Sentence Prosody and Register Variation in Arabic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Diglossia in Arabic
1.2. Sentence Prosody in Arabic
1.3. Sentence Prosody and Bilingualism
1.4. The Present Study
2. Methods
2.1. Participants, Materials and Procedure
2.2. Analysis
| 1. | a. | F | naˈqu:lu | ˈla-ha: |
| say.1PL | to-it | |||
| b. | W | naˈɡu:lu | ˈla-hu | |
| say.1PL | to-it | |||
| c. | A | nuˈɡulluh | ||
| say.1PL.to.it | ||||
| ‘we say for it’ | ||||
| 2. | a. | F | laˈdaj-na: |
| to-us | |||
| b. | W | laˈde:-na | |
| to-us | |||
| c. | A | ˈʕinda-na | |
| to-us | |||
| ‘we have’ |
3. Results
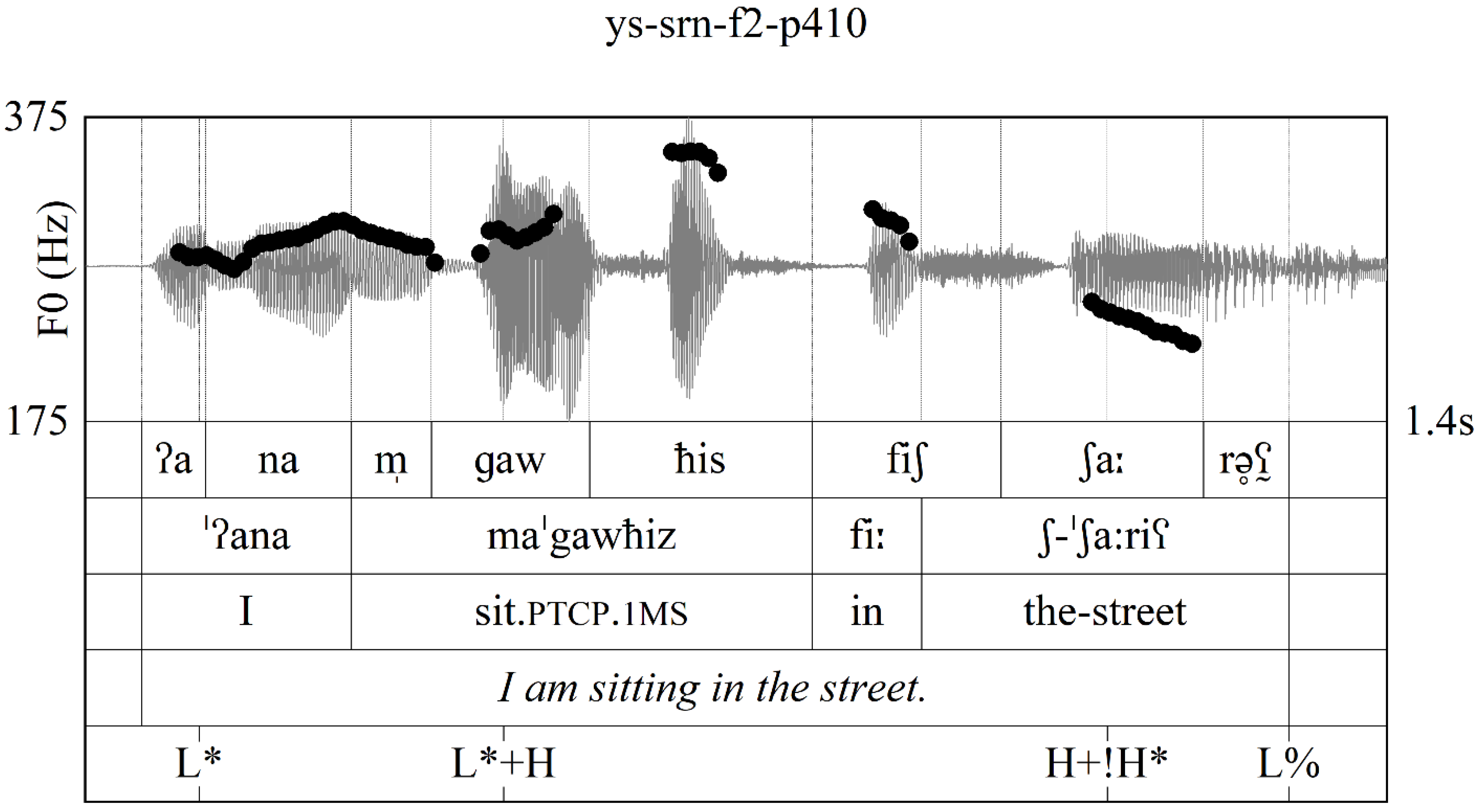
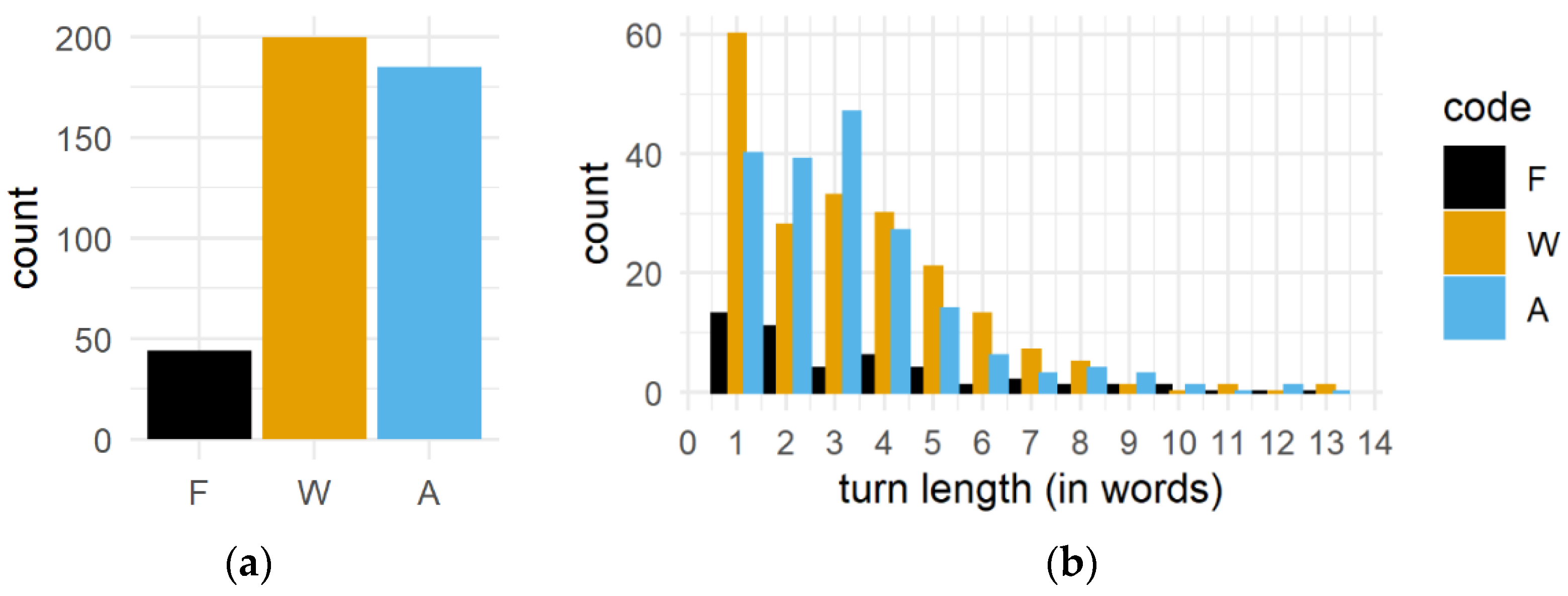
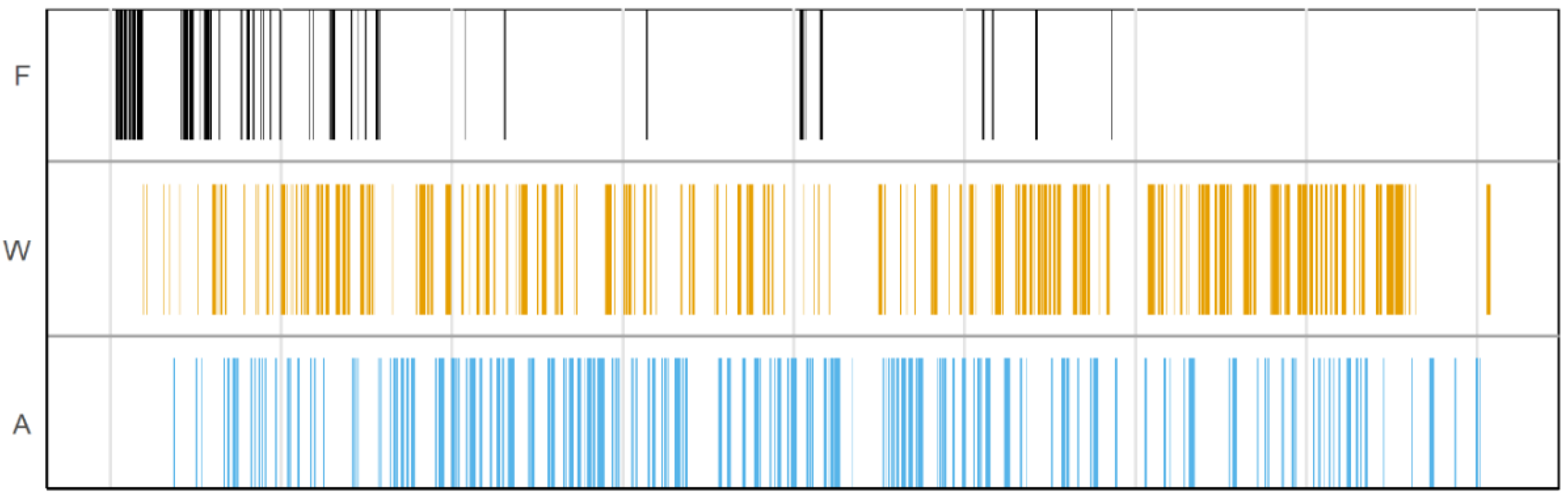
3.1. Overview of the Data
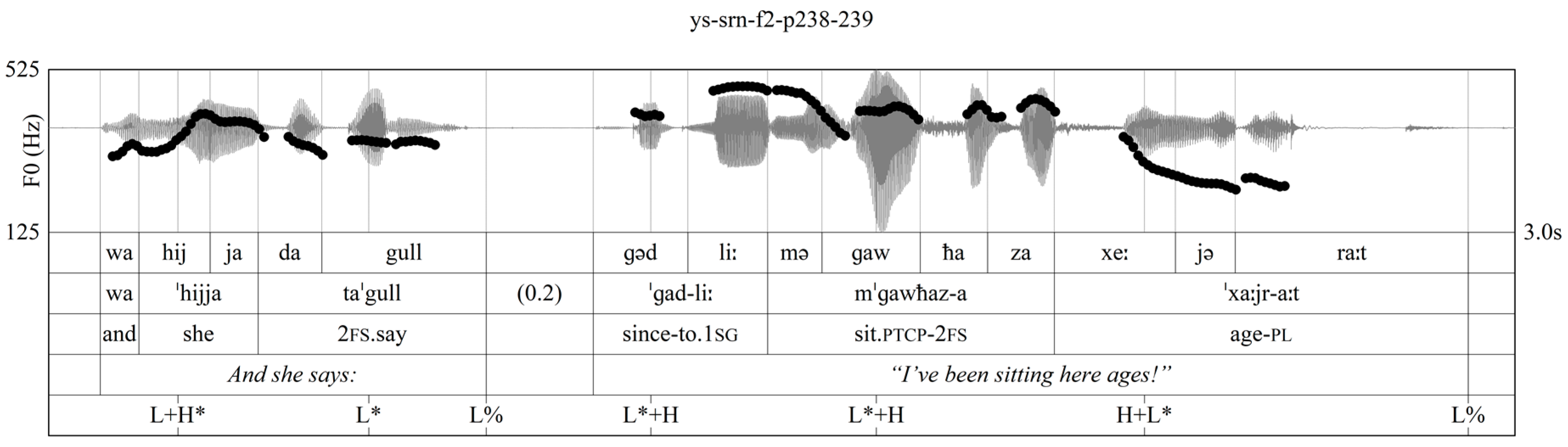
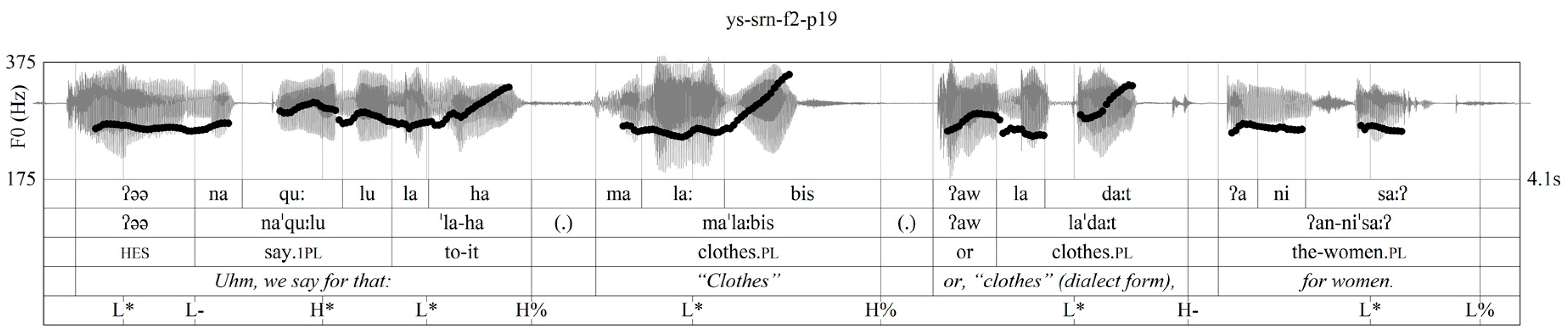
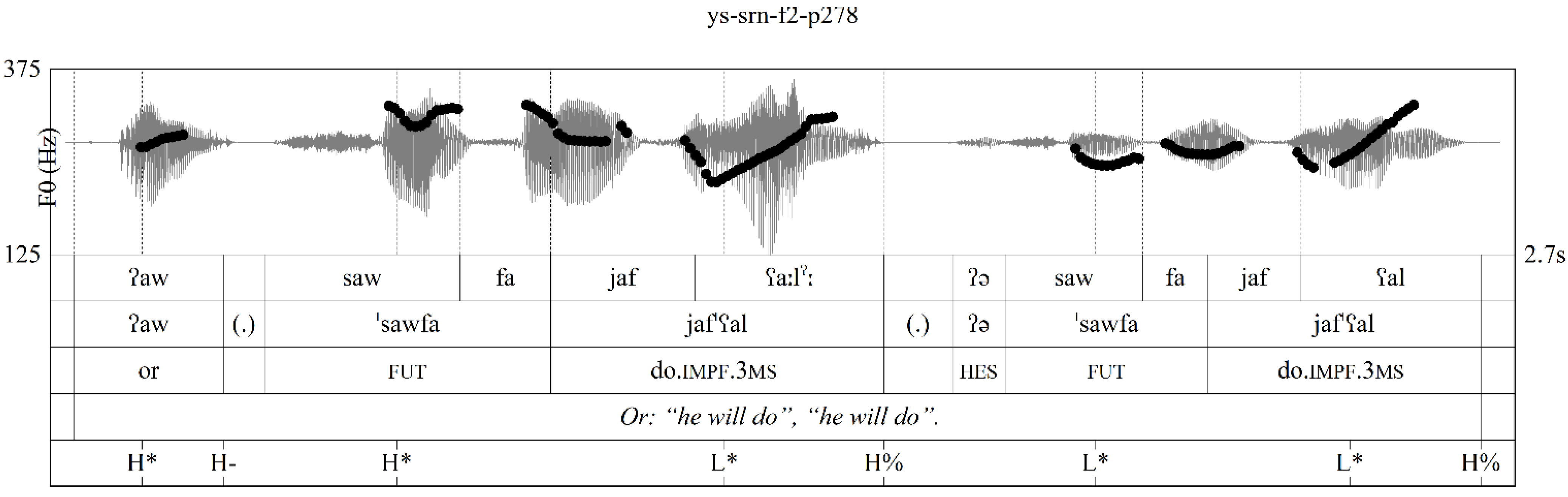
3.2. F0 Variation
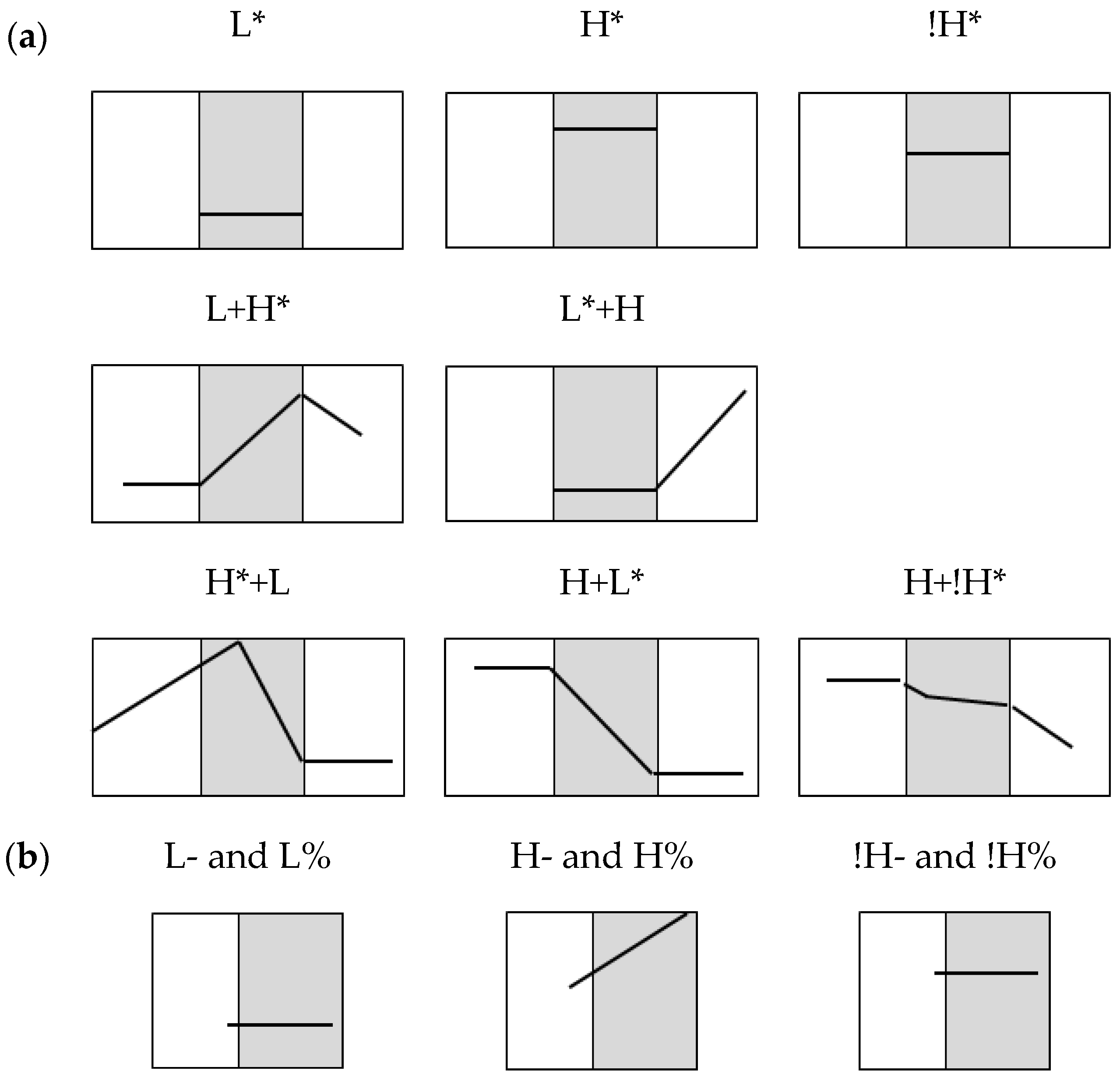
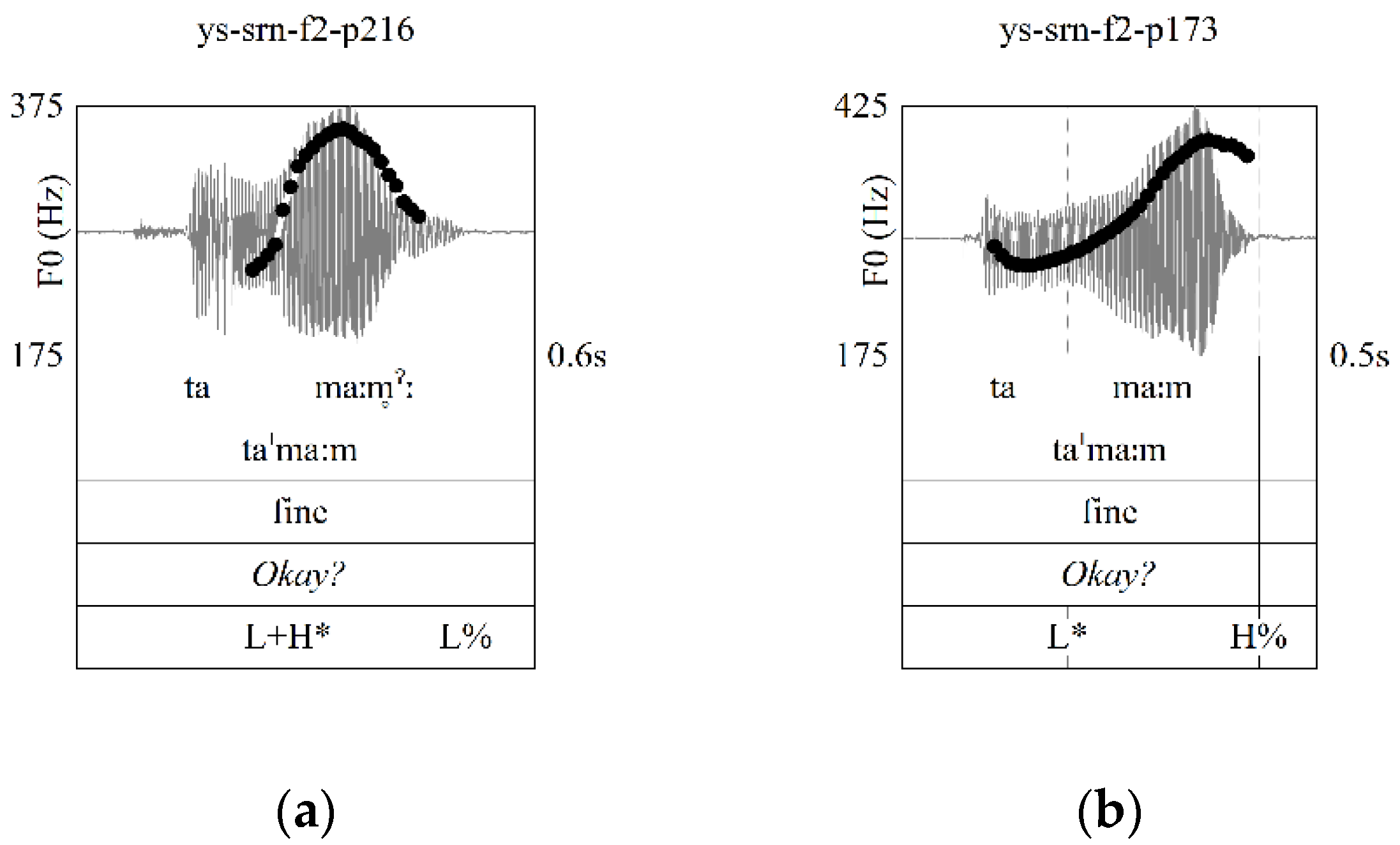
3.3. Intonational Phonology
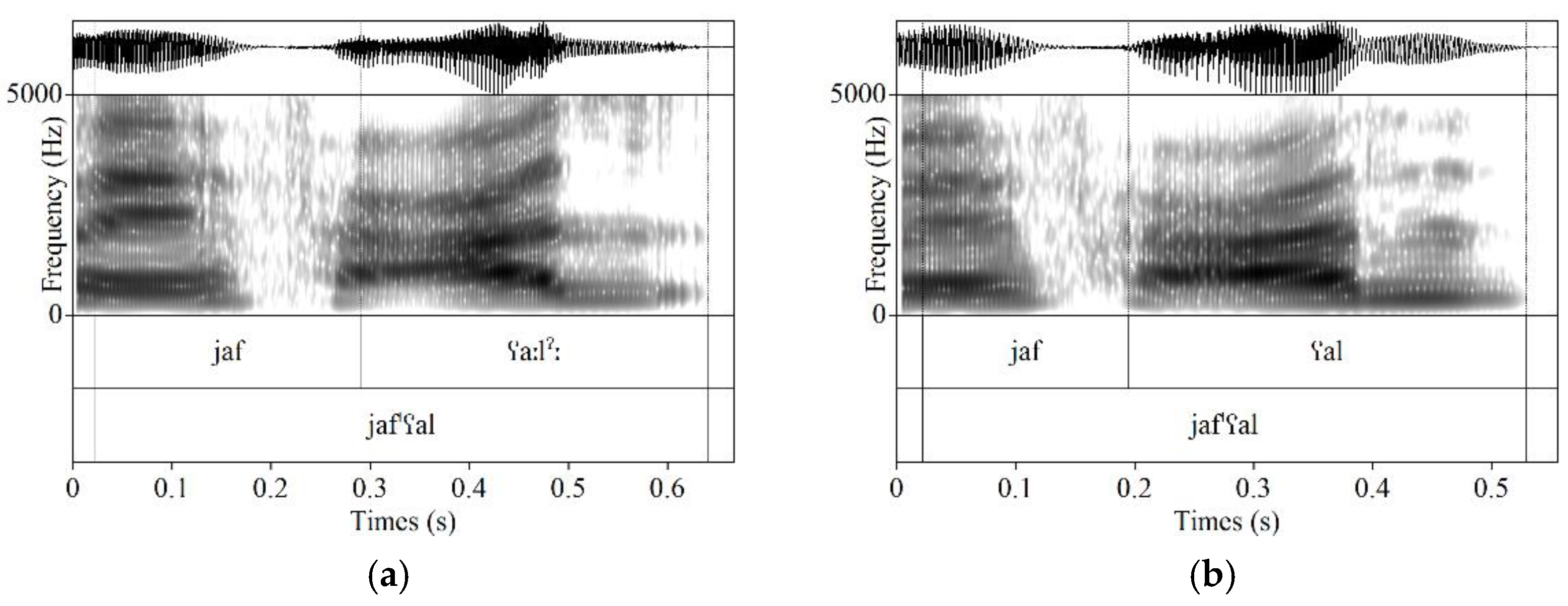
3.4. Post-Lexical Laryngealization
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Alharbi, Lafi. 1991. Formal Analysis of Intonation: The Case of the Kuwaiti Dialect of Arabic. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Herriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Albirini, Abdulkafi. 2016. Modern Arabic Sociolinguistics: Diglossia, Variation, Codeswitching, Attitudes and Identity. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Albirini, Abdulkafi. 2019. The acquisition of Arabic as a first language. In The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Enam Al-Wer and Uri Horesh. London: Routledge, pp. 227–48. [Google Scholar]
- Badawi, El-Said M. 1965. An Intonational Study of Colloquial Riyadhi Arabic. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, SOAS University of London, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Badawi, El-Said M. 1973. Mustawayaat al-’arabiiya al-mu’aasira fii miSr: BaHth ‘ilaaqat al-lugha bi al-HaDaara. Cairo: Daar al-Ma’aarif. [Google Scholar]
