Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
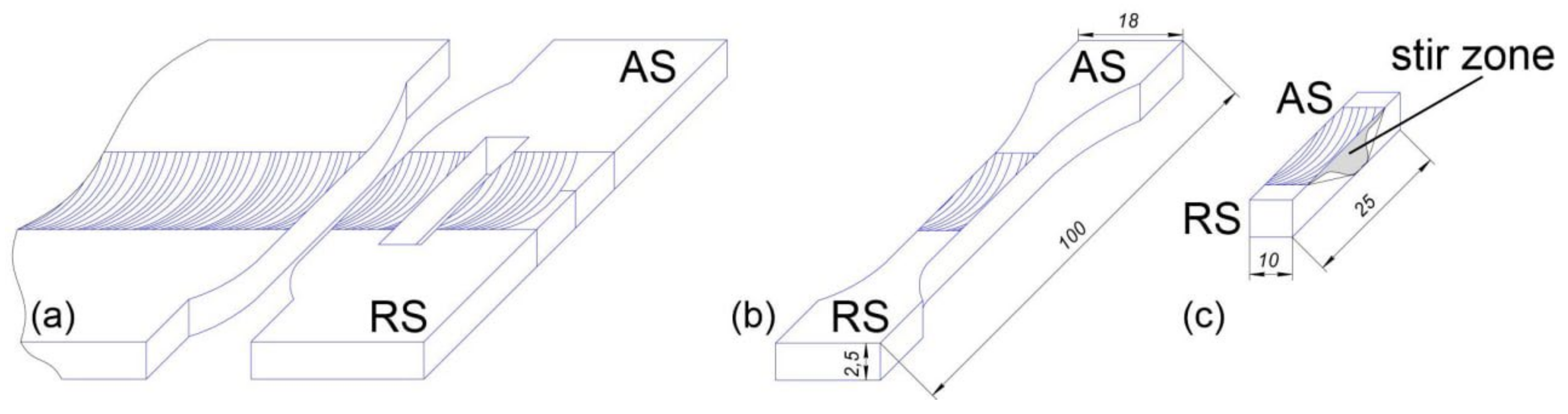
2.1. Experimental Set-Up and Materials
2.2. Equipment and Sample Preparation
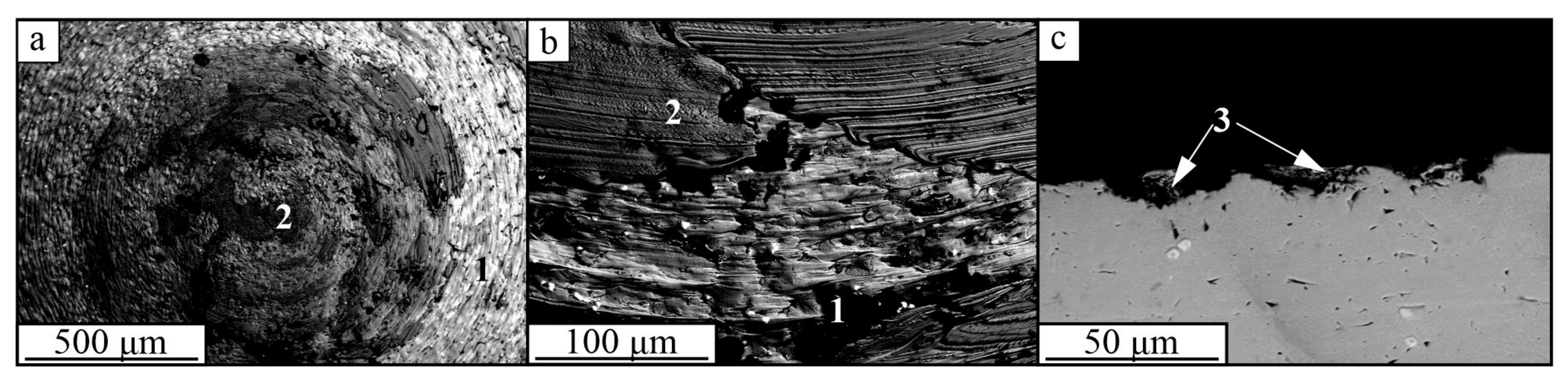
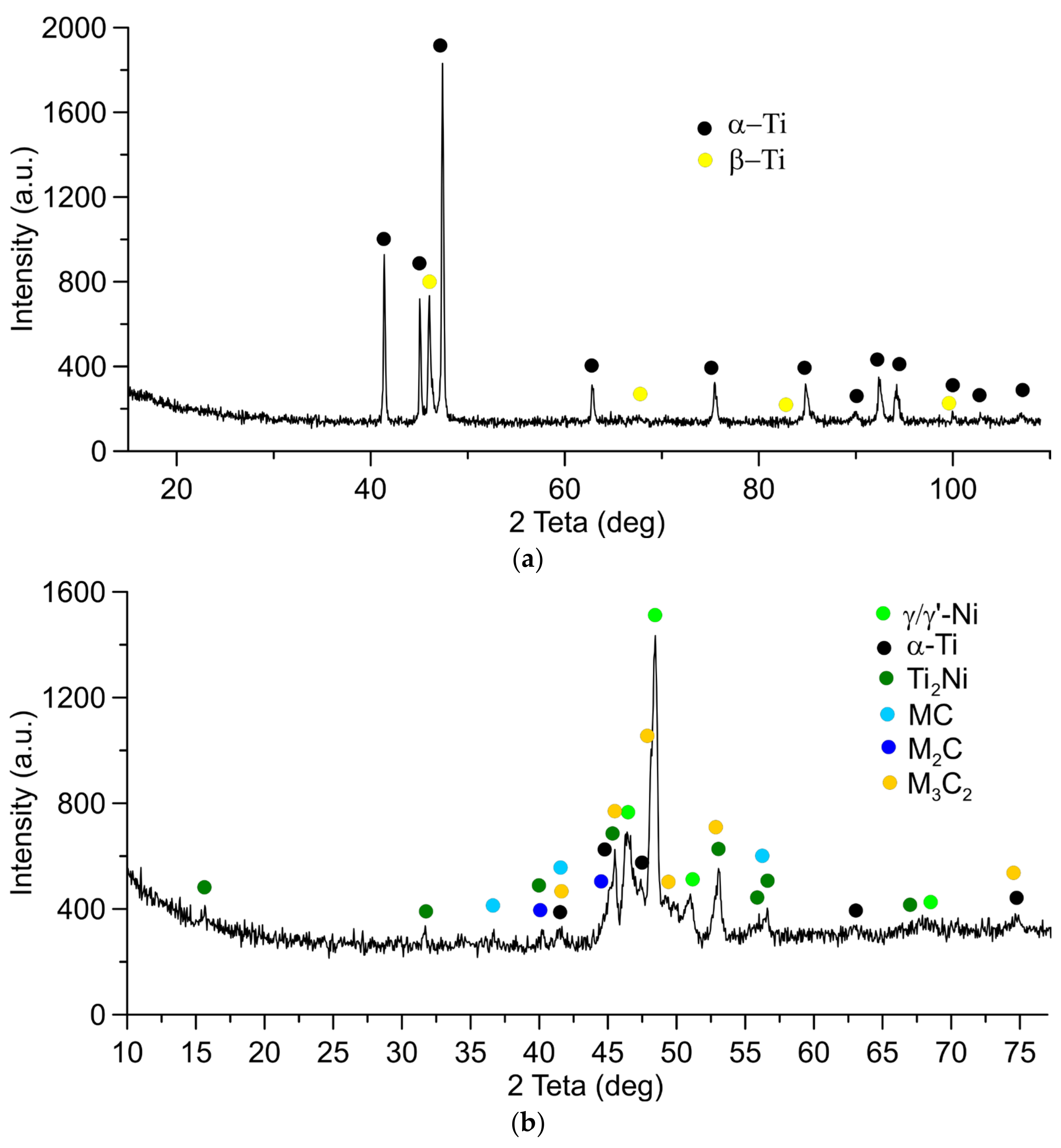
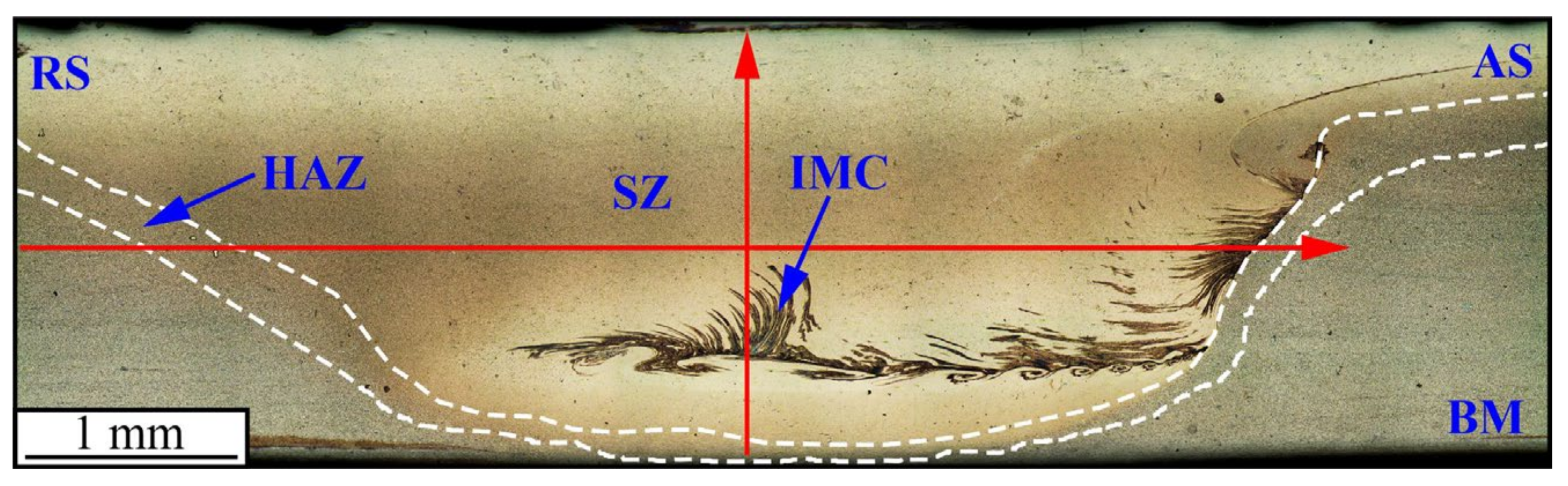
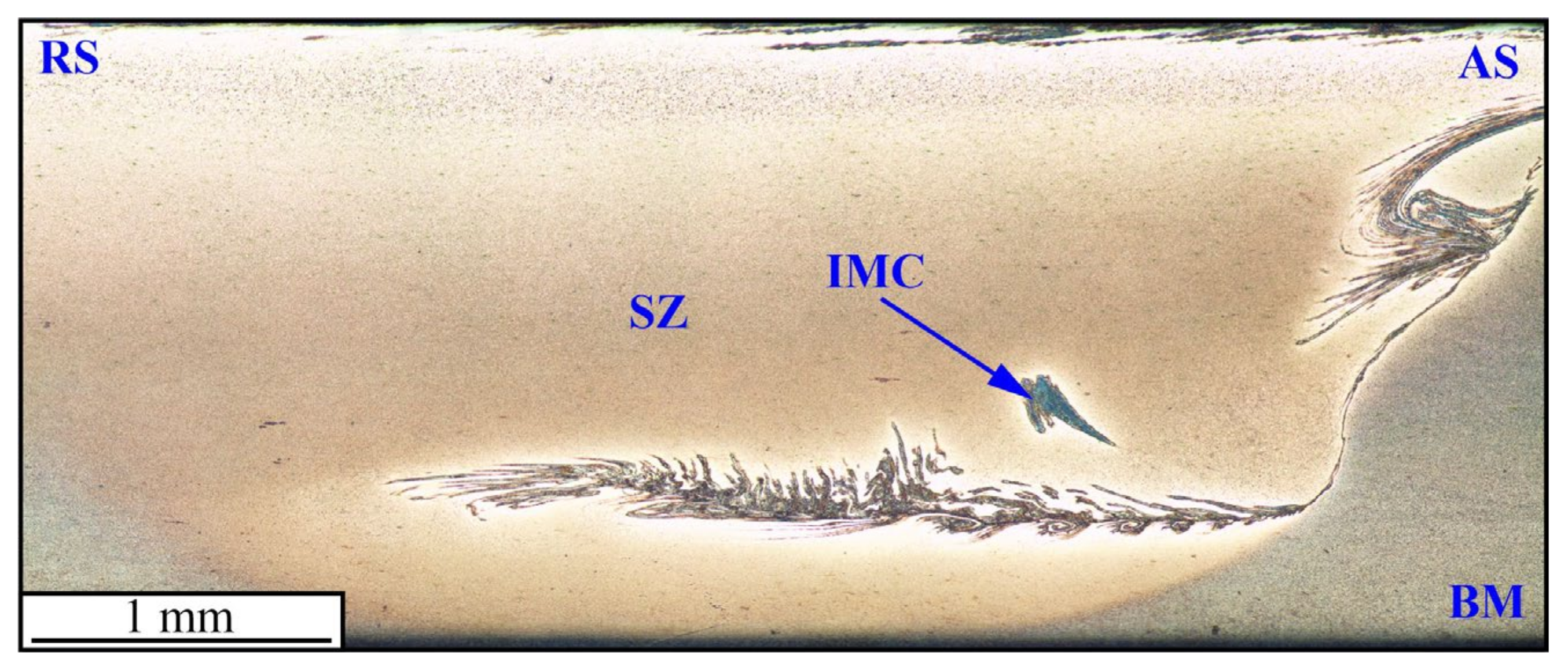
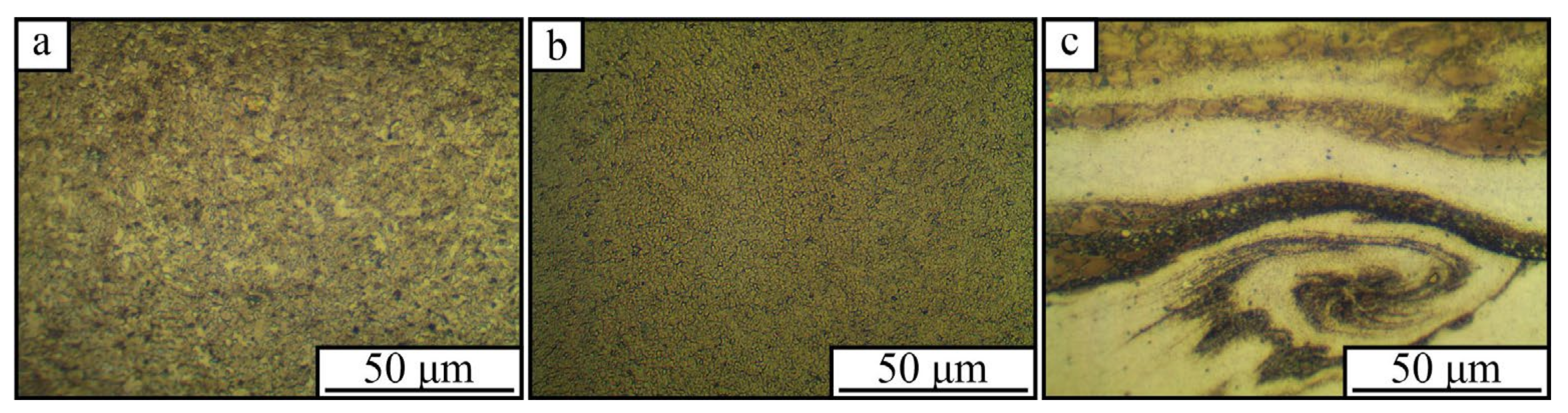
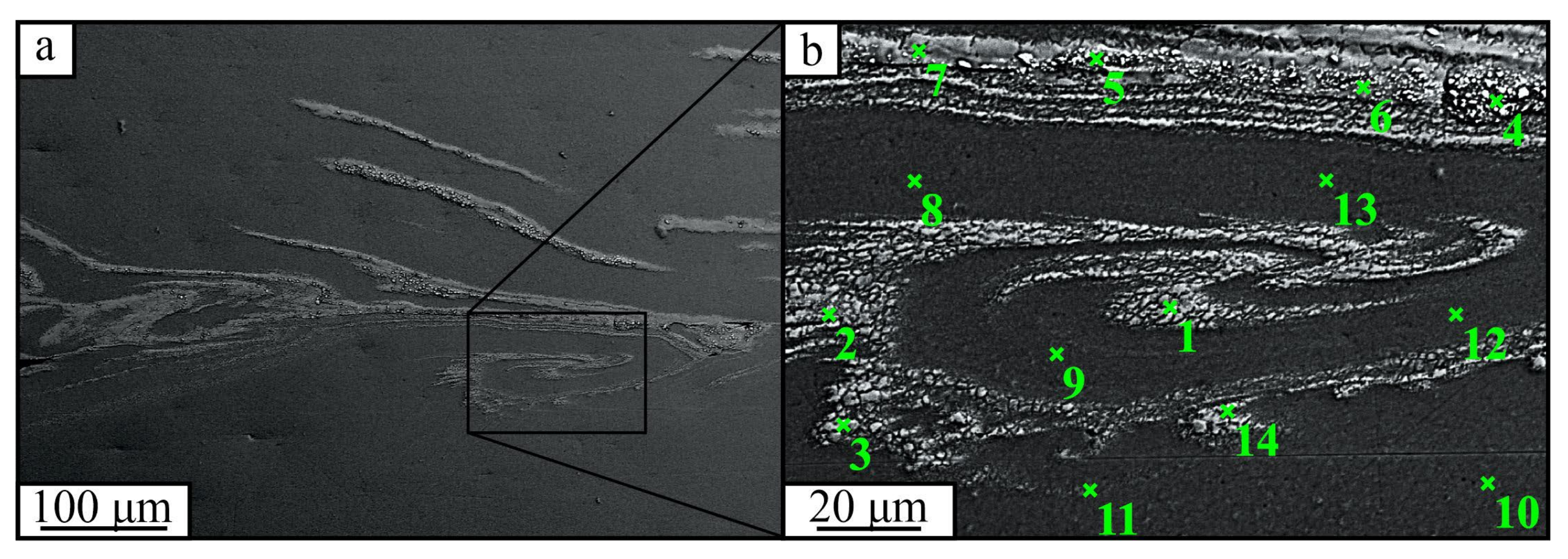
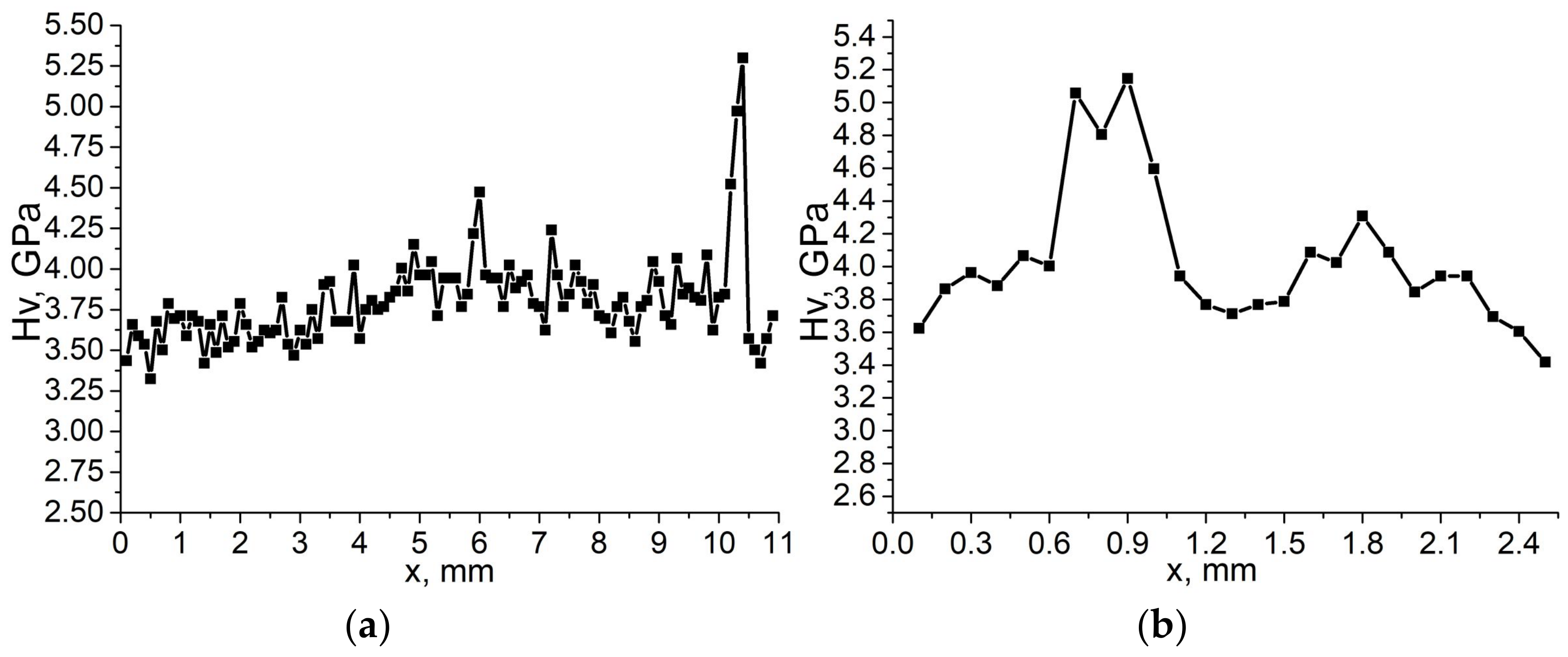
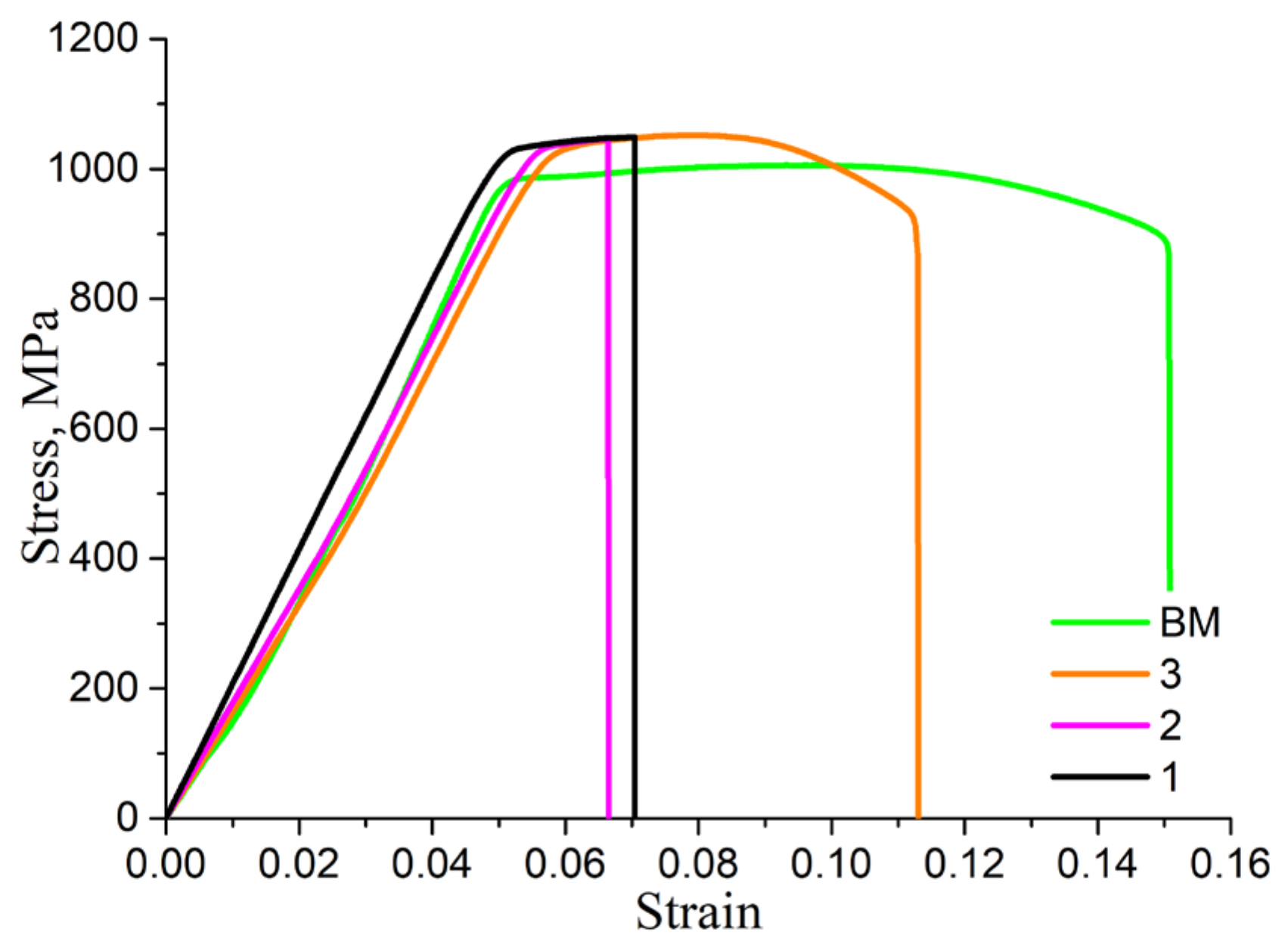
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pilchak, A.L.; Juhas, M.C.; Williams, J.C. Microstructural Changes Due to Friction Stir Processing of Investment-Cast Ti-6Al-4V. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundar, I.; Raghu, T.; Kashyap, B.P. Hot working and geometric dynamic recrystallisation behaviour of a near-α titanium alloy with acicular microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2014, 600, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Bo, C.H.E.N.; Tang, H.B.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H.M.; Jia, L.I. Influence of heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive manufacturing Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr titanium alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.C.; Hein, R.A.; He, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Ren, F.; Stock, H.R. Superconductivity of Titanium. J. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V/TiB composites with randomly oriented and aligned TiB reinforcements. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2427–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.T.; Dong, L.I.U.; Tian, X.J.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, H.M. Microstructure of TA2/TA15 graded structural material by laser additive manufacturing process. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.; Chai, L.; Yang, X.; Xu, Q. Microstructure, texture evolution and mechanical properties of pure Ti by friction stir processing with slow rotation speed. Mater. Charact. 2019, 148, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Development of grain structure during friction stir welding of pure titanium. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4519–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Liao, J.; Gao, Y.; Nakata, K. Influence of texture on strain localization in stir zone of friction stir welded titanium. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 626, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, H.; Cai, M.; Yang, W.; Li, J. Ultra-grain refinement and enhanced low-temperature superplasticity in a friction stir-processed Ti—6Al—4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2018, 727, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Rahman, K.; Khan, F.; Bakhsh, N.; Baig, M. Comparison of microstructure, mechanical properties, and residual stresses in tungsten inert gas, laser, and electron beam welding of Ti–5Al–2.5 Sn titanium alloy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L-J. Mater.-Des. Appl. 2019, 233, 1336–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X. Mechanical properties and microstructure in a fine grained Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–1Cr–1Fe titanium alloy deformed at a high strain rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fujii, H. Microstructural and mechanical properties of a beta-type titanium alloy joint fabricated by friction stir welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, P.J.; Jun, T.; Zhang, Z.; Britton, T.B.; Harte, A.M.; Leen, S.B.; Dunne, F.P.E. The effect of the beta phase on the micromechanical response of dual-phase titanium alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 100, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolubaev, E.A.; Luo, A.A. A Distinctions of structure forming of welded joints produced by friction stir welding. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threadgill, P.L. Terminology in friction stir welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2007, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Park, S.H.C.; Matsunaga, A.; Honda, A.; Kokawa, H. Novel production for highly formable Mg alloy plate. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Luo, S.; Dong, F.; Guo, N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of bobbin tool friction stir welded ZK60 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 776, 138953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Truster, T.; Das, H.; Gupta, V.; Soulami, A.; Upadhyay, P.; Herling, D. Microstructure-Based Modeling of Friction Stir Welded Joint of Dissimilar Metals Using Crystal Plasticity. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 143, 121008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Gupta, V.; Ortiz, A.; Das, H.; Upadhyay, P.; Barker, E.; Herling, D. Determining cohesive parameters for modeling interfacial fracture in dissimilar-metal friction stir welded joints. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2021, 216, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; De, A.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; DebRoy, T. Review: Friction stir welding tools. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, A.; Batalha, G.F.; Prados, E.F.; Magnabosco, R.; Delijaicov, S. Tool wear evaluations in friction stir processing of commercial titanium Ti–6Al–4V. Wear 2013, 302, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Park, S.H.C.; Hirano, S. Stir zone microstructure of commercial purity titanium friction stir welded using pcBN tool. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.H.; Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Tool wear and its effect on microstructure and properties of friction stir processed Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 146, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Friction-stir welding and processing of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurianov, D.A.; Fortuna, S.V.; Nikonov, S.Y.; Moskvichev, E.N.; Kolubaev, E.A. Heat Input Effect on the Structure of ZhS6U Alloy. Russ. Phys. J. 2021, 64, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, A.; Vorontsov, A.; Chumaevskii, A.; Gurianov, D.; Gusarova, A.; Kolubaev, E.; Tarasov, S. Structural evolution of contact parts of the friction stir processing heat-resistant nickel alloy tool used for multi-pass processing of Ti6Al4V/ (Cu+Al) system. Wear 2022, 488, 204138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.I.; Eliseev, A.A.; Rubtsov, V.E.; Utyaganova, V.R. Butt friction stir welding of commercially pure titanium by the tool from a heat-resistant nickel alloy. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2167, 020016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.I.; Eliseev, A.A.; Beloborodov, V.A.; Chumaevskii, A.V.; Gurianov, D.A. Formation of α’titanium welds by friction stir welding. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1611, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.; Eliseev, A.; Kolubaev, E.; Filippov, A.; Rubtsov, V. Wear of ZhS6U nickel superalloy tool in friction stir processing on commercially pure titanium. Metals 2020, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.I.; Chumaevskii, A.V.; Vorontsov, A.V. Formation of (α+ β) titanium welds by friction stir welding using heat-resistant alloy tool. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2310, 020017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, V.K.; Soderlind, J.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Microstructure, mechanical and wear properties of laser surface melted Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 32, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Grain structure evolution during friction-stir welding. Phys. Mesomech. 