Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A point-by-point discussion on whether IoT needs VLC for optimal network performance or not is presented.
- A network architecture prototype for the deployment of prospective VLC-IoT networks is proposed.
- The existing and proposed approaches used in the implementation of VLC for IoT are presented.
- The benefits and challenges of implementing VLC for IoT are presented and solutions are suggested where applicable.
- Future research directions are identified and discussed on different aspects of VLC and the application of VLC technology.
2. Related Works
3. Overview of the VLC-IoT Paradigm
3.1. VLC: An Overview
3.2. IoT: An Overview
4. VLC-IoT: Is VLC Really Necessary for IoT Networks Deployment?
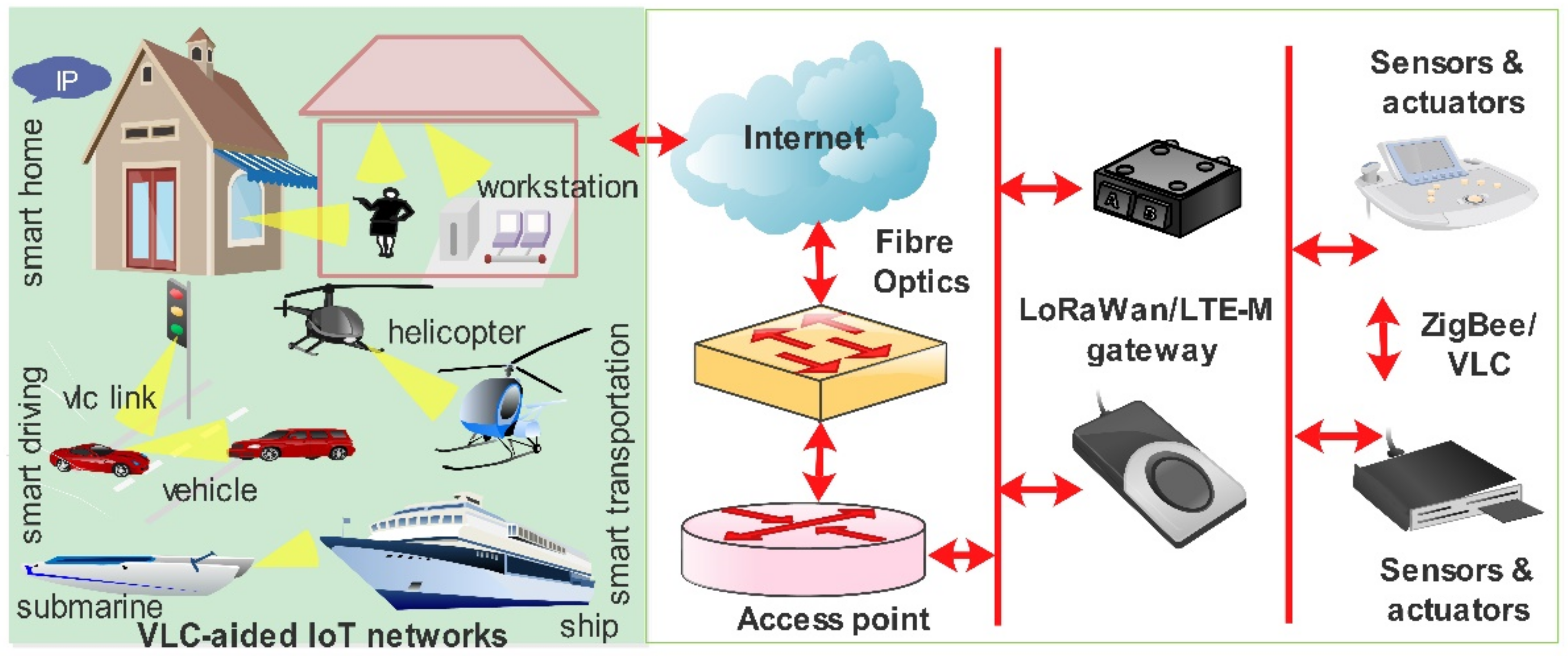
5. Proposed VLC-IoT Network Architecture
6. VLC-IoT: Existing and Proposed Approaches
6.1. Multiple Access Technique in VLC-IoT
6.1.1. Existing Approaches
- 1.
- Orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) scheme
- 2.
- Code division multiple access (CDMA) scheme
- 3.
- Space division multiple access (SDMA) scheme
- 4.
- Non orthogonal modulation access (NOMA)-aided VLC (in indoor down link VLC networks)
6.1.2. Proposed Approaches
- 1.
- NOMA to MIMO-VLC
- 2.
- Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA)-based VLCP
- 3.
- Filter bank multiple carrier (FBMC)-based VLCP
6.2. Modulation Techniques in VLC-IoT
6.2.1. Existing Approaches
- 1.
- On-off key (OOK) modulation
- 2.
- Pulse position modulation (PPM)
6.2.2. Proposed Approaches
- 1.
- Color shifting key (CSK)
- 2.
- Discrete multitone (DMT)
- 3.
- Carrier-less amplitude-phase (CAP)
6.3. Handover Mechanisms in VLC-IoT
6.3.1. Existing Approaches
- 1.
- Vertical Handover
- 2.
- Horizontal Handover
6.3.2. Proposed Approaches
- 1.
- Received signal intensity-based vertical handover (RSI-VH)
- 2.
- Non-line-of-sight-based vertical handover
6.4. VLC-IoT: Existing and Possible Network Topologies
6.4.1. Existing Network Topologies
6.4.2. Proposed Network Technology
7. VLC-IoT: VLC Benefits for IoT
- 1.
- Massive IoT device connectivity
- 2.
- Ultra-high-capacity hybrid radio-optical wireless networks
- 3.
- Low-energy-consuming networks with energy autonomous nodes
- 4.
- Highly reliable dense small cell networks for large scale VLC-IoT communications
8. VLC-IoT: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions
8.1. Challenges and Solutions
- 1.
- Limited modulation bandwidth of off-the-shelf LEDs
- 2.
- Suggested possible solutions
- 3.
- Extended link distance in outdoor VLC-IoT applications
- 4.
- Suggested possible solutions
- 5.
- Line-of-sight (LOS) signal loss and shadowing effects
- 6.
- Suggested possible solutions
- 7.
- Lack of recognized channel models for VLC-IoT communications
- 8.
- Suggested possible solutions
8.2. Future Research Directions
- 1.
- Development of improved handover mechanisms
- 2.
- Advancement of improved receiver camera for VLC-IoT infrastructure
- 3.
- Deploying VLC for vehicular communications in road tunnels
- 4.
- Software-based approach to VLC-IoT infrastructure
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cevik, T.; Yilmaz, S. An overview of visible light communication systems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Wilfert, O.; Simicek, T. Visible light communication beacon system for internet of things. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Microwave Techniques (COMITE), Brno, Czech Republic, 20–21 April 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, M.; O’Brien, D. Exploiting novel concepts for visible light communications: From light-based IoT to living surfaces. Optik 2019, 195, 163176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.N.; Salih, M.H. A review of visible light communication (VLC) technology. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; p. 020289. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, K.; Dhage, M.R. Visible light communication for IoT. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Computing and Communication Technology (iCATccT), Bengaluru, India, 21–23 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, C.; Selwal, C. Visible light communication system (VLC) Using Diversity Technique with 4 QAM OFDM FSO Link. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud), Palladam, India, 30–31 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Galisteo, A.; Juara, D.; Giustiniano, D. Research in visible light communication systems with OpenVLC1.3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 15–18 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam, K.; Pandharipande, A.; Caicedo, D. Connectivity in IoT indoor lighting systems with visible light communications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Online Conference on Green Communications (OnlineGreenComm), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 10–12 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-W.; Wang, W.-C.; Wu, J.-T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liang, K.; Wei, L.-Y.; Hsu, Y.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chow, C.-W.; Yeh, C.-H.; et al. Visible light communications for the implementation of internet-of-things. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 060501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, S.R.; Zvanovec, S.; Ghassemlooy, Z. Optical internet of things within 5G: Applications and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence System (IOTAIS), Bali, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, I.; Tanwar, S.; Tyagi, S.; Kumar, N. Blockchain for 5G-enabled IoT for industrial automation: A systematic review, solutions, and challenges. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 135, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.; Lima, E.; Cunha, M.; Abreu, M.; Arismar Cerqueira, S., Jr. RGB-based VLC system using 5G NR standard. Opt. Commun. 2021, 481, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabissi, D.; Mucchi, L.; Caputo, S.; Nizzi, F.; Pecorella, T.; Fantacci, R.; Nawaz, T.; Seminara, M.; Catani, J. Experimental measurements of a joint 5G-VLC communication for future vehicular networks. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, A.F.; AlFasfous, N.; Theodory, R.; Giha, S.; Darabkh, K.A. An experimental evaluation and prototyping for visible light communication. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 72, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibhaze, A.E.; Orukpe, P.E.; Edeko, F.O. High Capacity Data Rate System: A Review of Visible Light Communication Technology. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, W.-D.; Chen, C.; Alphones, A. Integration of visible light communication and positioning within 5G networks for Internet of Things. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Dobesch, A.; Wilfert, O. On human to database interface based on visible light communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 Global LIFI Congress (GLC), Paris, France, 8–9 February 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jurczak, C. LiFi: Enlightening communications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.01471 v2. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Chung, W.-Y. A novel indoor healthcare with time hopping-based visible light communication. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Reston, VA, USA, 12–14 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Vanus, J.; Stratil, T.; Martinek, R.; Bilik, P.; Zidek, J. The possibility of using VLC data transfer in the smart home. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, A.U.; Braud, T.; Hui, P. Spatial Interference Detection for Mobile Visible Light Communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Liu, Q.; Sheu, P.C.-Y. Foglight: Visible light-enabled indoor localization system for low-power IoT devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 5, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, M.; Meucci, M.; Tarani, F.; Riminesi, C.; Catani, J. Characterization of a VLC system in real museum scenario using diffusive LED lighting of artworks. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, M.; Seminara, M.; Tarani, F.; Riminesi, C.; Catani, J. Visible Light Communications through Diffusive Illumination of Sculptures in a Real Museum. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, M.; Seminara, M.; Nawaz, T.; Caputo, S.; Mucchi, L.; Catani, J. Bidirectional Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication System Based on VLC: Outdoor Tests and Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.; Ahmed, I. Opportunities and challenges for visible light communications in 6G. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd 6G wireless summit (6G SUMMIT), Levi, Finland, 17–20 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Almadani, Y.; Plets, D.; Bastiaens, S.; Joseph, W.; Ijaz, M.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Rajbhandari, S. Visible Light Communications for Industrial Applications—Challenges and Potentials. Electronics 2020, 9, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.Z.; Hasan, M.K.; Shahjalal, M.; Shin, E.B.; Jang, Y.M. Opportunities of optical spectrum for future wireless communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Okinawa, Japan, 11–12 February 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 004–007. [Google Scholar]
- Ndiaye, M.; Oyewobi, S.S.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P.; Kurien, A.M.; Djouani, K. IoT in the wake of COVID-19: A survey on contributions, challenges and evolution. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 186821–186839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewobi, S.S.; Djouani, K.; Kurien, A.M. A review of industrial wireless communications, challenges, and solutions: A cognitive radio approach. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020, 31, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefti, S.; Oussalah, M.; Djouani, K.; Pontnau, J. Intelligent adaptive mobile robot navigation. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2001, 30, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olwal, T.O.; Djouani, K.; Kurien, A. A survey of resource management toward 5G radio access networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1656–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, H.; Soyata, T.; Kantarci, B.; Boukerche, A.; Kaptan, C. Sensing, communication and security planes: A new challenge for a smart city system design. Comput. Netw. 2018, 144, 163–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinowski, G. Security of visible light communication systems—A survey. Phys. Commun. 2019, 34, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, R.J.; Goyal, R.; Kundu, R.K. Fault-tolerant and medium access control (FTMAC) protocol for IoT over VLC. In Proceedings of the 2019 TEQIP III Sponsored International Conference on Microwave Integrated Circuits, Photonics and Wireless Networks (IMICPW), Tiruchirappalli, India, 22–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, W.-D.; Chen, C.; Alphones, A.; Du, P. QoS-driven optimized design-based integrated visible light communication and positioning for indoor IoT networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, W.-D.; Chen, C.; Alphones, A.; Du, P.; Zhang, S.; Xie, X. Coordinated resource allocation-based integrated visible light communication and positioning systems for indoor IoT. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 4671–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkol, I.; Camps-Mur, D.; Paradells, J.; Combalia, M.; Popoola, W.; Haas, H. Powering the internet of things through light communication. IIEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palathingal, P.; Yuksel, M.; Guvenc, I.; Pala, N. A multi-element VLC architecture for high spatial reuse. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Visible Light Communications Systems, Paris, France, 11 September 2015; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Rajo, F.; Melian-Segura, A.; Guerra, V.; Perez-Jimenez, R.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, D. Hybrid rf/vlc network architecture for the internet of things. Sensors 2020, 20, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cen, N.; Jagannath, J.; Moretti, S.; Guan, Z.; Melodia, T. LANET: Visible-light ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 84, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, A.; Baig, S.; Asif, H.M. Non Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) for broadband communication in smart grids using VLC and PLC. Optik 2019, 188, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Li, R. Enhancing power allocation efficiency of NOMA aided-MIMO downlink VLC networks. Opt. Commun. 2019, 454, 124497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazarel, Y.K.; Yılmaz, A. Efficient scheduling and power allocation for multiuser decoding receivers in OFDMA networks with minimum rate requirements. Phys. Commun. 2018, 26, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georlette, V.; Moeyaert, V.; Bette, S.; Point, N. Outdoor Optical Wireless Communication: Potentials, standardization and challenges for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 29th Wireless and Optical Communications Conference (WOCC), Newark, NJ, USA, 1–2 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Gong, C.; Huang, N.; Xu, Z. Indoor Visible Light Communication Scheduling for IOT Scenarios with Short Blocklength. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Xiamen, China, 9–11 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Albraheem, L.I.; Alhudaithy, L.H.; Aljaser, A.A.; Aldhafian, M.R.; Bahliwah, G.M. Toward designing a Li-Fi-based hierarchical IoT architecture. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 40811–40825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepniak, G.; Schüppert, M.; Bunge, C.-A. Advanced modulation formats in phosphorous LED VLC links and the impact of blue filtering. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 4413–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Cai, S.; Yao, S.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. On the benefit of DMT modulation in nonlinear VLC systems. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 2618–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.M.; Cossu, G.; Corsini, R.; Choudhury, P.; Ciaramella, E. 1-Gb/s transmission over a phosphorescent white LED by using rate-adaptive discrete multitone modulation. IEEE Photon-J. 2012, 4, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, L.; Wei, J.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H.; Cunningham, D.G. 3 Gbit/s LED-based step index plastic optical fiber link using multilevel pulse amplitude modulation. In Proceedings of the 2013 Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition and the National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.M.; Lin, C.T.; Wei, C.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Huang, H.T.; Chi, S. Performance comparison of OFDM signal and CAP signal over high capacity RGB-LED-based WDM visible light communication. IEEE Photon-J. 2013, 5, 7901507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, M.M.; Guan, H.; Chassagne, L. Experimental multi-user visible light communication attocell using multiband carrierless amplitude and phase modulation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12742–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akande, K.O.; Haigh, P.A.; Popoola, W.O. On the implementation of carrierless amplitude and phase modulation in visible light communication. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 60532–60546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, M.I.; Zuo, T.; Jensen, J.B.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, X.; Popov, S.; Monroy, I.T. Multiband carrierless amplitude phase modulation for high capacity optical data links. J. Light. Technol. 2013, 32, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inn, A.; Hassan, R.; Aman, A.H.M.; Latiff, L.A. Framework for Handover process using Visible Light Communications in 5G. In Proceedings of the 2019 Symposium on Future Telecommunication Technologies (SOFTT), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 18–20 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Khreishah, A.; Paez, J. Passiveretro: Enabling completely passive visible light localization for IoT applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1540–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Mohammad, M.; Saha, S.; Chan, M.C.; Gilbert, S.; Leong, D. PSync: Visible light-based time synchronization for Internet of Things (IoT). In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2016—The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 April 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Monmasson, E.; Idkhajine, L.; Cirstea, M.N.; Bahri, I.; Tisan, A.; Naouar, M.W. FPGAs in industrial control applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 7, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.; Figueiredo, M.; Alves, L. Optimized Analog Multi-Band Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation for Visible Light Communication-Based Internet of Things Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.; Lloret, J.; Zikria, Y.B. Internet of Things (IoT)-Based Wireless Health: Enabling Technologies and Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellam, J.; Jeyachitra, R.K. Energy-efficient bi-directional visible light communication using thin-film corner cube retroreflector for self-sustainable IoT. IET Optoelectron. 