Experimental Validation for the Performance of MR Damper Aircraft Landing Gear
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MR Damper Landing Gear
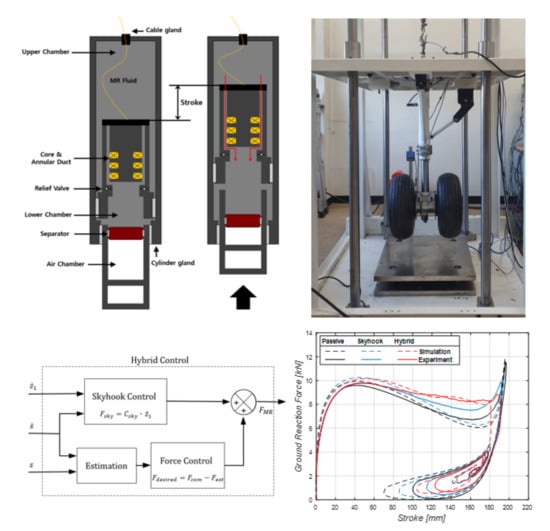
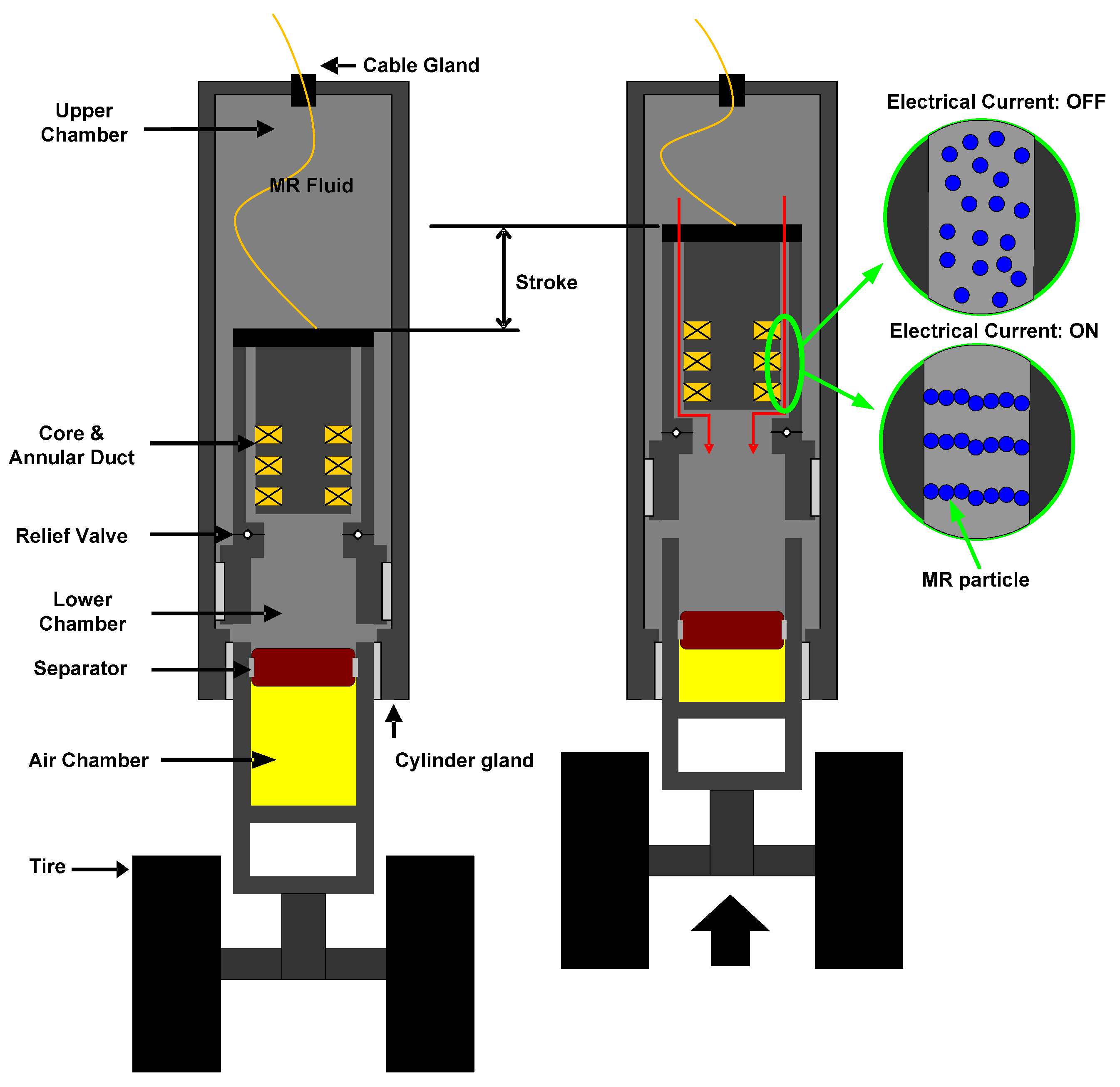
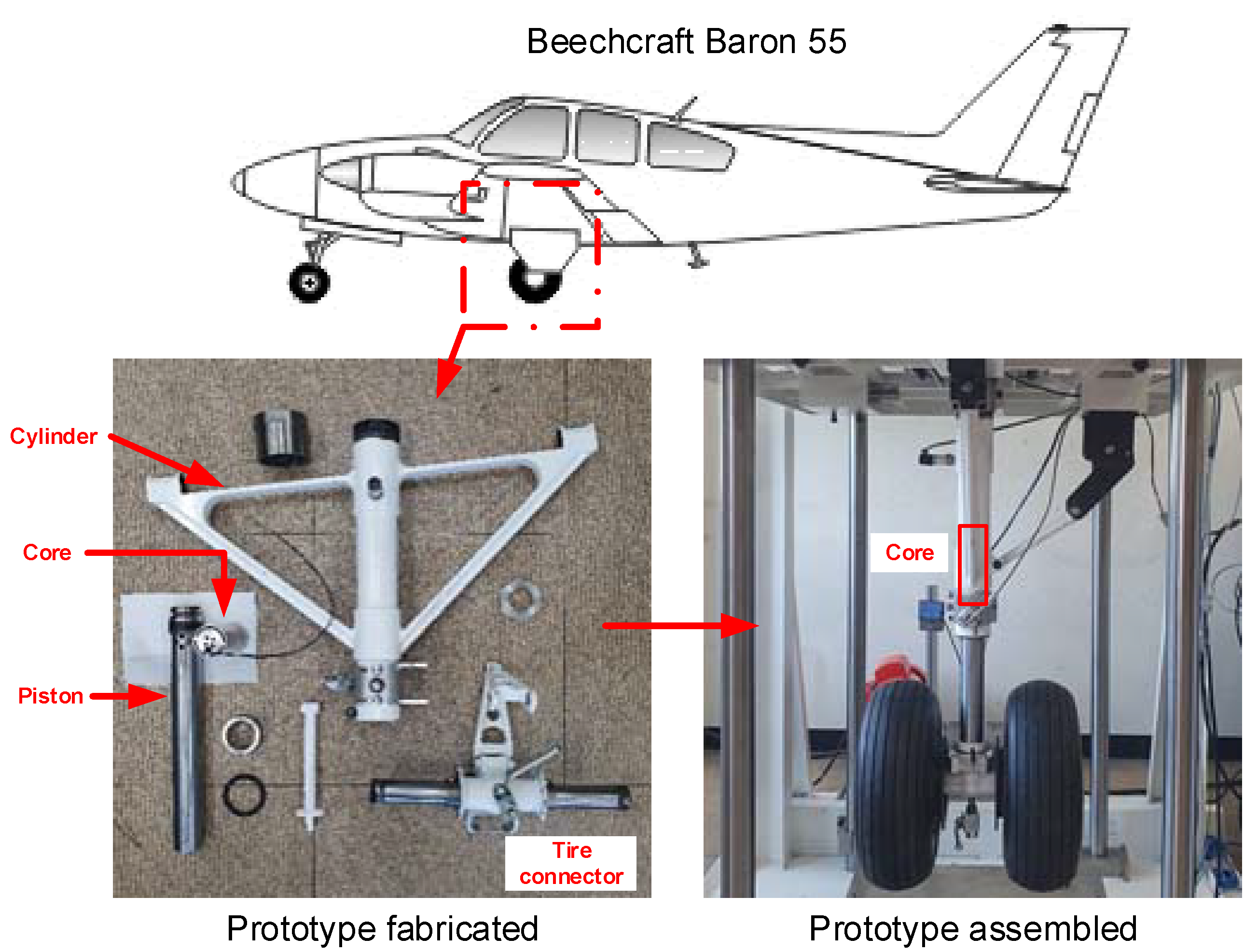
2.1. Structure of MR Damper Landing Gear
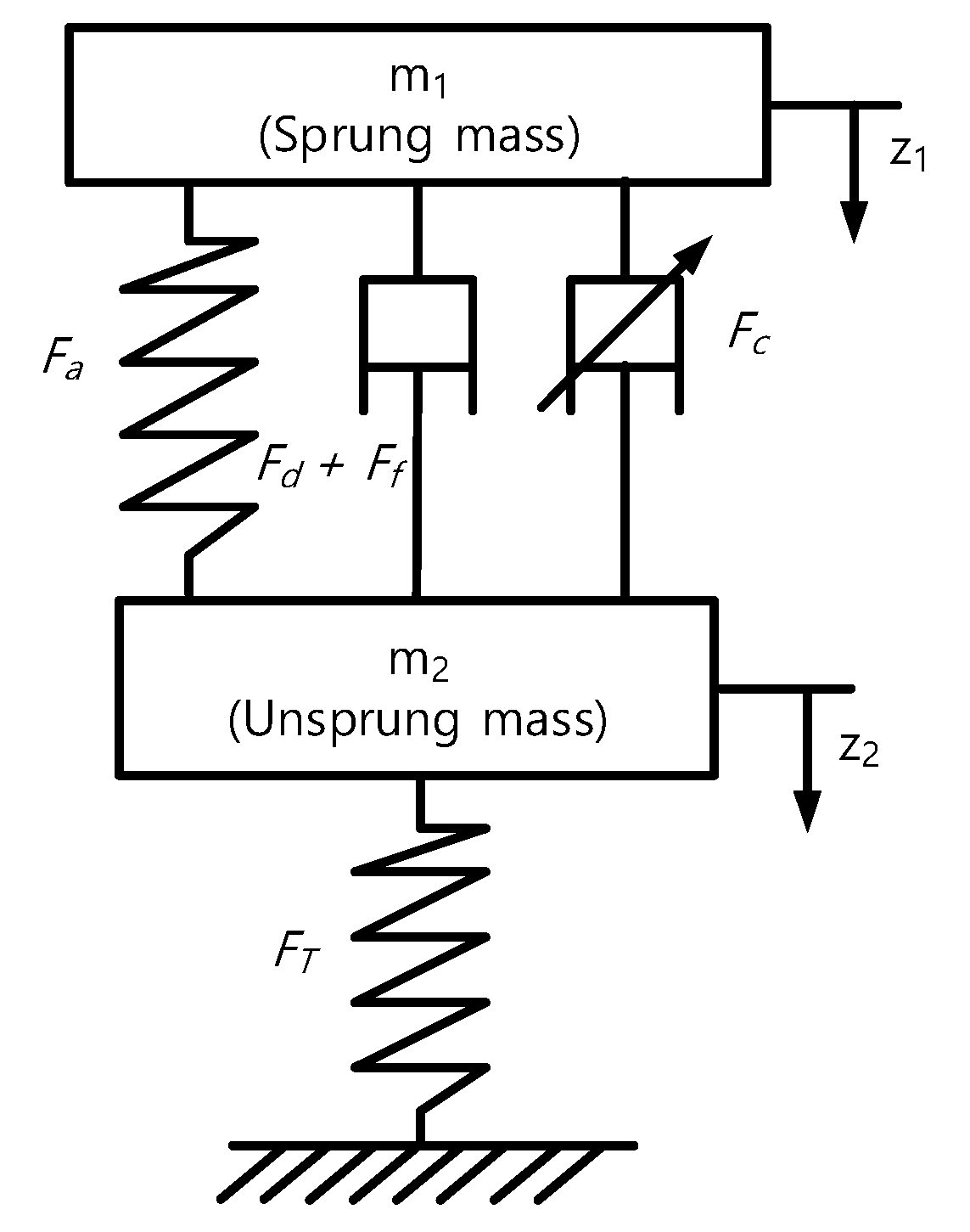
2.2. Mathematical Model
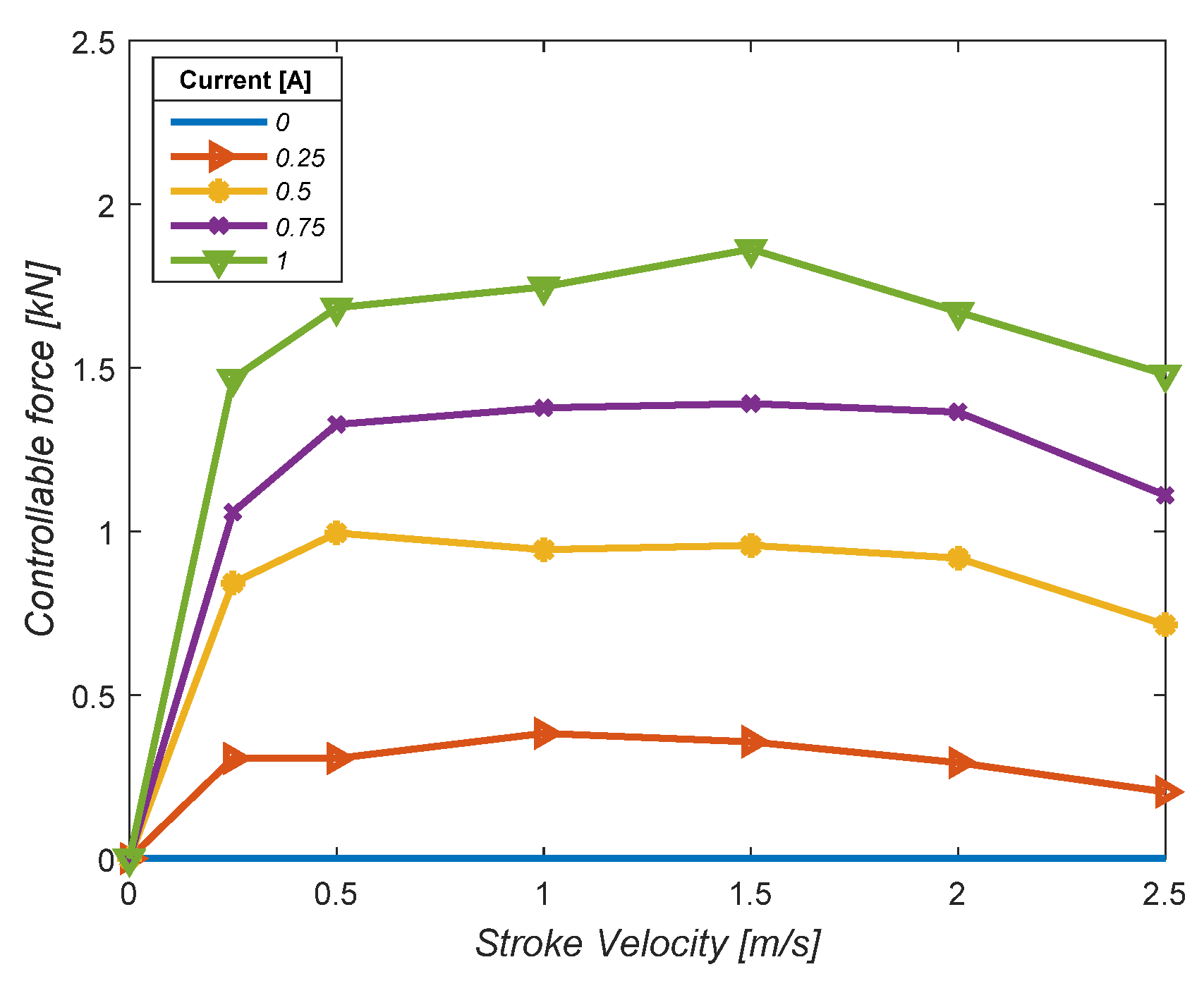
2.3. Controllable Force of the MR Damper
3. Experiment Setup
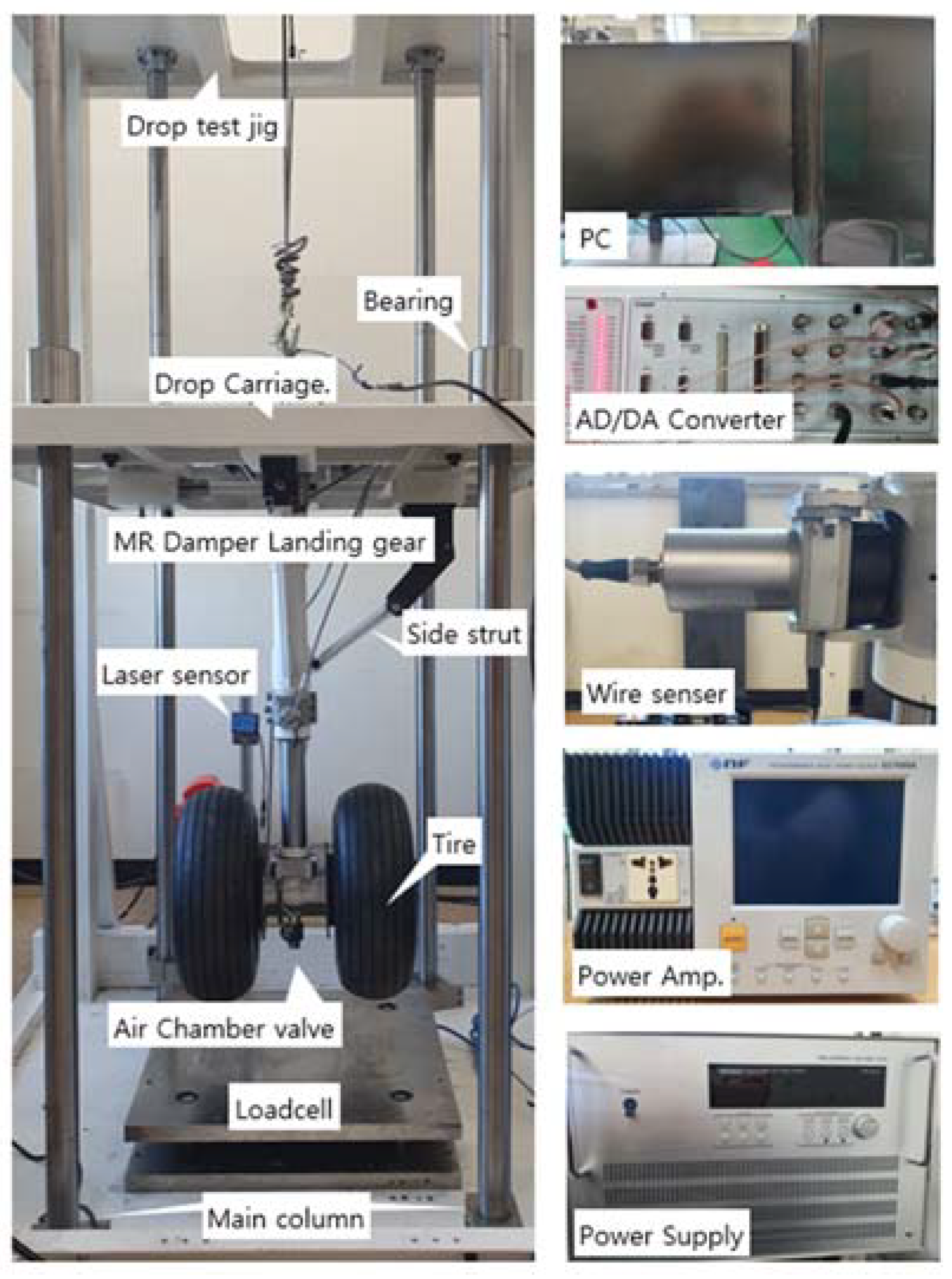
3.1. Test Jig and Components
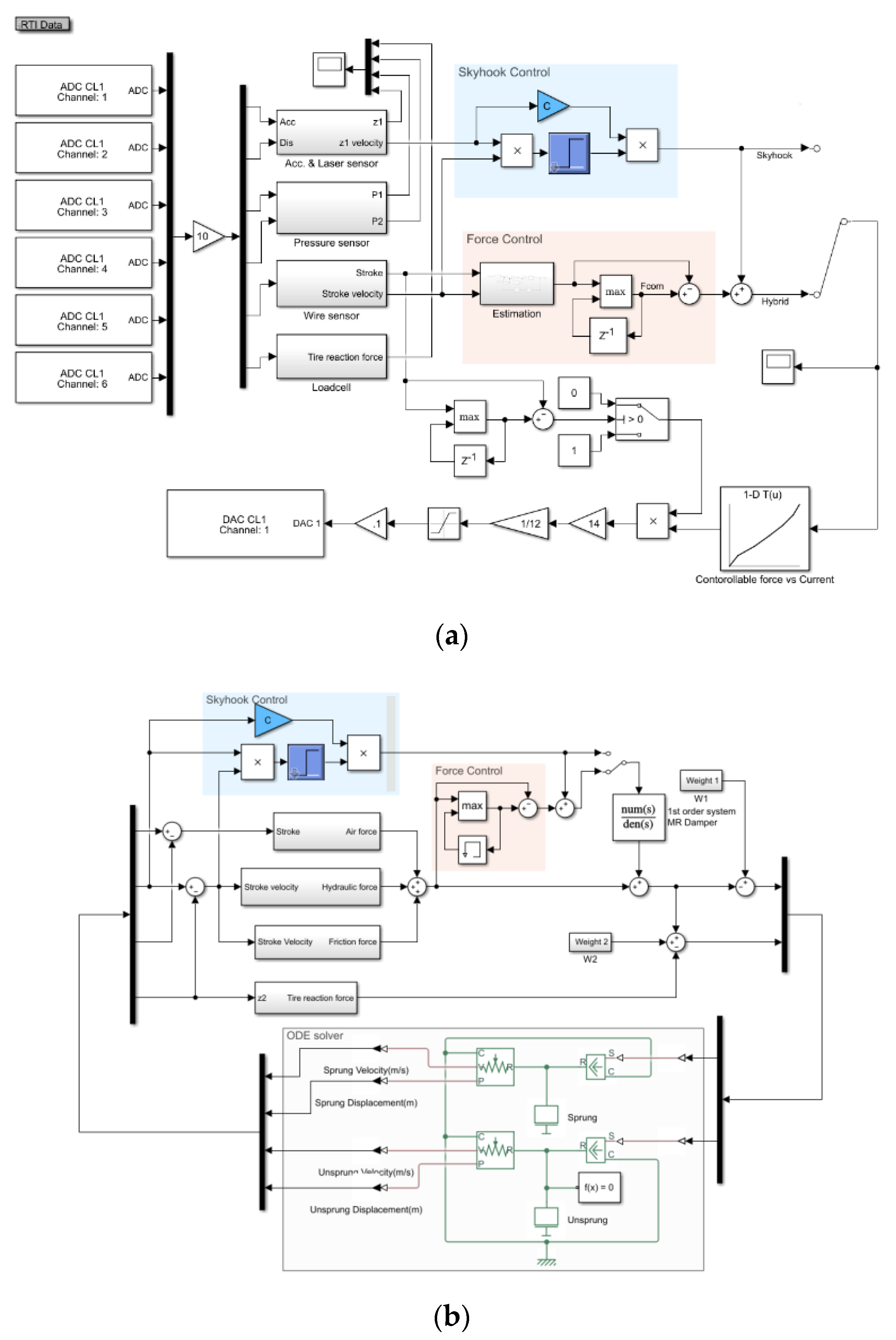
3.2. Data Acquisition and Control System
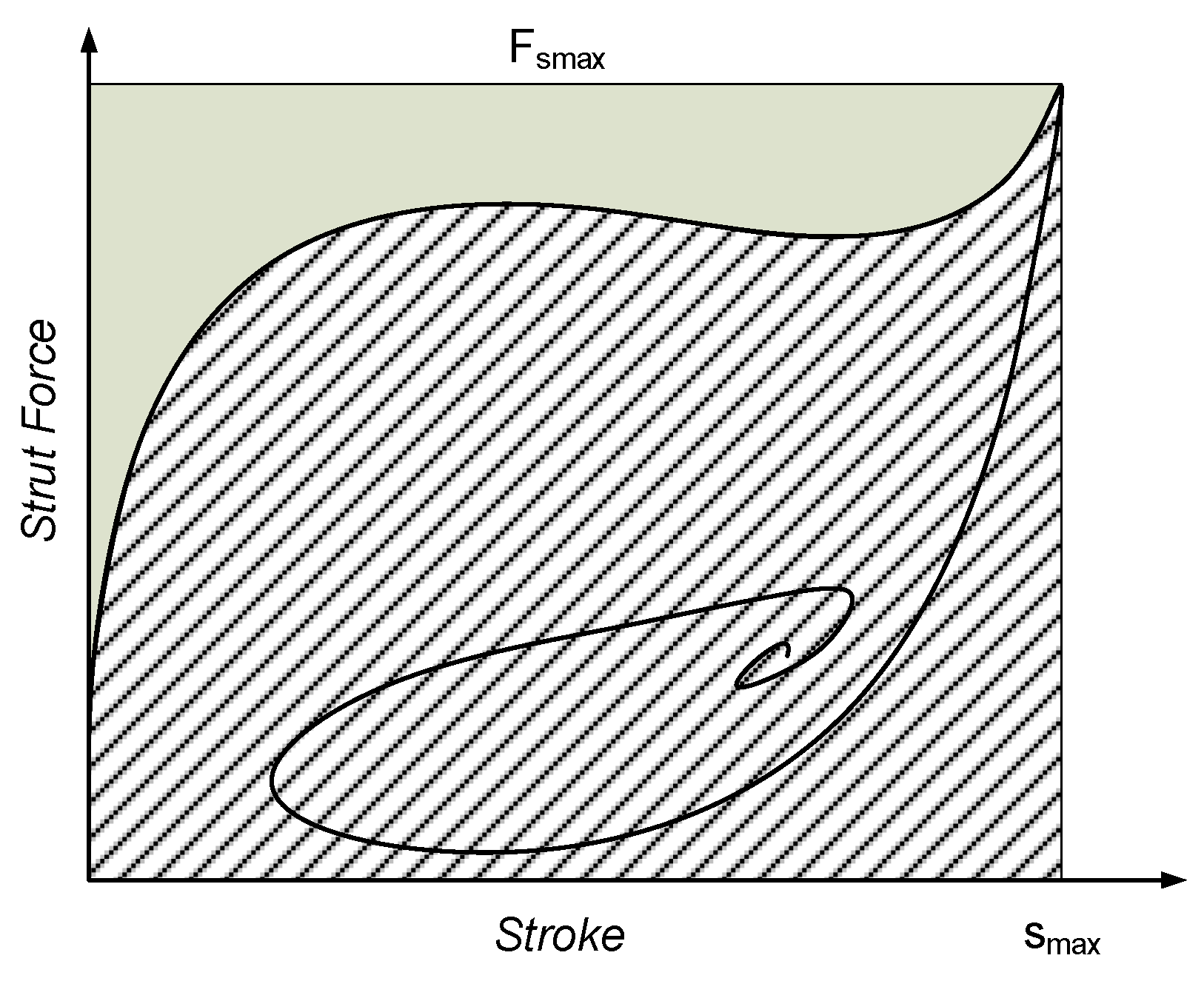
4. Drop Experiment
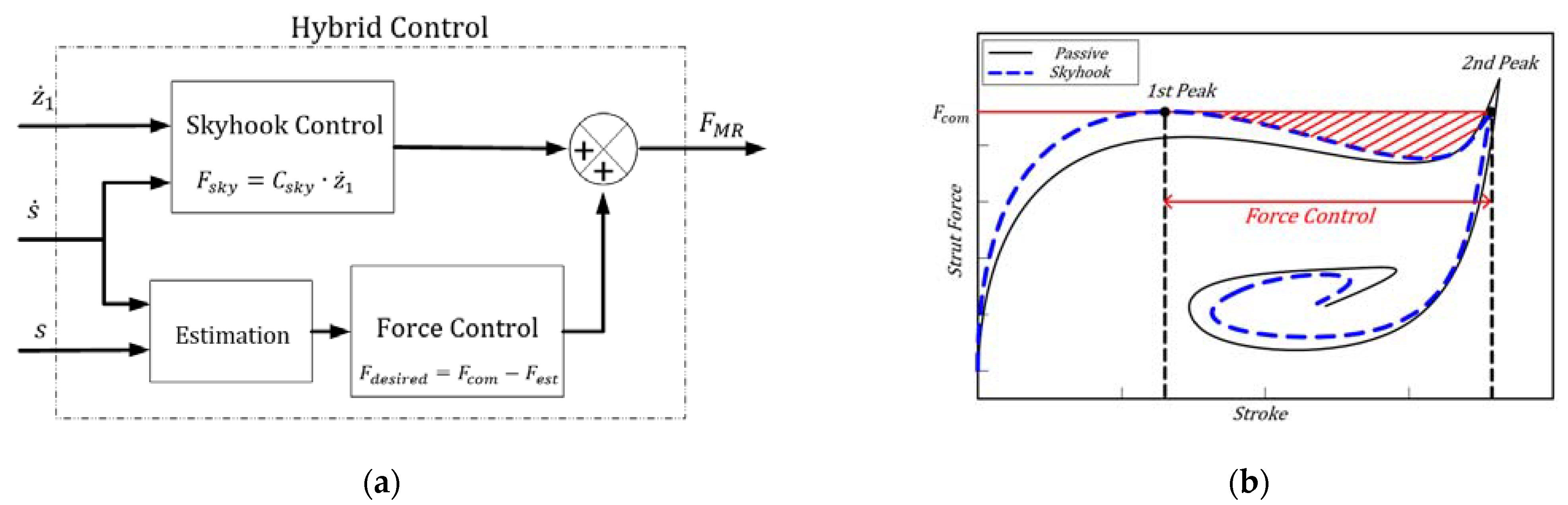
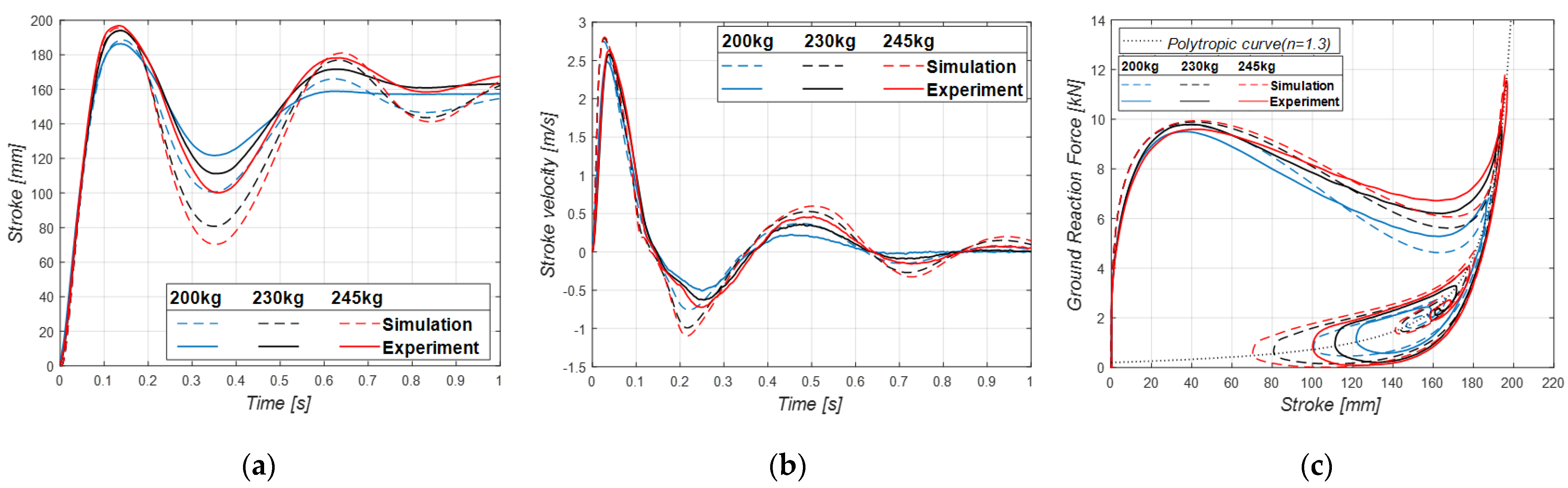
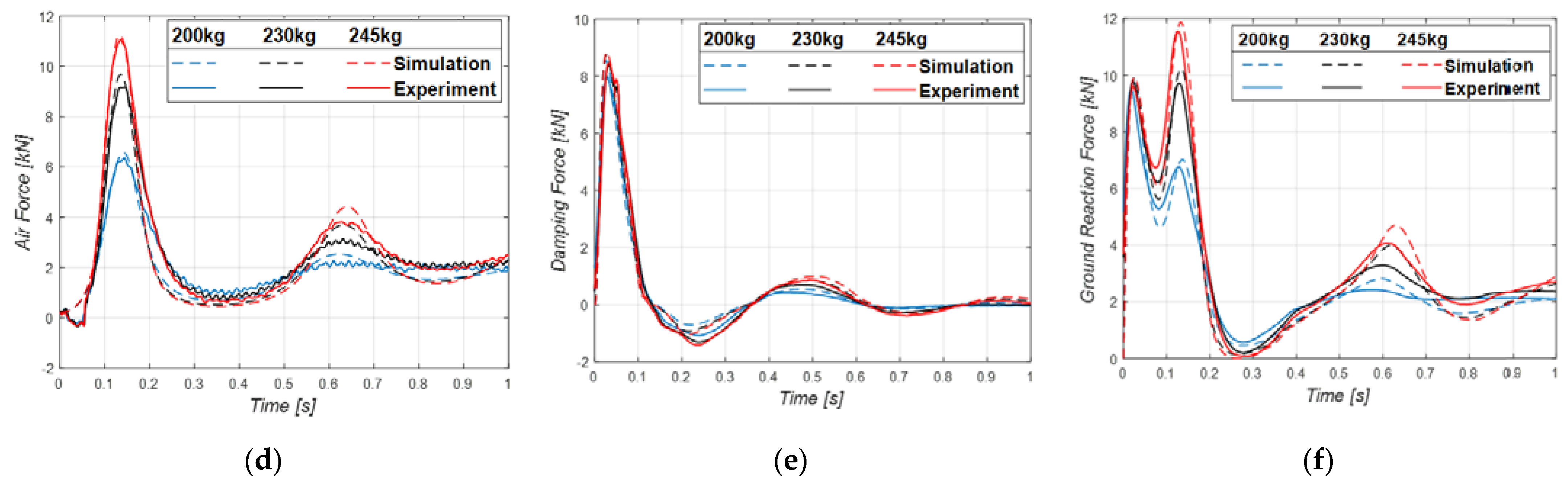
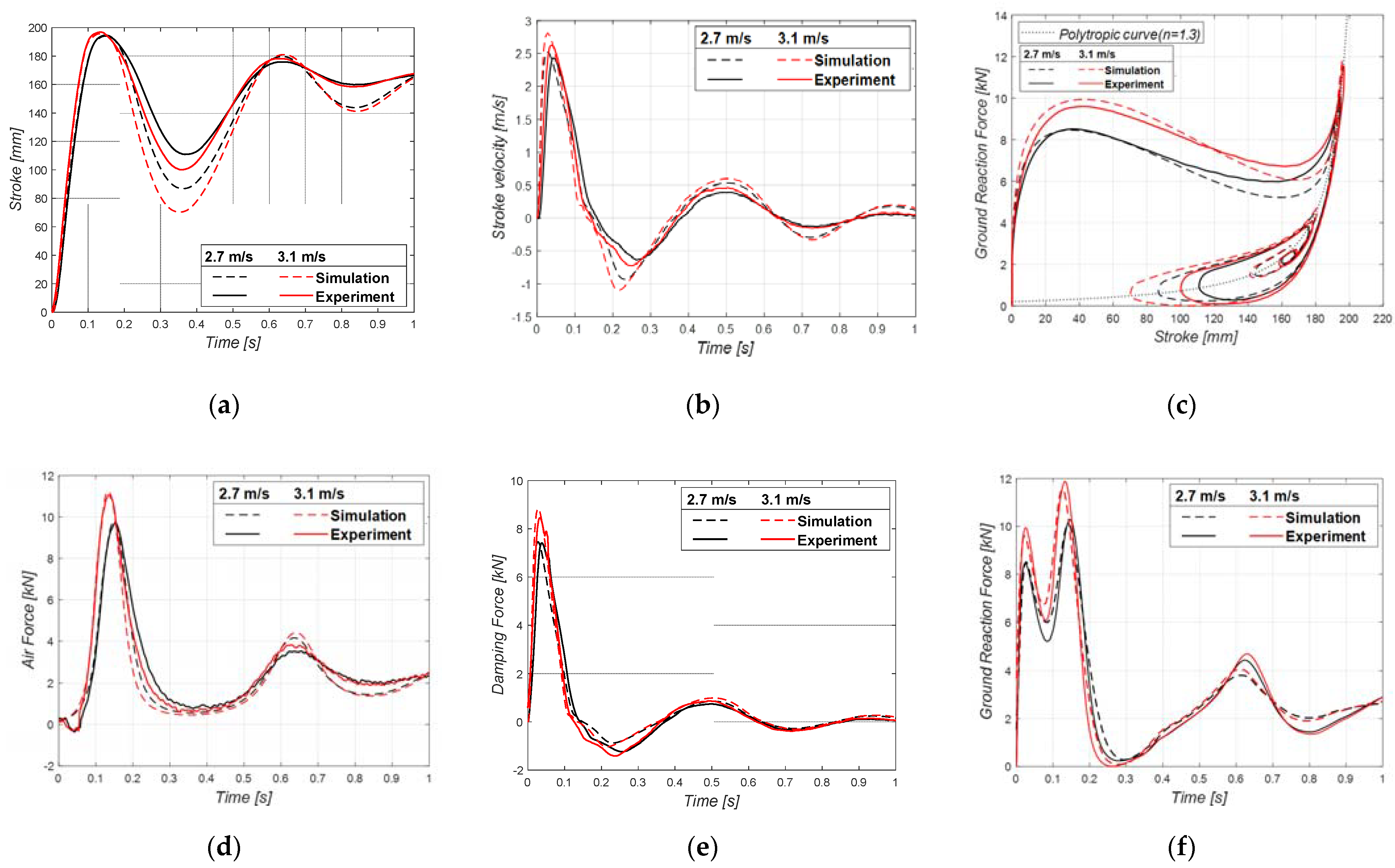
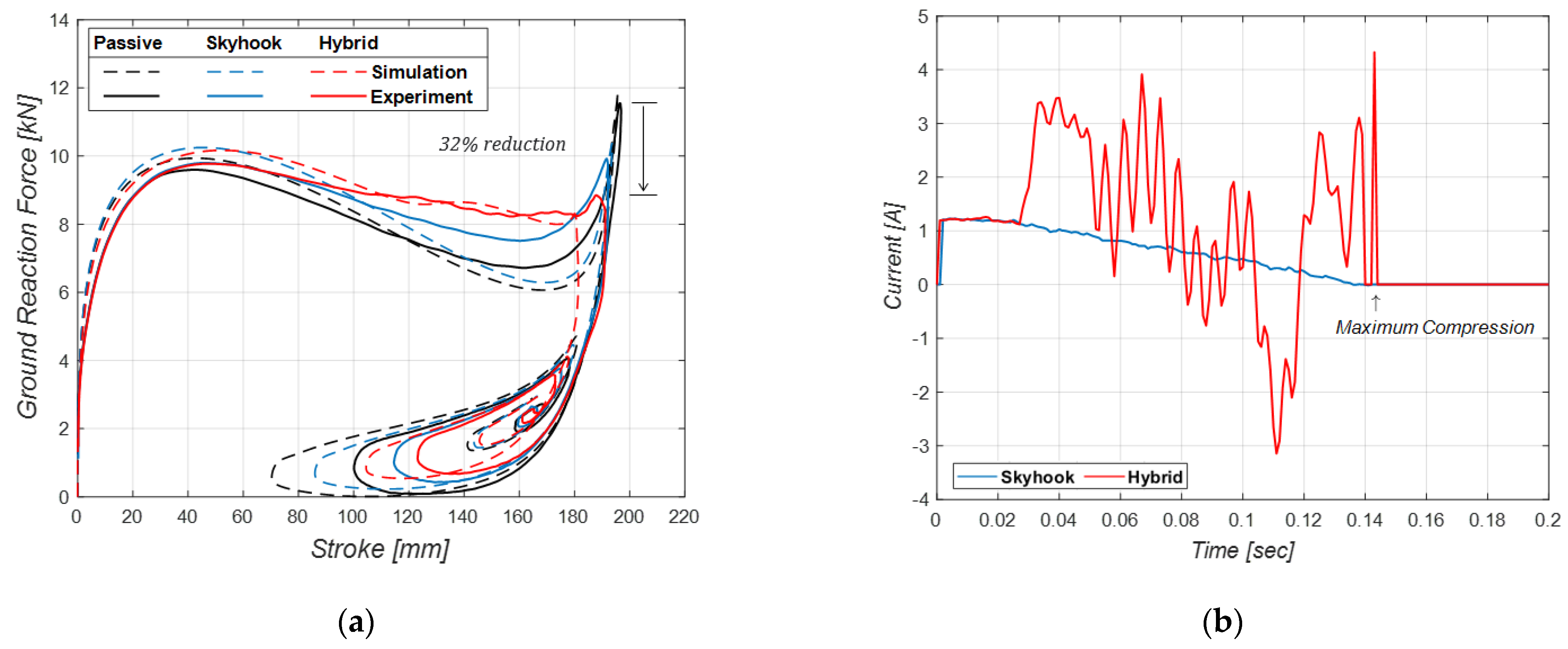
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGehee, J.R.; Carden, H.D. Analytical Investigation of the Landing Dynamics of a Large Airplane with a Load-Control System in the Main Landing Gear; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Milwitzky, B.; Cook, F.E. Analysis of Landing-Gear