Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and J.G.; methodology, J.G.; software, J.G.; validation, J.G.; formal analysis, J.G.; investigation, J.G. and Z.Z.; resources, Z.Z.; data curation, J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G.; writing—review and editing, J.G. and Z.Z.; visualization, J.G.; supervision, Z.Z.; project administration, Z.Z.; funding acquisition, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
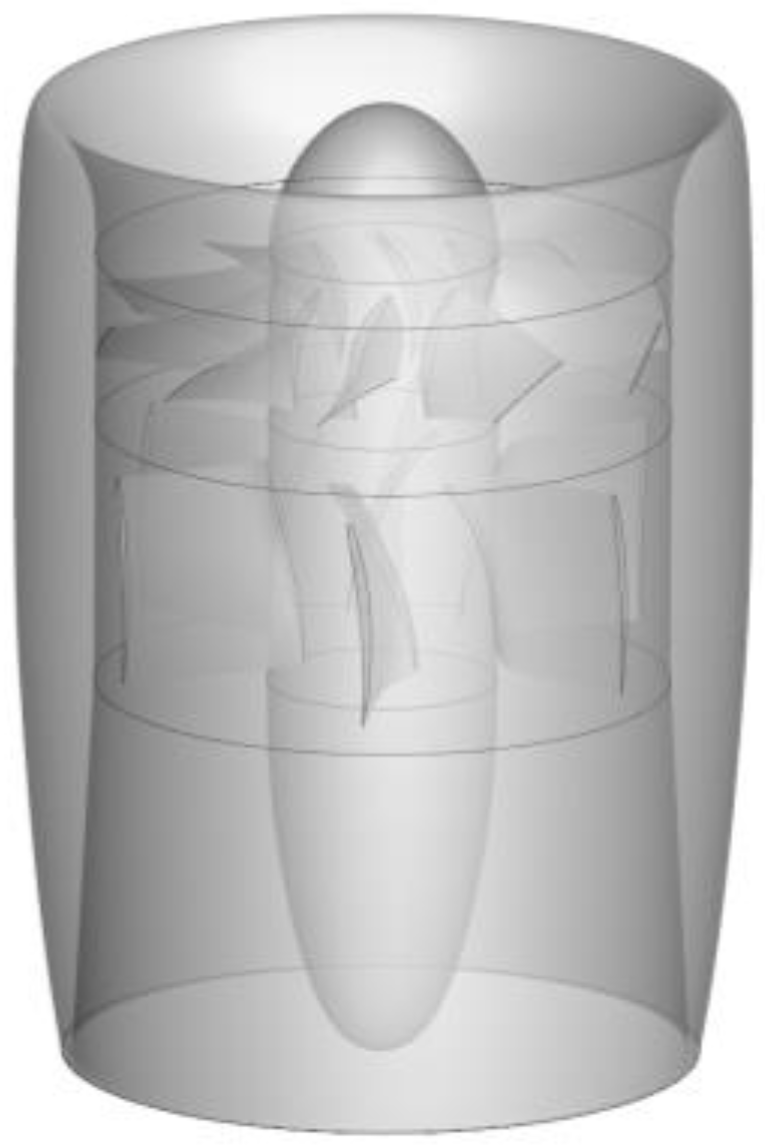