- Bassiouney, Reem. 2009. Arabic Sociolinguistics. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Benkirane, Thami. 1998. Intonation in Western Arabic (Morocco). In Intonation Systems: A Survey of Twenty Languages. Edited by Daniel Hirst and Albert Di Cristo. Cambridge: CUP, pp. 345–59. [Google Scholar]
- Boersma, Paul, and David Weenink. 1992–2018. Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer, Version 6.0.40. [Computer Program]; Available online: www.praat.org (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Bullock, Barbara E. 2009. Prosody in contact in French: A case study from a heritage variety in the USA. International Journal of Bilingualism 13: 165–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, Dana. 2006. Intonation. In Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics. Edited by Kees Versteegh. Leiden: Brill Academic, vol. 2, pp. 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Colantoni, Laura, and Jorge Gurlekian. 2004. Convergence and intonation: Historical evidence from Buenos Aires Spanish. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 7: 107–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Zarka, Dina. 2017. Arabic Intonation. Oxford Handbooks Online. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zarka, Dina, and Sam Hellmuth. 2008. Variation in the intonation of Egyptian Formal and Colloquial Arabic. Langues et Linguistique: Revue Internationale de Linguistique 22: 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fagyal, Zsuzsanna. 2005. Prosodic Consequences of Being a Beur: French in Contact with Immigrant Languages in Paris. University of Pennsylvania Working Papers in Linguistics 10: 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, Charles A. 1959. Diglossia. Word 15: 325–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froud, Karen, and Reem Khamis-Dakwar. 