Longitudinal Changes of Deep and Surface Learning in a Constructivist Pharmacy Curriculum
Abstract
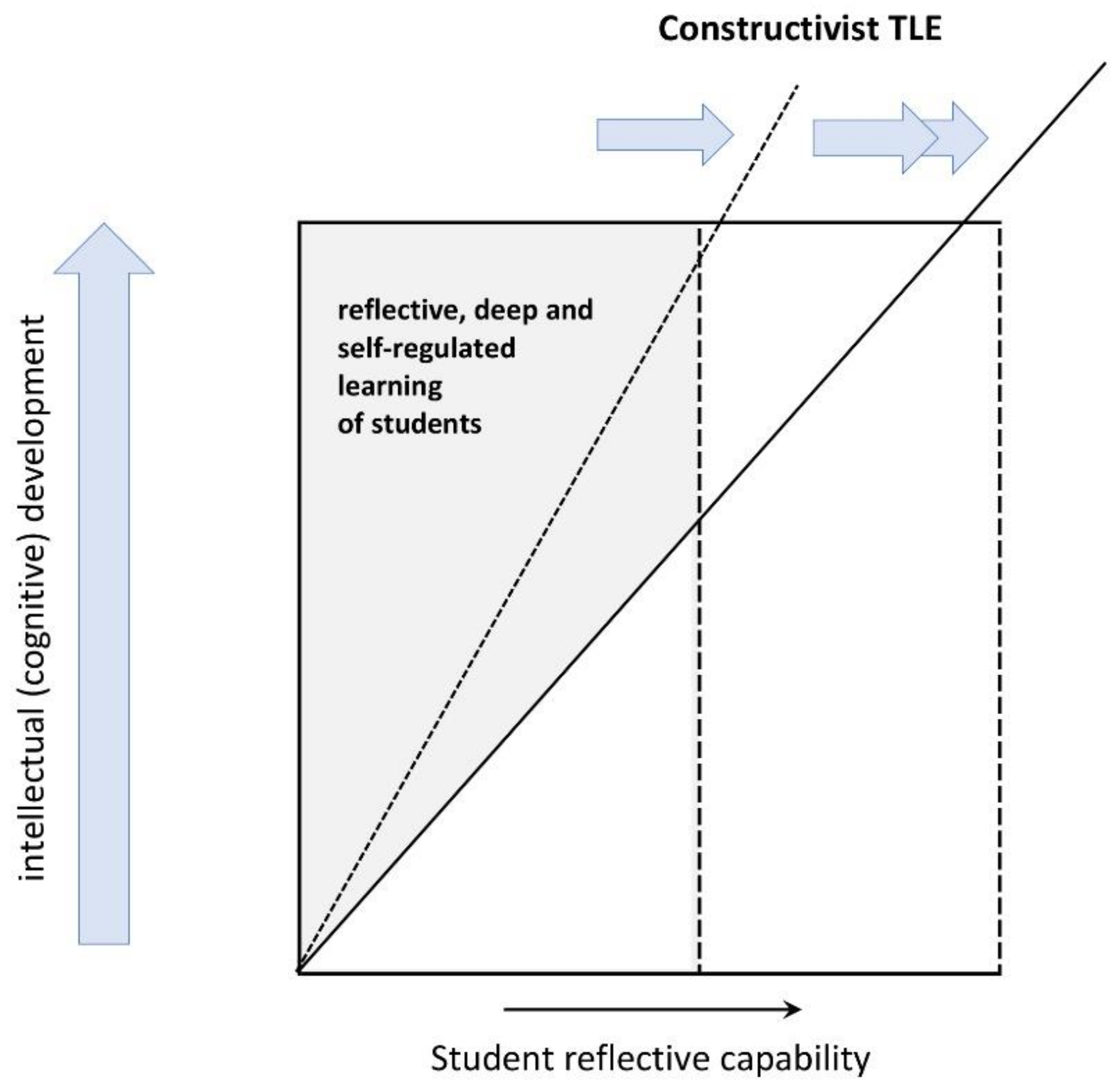
1. Introduction
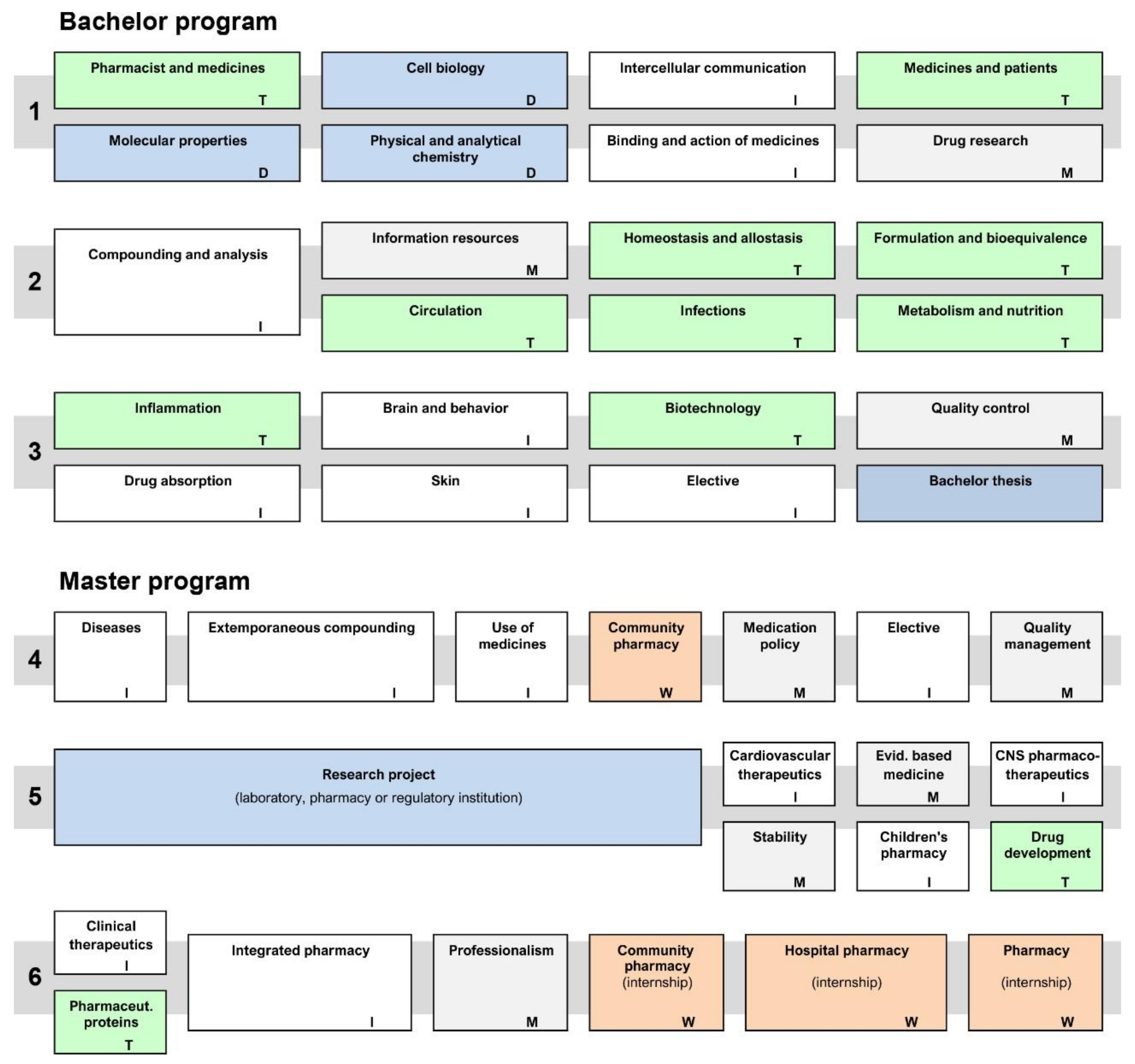
2. Context: The Undergraduate Curriculum
3. Methods
- ils0102: Deep processing was calculated as the average of ils01 (relating and structuring) and ils02 (critical processing);
- ils0304: Stepwise processing was calculated as the average of ils03 (memorizing and rehearsing) and ils04 (analyzing);
- ils0607: Self-regulation was calculated as the average of ils06 (self-regulation of learning process and outcomes) and ils07 (self-regulation of learning contents);
- ils0809: External regulation was calculated as the average of ils08 (external regulation of learning process) and ils09 (external regulation of learning outcomes).
