An Overview of Cube-Satellite Propulsion Technologies and Trends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
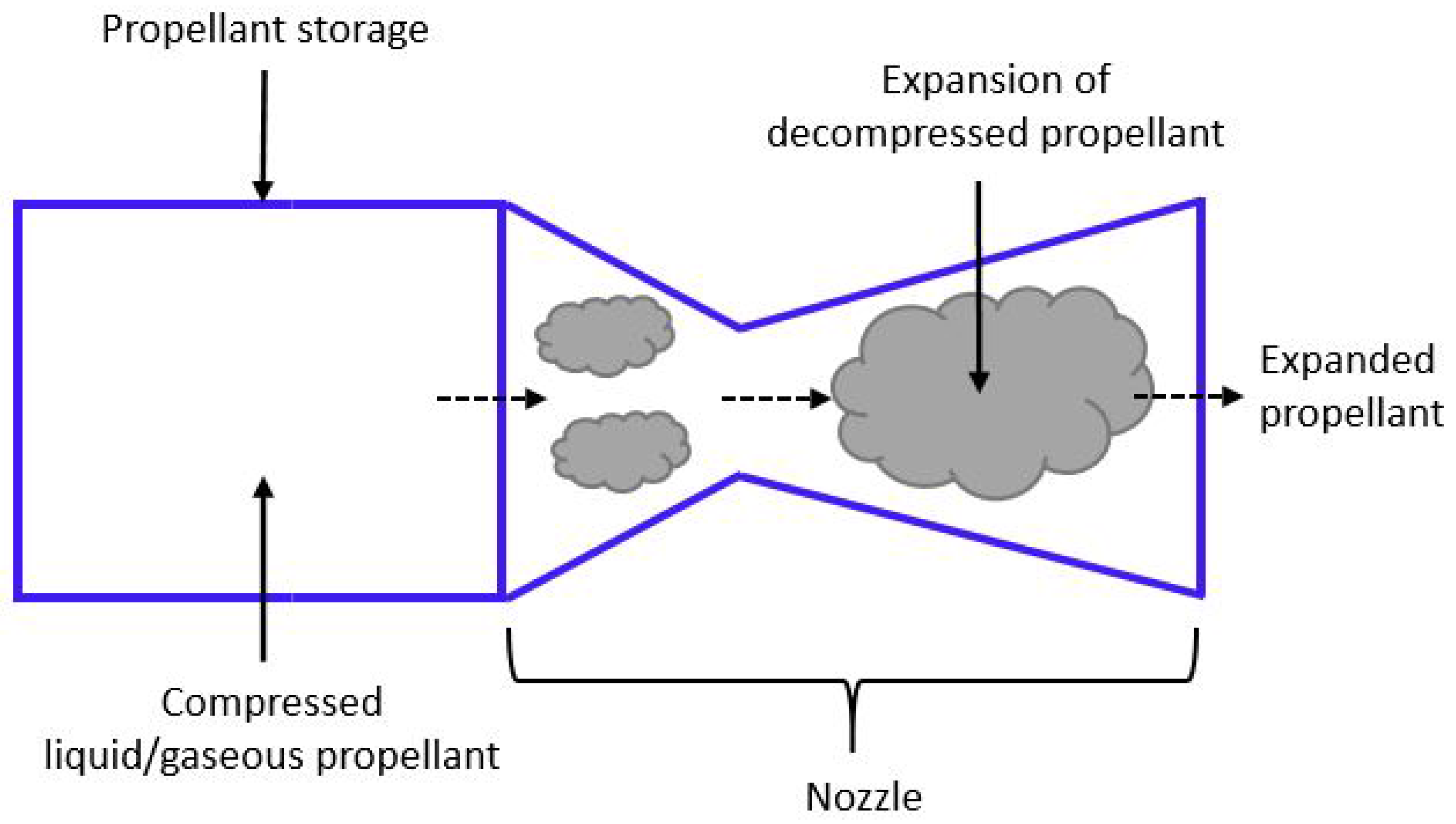
2. Cold Gas Propulsion (CGP) Systems
2.1. Operating Principle
2.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
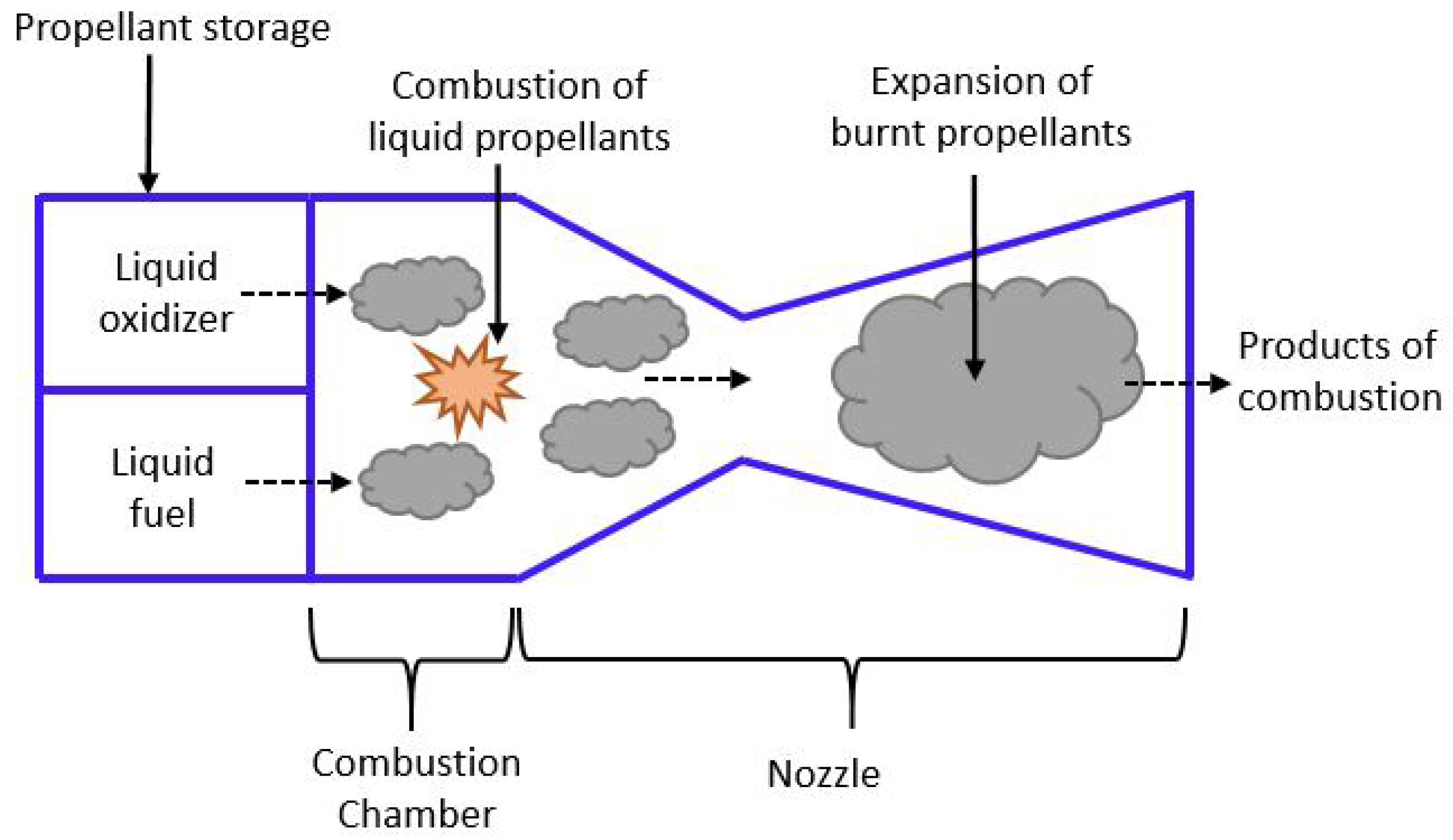
3. Liquid Propulsion (LP) Systems
3.1. Operating Principle
3.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
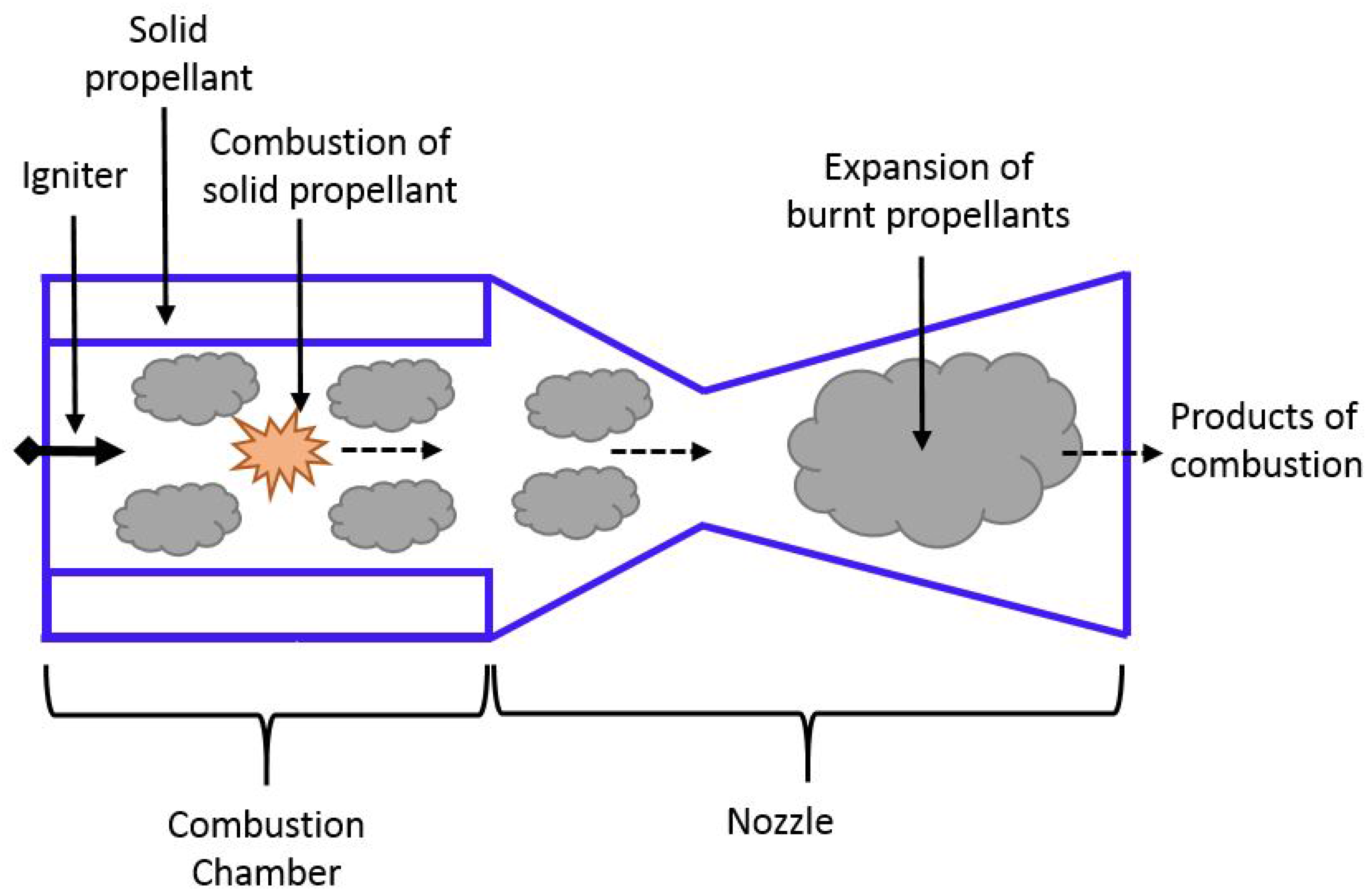
4. Solid Rocket Propulsion (SRP) Systems
4.1. Operating Principle
4.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
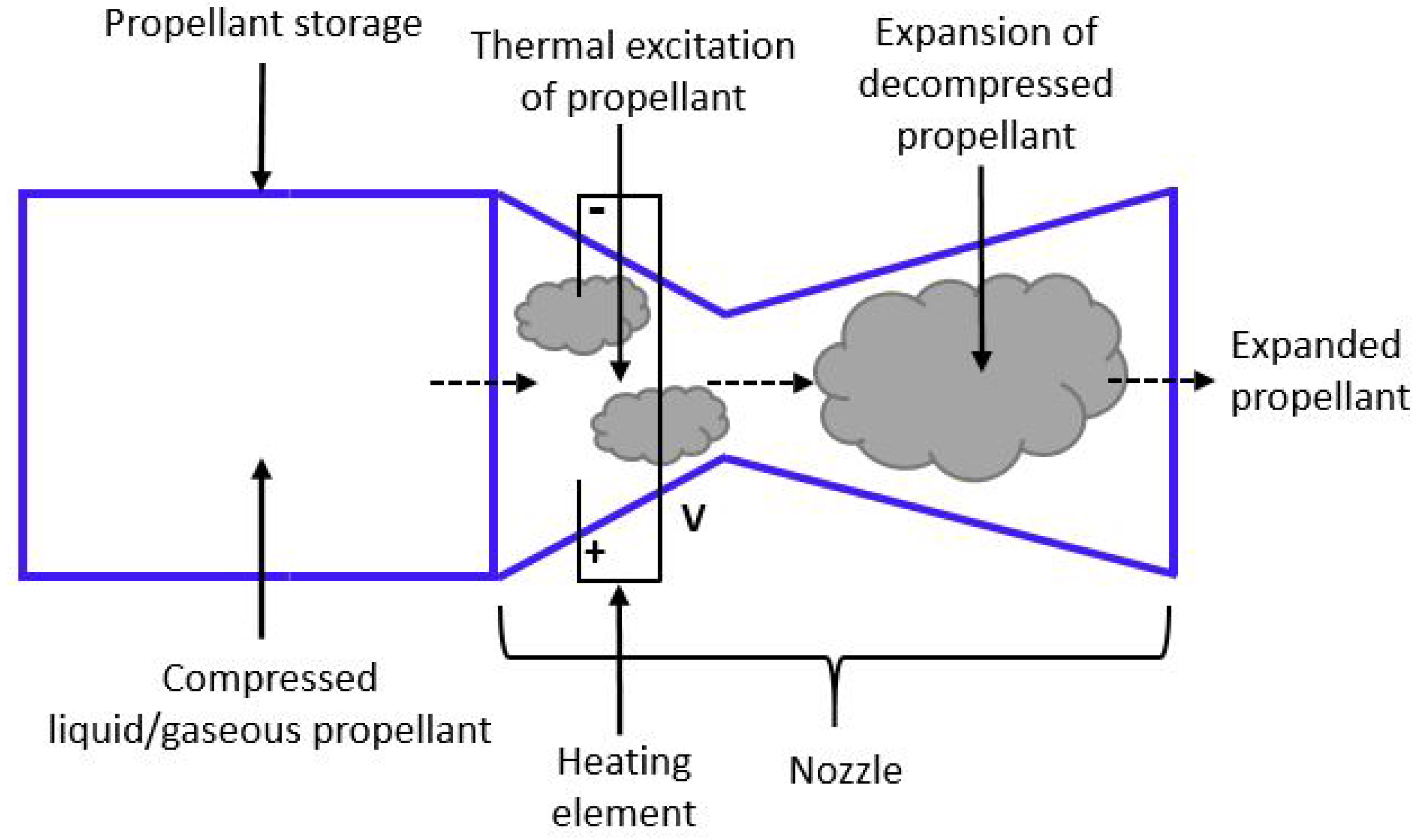
5. Resistojets
5.1. Operating Principle
5.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
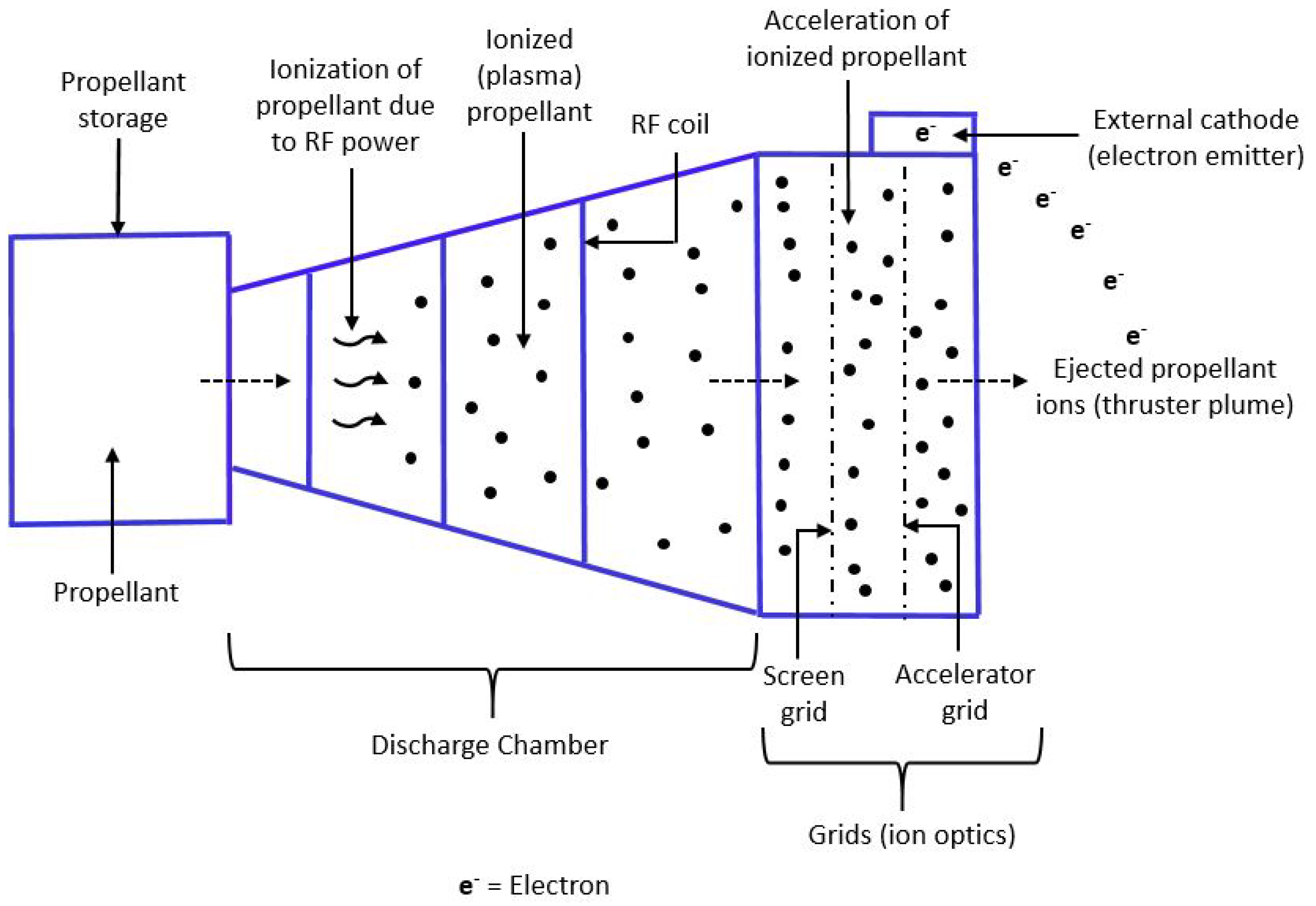
6. Radio-Frequency Ion Thruster (RIT)
6.1. Operating Principle
6.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
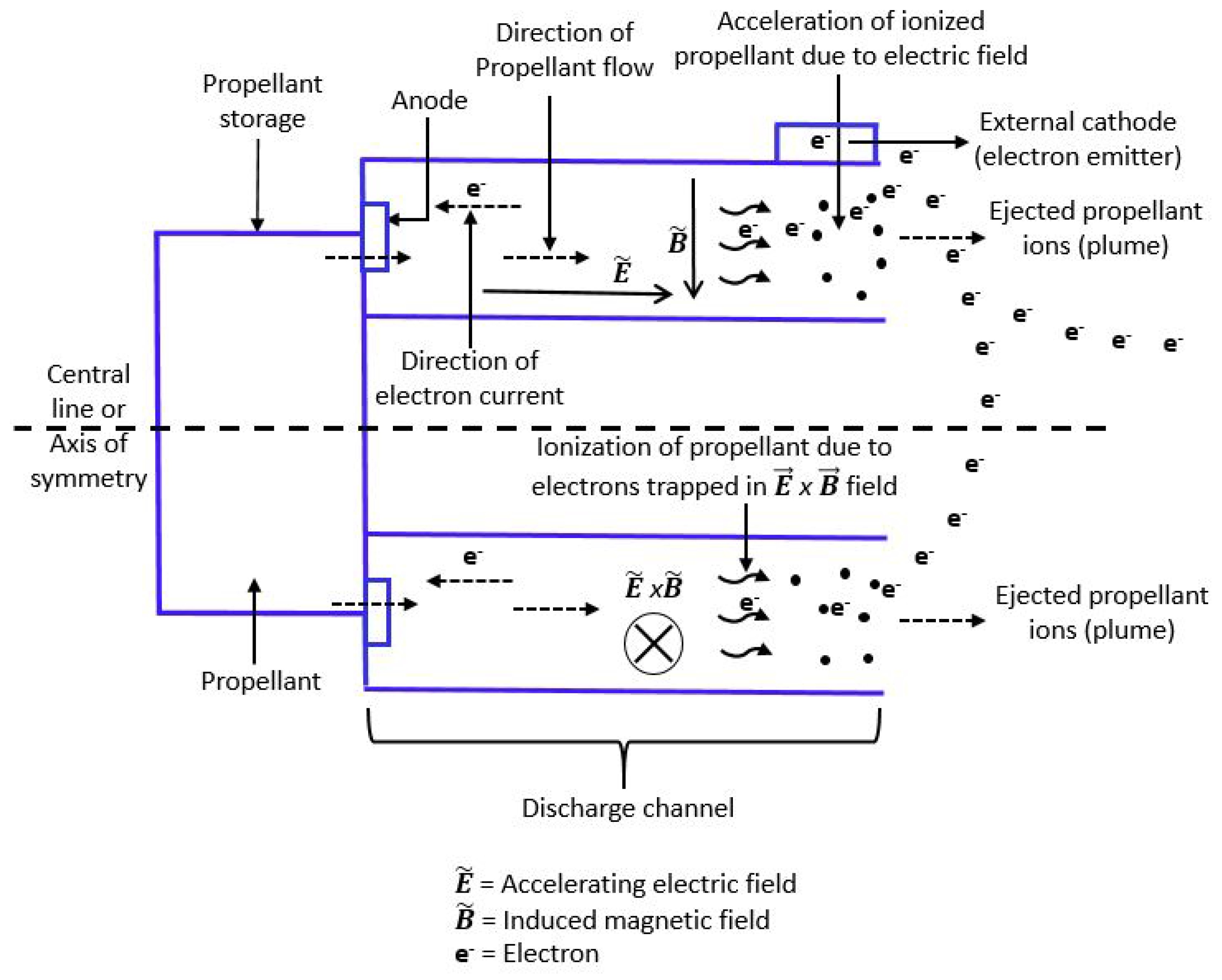
7. Hall Effect Propulsion/Hall Thrusters
7.1. Operating Principle
7.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
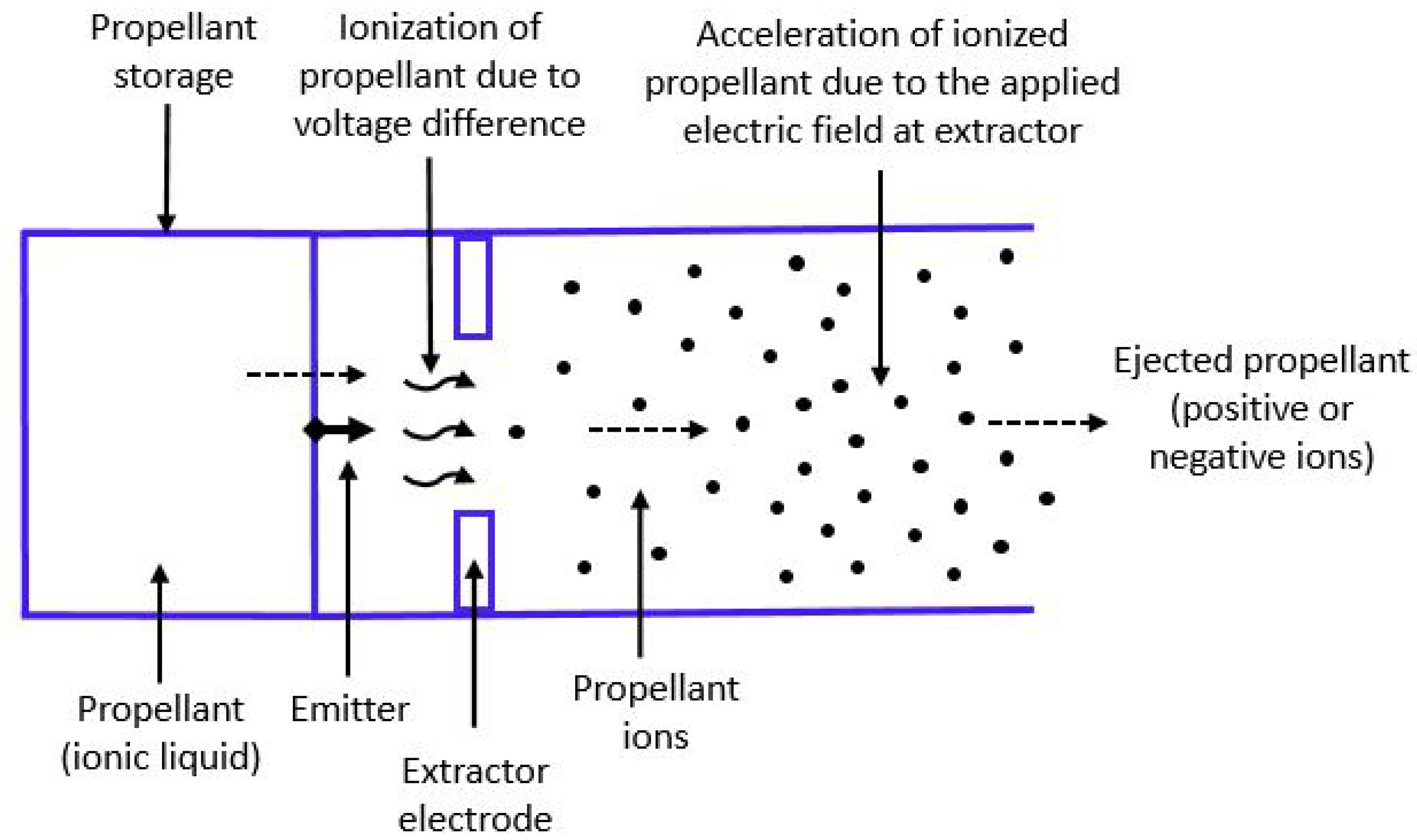
8. Electrospray Propulsion System/Electrospray Thrusters
8.1. Operating Principle
