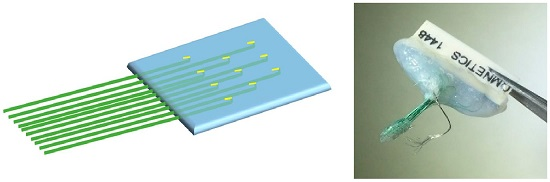
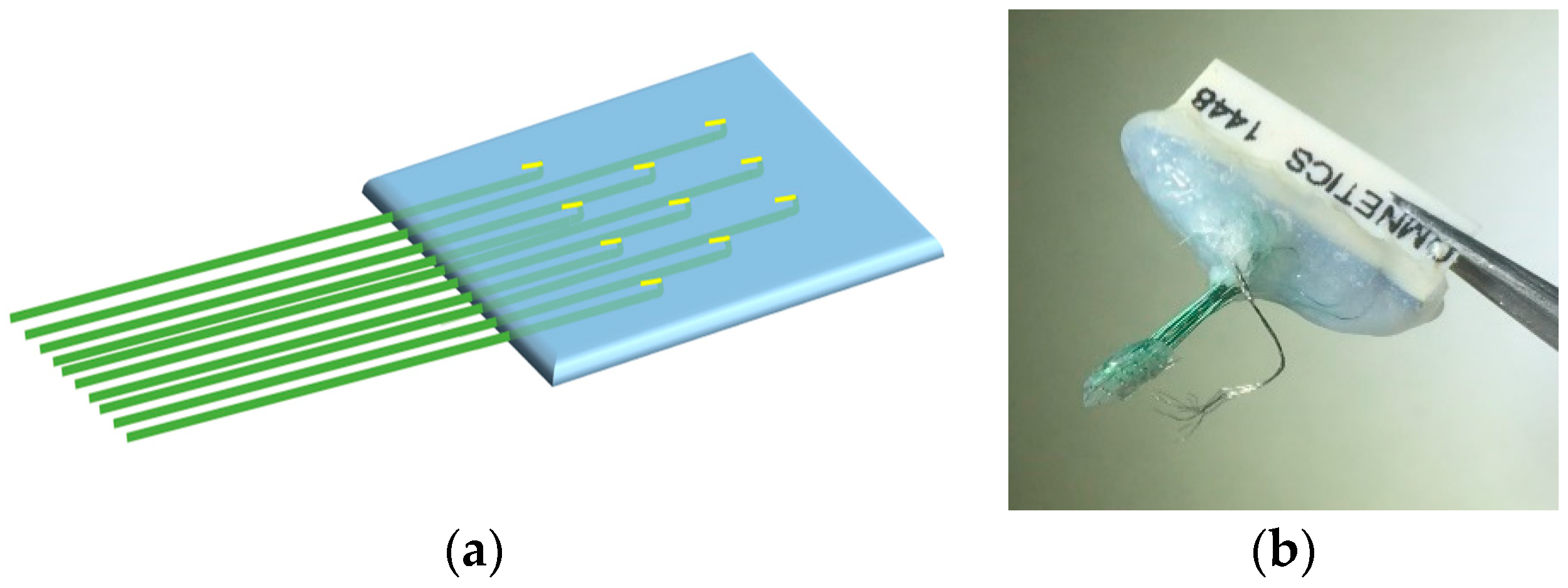
Handcrafted Electrocorticography Electrodes for a Rodent Behavioral Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
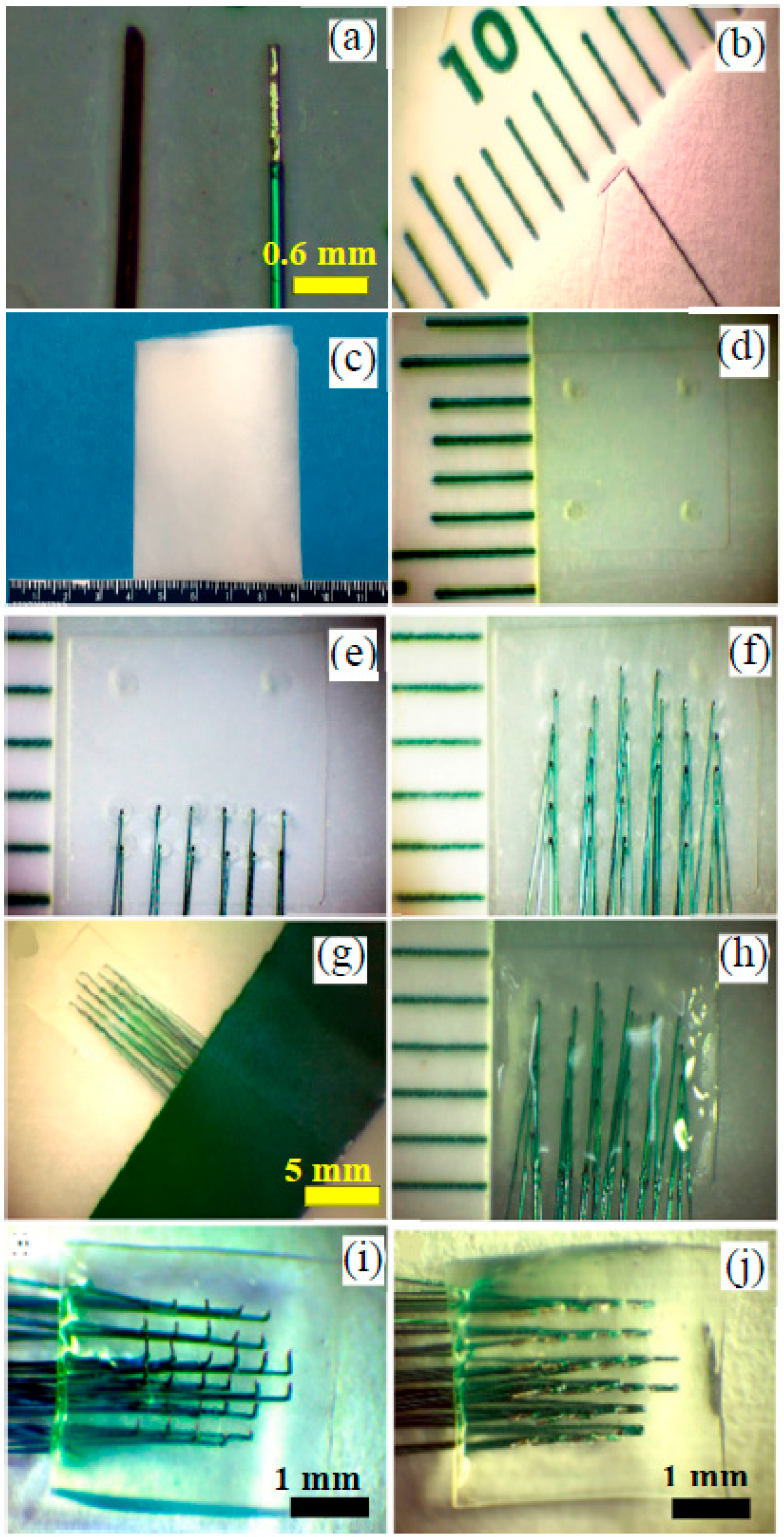
2.1. Fabrication of Handcrafted ECoG Electrode
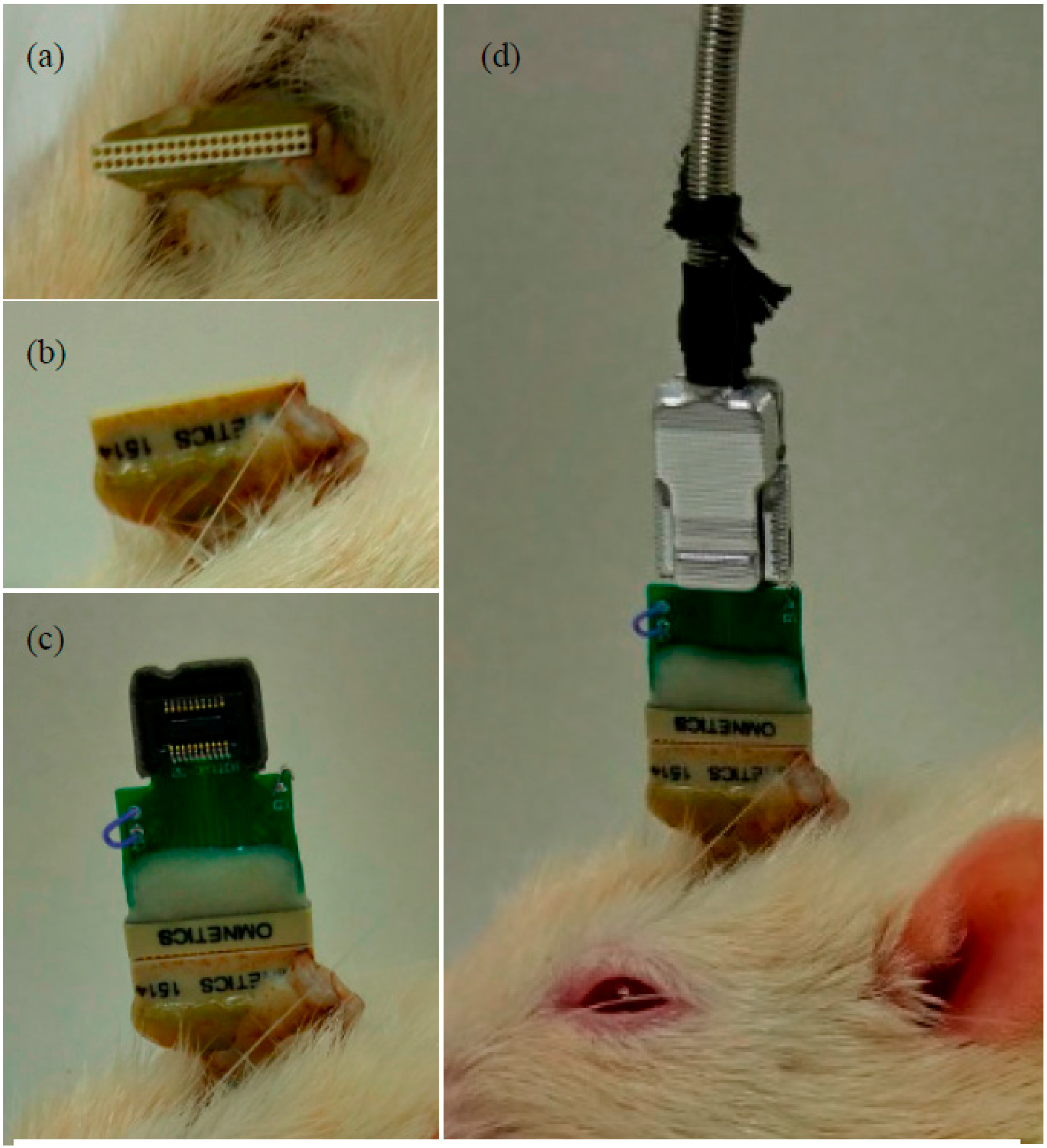
2.2. Implantation of Handcrafted ECoG Electrodes
