Abstract
Measurement of grasp configurations (position, orientation, and width) in unstructured environments is critical for robotic systems. Accurate and robust prediction relies on rich multi-scale object representations; however, detail loss and fusion conflicts in multi-scale processing often cause measurement errors, particularly for complex objects. This study proposes a multi-scale and cross-layer fusion grasp detection network (MCFG-Net) based on a skip-connected encoder–decoder architecture. The sampling module in the encoder–decoder is optimized, and the multi-scale fusion strategy is improved, enabling pixel-level grasp rectangles to be generated in real time. A multi-scale spatial feature enhancement module (MSFEM) addresses spatial detail loss in traditional feature pyramids and preserves spatial consistency by capturing contextual information within the same scale. In addition, a cascaded fusion attention module (CFAM) is designed to assist skip connections and mitigate redundant information and semantic mismatch during feature fusion. Experimental results show that MCFG-Net achieves grasp detection accuracies of 99.62% ± 0.11% on the Cornell dataset and 94.46% ± 0.22% on the Jacquard dataset. Real-world tests on an AUBO i5 robot yield success rates of 98.5% for single-target and 95% for multi-target grasping tasks, demonstrating practical applicability in unstructured environments.
1. Introduction
Due to the rapid advancement of robotics technology, robotic grasp detection is widely applied in both industrial and service domains. Grasp detection is one of the key tasks in robot operation, which identifies the optimal grasping pose from visual data to ensure that the robot can safely and stably grasp objects [1,2,3,4]. Traditional grasp detection methods rely on stable external environments and known 3D object models, and their high computational costs cannot meet the requirements of modern robotic systems for real-time performance and generalization capability [5].
Grasp detection based on deep learning has progressed from early two-stage CNNs to residual end-to-end networks that directly regress full 5-DoF grasp poses [6,7,8,9]. These models leverage large-scale RGB-D data to learn hierarchical visual features in place of hand-crafted descriptors, markedly improving speed and accuracy; however, their performance in cluttered scenes remains tied to how well multi-scale information is represented and fused. In parallel, attention mechanisms have been adopted to refine spatial focus and cross-modal fusion, evolving from self-attention filters to selective-kernel and cross-modal frameworks [10,11,12]. By dynamically highlighting graspable regions across multiple resolutions, attention-augmented networks suppress background noise and enhance robustness, yet they, too, are limited by sub-optimal multi-scale feature extraction and the risk of redundant or misaligned information during feature fusion.
This article proposes a multi-scale and cross-layer fusion grasp detection network (MCFG-Net) to improve the ability of the robot to stably grasp complex objects in unstructured environments. MCFG-Net employs an enhanced encoder–decoder architecture, utilizing a multi-scale spatial feature enhancement module (MSFEM) at the bottleneck layer to improve global structural comprehension for complex objects. Unlike traditional multi-scale methods, such as dilated convolutions and Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP), which rely on changing the dilation rate across multiple convolutional layers, MSFEM uses an intra-channel partitioning strategy. It simultaneously captures different spatial scales within a single feature map, alleviating semantic gaps and spatial misalignment. In encoder–decoder architectures, skip connections are used to fuse low-level features with high-level semantics to enhance spatial detail. However, direct fusion often leads to redundant information interference and semantic mismatch. We use a cascaded fusion attention module (CFAM) to assist in skip connections and avoid feature fusion conflict.
The main contributions of this work are summarized below:
- (1)
- This study proposes a real-time encoder–decoder grasp detection framework that fuses multi-scale and cross-layer features to produce pixel-level grasp rectangles from RGB-D inputs, ensuring high efficiency (27 FPS) and fine spatial detail preservation.
- (2)
- A multi-scale spatial feature enhancement module (MSFEM) is introduced at the bottleneck to alleviate detail loss in traditional pyramids by using channel partitioning and parallel convolutions with diverse receptive fields.
- (3)
- A cascaded fusion attention module (CFAM) is designed to resolve feature fusion conflicts through a dual-path spatial-channel attention scheme, enhancing semantic alignment and grasp region perception.
- (4)
- Extensive experiments on the Cornell and Jacquard datasets, along with real-world deployment on an AUBO i5 robot, demonstrate state-of-the-art accuracy and robust performance in unstructured environments.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 reviews related work on multi-scale learning and encoder–decoder architectures. Section 3 presents the problem formulation and the architecture of MCFG-Net. Section 4 presents the experimental setup, including datasets, evaluation metrics, implementation details, and results on both benchmark datasets and real-world scenes. Section 5 provides an in-depth discussion through ablation studies and failure case analysis. Section 6 concludes the paper and outlines future research directions.
2. Related Works
2.1. Multi-Scale Feature Learning
It is crucial for grasp detection to effectively extract and integrate multi-scale features for complex objects in unstructured environments. Yu et al. [13] proposed using extended convolutional kernels to capture multi-scale contextual information without increasing the number of parameters. Chen et al. [14] further developed the DeepLab model based on this, introducing the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) structure to fuse features with different expansion rates. In order to further enhance the global scene understanding ability of the model, Zhao et al. [15] proposed the Pyramid Scene Resolution Network (PSPNet) that uses a multi-scale pooling structure to capture and fuse global and local information at different scales in a top-down manner. At the same time, real-time performance and computational efficiency have gradually become the focus of multi-scale feature learning. Li et al. [16] designed a deep feature aggregation network (DFANet) with a lightweight cascade sub-network structure. It can perform real-time fusion of multi-scale features. Pang et al. [17] further proposed the Multi-Scale Interactive Network (MINet) that introduces an aggregation interaction module to enhance the mutual communication between features of different scales. In addition, Kumra and Kanan [18] utilized ResNet-based multi-scale feature learning methods to improve the accuracy of deep learning models for predicting the grasping poses of objects at different scales. These studies collectively highlight the importance and diversity of architectural strategies in achieving robust and efficient multi-scale feature integration. Despite significant progress in multi-scale feature learning, it remains a critical challenge to achieve semantically aligned and efficient feature fusion across scales.
2.2. Encoder–Decoder Architectures
The encoder extracts multi-scale grasp-related information (shape, edges, and depth) from the input image. The decoder generates precise grasp detection results by progressively restoring the spatial information compressed by the encoder. Therefore, the encoder–decoder architecture has become an effective design choice for deep learning-based grasp detection. Mahler et al. [19] developed a convolutional network GQ-CNN with an encoder–decoder architecture. This network effectively extracts grasp-related depth information while simultaneously predicting grasping success probability. Zhou et al. [20] proposed FC-GDN, a fully convolutional network that performs multi-scale grasp prediction by fusing spatially-distributed anchor boxes of different sizes and orientations across feature maps. Kumra et al. [9] proposed the Generative Residual Convolutional Neural Network (GR-ConvNet). The network employs deep residual connections to strengthen encoder–decoder information flow, significantly enhancing its ability to detect grasp poses for complex objects. In addition, Xiong et al. [21] proposed HMT-Grasp, which extracts local and global features through parallel convolution and Transformer modules, effectively improving the performance of grasping detection in complex environments. The fusion of features at different levels can effectively improve the accuracy of grasping detection, but existing methods are still insufficient in addressing the problems of redundant information interference and semantic mismatch.
3. Problem Formulation and MCFG-Net Architecture
3.1. Problem Statement
A universal grasp representation model is essential for handling unknown objects in 2D image coordinate systems [22]. To be applicable to MCFG-Net, we redesigned the directional rectangle grasping representation method proposed by Jiang et al. [23]. For an N-channel image with height h and width w, a grasp configuration in the image frame is defined as
Here, denotes the pixel grasp center in the image coordinate system. represents the rotation angle of the gripper endpoint relative to the horizontal axis of the image, ranging within . To avoid the challenges of directly learning the grasp angle, it is encoded as the two components of a unit vector, and . The final grasp angle is calculated as . represents the opening of gripper width in the image coordinate system. represents the confidence score ranging between 0 and 1. A confidence value close to 1 indicates a high grasp success rate.
In practical environments, robots require 3D spatial grasp pose information to successfully execute grasping tasks. We define the robot grasp pose in the 3D robot coordinate system as
where denotes the center position of the gripper endpoint in the robot coordinate system. represents the gripper rotation angle around the Z-axis, and indicates the required gripper width. corresponds to in (1), representing grasp confidence.
The transformation from the image coordinate system to the robotic 3D coordinate system is
The coordinates of in the camera coordinate system are . denotes the perspective projection transformation matrix from the camera coordinate system to the image coordinate system, typically computed using the principle of similar triangles:
The matrix form is:
The transformation matrix from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system is denoted as and can be decomposed into a rotation matrix and a translation vector :
The objective of robotic grasping is to identify the optimal grasp configuration with the highest confidence score from the detected candidate configurations, which can be expressed as
The optimal grasp is obtained by substituting into (3).