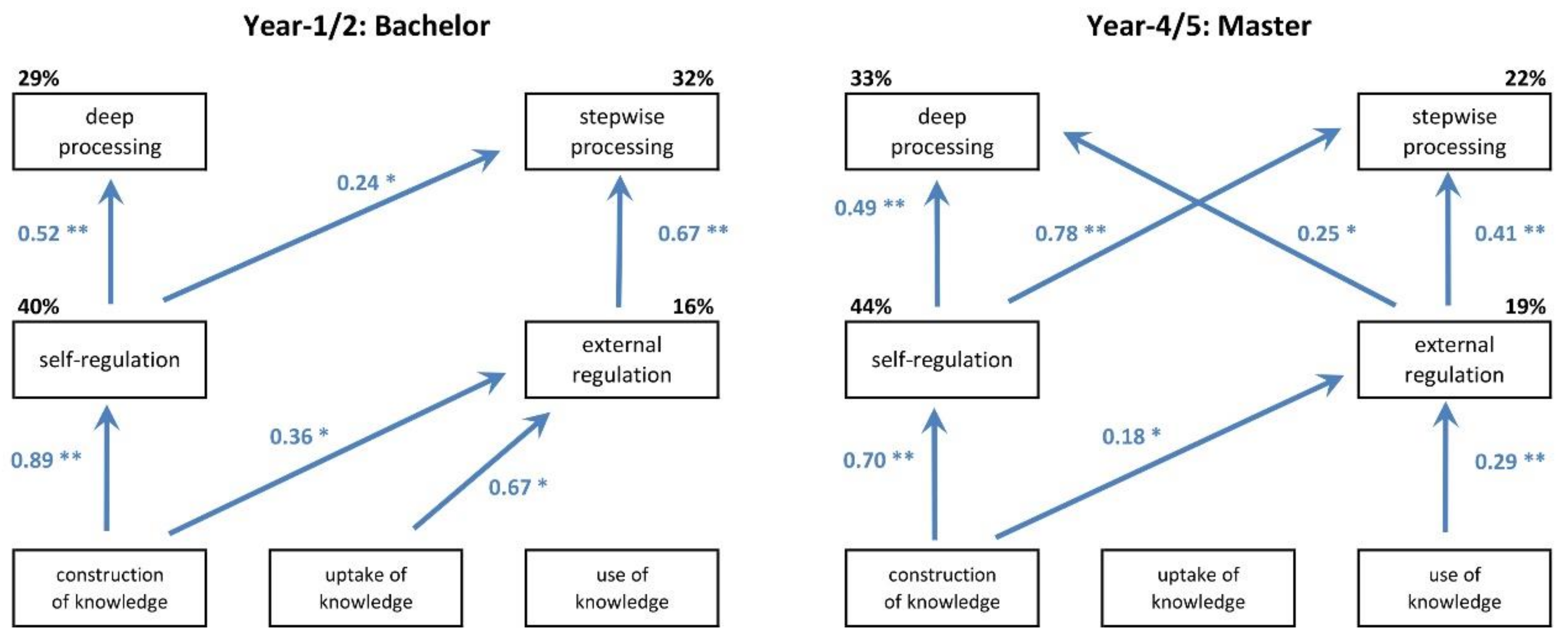
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Scale (# of Items) Scale Name | Scale Description Example Item |
|---|---|
| Processing Strategies | |
| ils01 (7 items) Relating and structuring | Relating elements of the subject matter to each other and to prior knowledge; structuring these elements into a whole. I try to discover the similarities and differences between the theories that are dealt with in a course. |
| ils02 (4 items) Critical processing | Forming one’s own view of the subjects that are dealt with, drawing one’s own conclusions, and being critical of the conclusions drawn by textbook authors and teachers. I check whether the conclusions drawn by the authors of a textbook follow the facts on which they are based logically. |
| ils03 (5 items) Memorizing and rehearsing | Learning facts, definitions, lists of characteristics, and the like by heart by rehearsing them. I repeat the main parts of the subject matter until I know them by heart. |
| ils04 (6 items) Analyzing | Going through the subject matter in a stepwise fashion and studying the separate elements thoroughly, in detail and one by one. I work through a chapter in a textbook item by item and I study each part separately. |
| ils05 (5 items) Concrete processing | Concretizing and applying subject matter by connecting it to one’s own experiences and by using in practice what one learns in a course. I pay particular attention to those parts of a course that have practical utility. |
| scale (# of items) Scale name | Scale description Example item |
| Regulation strategies | |
| ils06 (7 items) Self-regulation Learning process and outcomes | Regulating one’s own learning processes through regulation activities like planning learning activities, monitoring progress, diagnosing problems, testing one’s outcomes, adjusting, and reflecting. To test my learning progress when I have studied a textbook, I try to formulate the main points in my own words. |
| ils07 (4 items) Self-regulation Learning contents | Consulting literature and sources outside the syllabus. If I do not understand a study text well, I try to find other literature about the subject concerned. |
| ils08 (6 items) External regulation Learning process | Letting one’s own learning processes be regulated by external sources, such as introductions, learning objectives, directions, questions, or assignments of teachers or textbook authors. I study the subject matter in the same sequence as it is dealt with in the course. |
| ils09 (5 items) External regulation Learning outcomes | Testing one’s learning outcomes by external means, such as the tests, assignments, and questions provided. If I am able to complete all the assignments given in the study materials or by the teacher, I decide that I have a good command of the subject matter. |
| ils10 (6 items) Lack of regulation | Monitoring difficulties with the regulation of one’s own learning processes. I notice that it is difficult for me to determine whether I have mastered the subject matter sufficiently. |
| Conceptions of learning | |
| ils11 (9 items) Construction of knowledge | Learning viewed as constructing one’s own knowledge and insights. Most learning activities are seen as tasks of students. If I have difficulty understanding a particular topic, I should consult other books of my own accord. |
| ils12 (9 items) Intake of knowledge | Learning viewed as taking in knowledge provided by education through memorizing and reproducing; other learning activities are tasks of teachers. For me, learning means trying to remember the subject matter I am given. |
| ils13 (6 items) Use of knowledge | Learning viewed as acquiring knowledge that can be used by means of concretising and applying. These activities are seen as tasks of both students and teachers. The things I learn have to be useful for solving practical problems. |
