Abstract
The variable area bypass injector (VABI) plays a crucial role in variable cycle engines by regulating the flow mixing process in complex bypass ducts, and low-dimensional theoretical models are the key to revealing its working mechanism while estimating its aerodynamic performance. An improved VABI model using the control volume method is established, through which the feature parameters that determine the VABI aerodynamic performance are summarized. To acquire an accurate prediction of the injection ratio, a calibration item is introduced to the governing equations to consider the static pressure discrepancy on the mixing plane, and a numerical database is developed to obtain the calibration item. Results show that the aerodynamic parameters that determine the VABI performance include the bypass total pressure ratio, bypass backpressure, and the injection ratio, while the injection angle and the VABI opening area also influence the injection flow characteristics. The injection ratio is increased by reducing the bypass total pressure ratio, decreasing the bypass backpressure, and closing the VABI. Numerical validation shows that the calculation error of the improved model is generally below 3%. The improved VABI model is then validated by a well-arranged experiment, for which the annular flow is simplified into a rectangular duct flow with an error of less than 5%. The experimental validation also proves the accuracy of the model.
1. Introduction
Variable cycle engines (VCEs) can broaden the flight envelope of the airplane by significantly adjusting the bypass ratio and have become a hotspot for next-generation aircraft [1,2,3]. The compression system plays a major role in the bypass ratio adjustment of variable cycle engines, whereas the multi-bypass configuration is the key to their variation ability. To regulate the flow distribution in the bypass ducts, unique regulation components are designed for the VCE compression system, among which the variable area bypass injector (VABI) is a representative one. The invention of the VABI can be traced back to the early stage of VCE concept exploration [4,5,6], and it is now widely used in different VCE schemes [7,8]. The highly coupled flow between the components and bypass ducts makes it necessary to clarify the matching mechanism of the VABI.
It is well-known that the theory of injection is classic in fluid mechanics [9,10,11], and the injector is a mature product in the modern industry [12,13,14]. However, the VABI in variable cycle engines differs from conventional injectors in four ways: (a) function: a conventional injector aims to entrain a low energy flow with an accelerated high energy flow and compress the mixed flow in a diffuser, while the VABI works as a regulator between the bypass flows with no intention of compressing; (b) configuration: the two combining flows in the conventional injectors are generally coaxial, while those of the VABI are skewed; (c) geometric adjustability: the VABI has an adjustable structure to actively control the injecting process, while the conventional injectors are often nonadjustable; (d) the operating range: supersonic conditions are quite common in conventional injectors, as well as the change in fluid phase (e.g., air–water); however, the VABI prefers the subsonic condition and deals with air. Owing to the above differences, specialized models for the VABI are in great need, not to mention its corresponding experiments.
In recent years, there has been an increasing number of studies in the literature on the VABI, with most of the studies resorting to numerical methods [15,16,17]. By calculating the VABI flow field, the basic matching rules of the injection flow are summarized, while the flow details of the injection process are discussed. However, few studies have proposed a theoretical VABI model that could consider all the control parameters, as the validation of existing models still relies on further experiments. An experimental investigation concentrated on the overall performance of the VABI flow is given in Ref. [18], whereas the influence of the injection angle lies beyond its scope.
The purpose of the present study is to establish a valid theoretical model for the VABI and reveal the operating mechanism of the VABI through a detailed experimental measurement. The paper is structured as follows: A basic control volume injection flow model is first proposed and validated with numerical results; then, an error analysis is performed to unveil the source of calculation error; based on the theoretical analysis, an improved injection flow model is developed, and the model is validated with the numerical results again; finally, an experiment is designed under the guidance of the theoretical model, thus proving the accuracy of the improved VABI model.
2. The Basic Control Volume Injection Flow Model
Installed in variable cycle engines, the operating range of the VABI is extremely wide, and the factors that influence its aerodynamic performance are diverse. The two inlets of the VABI have different pressure, temperature, and mass flow rates, while the outlet of the VABI is also adjustable, not to mention the geometric regulation of the injector itself. Since it is impossible to test all the flow conditions in the experiment, some theoretical analysis that specifies the characteristic injection parameter is necessary.
2.1. Basic Control Volume Model
The injection flow to be investigated in the present study is illustrated in Figure 1. The injection process is carried out between bypass A (inner bypass) and bypass B (outer bypass) in a variable cycle engine, where the total pressure and temperature of the former are higher than those of the latter due to the disparity of upstream conditions. Meanwhile, the injection detail is controlled by modifying the through-flow area of the VABI. A control volume model is established to describe the injection flow quantitatively. As shown in Figure 1, the control volume model covers the space between the two combining bypass ducts and the downstream duct; duct B parallels with duct C, while duct A joins them with an inclination angle. Owing to the adjustability of the VABI, the locations of the two inflow surfaces, as well as the combining flow angle α, are variable. Naturally, the flow within the control volume must follow the conservation laws of mass flow, momentum, and energy:
where m denotes the mass flow rate, v is velocity, p is static pressure, and T* represents the total temperature. The subscripts of the parameters designate their location, corresponding to those in Figure 1. Note that parameter A represents the area of cross-sections at different bypass ducts. In Equation (2), the integration term denotes the moment of force from the hub and tip walls, which, in this study, is simplified as follows:
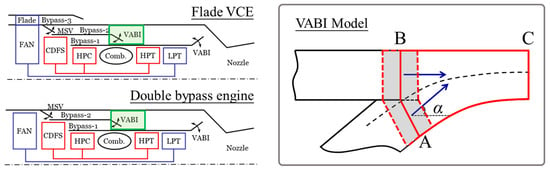
Figure 1.