Behavior; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1953; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Tourajizadeh, H.; Zare, S. Robust and Optimal Control of Shimmy Vibration in Aircraft Nose Landing Gear. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somieski, G. Shimmy Analysis of a Simple Aircraft Nose Landing Gear Model Using Different Mathematical Methods. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 1997, 1, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, N.S. Aircraft Landing Gear Design: Principles and Practices; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-930403-41-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Gu, H.; Liu, H. GA-Based Model Predictive Control of Semi-Active Landing Gear. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2007, 20, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnopp, D.; Crosby, M.J.; Harwood, R.A. Vibration Control Using Semi-Active Force Generators. J. Eng. Ind. 1974, 96, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Carl, U. Fuzzy Control of Aircraft Semi-Active Landing Gear System. In Proceedings of the 37th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 11–14 January 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, K. Integrated Design Process for the Development of Semi-Active Landing Gears for Transport Aircraft. Ph.D. Dissertation, Institut für Flugmechanik und Flugregelung der Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-T. Vibration Control of a Landing Gear System Featuring Electrorheological/Magnetorheological Fluids. J. Aircr. 2003, 40, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, M.; Stiharu, I.; Sedaghati, R. Magneto-Rheological (MR) Damper for Landing Gear System. In Proceedings of the AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.-H.; Kim, B.-G.; Choi, S.-B. Design of a New Magnetorheological Damper Based on Passive Oleo-Pneumatic Landing Gear. J. Aircr. 2018, 55, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.-H.; Kang, B.-H.; Choi, S.-B.; Tak, J.-M.; Hwang, J.-H. Control of Landing Efficiency of an Aircraft Landing Gear System with Magnetorheological Dampers. J. Aircr. 2019, 56, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.-O. Semi-Active Force Control of Landing Gear Using Magneto-Rheological Damper. Ph.D. Thesis, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang-si, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuré-Powell, L.A. Magnetorheological Fluids and Applications to Adaptive Landing Gear for a Lightweight Helicopter. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-T.; Robinson, R.; Hu, W.; Wereley, N.M.; Birchette, T.S.; Bolukbasi, A.O.; Woodhouse, J. Analysis and Control of a Magnetorheological Landing Gear System for a Helicopter. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2016, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, B.-H.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H. Internal Components Arrangement of MR Damper Landing Gear for Cavitation Prevention. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2020, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, O.; Rogers, C.A.; Kordonsky, W. Magneto-Rheological Fluids_Materials, Characterization, and Devices. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.D.; Catanzarite, D.M.; Clair, K.A.S. Commercial Magneto-Rheological Fluid Devices. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 1996, 10, 2857–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.Z.; Yap, F.F.; Chen, G.; Li, W.H.; Yeo, S.H. MR Damper and Its Application for Semi-Active Control of Vehicle Suspension System. Mechatronics 2002, 12, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.Q.; Oyadiji, S.O. Application of MR Damper in Structural Control Using ANFIS Method. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterbee, D.C.; Sims, N.D.; Stanway, R.; Wolejsza, Z. Magnetorheological Landing Gear: 1. A Design Methodology. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, H.-S.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H. Modeling of MR Damper Landing Gear Considering Incompletely Developed Fluid Flow. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2021, 15, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-U.; Lee, S.-W.; Shin, J.-W.; Lee, S.-K.; Kim, S.-C.; Hwang, I.-H.; Kang, S.-H. Drop Test of an Oleo-pneumatic Landing Gear. J. Korean Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2010, 38, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterbee, D.C.; Sims, N.D.; Stanway, R.; Rennison, M. Magnetorheological Landing Gear: 2. Validation Using Experimental Data. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Nam, Y.-J.; Yamane, R.; Park, M.-K. Performance Evaluation on Vibration Control of MR Landing Gear. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-U.; Hwang, J.-H.; Bae, J.-S.; Lim, K.-H. Drop Test Simulation of Semi-active Landing Gear using Commercial Magneto-Rheological Damper. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2010, 4, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, Y.-O.; Hwang, J.-U.; Hwang, J.-H.; Bae, J.-S.; Lim, K.-H.; Kim, D.-M.; Kim, T.-W.; Park, M.-H. Force Control of Main Landing Gear using Magneto-Rheological Damper. J. Korean Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2009, 37, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, J.-M.; Viet, L.Q.; Hwang, J.-H. Hybrid Control of Aircraft Landing Gear using Magnetorheological Damper. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2018, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, L.Q.; Lee, H.-S.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H. Sliding Mode Control for an Intelligent Landing Gear Equipped with Magnetorheological Damper. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2020, 14, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, L.Q.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H. Robust Adaptive Control for an Aircraft Landing Gear Equipped with a Magnetorheological Damper. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, L.Q.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H. Intelligent Control Based on a Neural Network for Aircraft Landing Gear with a Magnetorheological Damper in Different Landing Scenarios. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Aviation Administration. FAR Sec.23.725 Limit Drop Tests. Available online: https://www.risingup.com/fars/info/part23-725-FAR.shtml (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Hwang, J.-H. Aerospace Parts Technology Development Project: Intelligent Landing Gear with Variable Damping Force for 1500 Ib Class; Korea Evaluation Insititute of Industrial Technology: Daegu, Korea, 2020.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total weight of the MR damper, | |
| Maximum compressible stroke, | |
| Piston area, including the outer wall, | |
| Piston area, excluding the outer wall, | |
| Gap sizes of the annular passages, | |
| Center radii of the annular passages, | |
| Fluid density, | – |
| Fluid viscosity, | |
| Maximum yield stress, | |
| Number of turns, | |
| AWG of the wire |
| Type | Max. Stroke | Max. Strut Force | Efficiency (Experiment) | Efficiency (Simulation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive | 196.9 mm | 11.6 kN | 72.9% | 73.5% |
| Skyhook | 192.1 mm | 9.8 kN | 87.6% | 82.4% |
| Hybrid | 191.2 mm | 9.8 kN | 90.8% | 90.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, B.-H.; Jang, D.-S.; Hwang, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-H. Experimental Validation for the Performance of MR Damper Aircraft Landing Gear. Aerospace 2021, 8, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8090272
Jo B-H, Jang D-S, Hwang J-H, Choi Y-H. Experimental Validation for the Performance of MR Damper Aircraft Landing Gear. Aerospace. 2021; 8(9):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8090272
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Bang-Hyun, Dae-Sung Jang, Jai-Hyuk Hwang, and Yong-Hoon Choi. 2021. "Experimental Validation for the Performance of MR Damper Aircraft Landing Gear" Aerospace 8, no. 9: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8090272
APA StyleJo, B.-H., Jang, D.-S., Hwang, J.-H., & Choi, Y.-H. (2021). Experimental Validation for the Performance of MR Damper Aircraft Landing Gear. Aerospace, 8(9), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8090272