3.2. Model Architecture
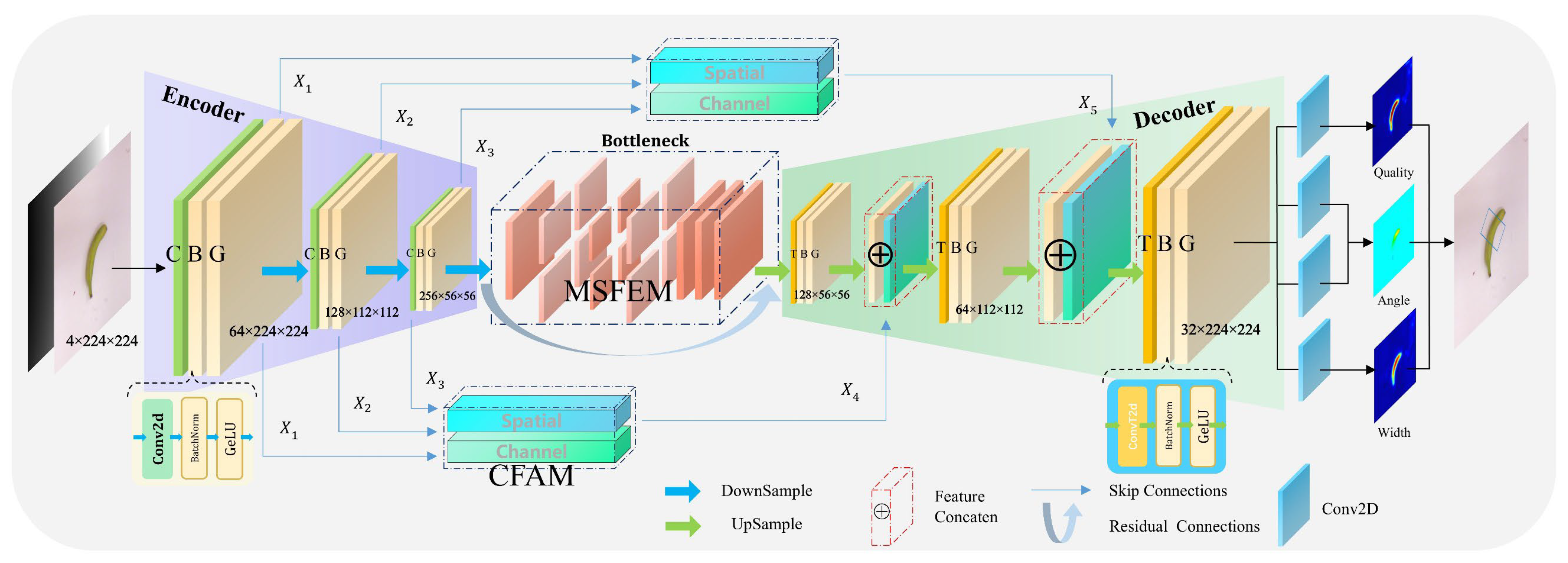
The MCFG-Net has an encoder–decoder structure, as shown in Figure 1. This network can be trained on single-modal data (RGB or depth) or multimodal data (RGB-D). The encoding stage includes three downsampling modules, each consisting of a specific convolutional layer, a Batch Normalization layer, and a Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GeLU), abbreviated as CBG. To prevent the “dead-neuron” issue with ReLU and promote smoother gradient flow, the network employs GeLU [24] in place of the conventional ReLU activation. GeLU has been shown to yield modest yet consistent performance gains across a variety of tasks. The formula is
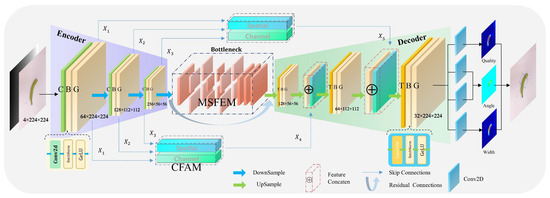
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of the proposed multi-scale cross-layer fusion grasp-detection network. It adopts an encoder–decoder structure with a multi-scale feature enhancement module (MSFEM) and a cascade fusion attention module (CFAM). The network supports RGB-D inputs and outputs pixel-level grasp quality, angle, and width maps for robust grasp prediction. CBG: Convolution + BatchNorm + GeLU module used for downsampling. TBG: Transposed Convolution + BatchNorm + GeLU module used for upsampling.
The first CBG layer utilizes a 9 × 9 convolutional kernel to maintain spatial dimensions and increase the number of channels. The second and third CBG layers perform downsampling through convolutional operations with a stride of 2, expanding the number of feature map channels and reducing their spatial dimensions. The obtained feature maps , , and (64 × 224 × 224, 128 × 112 × 112, and 256 × 56 × 56, respectively) are fed into subsequent processing.
At the end of the encoding stage, the 56 × 56 feature map passes through a bottleneck layer composed of MSFEM and residual connections. This bottleneck layer captures and integrates multi-scale contextual features while preserving structural consistency. To effectively interpret the feature maps, it is necessary to upsample and restore them to the original resolution. The convolutional layer in the downsampling module is replaced by a transposed convolution, leaving the remaining components unchanged; the resulting upsampling unit is termed TBG. After three successive upsampling stages, the feature map dimensions match those produced during downsampling, with channel counts of 128, 64, and 32, respectively. Fusing feature maps from different layers is known to improve results for the same task. The features , , and are fed into the CFAM. This module then outputs and and connects these two features to the first two layers of the decoder, respectively. This cascading operation enables the model to simultaneously perceive local geometry and global semantics, making it more suitable for complex objects. After the upsampling operation, the task head, composed of four convolutional layers, processes the output features. The output of MCFG-Net consists of three parts: confidence, angle, and width. MCFG-Net finds the pixel with the highest confidence in the confidence feature map and can extract matching angles and widths from the angle and width feature maps. Finally, these components are combined into the optimal grasp configuration for grasping complex objects.
3.3. Multi-Scale Spatial Feature Enhancement Module
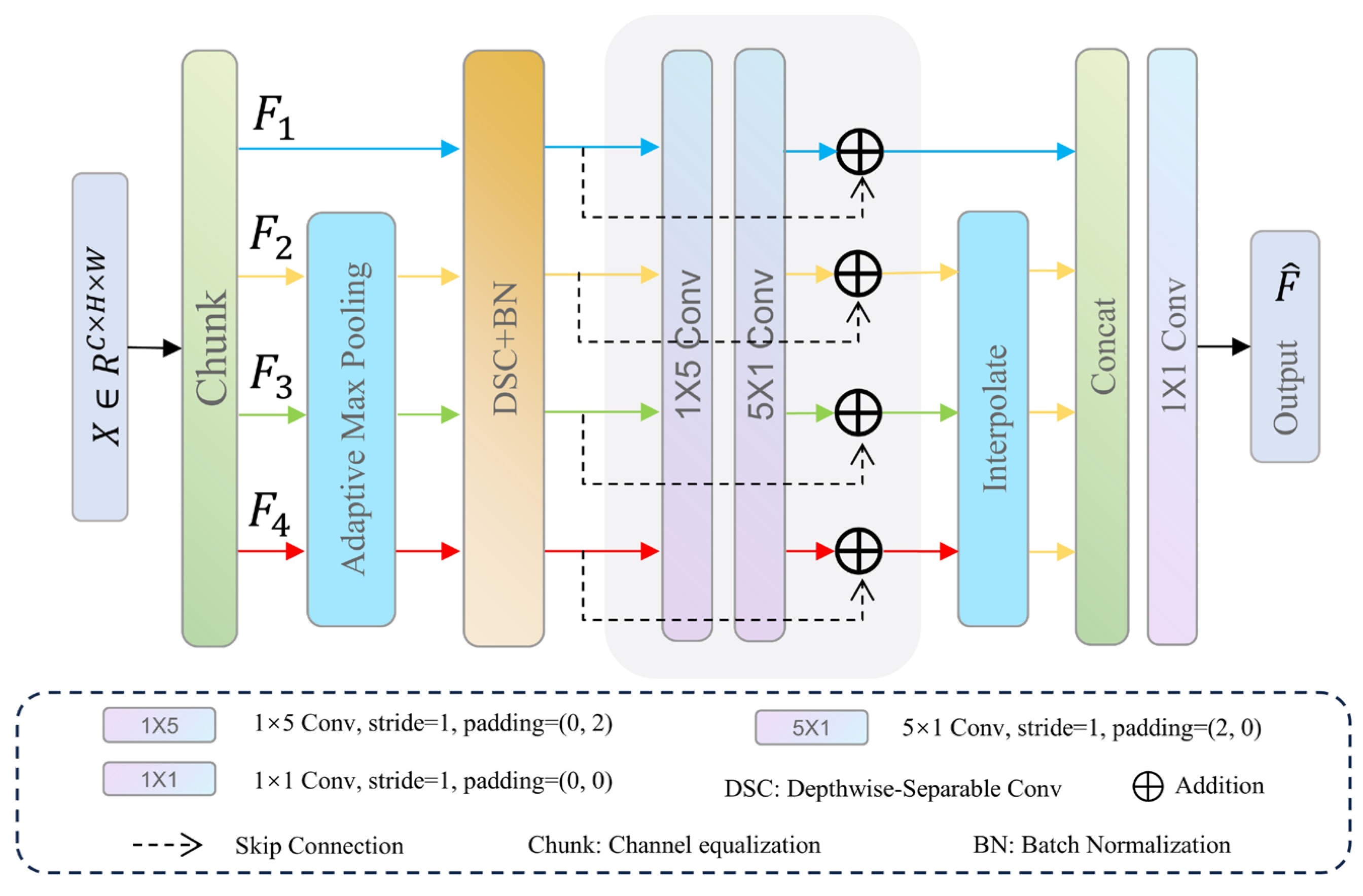
Conventional feature pyramid methods rely on multi-layer feature fusion, which often suffers from spatial misalignment due to resolution disparities and semantic gaps between different feature levels. In contrast, the multi-scale spatial feature enhancement module (MSFEM) achieves efficient and unified same-layer multi-scale feature modeling through intra-layer channel partitioning and direction-aware convolution. As shown in Figure 2, we divide the input feature into four groups along the channel dimension, denoted as , where . The input channel is uniformly split into four equal parts, so each group has channels. Specifically, consists of the first channels, consists of the next channels, and so on. This partitioning enables each to process its corresponding features independently while ensuring a balanced computational load. , , and are downsampled using adaptive max pooling. Their spatial resolutions are reduced to 1/2, 1/4, and 1/8 of the original, respectively. At this time, each contains different levels of feature map information. In order to improve the stability of feature maps and optimize computational efficiency, depthwise separable convolution and batch normalization are applied independently to each . Asymmetric convolutions (1 × 5 and 5 × 1) are applied to to capture spatially anisotropic features. Skip connections are used to enhance gradient flow stability. Interpolate the size of , and back to their original size (H × W) to ensure that the output feature map matches the input size. All features are concatenated along the channel dimension, and the concatenated tensor contains feature information from all levels. Finally, the concatenated tensor is processed by a convolutional layer to adjust the number of channels to 256 and is then passed to the decoder.