The injection flow in the variable cycle engine and the VABI model (A: inner bypass; B: outer bypass; C: total bypass).
To close the equations, the equilibrium of the static pressure is employed:
Equation (5) is widely used in low-dimensional combining flow models as long as the size of the juncture is ignorable in comparison with the length of the pipe [19,20].
The dimensional analysis of the injection flow equation simplifies the injection flow parameters into five nondimensional feature parameters, which are classified into geometric parameters and aerodynamic parameters in Table 1. It should be noted that the injection angle is definite upon each concrete flow path; hence, there are only four remaining parameters to be considered for a specific bypass configuration. At each VABI position, changes in the bypass backpressure and total pressure ratio are reflected by the variation in the injection ratio, thus instructing the following study.

Table 1.
Feature parameters for the VABI aerodynamic performance.
2.2. Validation with Numerical Results
At this point, we have summarized the feature parameters of the bypass static pressure ratio. To validate the theoretical model, a calibration database was developed based on numerical simulations, in which the injection flow fields under different feature control parameters are stored. As shown in Figure 2, the structured mesh of the VABI model totaled 0.8 million for 1/36 of the annular duct, and the near-wall grid was clustered to obtain better simulation accuracy. The orthogonality of the mesh was higher than 30°, while the expansion ratio of the grid was below 1.5. The aspect ratio of the mesh was smaller than 1500. The y+ of the first grid from the wall was below 1.0.
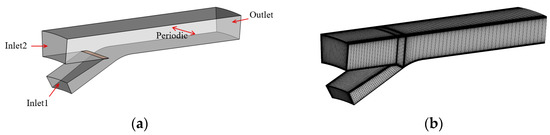
Figure 2.
Schematic and mesh of the VABI model: (a) boundary conditions; (b) simulation mesh.
The commercial flow solver ANSYS CFX was employed to calculate the injection flow field, using the SST turbulent model. As for the boundary conditions, the inner bypass and outer bypass of the VABI model were defined as the INLET of the domain, where the total pressure and total temperature were imposed. The flow direction of the inlet boundary was normal to the boundary surface. The total bypass of the VABI was the OUTLET of the domain, where the static pressure boundary condition was exerted. The two sidewalls were set as periodic walls. In the numerical simulation, the advection and the turbulence terms were both discretized using the high-resolution scheme, and the simulation fluid was ideal air.
The variation range of the calibration database is given in Table 2, covering the entire regulation range of the VABI. Note that not all the combinations of control parameters in Table 2 relate to a “healthy” injection flow field, and cases with critical conditions (Ma > 1.0 or u < 0) were eliminated from the database.

Table 2.
Calibration database for the VABI model.
The injection ratio is the most important parameter in the VABI model because it is directly related to the mass flow distribution (i.e., the bypass ratio of the compression system). The comparison of the VABI injection characteristic is demonstrated in Figure 3, in which the results of the theoretical model (Model-B) of the numerical database (CFD) are presented. The CFD data were calculated based on the area-weighted averaged results of the simulation model. As shown in Figure 3, the injection ratio exhibits an increasing trend with the decrease in bypass backpressure, while the increment in the bypass total pressure ratio weakens the injecting ability. Closing the VABI can significantly improve the injection ratio, which is a major way of controlling the engine bypass ratio. It can also be concluded from the results that the theoretical model underestimates the injection ratio, and the error increases as π decreases. In addition, a comparison of the results shown in Figure 3a–c suggests that the reduction in AVABI also improves the error of the theoretical model, so it is necessary to further improve the theoretical model.
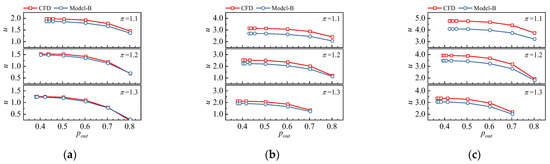
Figure 3.
The validation of injection characteristics of the basic VABI model: (a) AVABI = 0.8; (b) AVABI = 0.6; (c) AVABI = 0.4.
2.3. The Effect of the Streamline Curvature
To determine the reason why the basic injection flow model underestimates the injection ratio, Figure 4 presents the streamwise distribution of the static pressure of the inner bypass and the outer bypass. The results on the centerline of the bypass are depicted. The location of the combining surface is also depicted with shot dots to demonstrate the results more clearly. The most interesting aspect of Figure 4 is that, on the combining surface, the static pressure of the inner bypass is higher than that of the outer bypass, implying the assumption of static pressure equilibrium in Equation (5) to be the source of the error. Another notable phenomenon is that the inner bypass flow and outer bypass flow undergo different processes: The static pressure along the outer bypass wall is found to slowly decrease during the combining process, indicating the acceleration of the outer bypass flow, while the static pressure at the inner bypass first decreases and then increases, which means the flow successively accelerates and decelerates. In general, the pressure change in the inner bypass is more intensive than that of the outer bypass, while decreasing pout amplifies this gradient. The static pressure is finally uniform with the development of the mixing flow.