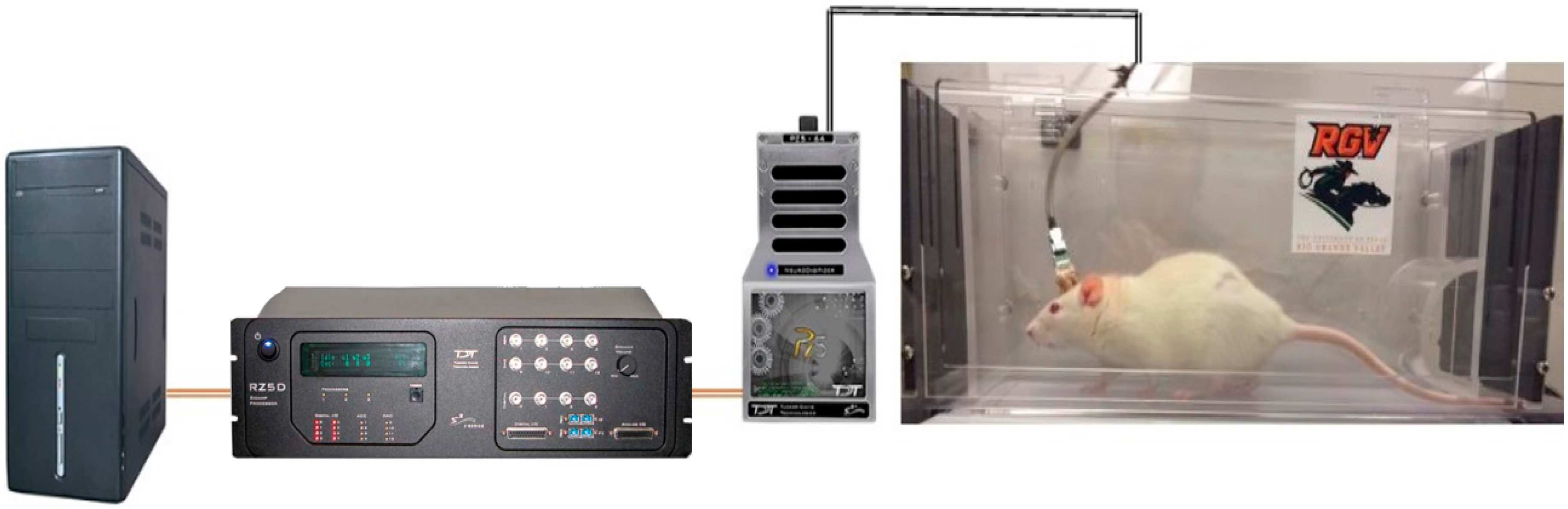
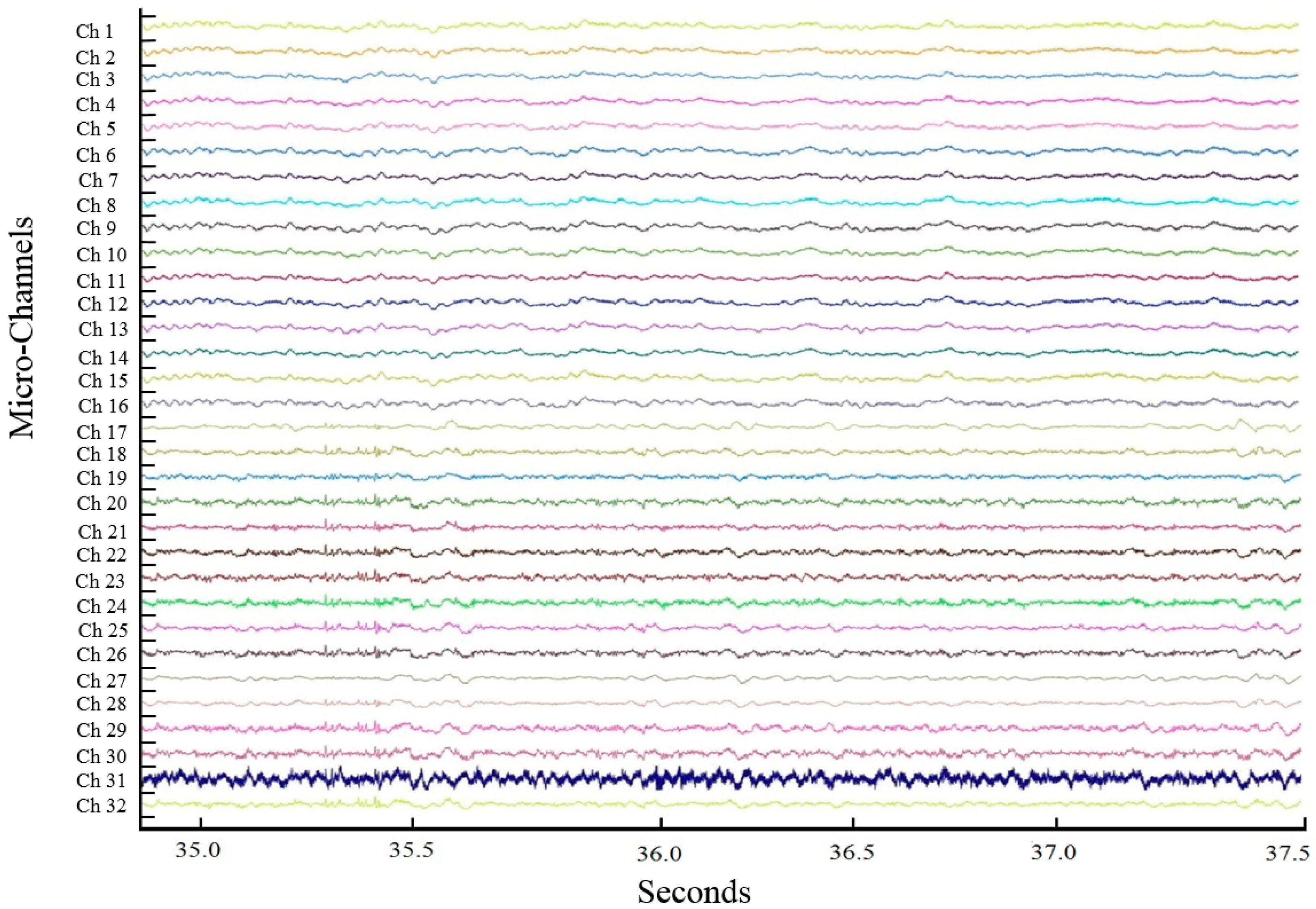
3. ECoG Acquisition Setup and Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navarro, X.; Krueger, T.B.; Lago, N.; Micera, S.; Stieglitz, T.; Dario, P. A critical review of interfaces with the peripheral nervous systemfor the control of neuroprostheses and hybrid bionic systems. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.C.; Gunduz, A.; Carney, P.R.; Principe, J.C. Extraction and localization of mesoscopic motor control signals for human ECoG neuroprosthetics. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 167, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalk, G.; McFarland, D.J.; Hinterberger, T.; Birbaumer, N.; Wolpaw, J.R. BCI2000: A general-purpose brain-computer interface (BCI) system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, Y.; Shimoda, K.; Fujii, N. Multidimensional Recording (MDR) and Data Sharing: An Ecological Open Research and Educational Platform for Neuroscience. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodagholy, D.; Doublet, T.; Quilichini, P.; Gurfinkel, M.; Leleux, P.; Ghestem, A.; Ismailova, E.; Hervé, T.; Sanaur, S.; Bernard, C.; et al. In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Degenhart, A.D.; Collinger, J.L.; Vinjamuri, R.; Sudre, G.P.; Adelson, P.D.; Holder, D.L.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Moran, D.W.; Boninger, M.L.; et al. Human motor cortical activity recorded with micro-ECoG electrodes during individual finger movements. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009.