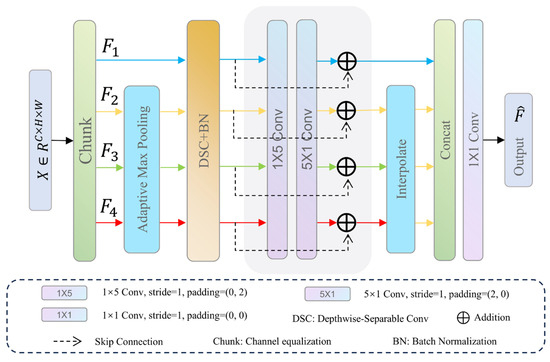
Figure 2.
Architecture of the multi-scale spatial feature enhancement module. It partitions the input feature into four channel groups, applies multi-scale pooling and direction-aware asymmetric convolutions to each, and then aligns and fuses them to enhance spatial representation within a single layer.
3.4. Cascade Fusion Attention Module
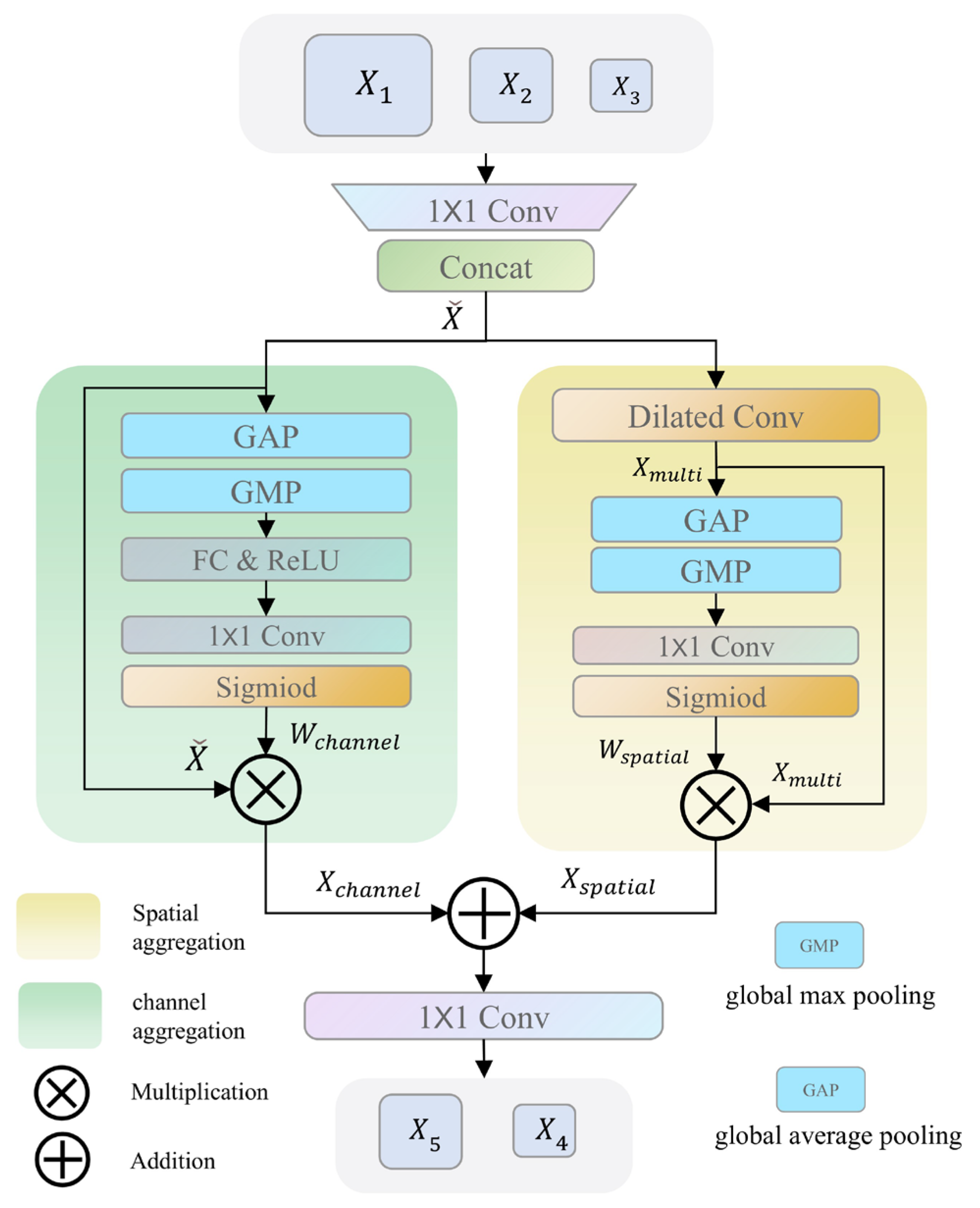
Spatial attention and channel attention mechanisms can eliminate background noise and suppress redundant information during the fusion of features at different levels [25,26]. Therefore, we design the cascade fusion attention module (CFAM) to guide the fusion of multi-scale features. As shown in Figure 3, CFAM takes multi-scale features , , and from the encoder, reduces their dimensions using convolutions, and concatenates them to form the aggregated feature . This reduces the computational load of subsequent operations. CFAM employs a “spatial-channel” dual-path aggregation structure.
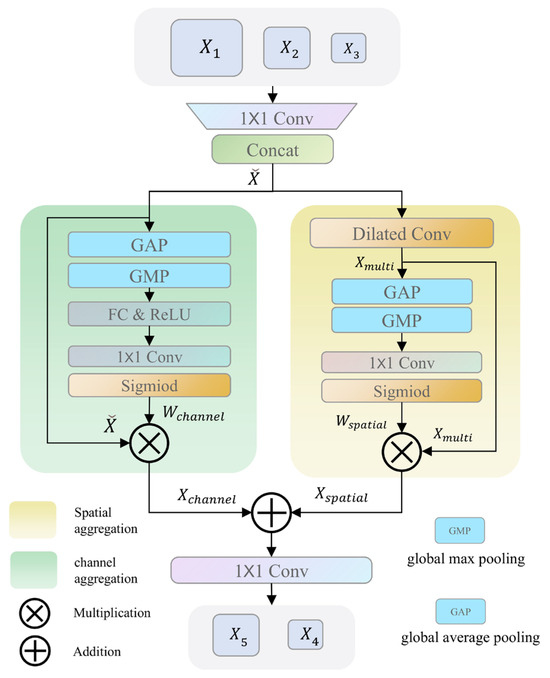
Figure 3.
Architecture of the cascaded fusion attention module. It concatenates reduced encoder features, applies parallel spatial attention with dilated convolutions and channel attention with global pooling, and then fuses the two reweighted results and outputs them for skip connection.
The purpose of the spatial feature aggregation branch is to focus the model on important spatial locations in the input feature maps, thereby enhancing its perception of key regions. Specifically, it utilizes dilated convolutions with different dilation rates (d = 1, 2, 3) to capture multi-scale features .
