Localization Meets Uncertainty: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Modal Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel uncertainty-aware multi-modal end-to-end localization framework that not only estimates the robot’s 3-DoF pose but also quantifies uncertainty associated with the predictions. The original FusionLoc architecture is extended to output uncertainty values by integrating MC dropout for epistemic uncertainty and direct variance regression for aleatoric uncertainty, enabling a more reliable and informative localization result.
- We introduce a percentile-based rejection method using the thresholds (e.g., 70%, 80%, and 90%) to reject low-confidence pose estimations, thereby improving localization robustness and safety in uncertain environments.
- The proposed approach is validated on three indoor datasets under various environmental conditions, demonstrating the effectiveness of uncertainty-aware localization over standard approaches.
2. Related Works
2.1. End-to-End Localization
2.2. Uncertainty Quantification
| Reference | Sensor Modality | Localization | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kendall et al. [5] | RGB Camera | ✓ | ✘ |
| Wang et al. [6] | RGB Camera | ✓ | ✘ |
| Li and Ling [7] | Multi-view Camera | ✓ | ✘ |
| Qiao et al. [8] | RGB Camera | ✓ | ✘ |
| Wang et al. [18] | RGB Camera | ✓ | ✘ |
| Wang et al. [9] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Yu et al. [10] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Yu et al. [20] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Ibrahim et al. [21] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Li et al. [11] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Lai et al. [24] | RGB Camera + 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Wang et al. [25] | RGB Camera + 2D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Nakamura et al. [26] | Fisheye RGB Camera + 2D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Lee et al. [14] | RGB Camera + 2D LiDAR | ✓ | ✘ |
| Chen et al. [36] | RGB Camera | ✓ | ✓ |
| Li et al. [12] | 3D LiDAR | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ours | RGB Camera + 2D LiDAR | ✓ | ✓ |
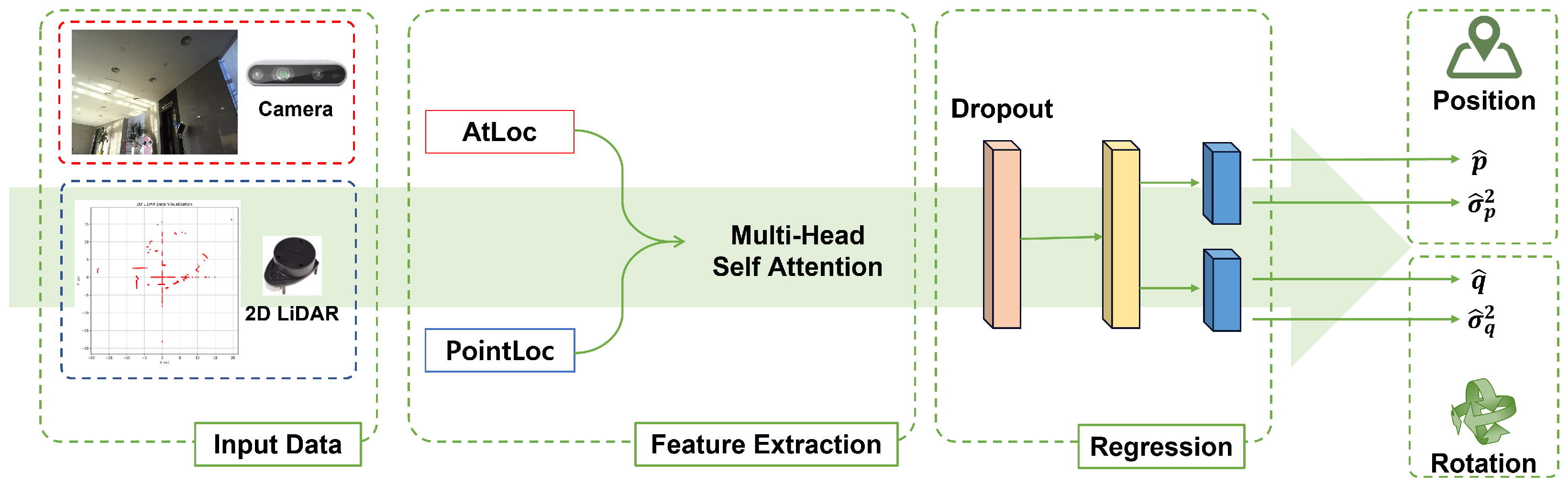
3. Method
3.1. Measuring Uncertainty
3.2. Uncertainty-Aware Localization Based on FusionLoc
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
- Straight corridor navigation: In this pattern, the robot navigates the entire space in a continuous loop before returning to its starting point.