8.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
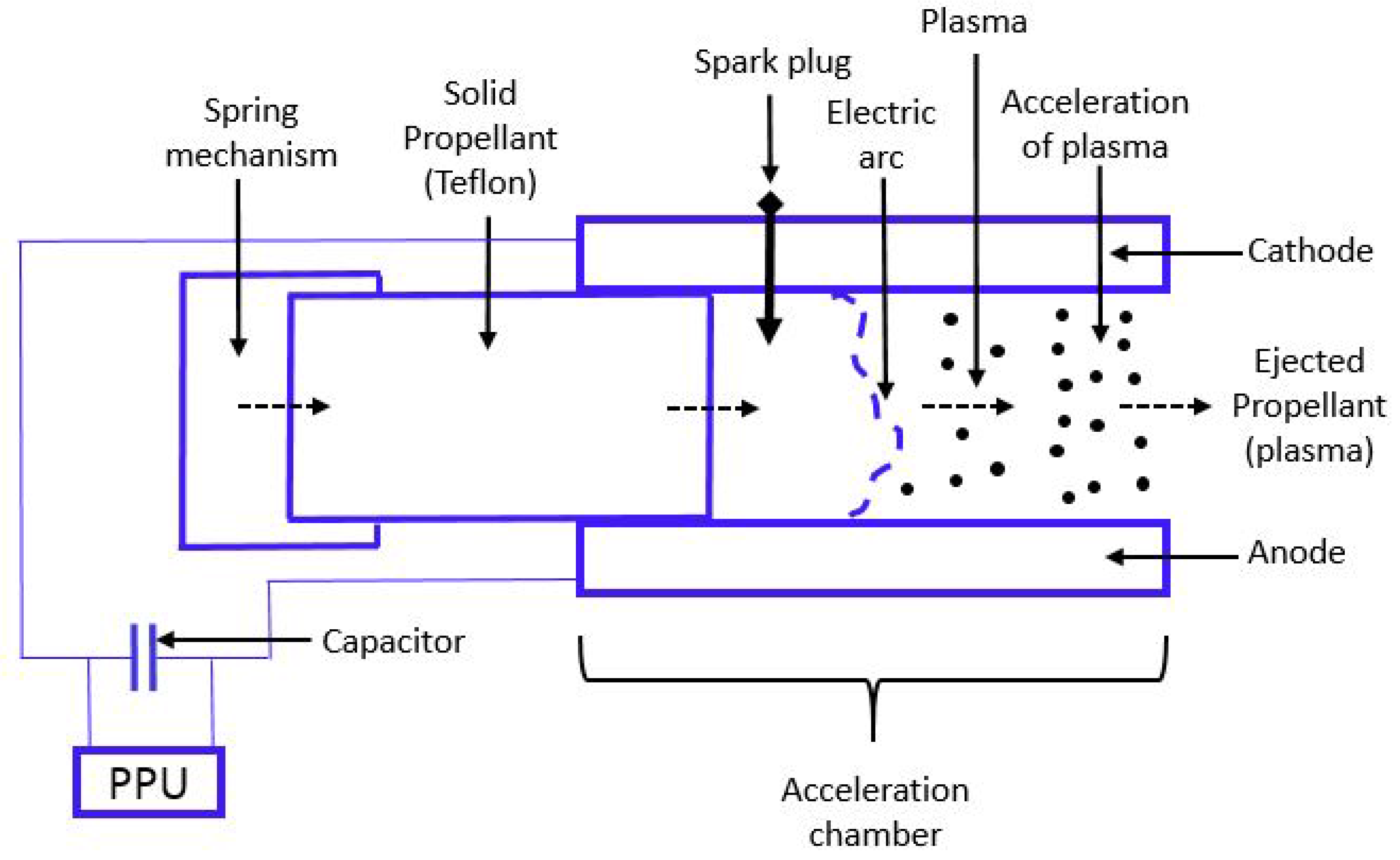
9. Pulse Plasma Thruster (PPT)
9.1. Operating Principle
9.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
10. Solar Sails
10.1. Operating Principle
10.2. Design Considerations and Technologies
11. Miscellaneous Propulsion Technologies and Design Methodologies
11.1. Propulsion Technologies
11.2. Design Methodologies
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Ammonia Micro Resistojet |
| CAPS | CubeSat Agile Propulsion System |
| CDM | CubeSat Delta-v Module |
| CHAMPS | CubeSat High-Impulse Adaptable Modular Propulsion System |
| CHIPS | Cubesat High Impulse Propulsion System |
| CHT | Cylindrical Hall Thruster |
| CNAPS | Canadian Nanosatellite Advanced Propulsion System |
| COTS | Commercial-Off-The-Shelf |
| ECAPS | Ecological Advanced Propulsion Systems |
| ET | Electrospray Thruster |
| FMMR | Free Molecule Micro Resistojet |
| GWU | George Washington University |
| HPGP | High Performance Green Propulsion |
| LPR | Low Power Resistojet |
| MPACS | Micro Propulsion Attitude Control System |
| CAT | Micro- Cathode Arc Thruster |