Figure 1.
Geometry of the 150 ducted fan.
Figure 1.
Geometry of the 150 ducted fan.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the duct profile.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the duct profile.
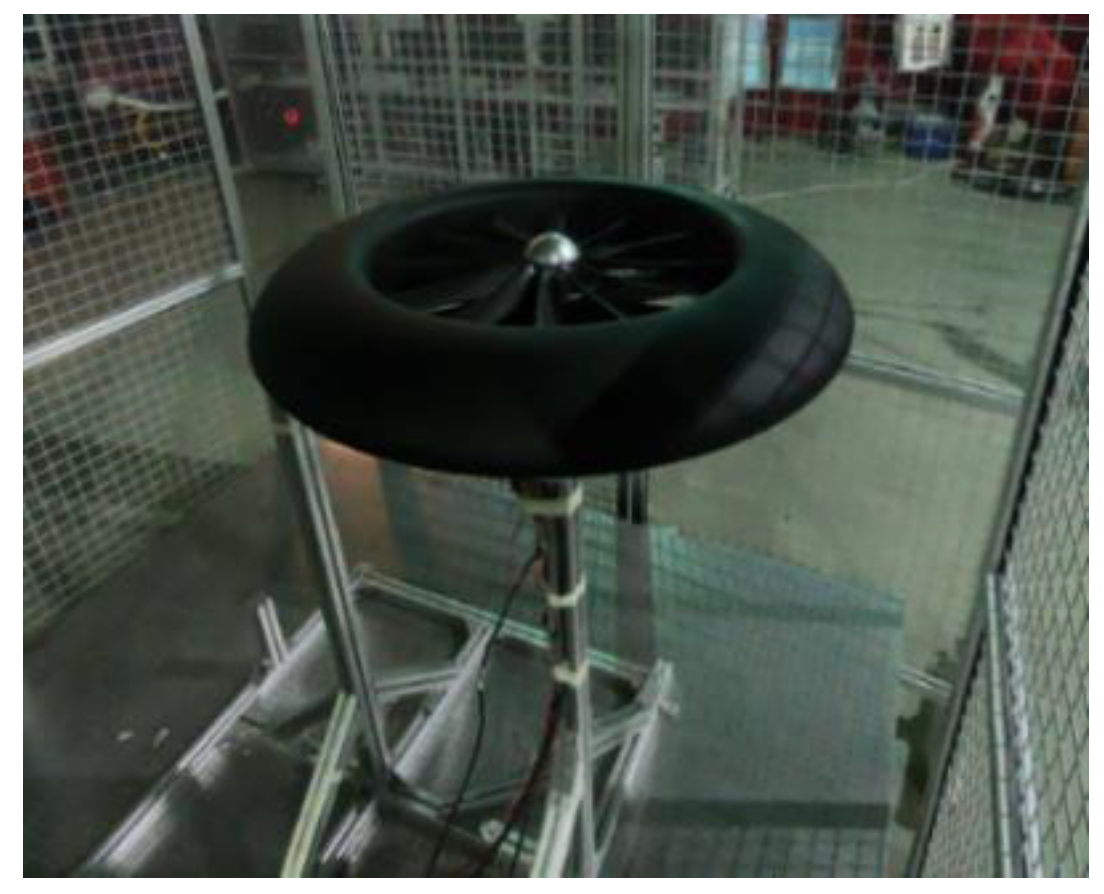
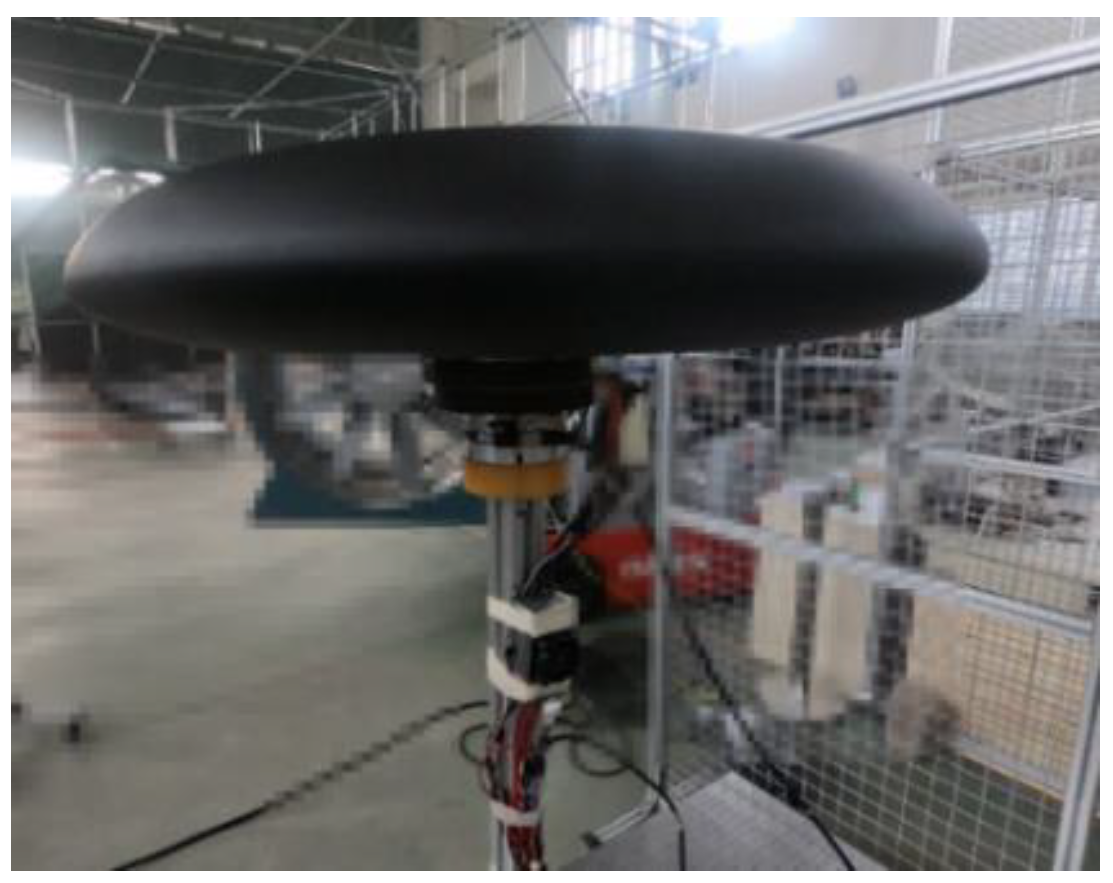
Figure 3.
Experimental site and connection mode of the 150 ducted fan.
Figure 3.
Experimental site and connection mode of the 150 ducted fan.
Figure 4.
