Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
- The Health Plan [33] outlines healthcare priorities in the “Terres de l’Ebre” Healthcare Region (Catalonia, Spain) from 2021 to 2025.
- The HC3 Patient Episode Dataset provides clinical information of care on inpatient and outpatient care in Catalan hospitals.
- The clinical database of 11 primary care teams includes comprehensive health data for 97.7% of residents, covering symptoms, tests, diagnoses, comorbidities, prescribed medication, and referrals.
- The Integrated System of Electronic Prescription (SIRE) captures information on prescribed medications.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Outcomes: AF patients who had a MACE.
- Inclusion criteria: Subjects aged 65–95 years who met the inclusion criteria: high risk-AF (according to the risk model and belonging to Q4) [19], active clinical history in any of the health centers of the territory with information accessible through the shared history (HC3), without previous AF or MACE, residing in the territory, and attached to any of the Primary Care Teams (EAP) of the territory.
- Exclusion criteria: under 65 years of age or over 95 years of age, living outside Terres de l’Ebre, a previous diagnosis of AF, treatment with anticoagulants, impaired cognitive status, Barthel score < 55 points, or pacemaker or defibrillator wearer. Non-availability or loss of accessibility to the information necessary for the study was considered a reason for exclusion.
2.3. Data and Preprocessing
2.4. Model Development
2.5. Model Performance Analysis
2.6. Model Interpretability
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Patient Characteristics
3.2. Machine Learning Model
3.2.1. Comparison between the Different Models
3.2.2. Predictors by Outcomes
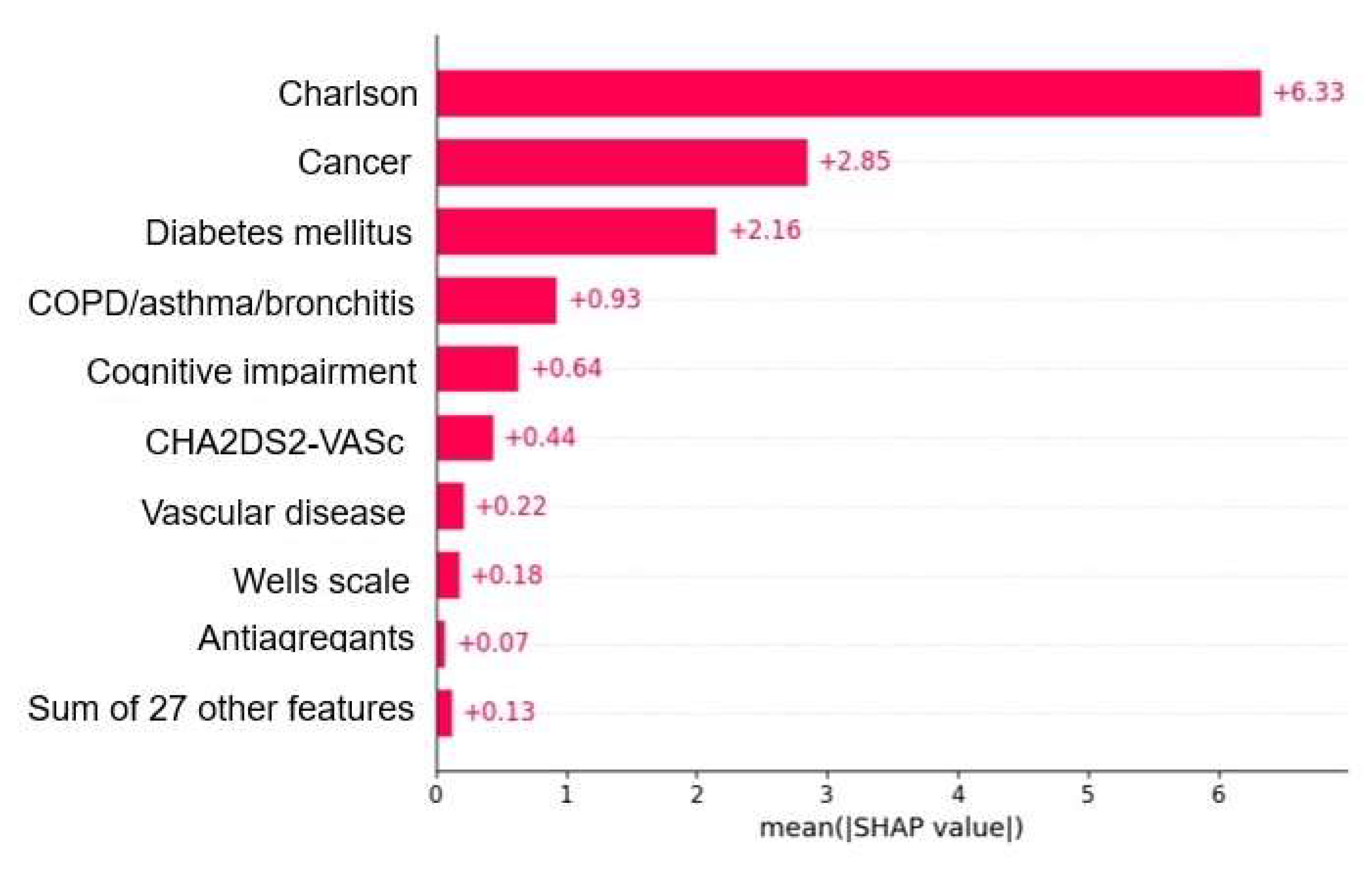
3.2.3. Model Interpretation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenstrøm, S.; Risom, S.S.; Hove, J.D.; Brødsgaard, A. Living with Atrial Fibrillation: A Family Perspective. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 7394445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez de la Nava, A.M.; Atienza, F.; Bermejo, J.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Artificial intelligence for a personalized diagnosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H1337–H1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odutayo, A.; Wong, C.X.; Hsiao, A.J.; Hopewell, S.; Altman, D.G.; Emdin, C.A. Atrial fibrillation and risks of cardiovascular disease, renal disease, and death: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 354, i4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.; Aeschbacher, S.; Coslovsky, M.; Meyre, P.B.; Reddiess, P.; Ammann, P.; Erne, P.; Moschovitis, G.; Di Valentino, M.; Shah, D.; et al. Long-term risk of adverse outcomes according to atrial fibrillation type. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, E.; Hsueh, L.; McConeghy, K.W.; Gravenstein, S.; Saade, E. Major adverse cardiovascular event definitions used in observational analysis of administrative databases: A systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltó-Balado, P.; Reverté-Villarroya, S.; Monclús-Arasa, C.; Balado-Albiol, M.T.; Baset-Martínez, S.; Carot-Domenech, J.; Clua-Espuny, J.L. Heart Failure and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation Patients: A Retrospective Primary Care Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriani, G.; Vitolo, M.; Diemberger, I.; Proietti, M.; Valenti, A.C.; Malavasi, V.L.; Lip, G.Y.H. Optimizing indices of atrial fibrillation susceptibility and burden to evaluate atrial fibrillation severity, risk and outcomes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lin, M.; Wang, W. The progression in atrial fibrillation patients with COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102420–102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Johnsen, S.P.; Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.H. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation: Geographic/Ecological Risk Factors, Age, Sex, Genetics. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardashev, A.V.; Belenkov, Y.N.; Matsiukevich, M.C.; Snezhitskiy, V.A. Atrial Fibrillation and Mortality: Prognostic Factors and Direction of Prevention. Kardiologiia 2021, 61, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Menichelli, D.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Sciacqua, A.; Violi, F.; Pignatelli, P.; ATHERO-AF study group†. Family History of Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Cardiovascular Events: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raparelli, V.; Pastori, D.; Pignataro, S.F.; Vestri, A.R.; Pignatelli, P.; Cangemi, R.; Proietti, M.; Davì, G.; Hiatt, W.R.; Lip, G.Y.H.; et al. Major adverse cardiovascular events in non-valvular atrial fibrillation with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The ARAPACIS study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romiti, G.F.; Pastori, D.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Ding, W.Y.; Gue, Y.X.; Menichelli, D.; Gumprecht, J.; Kozieł, M.; Yang, P.S.; Guo, Y.; et al. Adherence to the ’Atrial Fibrillation Better Care’ Pathway in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Impact on Clinical Outcomes-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 285,000 Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2023, 149, e1–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Vasan, R.S.; Pencina, M.