Assessing Learner Engagement and the Impact on Academic Performance within a Virtual Learning Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schunk, D.H. Goal and Self-Evaluative Influences During Children’s Cognitive Skill Learning. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1996, 33, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraw, G.; Crippen, K.; Hartley, K. Promoting self-regulation in science education: Metacognition as part of a broader perspective on learning. Res. Sci. Educ. 2006, 36, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voils, S.A.; Childs-Kean, L.M.; Thomas, A. Relationship between pharmacy students’ use of self-regulated learning strategies and course outcomes. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2019, 83, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard-Brak, L.; Paton, V.O.; Lan, W.Y. Profiles in self-regulated learning in the online learning environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2010, 11, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Hähnlein, I.; Ifenthaler, D. Cognitive, metacognitive and motivational perspectives on preflection in self-regulated online learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 32, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Walker, A.E.; Schroder, K.E.; Belland, B.R. Interaction, Internet self-efficacy, and self-regulated learning as predictors of student satisfaction in online education courses. Internet High. Educ. 2014, 20, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocdar, S.; Karadeniz, A.; Bozkurt, A.; Buyuk, K. Measuring Self-Regulation in Self-Paced Open and Distance Learning Environments. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukselturk, E.; Bulut, S. Predictors for student success in an online course. Educ. Technol. Society. 2007, 10, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, W.; Reiser, R.A. The effects of self-regulation and instructional control on performance and motivation in computer-based instruction. Int. J. Instr. Media. 2000, 27, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Pintrich, P.R.; De Groot, E.V. Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. J. Educ. Psychol. 1990, 82, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Ogrin, S.; Schmitz, B. Assessing self-regulated learning in higher education: A systematic literature review of self-report instruments. Educ. Assess. Eval. Acc. 2015, 28, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsmore, D.L.; Alexander, P.A.; Loughlin, S.M. Focusing the conceptual lens on metacognition, self-regulation, and self-regulated learning. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2008, 20, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Investigating self-regulation and motivation: Historical background, methodological developments, and future prospects. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2008, 45, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanZile-Tamsen, C. The predictive power of expectancy of success and task value for college students’ self-regulated strategy use. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2001, 42, 233. [Google Scholar]
- VanderStoep, S.W.; Pintrich, P.R.; Fagerlin, A. Disciplinary differences in self-regulated learning in college students. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 1996, 21, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, C.A.; Garavalia, L.S. Factors contributing to the academic achievement of pharmacy students: Use of the goal-efficacy framework. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2004, 68, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzimenti, M.A.; Axelson, R.D. Assessing student engagement and self-regulated learning in a medical gross anatomy course. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2014, 8, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, S.; Konan, A. Self-regulated learning strategies used in surgical clerkship and the relationship with clinical achievement. J. Surg. Educ. 2012, 69, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R. Oliphant, T.E., Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.A.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Excel. 