Diagram of rotor grids with different grid sizes: (a) 1.18 million, (b) 1.92 million, (c) 3.11 million.
Figure 4.
Diagram of rotor grids with different grid sizes: (a) 1.18 million, (b) 1.92 million, (c) 3.11 million.
Figure 5.
Diagram of background grids with different grid sizes: (a) 1.04 million, (b) 1.65 million.
Figure 5.
Diagram of background grids with different grid sizes: (a) 1.04 million, (b) 1.65 million.
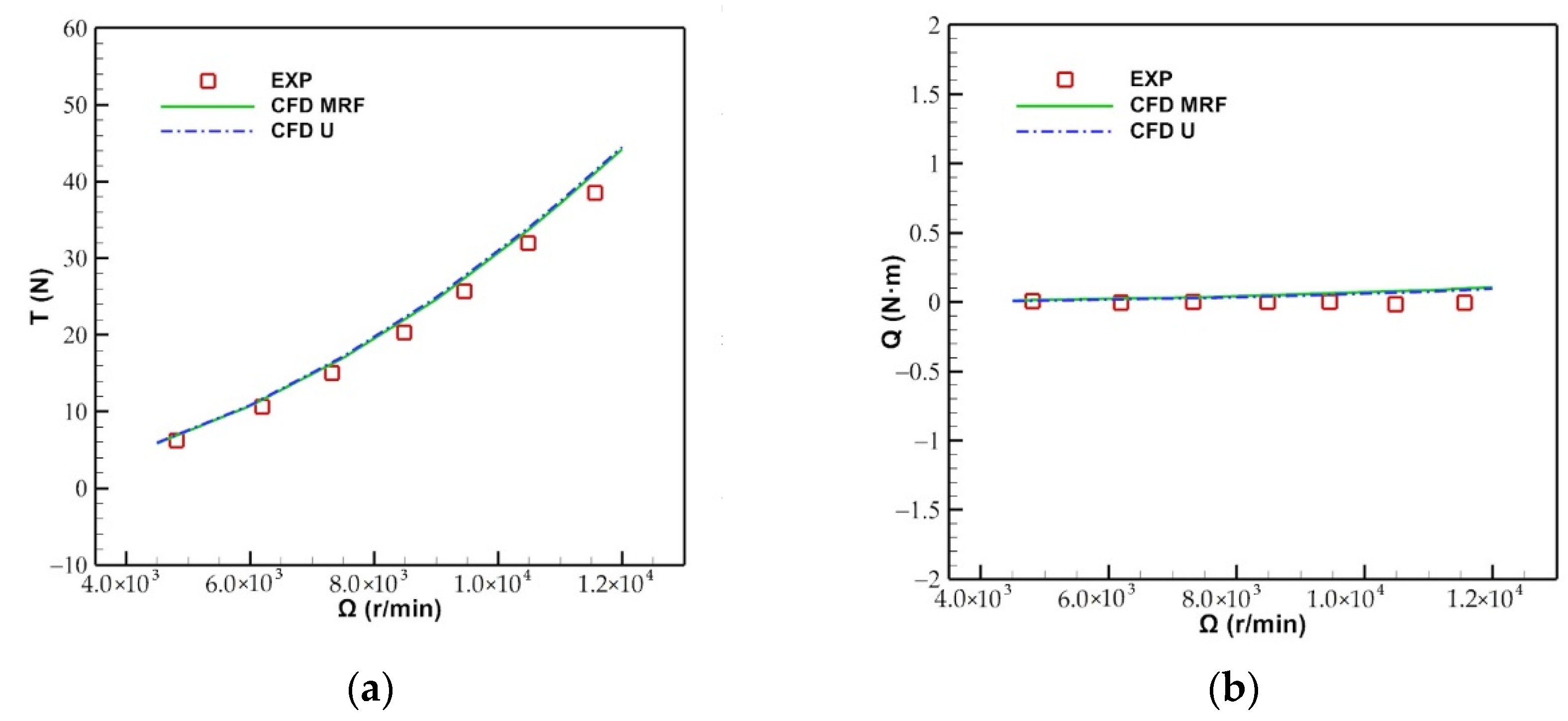
Figure 6.
Comparison of the results between the experiment and CFD methods: (a) Total thrust, (b) total torque.
Figure 6.
Comparison of the results between the experiment and CFD methods: (a) Total thrust, (b) total torque.
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of rotor element analysis.
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of rotor element analysis.
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the blade airfoil.
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the blade airfoil.