| PTFE | Poly-Tetra-Fluoro-Ethylene |
| PUC | Propulsion Unit for Cubesats |
| RIT | Radio Frequency Ion Thruster |
| RP1 | Rocket Propellant 1 |
| S-iEPS | Scalable ion Electrospray Propulsion System |
| UTIAS-SFL | University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies - Space Flight Laboratory |
| SRP | Solar Radiation Pressure |
References
- Woellert, K.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Ricco, A.J.; Hertzfeld, H. Cubesats: Cost-effective science and technology platforms for emerging and developing nations. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nervold, A.K.; Berk, J.; Straub, J.; Whalen, D. A Pathway to Small Satellite Market Growth. Adv. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, D.J.; Vladimirova, T.; Sweeting, M.N. Very-small-satellite design for distributed space missions. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2007, 44, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorian, A.; Blundell, E.; Suari, J.P.; Twiggs, R. CubeSats as responsive satellites. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 805, 756–6479. [Google Scholar]
- Hevner, R.; Holemans, W.; Puig-Suari, J.; Twiggs, R. An advanced Standard for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klesh, A.; Baker, J.; Castillo-Rogez, J.; Halatek, L.; Murphy, N.; Raymond, C.; Sherwood, B.; Bellardo, J.; Cutler, J.; Lightsey, G. Inspire: Interplanetary NanoSpacecraft Pathfinder In Relevant Environment. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2013 Conference and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schoolcraft, J.; Klesh, A.; Werne, T. MarCO: Interplanetary Mission Development on a CubeSat Scale. In Space Operations: Contributions from the Global Community; Springer: Daejeon, Korea, 2017; pp. 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, G.P.; Biblarz, O. Rocket Propulsion Elements, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 31–32, 34, 52, 133, 253, 260–261, 315, 417, 428, 608. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmer, K. Propulsion for CubeSats. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 134, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mission Design Division. Small Spacecraft Technology State of the Art; Number: NASA/TP-2015-216648/REV1; NASA: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 40–60.
