Abstract
Hot isostatic pressing can be utilized to reduce the anisotropic mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg alloys fabricated by laser powder-bed fusion (L-PBF). The implementation of post processing densification processes can open up new fields of application by meeting high quality requirements defined by aircraft and automotive industries. A gas pressure of 75 MPa during hot isostatic pressing lowers the critical cooling rate required to achieve a supersaturated solid solution. Direct aging uses this pressure related effect during heat treatment in modern hot isostatic presses, which offer advanced cooling capabilities, thereby avoiding the necessity of a separate solution annealing step for Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Hot isostatic pressing, followed by rapid quenching, was applied to both sand cast as well as laser powder-bed fused Al–Si–Mg aluminum alloys. It was shown that the critical cooling rate required to achieve a supersaturated solid solution is significantly higher for additively manufactured, age-hardenable aluminum alloys than it is for comparable sand cast material. The application of hot isostatic pressing can be combined with heat treatment, consisting of solution annealing, quenching and direct aging, in order to achieve both a dense material with a small number of preferred locations for the initiation of fatigue cracks and a high material strength.
1. Introduction
Hot isostatic pressing of Al–Si–Mg cast material is conventionally performed at a pressure of 75 MPa, a temperature of 510 C and for a duration of 120 min. Due to thermally activated dislocation creep and diffusional creep processes, hot isostatic pressing completely removes the shrinkage porosity from cast material [1,2,3]. Regular heat treatment, which consists of solution annealing, quenching and aging, and is performed separately after densification, is employed to achieve high material strength. Solution annealing requires high cooling rates to prevent diffusion and therefore avoid the dissolution of alloying elements during cooling. An oversaturated solid solution of alloying atoms is mandatory to achieve high material strength by precipitation of intermetallic phases during aging [4,5,6,7].
Laser powder-bed fusion (L-PBF) is established for the additive manufacturing of high quality lightweight components. The fine precipitates, the cellular silicon structure and the high cooling rate after solidification results in high mechanical strength in the as-built condition [8,9]. Particularity, the high cooling rates during the L-PBF result in a supersaturated solid solution of alloying elements, enabling to achieve high material strength via the precipitation of intermetallic phases during aging [4,5,6]. The mechanical properties of additively manufactured age-hardenable alloys vary in dependence of the distance between the processed layer and the substrate plate and are governed by the heat input via the laser during the fabrication process. Most of the heat is dissipated through the component, since the thermal conduction through the powder-bed is significantly slower, due to the large interface between the argon gas and the powder particles [10,11]. The overall time at elevated temperature is far shorter for layers processed near the end of the built job, compared to layers which are processed in the early stage and remain at elevated temperature for several hours, which in case of Al–Si–Mg often coincides with artificial aging temperatures. Anisotropic mechanical properties are documented for L-PBF material and are caused by the layer-by-layer generation and thus, are characteristic for the process.
L-PBF manufactured age-hardenable Al–Si–Mg alloys often possess a density as high as 99.99% of their theoretical density [9]. Nevertheless, pores within the alloy are preferred locations for the initiation of fatigue cracks and thereby, limit the field of applications of those components in variable load environments [12]. Residual porosity in L-PBF is scattered all across the samples, but is usually more frequent found close to the side surfaces, where pores influence the fatigue resistance stronger than in the center of the material [13]. Those hidden notches or local lack of fusion phenomena may facilitate crack initiation [12].
A heat treatment process consisting of solution annealing and aging can be applied to L-PBF material in order to reduce the anisotropy of the mechanical properties and at the same time, reduce the influence of the duration at aging temperature during the fabrication process [14]. Heat treatment at atmospheric pressure or vacuum is likely to increase the porosity of L-PBF material due to the expansion of gas filled pores at high temperatures [15]. Solution annealing is often found to be detrimental for the mechanical properties, in particular the elongation at fracture and the fatigue resistance, but is nevertheless a common procedure in order to increase the predictability of the component behavior [8,9,16,17,18,19].
Hot isostatic pressing has been established as a heat treatment of cast components to increase their density in order to meet the strict regulations for applications in the automotive and aircraft industries [20,21]. Conventional hot isostatic pressing of age hardenable Al–Si–Mg alloys is known to remove casting porosity entirely and is performed at a pressure of 75 MPa, at a temperature of 510 C and for a duration of 120 min. A complimentary heat treatment of solution annealing and aging is conventionally performed afterwards, to achieve a high material strength.
A recently published study by our research group [22] showed that the critical cooling rate necessary to achieve appreciable age-hardening for Laser-powder bed fused Al-Si-Mg ranged between 11 to 15 K/s under vacuum condition, whereas a quenching rate of 5 K/s was sufficient for cast reference material.