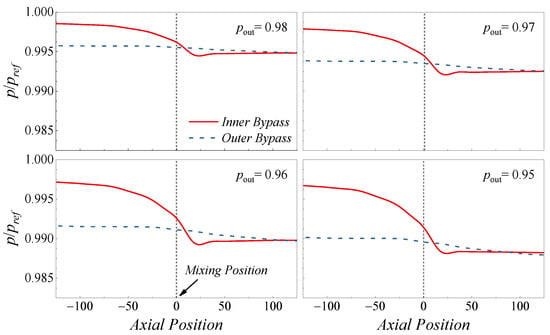
Figure 4.
The distribution of static pressure along the inner bypass and the outer bypass (αVABI = 35° and AVABI = 0.4).
Inspections of the injection flow field help to explain the static pressure difference at the combining surface. As shown in Figure 5, the combining surface at the inner bypass and the outer bypass is OA and OB, respectively. The distribution of the streamline depends on both the geometric condition and the aerodynamic conditions. For example, the bypass injection angle influences the static pressure in two ways: On the one hand, the increment in αVABI “warps” the streamline at point O toward the outer bypass, which induces a negative pressure gradient from O to B; on the other hand, a higher αVABI means a larger streamline curvature at point A, thus generating a negative pressure gradient from O to A. With the static pressure at point O shared by the two flow branches, the former effect reduces the average static pressure on OB, while the latter effect lowers the static pressure on OA. In other words, the size of the juncture is too large to be ignored at the VABI in the variable cycle engine, and the influence of streamline curvature on the static pressure is non-negligible. The following section focuses on the refinement of the VABI model.
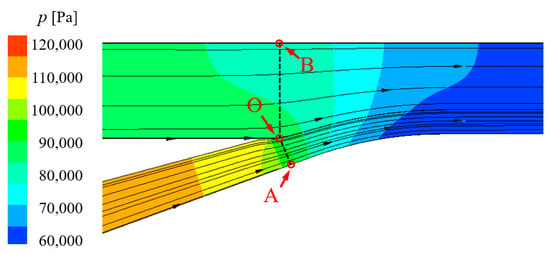
Figure 5.
Streamlines and static pressure distribution of the combining flow (AVABI = 0.6, αVABI = 25°, and pout = 0.6).
3. An Improved Injection Flow Model
3.1. Consideration of the Mixing Flow Static Pressure Correction
To quantify the influence of streamline curvature on the injection process, a calibration item is introduced to the pressure balance equation
where σ denotes the bypass static pressure ratio on the mixing surface. As shown in Figure 6, the values of σ at different geometric and aerodynamic conditions are depicted according to the numerical database, which indicates that the bypass static pressure ratio varies nonlinearly with injection angle. The value of σ is first increased and then decreased as αVABI increases from 15° to 35°. Moreover, the static pressure ratio at the combining surface tends to decrease with the reduction in bypass total pressure ratio, while the reduction in pout has the opposite effect. By introducing σ to the basic injection flow model (i.e., replacing Equation (5) in the governing equations with Equation (6)), some remarkable improvements can be expected.
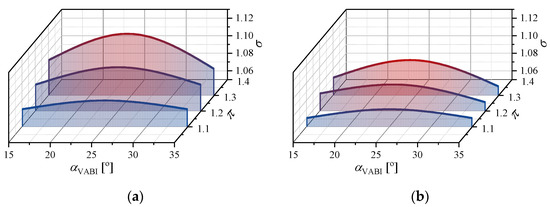
Figure 6.
The distribution of bypass static pressure ratio under different injection angles and aerodynamic conditions (AVABI = 0.6): (a) pout = 0.6; (b) pout = 0.7.
Obviously, the value of σ needs to be decided first before using the improved VABI model, so the theoretical analysis is conducted as follows:
Consider the radial equilibrium equation at the combining surface,
where r is the radius of curvature of any local streamline.
For the ideal gas, we have:
Substituting Equations (8)–(10) to Equation (7) gives:
According to Equation (11), the static pressure on the combining surface depends on the local streamline curvature and the flow Mach number; hence, the bypass static pressure ratio σ is also the function of these two parameters:
Naturally, the question becomes: What determines the streamline curvature? Inspection of some special streamlines provides the answer. Referring to Figure 5, for a flow case without separation, the streamlines at the hub of the inner bypass (bypass OA) and the casing of the outer bypass (bypass OB) follow the solid wall, so their curvatures depend on the bypass geometry:
On the other hand, the distribution of the streamline between the solid walls is related to the aerodynamic conditions. An examination of the stagnation line helps explain the question. According to Figure 5, ignoring the mass flow exchange, the stagnation line (the streamline against point O) is shared by the inner bypass flow and the outer bypass flow. Therefore, downstream of the stagnation point, the stagnation line obeys the static pressure equilibrium:
The injection ratio can be written as
where AA and AB are the throughflow area of the inner bypass and the outer bypass, respectively.
For a specific streamwise position (e.g., stream location = x), the area of the inner bypass flow and the outer bypass flow forms the total throughflow area:
where f(x) is a function of the bypass geometry, which can be considered as a constant value at each streamwise position.
In the variable cycle engine, the total temperature ratio of the inner and outer bypass flow is a small quantity in comparison with the bypass total pressure ratio, making the influence of the temperature difference ignorable in the VABI model; hence, Equations (14)–(16) can be solved if three more parameters are provided. With reference to the VABI feature parameter, we select u, π, and Ma; the curvature of the stagnation line can, therefore, be written as the function of these three parameters:
Once the streamlines at the solid wall (rw) and the stagnation line (rs) are determined, the curvature of streamlines in between can be calculated using Equation (11), thereby deciding the static pressure ratio between the two bypass flows. In other words, the bypass static pressure ratio depends on both the geometry factor and the aerodynamic factor, which can be expressed as
Therefore, the factors that influence the bypass static pressure ratio can be correlated as
thus unveiling the influencing factors of the bypass static pressure ratio.