- Toda, H.; Suzuki, T.; Sawahata, H.; Majima, K.; Kamitani, Y.; Hasegawa, I. Simultaneous recording of ECoG and intracortical neuronal activity using a flexible multichannel electrode-mesh in visual cortex. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tanaka, N.; Stufflebeam, S.; Ahlfors, S.; Hämäläinen, M. Functional mapping with simultaneous MEG and EEG. J. Vis. Exp. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.B.; Cui, X.T.; Weber, D.J.; Moran, D.W. Brain-controlled interfaces: Movement restoration with neural prosthetics. Neuron 2006, 52, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.J.; Lal, T.N.; Schröder, M.; Hinterberger, T.; Widman, G.; Elger, C.E.; Schölkopf, B.; Birbaumer, N. Classifying event-related desynchronization in EEG, ECoG and MEG signals. In Pattern Recognition; Franke, K., Müller, K.-L., Nickolay, B., Schäfer, R., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 404–413. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.K.; Larson, E.; Maddox, R.K. Mapping cortical dynamics using simultaneous MEG/EEG and anatomically-constrained minimum-norm estimates: An auditory attention example. J. Vis. Exp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.J.; Gupta, D.; Brunner, P.; Gunduz, A.; Adamo, M.A.; Ritaccio, A.; Schalk, G. Recording human electrocorticographic (ECoG) signals for neuroscientific research and real-time functional cortical mapping. J. Vis. Exp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, C.R.; Ellmore, T.M.; Pieters, T.A.; DiSano, M.A.; Tandon, N. Variability of the Relationship between Electrophysiology and BOLD-fMRI across Cortical Regions in Humans. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12855–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, K.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Ji, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, M. PET Mapping for Brain-Computer-Interface-Based Stimulation in a Rat Model with Intracranial Electrode Implantation in the Ventro-posterior Medial Thalamus. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistohl, T.; Ball, T.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Aertsen, A.; Mehring, C. Prediction of arm movement trajectories from ECoG-recordings in humans. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 167, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, E.M.; Nordhausen, C.T.; Normann, R.A. The Utah intracortical electrode array: A recording structure for potential brain-computer interfaces. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 102, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, N.Y.; Jarosiewicz, B.; Simeral, J.D.; Bacher, D.; Stavisky, S.D.; Cash, S.S.; Oakley, E.M.; Berhanu, E.; Eskandar, E.; Friehs, G.; et al. Non-causal spike filtering improves decoding of movement intention for intracortical BCIs. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 236, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perge, J.A.; Zhang, S.; Malik, W.Q.; Homer, M.L.; Cash, S.; Friehs, G.; Eskandar, E.N.; Donoghue, J.P.; Hochberg, L.R. Reliability of directional information in unsorted spikes and local field potentials recorded in human motor cortex. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavitt, M.L.; Pieper, F.; Sachs, A.; Joober, R.; Martinez-Trujillo, J.C. Structure of spike count correlations reveals functional interactions between neurons in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex area 8a of behaving primates. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, P.; Molina, A.; Balderas, D.C.; Grammatikou, D. Brain Computer Interfaces for Cerebral Palsy. InTech 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.A.; Felton, E.A.; Garell, P.C.; Schalk, G.; Williams, J.C. ECoG factors underlying multimodal control of a brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 14, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashaie, R.; Anikeeva, P.; Lee, J.H.; Prakash, R.; Yizhar, O.; Prigge, M.; Chander, D.; Richner, H.J.; Williams, J. Optogenetic Brain Interfaces. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 7, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, G.J.; Sola, R.G.; Pastor, J. Complex network analysis of human ECoG data. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 447, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towle, V.L.; Yoon, H.-A.; Castelle, M.; Edgar, J.C.; Biassou, N.M.; Frim, D.M.; Spire, J.-P.; Kohrman, M.H. ECoG gamma activity during a language task: Differentiating expressive and receptive speech areas. Brain 2008, 131, 2013–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Collinger, J.L.; Degenhart, A.D.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Schwartz, A.B.; Moran, D.W.; Weber, D.J.; Wodlinger, B.; Vinjamuri, R.K.; Ashmore, R.C.; et al. An Electrocorticographic Brain Interface in an Individual with Tetraplegia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escabí, M.A.; Read, H.L.; Viventi, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Higgins, N.C.; Storace, D.A.; Liu, A.S.K.; Gifford, A.M.; Burke, J.F.; Campisi, M.; et al. A high-density, high-channel count, multiplexed uECoG array for auditory-cortex recordings. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 112, 1566–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, E.H.; Frattini, S.A.; Robbiati, S.; Huerta, P.T. Construction of Microdrive Arrays for Chronic Neural Recordings in Awake Behaving Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, L.R.; Serruya, M.D.; Friehs, G.M.; Mukand, J.A.; Saleh, M.; Caplan, A.H.; Branner, A.; Chen, D.; Penn, R.D.; Donoghue, J.P. Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature 2006, 442, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghu, J.P. Bridging the brain to the world: A perspective on neural interface systems. Neuron 2008, 60, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fountas, K.N. Implanted Subdural Electrodes: Safety Issues and Complication Avoidance. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalk, G.; Leuthardt, E.C. Brain-computer interfaces using electrocorticographic signals. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 4, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microwire Material Specification. Available online: http://www.calfinewire.com/datasheets/100189-stablohm800a.html (accessed on 11 August 2016).