2017. Neurophysiological investigations in studies of Arabic linguistics: The case of Arabic diglossia. In The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Elabbas Benmamoun and Reem Bassiouney. London: Routledge, pp. 249–62. [Google Scholar]
- Froud, Karen, and Reem Khamis-Dakwar. 2021. The Study of Arabic Language Acquisition: A Critical Review. In The Cambridge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Karin C. Ryding and David Wilmsen. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 48–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gorman, Kyle, Jonathan Howell, and Michael Wagner. 2011. Prosodylab-Aligner: A tool for forced alignment of laboratory speech. Journal of the Canadian Acoustical Association 39: 192–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, Andreas. 2016. Case Endings in Spoken Standard Arabic. Lund: Studia Orientalia Lundensia. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmuth, Sam. 2014. Dialectal variation in Arabic intonation: Motivations for a multi-level corpus approach. In Perspectives on Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Samira Farwaneh and Hamid Ouali. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 63–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmuth, Sam. 2018. Variation in polar interrogative contours within and between Arabic dialects. Paper presented at the 9th International Conference on Speech Prosody 2018, Poznań, Poland, June 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hellmuth, Sam, and Rana Almbark. 2019. Intonational Variation in Arabic Corpus 2011–2017. Essex: UK Data Service. [Google Scholar]
