Monitoring Engagement in the Foreign Language Classroom: Learners’ Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
Measuring L2 Engagement
- observations from the learner’s or the observer’s perspective;
- measures of engagement in-the-moment or after the event;
- measuring engagement narrowly (at a particular time and in a particular place) or broadly (for example engagement levels across a semester);
- measuring engagement directly (e.g., using physiological measures such as heart rate trackers) or indirectly (e.g., using a learner diary).
This […] has important implications for practice and how teachers interpret learner behaviors, which may outwardly resemble engagement but may in fact be complete disengagement or acts of compliance as students enact the diligent learner role. Such behavior also threatens the validity of research approaches, which may rely strongly on observational data as a measure of engagement or at least behavioral engagement. (p. 143).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Questions
- What is the face validity of Classmoto as a measure of classroom L2 engagement?
- What are its constraints and benefits, as perceived by learners?
3.2. Regarding Classmoto
3.3. Participants
3.4. Procedures
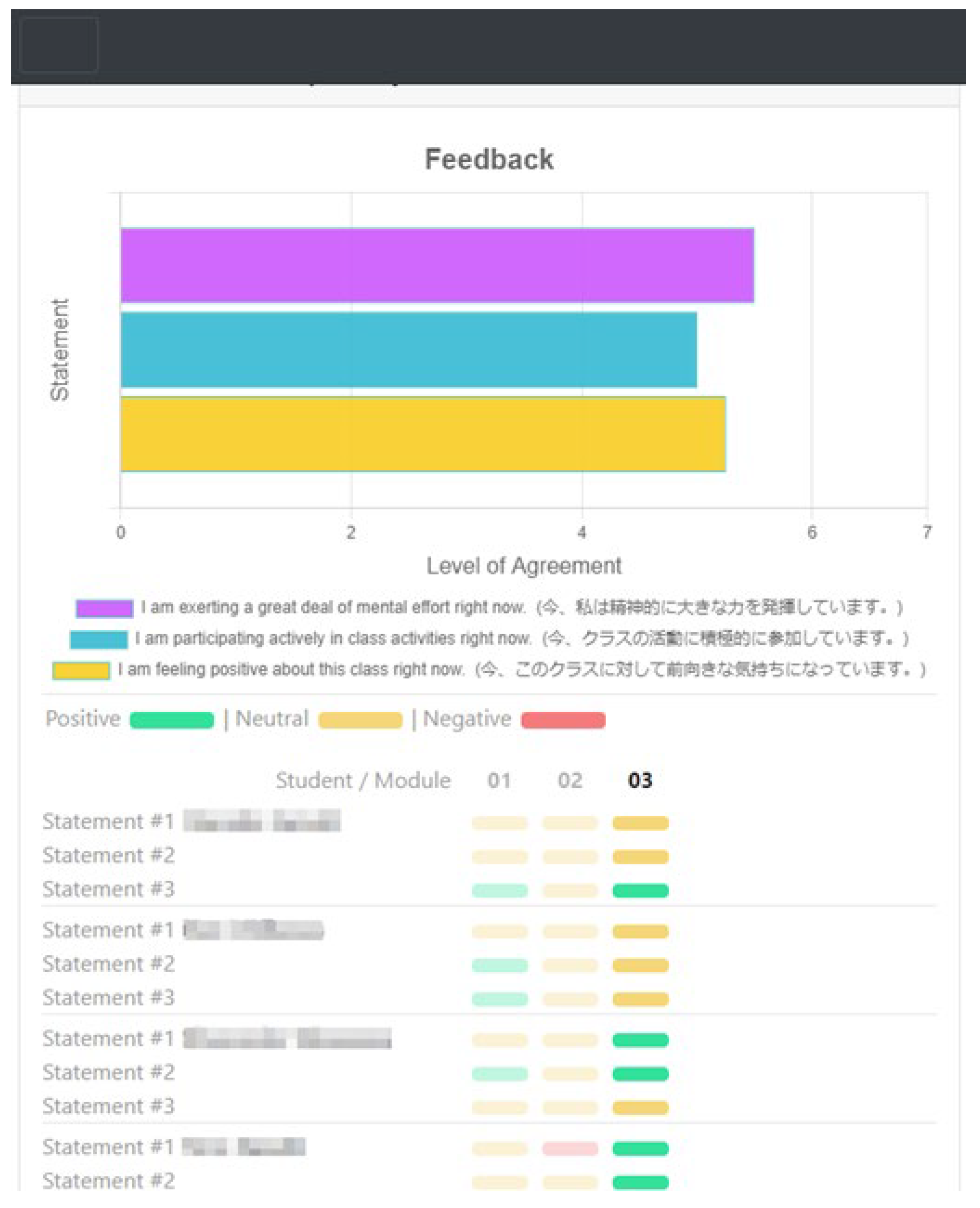
4. Results
4.1. Prompt One
- Am I trying to understand the class or not?