- Yeager, J.D.; Phillips, D.J.; Rector, D.M.; Bahr, D.F. Characterization of flexible ECoG electrode arrays for chronic recording in awake rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 173, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, G.J.; Stoetzner, C.R.; Richner, T.; Brodnick, S.K.; Williams, J.C.; Kipke, D.R. Surgical implantation of chronic neural electrodes for recording single unit activity and electrocortiographic signals. J. Vis. Exp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstosheeva, E.; Gordillo-González, V.; Biefeld, V.; Kempen, L.; Mandon, S.; Kreiter, A.K.; Lang, W. A multi-channel, flex-rigid ECoG microelectrode array for visual cortical interfacing. Sensors 2015, 15, 832–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubehn, B.; Bosman, C.; Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Stieglitz, T. A MEMS-based flexible multichannel ECoG-electrode array. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 036003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstosheeva, E.; Gordillo-Gonzalez, V.; Hertzberg, T.; Kempen, L.; Michels, I.; Kreiter, A.; Lang, W. A novel flex-rigid and soft-release ECoG array. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 2973–2976.
- Schalk, G.; Kubanek, J.; Miller, K.J.; Anderson, N.R.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Ojemann, J.G.; Limbrick, D.; Moran, D.; Gerhardt, L.A.; Wolpaw, J.R. Decoding two-dimensional movement trajectories using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, W.J.; Rogers, L.J.; Holmes, M.D.; Silbergeld, D.L. Spatial spectral analysis of human electrocorticograms including the alpha and gamma bands. J. Neurosci. Methods 2000, 95, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warda, M.P.; Rajdeva, P.; Ellisona, C.; Irazoquia, P.P. Toward a comparison of microelectrodes for acute and chronic recordings. Brain Res. 2009, 1282, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boppart, S.A.; Wheeler, B.C.; Wallace, C.S. A flexible perforated microelectrode array for extended neural recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 39, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.J.; Snyder, A.Z.; Zempel, J.M.; Smyth, M.D.; Raichle, M.E. Electrophysiological correlates of the brain’s intrinsic large-scale functional architecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16039–16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.J.; Pouget, P. Physical model of coherent potentials measured with different electrode recording site sizes. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 107, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Choi, J.H. Simultaneous recording of brain activity and functional connectivity in the mouse brain. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009.
- Hill, N.J.; Lal, T.N.; Schroder, M.; Hinterberger, T.; Wilhelm, B.; Nijboer, F.; Mochty, U.; Widman, G.; Elger, C.; Scholkopf, B.; et al. Classifying EEG and ECoG Signals without subject training for fast BCI implementation: Comparison of non-paralysed and completely paralysed subjects. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2006, 14, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurstjens, G.; Borau, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Rijkhoff, N.; Sinkjær, T. Intraoperative recording of electroneurographic signals from cuff electrodes on extradural sacral roots in spinal cord injured patients. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercanzini, A.; Cheung, K.; Buhl, D.L.; Boers, M.; Maillard, A.; Colin, P.; Bensadoun, J.-C.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P. Demonstration of cortical recording using novel flexible polymer neural probes. Sens. Actuators 2008, 143, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledochowitsch, P.; Félus, R.J.; Gibboni, R.R.; Miyakawa, A.; Bao, S.; Maharbiz, M.M. Fabrication and testing of a large area, high density, parylene MEMS µECoG array. In Proceedings of the 24th 2011 IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 January 2011.