3.2. Calibration of the Improved Injection Flow Model
According to the former analysis, the bypass static pressure ratio at the mixing plane depends on the VABI geometry, the bypass total pressure ratio, and the bypass backpressure (from which the injection ratio can also be determined). This outcome provides us with great convenience, as the aerodynamic factors that decide the bypass static pressure ratio are just the same as the feature parameters summarized for the VABI. The static pressure ratio can, therefore, be acquired using the numerical database.
As shown in Figure 7, the acquisition of the bypass static pressure ratio σ follows a two-step interpolation: First, under a given π and pout, the values of σ at all VABI opening conditions (AVABI) are extracted from the database using scattered data interpolation [21]; then, a spline interpolation is utilized to obtain the specific σ at the given VABI opening condition.
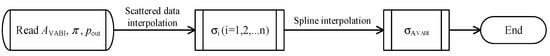
Figure 7.
The acquisition of σ using the calibration database.
To gain an overview of σ, the throttling process of the VABI is examined under different bypass total pressure ratios. The values of σ for are depicted to show the influence of various factors. As shown in Figure 8, under different VABI opening conditions, the distribution of σ is illustrated with π and pout varying between 1.1~1.3 and 0.50~0.75, respectively. The isolines denote the bypass total pressure ratio. Taking Figure 8b as an example, under the same bypass back backpressure, the reduction in bypass total pressure ratio increases the injection ratio, while the increase in injection ratio reduces the bypass static pressure ratio. On the other hand, when the bypass total pressure ratio is constant, the decrease in the bypass backpressure simultaneously increases the injection ratio and the bypass static pressure ratio, which means the errors of the old model (where σ = 1.0) are higher at lower bypass backpressures. A comparison of the results shown in Figure 8a–c reveals three effects of the VABI area: (a) Closing the VABI enhances its injecting ability; (b) closing the VABI improves the bypass static pressure ratio, thus strengthening the importance of σ; (c) σ is more sensitive to the injector aerodynamic performance under small VABI opening areas, and the variation rates for the cases (a)–(c) are 2.9%, 7.7%, and 8.7%, respectively. In a word, the results in Figure 8 highlight the importance of σ in the injection flow process, the indispensable role of which is further proved in the following section.
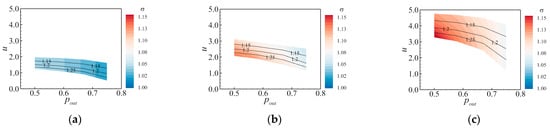
Figure 8.
The distribution of bypass static pressure ratio under different VABI opening conditions (αVABI = 25°): (a) AVABI = 0.8; (b) AVABI = 0.6; (c) AVABI = 0.4.
3.3. Validation of the Improved Injection Flow Model
The comparison of the VABI injection characteristic is presented in Figure 9, in which the results of the numerical database (CFD), the basic theoretical model (Model-B), and the improved theoretical model (Model-I) are all presented. It is apparent from Figure 9 that the calibration of the bypass static pressure ratio leads to a notable improvement in the model accuracy. The predicted injection ratio of the improved model is in much better conformity to the CFD results, compared with the basic model, over the whole operating range, and the discrepancy at different VABI opening conditions is also eliminated.
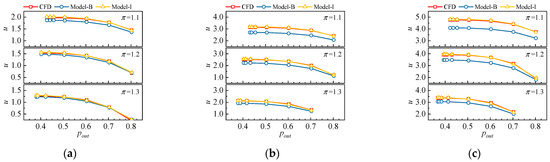
Figure 9.
The validation of injection characteristics of the improved VABI model: (a) AVABI = 0.8; (b) AVABI = 0.6; (c) AVABI = 0.4.
The quantitative evaluation of the model accuracy is demonstrated in Figure 10, in which the solid and hollowed symbols represent the basic model and the improved model, respectively. According to Figure 10a, at AVABI = 0.8, the absolute error of the basic model is generally between 3% and 7%, while the relative error of the improved model is below 3%. Furthermore, the advantage of the improved model is more pronounced at smaller VABI opening conditions: for the cases in Figure 10b,c, the calculation error of the improved model is decreased from over 10% to below 2%, thereby testifying to the advantage of the improved model.
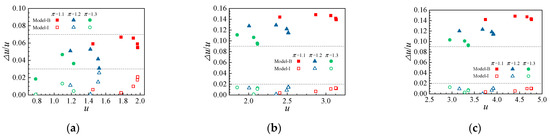
Figure 10.
The comparison of simulation error of the theoretical VABI models: (a) AVABI = 0.8; (b) AVABI = 0.6; (c) AVABI = 0.4.
As shown in Figure 1, the mixed flow downstream of the VABI undergoes another confluence process in front of the nozzle, so it is necessary to accurately calculate the total pressure loss of the mixing flow to determine the regulation rules of the aft VABI. The comparison of VABI loss characteristics between the CFD results and the model prediction results are given in Figure 11, in which KAC and KBC are the loss coefficient of the two bypass branches, respectively. The definition of the loss coefficient is given in Equation (22), which is widely used for evaluating the flow loss for conjecture flows [22,23,24].