2020, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhou, L. Microstructural zones and tensile characteristics of friction stir welded joint of TC4 titanium alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippold, J.C.; Livingston, J.J. Microstructure evolution during friction stir processing and hot torsion simulation of Ti—6Al—4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3815–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.; Ramulu, M. Fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth in Ti—6Al—4V friction stir welds. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, Q.W. Effect of rotation speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti—6Al—4V friction stir welded joints. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L. Joint formation and mechanical properties of back heating assisted friction stir welded Ti—6Al—4V alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.; Fesharaki, M.H.; Khodabandeh, A.R.; Jahazi, M. Tool wear characteristics and effect on microstructure in Ti—6Al—4V friction stir welded joints. Metals 2016, 6, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, A.P.; Vorontsov, A.V.; Chumaevskii, A.V.; Gurianov, D.A.; Gusarova, A.V.; Savchenko, N.L.; Kolubaev, E.A. The Influence of Multipass Friction Stir Processing on Formation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of VT6 Alloy. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2022, 63, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










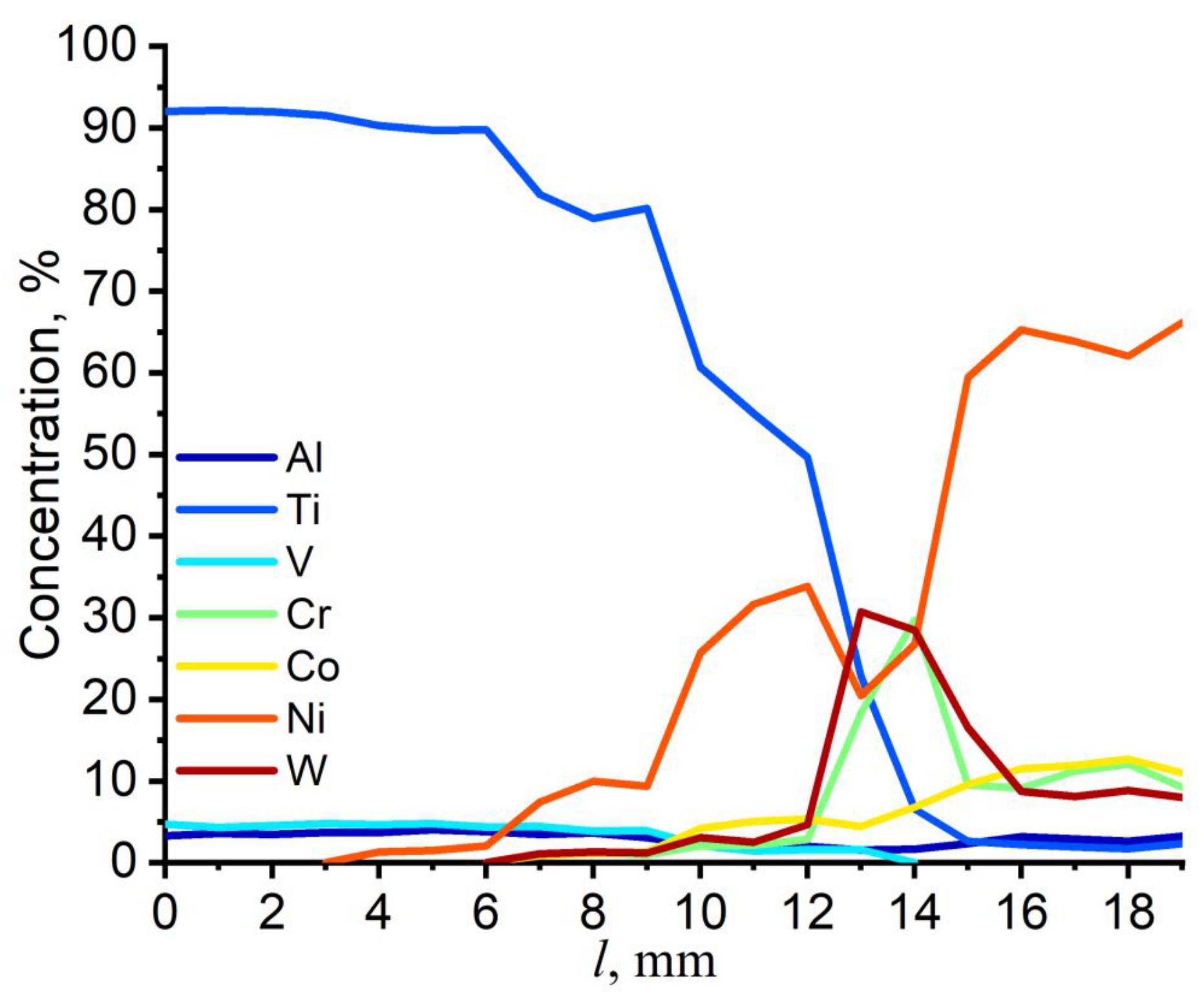


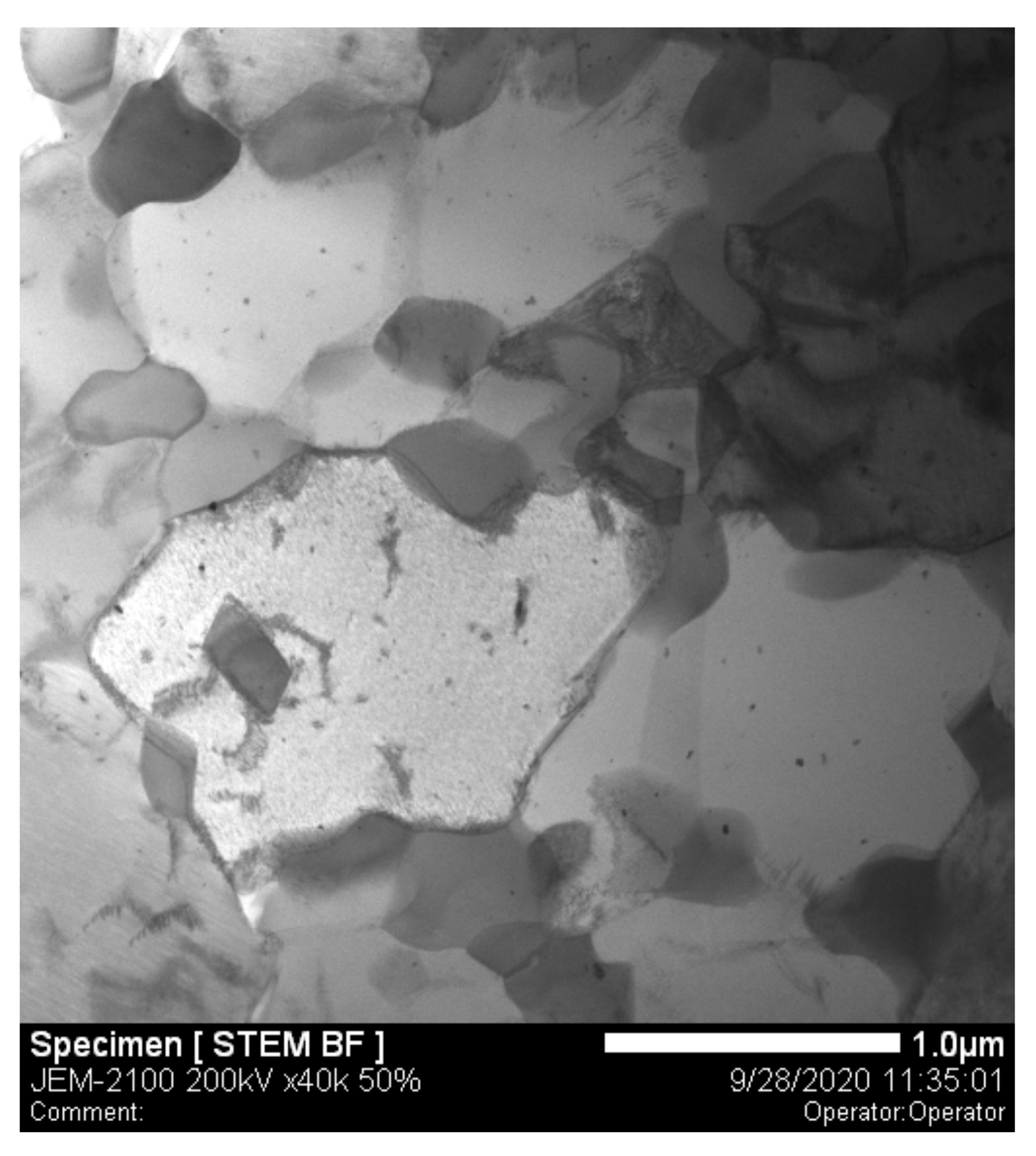