Here, represents dilated convolution. The use of multiple fixed dilation rates enables efficient multi-scale feature extraction while maintaining computational efficiency. In comparison with dynamic or learnable dilation rates [27,28], fixed dilation rates avoid additional complexity, training instability, and higher computational cost, providing a more stable and faster converging model, especially in resource-constrained environments. The feature maps containing spatial context information are obtained through average pooling and max pooling operations. These pooled features are further processed by a convolution followed by a sigmoid activation to generate the spatial attention map . Finally, and are multiplied to generate the enhanced spatial feature The process is shown in the following equation, where “⊗” stands for multiplication and “⊕” for addition:
The purpose of the channel feature aggregation branch is to enable the network to selectively focus on important channels in the input feature map. Specifically, it applies the same average and max pooling operations to but focuses on aggregating information along the channel dimension. The two pooled features are fed into a shared fully connected layer to learn the relative importance of each channel. Similarly, through convolution and function operation, a channel attention map similar to is obtained. Finally, and are multiplied to generate the enhanced channel feature The process is shown in the following equation:
The outputs of the channel and spatial feature branches are added together, and a convolution layer is used to adjust the channel dimensionality so that it can be concatenated with the corresponding layer in the decoder. The process is shown in the following equation:
Two features, and , are obtained with the CFAM and passed through skip connections to the first two layers of the decoder.
3.5. Loss Function
In this study, the robotic grasp detection task is formulated as a multi-task regression problem, where the model is required to predict continuous-valued grasp parameters, including position, angle, and width. The model is trained by minimizing the error between the predicted grasp configuration and the ground truth grasp label . The overall training objective is defined by a regression loss function that evaluates the average prediction error across the training samples. Specifically, the total loss is computed as:
where denotes the number of training samples in a batch, and represents the loss contribution of a single prediction, calculated using a smooth L1 loss function defined as:
This loss function combines the advantages of L2 loss for small errors and L1 loss for large deviations. It ensures numerical stability and prevents the training process from being overly influenced by outliers, which is particularly important when learning to regress grasp parameters across diverse and complex objects.
4. Dataset and Robot Grasping Experiment
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
This paper evaluates the performance of the proposed method on two widely used benchmark datasets: the Cornell grasping dataset and the Jacquard dataset [23,29]. The Cornell dataset includes 1035 RGB-D images of 240 different objects, providing 5110 positive and 2909 negative grasp annotations. The dataset is split into the training dataset and the testing dataset in a 9:1 ratio, and the evaluation follows the image-wise splitting (IW) and object-wise splitting (OW) principles:
- (1)
- IW: To evaluate the generalization ability of a network model when objects exhibit varied poses, thereby providing insight into the model’s adaptability to changes in object orientation.
- (2)
- OW: To evaluate the generalization ability of a network model when encountering entirely novel objects, thereby assessing its capacity to grasp previously unseen items in real-world applications.
The Jacquard dataset is generated in simulated environments and contains 11,619 scenes, 54,485 objects, and approximately 1.1 million positive grasp labels. All images are resized to 224 × 224 pixels, matching the model input dimensions.
Grasp evaluation is based on the rectangular metric, where a prediction is considered correct if the intersection over union (IoU) with the ground truth exceeds 0.25 and the angular deviation is less than 30°. The rectangular grasp metric is defined as follows:
4.2. Implementation Details
MCFG-Net is developed using the PyTorch framework. For the Cornell dataset, data augmentation techniques such as random cropping, scaling, and rotation are applied to improve the robustness and generalization ability of the model under limited data conditions. In contrast, no additional augmentation is performed on the Jacquard dataset due to its sufficient size and inherent diversity. All experiments are conducted on a workstation equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU (24 GB) and an Intel Core i9-13900K CPU, running Ubuntu 20.04 with CUDA 12.1. PyTorch 2.2.0 is used as the deep learning framework, and Python 3.10 serves as the programming language. The system uses NVIDIA driver version 535 to ensure efficient GPU performance.
The model is trained for 100 epochs on the Cornell dataset and 50 epochs on the Jacquard dataset, using a batch size of 16. The optimizer uses Adam with an initial learning rate set to 1 × 10−3, combined with the LambdaLR scheduler to implement a dynamic learning rate strategy. For the first 5 epochs, a linear warm-up strategy is applied, gradually increasing the initial learning rate from 0.2 times the base_lr to the base_lr value. Afterward, the learning rate enters an exponential decay phase, decreasing according to . This strategy helps improve stability and convergence in the later stages of training.
To assess result robustness, five additional independent runs were executed with identical training and evaluation settings. All results are reported as the mean ± standard deviation with 95% confidence intervals.
4.3. Results on Cornell
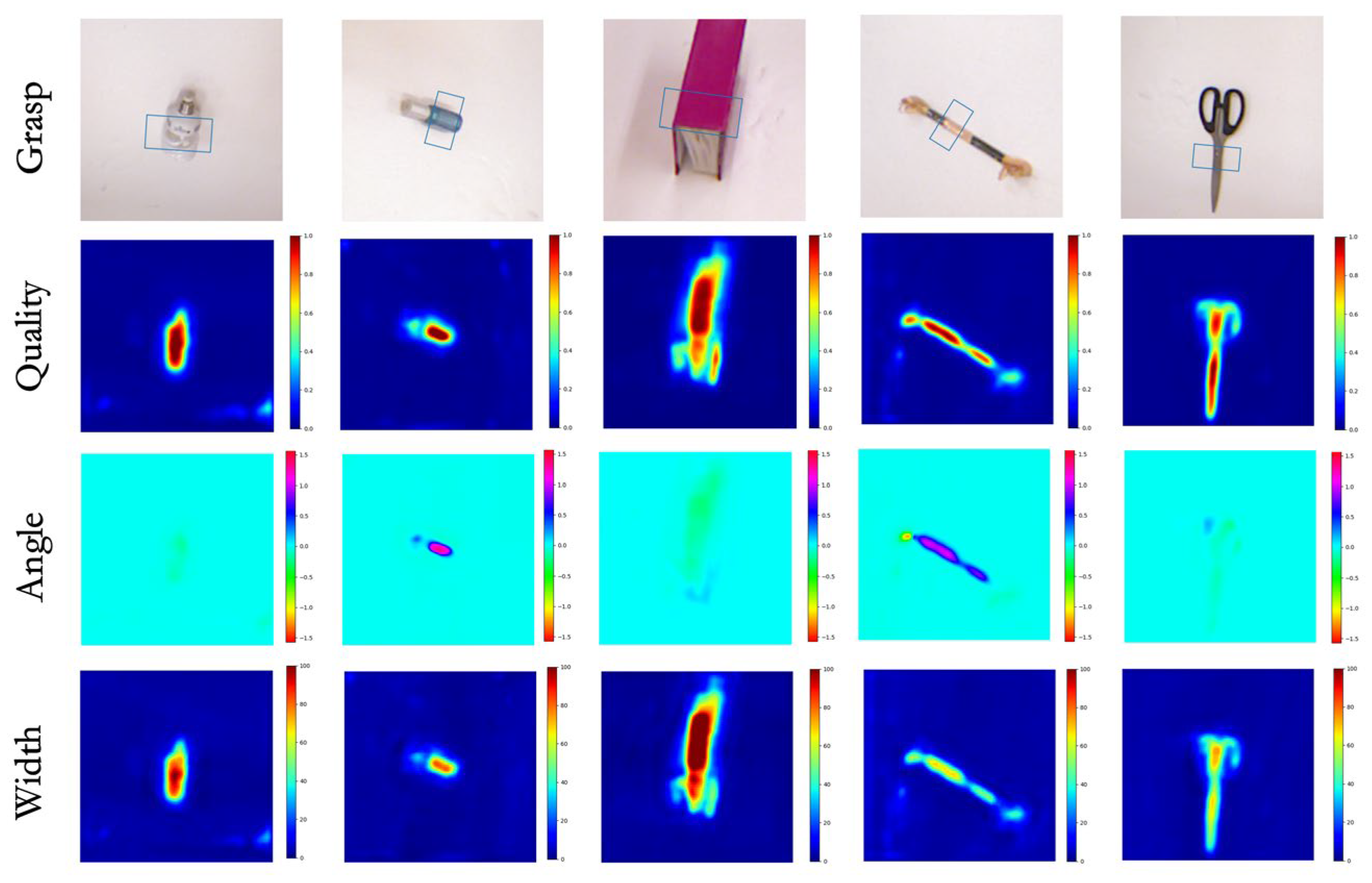
The performance of MCFG-Net was evaluated using two primary metrics: grasp detection accuracy and inference speed, as summarized in Table 1. On the Cornell dataset, MCFG-Net achieves 99.62% ± 0.11% (95% CI: 99.48–99.76%) in image-wise (IW) mode and 98.87% ± 0.15% (95% CI: 98.68–99.06%) in object-wise (OW) mode. In terms of efficiency, MCFG-Net achieves an inference speed of 27 milliseconds per image, indicating that it is capable of meeting the real-time processing requirements necessary for practical robotic applications. To further illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed model, Figure 4 presents qualitative results of grasp detection on various objects from the Cornell dataset. As shown in the examples, MCFG-Net is capable of filtering out background clutter and irrelevant features, allowing it to focus on the most suitable grasp regions with high precision. For instance, when presented with a light bulb whose appearance closely resembles that of the surrounding background, the network successfully localizes the grasp point, demonstrating its robustness in visually challenging scenarios.