| ils14 (8 items) Stimulating education | Learning activities are viewed as tasks of students, but teachers and textbook authors should continuously stimulate students to use these activities. The course team should encourage me to compare the various theories that are dealt with in a course. |
| ils15 (8 items) Cooperative learning | Attaching a lot of value to learning in co-operation with fellow students and sharing the tasks of learning with them. I have the need to work together with other students in my studies. |
| scale (# of items) Scale name | Scale description Example item |
| Learning orientations | |
| ils16 (5 items) Personally interested | Studying out of interest in the course subjects and to develop oneself as a person. I do these studies out of sheer interest in the topics that are dealt with. |
| ils17 (5 items) Certificate oriented | Striving for high study achievements; studying to pass examinations and to obtain certificates, credit points, and a degree. I study above all to pass the exam. |
| ils18 (5 items) Selftest oriented | Studying to test one’s own capabilities and to prove to oneself and others that one is able to cope with the demands of higher education I want to test myself to see whether I am capable of doing studies in higher education. |
| ils19 (5 items) Vocation oriented | Studying to acquire professional skill and to obtain a(nother) job. I have chosen this subject area because I am highly interested in the type of work for which it prepares. |
| ils20 (5 items) Ambivalent | A doubtful, uncertain attitude toward the studies, one’s own capabilities, the chosen subject area, the type of education, etc. I am afraid these studies are too demanding for me. |
Appendix B
| ils0102 | ils0304 | ils0607 | ils0809 | ils11 | ils12 | ils13 | |
| ils0102 | 1.000 | ||||||
| ils0304 | 0.191 | 1.000 | |||||
| ils0607 | 0.539 *** | 0.438 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| ils0809 | 0.146 | 0.481 *** | 0.300 ** | 1.000 | |||
| ils11 | 0.344 *** | 0.287 ** | 0.628 *** | 0.254 * | 1.000 | ||
| ils12 | −0.168 | 0.535 *** | −0.009 | 0.340 *** | 0.161 | 1.000 | |
| ils13 | 0.036 | 0.100 | 0.185 | 0.171 | 0.434 *** | 0.108 | 1.000 |
| ils0102 | ils0304 | ils0607 | ils0809 | ils11 | ils12 | ils13 | |
| ils0102 | 1.000 | ||||||
| ils0304 | 0.324 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| ils0607 | 0.468 *** | 0.357 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| ils0809 | 0.420 *** | 0.369 *** | 0.210 | 1.000 | |||
| ils11 | 0.454 *** | 0.261 * | 0.673 *** | 0.173 | 1.000 | ||
| ils12 | −0.116 | 0.375 *** | 0.051 | 0.218 * | −0.026 | 1.000 | |
| ils13 | 0.331 ** | 0.136 | −0.068 | 0.427 *** | 0.158 | 0.011 | 1.000 |
References
- Van Mil, J.W.F.; Schulz, M.; Tromp, T.F.J. Pharmaceutical Care, European Developments in Concepts, Implementation, Teaching, and Research: A Review. Pharm. Worlds Sci. 2004, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R. Policy and Professionalism in Pharmacy Education. Pharm. Educ. 2011, 11, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen-Koutaniemi, M.; Katajavuori, N. Enhancing the Development of Pharmacy Education by Changing Pharmacy Teaching. Pharm. Educ. 2006, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanudulkitti, C.; Farris, K.B.; Makmee, P.; Kittisopee, T. Deep Approach to Learning of Pharmacy Students: A Multilevel Analysis. Pharm. Educ. 2018, 18, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, W.G. Forms of Intellectual and Ethical Development in the College Years: A Scheme; Holt, Rinehart and Winston: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Brent, R. The Intellectual Development of Science and Engineering Students. Part 1: Models and Challenges. J. Eng. Educ. 2004, 93, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.M. Principles of Development and Developmental Change Underlying Theories of Cognitive and Moral Development. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2009, 50, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.T.E. Epistemological Development in Higher Education. Educ. Res. Rev. 2013, 9, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J.C.; Lee, S.H.; Litzinger, T.; Marra, R.M.; Palmer, B. A Report on a Four-year Longitudinal Study of Intellectual Development of Engineering Undergraduates. J. Adult Dev. 2004, 11, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, R.; Palmer, B. Encouraging Intellectual Growth: Senior College Student Profiles. J. Adult Dev. 2004, 11, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonka, K.; Lindblom-Ylänne, S. Epistemologies, Conceptions of Learning, and Study Practices in Medicine and Psychology. High. Educ. 1996, 31, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muis, K.R.; Duffy, M.C. Epistemic Climate and Epistemic Change: Instruction Designed to Change Students’ Beliefs and Learning Strategies and Improve Achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 105, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Päuler-Kuppinger, L.; Jucks, R. Perspectives on Teaching: Conceptions of Teaching and Epistemological Beliefs of University Academics and Students in Different Domains. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2017, 18, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonka, K.; Ketonen, E.; Vermunt, J.D. University Students’ Epistemic Profiles, Conceptions of Learning, and Academic Performance. High. Educ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.M.; Brent, R. The Intellectual Development of Science and Engineering Students. Part 2: Teaching to Promote Growth. J. Eng. Educ. 2004, 93, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Veken, J.; Valcke, M.; De Maeseneer, J.; Derese, A. Impact of the Transition from a Conventional to an Integrated Contextual Medical Curriculum on Students’ Learning Patterns: A Longitudinal Study. Med. Teach. 2009, 31, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veken, J.; Valcke, M.; Muijtjens, A.; De Maeseneer, J.; Derese, A. The Potential of the Inventory of Learning Styles to Study Students’ Learning Patterns in Three Types of Medical Curricula. Med. Teach. 2008, 30, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.; Abbiati, M.; Bonvin, R.; Gerbase, M.W.; Baroffio, A. Integrated Problem-Based Learning Versus Lectures: A Path Analysis Modelling of the Relationships between Educational Context and Learning Approaches. Med. Educ. Online 2018, 23, 1489690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tynjälä, P. Towards Expert Knowledge? A Comparison between a Constructivist and a Traditional Learning Environment in the University. Int. J. Educ. Res. 1999, 31, 357–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyens, S.M.M.; Gijbels, D. Understanding the Effects of Constructivist Learning Environments: Introducing a Multi-Directional Approach. Instr. Sci. 2008, 36, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, D. The Construction and Validation of a New Scale for Measuring Features of Constructivist Learning Environments in Higher Education. Frontline Learn. Res. 2014, 5, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Baeten, M.; Kyndt, E.; Struyven, K.; Dochy, F. Using Student-Centred Learning Environments to Stimulate Deep Approaches to Learning: Factors Encouraging Or Discouraging their Effectiveness. Educ. Res. Rev. 2010, 5, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, J.; Lindblom-Ylänne, S.; Lonka, K. The Development of Study Orientations and Study Success in Students of Pharmacy. Instr. Sci. 2004, 32, 387–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varunki, M.; Katajavuori, N.; Postareff, L. First-Year Students’ Approaches to Learning, and Factors Related to Change Or Stability in their Deep Approach during a Pharmacy Course. Stud. High. Educ. 2017, 42, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postareff, L.; Mattsson, M.; Parpala, A. The Effect of Perceptions of the Teaching-Learning Environment on the Variation in Approaches to Learning—between-Student Differences and within-Student Variation. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2018, 68, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Saini, B.; Krass, I.; Chen, T.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Sainsbury, E. Pharmacy Students’ Approaches to Learning in an Australian University. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, L.; Krass, I.; Sainsbury, E.; Rose, G. Pharmacy Students’ Approaches to Learning in Undergraduate and Graduate Entry Programs. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, A.S.; Meijerman, I.; Blom, L.T.G.; Schalekamp, T. Pharmacy Education at Utrecht University: An Educational Continuum. Dosis 2009, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, A.S.; Schalekamp, T.; Meijerman, I. Implementation of Competency-Based Pharmacy Education (CBPE). Pharmacy 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, J.D. The Regulation of Constructive Learning Processes. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 1998, 68, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, J.D.; Donche, V. A Learning Patterns Perspective on Student Learning in Higher Education: State of the Art and Moving Forward. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 29, 269–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, J.D. Surveys and Retrospective Self-Reports to Measure Strategies and Strategic Processing. In Handbook of Strategies and Strategic Processing; Dinsmore, D.L., Fryer, L.K., Parkinson, M.M., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 259–274. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, A.S.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Mulder, W.M.C.; Wilffert, B.; Schalekamp, T.; Buurma, H.; Wilting, I.; Westein, M.P.D. Alingment of CanMEDS-Based Undergraduate and Postgraduate Pharmacy Curricula in the Netherlands. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Ltd.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Asikainen, H.; Gijbels, D. Do Students Develop Towards More Deep Approaches to Learning during Studies? A Systematic Review on the Development of Students’ Deep and Surface Approaches to Learning in Higher Education. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 29, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.A.; Evans, P.; Duvall, E. Medical Students’ Approaches to Learning Over a Full Degree Programme. Med. Educ. Online 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.-K.; Elliott, D.; Fisher, D.; May, W. A Comparison of Medical Students’ Learning Approaches between the First and Fourth Years. South. Med. J. 2015, 108, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katajavuori, N.; Hakkarainen, K.; Kuosa, T.; Airaksinen, M.; Hirvonen, J.; Holm, Y. Curriculum Reform in Finnish Pharmacy Education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2009, 73, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Law, D.C.; Meyer, J.H. Initial Investigation of Hong Kong Post-Secondary Students’ Learning Patterns. Qual. Assur. Educ. 2011, 19, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyens, S.M.M.; Rikers, R.M.J.P.; Schmidt, H.G. Relationships between Students’ Conceptions of Constructivist Learning and their Regulation and Processing Strategies. Instr. Sci. 2008, 36, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmans, D.H.J.M.; Loyens, S.M.M.; Marcq, H.; Gijbels, D. Deep and Surface Learning in Problem-Based Learning: A Review of the Literature. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2016, 21, 1087–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, J.D.; Verloop, N. Congruence and Friction between Learning and Teaching. Learn. Instr. 1999, 9, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Processing Strategies | Regulation Strategies | |
|---|---|---|
| Deep learning | Deep processing scale 01: Relating and structuring scale 02: Critical processing | Self-regulation scale 06: Learning process and outcomes scale 07: Learning contents |