| Fe | Nb | Ti | Cr | Co | W | Ni | Al | Mo | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤1 | 0.8–1.2 | 2–2.9 | 8–9.5 | 9–10.5 | 9.5–11 | 54.3–62.7 | 5.1–6 | 1.2–2.4 | 0.13–0.2 |
| Ce | Si | Mn | P | S | Zr | Bi | B | Y | Pb |
| ≤0.02 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.0005 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 |
| Fe | C | Si | V | N | Ti | Al | Zr | O | H | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0.6 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.1 | 3.5–5.3 | ≤0.05 | 86.45–90.9 | 5.3–6.8 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.015 | 0.3 |
| Spectrum | Chemical Element Content, Atomic/Weight % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Ti | V | Cr | Co | Ni | W | |
| 1 | 9.91/5.68 | 79.35/80.71 | 3.48/3.76 | 1.13/1.24 | 0.92/1.16 | 4.85/6.05 | 0.36/1.40 |
| 2 | 9.55/5.50 | 78.41/80.16 | 3.56/3.87 | 1.09/1.21 | 1.10/1.39 | 6.28/7.86 | - |
| 3 | 9.93/5.70 | 80.22/81.79 | 3.65/3.96 | 1.00/1.10 | 0.68/0.85 | 4.18/5.22 | 0.35/1.37 |
| 4 | 9.65/5.34 | 70.04/68.82 | 3.11/3.25 | 1.94/2.07 | 1.75/2.11 | 12.69/15.28 | 0.83/3.12 |
| 5 | 8.17/4.55 | 74.06/73.23 | 3.07/3.22 | 1.80/1.93 | 1.83/2.22 | 10.53/12.76 | 0.55/2.08 |
| 6 | 9.97/5.63 | 74.24/74.40 | 3.29/3.51 | 1.31/1.42 | 1.31/1.62 | 9.39/11.54 | 0.49/1.88 |
| 7 | 10.09/5.79 | 79.23/80.69 | 3.44/3.72 | 0.82/0.91 | 1.04/1.31 | 5.06/6.31 | 0.32/1.27 |