- Hualde, José, and Pilar Prieto. 2016. Towards an International Prosodic Alphabet (IPrA). Laboratory Phonology: Journal of the Association for Laboratory Phonology 7: 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaye, Alan S. 1972. Remarks on diglossia in Arabic: Well-defined vs. ill-defined. Linguistics 10: 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis-Dakwar, Reem, and Karen Froud. 2014. Neurocognitive modeling of the two language varieties in Arabic Diglossia. In Perspectives on Arabic Linguistics XXVI. Edited by Reem Khamis-Dakwar and Karen Froud. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 285–302. [Google Scholar]
- Khamis-Dakwar, Reem, and Karen Froud. 2019. Diglossia and language development. In The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Sociolinguistics. Edited by Enam Al-Wer and Uri Horesh. London: Routledge, pp. 300–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, D. Robert. 2008. Intonational Phonology, 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Llamas, Carmen. 2007. A new methodology: Data elicitation for regional and social language variation studies. York Papers in Linguistics Series 8: 138–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mejdell, Gunvor. 2006. Mixed Styles in Spoken Arabic in Egypt. Leiden: Brill. [Google Scholar]
- Mejdell, Gunvor. 2019. Diglossia. In The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics. Edited by Enam Al-Wer and Uri Horesh. London: Routledge, pp. 332–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mennen, Ineke. 2015. Beyond segments: Towards a L2 intonation learning theory. In Prosody and Language in Contact. Edited by Elisabeth Delais-Roussarie, Mathieu Avanzi and Sophie Herment. Berlin: Springer, pp. 171–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, Terence Frederick. 1975. Principles of Firthian Linguistics. London: Longman. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, Terence Frederick. 1984. Soziolinguistische und stilistische Aspekte des gesprochenen Arabisch der Gebildeten in Ägypten und der Levante. Sitzungsberichte der Sächsischen Akad. d. Wissenschaften in Leipzig, Philolog. -hist. Klasse 123: 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, Terence Frederick. 