| Item examples | I try to combine subjects that are dealt with separately in the course into one whole I compare my view of a course topic with the views of textbook authors | To test my learning, I try to answer questions about the subject matter which I make up myself In addition to the syllabus, I study other related literature |
| Surface learning | Stepwise processing scale 03: Memorizing and rehearsing scale 04: Analyzing | External regulation scale 08: Learning process scale 09: Learning outcomes |
| Item examples | I memorize lists of characteristics of a phenomenon I analyze the separate components of a theory step by step | I study according to the instructions in the course manual I test my learning solely by completing the questions, tasks, and self-tests in the course material |
| ILS Scale | Bachelor (year 1/2) | Master (year 4/5) | p (Paired t-Test) | Effect Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Strategies | ||||||
| ils0102 | Deep processing | 2.72 ± 0.52 | 3.05 ± 0.68 | < 0.001 *** | 0.55 | ↑↑ |
| ils01 | Relating and structuring | 3.17 ± 0.60 | 3.18 ± 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.01 | |
| ils02 | Critical processing | 2.27 ± 0.58 | 2.92 ± 0.80 | < 0.001 *** | 0.94 | ↑↑↑ |
| ils0304 | Stepwise processing | 2.82 ± 0.57 | 2.98 ± 0.49 | < 0.014 * | 0.30 | ↑ |
| ils03 | Memorizing and rehearsing | 2.90 ± 0.81 | 2.91 ± 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.01 | |
| ils04 | Analyzing | 2.74 ± 0.51 | 3.04 ± 0.58 | < 0.001 *** | 0.55 | ↑↑ |
| ils05 | Concrete processing | 2.62 ± 0.63 | 3.12 ± 0.65 | < 0.001 *** | 0.78 | ↑↑ |
| Regulation Strategies | ||||||
| ils0607 | Self-regulation | 2.49 ± 0.58 | 2.92 ± 0.56 | < 0.001 *** | 0.75 | ↑↑ |
| ils06 | Learning process | 2.57 ± 0.65 | 2.78 ± 0.72 | 0.015 * | 0.31 | ↑ |
| ils07 | Contents | 2.31 ± 0.66 | 2.96 ± 0.75 | < 0.001 *** | 0.92 | ↑↑↑ |
| ils0809 | External regulation | 3.24 ± 0.50 | 3.30 ± 0.48 | 0.372 | 0.12 | |
| ils08 | Learning process | 3.00 ± 0.53 | 3.29 ± 0.62 | < 0.001 *** | 0.50 | ↑↑ |
| ils09 | Learning outcomes | 3.49 ± 0.65 | 3.00 ± 0.98 | < 0.001 *** | 0.60 | ↓↓ |
| ils10 | Lack of regulation | 2.35 ± 0.66 | 2.97 ± 0.79 | < 0.001 *** | 0.86 | ↑↑↑ |
| Conceptions of Learning | ||||||
| ils11 | Construction of knowledge | 3.25 ± 0.46 | 3.45 ± 0.57 | 0.005 ** | 0.39 | ↑ |
| ils12 | Intake of knowledge | 3.72 ± 0.43 | 3.58 ± 0.63 | 0.07 | 0.26 | |
| ils13 | Use of knowledge | 3.68 ± 0.45 | 3.44 ± 0.81 | 0.017 * | 0.38 | ↓ |
| ils14 | Stimulating education (teacher) | 3.08 ± 0.57 | 3.15 ± 0.57 | 0.32 | 0.12 | |
| ils15 | Cooperative learning (students) | 3.13 ± 0.61 | 3.07 ± 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.10 | |
| Learning Orientations | ||||||
| ils16 | Personally interested | 3.07 ± 0.46 | 3.17 ± 0.61 | 0.20 | 0.19 | |
| ils17 | Certificate oriented | 3.30 ± 0.56 | 3.19 ± 0.85 | 0.22 | 0.16 | |
| ils18 | Self-test oriented | 3.06 ± 0.81 | 3.49 ± 1.04 | < 0.001 *** | 0.46 | ↑ |
| ils19 | Vocation oriented | 3.95 ± 0.50 | 3.03 ± 1.32 | < 0.001 *** | 1.01 | ↓↓↓ |
| ils20 | Ambivalent | 2.02 ± 0.68 | 2.08 ± 0.92 | 0.58 | 0.08 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koster, A.S.; Vermunt, J.D. Longitudinal Changes of Deep and Surface Learning in a Constructivist Pharmacy Curriculum. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040200
Koster AS, Vermunt JD. Longitudinal Changes of Deep and Surface Learning in a Constructivist Pharmacy Curriculum. Pharmacy. 2020; 8(4):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040200
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoster, Andries S., and Jan D. Vermunt. 2020. "Longitudinal Changes of Deep and Surface Learning in a Constructivist Pharmacy Curriculum" Pharmacy 8, no. 4: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040200
APA StyleKoster, A. S., & Vermunt, J. D. (2020). Longitudinal Changes of Deep and Surface Learning in a Constructivist Pharmacy Curriculum. Pharmacy, 8(4), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040200