2018. Available online: https://office.microsoft.com/excel (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Rodriguez, F.; Rivas, M.J.; Matsumura, L.H.; Warschauer, M.; Sato, B.K. How do students study in STEM courses? Findings from a light-touch intervention and its relevance for underrepresented students. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susser, J.A.; McCabe, J. From the lab to the dorm room: Metacognitive awareness and use of spaced study. Instr. Sci. 2012, 41, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, M.K.; Dunlosky, J. Study strategies of college students: Are self-testing and scheduling related to achievement? Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2011, 19, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walck-Shannon, E.M.; Rowell, S.F.; Frey, R.F. To what extent do study habits relate to performance? CBE—Life Sci. Educ. 2021, 20, ar6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harthy, I.S.; Was, C.A.; Isaacson, R.M. Goals, Efficacy and Metacognitive Self-Regulation A Path Analysis. Int. J. Educ. 2010, 2, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarraju, M.; Nadler, D. Self-efficacy and academic achievement: Why do implicit beliefs, goals, and effort regulation matter? Learn. Individ. Differ. 2013, 25, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.J.; Trujillo, H. Motivational beliefs and learning strategies in organic chemistry. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2010, 9, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.J. Motivational factors, learning strategies and resource management as predictors of course grades. Coll. Stud. J. 2006, 40, 423. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsantas, A.; Winsler, A.; Huie, F. Self-regulation and ability predictors of academic success during college: A predictive validity study. J. Adv. Acad. 2008, 20, 42–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomkar, R.; Yazdani, K.; Fata, L.; Mehrdad, R.; Mirzazadeh, A.; Jalili, M.; Sandars, J. Using multiple self-regulated learning measures to understand medical students’ biomedical science learning. Med. Educ. 2020, 54, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.A.; Azevedo, R. A Theoretical review of winne and hadwin’s model of self-regulated learning: New perspectives and directions. Rev. Educ. Res. 2007, 77, 334–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadwin, A.F.; Nesbit, J.C.; Jamieson-Noel, D.; Code, J.; Winne, P. Examining trace data to explore self-regulated learning. Metacognition Learn. 2007, 2, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesope, O.O.; Zhou, M.; Nesbit, J.C. Achievement goal orientations and self-reported study strategies as predictors of online studying activities. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2015, 53, 436–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Ikeda, M. The effects of ePortfolio-based learning model on student self-regulated learning. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2015, 16, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R. Validating and adapting the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (mslq) for stem courses at an HBCU. AERA Open 2018, 4, 2332858418809346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.; Cromley, J.G. Does training on self-regulated learning facilitate students’ learning with hypermedia? J. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 96, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, N.; Kitsantas, A. Personal learning environments, social media, and self-regulated learning: A natural formula for connecting formal and informal learning. Internet High. Educ. 2012, 15, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzmann, T.; Ely, K. Sometimes you need a reminder: The effects of prompting self-regulation on regulatory processes, learning, and attrition. J. Appl. Psychol. 2010, 95, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata-Rivera, D. Open student modeling research and its connections to educational assessment. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2020, 31, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, D.H.; Hargis, J.; Bordner, R.; Chandler, P. Self-regulated learning as a critical attribute for successful teaching and learning. Int. J. Scholarsh. Teach. Learning. 2017, 11, n2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