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Cobain, M.; Massaro, J.M.; Kannel, W.B. General cardiovascular risk profile for use in primary care: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2008, 117, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.C.; Go, A.S.; Chang, Y.; Borowsky, L.H.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Singer, D.E. A new risk scheme to predict warfarin-associated hemorrhage: The ATRIA (Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Song, M.K.; Lee, E.; Bae, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.J.; Yoo, S. Predicting Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Using Machine Learning. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2022, 27, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muria-Subirats, E.; Clua-Espuny, J.L.; Ballesta-Ors, J.; Lorman-Carbo, B.; Lechuga-Duran, I.; Fernández-Saez, J.; Pla-Farnos, R.; On Behalf Members of Africat Group. Incidence and Risk Assessment for Atrial Fibrillation at 5 Years: Hypertensive Diabetic Retrospective Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Andrade, J.; Laksman, Z. Thromboembolic risk stratification in atrial fibrillation-beyond clinical risk scores. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Marín, F.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; Raña-Míguez, P.; Anguita, M.; Muñiz, J.; Cequier, Á.; Bertomeu-Martínez, V.; Valdés, M.; Vicente, V.; et al. Usefulness of the 2MACE Score to Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehlich, L.; Meyre, P.; Aeschbacher, S.; Blum, S.; Djokic, D.; Kuehne, M.; Osswald, S.; Kaufmann, B.A.; Conen, D. Left atrial dimension and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2019, 105, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.E.; Kueper, J.K.; Williamson, T.S. An introduction to machine learning for classification and prediction. Fam. Pract. 2023, 40, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Xu, X.; Hajra, A.; Apple, S.; Kharawala, A.; Duarte, G.; Liaqat, W.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Current Advancement in Diagnosing Atrial Fibrillation by Utilizing Wearable Devices and Artificial Intelligence: A Review Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Carter, R.E.; Yao, X.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: A retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019, 394, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, R.; Wu, J.; Hogg, D.; Raveendra, K.; Nakao, Y.M.; Nakao, K.; Arbel, R.; Haim, M.; Zahger, D.; Parry, J.; et al. Prediction of short-term atrial fibrillation risk using primary care electronic health records. Heart 2023, 109, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Wulan, N.