Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
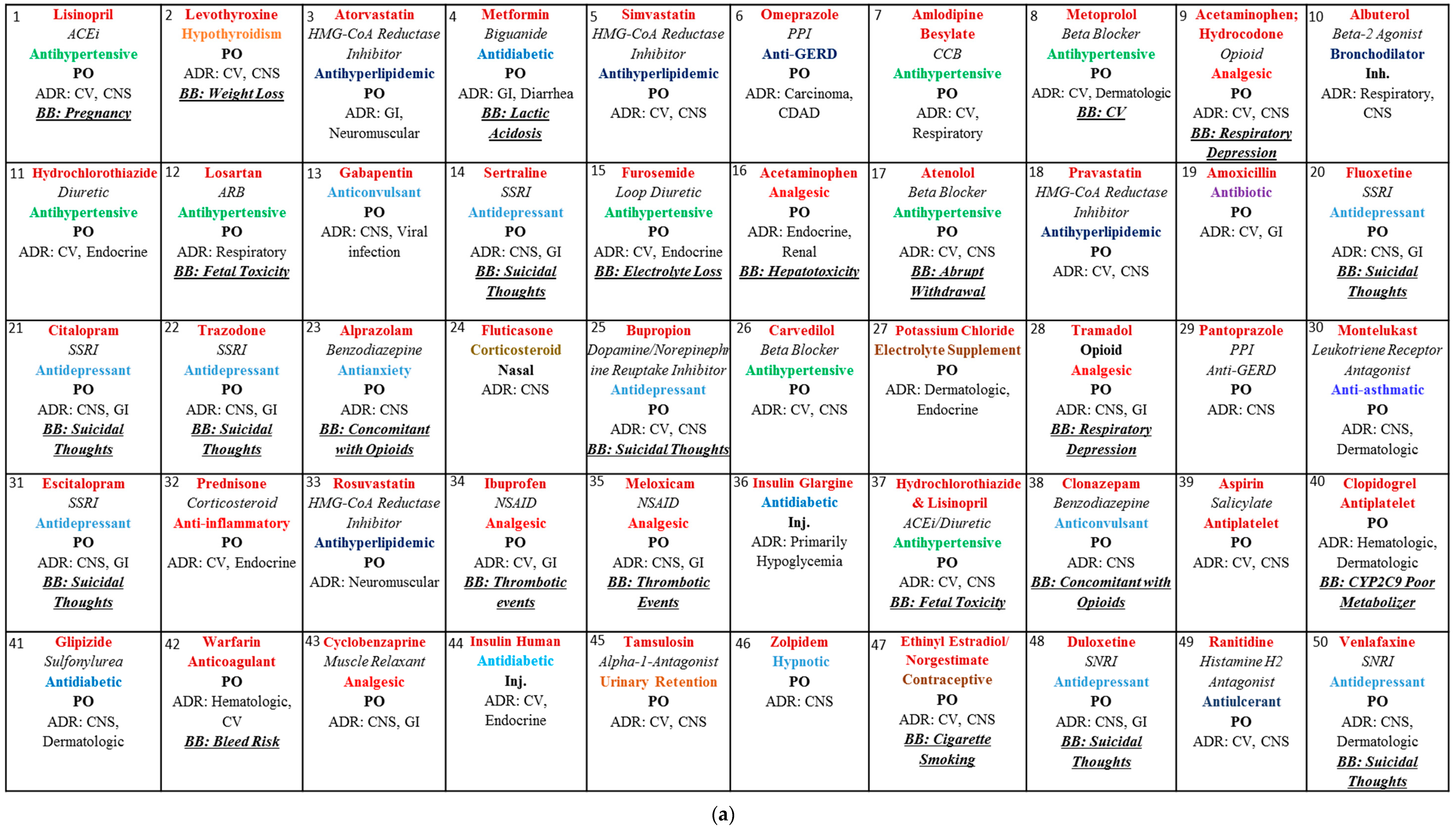
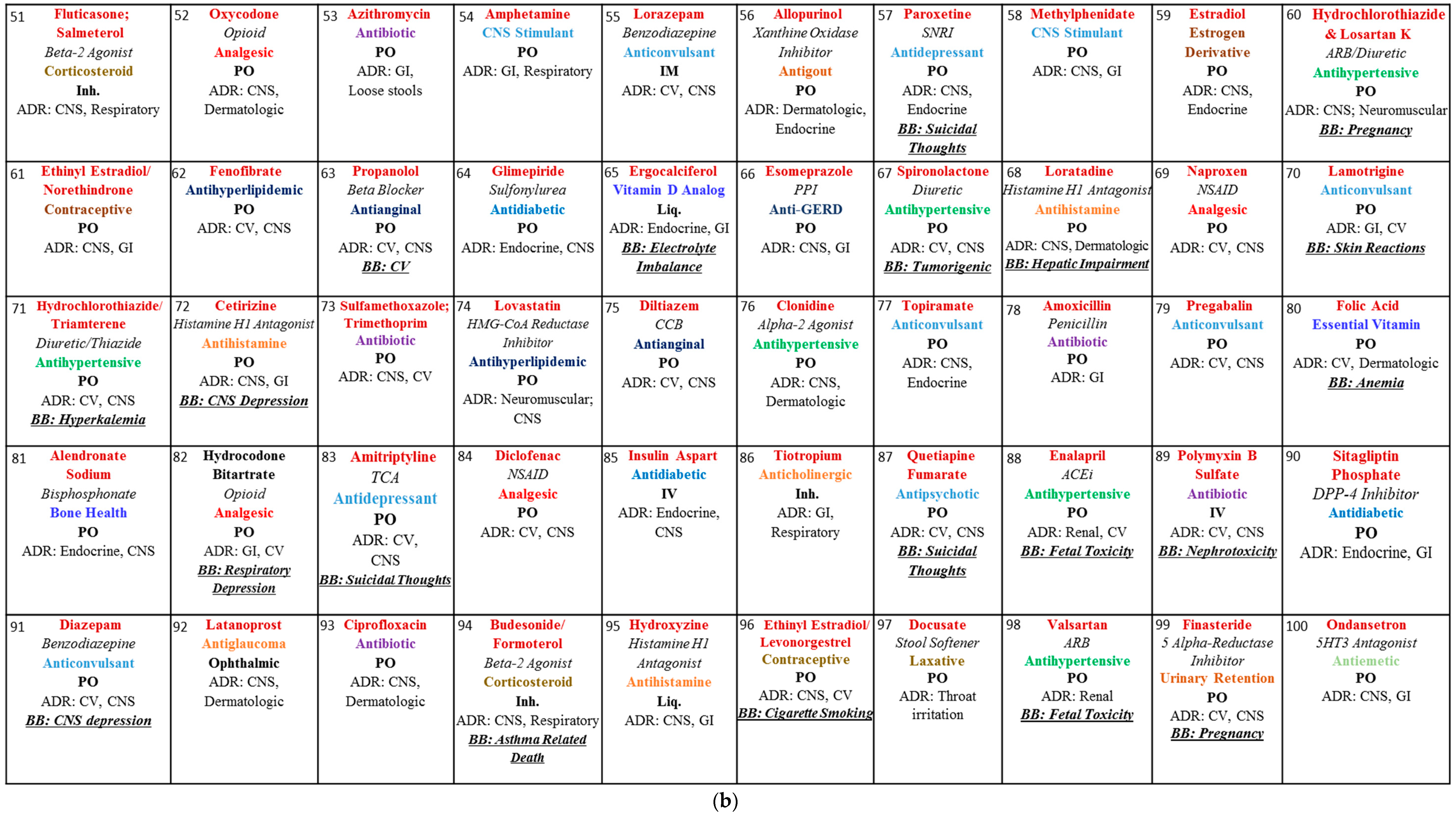
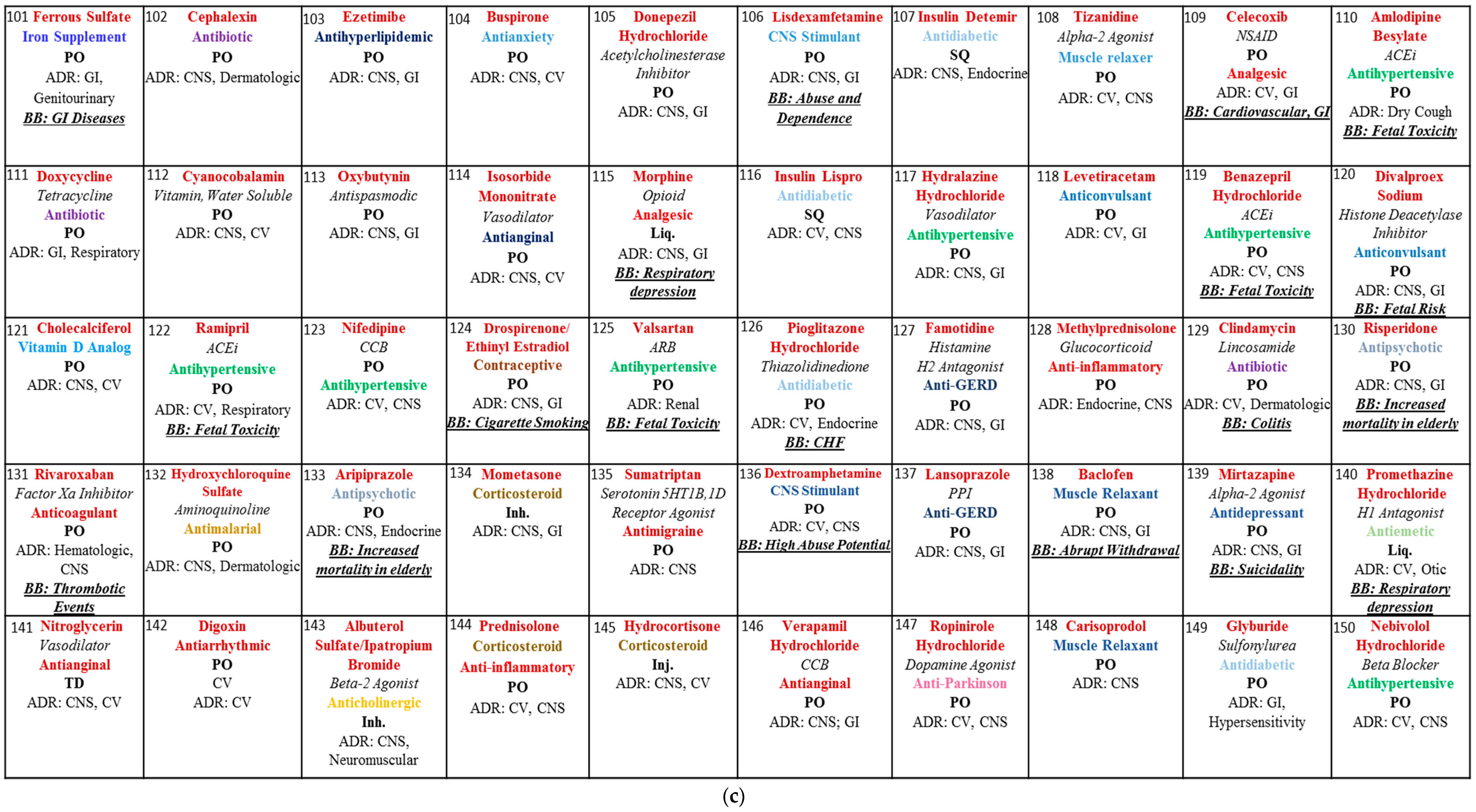
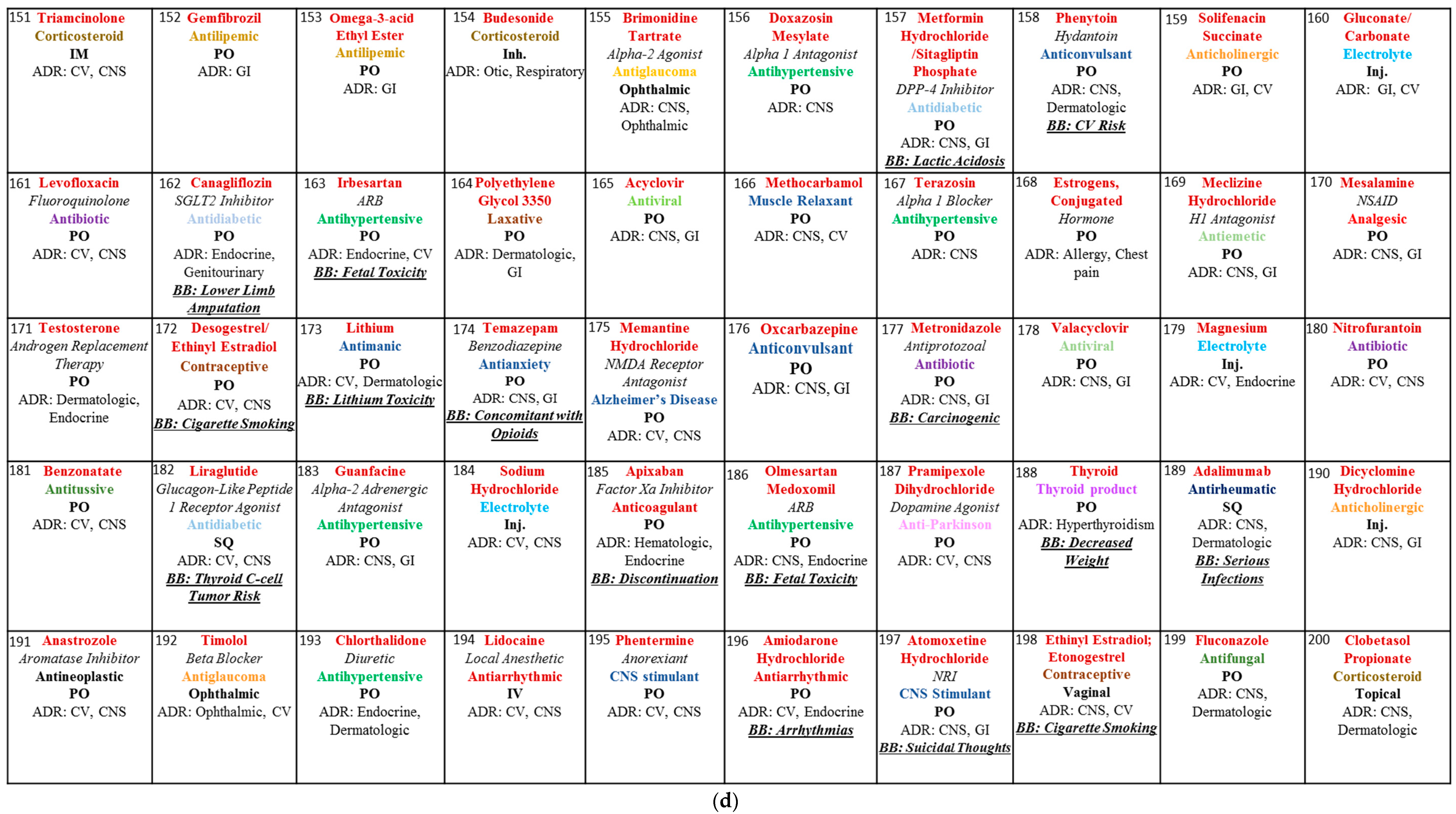
2. Materials and Methods
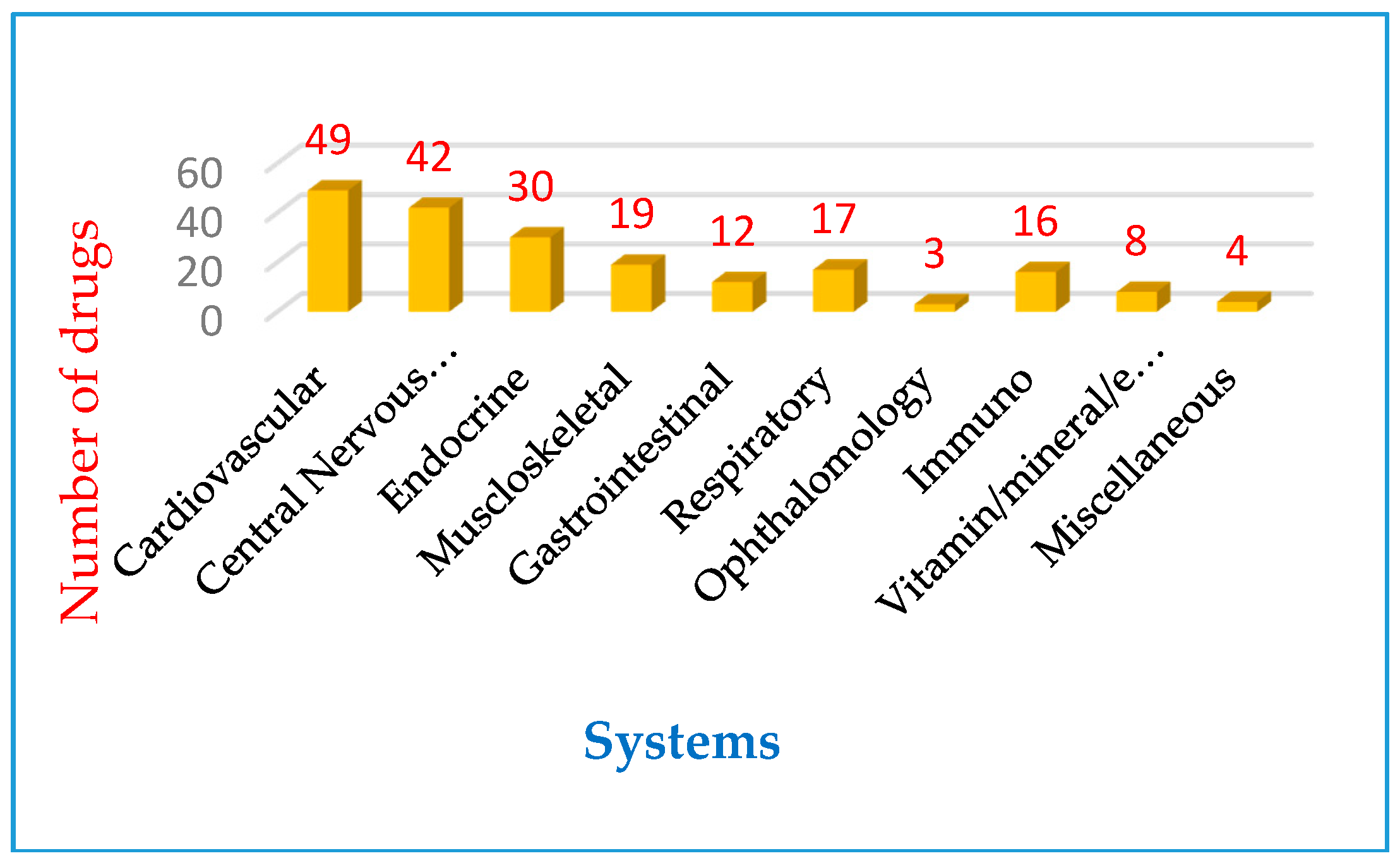
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Blackbox Warning
3.2. Dosage Forms
3.3. Biologicals and Chemicals
3.4. Opioids
3.5. Adverse Drug Reactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| IM | intramuscular |
| Opth | Ophthalmic |
| Inj | Injection |
| ADR | Adverse Drug Reaction |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| PO | Oral |
| IV | Intravenous |
| Inh | Inhalation |
| Liq | Liquid |
| BB | Black Box Warning |
| SQ | Subcutaneous |
| TD | Transdermal |
| CDAD | Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhea |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
| ACEi | Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor | 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase Inhibitor |
| PPI | Proton Pump Inhibitor |
| CCB | Calcium Channel Blocker |
| SSRI | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors |
| SNRI | Serotonin–Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors |
| TCA | Tricyclic Antidepressant |
| NRI | Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor |
| NSAID | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| SGLT2 Inhibitor | Sodium-Glucose co-Transporter-2 Inhibitor |
| DPP-4 Inhibitor | Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor |
References
- Exploring Pharmacists’ Role in a Changing Healthcare Environment. Available online: https://www.nacds.org/pdfs/comm/2014/pharmacist-role (accessed on 15 January 2018).