- This is asking my level of concentration.
- Am I focused on the lesson?
- Is the lesson easy or difficult?
- How much did I understand the lesson?
4.2. Prompt Two
- Am I participating in pair work or group work?
- Am I active in class or not?
- Do I try to improve my English through the class?
4.3. Prompt Three
- I am not exactly sure about this one
- I am comfortable that the teaching method is good or not
- If I feel good or no confidence in this class
- Do I think this class can be useful for my future?
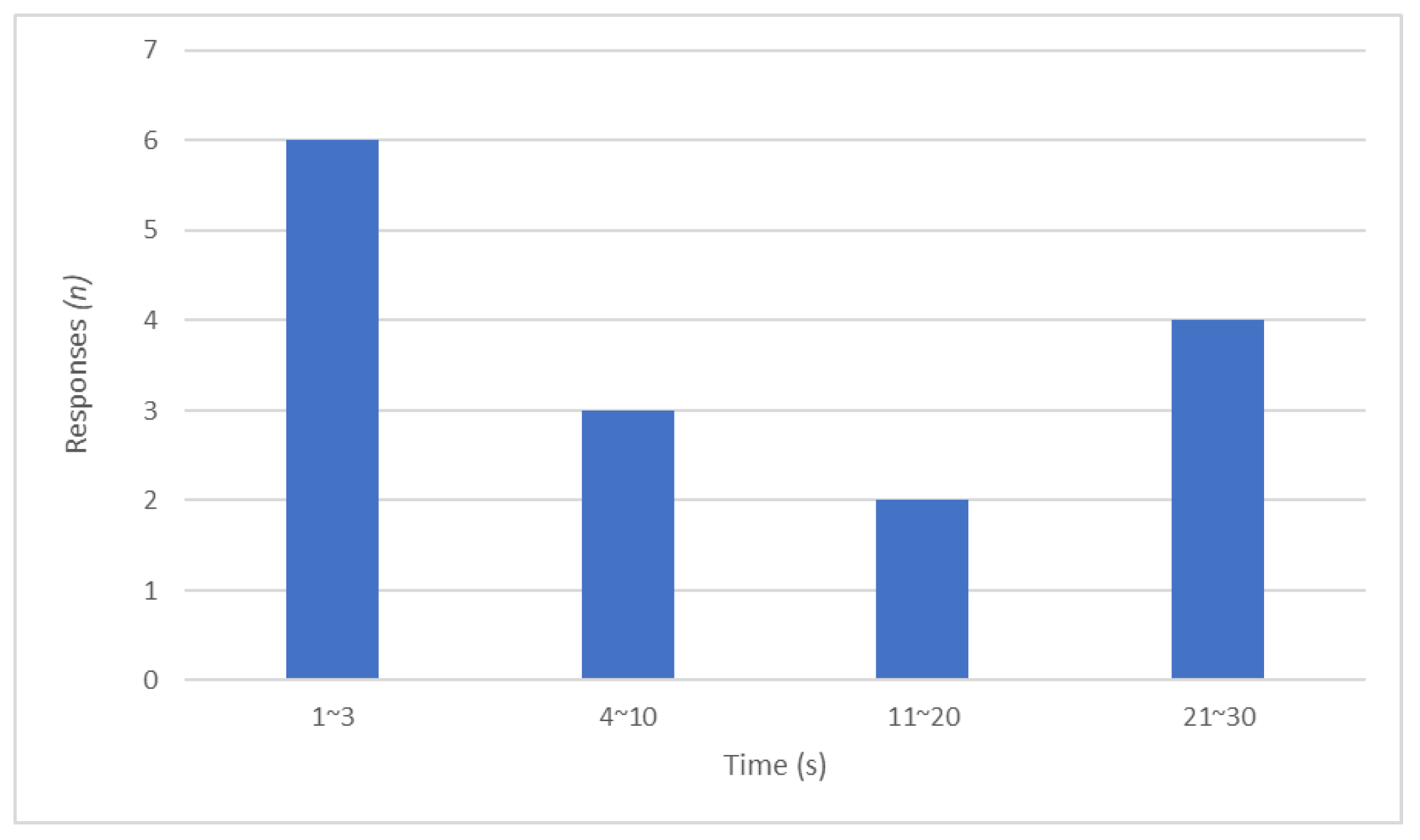
4.4. Response Times
4.5. Reflections on Using the App
I think it’s great to get in the habit of self-reflection, an opportunity to ask myself how much I am truly understanding in-the-moment. Making time for such confirmation each lesson is, I think, very important. Not only is it ok to pause during a lesson, I think we NEED to pause and make that time.