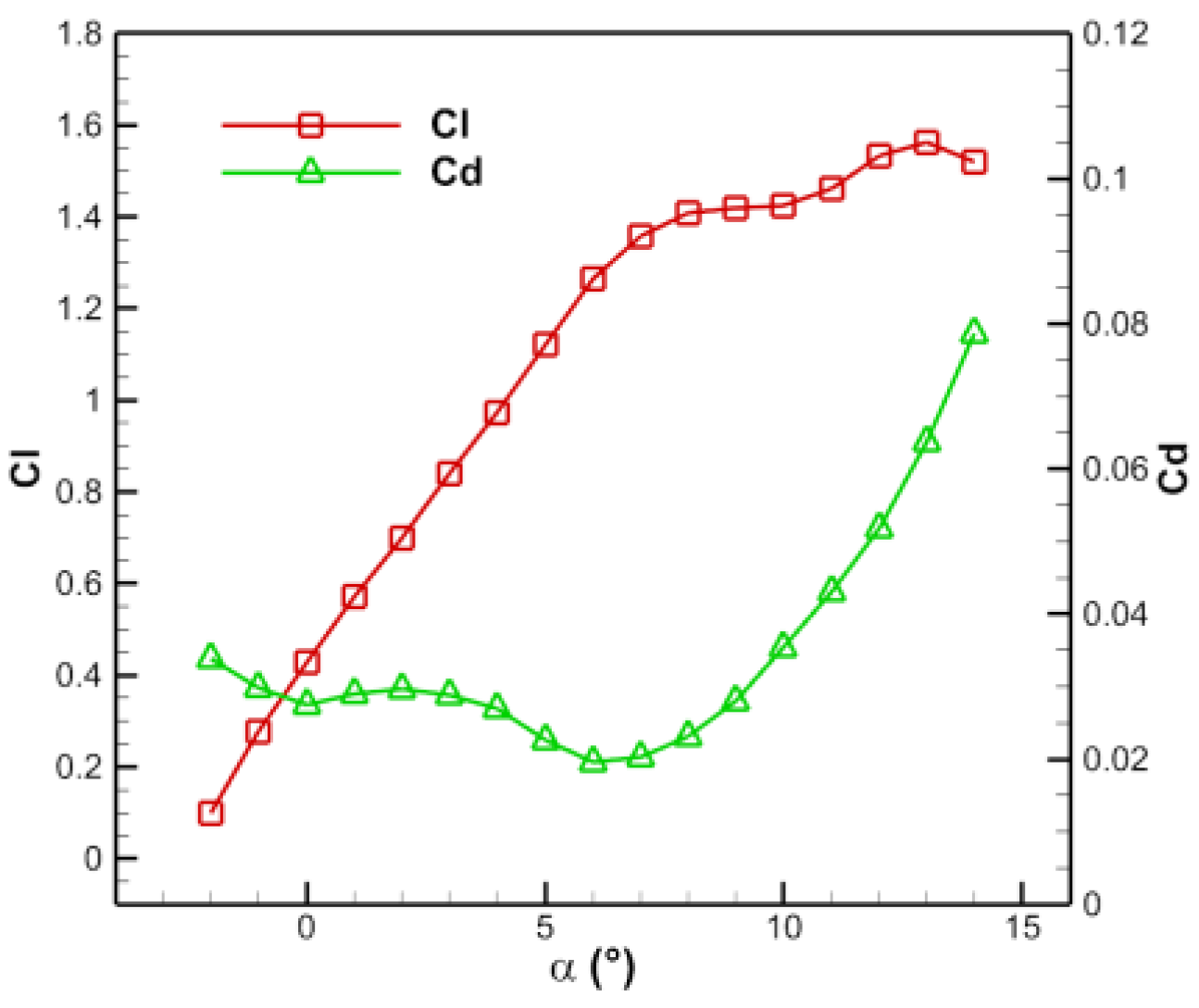
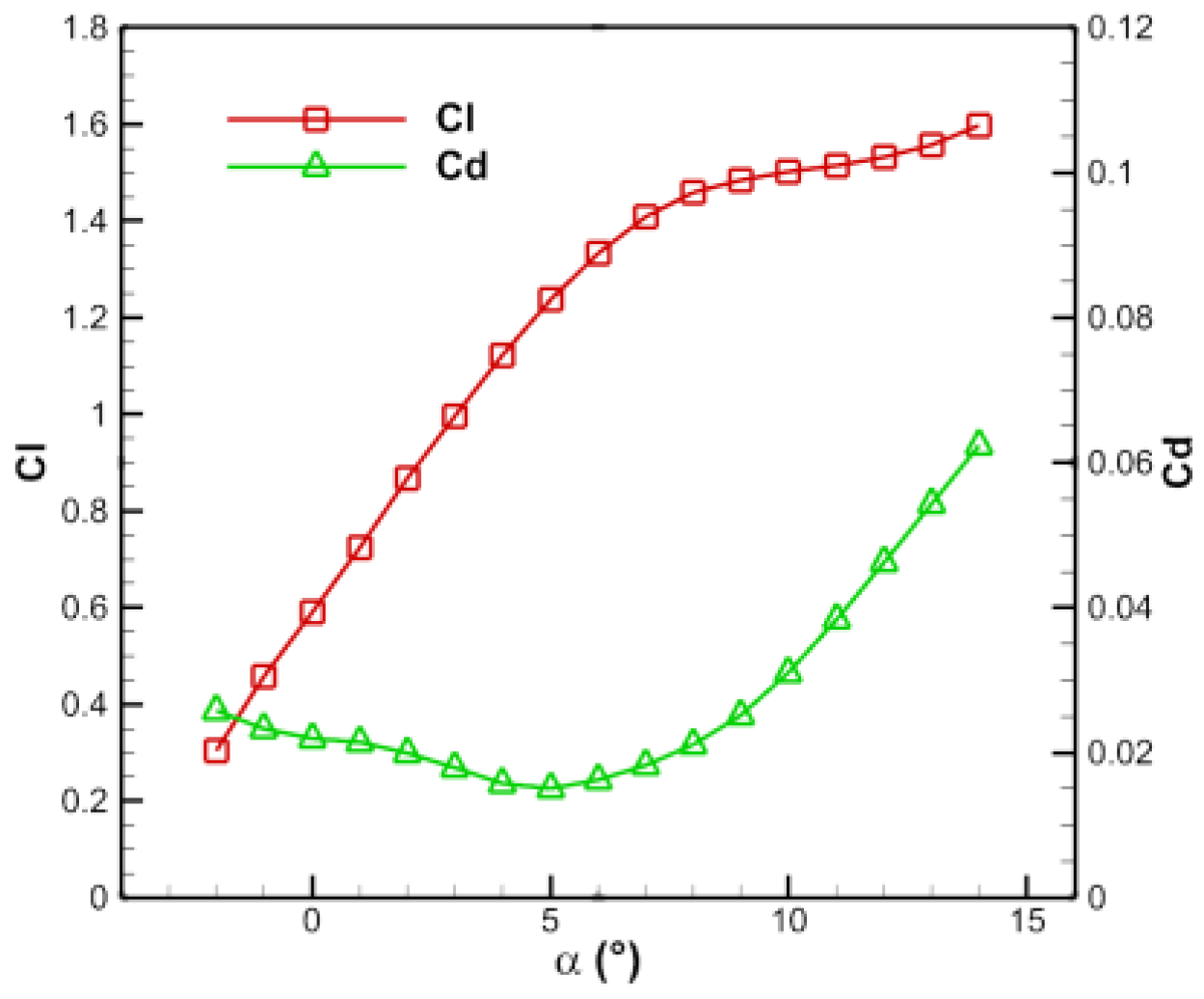
Figure 9.
Aerodynamic curves of the stator.