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H. Detecting atrial fibrillation by deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 93, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.R.; Ayoubkhani, D.; McEwan, P.; Sugrue, D.M.; Farooqui, U.; Lister, S.; Lumley, M.; Bakhai, A.; Cohen, A.T.; O’Neill, M.; et al. Predicting atrial fibrillation in primary care using machine learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoshina, P.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; Rodriguez, B. Dual Transcriptomic and Molecular Machine Learning Predicts all Major Clinical Forms of Drug Cardiotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, C.H.; He, Z. Extracting deep features from short ECG signals for early atrial fibrillation detection. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Mansourvar, M.; Puthusserypady, S.; Wiil, U.K.; Peimankar, A. Short-term atrial fibrillation detection using electrocardiograms: A comparison of machine learning approaches. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2022, 163, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselius, F.J.; van Schie, M.S.; De Groot, N.M.S.; Hendriks, R.C. Digital biomarkers and algorithms for detection of atrial fibrillation using surface electrocardiograms: A systematic review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, P.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, X. Automatic Detection of Short-Term Atrial Fibrillation Segments Based on Frequency Slice Wavelet Transform and Machine Learning Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla de salut de la Regió Sanitària Terres de l’Ebre 2021–2025. Direcció General de Planificació i Recerca en Salut: Tortosa, Spain, 2022. Available online: https://scientiasalut.gencat.cat/handle/11351/7964 (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Idescat. Anuario Estadístico de Cataluña. Densidad de Población. Comarcas y Aran, Ámbitos y Provincias. Available online: https://www.idescat.cat/indicadors/?id=aec&n=15227&lang=es (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Idescat. Indicadors Demogràfics i de Territori. Estructura Per Edats, Envelliment i Dependència. Comarques i Aran. Available online: https://www.idescat.cat/pub/?id=inddt&n=915&lang=en (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Sociedad Española de Cardiología. Atlas del Mal Control de la Anticoagulación en Pacientes con Fibrilación Auricular No Valvular. Available online: https://secardiologia.es/images/secciones/clinica/atlas-mal-control-anticoagulacion-INFOGRAFIA.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Li, X.; Tse, V.C.; Au-Doung, L.W.; Wong, I.C.; Chan, E.W. The impact of ischaemic stroke on atrial fibrillation-related healthcare cost: A systematic review. Europace 2017, 19, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, P.E.; Tsioufis, K. Optimizing Anticoagulation Management in Atrial Fibrillation: Beyond the Guidelines. How and for Whom? J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2023, 81, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheugt, F.W.A.; Fox, K.A.A.; Virdone, S.; Ambrosio, G.; Gersh, B.J.; Haas, S.; Pieper, K.S.; Kayani, G.; Camm, A.J.