- Robert, A.B.; Michael, L.A. The Role of the Pharmacist in Health Care Expanding and Evolving. N. C. Med. J. 2017, 78, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process. Available online: https://jcpp.net/patient-care-process (accessed on 15 March 2018).
- Role of a Pharmacist. Available online: http://www.pharmcas.org/preparing-to-apply/about-pharmacy/role-of-a-pharmacist (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- The Pharmacist’s Expanded Role. Available online: http://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/issue /2015/october2015/the-pharmacists-expanded-role (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- 2014 National Pharmacist Workforce Survey. Available online: https://www.aacp.org/sites/default/files /finalreportofthenationalpharmacistworkforcestudy2014 (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Winit-Watjana, W.; Francis, D.; Ho, H.M. Top 200 Prescribed drugs as a tool for pharmacy teaching and training. Pharm. Educ. 2011, 11, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tanjung, H.R.; Nasution, E.S. Top 200 Prescribed Drugs Mostly Prescribed by the Physician in Pharmacies at Medan City. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 180, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Total Number of Medical Prescriptions Dispensed in the U.S. from 2009 to 2016. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/238702/us-total-medical-prescriptions-issued (accessed on 18 March 2018).
- The Top 200 Drugs of 2018. Available online: http://clincalc.com/DrugStats (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Evans, C.; Foushee, L.; Al-Achi, A. Top 200 prescribed drugs learning tool and objective evaluation instruments in community pharmacy clerkship sites. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2006, 46, 292–293. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, T. The Top 200 Drugs of 2017. Available online: http://www.pharmacytimes.com/contributor/tony-guerra-pharmd/2017/03/the-top-200-drugs-of-2017 (accessed on 15 February 2018).
- Top 200 Drugs to Memorize. Available online: https://www.pharmacy-tech-test.com/top-200-drugs.html (accessed on 18 January 2018).
- McGrath, N.A.; Brichacek, M.; Njardarson, J.T. A Graphical Journey of Innovative Organic Architectures That Have Improved Our Lives. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1348–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santee, J. A Web-Based Practice Examination to Improve Student Performance Concerning the 200 Most Prescribed Drugs. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2003, 67, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Access Pharmacy. Available online: http://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com (accessed on 18 January 2018).
- Lexicomp Online. Available online: http://online.lexi.com/crlsql/servlet/crlonline (accessed on 18 January 2018).
- Boxed Warning. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resourcesforyou/consumers /prescriptiondrugadvertising/ucm072025.htm#B (accessed on 18 January 2018).

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes, A.V.; Pineda, M.D.; Venkata, K.C.N. Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice. Pharmacy 2018, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy6020043
Fuentes AV, Pineda MD, Venkata KCN. Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice. Pharmacy. 2018; 6(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy6020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes, Andrea V., Moises D. Pineda, and Kalyan C. Nagulapalli Venkata. 2018. "Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice" Pharmacy 6, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy6020043
APA StyleFuentes, A. V., Pineda, M. D., & Venkata, K. C. N. (2018). Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice. Pharmacy, 6(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy6020043