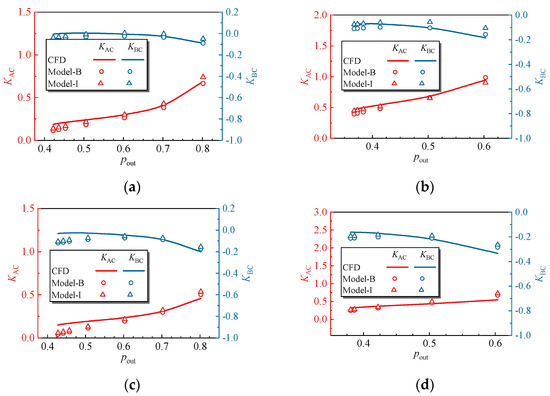
Figure 11.
The comparison of the VABI loss characteristics: (a) AVABI = 0.4, π = 1.1; (b) AVABI = 0.4, π = 1.3; (c) AVABI = 0.8, π = 1.1; (d) AVABI = 0.8, π = 1.3.
According to Figure 11, KAC and KBC increase and decrease with an increase in bypass backpressure, respectively. A positive value of KAC suggests a reduction in the total pressure of the inner bypass flow. However, the loss coefficient of the outer bypass is below zero, which means the outer bypass flow is energized as the flow mixing occurs. Furthermore, the loss characteristic of the theoretical VABI model is in good agreement with the CFD results, and the improved VABI model is found to provide a slightly higher loss than the old model; nevertheless, the accuracy of the two models is virtually identical. As a matter of fact, the VABI model in this paper is a low-dimensional theoretical model that assumes the aerodynamic parameters to be uniform on the mixing planes; hence, errors are inevitable. Given the overall trend exhibited in Figure 11, it is safe to conclude that the control volume model can be utilized to evaluate the mixing loss of the injection flow.
4. Experimental Validation of the Improved Control Volume Model
Based on the analysis above, the improved injection flow model proposed in this paper could predict the injection ratio and the mixing loss of the VABI with satisfying correspondence to the CFD results. Further validation of the theoretical model calls for experimental measurements, which is the topic of this section. The following sections introduce the determination of the model geometry and the detailed experimental setups, respectively.
4.1. Design of a Simplified Injection Flow Test Model
As shown in Figure 12a, in the real engine environment, the bypass ducts are annulus ducts, and the regulation assemblies (e.g., MSV, VABI) are annularly symmetrical. However, in an experimental study, it would be more convenient to simplify the annular flow into a rectangular duct flow and use the measured parameters on the centerline to evaluate the overall performance, as shown in Figure 12b. This section focuses on the feasibility of the above simplification.

Figure 12.
Simplification scheme for the VABI model (axial view): (a) actual bypass geometry: annular; (b) simplified bypass geometry: rectangular.
Theoretically, the simplification of an annular flow into a rectangular duct flow comes with two changes: One is the mass flow redistribution in the radial direction due to the variation in the throughflow area, and the other is the viscous effect brought about by the sidewalls. The variation in the throughflow area is weakened with an increase in bypass hub-to-tip ratio (which is commonly quite high in real life), while the sidewall effect can be correlated to the duct’s width/height ratio (Figure 12b, a/b). With b determined, the conflict remains for the selection of a, as the experiment expects a smaller throughflow area to obtain a higher Mach number, whereas a low a/b magnifies the influence of the sidewalls and reduces the model accuracy.
To reach a balance between experiment feasibility and model accuracy, in the first place, a series of duct configurations are evaluated using numerical simulations. The duct width/height ratio ranges from 0.4 to 1.0. Unlike the annular model in which aerodynamic conditions are identical over the circumferential direction, in the simplified model, the flow field would be influenced by the sidewalls. Therefore, parameters on the centerline are utilized to derive the aerodynamic performance of the simplified model. As shown in Figure 13, with the annular duct considered the baseline (ORI), the deviation of loss coefficient tends to increase with a decrease in duct width/height ratio, whereas the error of KBC is higher than that of KAC. The loss characteristic of the a/b = 1.0 case is approximately identical to that of the a/b = 0.8 case; thus, there is less benefit by further increasing a/b in improving the model accuracy. Figure 14 further provides the error of injection ratio for the rectangular bypass duct, where the annular bypass case is set as the baseline. The results show that the absolute error of u rises with the throttling of the total bypass, whereas the increase in a/b promotes the simplified model. Since the current experiment aims to validate the VABI operating characteristic while revealing the underlying matching mechanics, errors below 5% are considered acceptable; hence, a/b = 0.8 is selected for the experiment geometry.
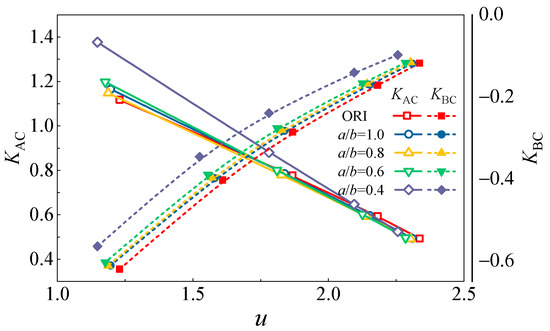
Figure 13.
The distribution of injection flow loss with the variation in injection ratio.
