Long-Term Impact of Sustained Knowledge, Confidence, and Clinical Application Following a First-Year Student Pharmacist Diabetes Self-Care Education Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and DSEP Training Design
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
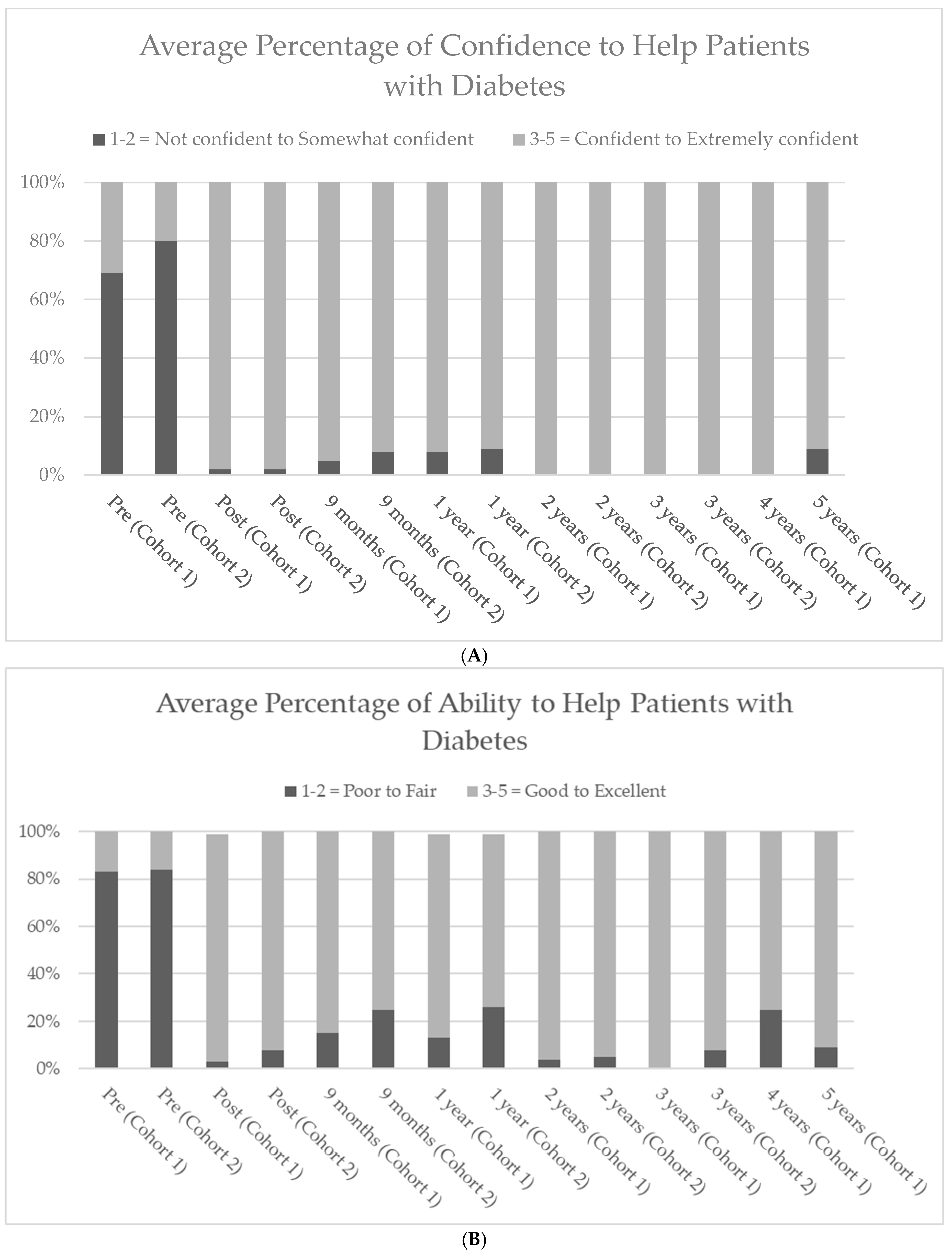
3.2. Overall Confidence and Ability to Provide Diabetes Care
3.3. Overall Diabetes Knowledge and Confidence with Monitors, Insulin Use, and Foot Exams
3.4. Knowledge Assessment by Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Case-Based Knowledge Test
3.5. Clinical Applicability and Use of DSEP Knowledge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report Website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/ (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- International Diabetes Federation; Facts and Figures. Available online: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/ (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Parker, E.D.; Lin, J.; Mahoney, T.; Ume, N.; Yang, G.; Gabbay, R.A.; ElSayed, N.A.; Bannuru, R.R. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2022. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853, Erratum in: Lancet 1999, 354, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, D.M.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, J.; Thompson, T.J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, P.; Gregg, E.; Rolka, D.B. Projection of the future diabetes burden in the United States through 2060. Popul. Health Metr. 2018, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nazir, S.U.; Hassali, M.A.; Saleem, F.; Bashir, S.; Aljadhey, H. Association Between Diabetes-related Knowledge and Medication Adherence: Results From Cross-sectional Analysis. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2016, 22, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.D.; Kong, N.; Nguyen, K.T.; Cadiz, C.L.; Zhou, C.; Bajorek, S.A.; Bounthavong, M.; Morello, C.M. Improved Patient-Reported Medication Adherence, Patient Satisfaction, and Glycemic Control in a Collaborative Care Pharmacist-Led Diabetes “Tune-Up” Clinic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Torres, H.C.; Pace, A.E.; Chaves, F.F.; Velasquez-Melendez, G.; Reis, I.A. Evaluation of the effects of a diabetes educational program: A randomized clinical trial. Rev. Saude Publica. 2018, 52, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, R.F.; Kelly, P.; Tam, A.; Bronner, J.; Morello, C.M.; Hirsch, J.D. Evaluation of a short, interactive diabetes self-management program by pharmacists for type 2 diabetes. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Badi, S.; Suliman, S.Z.; Almahdi, R.; Aldomah, M.A.; Ahmed, M.H.; Elkheir, H.K.; Ibrahim, M.I.M. The Impact of Diabetes Education by Clinical Pharmacist on Quality of Life and Treatment Satisfaction of Sudanese Individuals With Type II Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2024, 15, 21501319241279681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. American Diabetes Association (ADA) Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025 is Diabetes Care. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S1–S5. Available online: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/issue/48/Supplement_1 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education. Standards 2025. Available online: https://www.acpe-accredit.org/pharmd-program-accreditation/#tab-Standards (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Medina, M.; Stolte, S.; Conry, J.; Culhane, N.; Farland, M.Z.; Kennedy, D.R.; Lockman, K.; Malcom, D.R.; Mirzaian, E.; Vyas, D.; et al. Revising the Center for the Advancement of Pharmacy Education (CAPE) Educational Outcomes and Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs): The Report of the 2021–2022 Academic Affairs Standing Committee. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2023, 87, ajpe9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fazel, M.; Cooley, J.; Kurdi, S.; Fazel, M. A co-curricular diabetes-specific elective with interprofessional students and faculty. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2019, 11, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westberg, S.M.; Bumgardner, M.A.; Brown, M.C.; Frueh, J. Impact of an elective diabetes course on student pharmacists’ skills and attitudes. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Knezevich, E.; Fuji, K.T.; Larson, K.; Muniz, G. A Cross-Sectional Survey Study Examining the Provision of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Education in U.S. Doctor of Pharmacy Programs. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McIntosh, T.; Divine, H.; Taylor, S. Student pharmacist’s application of the pharmacists’ patient care process during an interprofessional diabetes camp introductory pharmacy practice experience. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2024, 16, 102169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, G.J.; Foster, K.T.; Unterwagner, W.; Jia, H. Impact of a diabetes certificate program on PharmD students’ knowledge and skills. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morello, C.M.; Neighbors, M.; Luu, L.; Kobayashi, S.; Mutrux, B.; Best, B.M. Impact of a first-year student pharmacist diabetes self-care education program. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2013, 77, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Assemi, M.; Morello, C.M. Diabetes Mellitus. In Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self-Care, 16th ed.; Berardi, R.R., Ferreri, S., Hume, A.L., Kroon, L.A., Newton, G.D., Popovich, N.G., Remington, T.L., Rollins, C.J., et al., Eds.; American Pharmaceutical Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Chapter 47; pp. 837–850. [Google Scholar]
- ACDES. The Art Science of Diabetes Care Education, 6th ed.; Cornell, S., Miller, D.K., Urbanski, P., Eds.; Association of Diabetes Care and Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 1–972. Available online: https://www.adces.org/store/publications/detail/ebook_the-art-and-science-of-diabetes-care-and-education-6th-edition (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self-Care, 21st edition. Available online: https://ebusiness.pharmacist.com/PersonifyEbusiness/Shop-APhA/Product-Details/productId/362610550 (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Smith, S.D.; Marrone, L.; Johnson, M.; Gomez, A.; Edland, S.; Beck, E. Clinical Outcomes of Diabetic Patients at a Student-Run Free Clinic. Fam. Med. 2014, 43, 198–203. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2465263 (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. Academic Pharmacy’s Vital Statistics. Available online: https://www.aacp.org/article/academic-pharmacys-vital-statistics (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- International Pharmaceutical Federation, FIP World List of Pharmacy Schools. Available online: https://www.fip.org/world-list-of-pharmacy-schools (accessed on 17 January 2025).