1986. What is educated spoken Arabic? International Journal of the Sociology of Language, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, Claire. 2015. Intonational variation and change in Scottish Gaelic. Lingua 160: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, Erin. 2004. Peak placement in two regional varieties of Peruvian Spanish intonation. In Contemporary Approaches to Romance Linguistics. Selected Papers from the 33rd Linguistic Symposium on Romance Languages (LSRL). Edited by Julie Auger, J. Clancy Clements and Barbara Vance. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 321–42. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, Jonathan. 2019. Style and sociolinguistics. In The Routledge Handbook of Arabic Sociolinguistics. Edited by Enam Al-Wer and Uri Horesh. London: Routledge, pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, Dilworth B. 1991. Searching for Modern Fusha: Real-life formal Arabic. Al-Arabiyya 24: 31–64. [Google Scholar]
- Queen, Robin. 2012. Turkish-German bilinguals and their intonation: Triangulating evidence about contact-induced language change. Language 88: 791–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. 2014. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Core Team. [Google Scholar]
- Raabe. 2021. Vistime: Pretty Timelines in R, Version 1.2.1. [Computer Program]; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vistime/ (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Rastegar-El Zarka, Dina. 1997. Prosodische Phonologie des Arabischen. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Karl-Franzens-Universität, Graz, Austria. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenhouse, Judith. 2011. Intonation in the colloquial Arabic of Haifa: A syntactic-phonetic sociolinguistic study. Israel Studies in Language and Society 4: 117–42. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, Nada Mohammed, and Stefanie Pillai. 2020. An Acoustic Analysis of Intonation in the Taizzi variety of Yemeni Arabic. Linguistics Journal 14: 154–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sloetjes, Han, and Peter Wittenburg. 2008. Annotation by category: ELAN and ISO DCR. Paper presented at the 6th international Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2008), Marrakech, Morocco, May 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sorace, Antonella. 2004. Native language attrition and developmental instability at the syntax-discourse interface: Data, interpretations and methods. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 7: 143–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soraya, Helmy A. I. 1966. An Intonational Study of Egyptian Colloquial Arabic. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, SOAS University of London, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E. 1993. A Syntax of San’ani Arabic. Wiesbaden: Harrossowitz Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E. 1996. Sbahtu! A Course in San’ani Arabic. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E. 2000. Wasf San’a: Texts in San’ani Arabic. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E. 2002. The Phonology and Morphology of Arabic. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E., and Yahya Asiri. 2008. Pre-pausal devoicing and glottalisation in varieties of the south-western Arabian Peninsula. Langues et Linguistique: Revue Internationale de Linguistique 22: 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E., and Alex Bellem. 2011. Glottalisation and neutralisation in Yemeni Arabic and Mehri: An acoustic study. In Instrumental Studies in Arabic Phonetics. Edited by Zeki Majeed Hassan and Barry Heselwood. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 235–56. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, Janet C. E., and Jack Wilson. 2017. Gesture in Modern South Arabian Languages: Variation in multimodal constructions during task-based interaction. Brill’s Journal of Afroasiatic Languages and Linguistics 9: 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, Hadley. 2010. ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis. Journal of Statistical Software 35: 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, Bodo, and Sven Grawunder. 2012. The phonetic profile of Korean formal and informal speech registers. Journal of Phonetics 40: 808–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, Munther. 2014. The Integrated Approach to Arabic Instruction. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
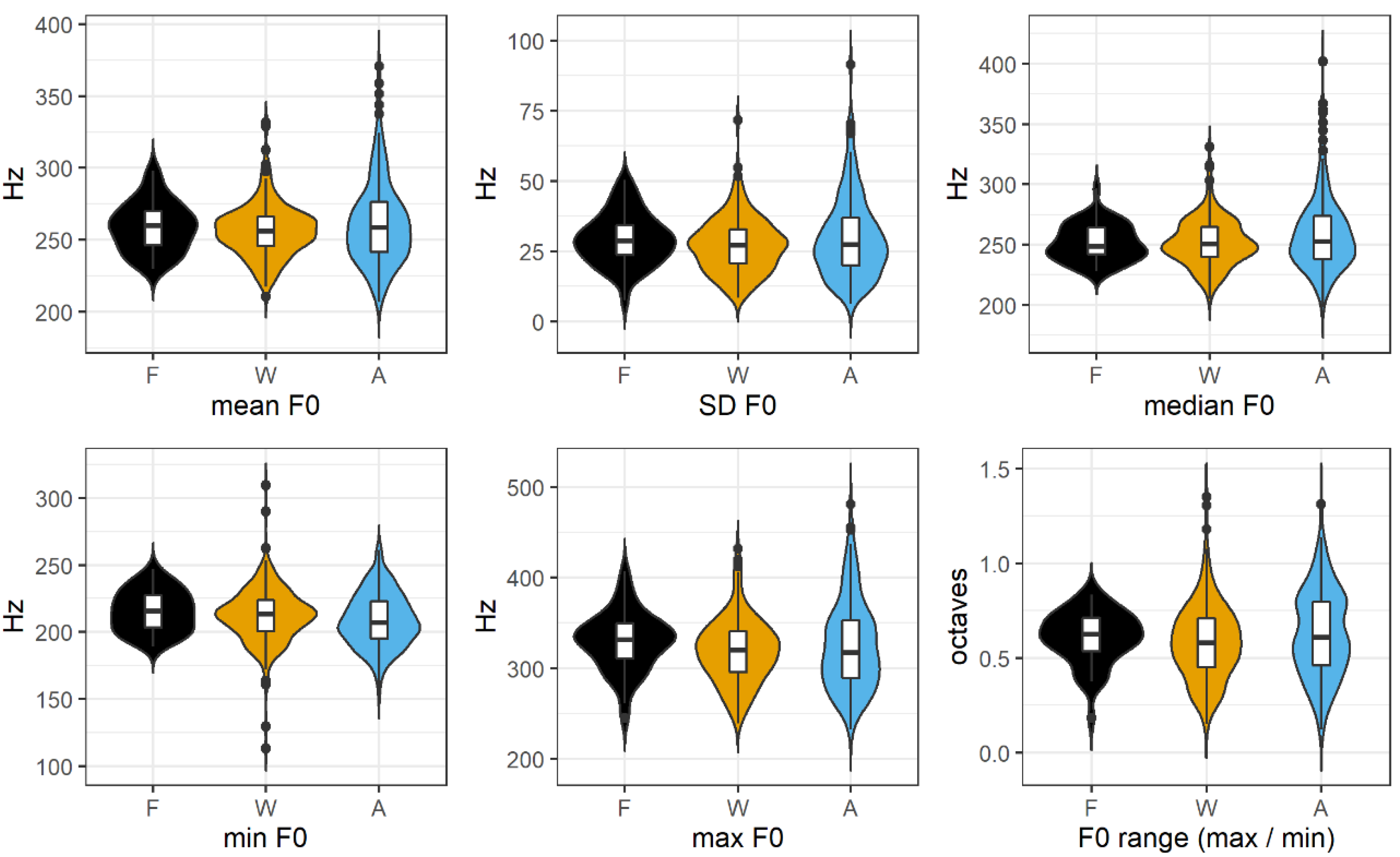




| Register | Min (Hz) | Max (Hz) | Mean (Hz) | SD (Hz) | Median (Hz) | Range (Octaves) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 215.58 (15.35) | 329.68 (32.51) | 258.97 (17.17) | 29.34 (9.27) | 251.84 (15.20) | 0.61 (0.14) |
| W | 212.41 (21.53) | 318.89 (35.86) | 256.64 (18.84) | 27.09 (9.80) | 252.00 (19.79) | 0.58 (0.20) |
| A | 209.11 (19.83) | 325.53 (48.69) | 261.74 (29.29) | 29.77 (14.43) | 259.46 (31.85) | 0.63 (0.23) |
| Register | L* | H* | !H* | L+H* | L*+H | H*+L | H+L* | H+!H* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 66 | 28 | 5 | 14 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| W | 246 | 144 | 56 | 33 | 15 | 11 | 3 | 7 |
| A | 170 | 112 | 58 | 32 | 37 | 28 | 3 | 36 |
| Register | L- | H- | !H- | Total | L% | H% | !H% | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 1 | 19 | 0 | 20 | 13 | 31 | 6 | 50 |
| W | 25 | 48 | 0 | 73 | 108 | 114 | 0 | 222 |
| A | 25 | 47 | 3 | 75 | 144 | 51 | 12 | 207 |
| Register | Turns with > 1 Phrase | Turns with > 1 Word | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | 15 | 31 | 48% |
| W | 74 | 140 | 52% |
| A | 74 | 145 | 51% |