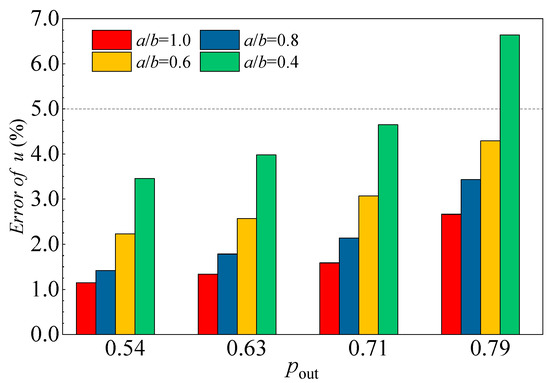
Figure 14.
The error of injection ratio under different bypass backpressures.
4.2. Experimental Setup
The experiment was conducted at Beihang University, based on a specially designed test facility, with the scale factor considered carefully. On the one hand, the maximum power of the gas system is limited; hence, a wider operation range could be achieved by rescaling the experimental geometry to a smaller size. On the other hand, the enlargement of the test rig is convenient for the manufacturing and measurement process. Since the rescaling of the VABI model essentially changes the Reynolds number, the influence of the Reynolds number was first clarified to decide the dimension of the test rig. As listed in Table 3, four scale factors were investigated in the present study, with the flow Reynolds number ranging from 1.4 × 105 to 3.5 × 105.

Table 3.
Scale factor and the corresponding Reynolds number.
The variation in injection ratio with the bypass backpressure is given in Figure 15, and the demonstrated cases are consistent with those in Table 3. The results suggested that the deviation in the injection ratio was below 5% when the VABI model was scaled between 0.8 and 2.0; errors were relatively larger at low injection ratios, which is because the relative error was calculated using the absolute injection ratio. In general, the Reynolds number between 1.4 × 105 and 3.5 × 105 was considered reasonable in the present study.
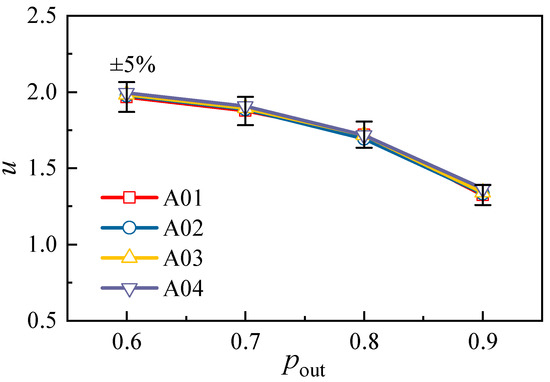
Figure 15.
The influence of Reynolds number on the predicted values (α = 25° and AVABI = 0.6).
As shown in Figure 16, the VABI test facility was set up comprising three parts: the inlet section, the test section, and the outlet section. The test section was 80 mm in width and 100 mm in height, corresponding to the Reynolds number of 3.0 × 105. There were two inlets for the test facility: The ambient air directly flowed into the inner bypass (Inlet Section2), while an orifice control valve was placed at the inlet of the outer bypass (Inlet Section1) to control the bypass total pressure ratio. A ventilator was installed after the outlet duct to regulate the backpressure at the outlet of the total bypass. To investigate the impact of the VABI opening condition, a retractable diaphragm valve was installed at the juncture of the bypass ducts, while the inner bypass duct was designed to be replaceable so that the injection angle could be conveniently changed. The variation range of the VABI is demonstrated in Table 4, with the maximum Mach number approaching 0.4.
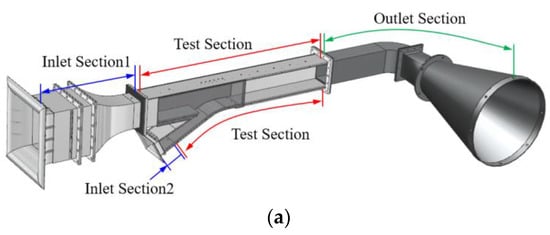

Figure 16.
Schematic of the VABI test facility: (a) structure of the test rig; (b) the orifice control valve; (c) the replaceable inner bypass duct.

Table 4.
Variation range of the VABI test rig.
The locations of pneumatic probes are illustrated in Figure 17. Static pressure taps at the inlet of the bypass ducts helped to provide the mass flow rate, while the wall static pressure along the bypass ducts was measured using a series of pressure taps on the bypass centerline. To observe the flow combining process clearly, more measurement points were arranged near the combining surface. Moreover, a five-hole probe was employed to measure the pressure profiles within the flow field; the measurement locations were also along the model centerline.
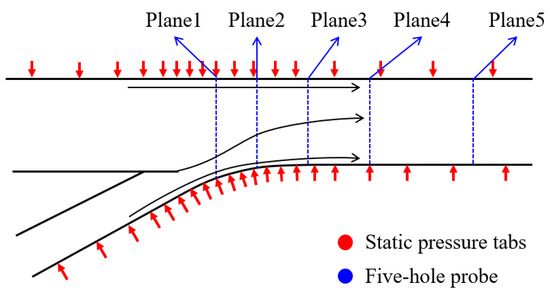
Figure 17.
Measurement locations of the pneumatic probe.
As shown in Figure 18, the five-hole probe used in the experiment was an L-shaped probe with a 90° cone head, followed by a 2 mm diameter cylinder. The distance between the probe tip and the axis the of probe rod was 2.5 d (d is the diameter of the probe head and tip end of the probe rod). To extend the measurement range of the five-hole probe, a novel two-step zonal calibration method was proposed by the authors’ research team, through which the calibration range was extended to ±60° [25].
