A Longitudinal Exploration of Perception and Production of English Codas in CLIL Settings
Abstract
1. Literature Review
1.1. Pronunciation Research in Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL)
1.2. The Acquisition of English Codas by L2 Speakers
1.3. Acquisition of L2 Sound Perception and Production
2. Research Questions
3. Method
3.1. Participants
3.2. Identification Testing
3.3. Production Testing
4. Results
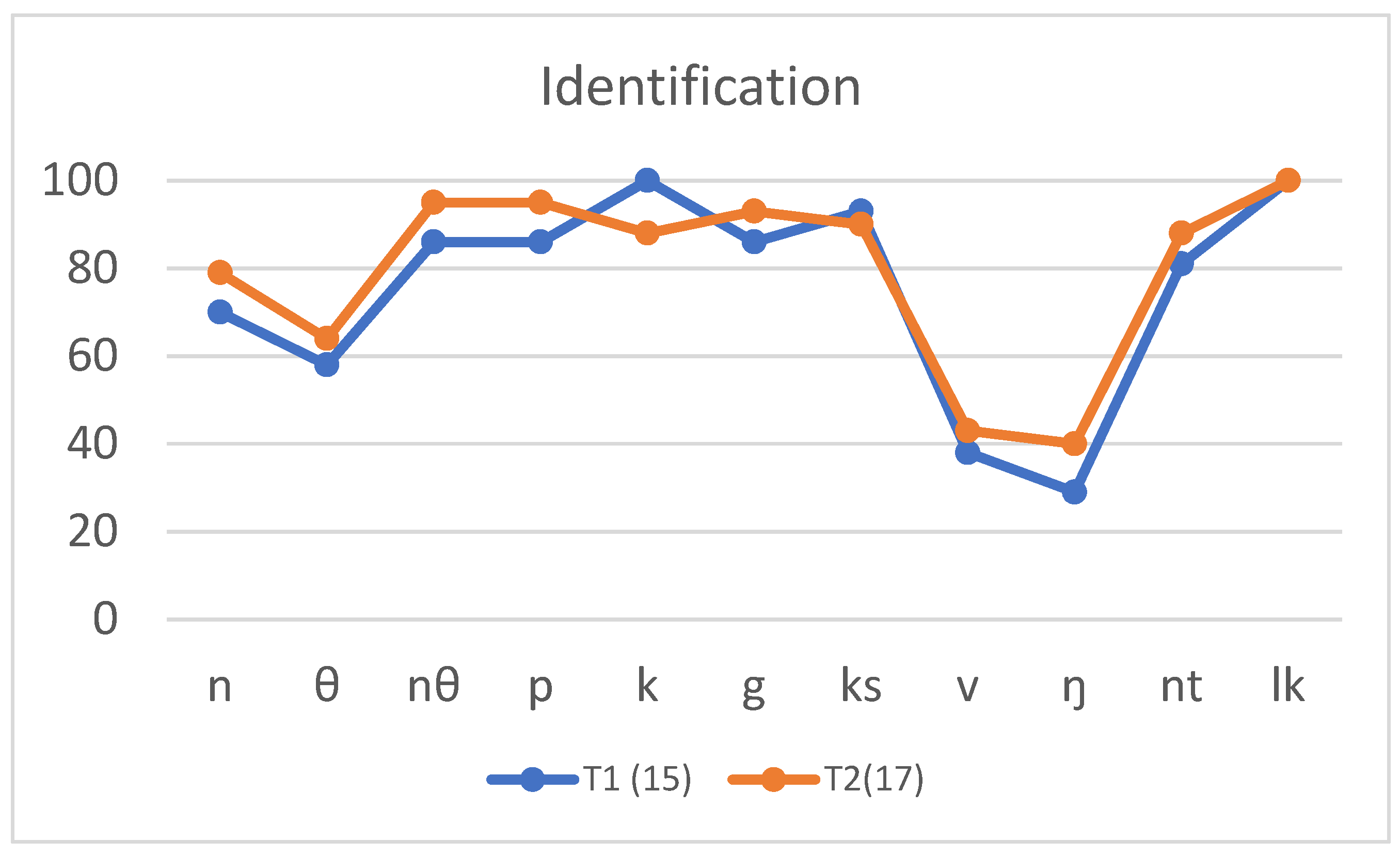
4.1. Identification Results
4.2. Production Results
4.3. Perception–Production Interplay Results
4.4. Error Analyses
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | English translation: (they) are, to go, sun, crisis, watch, peace. |
| 2 | English translation: Spanish surname, waltz. |
| 3 | English translation: to obtain, apt, to acquire, ethnicity, dogma, act. |
| 4 | English translation: sharp, instant, to obstruct, exterior. |
| 5 | English translation: ordinary, five, where to, who (with transitive verb), Basque surname. |
References
- Avello, Pilar, Joan Carles Mora, and Cármen Perez-Vidal. 2013. Phonological development in L2 speech production during study abroad programmes differing in length of stay. In Language Acquisition in Study Abroad and Formal Instruction Contexts. Edited by Carme-Perez Muñoz. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 137–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brannen, Kathleen. 2002. The role of perception in differential substitution. Canadian Journal of Linguistics 47: 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broselow, Ellen, and Danie Finer. 1991. Parameter setting in second language phonology and syntax. Second Language Research 7: 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broselow, Ellen, Su-I Cheng, and Chilin Wang. 1998. The emergence of the unmarked in second language phonology. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 20: 261–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broselow, Ellen. 1984. An Investigation of Transfer in Second Language Phonology. International Review of Applied Linguistics 22: 253–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broselow, Ellen. 2009. Stress adaptation in loanword phonology: Perception and learnability. In Phonology in Perception. Edited by Paul Boersma and Silke Hamann. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 191–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, Walcir. 2007. The variable development of English word-final stops by Brazilian Portuguese speakers: A stochastic optimality theoretic account. Language Variation and Change 19: 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, Walcir. 2011. The development of coda perception in second language phonology: A variationist perspective. Second Language Research 27: 433–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, Robert S. 1997. The modification of onsets in a markedness relationship: Testing the interlanguage structural conformity hypothesis. Language Learning 47: 327–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, Robert S. 1998. The acquisition of onsets in a markedness relationship: A longitudinal study. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 20: 245–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, Robert S. 2001. Syllable structure universals and second language acquisition. International Journal of English Studies 1: 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Casserly, Elisabeth D., and David B. Pisoni. 2010. Speech perception and production. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science 1: 629–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, Juli. 2007. Interaction of L2 phonotactics and L1 syllable structure in L2 vowel production. In New Sounds 2007: Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on the Acquisition of Second Language Speech. Florianópolis: Federal University of Santa Catarina, pp. 107–13. [Google Scholar]