Table 1.
The results of different methods on the Cornell dataset.
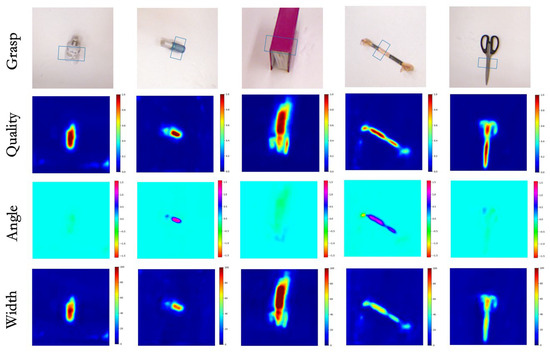
Figure 4.
Detection results on the Cornell dataset.
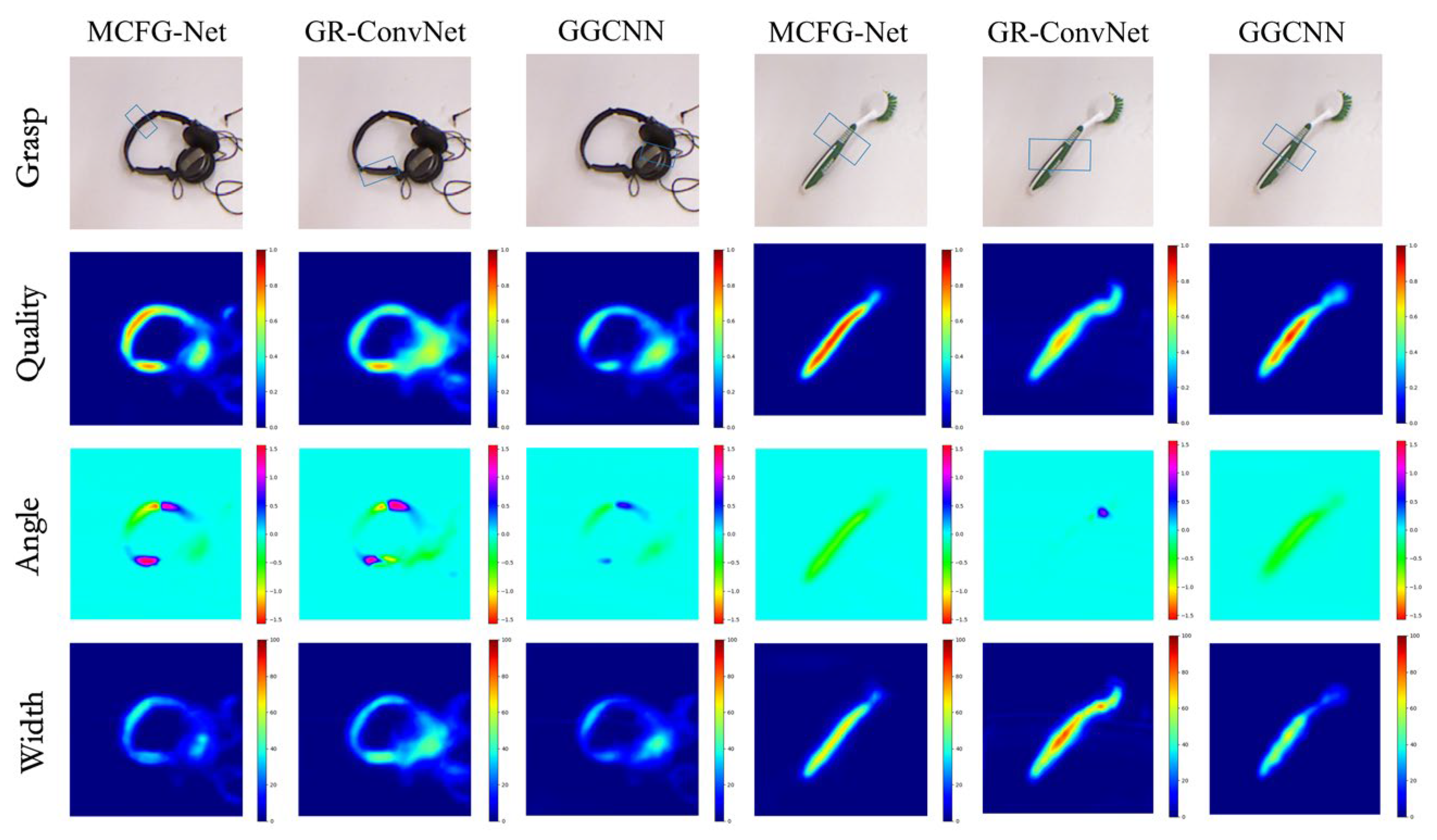
As illustrated in Figure 5, we conducted comparative visualization experiments by randomly selecting representative samples from the Cornell dataset. To ensure a fair comparison, all baseline networks—GR-ConvNet and GGCNN—were retrained under the same experimental conditions as MCFG-Net. Although all models generate reasonable grasp predictions, notable differences appeared in the quality and consistency of their outputs. GR-ConvNet performs well in terms of grasp location and width, but its angle predictions are unstable. This is mainly due to its local convolutional structure, which limits its ability to capture geometric variations of objects across scales. For the headphone example, GGCNN fails to identify reliable high-confidence grasp regions, reflecting its weakness in integrating multi-level features. By contrast, MCFG-Net produces clearer grasp quality maps, more accurate angle predictions, and consistent width estimations. Its advantage is especially evident for objects with complex shapes or low contrast backgrounds. This is attributed to its multi-scale and cross-layer fusion strategy, which effectively combines local and global features, improving robustness in unstructured environments.

Figure 5.
Comparative experiment of MCFG-Net with GR-ConvNet and GGCNN on the Cornell dataset.
4.4. Results on Jacquard
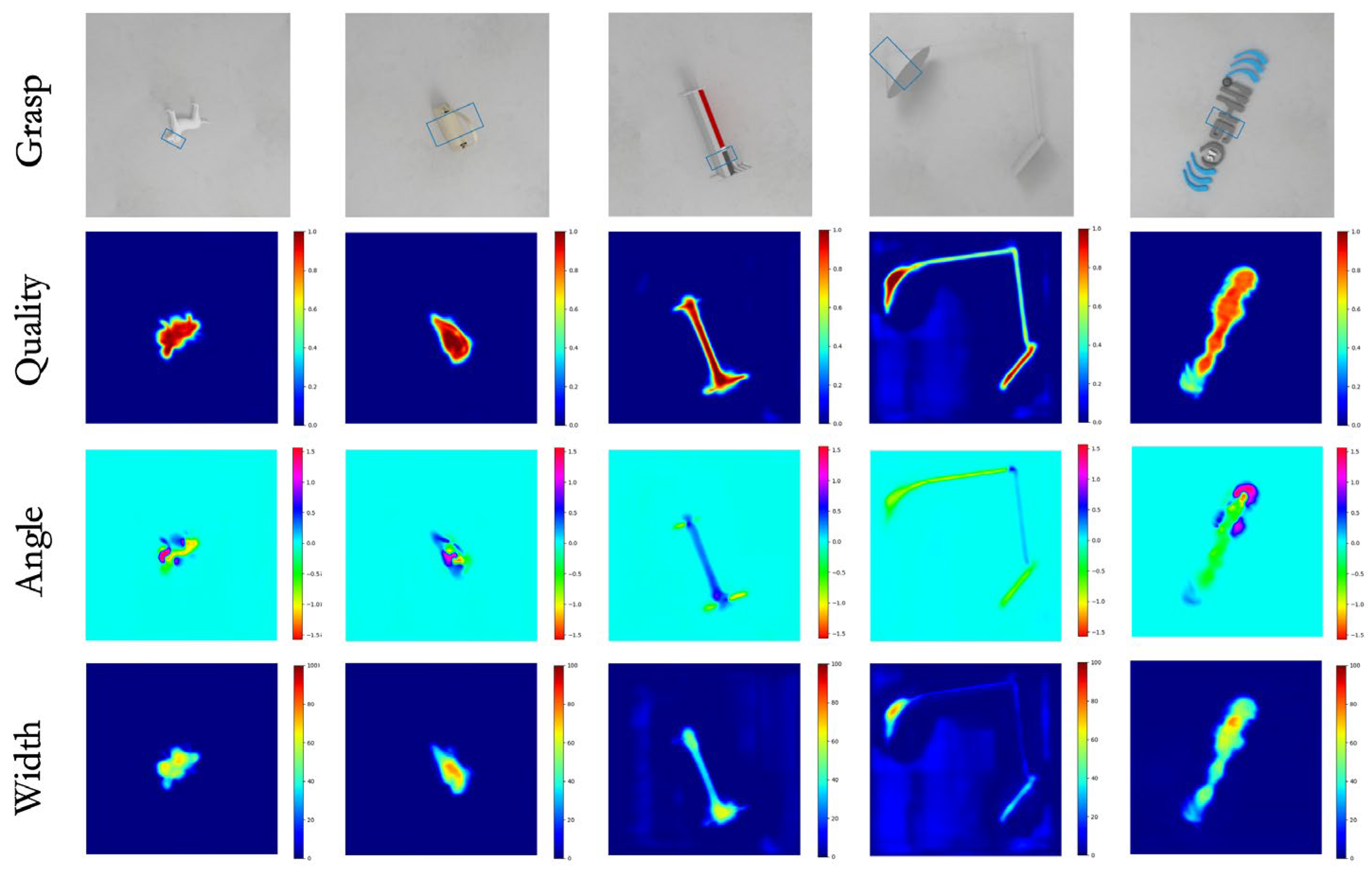
Table 2 presents the grasp detection accuracy of MCFG-Net in comparison with several representative state-of-the-art methods on the Jacquard dataset. Evaluation is performed using three input modalities: depth (D) yields 94.58% ± 0.18%, RGB yields 94.46% ± 0.22%, and RGB-D fusion achieves 95.48% ± 0.13%. The RGB-D modality significantly outperforms the RGB-only setting. Compared with the representative TF-Grasp method (94.6%), it shows an improvement of approximately 0.9 percentage points. These findings confirm that the proposed multi-modal fusion strategy delivers consistent, statistically significant gains in grasp-detection performance. Additional qualitative tests on previously unseen objects from the Jacquard dataset (Figure 6) further validate generalization: graspable regions were accurately identified on both small, fine-detail items (e.g., a toy head) and larger, complex shapes (e.g., a desk lamp).