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patients With or Without Comorbid Vascular Disease: Insights From the GARFIELD-AF Registry. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.U.; Chhatwal, K.; Sanaka, K.; Xu, B. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Medicine: Current Insights and Future Prospects. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoz, C.; Cardenas, J.; Salinero-Fort, M.Á.; Mostaza, J.M. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated anticoagulant therapy in the nonagenarian population of the Community of Madrid, Spain. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Mackman, N.; Falanga, A.; Pabinger, I.; Noble, S.; Ageno, W.; Moik, F.; Lee, A.Y.Y. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2022, 8, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Fradley, M.G.; Dent, S.F.; Weintraub, N.L.; Lustberg, M.B.; Alonso, A.; Addison, D. Incidence, risk factors, and mortality of atrial fibrillation in breast cancer: A SEER-Medicare analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, L.L.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Peng, X.D.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Ruan, Y.F.; Bai, R.; Liu, N.; Ma, C.S. The Association of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 27, 2372067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorigue, M.; Miljkovic, M.D. Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Risk in Patients with Cancer: A Primer for Oncologists. J. Oncol. Pract. 2019, 15, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Norby, F.L.; Alonso, A.; Cushman, M.; Chen, L.Y.; Michos, E.D.; Folsom, A.R. Atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: Evidence of bidirectionality in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandasundaram, B.; Lane, D.A.; Apostolakis, S.; Lip, G.Y. The impact of atherosclerotic vascular disease in predicting a stroke, thromboembolism and mortality in atrial fibrillation patients: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabauer, M.; Oeff, M.; Gerth, A.; Wegscheider, K.; Buchholz, A.; Haeusler, K.G.; Hanrath, P.; Meinertz, T.; Ravens, U.; Sprenger, C.; et al. Prognostic markers of all-cause mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation: Data from the prospective long-term registry of the German Atrial Fibrillation NETwork (AFNET). Europace 2021, 23, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Murphy, R.R.; Sahiar, F.; Ingall, T.J.; Dhamane, A.D.; Ferri, M.; Hlavacek, P.; Preib, M.T.; Keshishian, A.; Russ, C.; et al. Risk Levels and Adverse Clinical Outcomes Among Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Oral Anticoagulants. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2229333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, T.M.; Baljoon, A.; Kilanko, O.; Sherbeny, F.; Ali, A.A. Machine learning algorithms to predict major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 164, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Yang, Y.M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, L.T.; Liu, L.S.; Zhao, L.; Yu, P.F.; et al. Comparison of the clinical features and outcomes in two age-groups of elderly patients with atrial fibrillation. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Kasagi, S.; Maeno, K.I.; Naito, R.; Kumagai, T.; Kimura, Y.; Kato, M.; Kawana, F.; Tomita, Y.; Narui, K.; et al. Cross-Sectional Relationship Between Atrial Conduction Delay and Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.F.S.; Fagundes, T.P.; Teixeira, B.C.; Chiavegatto Filho, A.D.P. Machine Learning for Hypertension Prediction: A Systematic Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.B.; Teeple, S.; Navathe, A.S. Addressing Bias in Artificial Intelligence in Health Care. JAMA 2019, 322, 2377–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areti, P.; Daniel, H.; Greg, S.; Eirini, M.; Panos, D. Prediction of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Using Machine Learning Models in UK Biobank. (Available at SSRN). Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.10.28.22281669v1 (accessed on 10 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Arero, G.; Arero, A.G.; Mohammed, S.H.; Vasheghani-Farahani, A. Prognostic Potential of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score in Predicting All-Cause Mortality and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 850641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essien, U.R.; Kornej, J.; Johnson, A.E. Social determinants of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 118, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palà, E.; Bustamante, A.; Clúa-Espuny, J.L.; Acosta, J.; González-Loyola, F.; Santos, S.D.; Ribas-Segui, D.; Ballesta-Ors, J.; Penalba, A.; Giralt, M.; et al. Blood-biomarkers and devices for atrial fibrillation screening: Lessons learned from the AFRICAT (Atrial Fibrillation Research in CATalonia) study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentille-Lorente, D.; Hernández-Pinilla, A.; Satue-Gracia, E.; Muria-Subirats, E.; Forcadell-Peris, M.J.; Gentille-Lorente, J.; Ballesta-Ors, J.; Martín-Lujan, F.M.; Clua-Espuny, J.L. Echocardiography and Electrocardiography in Detecting Atrial Cardiomyopathy: A Promising Path to Predicting Cardioembolic Strokes and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Galvez, R.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Roldán, V.; Orenes-Piñero, E.