- Colantoni, Laura, and Jeffrey Steele. 2008. Integrating articulatory constraints into models of second language phonological acquisition. Applied Psycholinguistics 29: 489–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton-Puffer, Christiane. 2008. Outcomes and processes in content and language integrated learning (CLIL): Current research from Europe. In Future Perspectives for English Language Teaching. Edited by Werner Delanoy and Laurenz Volkmann. Heidelberg: Carl Winter, pp. 139–57. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, Lisa, and Jason A. Shaw. 2012. Sources of illusion in consonant cluster perception. Journal of Phonetics 40: 234–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, Lisa. 2006. Phonology, phonetics, or frequency: Influences on the production of non-native sequences. Journal of Phonetics 34: 104–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, Lisa. 2010. Phonetic bases of similarities in cross-language production: Evidence from English and Catalan. Journal of Phonetics 38: 272–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, Lisa. 2011. Phonetic. phonemic and phonological factors in cross-language discrimination of phonotactic constraints. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 37: 270–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derwing, Tracey M., and Murray J. Munro. 2013. The development of L2 oral language skills in two L1 groups: A 7-year study. Language Learning 63: 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd, Olena. 2003. Sonority and Its Role in the Acquisition of Complex Coda Clusters by Spanish Speakers Learning English as a Second Language. Master’s thesis, Florida International University, Florida, FL, USA. FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations. 3087. [Google Scholar]
- Dupoux, Emmanuel, Christophe C. Pallier, Kazuhiko Kakehi, and Jacques Mehler. 2001. New evidence for prelexical phonological processing in word recognition. Language and Cognitive Processes 16: 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupoux, Emmanuel, Erika Parlato, Sonia Frota, Yuki Hirose, and Sharon Peperkamp. 2011. Where do illusory vowels come from? Journal of Memory and Language 64: 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupoux, Emmanuel, Kazuhiko Kakehi, Yuki Hirose, Christophe C. Pallier, and Jacques Mehler. 1999. Epenthetic vowels in Japanese: A perceptual illusion? Journal of Experimental Psychology 25: 1568–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckman, Fred, and Gregory Iverson. 1993. Sonority and markedness among onset clusters in the interlanguage of ESL learners. Second Language Research 9: 234–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flege, James E. 1995. Second language speech learning theory, findings, and problems. In Speech Perception and Linguistic Experience. Edited by Winifred Strange. Timonium: York Press, pp. 233–77. [Google Scholar]
- Flege, James E., Ian R. A. MacKay, and Diane Meador. 1999. Native Italian speakers’ perception and production of English vowels. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 106: 2973–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flege, James Emil, and Ocke-Schwen Bohn. 2020. The revised speech learning model (SLM-r). In Second Language Speech Learning: Theoretical and Empirical Progress. Edited by Ratree Waylan. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 3–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo-del-Puerto, Francisco. 2005. La Adquisición de la Pronunciación del Inglés como Tercera Lengua. Leioa: Universidad del País Vasco. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo-del-Puerto, Francisco, and Esther Gómez-Lacabex. 2013. The impact of additional CLIL exposure on oral English. Journal of English Studies 11: 113–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-del-Puerto, Francisco, and Esther Gómez-Lacabex. 2017. Oral production outcomes in CLIL: An attempt to manage amount of exposure. European Journal of Applied Linguistics 5: 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-del-Puerto, Francisco, Esther Gómez-Lacabex, and María L. García-Lecumberri. 2009. Testing the effectiveness of content and language integrated learning in foreign language contexts: The assessment of English pronunciation. In Content and Language Integrated Learning: Evidence from Research in Europe. Edited by Yolanda Ruiz de Zarobe and Rosa M. Jiménez Catalán. Bristol: Multilingual Matters, pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Lacabex, Esther, and Francisco Gallardo-del-Puerto. 