- Anis, A. Cold gas propulsion system-an ideal choice for remote sensing small satellites. In Remote Sensing-Advanced Techniques And Platforms; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbon, D. A Review of the use of butane as a low cost propellant. In Proceedings of the 2010 Space Propulsion, San Sebastian, Spain, 3–6 May 2010; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, H. Stability boundaries of liquid-propelled space vehicles with sloshing. AIAA J. 1963, 1, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.R.; Scharfe, D.B.; Saleem, F.A.; Webb, R.N. Preheating Cold Gas Thruster Flow through a Thermal Energy Storage Conversion System. J. Propuls. Power 2013, 29, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, C.I.; Richardson, G.; Savignol, J. In-orbit results from the SNAP-1 nanosatellite and its future potential. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2003, 361, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, A.; Davies, P.; Liddle, D.; Paffett, J.; Sweeting, M.; Tondryk, W.; Gatti, G.; Garutti, A. The GIOVE-A Small Navigation Mission. In Proceedings of the Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bonin, G.; Roth, N.; Armitage, S.; Newman, J.; Risi, B.; Zee, R.E. CanX–4 and CanX–5 Precision Formation Flight: Mission Accomplished! In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USA Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, G.; Brama, Y.L. Cubesat Micropropulsion Characterization in Low Earth Orbit. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USA Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, S.; Jacobsson, B.; Gill, E. PRISMA—Demonstration Mission For Advanced Rendezvous and Formation Flying Technologies and Sensors. In Proceedings of the 56th International Astronautical Congress, Fukuoka, Japan, 17–21 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Mu, Z.; Chen, W.; Rodrigues, P.; Mendes, R.; Alminde, L. TW-1: A CubeSat Constellation for Space Networking Experiments. In Proceedings of the 6th European CubeSat Symposium, Estavayer-le-Lac, Switzerland, 16 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe, C.W.; Westphal, J.J.; Griesbach, J.D.; Schaub, H. Formation establishment and reconfiguration using differential elements in J2-perturbed orbits. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2015, 38, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.; Villa, M.; Williams, A. CubeSat based Rendezvous, Proximity Operations, and Docking in the CPOD Mission. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USA Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmas, J.; Banazadeh, P.; Koenig, A.W.; Macintosh, B.; D’Amico, S. System design of a miniaturized distributed occulter/telescope for direct imaging of star vicinity. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Aerospace, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, W.; Wittmann, K.; Hallmann, W. Handbook of Space Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 22, p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Stratton, J. The use of the AEROJET MR-103H thruster on the New Horizons mission to Pluto. In Proceedings of the 55th International Astronautical Congress 2004, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–8 October 2004; Vulume 30, p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Sackheim, R.L.; Masse, R.K. Green propulsion advancement: Challenging the maturity of monopropellant hydrazine. J. Propuls. Power 2014, 30, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spores, R.A. GPIM AF-M315E propulsion system. In Proceedings of the 51st AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference number AIAA, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 July 2015; p. 3753. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, S.A. Three-Dimensional Printing of “Green” Fuels for Low-Cost Small Spacecraft Propulsion Systems. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2017, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spores, R.A.; Masse, R.; Kimbrel, S.; McLean, C. GPIM AF-M315E propulsion system. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 15–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Legge, R.S.; Clements, E.B.; Shabshelowitz, A. Enabling microsatellite maneuverability: A survey of microsatellite propulsion technologies. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honololu, HI, USA, 4–9 June 2017; pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Schmuland, D.T.; Carpenter, C.; Masse, R.K. Mission Applications of the MRS-142 CubeSat High-Impulse Adaptable Monopropellant Propulsion System (CHAMPS). In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Atlanta, GA, USA, 30 July–1 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, C.B.; Schmuland, D.; Overly, J.; Masse, R. CubeSat Modular Propulsion Systems Product Line Development Status and Mission Applications. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schmuland, D.; Masse, R.; Sota, C. Hydrazine propulsion module for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kolosa, D.; Spangelo, S.; Lemmer, K.; Hudson, J. Mission analysis for a micro rf ion thruster for cubesat orbital maneuvers. In Proceedings of the Joint Propulsion Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 28–30 July 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Friedhoff, P.; Hawkins, A.; Carrico, J.; Dyer, J.; Anflo, K. On-Orbit Operation and Performance of Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN) Based High Performance Green Propulsion (HPGP) Systems. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–12 July 2017; p. 4673. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, M.; Feng, C.; Zwahlen, J. System-Level Demonstration of Busek’s 1U CubeSat Green Propulsion Module “AMAC”. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–12 July 2017; p. 4946. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, M.; Zwahlen, J.; Lafko, D.; Feng, C.; Robin, M. Complete EM System Development for Busek’s 1U CubeSat Green Propulsion Module. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- James, K.; Moser, T.; Conley, A.; Slostad, J.; Hoyt, R. Performance Characterization of the HYDROS Water Electrolysis Thruster. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zondervan, K.; Fuller, J.; Rowen, E. CubeSat Solid Rocket Motor Propulsion Systems providing Delta-Vs greater than 500 m/s. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual AIAA/USA Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–7 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sathiyanathan, K.; Lee, R.; Chesser, H.; Dubois, C.; Stowe, R.; Farinaccio, R.; Ringuette, S. Solid propellant microthruster design for nanosatellite applications. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Larangot, B.; Pham, P.Q.; Briand, D.; de Rooij, N.F.; Puig-Vidal, M.; Samitier, J. Solid propellant microthrusters on silicon: Design, modeling, fabrication, and testing. J. Microelectron. Syst. 2006, 15, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chou, S.; Ang, S.S. Development of a solid propellant microthruster with chamber and nozzle etched on a wafer surface. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasher, J.; Williams, S.; Takahashi, P.; Sousa, J. Pulsed Plasma Thruster Development Using a Novel HAN-Based Green Electric Monopropellant. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016; p. 4846. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, A.; Finne, T.; Galysh, I.; Mai, A.; Yen, J.; Sawka, W.; Ransdell, J.; Williams, S. SpinSat Mission Overview. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual AIAA/USA Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 10–15 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- David, A.O.; Knoll, A.K. Experimental Demonstration of an Aluminum-Fueled Propulsion System for CubeSat Applications. J. Propuls. Power 2017, 33, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Ziemer, J.; Hofer, R.; Wirz, R.; O’Donnell, T. A Survey of Micro-thrust Propulsion Options for Microspacecraft and Formation Flying Missions. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual CubeSat Developers Workshop, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 9 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sawka, W.N.; McPherson, M. Electrical solid propellants: A safe, micro to macro propulsion technology. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 14–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Frisbee, R.H. Advanced space propulsion for the 21st century. J. Propuls. Power 2003, 19, 1129–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Brogan, T.; Cardiff, E. An Ammonia Microresistojet (MRJ) for micro Satellites. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Hartford, CT, USA, 21–23 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Sanchez, M.; Pollard, J.E. Spacecraft electric propulsion—An overview. J. Propuls. Power 1998, 14, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matticari, G.; Noci, G.; Siciliano, P.; Colangelo, G.; Schmidt, R. Cold gas micro propulsion prototype for very fine spacecraft attitude/position control. In Proceedings of the AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE 42nd joint propulsion conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–12 July 2006; pp. 5378–5390. [Google Scholar]
- Skuhersky, M.; Balestrero Machado, L.; Wilde, M.; Brett, C. CERBERUS: Prototype for an Agile Inspection and Servicing Satellite Using Thrust-Vectoring Cold-Gas Propulsion. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE and Astronautics Forum and Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–14 September 2017; p. 5116. [Google Scholar]
- Slough, J.; Andreason, S.; Ziemba, T.; Ewing, J. Micro-discharge micro-thruster. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005; Volume 4047. [Google Scholar]
- Chianese, S.G.; Micci, M.M. Microwave electrothermal thruster chamber temperature measurements and performance calculations. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketsdever, A.D.; Wadsworth, D.C.; Muntz, E. Gas-surface Interaction Model Influence on Predicted Performance of Microelectromechanical System Resistojet. J. Thermo Phys. Heat Transf. 2001, 15, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.H.; Bauer, A.; Killingsworth, M.D.; Lilly, T.; Duncan, J.; Ketsdever, A. Free-molecule-microresistojet performance using water propellant for nanosatellite applications. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2008, 45, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Gimelshein, S.F.; Ketsdever, A.D. Numerical analysis of free-molecule microresistojet performance. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejmanowski, N.J.C.A.; Woodruff, R.B. CubeSat High Impulse Propulsion System (CHIPS). In Proceedings of the 62nd JANNAF Propulsion Meeting (7th Spacecraft Propulsion), Nashville, TN, USA, 1–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Coxhill, I.; Gibbon, D. A Xenon Resistojet Propulsion System for Microsatellites. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.; Whittaker, P.; Bird, R.; Gomes, L.; Stern, B.; Sweeting, M.; Cohen, M.; Hall, D. NovaSAR–bringing radar capability to the disaster monitoring constellation. In Proceedings of the Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, D.L.J.M.; Cardin, R.L.B. Propulsion Unit for CubeSats (PUC). In Proceedings of the 62nd JANNAF Propulsion Meeting (7th Spacecraft Propulsion), Nashville, TN, USA, 1–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, K.I. State-of-the-Art for Small Satellite Propulsion Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 Biennial Aerospace Systems Conference of the National Society of Black Engineers (NSBE), Arlington, VA, USA, 24–27 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, D.M.; Katz, I. Fundamentals of Electric Propulsion: Ion and Hall Thrusters; Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL): Pasadena, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 6–7, 22, 26, 148, 189, 192, 243–244, 325, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Fearn, D.G.; Solutions, E.; Crookham, C. The Future Development of Gridded Ion Engines. In Proceedings of the 39th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville, AL, USA, 20–23 July 2003; p. 4714. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, D.M.; Polk, J.E.; Mikellides, I.G. Ion thruster performance impacts due to cathode wear. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinza, D.; Wang, J.; Polk, J.; Henry, M. Deep space 1 measurements of ion propulsion contamination. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2001, 38, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikellides, I.G.; Katz, I. Wear mechanisms in electron sources for ion propulsion, 1: Neutralizer hollow cathode. J. Propuls. Power 2008, 24, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, R.D.; Polk, J.E. Characterization of cathode keeper wear by surface layer activation. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbur, P.J.; Wilson, M.; Hutchings, K.; Williams, J.D. Emissive membrane ion thruster concept. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauth, P.; Tuller, H.L. Solid-State Ionics: Roots, Status, and Future Prospects. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 1654–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, M.; Frongillo, J.; Zwahlen, J. Maturation of Iodine Fueled BIT-3 RF Ion Thruster and RF Neutralizer. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016; p. 4544. [Google Scholar]
- Bosanac, N.; Cox, A.; Howell, K.C.; Folta, D.C. Trajectory Design for a Cislunar Cubesat Leveraging Dynamical Systems Techniques: The Lunar Icecube Mission. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, H. Evolution of the AIRBUS DS GmbH Radio Frequency Ion Thruster Family. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference of 30th ISTS, 34th IEPC and 6th NSAT, Kobe-Hyogo, Japan, 4–10 July 2015; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.H. On a New Action of the Magnet on Electric Currents. Am. J. Math. 1879, 2, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikel, G.; Reshotko, E. Hall current ion accelerator. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. Ser. II 1962, 7, 414. [Google Scholar]
- Lary, E.; Meyerand, R.; Salz, F. Ion acceleration in a gyro-dominated neutral plasma-theory. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. Ser. II 1962, 7, 441. [Google Scholar]