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; López-García, C.; Saura, D.; González, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Marín, F. Imaging in atrial fibrillation: A way to assess atrial fibrosis and remodeling to assist decision-making. Am. Heart J. 2023, 258, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Stubbendorff, A.; Ericson, U. The EAT-Lancet diet, genetic susceptibility and risk of atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Jing, J.; Gu, H.-Q.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, X.; Du, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; et al. Rationale and design of the GOLDEN BRIDGE II: A cluster-randomised multifaceted intervention trial of an artificial intelligence-based cerebrovascular disease clinical decision support system to improve stroke outcomes and care quality in China. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2023, svn-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
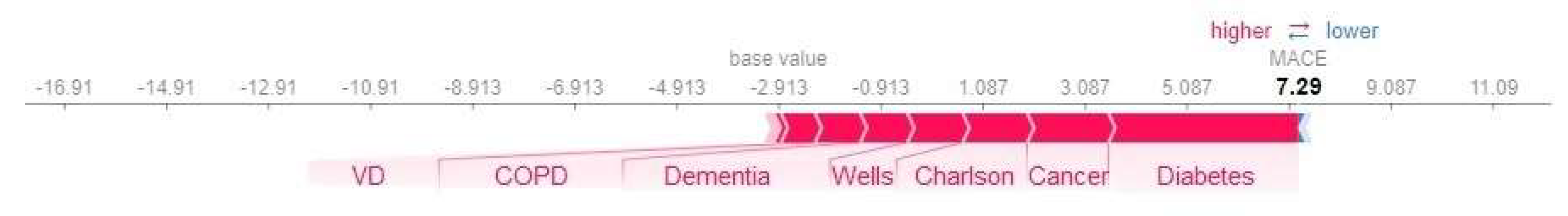
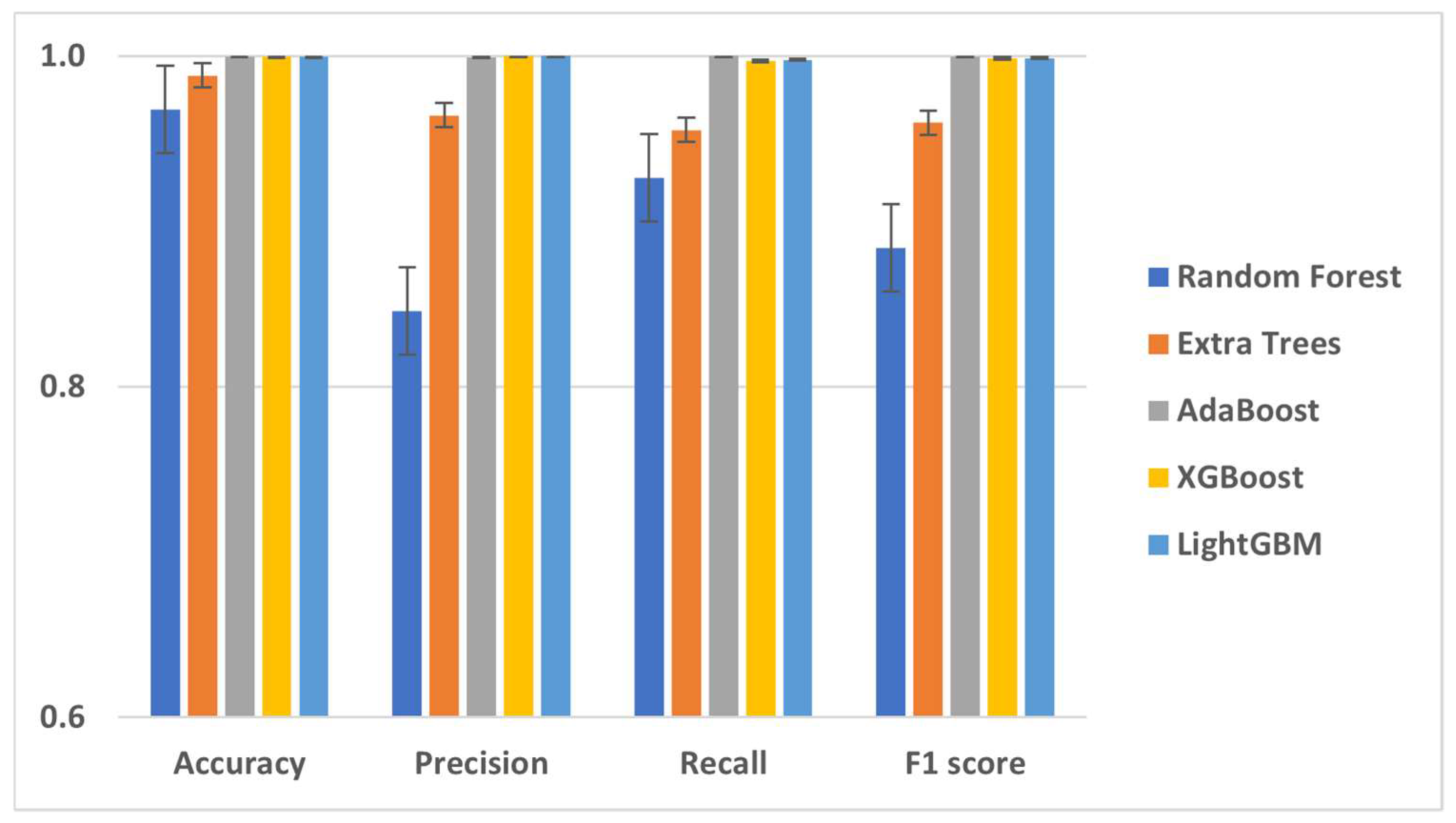
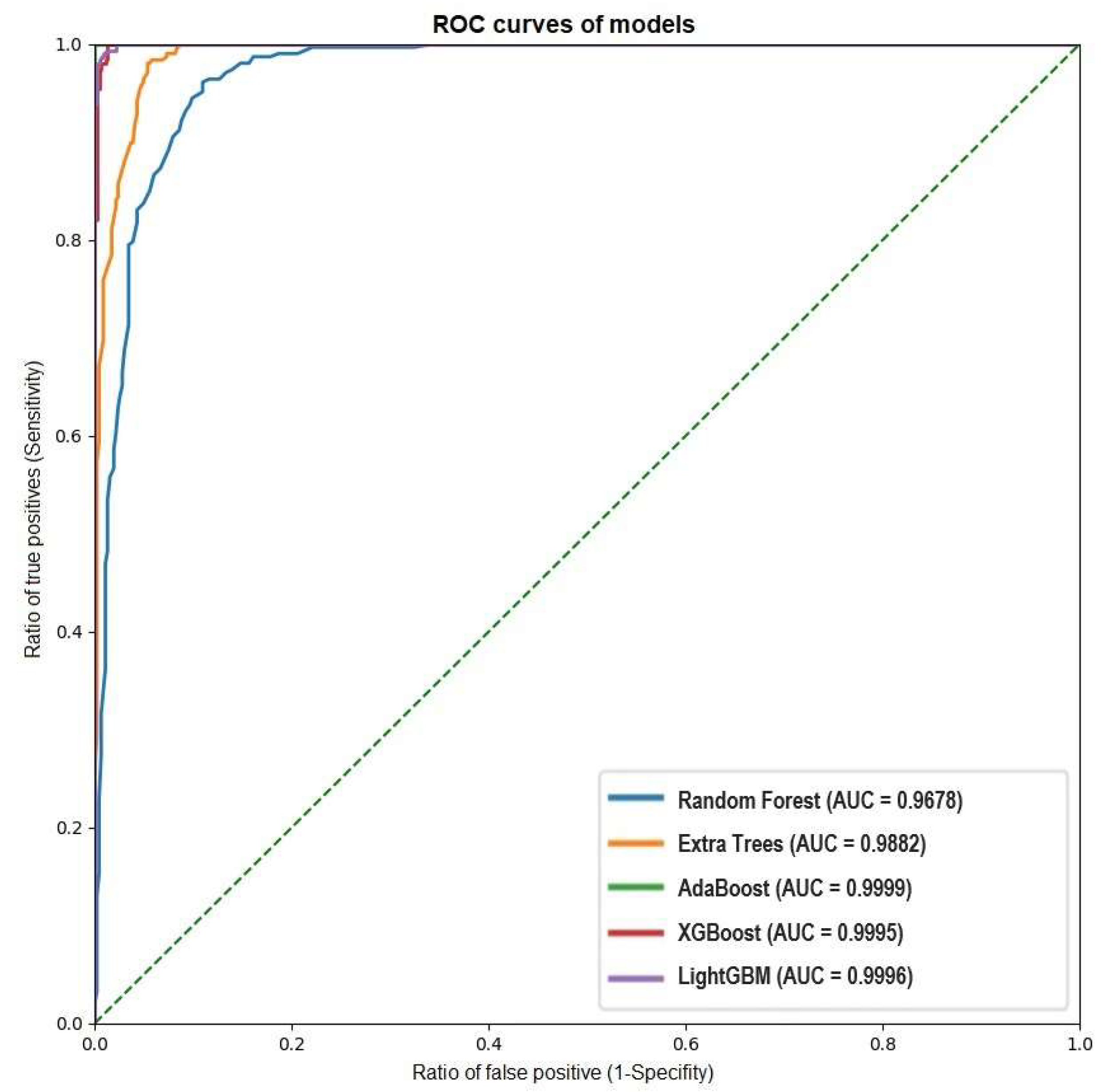
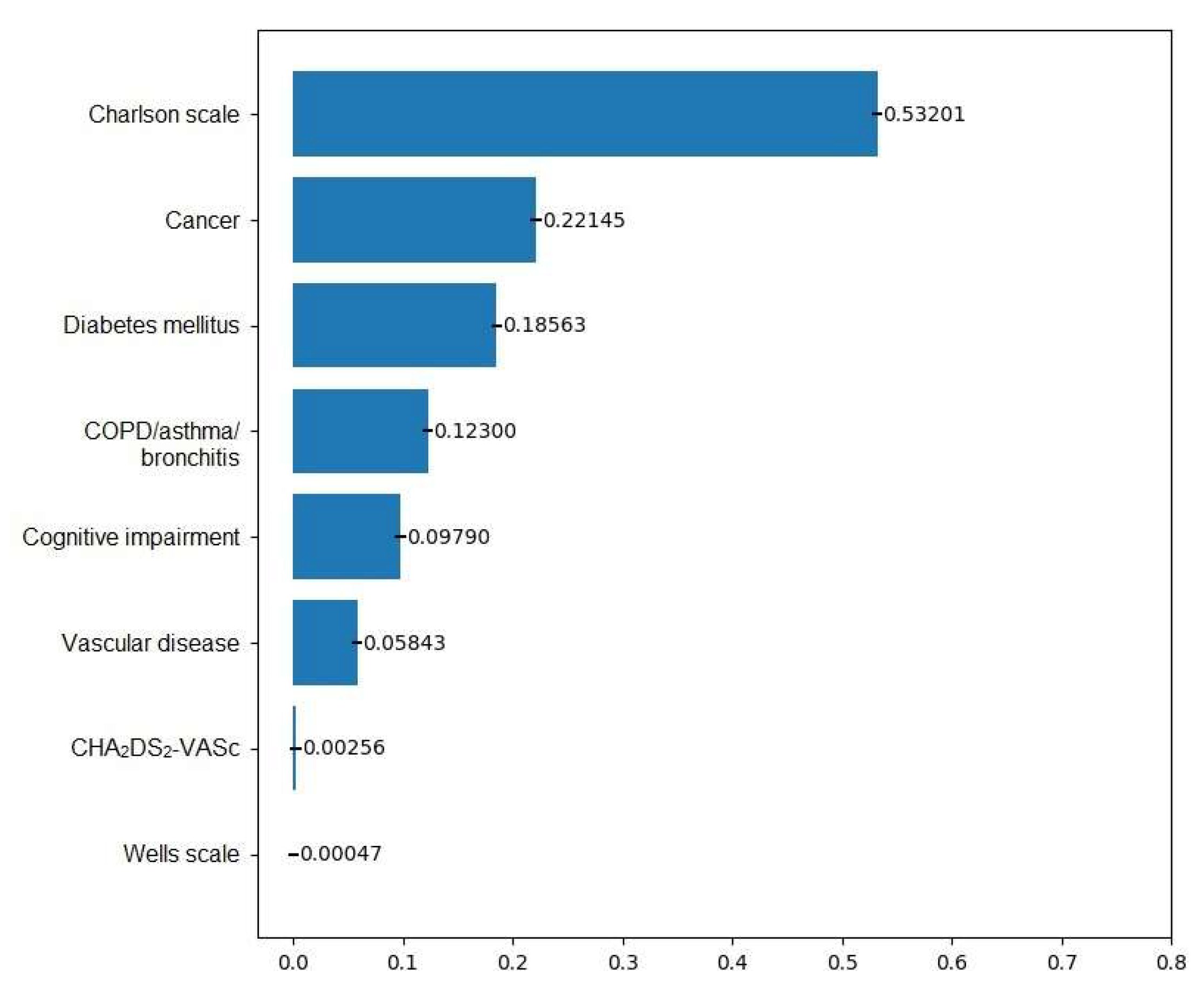
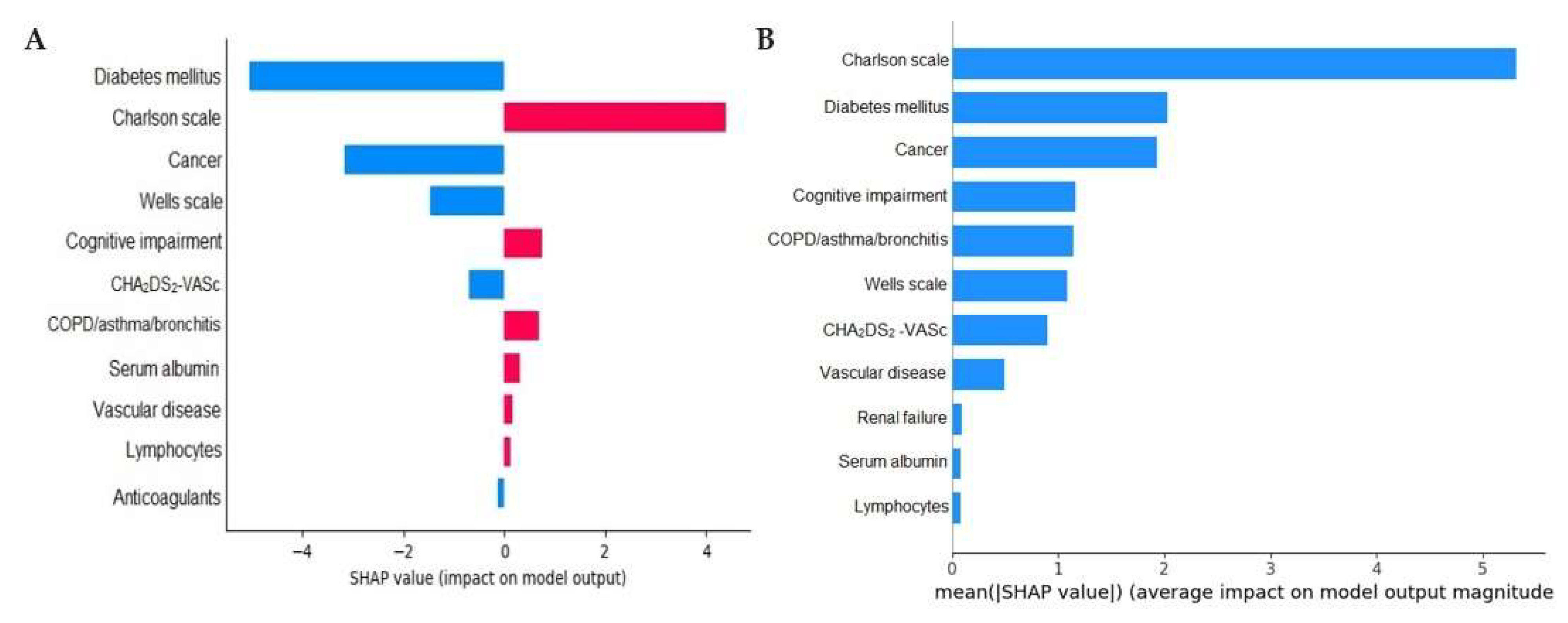

| Machine Learning Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 96.78% | 0.8456 | 0.9263 | 0.8841 | 0.9885 | 0.8456 | 0.9741 | 0.9263 | 96.78% |
| Extra Trees | 98.82% | 0.9641 | 0.9554 | 0.9597 | 0.9923 | 0.9641 | 0.9938 | 0.9554 | 98.82% |
| AdaBoost | 99.99% | 0.9994 | 1 | 0.9997 | 1 | 0.9994 | 0.9999 | 1 | 99.99% |
| XGBoost | 99.95% | 1 | 0.9971 | 0.9985 | 0.9995 | 1 | 1 | 0.997 | 99.95% |
| LightGBM | 99.96% | 1 | 0.9977 | 0.9988 | 0.9996 | 1 | 1 | 0.9977 | 99.96% |
| Variables | No MACE | (%) | MACE | (%) | p | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 1527 | 59.32% | 1047 | 40.68% | 2574 | |
| Woman | 785 | 51.41% | 558 | 53.30% | 0.356 | 1343 |
| Age average | 80.53 ± 8.05 | 82.23 ± 7.59 | <0.001 | 81.22 ± 7.91 | ||
| Hypertension, arterial | 1112 | 72.82% | 833 | 79.56% | <0.001 | 1945 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 406 | 26.59% | 363 | 34.67% | <0.001 | 769 |
| Dyslipemia | 692 | 45.32% | 524 | 50.05% | 0.020 | 1216 |
| Vascular disease | 59 | 3.86% | 286 | 27.32% | <0.001 | 345 |
| Dementia/cognitive impairment | 174 | 11.39% | 136 | 12.99% | <0.001 | 310 |
| Liver disease | 6 | 0.39% | 4 | 0.38% | 1.000 | 10 |
| Renal failure | 339 | 22.20% | 337 | 32.19% | <0.001 | 676 |
| Cancer | 516 | 33.79% | 340 | 32.47% | 0.496 | 856 |
| Thyroid disease | 109 | 7.14% | 106 | 10.12% | 0.018 | 215 |
| OSAHS 1 | 60 | 3.93% | 66 | 6.30% | 0.007 | 126 |
| COPD 2 | 225 | 14.73% | 222 | 21.20% | <0.001 | 447 |
| Inflammatory disease (Crohn’s and Colitis) | 9 | 0.59% | 7 | 0.67% | 0.804 | 16 |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 20 | 1.31% | 17 | 1.62% | 0.506 | 37 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.47 ± 5.7 | 78.03 ± 16.51 | 0.038 | 77.69 ± 16.04 | ||