The critical cooling rate after solution annealing is connected to the diffusivity of alloying elements, which is known to be pressure dependent [23,24,25]. A pressure induced decease in the critical cooling rate allows direct aging of cast Al–Si–Mg alloys, if the cooling rate after hot isostatic pressing is high enough to avoid the precipitation of alloying elements during cooling [21,26,27,28]. Modern hot isostatic presses are offering enhanced cooling capabilities, which allow the implementation of direct aging, a combined process of densification, solution annealing and artificial aging [29,30]. By avoiding pre-precipitate clustering of alloying elements at room temperature, direct aging of Al–Si–Mg alloys results in higher strength, compared to regular heat treatment [31,32,33].
Due to microstructural differences, the ideal process parameters for hot isostatic pressing of additively manufactured materials seem to be different to those established for cast material. Hot isostatic pressing can nevertheless be utilized to reduce the porosity of different L-PBF materials [34,35,36].
2. Experimental
The alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 was processed via sand casting by the Georg Fischer AG, Schaffhausen, Schweiz. A spark emission spectrometer, type SPECTROMAXx LMM16 (Spectro, Kleve, Germany) was used to determine the chemical composition of the alloy, shown in Table 1. Details on the fabrication process can be found in [26,28]. The alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 was processed by L-PBF in an SLM 280HL selective laser melting machine (SLM Solutions GmbH, Lübeck, Germany), equipped with a 400 W Yb-fiber-laser and a build space of 280 × 280 × 320 mm. Powder with an average particle diameter of 37 µm was used to fabricate tapered cylindrical samples with a diameter of 14 mm, a diameter of 10 mm along the gauge length and a total length of 75 mm. The samples were built in 0, 45 and 90 inclinations to the substrate plate. The fabrication parameters of the laser powder-bed fusion samples are listed in Table 2.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the aluminum cast alloys AlSi7Mg0.3 and AlSi10Mg0.3. The alloys meet the specifications defined by the standard Aluminum–Silicon EN 1706:2010 [37].

Table 2.
Fabrication parameters of laser powder-bed fusion samples.
The alloys were tensile tested on an Instron 4505 tensile testing machine at a strain rate of 10 s. The tensile test samples were machined according to DIN 50125:2016-12, type B, size M10 [38]. The strain was measured in parallel to the axis of the cylinder by use of an extensometer attached to the specimens. Hardness measurements were performed according to DIN EN ISO 6506-2 using an M4U-025 hardness testing machine (EMCO-TEST, Kuchl, Austria) [39].