- Tamida, T.; Osuga, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Takegahara, H.; Aoyagi, J.; Kuriki, K. Performance Improvement of Hall Thrusters Using a Pulse-Synchronous Driver System. J. Propuls. Power 2015, 31, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankanich, J.W. Direct drive for low power Hall thrusters. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005; Volume 4118, pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pigeon, C.E.; Nathan, G.; Orr, B.P.L. A Low Power Cylindrical Hall Thruster for Next Generation Microsatellites. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Gascon, N.; Crawford, W.S.; Cappelli, M.A. Experimental characterization of a micro-Hall thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Komurasaki, K.; Arakawa, Y. Discharge current oscillation in Hall thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2005, 21, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhurin, V.; Kaufman, H.; Robinson, R. Physics of closed drift thrusters. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1999, 8, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieckhafer, A.; King, L.B. Energetics of propellant options for high-power Hall thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.; Branam, R.; Huffman, R.; Szabo, J.; Paintal, S. High thrust density propellants in Hall thrusters. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2011; p. 524. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Martinez-Sanchez, M. Hybrid particle-in-cell erosion modeling of two Hall thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2008, 24, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikellides, I.G.; Katz, I.; Hofer, R.R.; Goebel, D.M. Magnetic shielding of a laboratory Hall thruster. I. Theory and validation. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 043303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, L.; Saverdi, M.; Andrenucci, M. Scaling and performance prediction of Hall effect thrusters. In Proceedings of the 39th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville, AL, USA, 20–23 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dannenmayer, K.; Mazouffre, S. Elementary scaling relations for Hall effect thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.D.; Hargus, W.A.; VanGilder, D.B. Comparison of Numerical and Experimental Near-Field Plasma Properties of the BHT-200-X3 Hall Thruster (Preprint); Technical Report; Air Force Research Lab, Edwards Air Force Base: Kern, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gregucci, S.; Raiji, H.; Pergola, P.; Marcuccio, S. Analytical constellation design and link budget computation tool for EO missions. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences (EUCASS), Milan, Italy, 3–6 July 2017; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Biagioni, L.; Cesari, U.; Saverdi, M.; Andrenucci, M. Development status of the HT-100 miniaturized hall effect thruster system. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2015; p. 3875. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatore, V.; Battista, F.; Ricci, D.; Invigorito, M. CIRA Development Activities in Electric Propulsion Testing. In Proceedings of the 66th International Astronautical Congress, Jerusalem, Israel, 12–16 October 2015; Volume 4, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Grustan-Gutierrez, E.; Gamero-Castaño, M. Microfabricated Electrospray Thruster Array with High Hydraulic Resistance Channels. J. Propuls. Power 2017, 33, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejci, D.; Mier-Hicks, F.; Fucetola, C.; Lozano, P.; Schouten, A.H.; Martel, F. Design and Characterization of a Scalable ion Electrospray Propulsion System. In Proceedings of the 30th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science, 34th International Electric Propulsion Conference and 6th Nano-satellite Symposium, Hyogo-Kobe, Japan, 4–10 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Legge, R.S.; Lozano, P.C. Electrospray propulsion based on emitters microfabricated in porous metals. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejci, D.; Mier-Hicks, F.; Thomas, R.; Haag, T.; Lozano, P. Emission Characteristics of Passively Fed Electrospray Microthrusters with Propellant Reservoirs. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2017, 54, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier-Hicks, F.; Lozano, P.C. Spacecraft-Charging Characteristics Induced by the Operation of Electrospray Thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2016, 33, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Shumlak, U. Ultrasonically aided electrospray source for charged particles approaching monodisperse distributions. J. Propuls. Power 2010, 26, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, D.G.; Dandavino, S.; Shea, H. Comparing Direct and Indirect Thrust Measurements from Passively Fed Ionic Electrospray Thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2015, 32, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.S.; Stark, J.; Smith, K.L.; Stevens, B.; Kent, B. Electrospray performance of Microfabricated colloid thruster arrays. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamero-Castano, M.; Hruby, V. Electrospray as a source of nanoparticles for efficient colloid thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2001, 17, 977–987. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M.S.; Smith, K.L.; Paine, M.D.; Stark, J.P. Voltage-modulated flow rate for precise thrust control in colloid electrospray propulsion. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.W.; Prince, B.D.; Bemish, R.J.; Rovey, J.L. Electrospray of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Dicyanamide Under Variable Flow Rate Operations. J. Propuls. Power 2014, 30, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Micci, M.M. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of a Liquid Gallium Electrospray Thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2013, 29, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.; Stevens, B.; Alexander, M.; Kent, B. Fabrication and operation of microfabricated emitters as components for a colloid thruster. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2005, 42, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, D.H.K. AeroCube-8—Orbital Debris Assessment Report (ODAR); Tech Report; The Aerospace Corporation: El Segundo, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, D.; Ehrbar, E.; Rosenbald, N.; Demmons, N.; Roy, T.; Hoffman, S.; Williams, W.D.; Tsay, M.; Zwahlen, J.; Hohman, K. Electrospray Propulsion Systems for Small Satellites and Satlets. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2013 Conference and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 September 2013; p. 5329. [Google Scholar]