- Zigzag movement: Here, the robot moves in a zigzag manner, weaving between obstacles.
- Repetitive back-and-forth motion: This pattern involves the robot moving back and forth within a confined space before proceeding with further exploration.
- Rotational maneuvers: In this last pattern, the robot performs in-place rotations at specific locations before retracing the same trajectory as in the first pattern.

| Attribute | TheGardenParty | ETRI | SusungHotel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image resolution (pixels) | 320 × 240 | 640 × 480 | 640 × 480 |
| Robot movement type | Predefined | 4 patterns | Predefined + random perturbation |
| Environment type | Restaurant | Wide lobby | Long and narrow curved corridor |
| Sequence type | Fragment | Full | Full |
| # Training tuples (# Sequences) | 7848 (24) | 12,688 (66) | 7625 (16) |
| # Validation tuples (# Sequences) | 2294 (5) | 2964 (16) | 1258 (2) |
| # Test tuples (# Sequences) | 3184 (6) | 2794 (16) | 1276 (2) |
| Total tuples (# Sequences) | 13,326 (35) | 19,014 (100) | 9625 (20) |

4.2. Training and Inference Details
4.3. Evaluation
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thrun, S.; Burgard, W.; Fox, D. Probabilistic Robotics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cadena, C.; Carlone, L.; Carrillo, H.; Latif, Y.; Scaramuzza, D.; Neira, J.; Reid, I.; Leonard, J.J. Past, Present, and Future of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: Toward the Robust-Perception Age. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, S.; Sünderhauf, N.; Newman, P.; Leonard, J.J.; Cox, D.; Corke, P.; Milford, M.J. Visual Place Recognition: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Li, J. Lidar-Based Place Recognition for Autonomous Driving: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 57, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.; Grimes, M.; Cipolla, R. Posenet: A Convolutional Network for Real-Time 6-DOF Camera Relocalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 2938–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Lu, C.X.; Zhao, P.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. AtLoc: Attention Guided Camera Localization. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10393–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, H. GTCaR: Graph Transformer for Camera Re-localization. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022), Tel-Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Xiang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhao, X.; Fu, J. TransAPR: Absolute Camera Pose Regression With Spatial and Temporal Attention. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4633–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Zhao, P.; Chen, C.; Clark, R.; Yang, B.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. PointLoc: Deep Pose Regressor for LiDAR Point Cloud Localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Wen, C.; Cheng, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. LiDAR-based localization using universal encoding and memory-aware regression. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 128, 108685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, G.; Shen, S.; Wen, C. SGLoc: Scene Geometry Encoding for Outdoor LiDAR Localization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 9286–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Hu, G.; Wen, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, C. DiffLoc: Diffusion Model for Outdoor LiDAR Localization. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 15045–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, S.; Caruso, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Furukawa, Y. Neural Inertial Localization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Oh, J. FusionLoc: Camera-2D LiDAR Fusion Using Multi-Head Self-Attention for End-to-End Serving Robot Relocalization. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 75121–75133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Kim, E. New Monte Carlo Localization Using Deep Initialization: A Three-Dimensional LiDAR and a Camera Fusion Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 74485–74496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Lin, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Akhtar, N. EFRNet-VL: An end-to-end feature refinement network for monocular visual localization in dynamic environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Stiefelhagen, R. Scene-agnostic Pose Regression for Visual Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y.; Wen, C.; Cheng, M.; Hu, G. STCLoc: Deep LiDAR Localization With Spatio-Temporal Constraints. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Akhtar, N.; Anwar, S.; Wise, M.; Mian, A. Slice Transformer and Self-supervised Learning for 6DoF Localization in 3D Point Cloud Maps. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 11763–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Sun, X.; Li, W.; Wen, C.; Yang, Y.; Si, B.; Hu, G.; Wang, C. NIDALoc: Neurobiologically Inspired Deep LiDAR Localization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 4278–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Lil, W.; Cai, Z.; Wen, C.; Zang, Y.; Muller, M.; Wang, C. LiSA: LiDAR Localization with Semantic Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 15271–15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Yin, P.; Scherer, S. AdaFusion: Visual-LiDAR Fusion With Adaptive Weights for Place Recognition. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 12038–12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Chen, D.; Fu, T.; Ma, L. A Robot Relocalization Method Based on Laser and Visual Features. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 11th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), Emei, China, 3–5 August 2022; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Toda, Y.; Kubota, N. Localization Fault Detection Method using 2D LiDAR and Fisheye Camera for an Autonomous Mobile Robot Control. In Proceedings of the 2024 SICE International Symposium on Control Systems (SICE ISCS), Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan, 18–20 March 2024; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What Uncertainties Do We Need in Bayesian Deep Learning for Computer Vision? In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshov, V.; Fenner, N.; Ermon, S. Accurate Uncertainties for Deep Learning Using Calibrated Regression. In Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Dy, J., Krause, A., Eds.; JMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 80, pp. 2796–2804. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J.C. Probabilistic Outputs for Support Vector Machines and Comparisons to Regularized Likelihood Methods. In Advances in Large Margin Classifiers; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J. Calibrated Reliable Regression using Maximum Mean Discrepancy. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17164–17175. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, D.; Mani, K.; Bansal, D.; Murthy, K.; Lee, H.; Paull, L. f-Cal: Aleatoric uncertainty quantification for robot perception via calibrated neural regression. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 6533–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Franchi, G.; Aldea, E. SLURP: Side Learning Uncertainty for Regression Problems. In Proceedings of the 32nd British Machine Vision Conference, BMVC, Virtual, 22–25 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Corbière, C.; Thome, N.; Saporta, A.; Vu, T.H.; Cord, M.; Pérez, P. Confidence Estimation via Auxiliary Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6043–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdar, M.; Pourpanah, F.; Hussain, S.; Rezazadegan, D.; Liu, L.; Ghavamzadeh, M.; Fieguth, P.; Cao, X.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R.; et al. A review of uncertainty quantification in deep learning: Techniques, applications and challenges. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 243–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlikowski, J.; Tassi, C.R.N.; Ali, M.; Lee, J.; Humt, M.; Feng, J.; Kruspe, A.; Triebel, R.; Jung, P.; Roscher, R.; et al. A survey of uncertainty in deep neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 1513–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Monica, J.; Chao, W.L.; Campbell, M. Probabilistic Uncertainty Quantification of Prediction Models with Application to Visual Localization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 4178–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dataset | Metric | Threshold | 100% th. | 90% th. | 80% th. | 70% th. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TheGardenParty | Position (m) | Min | 0.072 | 0.074 | 0.069 | 0.098 |
| Median | 0.573 | 0.567 | 0.552 | 0.523 | ||
| Max | 5.559 | 5.288 | 4.317 | 4.192 | ||
| Mean | 0.776 | 0.738 | 0.712 | 0.682 | ||
| Orientation () | Min | 0.0204 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.015 | |
| Median | 2.672 | 2.544 | 2.512 | 2.299 | ||
| Max | 72.738 | 54.508 | 49.384 | 48.397 | ||
| Mean | 4.880 | 3.783 | 3.358 | 3.126 | ||
| ETRI | Position (m) | Min | 0.023 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.031 |
| Median | 0.289 | 0.298 | 0.300 | 0.298 | ||
| Max | 1.610 | 1.613 | 1.287 | 1.490 | ||
| Mean | 0.324 | 0.326 | 0.327 | 0.327 | ||
| Orientation () | Min | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.010 | |
| Median | 1.127 | 1.052 | 0.978 | 0.902 | ||
| Max | 26.224 | 16.182 | 15.569 | 11.024 | ||
| Mean | 1.990 | 1.661 | 1.527 | 1.409 | ||
| SusungHotel | Position (m) | Min | 0.022 | 0.028 | 0.031 | 0.019 |
| Median | 0.659 | 0.561 | 0.477 | 0.424 | ||
| Max | 66.392 | 66.279 | 59.829 | 59.753 | ||
| Mean | 4.262 | 2.788 | 2.211 | 1.575 | ||
| Orientation () | Min | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.008 | |
| Median | 2.732 | 2.466 | 2.168 | 2.020 | ||
| Max | 179.385 | 174.738 | 173.323 | 127.828 | ||
| Mean | 13.711 | 9.008 | 5.861 | 4.329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Won, H.-M.; Lee, J.; Oh, J. Localization Meets Uncertainty: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Modal Localization. Technologies 2025, 13, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090386
Won H-M, Lee J, Oh J. Localization Meets Uncertainty: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Modal Localization. Technologies. 2025; 13(9):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090386
Chicago/Turabian StyleWon, Hye-Min, Jieun Lee, and Jiyong Oh. 2025. "Localization Meets Uncertainty: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Modal Localization" Technologies 13, no. 9: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090386
APA StyleWon, H.-M., Lee, J., & Oh, J. (2025). Localization Meets Uncertainty: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Modal Localization. Technologies, 13(9), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090386