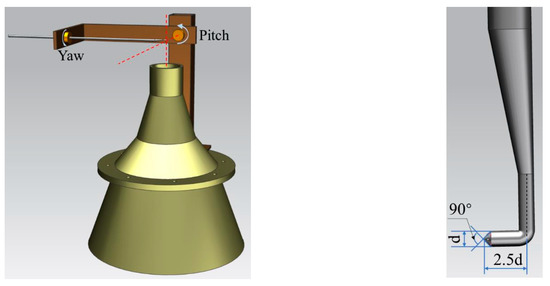
Figure 18.
The schematic of the calibration setup of the five-hole probe.
The five-hole probe was calibrated in an open jet wind tunnel with a 70 mm diameter cylindrical test section. In the jet core, the uncertainty of the velocity angle of the flow was 0.3°, while the turbulence intensity of the flow was smaller than 0.8%. During the calibration process, the probe was driven by two elaborate stepping motors that were automatically controlled by a data acquisition computer (DAC). Moreover, the total pressure of the wind tunnel and the sensed pressure of the five-hole probe were measured by a series of Rosemount 3051S pressure transducers, and the measurement range and accuracy were ±6.22 kPa and 0.025% FS, respectively. It is worth noting that the Rosemount 3051S1 pressure transducers were calibrated each time ahead of the calibration experiment to guarantee measurement accuracy. Based on the present test capability, the uncertainty of the measured total pressure was less than 0.8%, while that of the velocity was below 2.0% [25,26].
4.3. Model Validation
In this section, the comparison of the VABI characteristics from the experiment and the theoretical model is presented to demonstrate the general changing rules while validating the models.
The variation in the VABI injection ratio with bypass total pressure ratio is presented in Figure 19. At each experimental point, the backpressure of the total bypass was fixed at pout = 0.98, while the bypass total pressure ratio was adjusted by changing the orifice control valves. With the variation in the injection angle and VABI area, the theoretical model and the experimental result followed the same trend; that is, the absolute error of u was below 0.4, which verified the reliability of the improved injection flow model. It can also be concluded from the results that the closure of the VABI significantly improved the injection ratio, which is consistent with the previous analysis. Moreover, a comparison of the results shown in Figure 19a–c suggests that the injecting ability of the VABI is related to the injection angle; hence, the flow path of the bypass ducts should be carefully designed to optimize the injector’s performance.
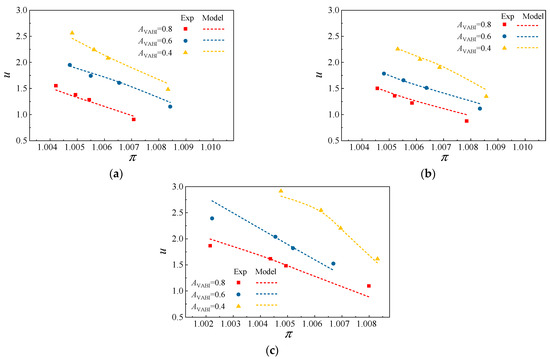
Figure 19.
The variation in the VABI injection ratio with bypass total pressure ratio: (a) αVABI = 35°, (b) αVABI = 25°, and (c) αVABI = 15°.
As regards the loss characteristics, the comparison of pressure loss coefficients for the inner and outer bypass is illustrated in Figure 20. The presented cases are the same as those in Figure 19. The loss coefficients from the theoretical model exhibited good correlations with experimental results at various injection angles and injection ratios, which means the improved control volume model proposed in this study is highly reliable.
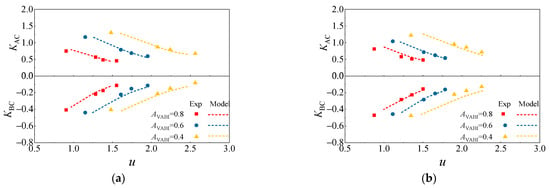
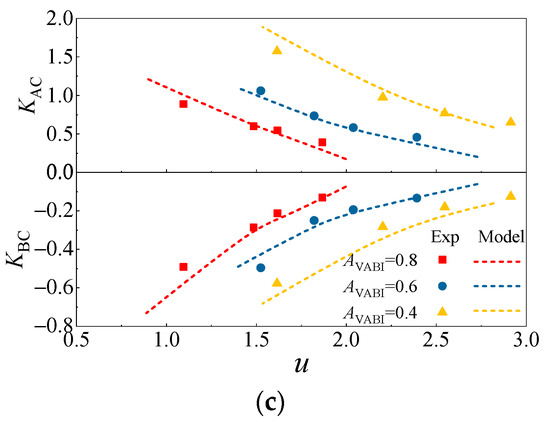
Figure 20.
The variation in the combining flow loss with total pressure ratio: (a) αVABI = 35°; (b) αVABI = 25°; (c) αVABI = 15°.
5. Conclusions
In the present work, we focused on the injection flow in variable cycle engines and established an improved control volume model of the VABI to reveal its operating mechanism. The feature parameters that determine the VABI’s aerodynamic performance were summarized, and an experiment was conducted to validate the theoretical model. The main conclusions are drawn as follows:
The aerodynamic performance of the VABI was determined by three aerodynamic parameters and two geometric parameters: the former included the total pressure ratio, bypass backpressure, and the injection ratio, while the latter factors were the injection angle and the VABI opening area.
The size of the VABI was too large to ignore the influence of the local flow field. The curvature of the local streamline induced a static pressure discrepancy on the combining surface, making the basic VABI model underestimate the injection ratio.