Table 2.
The results of different methods on the Jacquard dataset.
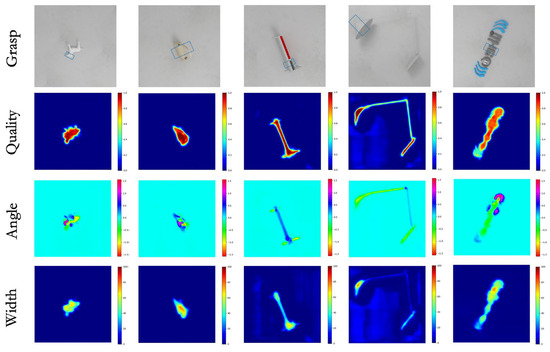
Figure 6.
Detection results on the Jacquard dataset.
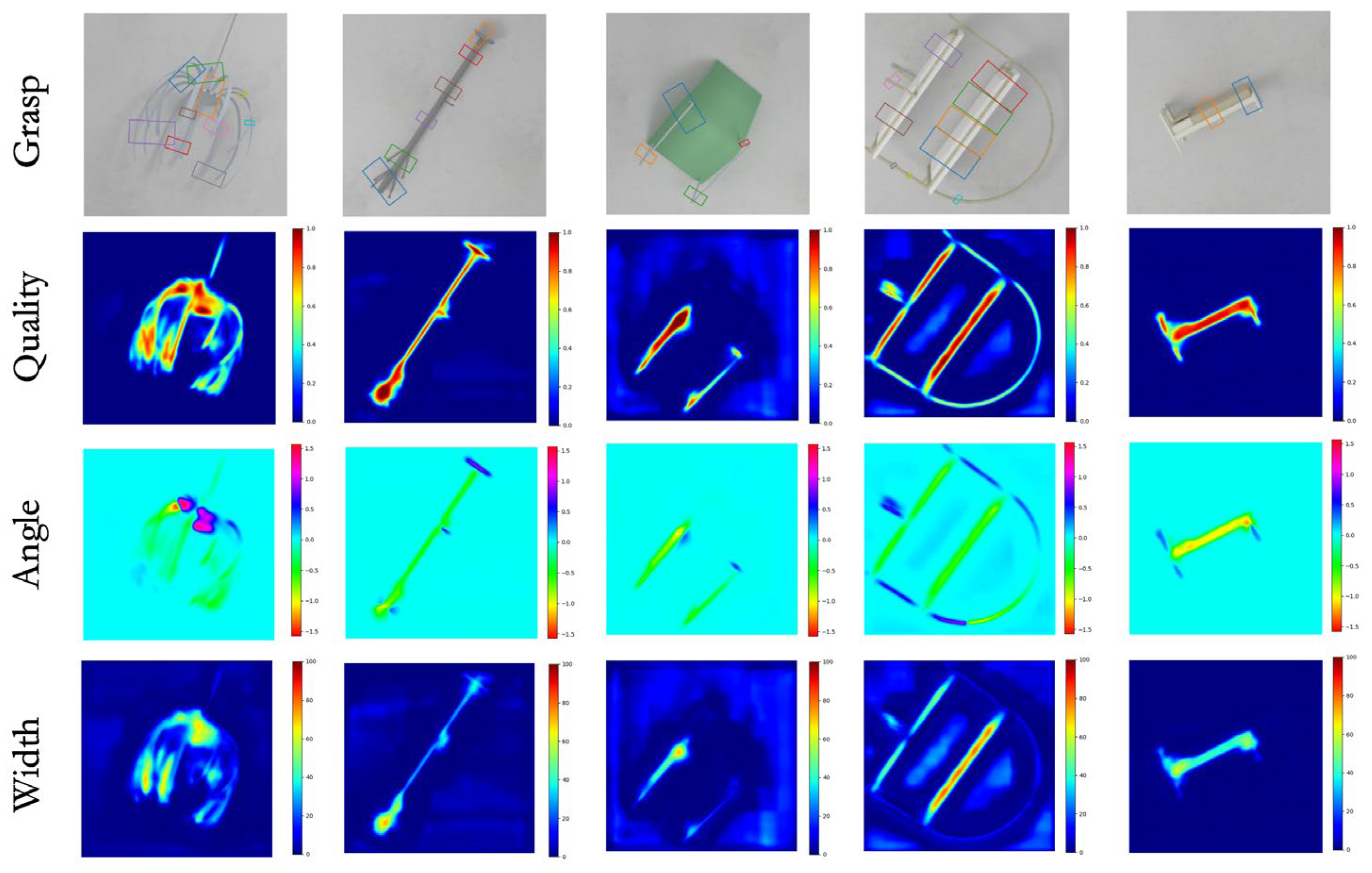
Considering the complexity of real-world environments, including variations in object shapes, poses, and material properties, we propose a multi-pose grasping strategy designed to generate diverse and feasible grasp configurations for a single object. As illustrated in Figure 7, our method is capable of producing multiple high-quality grasp predictions for each object instance. These grasp candidates vary in position, orientation, and width, which allows the robotic system to flexibly adapt to different manipulation constraints and environmental conditions. This capability is particularly beneficial when the primary grasp pose is occluded or physically infeasible, thereby enhancing the robustness and reliability of the grasping system in practical applications.
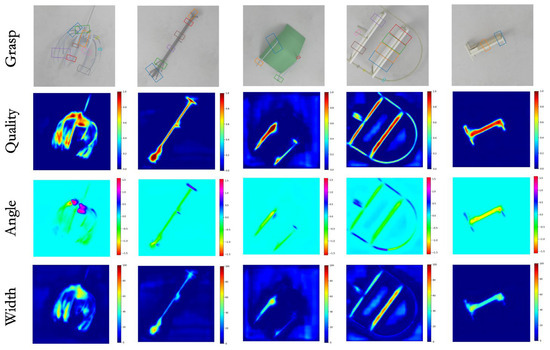
Figure 7.
Single-object multiple grasps.