I was able to respond at the end of different parts of the lecture, for example, vocabulary, or grammar, or listening, so I was able to analyze which parts were easy and which parts I wasn’t so good at. So it was a good thing for me to think about my learning. The frequent stopping to reflect didn’t interrupt my learning, I think.
Well, it was much more refined than the usual, end-of-semester type of questionnaires that just ask for a general reaction. With this, we could give our response to each individual activity, so it’s much more useful, I think. I mean, everything just gets garbled into one if we only do it one time.
Responding to the survey didn’t interfere with my concentration, etc. I mean, we were changing topics in the class anyway, like from vocabulary study to grammar, so my mind had to reset anyway.
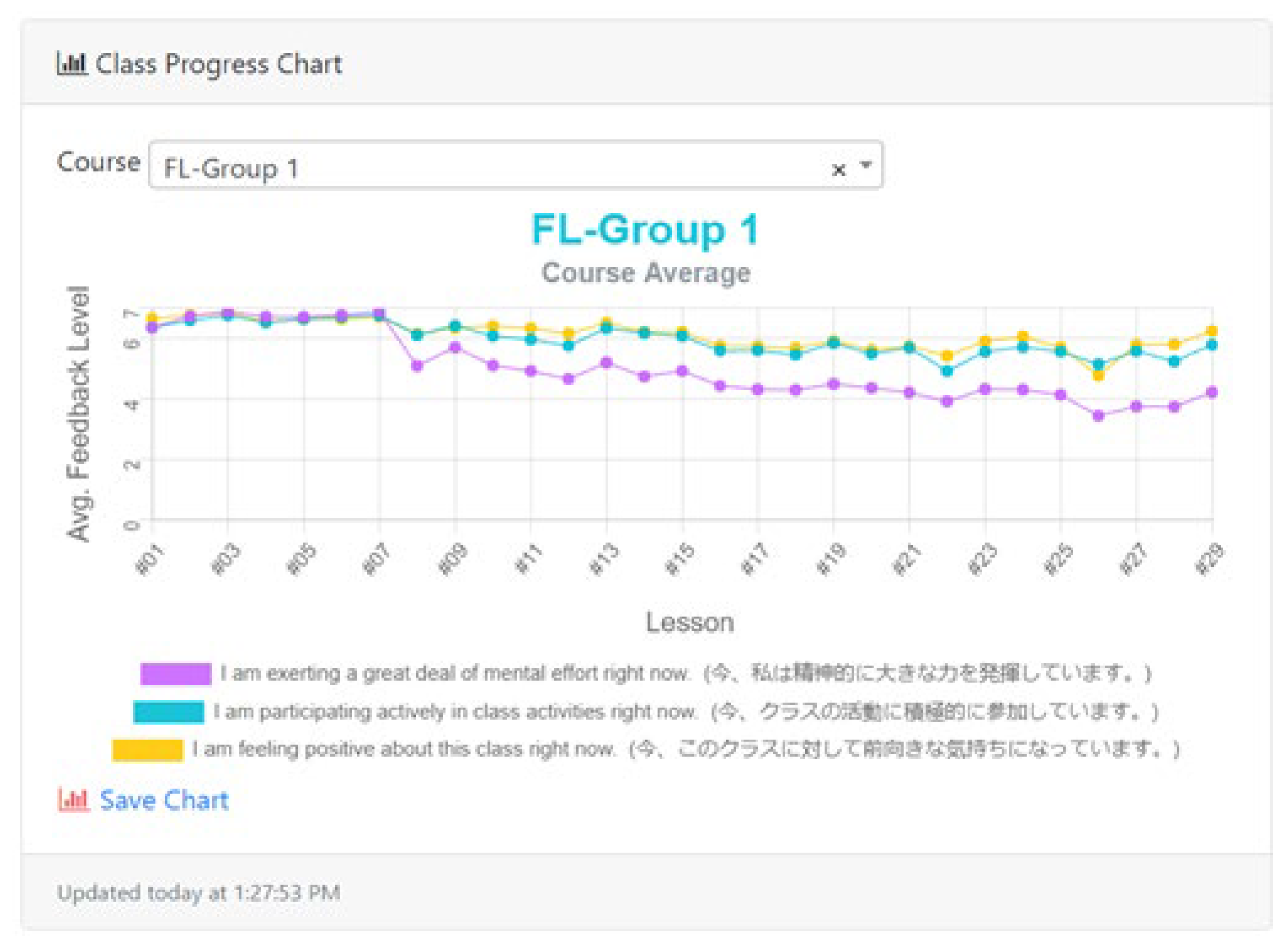
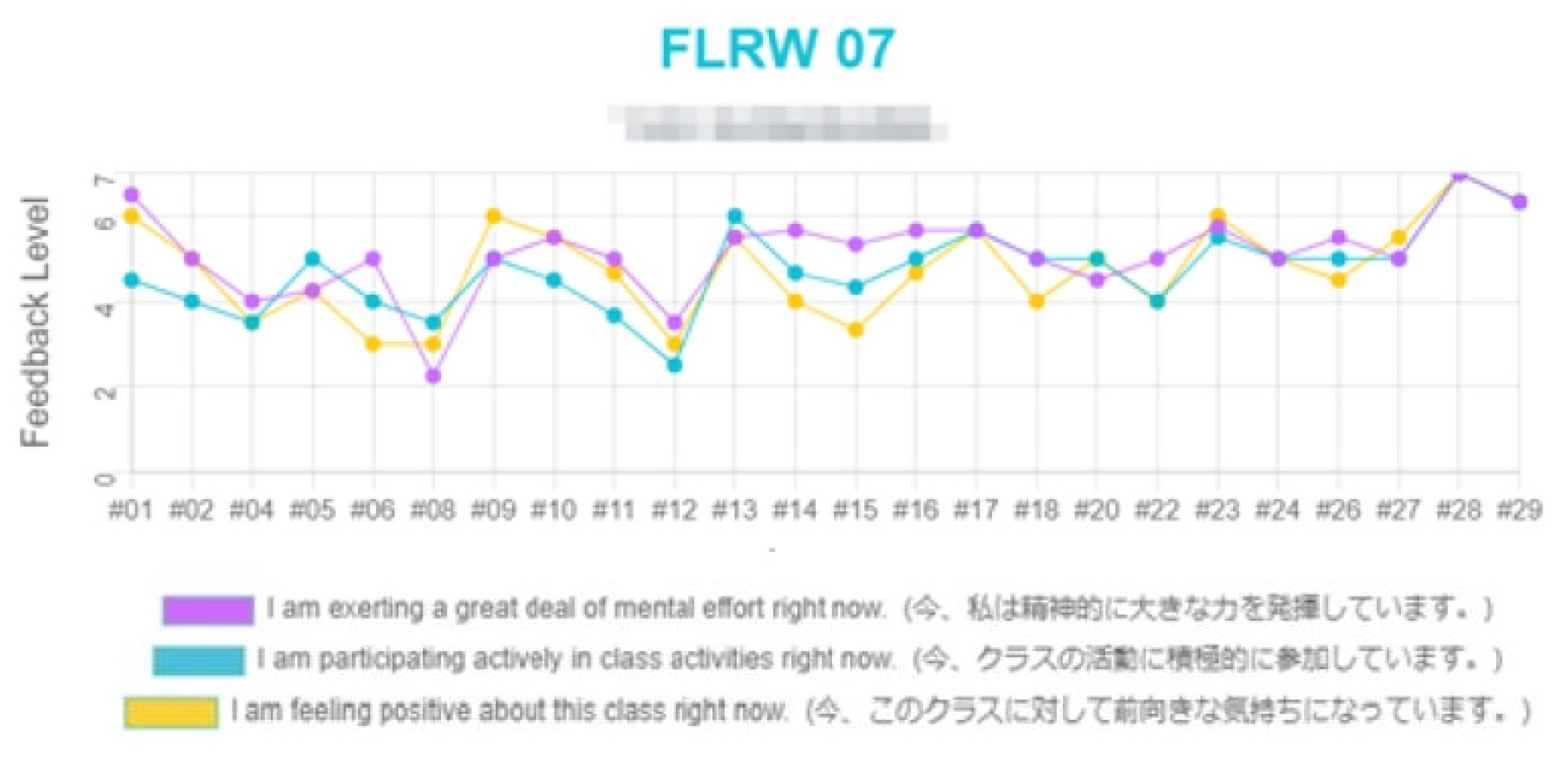
4.6. Individual Discussion of Results
- Interviewer:
- So here, there’s a slight dip in your responses to Q1. Was there a reason for that?