- Santos, L.; Opris, I.; Fuqua, J.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. A novel tetrode microdrive for simultaneous multi-neuron recording from different regions of primate brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 205, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, A.; Máthé, K.; Petykó, Z.; Szabó, I.; Czurkó, A. Implementation of a galvanically isolated low-noise power supply board for multi-channel headstage preamplifiers. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 171, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-H.; Li, J.-J.; Lu, Q.-C.; Gong, H.-Q.; Liang, P.-J.; Zhang, P.-M. Involvement of Thalamus in Initiation of Epileptic Seizures Induced by Pilocarpine in Mice. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014, 675128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Tsien, J.Z. Large-Scale Neural Ensembles in Mice: Methods for Recording and Data Analysis. Electrophysiol. Rec. Tech. 2011, 54, 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- Janetsian, S.S.; Linsenbardt, D.N.; Lapish, C.C. Memory impairment and alterations in prefrontal cortex gamma band activity following methamphetamine sensitization. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, F.; Chung, S.; Beier, K.T.; Xu, M.; Luo, L.; Dan, Y. Control of REM sleep by ventral medulla GABAergic neurons. Nature 2015, 526, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvadè, A.; D’Angelo, V.; Di Giovanni, G.; Tinkhauser, G.; Sancesario, G.; Städler, C.; Möller, J.C.; Stefani, A.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Galati, S. Distinct roles of cortical and pallidal β and γ frequencies in hemiparkinsonian and dyskinetic rats. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galati, S.; Salvadè, A.; Pace, M.; Sarasso, S.; Baracchi, F.; Bassetti, C.L.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Städler, C.; Stanzione, P.; Möller, J.C. Evidence of an association between sleep and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Dai, J.; Zheng, X. Field-programmable gate array implementation of a probabilistic neural network for motor cortical decoding in rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 185, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babb, T.L.; Pretorius, J.K.; Kupfer, W.R.; Feldblum, S. Recovery of decreased glutamate decarboxylase immunoreactivity after rat hippocampal kindling. Epilepsy Res. 1989, 3, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S.; Yoon, T.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Weiss, C. Functional Reorganization of a Prefrontal Cortical Network Mediating Consolidation of Trace Eyeblink Conditioning. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, T.R.; Weir, R.F. A Comparison of the Effects of Electrode Implantation and Targeting on Pattern Classification Accuracy for Prosthesis Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2198–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasnim, N.; Ajam, A.; Ramos, R.; Koripalli, M.K.; Chennamsetti, M.; Choi, Y. Handcrafted Electrocorticography Electrodes for a Rodent Behavioral Model. Technologies 2016, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies4030023
Tasnim N, Ajam A, Ramos R, Koripalli MK, Chennamsetti M, Choi Y. Handcrafted Electrocorticography Electrodes for a Rodent Behavioral Model. Technologies. 2016; 4(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies4030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasnim, Nishat, Ali Ajam, Raul Ramos, Mukhesh K. Koripalli, Manisankar Chennamsetti, and Yoonsu Choi. 2016. "Handcrafted Electrocorticography Electrodes for a Rodent Behavioral Model" Technologies 4, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies4030023
APA StyleTasnim, N., Ajam, A., Ramos, R., Koripalli, M. K., Chennamsetti, M., & Choi, Y. (2016). Handcrafted Electrocorticography Electrodes for a Rodent Behavioral Model. Technologies, 4(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies4030023