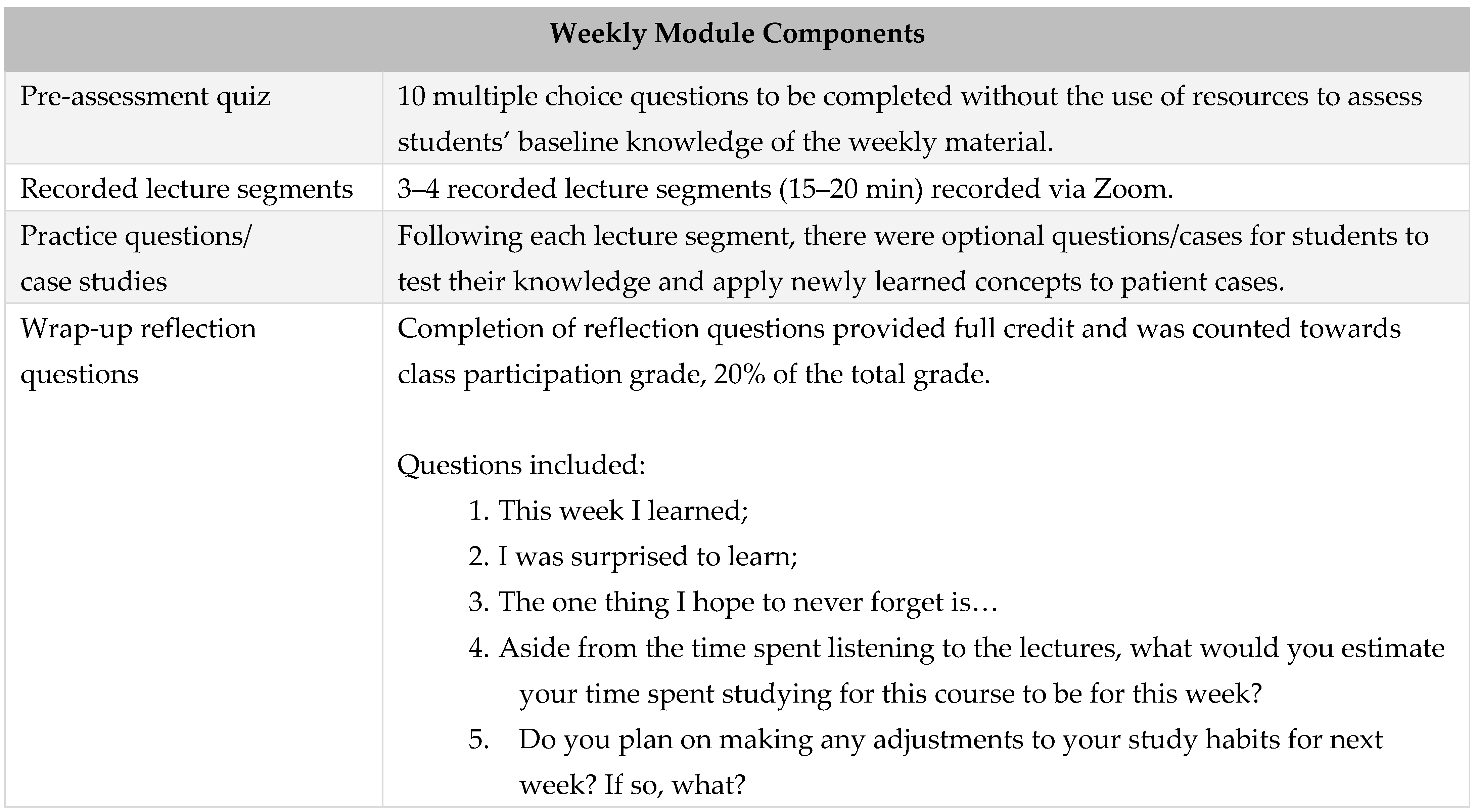
| Measure | Mean | SD | Exam Score | Case Submission | On-Time Submission | Extra Attempts | Median Study Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exam Score | 0.85 | 0.09 | |||||
| Case Submission | 0.65 | 0.35 | 0.17 * | ||||
| On-time Submission | 0.19 | 0.3 | 0.28 *** | 0.37 *** | |||
| Extra Attempts | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.17 * | 0.31 *** | 0.4 *** | ||
| Median Study Time | 2.48 | 1.72 | 0.04 | 0.03 | −0.12 | 0.04 | |
| SD of Study Time | 1.64 | 1.69 | −0.01 | 0.13 | −0.15 | 0.01 | 0.45 *** |
| Measure | Mean | SD |
Exam Score | MSLQ-CS | MSLQ-IV | MSLQ-SE | MSLQ-SR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exam Score | 0.85 | 0.09 | |||||
| MSLQ-CS | 5.09 | 0.64 | 0.10 | ||||
| MSLQ-IV | 5.96 | 0.67 | 0.21 ** | 0.63 *** | |||
| MSLQ-SE | 5.10 | 1.04 | 0.35 *** | 0.58 *** | 0.56 *** | ||
| MSLQ-SR | 4.93 | 0.75 | 0.23 ** | 0.62 *** | 0.58 *** | 0.62 *** | |
| MSLQ-TA | 4.89 | 1.45 | −0.14 | −0.01 | −0.01 | −0.25 ** | −0.31 *** |
| Measure | Mean | SD | Case Submissions | Submission on Time | Extra Attempts | Median Study Time | SD of Study Time | MSLQ-CS | MSLQ-IV | MSLQ-SE | MSLQ-SR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Submissions | 0.65 | 0.35 | |||||||||
| Submission on time | 0.19 | 0.3 | 0.4 *** | ||||||||
| Extra Attempts | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.32 ** | 0.42 *** | |||||||
| Median study time | 2.48 | 1.72 | −0.03 | −0.18 | 0.06 | ||||||
| SD of study time | 1.64 | 1.69 | 0.17 | −0.19 | 0.04 | 0.4 *** | |||||
| MSLQ-CS | 5.09 | 0.64 | 0.2 | −0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | ||||
| MSLQ-IV | 5.96 | 0.67 | 0.24 * | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.06 | 0.09 | 0.63 *** | |||
| MSLQ-SE | 5.1 | 1.04 | 0.27 ** | 0.19 | 0.13 | −0.04 | −0.08 | 0.56 *** | 0.54 *** | ||
| MSLQ-SR | 4.93 | 0.75 | 0.29 ** | 0.1 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.02 | 0.62 *** | 0.59 *** | 0.52 *** | |
| MSLQ-TA | 4.89 | 1.45 | 0.06 | −0.05 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.21 * | −0.13 | −0.15 | −0.39 *** | −0.46 *** |
| Measure | Mean | SD | Case Submissions | Submission on Time | Extra Attempts | Median Study Time | SD of Study Time | MSLQ-CS | MSLQ-IV | MSLQ-SE | MSLQ-SR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Submissions | 0.65 | 0.35 | |||||||||
| Submission on time | 0.19 | 0.3 | 0.27 * | ||||||||
| Extra Attempts | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.28 * | 0.26 * | |||||||
| Median study time | 2.48 | 1.72 | 0.06 | −0.07 | −0.03 | ||||||
| SD of study time | 1.64 | 1.69 | 0.07 | −0.07 | −0.09 | 0.53 *** | |||||
| MSLQ-CS | 5.09 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.11 | ||||
| MSLQ-IV | 5.96 | 0.67 | 0.24 * | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.63 *** | |||
| MSLQ-SE | 5.1 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 0.28 * | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.61 *** | 0.57 *** | ||
| MSLQ-SR | 4.93 | 0.75 | −0.02 | 0.15 | 0.22 * | 0.26 * | 0.13 | 0.64 *** | 0.55 *** | 0.7 *** | |
| MSLQ-TA | 4.89 | 1.45 | 0.1 | −0.17 | −0.09 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.14 | −0.1 | −0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galal, S.; Vyas, D.; Ndung’u, M.; Wu, G.; Webber, M. Assessing Learner Engagement and the Impact on Academic Performance within a Virtual Learning Environment. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11010036
Galal S, Vyas D, Ndung’u M, Wu G, Webber M. Assessing Learner Engagement and the Impact on Academic Performance within a Virtual Learning Environment. Pharmacy. 2023; 11(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalal, Suzanne, Deepti Vyas, Martha Ndung’u, Guangyu Wu, and Mason Webber. 2023. "Assessing Learner Engagement and the Impact on Academic Performance within a Virtual Learning Environment" Pharmacy 11, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11010036
APA StyleGalal, S., Vyas, D., Ndung’u, M., Wu, G., & Webber, M. (2023). Assessing Learner Engagement and the Impact on Academic Performance within a Virtual Learning Environment. Pharmacy, 11(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11010036