- Student:
- I think that lesson, I had trouble understanding the nuance between English my native language, because that nuance does not exist between [student’s native language] and Japanese.
- Interviewer:
- In that case, wouldn’t your ratings go UP, as you had to concentrate harder to understand the lesson? But you input a lower score?
- Student:
- I gave a lower score because I think I understood less. Oh, did I make a mistake?
- Interviewer:
- Yes, but don’t worry about it. But didn’t you understand when I explained about the questions and how to answer at the beginning of the semester?
- Student:
- Yes, I did. I think I answered correct [SIC] at first, but then one time I forgot and answered wrong thing [SIC] and then everything after that was wrong thing [SIC].
- Interviewer:
- Looking at your responses to Q2 and Q3, at first your engagement seemed a bit low, but then it rose up and stayed high?
- Student:
- In the beginning of the semester, I was very worried about if I’d be able to keep up in class.
- Interviewer:
- Ah, but as you got used to the class …
- Student:
- Yeah, once I got used to you and the class.
- Interviewer:
- Your ratings for Q3 are high, but not at the max. So I take it to mean that you feel the class had value for you, but some things could be better?
- Student:
- Yeah, we do a lot of listening and answering questions from the book, right? But I don’t want to improve my writing, I want to improve my speaking, so that’s where I think the class could be better for me. Then you made free-talk conversation warm-up activities for us and I was very happy and felt more positive after that.
5. Discussion
5.1. Research Question 1
5.2. Research Question 2
6. Limitations and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Did you understand the three prompts in the Classmoto app clearly?
- In your own words, please describe what you think the prompts were asking you.
- How long did it take you to respond each time?
- Did you find anything positive about using Classmoto?
- Did you find any negative aspects of using Classmoto?
References
- Beal, Daniel, and Howard M. Weiss. 2003. Methods of Ecological Momentary Assessment in Organizational Research. Organizational Research Methods 6: 440–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, Euan, Kevin Garvey, Matthew Miner, Sam Godin, and Hayo Reinders. 2022. Measuring real-time learner engagement in the Japanese EFL classroom. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching 17: 254–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogol, Katarzyna, Martin Brunner, Thomas Goetz, Romain Martin, Sonja Ugen, Ulrich Keller, Antoine Fischbach, and Franzis Preckel. 2014. “My Questionnaire is Too Long!” The assessments of motivational-affective constructs with three-item and single-item measures. Contemporary Educational Psychology 39: 188–205. Available online: https://kops.uni-konstanz.de/bitstream/handle/123456789/29722/Gogol_0-262761.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hiver, Phil, Ali H. Al-Hoorie, Joseph P. Vitta, and Janice Wu. 2021. Engagement in language learning: A systematic review of 20 years of research methods and definitions. Language Teaching Research 28: 201–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen-Freeman, Diane, Paul Driver, Xuesong Gao, and Sarah Mercer. 2021. Learner Agency: Maximizing Learner Potential [PDF]. Available online: http://www.oup.com/elt/expert (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Larson, Reed, and Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. 2014. The experience sampling method. In Flow and the Foundations of Positive Psychology: The Collected Works of Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Bradford J. 2020. Enhancing listening comprehension through kinesthetic rhythm training. RELC Journal 53: 567–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Hao, Yunhuo Cui, and Wenye Zhou. 2018. Relationships between student engagement and academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal 46: 517–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Andrew J. 2009. Motivation and engagement across the academic life span: A developmental construct validity study of elementary school, high school, and university/college students. Educational and Psychological Measurement 69: 794–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, Sarah, Kyle R. Talbot, and Isobel K. H. Wang. 2021. Fake or real engagement–Looks can be deceiving. In Student Engagement in the Language Classroom. Edited by Paul Hiver, Ali Al-Hoorie and Sarah Mercer. Bristol and Blue Ridge Summit: Multilingual Matters, pp. 143–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oga-Baldwin, W. L. Quint. 