Figure 9.
Aerodynamic curves of the stator.
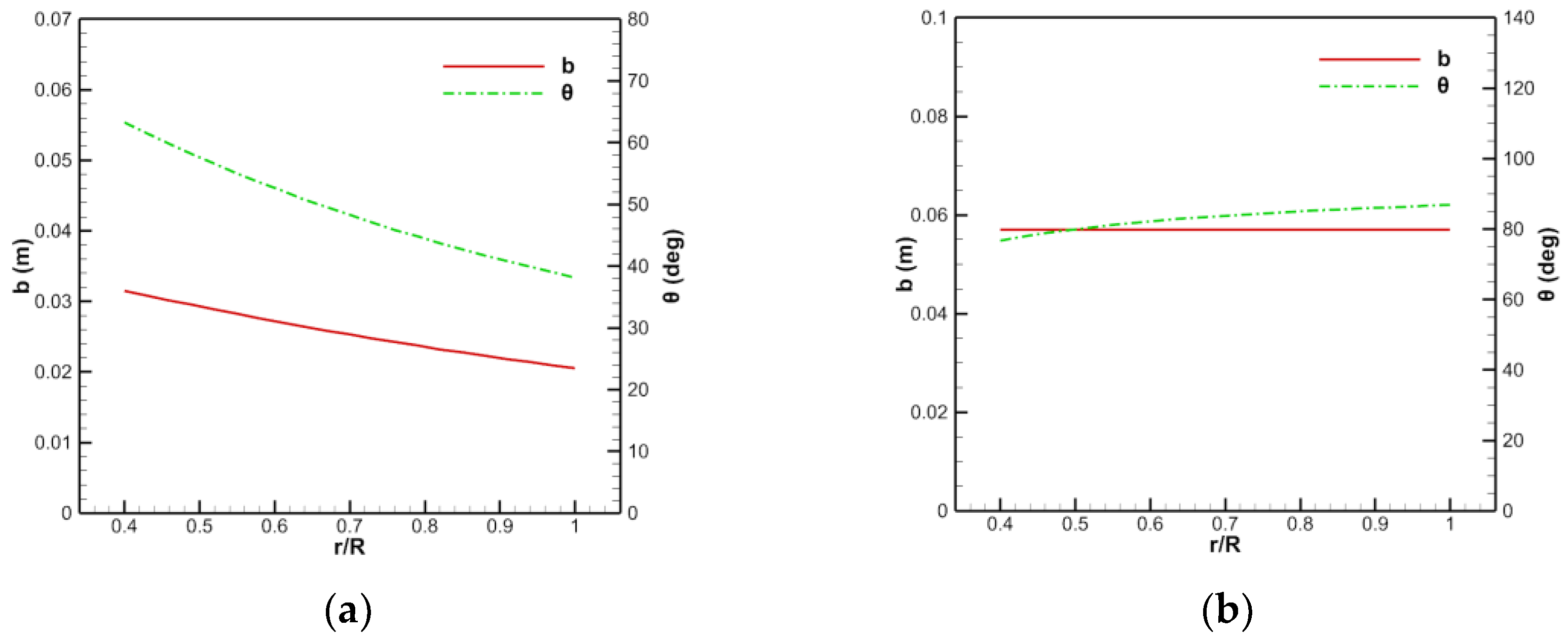