2014. Two phonetic-training procedures for young learners: Investigating instructional effects on perceptual awareness. Canadian Modern Language Review 70: 500–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lacabex, Esther, and Francisco Gallardo-del-Puerto. 2020. Explicit phonetic instruction vs. implicit attention to native exposure: Phonological awareness of English schwa in CLIL. International Review of Applied Linguistics in Language Teaching 58: 419–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lacabex, Esther, and Francisco Gallardo-del-Puerto. 2021. Pronunciation in EMI: A preliminary study of Spanish university students’ intelligibility and comprehensibility. In Language Use in English-Medium Instruction at University. Edited by David Lasagabaster and Aintzane Doiz. London: Routledge, pp. 126–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Lacabex, Esther, Francisco Gallardo-del-Puerto, and Jian Gong. 2022. Perception and production training effects on production of English lexical schwa by young Spanish learners. Journal of Second Language Pronunciation 8: 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorba, Celia, and Juli Cebrian. 2021. The role of L2 experience in L1 and L2 perception and production of voiceless stops by English learners of Spanish. Journal of Phonetics 88: 101094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallé, Pierre, Juan Segui, Uli Frauenfelder, and Christine Meunier. 1998. Processing of illegal consonant clusters: A case of perceptual assimilation? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 24: 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancin-Bhatt, Barbara, and Rakesh M. Bhatt. 1997. Optimal L2 syllables: Interactions of transfer and developmental effects. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 19: 331–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancin-Bhatt, Barbara. 2000. Optimality in second language phonology: Codas in Thai ESL. Second Language Research 16: 201–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, Jette G. 2004. Developmental sequences in the acquisition of English L2 syllable codas: A preliminary study. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 26: 85–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huensch, Amanda, and Annie Tremblay. 2015. Effects of perceptual phonetic training on the perception and production of second language syllable structure. Journal of Phonetics 52: 105–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabak, Bariş, and William J. Idsardi. 2007. Perceptual distortions in the adaptation of English consonant clusters: Syllable structure or consonantal contact constraints? Language and Speech 50: 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartushina, Natalia, Alexis Hervais-Adelman, Ulrich-Hans Frauenfelder, and Nalri Golestani. 2015. The effect of phonetic production training with visual feedback on the perception and production of foreign speech sounds. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 138: 817–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasagabaster, David. 2008. Foreign language competence in content and language integrated courses. The Open Applied Linguistics Journal 1: 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, Amparo, and María del Pilar García Mayo. 2012. L1 use and morphosyntactic development in the oral production of EFL learners in a CLIL context. International Review of Applied Linguistics in Language Teaching 50: 135–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, Andrea, Peter W. Jusczyk, Janice Murray, and Guy Carden. 1988. Context effects in two-month-old infants’ perception of labiodental/interdental fricative contrasts. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 14: 361. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Soto, Teresa, and Diane Kewley-Port. 2009. Relation of perception training to production of codas in English as a second language. In Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics. Melville: AIP Publishing, vol. 6, p. 