2.1. HIP Process and Heat Treatment
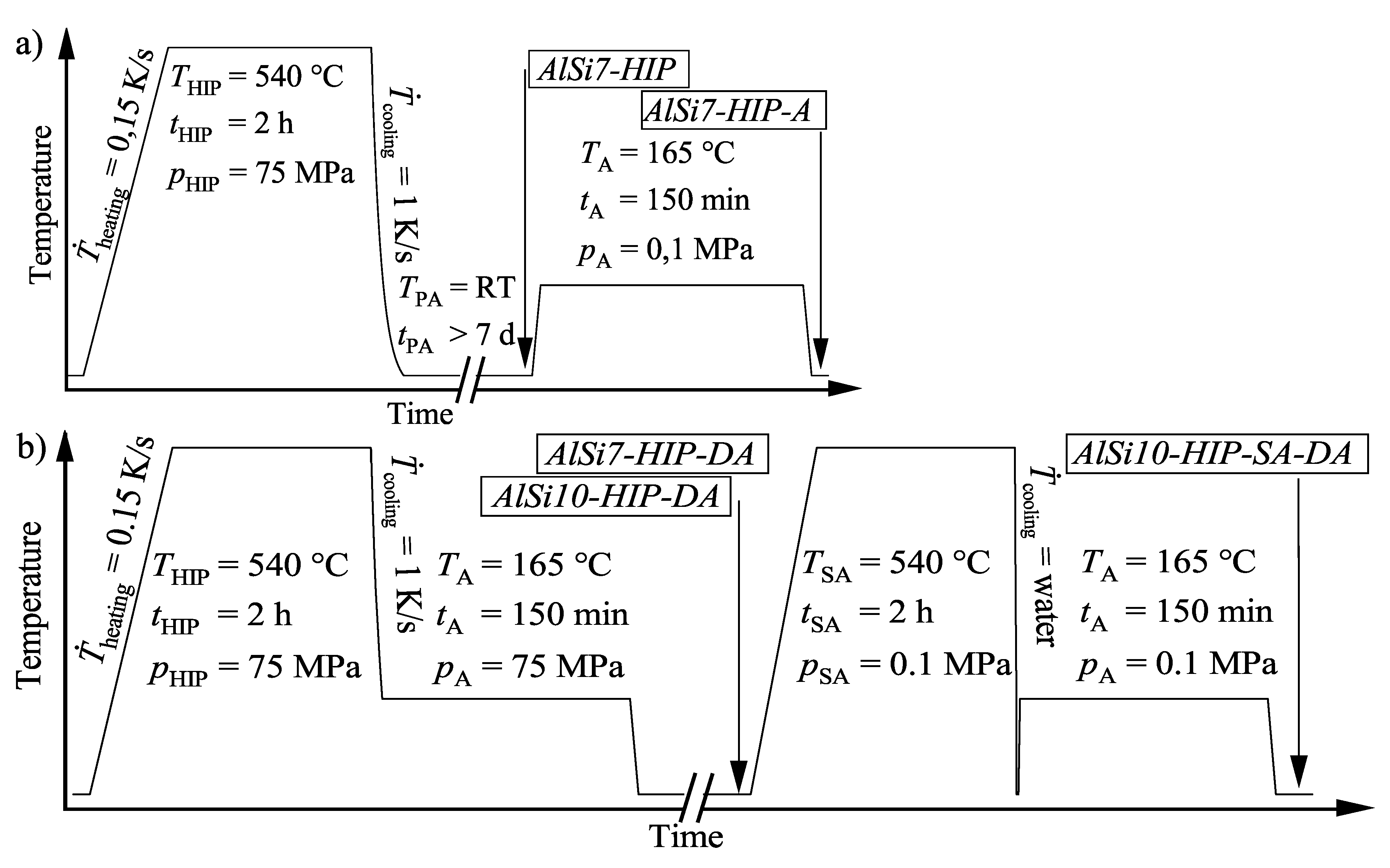
The mechanical properties of the L-PBF fabricated alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 were determined in as-built, hot isostatically pressed as well as hot isostatically pressed and heat treated conditions. The mechanical properties were than compared to those of hot isostatically pressed samples made from the alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 using conventional sand cast technique. Samples of the series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-HIP were sand cast and then hot isostatically pressed. Samples of series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-HIP-A were first hot isostatically pressed, preaged at room temperature for more than seven days and then artificially aged at 165 C for 150 min. The process parameters are illustrated in Figure 1a. Samples of the series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-HIP-DA were quenched with a cooling rate of 1 K/s within the temperature range between 540 and 200 C and then held at 165 C for 150 min. The process parameters are shown in Figure 1b.
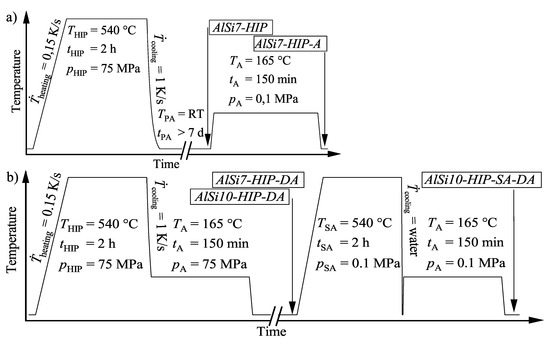
Figure 1.
(a) Temperature over time profile of the heat treatment conditions AlSi7-HIP and AlSi7-HIP-A; (b) Temperature over time profile of the heat treatment conditions AlSi7-HIP-DA, AlSi10-HIP-DA and AlSi10-HIP-SA-DA.
Tensile test samples of the alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 were built in 0, 45 and 90 inclination to the substrate plate. Series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-HIP-DA was hot isostatically pressed, the same as sample series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-HIP-DA. Series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-HIP-SA-DA was additionally heat treated by solution annealing followed by water quenching and immediate artificial aging at 165 C for 150 min.
3. Results and Discussion
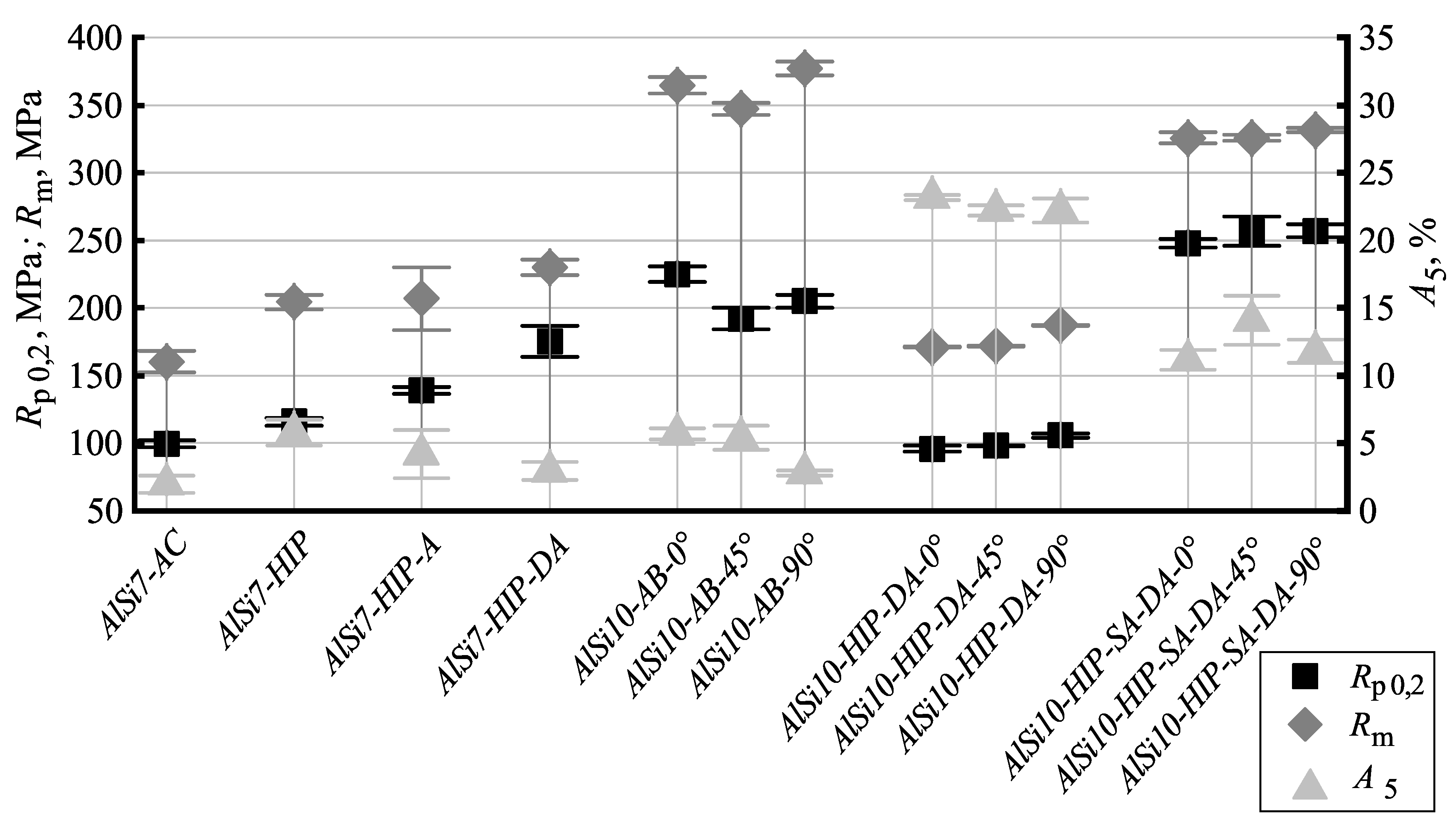
The tensile test results for all hot isostatically pressed and heat treated conditions are depicted in Figure 2. The quasistatic mechanical properties of the sand cast aluminum alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 were improved by the application of hot isostatic pressing followed by quenching at 1 K/s. The same hot isostatic pressing resulted in a higher material strength, if the samples were subsequently artificially aged (Series Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-HIP-DA). The same process of hot isostatic pressing and direct aging did result in a strength decrease of