4.5. Real-Scene Evaluation
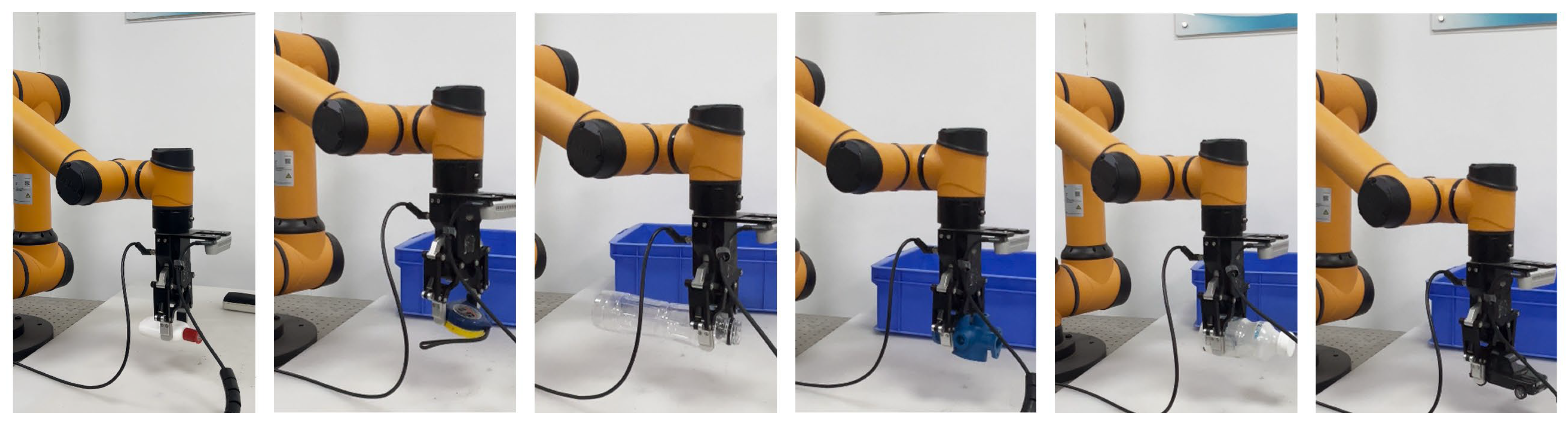
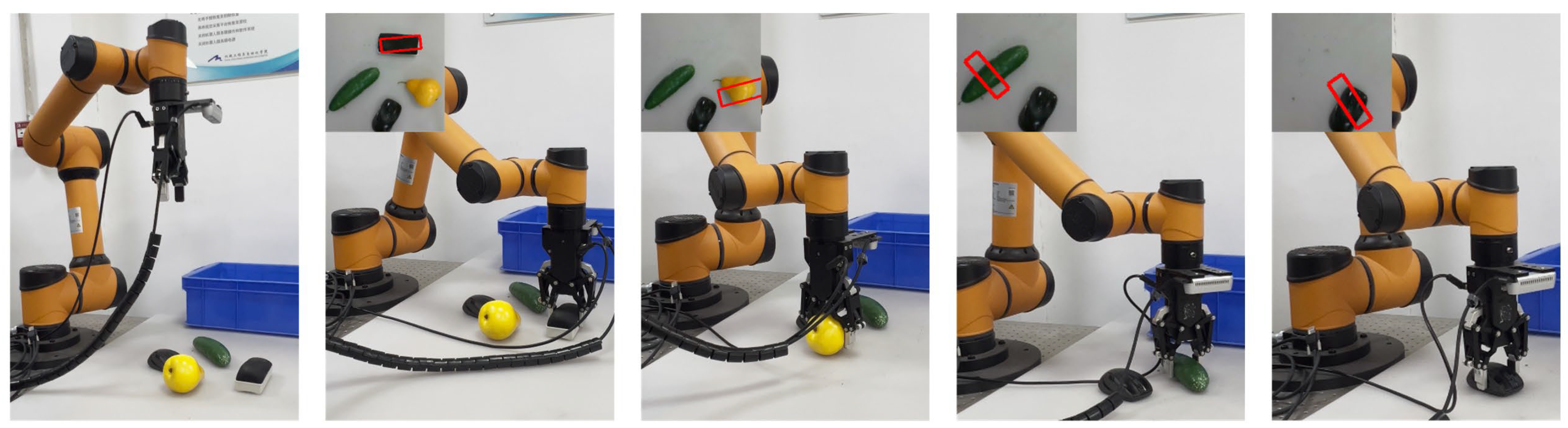
To comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness and practical applicability of the proposed method in real-world scenarios, we conducted physical grasping experiments under both single-object and multi-object settings. The experimental setup was built upon an AUBO i5 robotic arm equipped with a DH-AG-95 parallel gripper, and a RealSense D435i depth camera was used to capture real-time RGB-D images of the scene. The camera intrinsic calibration yields a maximum reprojection error of 0.39 pixels, which is well within the acceptable tolerance. The DH-AG95 gripper provides a maximum gripping force of approximately 160 N, a positioning accuracy of about 0.1 mm, and completes a full open/close cycle in 0.7 s. End-to-end execution latency—from command issuance to action completion—averages approximately 700 ms in our experiments.
The experimental procedure is structured as follows: First, RGB-D images of objects randomly placed on the operating platform are acquired by the RealSense camera. These images are fed into the trained MCFG-Net model, which outputs the grasp pose parameters—including position, orientation, and width—in pixel coordinates. The predicted grasp poses are then transformed from the image coordinate system to the robot’s world coordinate system using standard camera-to-robot calibration techniques. Finally, the robotic arm executes the grasp at the optimal predicted pose. The evaluation is conducted across two types of scenes: single-object scenes (Figure 8) and multi-object scenes (Figure 9). In the multi-object setting, the system is tested for its ability to perform sequential grasps until all objects are successfully removed. To test generalization ability, all grasping experiments are performed using objects that are not present in the training dataset. These include challenging items such as complex metal components with reflective surfaces and transparent objects like mineral water bottles, which introduce significant difficulties in both detection and grasp execution due to poor visual contrast and ambiguous boundaries.
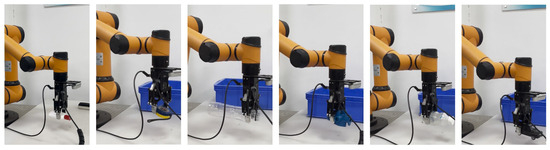
Figure 8.
Robot grasping experiments in single-object scenes.

Figure 9.
Robot grasping experiments in multi-object scenes. The red box represents the real-time detected grasping pose.
Quantitative results are summarized in Table 3. In the single-object setting, each object is grasped 20 times from randomized initial poses, resulting in a total of 200 grasp attempts. The system achieves a high grasp success rate of 98.5%, demonstrating its precision and stability under isolated conditions. In the multi-object setting, each test scene contains four randomly placed targets, and a total of 100 grasp attempts are carried out. The system achieves a success rate of 95%, indicating strong robustness in cluttered environments with occlusion and object overlap.

Table 3.
Experimental results in different scenarios.
5. Discussion
5.1. Ablation Study
To further evaluate the effectiveness of each proposed component, we conducted ablation experiments on the Cornell datasets. All experiments were carried out under identical training and implementation settings to ensure fair comparison. Four model variants were constructed: MCFG-Net-I (baseline without MSFEM and CFAM), MCFG-Net-II (with MSFEM only), MCFG-Net-III (with CFAM only), and the complete MCFG-Net (with both modules). All variants retain the same encoder–decoder backbone to isolate the effects of the two modules.
As shown in Table 4, MCFG-Net-I achieves 93.28% ± 0.49% accuracy on the Cornell dataset. Adding MSFEM (MCFG-Net-II) improves accuracy to 97.78% ± 0.14%, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing multi-scale feature extraction. Similarly, MCFG-Net-III, which includes only CFAM, achieves 98.88% ± 0.14%, indicating its strong capability in feature fusion and decoding. The complete MCFG-Net achieves the highest accuracy—99.62% ± 0.11% on the Cornell dataset—representing a 6.34% improvement over the baseline.

Table 4.
Ablation experiments of different modules.
With respect to parameter count, MCFG-Net-I has 2.93 M parameters; adding MSFEM increases this to 3.14 M (MCFG-Net-II), while MCFG-Net-III with CFAM has 2.99 M. The full MCFG-Net, incorporating both MSFEM and CFAM, comprises 3.20 M parameters. These results demonstrate that although the inclusion of additional modules slightly increases the model size, the resulting accuracy improvements far outweigh the added complexity. Moreover, the integration of MSFEM and CFAM provides complementary benefits, significantly enhancing overall grasp detection performance without introducing excessive computational overhead.