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, Carmen. 2007. Age-related differences and second language learning practice. In Practice in a Second Language: Perspectives from Applied Linguistics and Cognitive Psychology. Edited by Robert DeKeyer. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 229–55. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, Charles L., and Melissa M. Baese-Berk. 2022. Advancing the state of the art in L2 speech perception-production research: Revisiting theoretical assumptions and methodological practices. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 44: 580–605. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto Moreno-de-Diezmas, Esther. 2016. The impact of CLIL on the acquisition of L2 competences and skills in primary education. International Journal of English Studies 16: 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peperkamp, Sharon, and Emmanuel Dupoux. 2003. Reinterpreting loanword adaptations: The role of perception. Paper presented at 15th International Congress of Phonetics Science, Barcelona, Spain, August 3–9; pp. 367–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Cañado, María Luisa, and Nina Karen Lancaster. 2017. The effects of CLIL on oral comprehension and production: A longitudinal case study. Language, Culture and Curriculum 30: 300–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Cañado, María Luisa. 2018. CLIL and educational level: A longitudinal study on the impact of CLIL on language outcomes. Porta Linguarum 29: 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo Fabra, Lucrecia, and Karen Jacob. 2015. Does CLIL enhance oral skills? Fluency and pronunciation errors by Spanish-Catalan learners of English. In Content-Based Language Learning in Multilingual Educational Environment. Edited by María Juan-Garau and Joana Salazar-Noguera. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, pp. 163–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rallo-Fabra, Lucrecia, and María Juan-Garau. 2010. Intelligibility and foreign accentedness in a context-and-language-integrated-learning (CLIL) setting. In New Sounds 2010: Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on the Acquisition of Second Language Speech. Edited by Katarzyna Dziubalska-Kołaczyk, Magdalena Wrembel and Małgorzata Kul. Poznan: Federal Adam Mickiewicz University, pp. 373–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rochet, Bernard L. 1995. Perception and production of second language speech sounds by adults. In Speech Perception and Linguistic Experience. Edited by Winifred Strange. Timonium: York Press, pp. 171–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Zarobe, Yolanda. 2008. CLIL and foreign language learning: A longitudinal study in the Basque Country. International CLIL Research Journal 1: 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Zarobe, Yolanda. 2011. Which language competencies benefit from CLIL? An insight into Applied Linguistics Research. In Content and Foreign Language Integrated Learning: Contributions to Multilingualism in European Contexts. Edited by Yolanda Ruiz de Zarobe, Juan Manuel Sierra and Francisco Gallardo del Puerto. Bern: Peter Lang, pp. 129–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, Mari, and Colleen Moorman. 2018. Can perception training improve the production of second language phonemes? A meta-analytic review of 25 years of perception training research. Applied Psycholinguistics 39: 187–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, Marguerite Ann. 1990. Language immersion: An overview and comparison. In Foreign Language Education: Issues and Strategies. Edited by Amado Padilla, Halford H. Fairchild and Concepción M. Valadez. Newbury Park: Sage, pp. 109–26. [Google Scholar]
- Walden, Melissa Lea. 2014. Native Mandarin Speakers’ Perception and Production of English Stop + Liquid Clusters in Onset Position. Master’s thesis, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, USA. Theses-ALL. 81. Available online: https://surface.syr.edu/thesis/81 (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Zsiga, Elisabeth C. 2003. Articulatory timing in a second language. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 25: 399–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Coda Sound | Perception | Production |