the L-PBF material, compared to its as-built condition. This can be explained by the cooling rate within the hot isostatic press, which was significantly lower than cooling after solidification in the L-PBF process. Pressure is known to decrease the critical cooling rate necessary for solution annealing of age-hardenable Al–Si–Mg alloys [29]. The supersaturation of alloying elements and therefore, the resulting age-hardenability of an Al–Si–Mg alloy is usually higher when quenching at the same cooling rate is performed at high pressure [28]. The tensile test results shown in this study indicate that the difference in the cooling rate between the L-PBF process and hot isostatic pressing was not compensated by the effect of pressure. Even though a cooing rate of 1 K/s resulted in a reasonable material strength for hot isostatic pressing of cast material, the same cooing rate was not high enough for L-PBF material to reach its strength in the as-built condition.
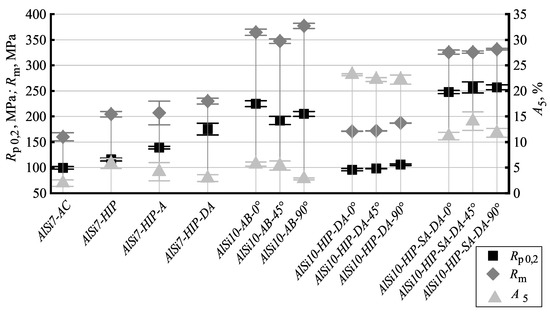
Figure 2.
Tensile test results for all hot isostatically pressed and heat treated conditions. R is the yield strenght, R is the ultimate tensile strength, A is the elongation at fracture. Aluminum–Silicon AlSi7-AC is the as cast condition of the sand cast material. Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-AB... denotes the as build condition of the L-PBF material. The labels Aluminum–Silicon ...-HIP, ...HIP-A, ...-HIP-DA, ...HIP-SA-DA indicate the utilized heat treatment which is explained in Section 2.1. The labels ...0, ...45 and ...90 indicate the orientation of the samples to the substrate plate.
While lower strength aluminum alloys are usually more ductile than high strength variants, this effect is not large enough to explain the high elongation at fracture measured for the hot isostatically pressed AlSi10Mg0.3 sample series (22–23%). The alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 processed by sand casting had an initial porosity of 0.17% (obtained in the Archimedes method). After hot isostatic pressing no pores could be determined by means of optical methods and a density of 100% was calculated using the results from Archimedes measurements and the calculated density. Samples of the L-PBF alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 possessed a porosity of 0.30% in as-built condition, while a porosity of 0.02% was determined after hot isostatic pressing. Voids in cast samples are usually caused by shrinking. These pores are mostly empty and do usually not expand during heat treatment. Pores in L-PBF samples are likely to contain either the inert gas utilized during the fabrication process, or hydrogen, which stems from moisture in the powder.