| BMI 3 | 29.32 ± 5.28 | 29.75 ± 5.51 | 0.041 | 29.49 ± 5.38 | ||
| Heart rate/min | 76.05 ± 1847 | 75.71 ± 18.47 | 0.625 | 75.91 ± 18.47 | ||
| Cholesterol mg/dL | 184.23 ± 38.07 | 164.98 ± 38.14 | <0.001 | 176.4 ± 39.24 | ||
| ProBNP (pg/mL) | 1550 | 3301.75 ± 2882.7 | 0.625 | 2951.4 ± 2616.52 | ||
| Dimer D (ng/mL) | 1753.59 ± 2714.47 | 1319.72 ± 2954.13 | 0.337 | 1532.56 ± 2838.47 | ||
| Glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 66.11 ± 19.8 | 59.85 ± 20.74 | <0.001 | 63.48 ± 20.43 | ||
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.94 ± 5.43 | 5.04 ± 14.85 | 0.835 | 4.98 ± 10.68 | ||
| Lymphocytes (×103/μL) | 2.12 ± 1.11 | 2.02 ± 1.62 | 0.072 | 2.08 ± 1.34 | ||
| Statins | 505 | 33.07% | 607 | 57.98% | <0.001 | 945 |
| Anticoagulation | 1207 | 79.04% | 787 | 75.16% | 0.021 | 1994 |
| Antivitamin-K | 613 | 40.14% | 331 | 31.61% | <0.001 | 944 |
| NOAC 4 | 595 | 38.96% | 458 | 43.74% | 0.015 | 1053 |
| Anti-aggregants | 67 | 4.38% | 74 | 7.06% | 0.003 | 141 |
| Pfeiffer score ± SD | 2.91 ± 3.1 | 2.61 ± 2.8 | 0.218 | 2.75 ± 2.94 | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc ± SD | 3.26 ± 0.95 | 4.62 ± 1.02 | <0.001 | 3.81 ± 1.20 | ||
| CCI 5 ± SD | 1.24 ± 1.19 | 2.67 ± 1.31 | <0.001 | 1.82 ± 1.43 | ||
| CONUT score ± SD | 1.31 ± 0.54 | 1.48 ± 0.61 | <0.001 | 1.38 ± 0.58 | ||
| Wells score ± SD | 1.35 ± 0.48 | 1.33 ± 0.47 | 0.415 | 1.34 ± 0.47 | ||
| COVID-19 | 150 | 9.82% | 110 | 10.51% | 0.573 | 260 |
| Death | 1279 | 83.76% | 777 | 74.21% | <0.001 | 2056 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moltó-Balado, P.; Reverté-Villarroya, S.; Alonso-Barberán, V.; Monclús-Arasa, C.; Balado-Albiol, M.T.; Clua-Queralt, J.; Clua-Espuny, J.-L. Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation. Technologies 2024, 12, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12020013
Moltó-Balado P, Reverté-Villarroya S, Alonso-Barberán V, Monclús-Arasa C, Balado-Albiol MT, Clua-Queralt J, Clua-Espuny J-L. Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation. Technologies. 2024; 12(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoltó-Balado, Pedro, Silvia Reverté-Villarroya, Victor Alonso-Barberán, Cinta Monclús-Arasa, Maria Teresa Balado-Albiol, Josep Clua-Queralt, and Josep-Lluis Clua-Espuny. 2024. "Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation" Technologies 12, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12020013
APA StyleMoltó-Balado, P., Reverté-Villarroya, S., Alonso-Barberán, V., Monclús-Arasa, C., Balado-Albiol, M. T., Clua-Queralt, J., & Clua-Espuny, J.-L. (2024). Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation. Technologies, 12(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12020013