| Pre | Pre | Post | Post | 9 Months | 9 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year | 2 Years | 2 Years | 3 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of Participants | 59 | 60 | 59 | 60 | 59 | 60 | 52 | 47 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| Perception of Knowledge: | Average Percentage (%) Response Rating 3–5 = Confident to Excellent | |||||||||||||
| Diabetes as a disease | 53 | 42 | 92 | 100 | 92 | 91 | 98 | 83 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 91 | 100 | 91 |
| Risk factors for DM | 55 | 38 | 95 | 100 | 92 | 91 | 96 | 83 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 91 |
| Complications DM | 47 | 34 | 97 | 100 | 91 | 81 | 98 | 87 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 90 |
| DM1 vs. DM2 | 59 | 53 | 99 | 100 | 94 | 94 | 96 | 96 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 91 |
| Signs and symptoms | 42 | 32 | 98 | 100 | 93 | 93 | 96 | 88 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 90 |
| Nutrition therapy | 30 | 29 | 95 | 95 | 86 | 83 | 86 | 81 | 96 | 95 | 100 | 91 | 75 | 90 |
| Exercise guidelines | 36 | 20 | 94 | 94 | 93 | 81 | 90 | 85 | 92 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 75 | 81 |
| Insulin therapy | 22 | 15 | 93 | 90 | 75 | 79 | 73 | 58 | 96 | 96 | 94 | 83 | 100 | 91 |
| Glucose monitors | 24 | 16 | 95 | 99 | 92 | 90 | 88 | 88 | 92 | 96 | 83 | 92 | 75 | 72 |
| Diabetic foot exams | 10 | 2 | 97 | 98 | 78 | 83 | 76 | 67 | 65 | 95 | 84 | 92 | 100 | 54 |
| Perception of Confidence: | Average Percentage (%) Response Rating 3–5 = Confident to Excellent | |||||||||||||
| Explaining how to use a glucose meter | 25 | 16 | 100 | 100 | 95 | 97 | 96 | 89 | 97 | 95 | 88 | 100 | 100 | 91 |
| Recommending a glucose meter | 22 | 15 | 94 | 100 | 82 | 79 | 88 | 84 | 80 | 92 | 67 | 100 | 100 | 81 |
| Performing a self-fingerstick | 25 | 20 | 98 | 100 | 94 | 98 | 96 | 96 | 97 | 99 | 95 | 99 | 100 | 90 |
| Performing a patient fingerstick | 18 | 18 | 95 | 98 | 95 | 97 | 95 | 96 | 96 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Teaching how to perform a fingerstick | 17 | 16 | 98 | 100 | 94 | 96 | 98 | 93 | 96 | 96 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 81 |
| Explaining different types of insulin | 9 | 15 | 95 | 97 | 82 | 54 | 53 | 45 | 100 | 100 | 94 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Teaching insulin injection | 5 | 4 | 98 | 100 | 90 | 81 | 89 | 68 | 100 | 100 | 95 | 101 | 100 | 90 |
| Discussing insulin therapies | 7 | 6 | 87 | 97 | 70 | 52 | 55 | 54 | 100 | 101 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Administering insulin injection | 5 | 5 | 89 | 99 | 88 | 90 | 80 | 75 | 96 | 91 | 83 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Giving insulin injection to patient | 3 | 3 | 94 | 92 | 77 | 89 | 72 | 65 | 85 | 82 | 78 | 99 | 100 | 81 |
| Teaching patients about hypoglycemia | 17 | 13 | 99 | 100 | 87 | 83 | 86 | 85 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 101 | 100 | 90 |
| How to treat hypoglycemia | 18 | 10 | 99 | 100 | 95 | 87 | 86 | 84 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Performing a diabetic foot exam | 2 | 0 | 95 | 96 | 74 | 69 | 72 | 63 | 53 | 91 | 77 | 91 | 75 | 73 |
| How to perform a diabetic foot exam | 2 | 2 | 95 | 94 | 77 | 67 | 73 | 61 | 57 | 96 | 77 | 100 | 75 | 72 |
| Discussing foot exams with patients | 5 | 3 | 100 | 96 | 94 | 90 | 90 | 78 | 92 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 75 | 81 |
| Discussing foot risk factors | 3 | 5 | 100 | 96 | 90 | 70 | 88 | 64 | 84 | 100 | 94 | 100 | 75 | 82 |
| Recommending non-drug foot care | 3 | 2 | 79 | 81 | 73 | 63 | 62 | 60 | 69 | 87 | 56 | 83 | 50 | 72 |
