall | Student Engagement | 0.210 | 0.418 | −0.307 | 0.623 |
| Teacher Facilitation | 0.049 | 0.851 | −0.443 | 0.517 | |
| Overall | 0.158 | 0.545 | −0.354 | 0.590 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakes, C.R.; Stites, M.L.; Ronau, R.N.; Bush, S.B.; Fisher, M.H.; Safi, F.; Desai, S.; Schmidt, A.; Andreasen, J.B.; Saderholm, J.; et al. Teaching Mathematics with Technology: TPACK and Effective Teaching Practices. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020133
Rakes CR, Stites ML, Ronau RN, Bush SB, Fisher MH, Safi F, Desai S, Schmidt A, Andreasen JB, Saderholm J, et al. Teaching Mathematics with Technology: TPACK and Effective Teaching Practices. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(2):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020133
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakes, Christopher R., Michele L. Stites, Robert N. Ronau, Sarah B. Bush, Molly H. Fisher, Farshid Safi, Siddhi Desai, Ashley Schmidt, Janet B. Andreasen, Jon Saderholm, and et al. 2022. "Teaching Mathematics with Technology: TPACK and Effective Teaching Practices" Education Sciences 12, no. 2: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020133
APA StyleRakes, C. R., Stites, M. L., Ronau, R. N., Bush, S. B., Fisher, M. H., Safi, F., Desai, S., Schmidt, A., Andreasen, J. B., Saderholm, J., Amick, L., Mohr-Schroeder, M. J., & Viera, J. (2022). Teaching Mathematics with Technology: TPACK and Effective Teaching Practices. Education Sciences, 12(2), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020133