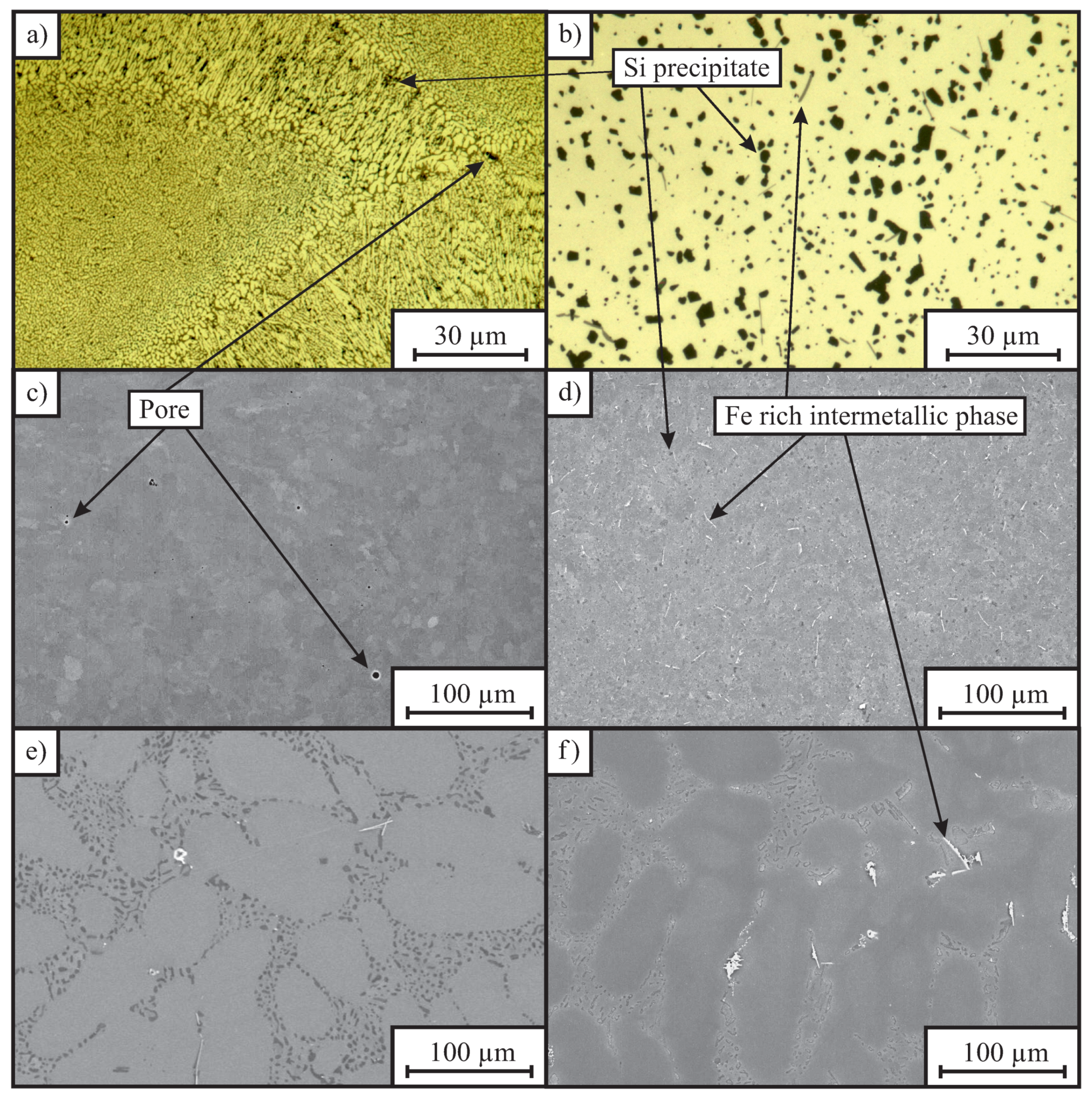
Micrographs of L-PBF samples are shown in Figure 3a–d. When comparing the microstructure of the L-PBF alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 in as-built condition (Figure 3a,c) to its microstructure after two hours of hot isostatic pressing at a temperature of 540 C and a pressure of 75 MPa (Figure 3b,d) it could be noted that the microstucture of the alloy coarsened significantly at 540 C during hot isostatic pressing. Pores evident in the as-built condition (Figure 3c) were absent after hot isostatic pressing. The material’s porosity has a strong influence on the elongation at fracture and its fatigue resistance, but exerts a smaller effect on its hardness, yield strength and ultimate tensile strength [40,41]. Hot isostatic pressing reduced the porosity from 0.30% in the as-built condition to 0.02% after hot isostatic pressing. The application of additional solution annealing usually does increase the porosity of as-built L-PBF material due to the expansion of the entrapped inert gas contained in the pores. Inert gases like Argon, which are typically used to prevent oxidation in the L-PBF process, have no solubility in the alloy and can, therefore, not diffuse through the material. Even though the L-PBF process was performed in Argon atmosphere, solution annealing did not increase the porosity of the material that has been hot isostatically pressed beforehand. It can be concluded, that the majority of pores within the L-PBF material did not contain argon gas.