| Register | L* L% | L* H% | L* !H% | H* H% | H* L% | !H* L% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 16% | 56% | 14% | 0% | 5% | 7% |
| W | 17% | 43% | 0% | 5% | 10% | 18% |
| A | 21% | 15% | 4% | 3% | 11% | 21% |
| Register | L+H* L% | L+H* H% | L+H* !H* | L*+H H% | H*+L L% | H*+L H% | H+!H* L% | H+!H* H% | H+L* L% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 0% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| W | 1% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 1% | 2% | 4% | 0% | 1% |
| A | 0% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 5% | 0% | 13% | 3% | 2% |
| Laryngealized? | L* H% | L* !H% | H* L% | L+H* L% | H*+L L% | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| yes | 5 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 9 |
| no | 27 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 32 |
| Total | 32 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 41 |
| Pattern | F0 Variation | Intonation | Laryngealization |
|---|---|---|---|
| F&W vs. A | bimodal median F0 level of median F0 | pitch accent inventory size use of secondary accents | % laryngealization |
| F vs. W&A | -- | broadcast MSA-style contours | -- |
| F vs. W vs. A | -- | -- | -- |
| F&W&A | -- | density of phrasing boundaries | -- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hellmuth, S. Sentence Prosody and Register Variation in Arabic. Languages 2022, 7, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7020129
Hellmuth S. Sentence Prosody and Register Variation in Arabic. Languages. 2022; 7(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7020129
Chicago/Turabian StyleHellmuth, Sam. 2022. "Sentence Prosody and Register Variation in Arabic" Languages 7, no. 2: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7020129
APA StyleHellmuth, S. (2022). Sentence Prosody and Register Variation in Arabic. Languages, 7(2), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages7020129