|---|---|---|
| n | 68.18 | 90.9 |
| θ | 59.09 | 86.36 |
| nθ | 81.81 | 68.18 |
| p | 86.36 | 90.9 |
| k | 100 | 90.9 |
| g | 77.27 | 22.72 |
| ks | 90.9 | 90.9 |
| v | 45.45 | 0 |
| ŋ | 27.27 | 36.36 |
| nt | 77.27 | 81.81 |
| lk | 100 | 90.9 |
| Perception | Production | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Student | T1 | T2 | Gain Score | T1 | T2 | Gain Score |
| 1 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.27 | 0.82 | 0.73 | −0.09 |
| 2 | 0.91 | 0.73 | −0.18 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.18 |
| 3 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 | 1.00 | ||
| 4 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.09 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.18 |
| 5 | 0.64 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 |
| 7 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.18 |
| 8 | 0.82 | 0.64 | −0.18 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.09 |
| 9 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.18 | 0.91 | 0.73 | −0.18 |
| 10 | 0.64 | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 |
| 11 | 0.64 | 1.00 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 0.91 | 0.80 | −0.11 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 |
| 13 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| 14 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| 15 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.09 |
| 16 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.09 |
| 17 | 0.45 | 0.73 | 0.27 | 0.73 | 0.64 | −0.09 |
| 18 | 0.64 | 0.55 | −0.09 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.00 |
| 19 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.00 |
| 20 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.45 |
| 21 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.18 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 |
| 22 | 0.82 | 0.64 | −0.18 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.18 |
| % | n | θ | nθ | p | k | g | ks | v | ŋ | nt | lk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 75 | 4.54 | 11.36 | ||||||||
| θ | 63.63 | 4.54 | |||||||||
| nθ | 90.9 | ||||||||||
| p | 88.63 | ||||||||||
| k | 95.45 | 4.54 | |||||||||
| g | 4.54 | 81.81 | |||||||||
| ks | 90.90 | ||||||||||
| v | 40.90 | ||||||||||
| ŋ | 22.7 | 40.90 | |||||||||
| nt | 84.90 | ||||||||||
| lk | 100 | ||||||||||
| m | 1.6 | ||||||||||
| f | 11.36 | 18.18 | 59.09 | ||||||||
| ð | 11.36 | ||||||||||
| d | 11.36 | ||||||||||
| ng | 2.27 | 52.27 | |||||||||
| b | 2.27 | ||||||||||
| t | 9.01 | 15.90 | |||||||||
| θn | |||||||||||
| sk | 2.27 |
| % | n | θ | nθ | p | k | g | ks | v | ŋ | nt | lk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 100 | 9.1 | 4.54 | 4.54 | |||||||
| θ | 86.36 | 2.27 | |||||||||
| nθ | 88.63 | ||||||||||
| p | 100 | ||||||||||
| k | 100 | 4.54 | 2.27 | ||||||||
| g | 43.18 | ||||||||||
| ks | 95.45 | ||||||||||
| v | 13.63 | ||||||||||
| ŋ | 40.90 | ||||||||||
| nt | 93.18 | ||||||||||
| lk | 100 | ||||||||||
| f | 81.81 | ||||||||||
| ng/nx | 52.27 | ||||||||||
| t | 4.54 | ||||||||||
| d | 6.81 | ||||||||||
| x | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallardo-del-Puerto, F.; Gómez-Lacabex, E. A Longitudinal Exploration of Perception and Production of English Codas in CLIL Settings. Languages 2024, 9, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9090303
Gallardo-del-Puerto F, Gómez-Lacabex E. A Longitudinal Exploration of Perception and Production of English Codas in CLIL Settings. Languages. 2024; 9(9):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9090303
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallardo-del-Puerto, Francisco, and Esther Gómez-Lacabex. 2024. "A Longitudinal Exploration of Perception and Production of English Codas in CLIL Settings" Languages 9, no. 9: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9090303
APA StyleGallardo-del-Puerto, F., & Gómez-Lacabex, E. (2024). A Longitudinal Exploration of Perception and Production of English Codas in CLIL Settings. Languages, 9(9), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9090303