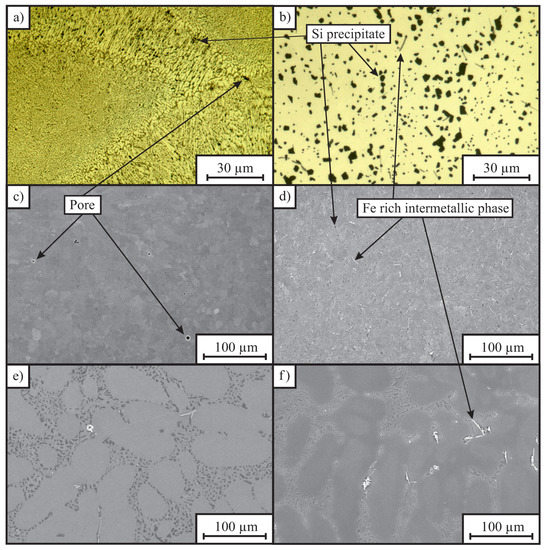
Figure 3.
Micrographs of the alloys; (a) image of the laser powder-bed fusion (L-PBF) alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 in as-built condition obtained with an optical microscope; (b) image of the L-PBF alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 in hot isostatically pressed and direct-aged condition obtained with an optical microscope; (c) scanning electron image of the L-PBF alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 in as-built condition; (d) scanning electron image of the L-PBF alloy AlSi10Mg0.3 in hot isostatically pressed and direct-aged condition; (e) scanning electron image of the sand-cast alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 in as-cast condition, (f) scanning electron image of the sand-cast alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 in hot isostatically pressed and direct-aged condition.
The results of the mechanical testing show that the application of hot isostatic pressing can be utilized for L-PBF Al-Si-Mg alloys to defeat porosity. The yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength of direct aged hot isostatically pressed condition Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-HIP-DA was lower than for the as-build condition. The mechanical strength of the heat treated condition Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-HIP-SA-DA was found to be significantly higher when compared to those of the conditions Aluminum–Silicon AlSi10-HIP-DA. This indicates that some of the materials strength in L-PBF as-build condition, which decreased by hot isostatic pressing, can be restored by the application of additional solution annealing, if quenching is performed at a high cooling rate.
Figure 3e shows scanning electron image of the sand-cast alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 in as-cast condition, Figure 3f scanning electron image of the sand-cast alloy AlSi7Mg0.3 in hot isostatically pressed and direct-aged condition. The effects of hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure of the sand-cast alloy were comparably small, compared to the microstructural changes during hot isostatic pressing of the L-PBF alloy. Nevertheless, the high temperature (540 C) has a pressure dependent effect on the coarsening of silicon precipitates in sand-cast Al-Si–Mg alloys, as demonstrated in [28,29]. While the microstructure of the L-PBF aluminum alloys is very fine, when compared to the heat treated and the sand cast microstructure, the silicon precipitates in all of the investigated alloys are not the main reason for the high strength of these age-hardenable aluminum alloys. The high strength of age-hardenable aluminum alloy is more likely based on a fine dispersion of various phases, predominately GP-I zones and particles which precipitate from an supersaturated solid solution during artificial aging [4,5,7]. Those strength relevant phases have a size of 50 µm × 500 µm, and a weak contrast to the aluminum matrix. Therefore, the most strength relevant precipitates cannot be seen in the micrograhps of Figure 3.
The application of additional solution annealing followed by direct-aging resulted in a significant increase in the mechanical properties. Particularly, the achieved yield strength was found to the highest of all investigated conditions. While significant changes were observed in the microstructure when comparing those heat treatment conditions, it can be concluded that neither the time at high temperature during hot isostatic pressing, nor the time during solution annealing modified the microstructure in a way, which would obstruct the alloy to posses high strength after additional heat treatment. Even though this heat treatment condition results in high strength, the elongation at fracture of all inclinations was between 11% and 14% and therefore, significantly higher when compared to the as-built condition (3–6%). This effect could be explained by the reduction of porosity, which resulted from hot isostatic pressing. In the as-built condition, Al grain boundaries are surrounded with Si particles. These particles are heterogeneously distributed and occur predominantly in overlapping regions (adjacent scan tracks and subsequent layers). Due to the alteration in the scan track pattern the effect of the local embrittlement caused by the increased presence of Si particles is more pronounced between the repetitive layering. Dedicated studies on destructive material testing revealed brittle shear fracturing between layers, leading to a similar yield strength in tension and compression, with minima at the constellation of a 45 angle between external uniaxial load with respect to the layering [9]. Moreover, the fracture toughness was reported to be significantly reduced in instances of crack propagation parallel to the layering [42].