2020, 14, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georlette, V.; Moeyaert, V.; Bette, S.; Point, N. Visible Light Communication Challenges in the Frame of Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 19–23 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yuksel, H.; Altunay, Ö. Host-to-host TCP/IP connection over serial ports using visible light communication. Phys. Commun. 2020, 43, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Ma, Z.; Ding, Z.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Simultaneous lightwave information and power transfer: Policies, techniques, and future directions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28250–28257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perković, T.; Čagalj, M.; Kovačević, T. LISA: Visible light based initialization and SMS based authentication of constrained IoT devices. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn, A.; Hoeher, P.A.; Pachnicke, S. Visible light tricolor LED-to-camera data transmission suitable for Internet-of-Things and sensor applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Roma, Italy, 23–27 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Haus, M.; Ding, A.Y.; Ott, J. LocalVLC: Augmenting smart IoT services with practical visible light communication. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 20th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks"(WoWMoM), Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Zapata, E.; Guerra, V.; Rabadan, J.; Perez-Jimenez, R.; Luna-Rivera, J.M. Vehicular communications in tunnels using VLC. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on Telecommunications (ConTEL), Graz, Austria, 3–5 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, T.R.; Mangold, S.; Schmid, S. Software-centric VLC networking for the IoT. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Photonics Society Summer Topical Meeting Series (SUM), Newport Beach, CA, USA, 11–13 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.-M.; Choi, S.-I.; Koh, S.-J. IDMP-VLC: IoT device management protocol in visible light communication networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeongchang, Korea, 19–22 February 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 578–583. [Google Scholar]


| Ref. | Year | Applied VLC for | Proposed a VLC Design/ Architecture | Reviewed Prospects and Approaches of VLC | Reviewed VLC-IoT Challenges | Offered Solutions to Challenges | Identified Future Research Directions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | 2015 | VLC systems | ✓ | X | X | X | X |
| [5] | 2016 | IoT | ✓ | X | X | X | X |
| [9] | 2016 | IoT | ✓ | X | X | X | X |
| [18] | 2018 | VLC systems | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X |
| [28] | 2019 | 5G, IoT | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | X |
| [3] | 2019 | IoT, LS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| [4] | 2020 | V2V, LiFi | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| [26] | 2020 | 6G | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| [27] | 2020 | Industrial application | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| [10] | 2020 | OIoT | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| This paper | 202x | IoT | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S/N | Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Limited modulation bandwidth of off-the-shelf LEDs. | 1. The use of multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) advanced modulation and multiple access schemes; 2. the use of smart LEDs. |
| 2 | Extended link distance in outdoor VLC-IoT applications. | 1. Using relays to extend the transmission range of VLC-IoT applications; 2. deploying LEDs-to-camera VLC for extended range of transmission; 3. development of hybrid OFDM and CDMA resource allocation algorithms. |
| 3 | Line-of-sight (LOS) signal loss and shadowing effects. | 1. Using high spatial diversity to guaranteed connection; 2. use multiple MIMO antennas to reduce the risk of LOS signal loss due to interrupted signals; 3. using transmitters with ultra-wide FOVs to eliminate loss of signals. |
| 4 | Lack of recognized channel models for VLC-IoT communications. | 1. Study characteristics and theoretical details of indoor and outdoor VLC; 2. Validate identified channel model in different transmission medium for possible standardization |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oyewobi, S.S.; Djouani, K.; Kurien, A.M. Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions. Technologies 2022, 10, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10010028
Oyewobi SS, Djouani K, Kurien AM. Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions. Technologies. 2022; 10(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleOyewobi, Stephen S., Karim Djouani, and Anish Matthew Kurien. 2022. "Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions" Technologies 10, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10010028
APA StyleOyewobi, S. S., Djouani, K., & Kurien, A. M. (2022). Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions. Technologies, 10(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10010028