5.2. Failure Case Analysis
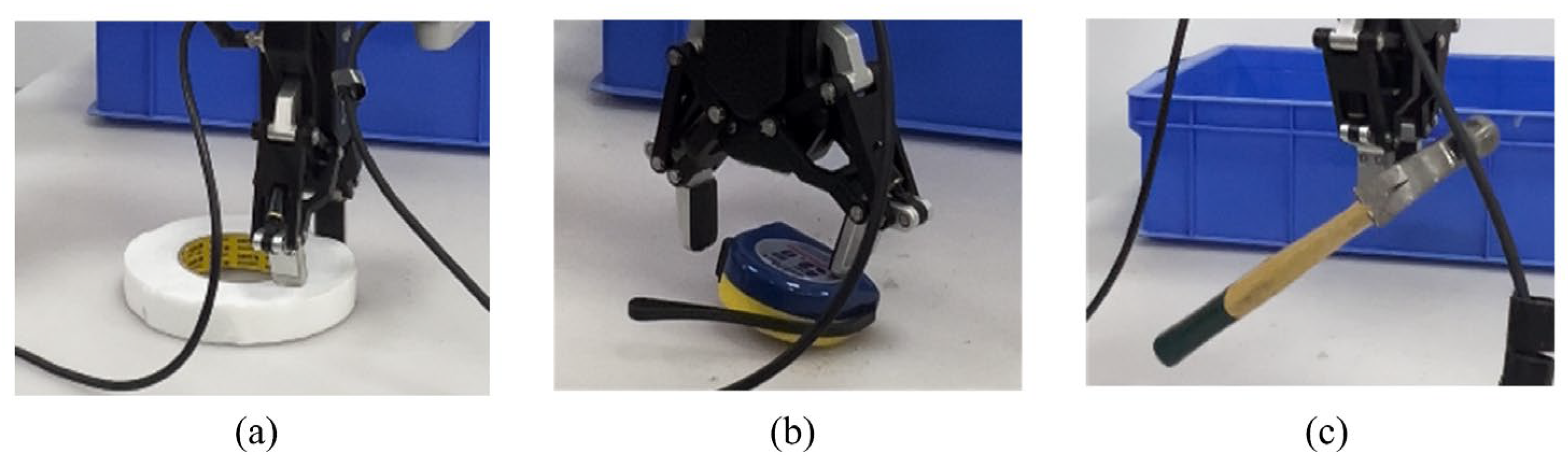
Grasping failures are inevitable in real-world robotic experiments due to environmental variability and physical uncertainties. Figure 10 shows the fault situations that occurred during the experimental process. In Figure 10a, recognition errors occur when the object color is too similar to the background, resulting in inaccurate grasp detection due to low visual contrast. Figure 10b shows a failure caused by improper motion planning, where premature contact between the gripper and the object shifts its pose, leading to a failed grasp. In Figure 10c, insufficient gripping force or low friction leads to object slippage, particularly when handling smooth or heavy items. These cases highlight the limitations of vision-only grasping systems. A failure is defined as an attempt where the target object is not successfully grasped. The grasp success rate is calculated as follows:
where is the grasp success rate, the number of successful grasps, and is the total number of grasp attempts. To further analyze the reasons for failure, we categorized the eight failures observed in 300 grasping trials. The results are shown in Table 5. These failures can be classified into two main types: recognition failure (six cases) and execution failure (two cases). Recognition failure occurred due to factors such as low contrast between the object and the background, severe occlusion, or background interference, which led to the model’s inability to accurately predict the grasp region. Execution failure, on the other hand, occurred even when the object was correctly detected, but the grasp failed due to factors like gripper slippage, unstable contact, or premature contact, causing a shift in the object’s pose. In response to these failure cases, future work will include specific measures. For recognition failures, we plan to incorporate an attention supervision mechanism or use semantic segmentation-based region priors to help the model focus more precisely on the graspable regions, reducing attention misalignment. For execution failures, we will introduce tactile sensors for real-time feedback on contact status and implement adaptive control of the grasping force to enhance the stability of the grasping process.
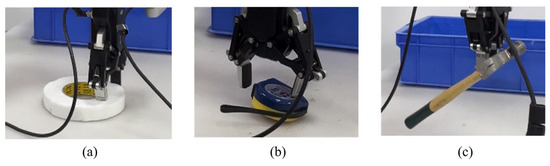
Figure 10.
Failure case of robot grasping experiments. (a) represents recognition error; (b) indicates improper exercise planning; (c) indicates insufficient grip strength.

Table 5.
Statistics of failed experimental results.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents MCFG-Net, a multi-scale and cross-layer fusion network for robotic grasp detection, designed to improve accuracy and robustness in unstructured environments. The proposed MSFEM module effectively preserves spatial details by capturing multi-scale contextual features at a consistent resolution, while the CFAM module addresses semantic mismatches during feature fusion through a dual-path attention mechanism. Extensive experiments on the Cornell and Jacquard datasets demonstrate the model’s superior performance, achieving grasp detection accuracies of 99.62% ± 0.11% and 95.48% ± 0.13%, respectively. Real-world validation on the AUBO i5 robotic platform further confirms its practicality, with success rates of 98.5% and 95% in single- and multi-object grasping tasks.
Future research directions will focus on the following: (1) integrating tactile feedback and force adaptation mechanisms to improve grasp stability, particularly for slippery or deformable objects; (2) developing dynamic attention mechanisms to better handle severe occlusions and enhance robustness to input noise; and (3) exploring lightweight versions of the network for deployment on resource-constrained robotic systems. These enhancements aim to further bridge the gap between controlled laboratory performance and real-world industrial deployment. Overall, MCFG-Net provides a reliable and efficient solution for robotic grasp detection, offering strong potential for industrial and service applications in complex environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.H. and J.X.; methodology, C.H.; software, C.H.; validation, J.X., C.H., X.C. and S.S.; formal analysis, C.H.; investigation, J.X.; resources, J.X.; data curation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.H.; writing—review and editing, J.X.; visualization, S.S.; supervision, J.X.; project administration, S.S.; funding acquisition, J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Plan Joint Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (2024-BSLH-174), and the Fundamental Research Funds of Liaoning Education Department, China (LJ212510142031).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request due to confidentiality reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Newbury, R.; Gu, M.; Chumbley, L.; Inaba, M. Deep learning approaches to grasp synthesis: A review. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3994–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Deng, L. PDCNet: A Lightweight and Efficient Robotic Grasp Detection Framework via Partial Convolution and Knowledge Distillation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2025, 259, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Bai, X.; Mao, Z. Predicting flow status of a flexible rectifier using cognitive computing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 264, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Suzuki, S.; Nabae, H.; Miyagawa, S.; Suzumori, K.; Maeda, S. Machine learning-enhanced soft robotic system inspired by rectal functions for investigating fecal incontinence. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10999. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, F. Deep reinforcement learning for robotic pushing and picking in cluttered environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 619–626. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, I.; Lee, H.; Saxena, A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Angelova, A. Real-time grasp detection using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1316–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.; Pastor, P.; Krizhevsky, A.; Quillen, D. Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumra, S.; Joshi, S.; Sahin, F. Antipodal robotic grasping using generative residual convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 9626–9633. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. Grasp stability assessment through attention-guided cross-modality fusion and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 9472–9479. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y. SKGNet: Robotic grasp detection with selective kernel convolution. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Ma, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, X. RGB-D grasp detection via depth guided learning with cross-modal attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 8003–8009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1 April 2018; pp. 834–848. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. DFANet: Deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9522–9531. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9413–9422. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Kanan, C. Robotic grasp detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, J.; Liang, J.; Niyaz, S.; Laskey, M.; Doan, R.; Liu, X.; Lin, J.; Vuong, A.; Goldberg, K. Dex-Net 2.0: Deep learning to plan robust grasps with synthetic point clouds and analytic grasp metrics. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Cambridge MA, USA, 12–16 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y. Fully convolutional grasp detection network with oriented anchor box. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7223–7230. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Kasaei, S. HMT-Grasp: A hybrid Mamba-Transformer approach for robot grasping in cluttered environments. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.03522. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Learning robust, real-time, reactive robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Moseson, S.; Saxena, A. Efficient grasp detection from RGB-D images: Learning using a new rectangle representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3304–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Gimpel, K. Gaussian error linear units (gelus). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.08415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Dilated Convolution with Learnable Spacings. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Tang, M.; Wu, S.; Li, H. Dynamic Dilated Convolutions (D2Conv3D) for Object Segmentation in Videos. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.09876. [Google Scholar]
- Depierre, A.; Dellandréa, E.; Chen, L. Jacquard: A large scale dataset for robotic grasp detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1 October 2018; pp. 3511–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Closing the loop for robotic grasping: A real-time, generative grasp synthesis approach. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Song, K.; Li, S.; Ma, S.; Yan, Y. Lightweight pixel-wise generative robot grasping detection based on RGB-D dense fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5017912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, H.; Liao, J. SE-ResUNet: A novel robotic grasp detection method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5238–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wen, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L. Deep robotic grasp prediction with hierarchical RGB-D fusion. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Kan, Z. When transformer meets robotic grasping: Exploits context for efficient grasp detection. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8170–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Dang, X. Light-weight convolutional neural networks for generative robotic grasping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 6696–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.-H.; Yu, S.; Xia, Y. FANet: Fast and accurate robotic grasp detection based on keypoints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Tao, B. ODGNet: Robotic grasp detection network based on omni-dimensional dynamic convolution. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Pei, R.; Zhou, L.; Qin, H.; Sun, W.; Liang, Q. An Efficient Generative Intelligent Multiobjective Grasping Model for Kitchen Waste Sorting. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2522810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lan, X.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Q. ROI-based robotic grasp detection for object overlapping scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 4768–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Ainetter, S.; Fraundorfer, F. End-to-end trainable deep neural network for robotic grasp detection and semantic segmentation from RGB. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13452–13458. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Robotic objects detection and grasp in clutter based on cascaded deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 5004210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Y. A model for robot grasping: Integrating transformer and CNN with RGB-D fusion. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).