4. Summary and Outlook
Hot isostatic pressing can be utilized for L-PBF Al-Si-Mg alloys to defeat porosity and to reduce the influence of the anisotropy effects caused by the layering and resulted in a high elongation at fracture of more than 20%.
A cooling rate of 1 K/s was found to slow to perform direct ageing immediately after hot isostatic pressing. The strength decrease of the L-PBF material induced by hot isostatic pressing was the result of a significantly slower cooling in the hot isostatic press, compared to the cooling after solidification in the L-PBF process. The critical cooling rate was found to be higher for the additively manufactured AlSi10Mg0.3 alloy than for comparable sand cast material.
Additional solution annealing did not increase the porosity of hot isostatically pressed L-PBF material (fabricated in argon atmosphere). Therefore, some of the materials strength which decreased by hot isostatic pressing can be restored by the application of additional solution annealing, if quenching is performed at a higher rate.
The mechanical properties, in particular the yield strength of hot isostatically pressed and heat treated L-PBF material, were at a very promising level. The exposure to high temperature during hot isostatic pressing and solution annealing modifies the microstructure of additively manufactured material in a way, which would obstruct the alloy to posses high strength after heat treatment. A combined process of densification, solution annealing and aging might be realized, if the lowering effect of pressure on the critical cooling rate, combined with advanced cooling technology (made accessible in modern hot isostatic presses) are sufficient to arrive at a supersaturated condition of the alloying elements silicon and magnesium by hot isostatic pressing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., L.H. and E.W.; methodology, S.H., L.H.; validation, L.H. and E.S.; formal analysis, S.H., L.H. and E.W.; investigation, S.H.; resources, E.W., M.M. and A.Ö.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H., L.H. and E.S.; writing—review and editing, A.Ö., E.W.; visualization, S.H., L.H. and E.S.; supervision, M.M., A.Ö. and E.W.; project administration, S.H., L.H. and E.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brummer, M.; Hoffmann, H.; Werner, E. Heat Treatment of Aluminum Castings Combined with Hot Isostatic Pressing. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, Yokohama, Japan, 5–9 September 2010; Kumai, S., Umezawa, O., Takayama, Y., Tsuchida, T., Sato, T., Eds.; The Japan Institute of Light Metals: Yokohama, Japan, 2010; pp. 1095–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.G.; Davidson, C.J. Solidification and precipitation behaviour of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W. HIP und Wärmebehandlung von Aluminiumguss—Zwei Prozesse werden neu kombiniert. Z. Werkst. Wärmebehandlung Fert. 2008, 63, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.H. The structure of the metastable precipitates formed during ageing of an Al–Mg–Si alloy. Philos. Mag. 1972, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.A.; Stiller, K.; Dunlop, G.L.; Couper, M.J. The precipitation sequence in Al–Mg–Si alloys. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, I.; Allen, S.M. A calorimetric study of precipitation in commercial aluminium alloy 6061. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.J.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Jansen, C.; Tundal, U.; Reiso, O. The crystal structure of the beta” phase in Al–Mg–Si alloys. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, K.G.; Scudino, S.; Klauss, H.J.; Surreddi, K.B.; Löber, L.; Wang, Z.; Chaubey, A.K.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–12Si produced by selective laser melting: Effect of heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 590, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Schoch, N.; Heine, B.; Merkel, M.; Hall, W.; Öchsner, A. Compressive behaviour of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg. Mater. Werkst. 2018, 49, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenstein, S.; Werner, E.; Wilzer, J.; Theisen, W.; Weber, S.; Sunderkötter, C.; Bachmann, M. Influence of temperature and tempering conditions on thermal conductivity of hot work tool steels for hot stamping applications. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenstein, S.; Werner, E.; Wilzer, J.; Theisen, W.; Weber, S.; Sunderkötter, C.; Bachmann, M. Einfluss der Temperatur und des Vergütungszustands auf die Wärmeleitfähigkeit von Warmarbeitsstählen für das Presshärten. HTM J. Heat Treat. Mater. 2017, 72, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Merkel, M.; Hall, W.; Öchsner, A. A Review of Metal Fabricated with Laser- and Powder-Bed Based Additive Manufacturing Techniques: Process, Nomenclature, Materials, Achievable Properties, and its Utilization in the Medical Sector. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Janousch, C.; Schanz, J.; Merkel, M.; Mack, F.; Öchsner, A. Non-destructive evaluation of AlSi10Mg prismatic samples generated by Selective Laser Melting: Influence of manufacturing conditions. Mater. Werkst. 2016, 47, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Maskery, I.; Tuck, C.; Ashcroft, I.; Everitt, N.M. The microstructure and mechanical properties of selectively laser melted AlSi10Mg: The effect of a conventional T6-like heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 667, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Simonelli, M.; Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R. 3D printing of Aluminium alloys: Additive Manufacturing of Aluminium alloys using selective laser melting. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Janousch, C.; Schanz, J.; Merkel, M.; Heine, B.; Mack, F.; Hall, W.; Öchsner, A. Direction and location dependency of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg specimens. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 243, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Charles, A.; Öchsner, A. The Influence of Post-Heat-Treatments on the Tensile Strength and Surface Hardness of Selective Laser Melted AlSi10Mg. Defect Diffus. Forum 2016, 370, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilgeist, S.; Hitzler, L.; Javanbakht, Z.; Merkel, M.; Heine, B.; Öchsner, A. The Influence of Post-Heat Treatments on the Tensile Strength and Surface Hardness of Selectively Laser-Melted AlSi10Mg. Mater. Werkst. 2019, 50, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, E.; Schuch, E.; Hitzler, L.; Werner, E.; Öchsner, A.; Merkel, M. Tensile strength performance with determination of Poisson’s ratio of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg samples. Mater. Werkst. 2019, 50, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenpohl, D. Aluminium und Aluminiumlegierungen; Reine und Angewandte Metallkunde in Einzeldarstellungen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Hafenstein, S.; Werner, E. Simultaneous hot isostatic pressing and solution annealing of aluminum cast alloys followed by instantaneous aging at elevated temperatures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 416, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, L.; Hafenstein, S.; Mendez Martin, F.; Clemens, H.; Sert, E.; Öchsner, A.; Merkel, M.; Werner, E. Heat Treatments and Critical Quenching Rates in Additively Manufactured Al-Si-Mg Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, B.E. The effect of alloying elements and pressure on the growth of pearlite. Acta Metall. 1969, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrer, H. Diffusion in Solids: Fundamentals, Methods, Materials, Diffusion-Controlled Processes; Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 155. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadeshia, H.; Honeycombe, R.W.K. Steels: Microstructure and Properties, 3rd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann, Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hafenstein, S.; Brummer, M.; Ahlfors, M.; Werner, E. Combined hot Isostatic pressing and heat treatment of aluminum A356 cast alloys. HTM J. Heat Treat. Mater. 2016, 71, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenstein, S.; Brummer, M.; Ahlfors, M.; Werner, E. Kombiniertes Heißisostatisches Pressen (HIP) und Wärmebehandlung von einer A356 Aluminiumgusslegierung. Giess. Prax. 2016, 7–8, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hafenstein, S. Heißisostatisches Pressen von Aluminiumgusslegierungen mit Integrierter Wärmebehandlung; Springer Vieweg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hafenstein, S.; Werner, E. Pressure dependence of age-hardenability of aluminum cast alloys and coarsening of precipitates during hot isostatic pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 757, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenstein, S.; Werner, E. Direct aging of a hot isostatically pressed A356 aluminum cast alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 768, 138417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Arunkumar, Y.; Chetty, P.V.J.; Raman, K.S.; Murthy, K.S.S. The effect of preaging on the delayed aging of Al–7Si–0.3Mg. JOM 1997, 49, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; Alejandro, G.J.; Talamantes, S.J.; Colás, R. Effect of the delay in time between cooling and aging in heat-treated cast aluminum alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Kang, S.B. The effect of pre-aging on microstructure and tensile properties of Al–Mg–Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammas-Williams, S.; Withers, P.J.; Todd, I.; Prangnell, P.B. Porosity regrowth during heat treatment of hot isostatically pressed additively manufactured titanium components. Scr. Mater. 2016, 122, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Wei, Q.; Liu, J.H. Manufacturing AISI316L Components via Selective Laser Melting Coupled with Hot Isostatic Pressing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 675–677, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, N.P.; Cherry, J.; Mehmood, S.; Davies, H.; Girling, B.; Sackett, E.; Brown, S.G.R.; Sienz, J. Effects of hot isostatic pressing on the elastic modulus and tensile properties of 316L parts made by powder bed laser fusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 693, 186–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 1706:2010. Aluminium und Aluminiumlegierungen—Gussstücke—Chemische Zusammensetzung und mechanische Eigenschaften; Deutsche Fassung; DIN e.V.: Berlin, Germany, December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 50125. Prüfung metallischer Werkstoffe—Zugproben; Deutsche Fassung; DIN e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN ISO 6506-2. Metallische Werkstoffe—Härteprüfung nach Brinell—Teil 2: Überprüfung und Kalibrierung der Prüfmaschinen; Deutsche Fassung; DIN e.V.: Berlin, Germany, April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelbacher, G. Einfluss unterschiedlicher Porosität auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften der Legierung GD-AlSi9Cu3. Giess. Prax. 1993, 19, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Skrinsky, Y. Einfluß von heiß- und Kaltisostatischem Pressen auf die Statischen Mechanischen Werkstoffkennwerte von Gußteilen aus Aluminiumlegierungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität, Magdeburg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hitzler, L.; Hirsch, J.; Schanz, J.; Heine, B.; Merkel, M.; Hall, W.; Öchsner, A. Fracture toughness of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2019, 233, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).