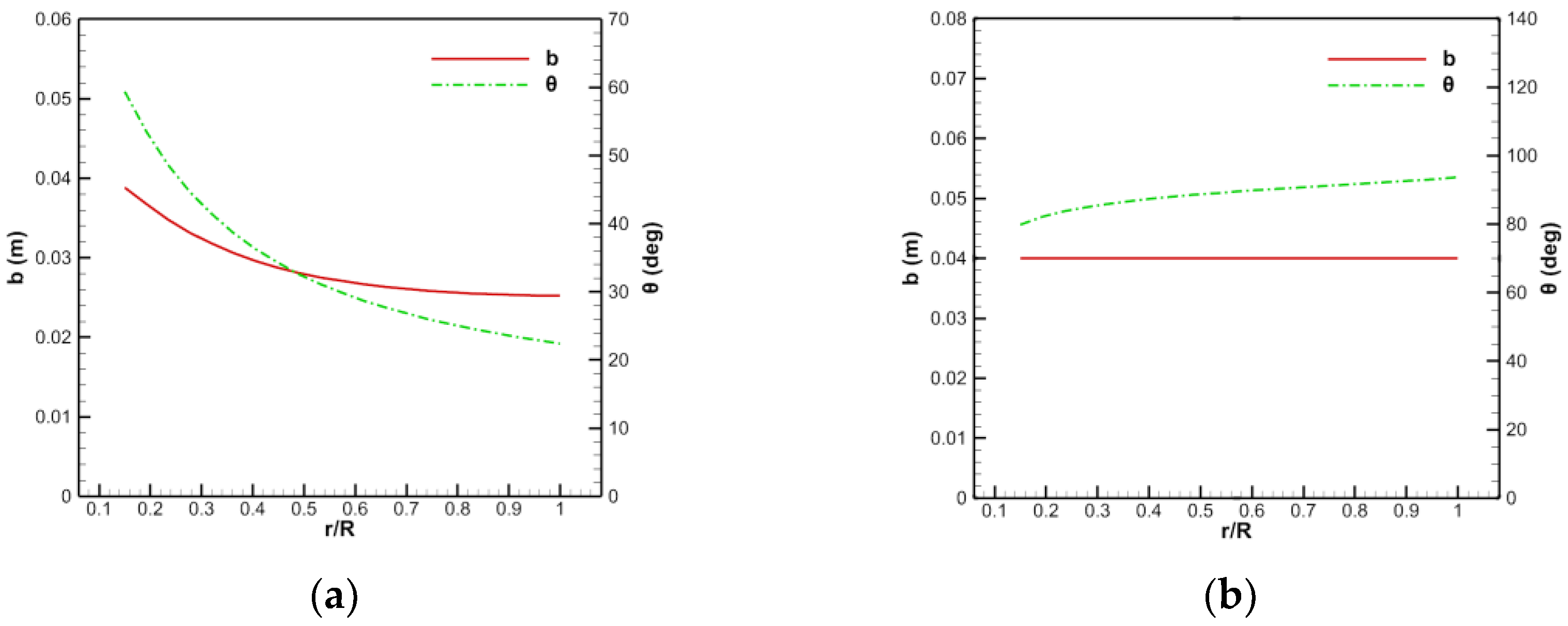
Figure 10.
Design results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 10.