An improved VABI model was developed to obtain better model accuracy. In the improved model, we considered the static pressure difference at the mixing plane by introducing the static pressure ratio as a calibration item to the governing equations. The theoretical analysis revealed that the static pressure ratio at the mixing plane is related to the VABI geometry, the bypass backpressure, and the bypass total pressure. A calibration database was developed to acquire the static pressure ratio at the mixing plane. The improved VABI model exhibited excellent accuracy in predicting the injection ratio. The calculation error of the improved model decreased from >10% to <2% at AVABI = 0.4.
A specially designed test facility was established to experimentally validate the injection flow model, where the injection flow in the annular bypass duct was simplified to a rectangular duct flow. The aerodynamic performance of the VABI was calculated using the measured parameters on the centerline. The width/height ratio of the bypass duct was 0.8 to balance experiment feasibility and model accuracy, with an error of less than 5%. The results showed that the improved VABI model developed in this paper has high accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.W. and X.Y.; methodology, R.W. and X.Y.; validation, K.Z. and G.A.; formal analysis, R.W. and X.Y.; resources, X.Y. and B.L.; data curation, K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, R.W.; writing—review and editing, R.W., X.Y., and B.L.; supervision, X.Y. and B.L.; project administration, B.L.; funding acquisition, X.Y. and B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This investigation was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51790511) and the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. J2019-II-0020-0041).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their appreciation to Yong Qin for his devotion to the typesetting of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- General Electric. GE Successfully Concludes Phase 1 Testing on Second XA100 Adaptive Cycle Engine. 2021. Available online: https://www.ge.com/news/press-releases/ge-successfully-concludes-phase-1-testing-on-second-xa100-adaptive-cycle-engine (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Zheng, J.C.; Chen, M.; Tang, H.L. Matching mechanism analysis on an adaptive cycle engine. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyvey, P.; Bosschaerts, W.; Villace, V.F.; Paniagua, G. Study of an airbreathing variable cycle engine. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, San Diego, CA, USA, 31 July–3 August 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.D. General Electric company variable cycle engine technology demonstrator programs. In Proceedings of the 15th Joint Propulsion Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 18–20 June 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E. Variable cycle engine developments at General Electric-1955-1995. In Developments in High-Speed Vehicle Propulsion System; Murphy, S., Curran, E.T., Eds.; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 1996; pp. 105–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, D.W.; Guy, K.F. Individual Bypass Injector Valves for a Double Bypass Variable Cycle Turbofan Engine. U.S. Patent US4175384, 27 November 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.J. Design and Control of a Variable Geometry Turbofan with and Independently Modulated Third Stream. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bachelder, K.A.; Welty, D.J. Methods and Apparatus for Supporting Variable Bypass Valve Systems. U.S. Patent US6742324B2, 1 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, J.H.; Neumann, E.P.; Lustwerk, F. An investigation of ejector design by analysis and experiment. J. Appl. Mech. 1950, 17, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.A.; Coogan, C.H. Some two-dimensional aspects of the ejector problem. J. Appl. Mech. 1942, 9, A151–A154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, K.R.; Hill, P.G. Compressible flow ejectors: Part I—Development of a finite-difference flow model. J. Fluids Eng. 1974, 96, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Inzoli, F. Ejector refrigeration: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 53, 373–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nimr, M.A.; Tashtoush, B.; Hasan, A. A novel hybrid solar ejector cooling system with thermoelectric generators. Energy 2020, 198, 117318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Karvounis, N.; Walther, J.H.; Ding, H.B.; Wen, C. Effect of area ratio of the primary nozzle on steam ejector performance considering nonequilibrium condensations. Energy 2021, 237, 121483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Li, M.; Tang, H.L.; Chen, M. A multi-fidelity simulation method research on front variable area bypass injector of an adaptive cycle engine. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.X.; Lin, Z.F.; Shi, J.W. Integration of high-fidelity model of forward variable area bypass injector into zero-dimensional variable cycle engine model. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.P.; Li, C.; Xia, C.; Li, Q. Investigations of entrainment characteristics and shear-layer vortices evolution in an axisymmetric rear variable area bypass injector. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.H.; Liu, H. Experimental research on the performance of the forward variable area bypass injector for variable cycle engines. Int. J. Turbo Jet Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, R.S.; Woollatt, D.; Woods, W.A. Unsteady flow in simple branch systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1963, 178, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, M.D.; Winterbone, D.E.; Pearson, R.J. Calculation of steady flow pressure loss coefficients for pipe junctions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2001, 215, 861–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidror, I. Scattered data interpolation methods for electronic imaging systems: A survey. J. Electron. Imaging 2002, 11, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.S. Internal Flow Systems, 2nd ed.; BHRA: Bedford, UK, 1990; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Haidar, N.I.; Dixon, S.L. Pressure losses in combining subsonic flows through branched ducts. J. Turbomach. 1992, 114, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Liu, B.J.; Yu, X.J.; An, G.F. The exploration of bypass matching limitation and mechanisms in a double bypass engine compression system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 119, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Qiu, Y.; An, G.F.; Yu, X.J. Utilization of zonal method for five-hole probe measurements of complex axial compressor flows. J. Fluids Eng. 2020, 142, 061504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; An, G.F.; Yu, X.J.; Zhang, Z.B. Experimental investigation of the effect of rotor tip gaps on 3D separating flows inside the stator of a highly loaded compressor stage. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 75, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).