| Pre | Pre | Post | Post | 9 Months | 9 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year | 2 Years | 2 Years | 3 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of Participants | 59 | 60 | 59 | 60 | 59 | 60 | 52 | 47 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| Case 1 Average Percentage (%) Score | 46 | 44 | 94 | 88 | 88 | 82 | 87 | 81 | 95 | 89 | 96 | 92 | 97 | 95 |
| Case 2 Average Percentage (%) Score | 32 | 32 | 79 | 81 | 79 | 60 | 61 | 63 | 78 | 77 | 75 | 80 | 75 | 81 |
| 9 Months | 9 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year | 2 Years | 2 Years | 3 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of Participants | 59 | 60 | 52 | 47 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| Types of Pharmacy Settings | Median Scores | |||||||||
| Large chain community pharmacy | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3.5 | 3 | 5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Clinic/community pharmacy | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3.5 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Community mass-merchandise pharmacy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Inpatient hospital pharmacy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Independently owned community pharmacy, supermarket, small chain, outpatient hospital or others not listed. | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 Months | 9 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year | 2 Years | 2 Years | 3 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of Participants | 54 | 48 | 52 | 47 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| Percentage (%) of students that had the opportunity to assist a patient with diabetes | 61 | 75 | 81 | 83 | 88 | 91 | 89 | 100 | 75 | 90 |
| Percentage (%) of students that had the opportunity to assist a caregiver of a patient with diabetes | 17 | 19 | 42 | 32 | 65 | 68 | 89 | 92 | 75 | 64 |
| How many patients with diabetes have you assisted in any way? | 1295 | 664 | 3287 | 1162 | 2957 | 1594 | 2246 | 1814 | 1050 | 2429 |
| How many caregivers of patients with diabetes have you assisted in any way? | 118 | 138 | 907 | 255 | 787 | 380 | 460 | 261 | 475 | 706 |
| How many times used overall knowledge of diabetes? | 1506 | 691 | 3925 | 3849 | 3415 | 1745 | 3081 | 2255 | 1050 | 3550 |
| How many times discussed with a patient the different types of diabetes? | 284 | 216 | 1457 | 2964 | 936 | 659 | 606 | 327 | 120 | 480 |
| How many times explained the signs and symptoms of diabetes. | 621 | 234 | 1458 | 2942 | 2139 | 1044 | 1160 | 770 | 240 | 675 |
| How many times discussed pre-diabetes with a patient? | 680 | 280 | 1198 | 2329 | 789 | 308 | 426 | 350 | 60 | 332 |
| How many times informally or formally screened a person for diabetes? | 1083 | 665 | 2648 | 3266 | 1683 | 880 | 751 | 1050 | 182 | 710 |
| How many times discussed the risk factors involved with diabetes? | 923 | 449 | 2150 | 2815 | 1838 | 797 | 785 | 770 | 200 | 756 |
| How many times make dietary recommendations to a patient with diabetes? | 609 | 311 | 1881 | 2766 | 1540 | 713 | 979 | 1013 | 110 | 371 |
| How many times discussed goals of therapy with a patient? | 437 | 151 | 1335 | 2493 | 1429 | 941 | 903 | 829 | 235 | 1630 |
| How many times provided glucose monitor education? | 686 | 289 | 1818 | 3206 | 1256 | 543 | 471 | 555 | 420 | 435 |
| How many times helping with glucose monitor selection? | 314 | 88 | 1241 | 2504 | 303 | 253 | 317 | 152 | 190 | 230 |
| How many times providing education regarding finger-stick supplies? (e.g., lancets and device) | 448 | 156 | 2194 | 3337 | 729 | 478 | 722 | 490 | 804 | 408 |
| How many times performing a finger stick on a patient? | 967 | 643 | 2509 | 3226 | 1609 | 840 | 469 | 995 | 145 | 636 |