2019. Acting, thinking, feeling, making, collaborating: The engagement process in foreign language learning. System 86: 102–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oga-Baldwin, W. L. Quint, and Yoshiyuki Nakata. 2017. Engagement, gender, and motivation: A predictive model for Japanese young language learners. System 65: 151–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, Hayo, Bradford J. Lee, and Euan Bonner. 2023. Tracking learner engagement in the L2 classroom with experience sampling. Research Methods in Applied Linguistics 2: 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, Ellen A., Thomas A. Kindermann, and Carrie J. Furrer. 2009a. A motivational perspective on engagement and disaffection: Conceptualization and assessment of children’s behavioral and emotional participation in academic activities in the classroom. Educational and Psychological Measurement 69: 493–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, Ellen A., Thomas A. Kindermann, James P. Connell, and James G. Wellborn. 2009b. Engagement and disaffection as organizational constructs in the dynamics of motivational development. In Educational Psychology Handbook Series. Handbook of Motivation at School. Edited by Kathryn R. Wenzel and Allan Wigfield. London: Routledge, pp. 223–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sulis, Giulia. 2022. Engagement in the foreign language classroom: Micro and macro perspectives. System 110: 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, Jennifer E., Avi Kaplan, Katja Upadyaya, Katarilna Salmela-Aro, Benjamin M. Torsney, Ellen Skinner, and Jacquelynne S. Eccles. 2021a. Momentary Engagement as a Complex Dynamic System. PsyArXiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, Jennifer E., James B. Schreiber, and Benjamin M. Torsney. 2021b. Silver linings and storm clouds: Divergent profiles of student momentary engagement emerge in response to the same task. Journal of Educational Psychology 113: 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Yang, Yu Meng, Zhenya Gao, and Xiangdong Yang. 2022. Perceived teacher support, student engagement, and academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology 42: 401–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teravainen-Goff, Anne. 2022. Why motivated learners might not engage in language learning: An exploratory interview study of language learners and teachers. Language Teaching Research, 13621688221135399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekveld, Adriana A., and Sophia E. Kramer. 2014. Cognitive processing load across a wide range of listening conditions: Insights from pupillometry. Psychophysiology 51: 277–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Shiyao, Phil Hiver, and Ali H. Al-Hoorie. 2021. Measuring L2 engagement: A review of issues and applications. In Student Engagement in the Language Classroom. Edited by Phil Hiver, Ali Al-Hoorie and Sarah Mercer. Bristol and Blue Ridge Summit: Multilingual Matters, pp. 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Yes | Maybe | No | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Q1) Did you understand the three prompts in the Classmoto app clearly? | 13 (86.7%) | 2 (13.3%) | 0 |
| (Q2) In Your Own Words, Please Describe What You Think the Prompts Were Asking You. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Correct | Ambiguous | Incorrect | |
| Prompt One (cognitive) | 11 (73.3%) | 2 (13.3%) | 2 (13.3%) |
| Prompt Two (behavioral) | 12 (80%) | 3 (20%) | 0 |
| Prompt Three (emotive) | 14 (93.3%) | 0 | 1 (6.7%) |
| Yes | No | |
|---|---|---|
| (Q4) Did you find anything positive about using Classmoto? | 15 | 0 |
| (Q5) Did you feel there were any negative aspects of Classmoto? | 0 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.J.; Reinders, H.; Bonner, E. Monitoring Engagement in the Foreign Language Classroom: Learners’ Perspectives. Languages 2024, 9, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9020053
Lee BJ, Reinders H, Bonner E. Monitoring Engagement in the Foreign Language Classroom: Learners’ Perspectives. Languages. 2024; 9(2):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9020053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Bradford J., Hayo Reinders, and Euan Bonner. 2024. "Monitoring Engagement in the Foreign Language Classroom: Learners’ Perspectives" Languages 9, no. 2: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9020053
APA StyleLee, B. J., Reinders, H., & Bonner, E. (2024). Monitoring Engagement in the Foreign Language Classroom: Learners’ Perspectives. Languages, 9(2), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages9020053