Design results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
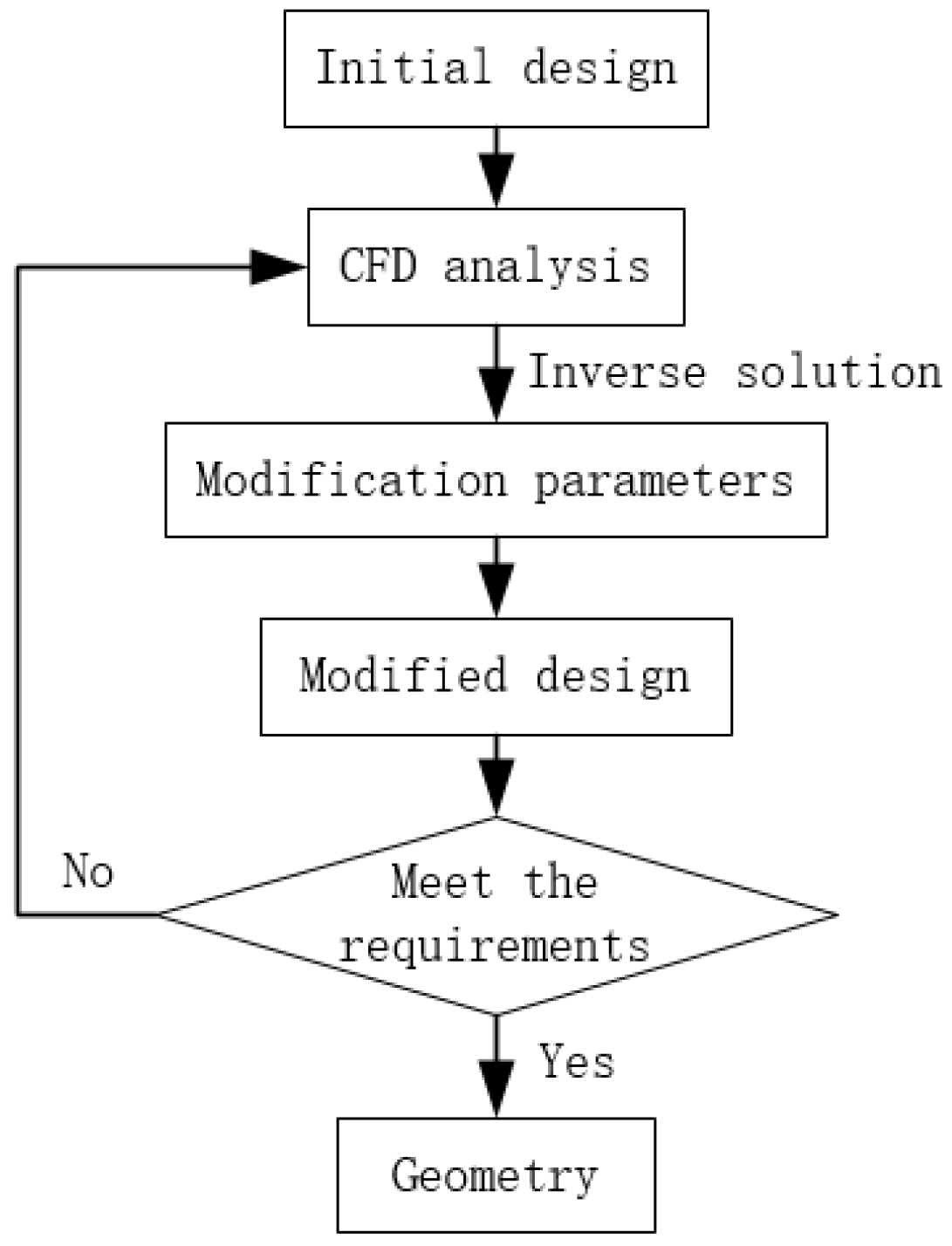
Figure 11.
Design process of the efficient blade design method.
Figure 11.
Design process of the efficient blade design method.
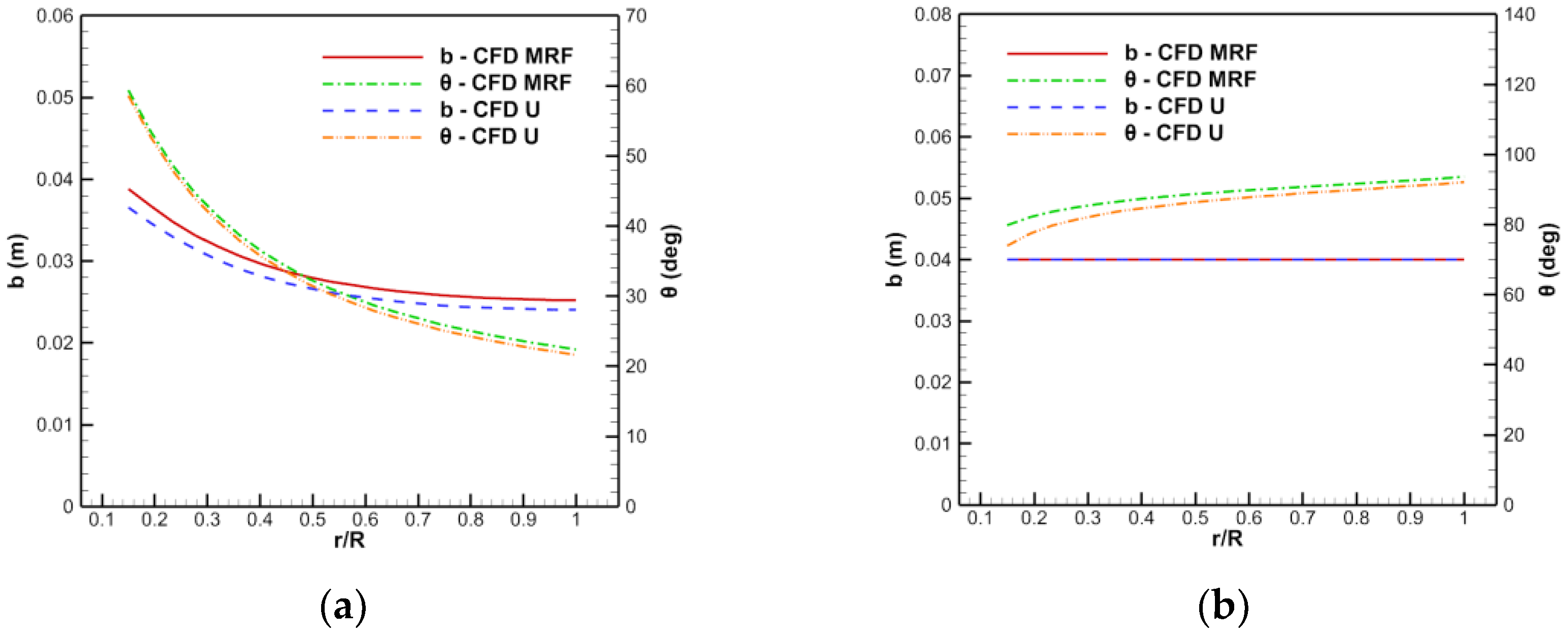
Figure 12.