| How many times demonstrating for a patient how to perform finger stick tests? | 578 | 299 | 1923 | 3099 | 893 | 327 | 443 | 244 | 180 | 309 |
| How many times discussing insulin therapy with a patient? | 42 | 34 | 723 | 2021 | 1202 | 469 | 461 | 603 | 505 | 1573 |
| How many times providing insulin therapy education? | 55 | 37 | 648 | 1868 | 616 | 463 | 568 | 557 | 304 | 1438 |
| How many times teaching a patient the proper technique for insulin administration? | 61 | 58 | 629 | 2434 | 498 | 284 | 311 | 382 | 280 | 1234 |
| How many times administering an insulin injection to a patient? | 21 | 10 | 523 | 2213 | 36 | 110 | 41 | 65 | 6 | 93 |
| How many times performing a foot exam on a diabetic patient? | 13 | 77 | 326 | 2118 | 203 | 403 | 72 | 283 | 11 | 84 |
| How many times explaining to a patient the importance of foot exams? | 114 | 96 | 984 | 2509 | 479 | 514 | 271 | 444 | 90 | 363 |
| How many times teaching a patient how to perform a foot exam? | 22 | 62 | 347 | 2144 | 161 | 360 | 138 | 242 | 21 | 98 |
| How many times providing foot self-care education? (e.g., risks, prevention, fungal infections). | 96 | 94 | 427 | 2022 | 254 | 453 | 208 | 374 | 71 | 113 |
| How many times recommending an OTC product for a foot care for a diabetic patient? | 39 | 82 | 701 | 2023 | 241 | 339 | 131 | 96 | 65 | 108 |
| 9 Months | 9 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year | 2 Years | 2 Years | 3 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. of Participants | 54 | 48 | 52 | 47 | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| Additional DSEP Questions | Mean Scores | |||||||||
| Participating in the Pharmacy practice Diabetes Education Program has increased my overall knowledge of diabetes | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Participating in the Pharmacy practice Diabetes Education Program has increased my overall confidence in helping people with diabetes. | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4.5 | 5 |
| Overall, I feel the Pharmacy Practice Diabetes Education Program prepared me to educate people with diabetes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4.5 | 5 |
| Overall, I feel the Pharmacy Practice Diabetes Education Program prepared me to help people with diabetes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4.5 | 5 |
| Overall, I feel the Pharmacy Practice Diabetes Education Program increased my interest in diabetes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 4.5 | 4 |
| I plan to pursue further diabetes education as a result of my experience in the Pharmacy Practice Diabetes Education Program | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morello, C.M.; Fricovsky, E.S. Long-Term Impact of Sustained Knowledge, Confidence, and Clinical Application Following a First-Year Student Pharmacist Diabetes Self-Care Education Program. Pharmacy 2025, 13, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13020042
Morello CM, Fricovsky ES. Long-Term Impact of Sustained Knowledge, Confidence, and Clinical Application Following a First-Year Student Pharmacist Diabetes Self-Care Education Program. Pharmacy. 2025; 13(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorello, Candis M., and Eduardo S. Fricovsky. 2025. "Long-Term Impact of Sustained Knowledge, Confidence, and Clinical Application Following a First-Year Student Pharmacist Diabetes Self-Care Education Program" Pharmacy 13, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13020042
APA StyleMorello, C. M., & Fricovsky, E. S. (2025). Long-Term Impact of Sustained Knowledge, Confidence, and Clinical Application Following a First-Year Student Pharmacist Diabetes Self-Care Education Program. Pharmacy, 13(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13020042