| 8 | 9.86/5.79 | 86.42/90.09 | 3.72/4.12 | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | 9.72/5.70 | 86.59/90.20 | 3.70/4.10 | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | 9.99/5.87 | 86.14/89.84 | 3.87/4.29 | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | 10.25/6.03 | 86.28/90.12 | 3.47/3.85 | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | 9.77/5.73 | 86.19/89.79 | 4.04/4.48 | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | 10.13/5.96 | 85.95/89.69 | 3.92/4.35 | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | 10.08/5.79 | 80.18/81.69 | 3.43/3.71 | 0.84/0.93 | 0.67/0.84 | 4.41/5.51 | 0.39/1.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarasov, S.; Amirov, A.; Chumaevskiy, A.; Savchenko, N.; Rubtsov, V.E.; Ivanov, A.; Moskvichev, E.; Kolubaev, E. Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool. Technologies 2022, 10, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10060118
Tarasov S, Amirov A, Chumaevskiy A, Savchenko N, Rubtsov VE, Ivanov A, Moskvichev E, Kolubaev E. Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool. Technologies. 2022; 10(6):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10060118
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarasov, Sergei, Alihan Amirov, Andrey Chumaevskiy, Nikolay Savchenko, Valery E. Rubtsov, Aleksey Ivanov, Evgeniy Moskvichev, and Evgeny Kolubaev. 2022. "Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool" Technologies 10, no. 6: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10060118
APA StyleTarasov, S., Amirov, A., Chumaevskiy, A., Savchenko, N., Rubtsov, V. E., Ivanov, A., Moskvichev, E., & Kolubaev, E. (2022). Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool. Technologies, 10(6), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10060118