Comparison of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade before and after the modification: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 12.
Comparison of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade before and after the modification: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 13.
Design results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade in the incoming flow state: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 13.
Design results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade in the incoming flow state: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of the duct profile of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of the duct profile of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 15.
Aerodynamic curves of the stator of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 15.
Aerodynamic curves of the stator of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 16.
Results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 16.
Results of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 17.
Test picture of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 17.
Test picture of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 18.
Connection mode of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 18.
Connection mode of the 400 ducted fan.
Figure 19.
Comparison between the experimental results and CFD results of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Total thrust, (b) total torque.
Figure 19.
Comparison between the experimental results and CFD results of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Total thrust, (b) total torque.
Figure 20.
Comparison of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Figure 20.
Comparison of the chord length and torsion angle of the blade of the 400 ducted fan: (a) Rotor, (b) stator.
Table 1.
Performance comparison of the ducted fan with different blade grids.
Table 1.
Performance comparison of the ducted fan with different blade grids.
| Grid Sizes (million) | Ω (rpm) | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| 1.18 | 11,000 | 14.194 | 0.883 | 2.869 | 0.973 | 37.042 |
| 1.92 | 11,000 | 14.343 | 0.885 | 2.903 | 0.971 | 37.107 |
| 3.11 | 11,000 | 14.250 | 0.878 | 2.873 | 0.960 | 37.013 |
Table 2.
Performance comparison of the ducted fan with different background grids.
Table 2.
Performance comparison of the ducted fan with different background grids.
| Grid Sizes (million) | Ω (rpm) | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| 1.04 | 11,000 | 14.343 | 0.885 | 2.903 | 0.971 | 37.013 |
| 1.65 | 11,000 | 14.488 | 0.887 | 2.966 | 0.972 | 37.334 |
Table 3.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan.
Table 3.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan.
| Type | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| Design | 14.987 | 0.799 | 1.765 | 0.799 | 37.000 |
| MRF | 13.283 | 0.737 | 1.543 | 0.677 | 32.796 |
Table 4.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan before and after the modification.
Table 4.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan before and after the modification.
| Process | Type | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| Initial design | Design | 14.987 | 0.799 | 1.765 | 0.799 | 37.000 |
| MRF | 13.283 | 0.737 | 1.543 | 0.677 | 32.796 |
| Modification 1 | Design | 14.983 | 0.904 | 2.063 | 0.904 | 37.000 |
| MRF | 14.658 | 0.869 | 1.939 | 0.829 | 36.761 |
| Modification 2 | Design | 14.736 | 0.876 | 1.899 | 0.876 | 37.000 |
| MRF | 14.647 | 0.864 | 1.934 | 0.859 | 36.549 |
| Modification 3 | Design | 14.801 | 0.879 | 1.964 | 0.879 | 37.000 |
| MRF | 14.687 | 0.873 | 1.960 | 0.873 | 36.910 |
Table 5.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan in the incoming flow state.
Table 5.
Performance comparison of the 150 ducted fan in the incoming flow state.
| Type | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| Design | 11.652 | 0.744 | 0.819 | 0.744 | 15.500 |
| MRF | 11.596 | 0.739 | 0.823 | 0.741 | 15.273 |
Table 6.
Performance comparison of the 400 ducted fan.
Table 6.
Performance comparison of the 400 ducted fan.
| Type | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| Design | 112.403 | 8.243 | 3.299 | 8.243 | 200.000 |
| MRF | 113.314 | 8.350 | 2.967 | 8.465 | 201.195 |
Table 7.
Performance comparison of the redesigned 400 ducted fan.
Table 7.
Performance comparison of the redesigned 400 ducted fan.
| Type | Tr (N) | Qr (N·m) | Ts (N) | Qs (N·m) | T (N) |
|---|
| Design | 108.499 | 7.957 | 4.881 | 7.957 | 200.000 |
| MRF | 108.348 | 7.955 | 4.876 | 7.898 | 199.315 |