- Ziemer, J.K.; Gamero-Castaño, M.; Hruby, V.; Spence, D.; Demmons, N.; McCormick, R.; Roy, T.; Gasdaska, C.; Young, J.; Connolly, B. Colloid Micro-Newton Thruster Development for the ST7-DRS and LISA Missions; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Falcoz, A.; Boquet, F.; Flandin, G.; Blanc-Paques, P. Robust Hinfinity/H- thruster failure detection and isolation with application to the LISA Pathfinder spacecraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 August 2010; p. 7906. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, R.L.; Turchi, P. Pulsed plasma thruster. J. Propuls. Power 1998, 14, 716–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, C.M.; Elaskar, S.A.; Brito, H.H.; Paoletti, N.R. Zero-dimensional model for preliminary design of ablative pulsed plasma Teflon® thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzin, K.A. Comprehensive review of planar pulsed inductive plasma thruster research and technology. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Boyd, I.D.; Antonsen, E.L.; Gulczinski, F.S.; Spanjers, G.G. Propellant charring in pulsed plasma thrusters. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Boyd, I.D.; Beilis, I.I. Model of Particulate Interaction with Plasma in a Te on Pulsed Plasma Thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2001, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikellindes, P.G.; Turchi, P.J. Modeling of Late-Time Ablation in Teflon Pulsed Plasma Thruster. In Proceedings of the AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 1–3 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.W.; Richard, D.; Branam, R.E.H. Nano-Satellite Gatling-Gun Pulsed Plasma Thruster. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2011; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, S.; Glascock, J.L.; Rovey, S.W.; Thrasher, J. Observation of Late-Time Ablation in Electric Solid Propellant Pulsed Microthrusters. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rayburn, C.D.; Campbell, M.E.; Mattick, A.T. Pulsed Plasma Thruster System for Microsatellites. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2005, 42, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.; Ravi, V.; Kushari, A. Discharge frequency modulation of pulsed plasma thruster. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2005, 42, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M. Micro-Cathode Arc Thruster for small satellite propulsion. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 5–9 January 2015; p. 0938. [Google Scholar]
- Polk, J.E.; Sekerak, M.J.; Ziemer, J.K.; Schein, J.; Qi, N.; Anders, A. A theoretical analysis of vacuum arc thruster and vacuum arc ion thruster performance. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.M.; Coletti, M.; Gabriel, S. A micro PPT for nano-satellite applications: Design and experimental results. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference Exhibit, Atlanta, GA, USA, 30 July–1 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, R.; Cassady, W.; Andrew Hoskins, M.C.C.R. A Micro Pulsed Plasma Thruster (PPT) for the “Dawgstar” Spacecraft. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 25 March 2000; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.; Bruckner, A.; Ewig, R.; Beltran, E.; Carlson, E.; Carpenter, K.; Chung, S.; Davenport, B.; Forouhar, F.; Halligan, J. UW Dawgstar: One Third of ION-F—An element of the Ionospheric Observation Nanosatellite Formation (ION-F). In Proceedings of the 13th AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 23–26 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.B.; Richie, D.J. Stabilization and Attitude Determination Methods for FalconSAT-3. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2016, 53, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbeck, J.; Lukas, J.; Teel, G.; Keider, M.; Hanlon, E.; Pittman, J.; Lange, M.; Kang, J. μCAT Micro-Propulsion Solution for Autonomous Mobile On-Orbit Diagnostic System. In Proceedings of the Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kronhaus, I.; Pietzka, M.; Schilling, K.; Schein, J. Pico-Satellite Orbit Control by Vacuum Arc Thrusters as enabling Technology for Formations of small Satellites. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Spacecraft Formation Flying Missions and Technologies, Munich, Germany, 29–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, S.C.; Dowell, E.H. Membrane paradox for solar sails. AIAA J. 2014, 52, 2904–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, D.; Souder, M.W. Solar Sail Technology for Nanosatellites. In Proceedings of the 5th AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 August 2008; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.; Murphey, T.; Gierow, P. Scalable solar sail subsystem design considerations. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 22–25 April 2002; p. 1703. [Google Scholar]
- Eldad, O.; Lightsey, E.G.; Claudel, C. Minimum-Time Attitude Control of Deformable Solar Sails with Model Uncertainty. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2017, 54, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, F. Solar Sail Coning Control to Induce Orbital Effects in Spinning Versus Non-Spinning Sails. In Advances in Solar Sailing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 737–753. [Google Scholar]
- Botter, T.; Coverstone, V.L.; Burton, R.L. Structural Dynamics of Spin-Stabilized Solar Sails with Applications to UltraSail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2008, 31, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzlander, G.A. Radiation pressure on a diffractive sailcraft. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2017, 34, C25–C30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrk, H.; Auweter-Kurtz, M. Thrust measurement of the hybrid electric thruster TIHTUS by a baffle plate. J. Propuls. Power 2009, 25, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Gilchrist, B.; Squire, J. Characterization of Ion Cyclotron Resonance Acceleration for Electric Propulsion with Interferometery. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horisawa, H.; Kimura, I. Fundamental Study on Laser Plasma Accelerator for Propulsion Applications. Vacuum 2002, 65, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, S. Laser-Ablation Propulsion. J. Propuls. Power 2010, 26, 609–637. [Google Scholar]
- Rovey, J.L.; Friz, P.D.; Hu, C.; Glascock, M.S.; Yang, X. Plasmonic Force Space Propulsion. J. Spacecr. Rocket 2015, 52, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, T.D.; Osborn, M. Numerical optimization of micro-nozzle geometries for low reynolds number resistojets. In Proceedings of the 51st AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 July 2015; p. 3923. [Google Scholar]
- Ketsdever, A.D. Facility effects on performance measurements of micropropulsion systems that utilize gas expansion. J. Propuls. Power 2002, 18, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
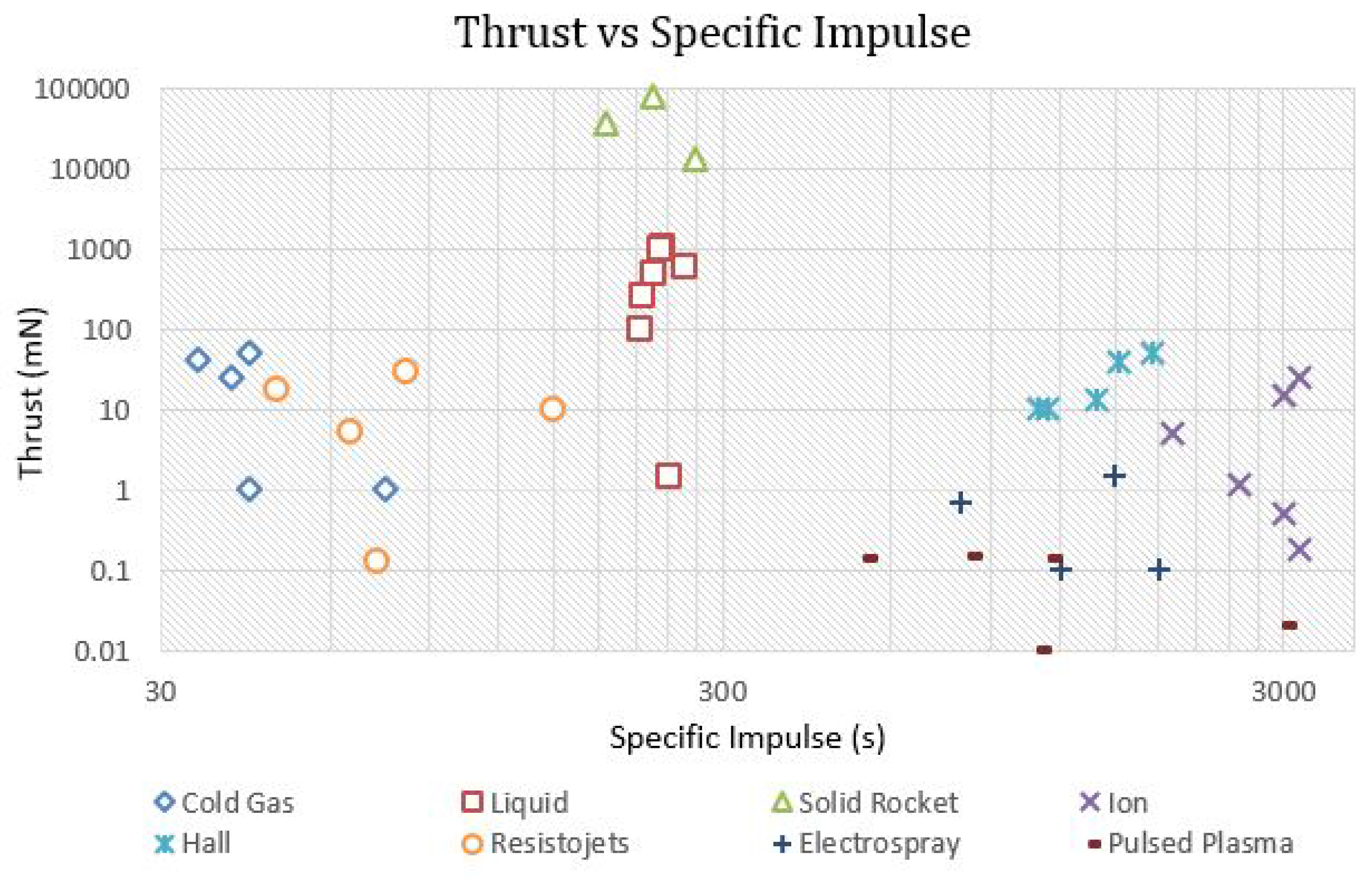
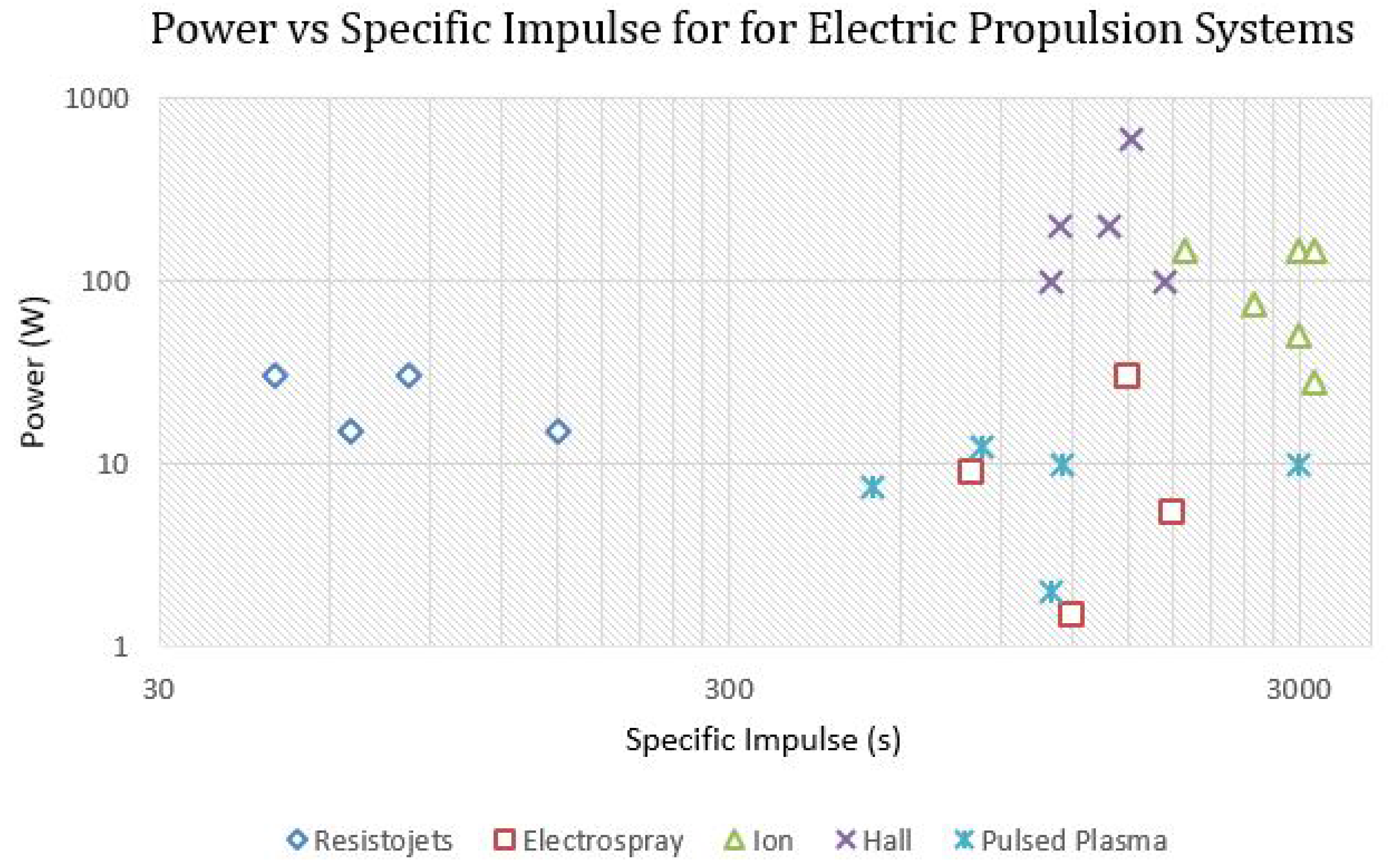
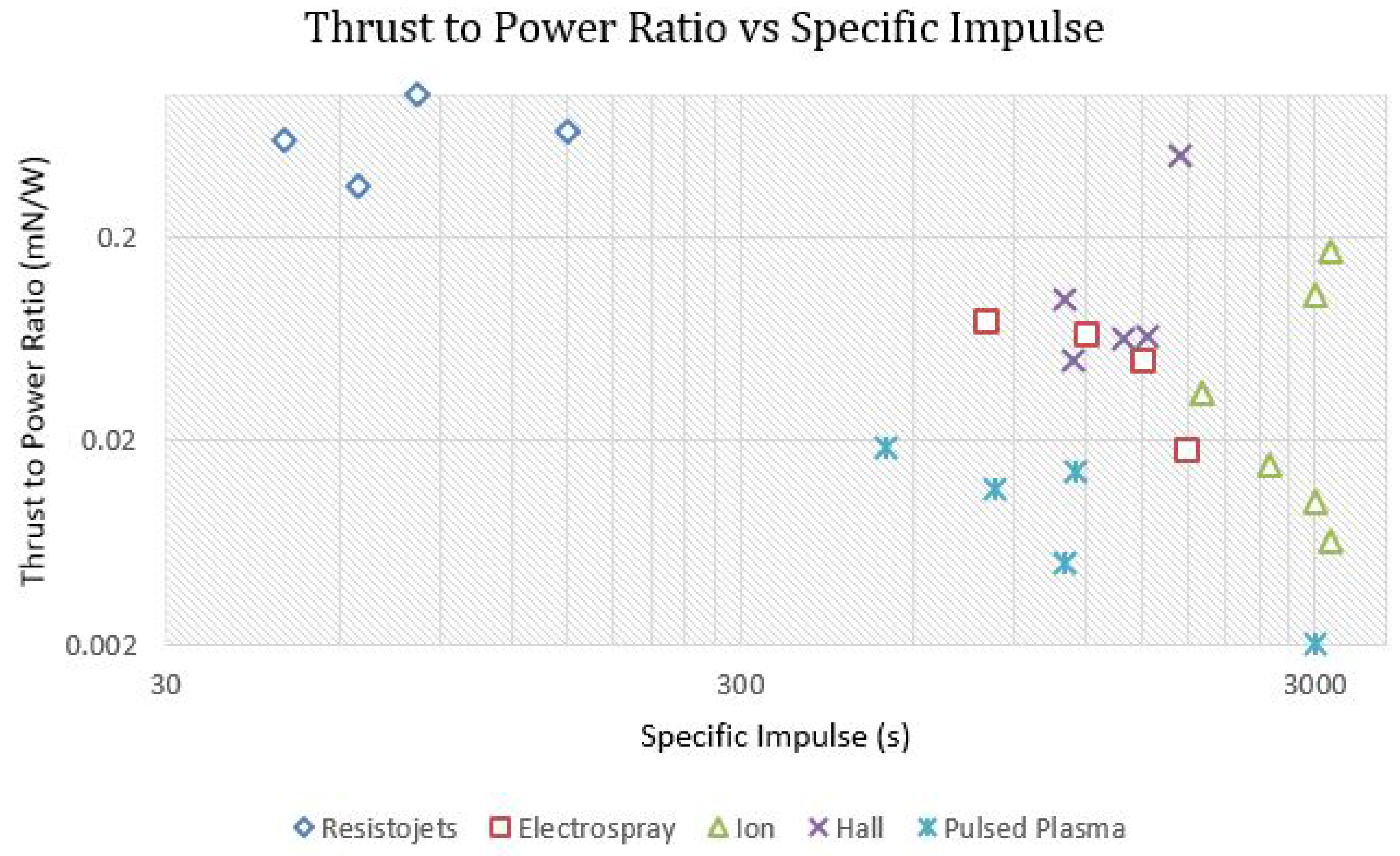
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Propellant | Heritage | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSTL, Guildford, UK | SNAP 1 | 50 | 43 | Liq. Butane | - | flown on Giove-A (600 kg) | [12,15,16] |
| UTIAS-SFL, Toronto, ON, Canada | CNAPS | 10–40 | <35 | CanX-4 (6 kg), CanX-5 (6 kg) | - | [17] | |
| Microspace Rapid, Singapore | POPSAT-HIP1 | 1 | 43 | Argon | POPSAT-HIP1 (3U/3.3 kg) | - | [18] |
| GOMSpace, Denmark | MEMS Cold Gas | 1 | 50–75 | Methane | TW-1 (one 3U and two 2U) | also flown on PRISMA (180 kg) | [9,19,20] |
| VACCO Industries, El Monte, CA, USA | CPOD | 25 | 40 | R134a | CPOD (3U) | - | [21,22,23] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Propellant | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerojet Rocketdyne, Sacramento, CA, USA | GPIM Propulsion System | 400–1100 | 235 | AF-M315E | - | [29] |
| Aerojet Rocketdyne, Sacramento, CA, USA | MPS-120 CHAMPS | 260 | 215 | Hydrazine | - | [30,31,32,33,34] |
| Aerojet Rocketdyne, Sacramento, CA, USA | MPS-130 CHAMPS | 1.5 | 240 | AF-M315E | - | [30,32] |
| ECAPS, Solna, Sweden | HPGP | 1000 | 231–232 | ADN based LMP-103S | flown on PRISMA (180 kg) and SkySat-3 (10.5 kg tank) | [19,35] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BGT-X1 | 100 | 214 | AF-M315E | - | [9,36] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BGT-X5 | 500 | 220–225 | AF-M315E | - | [36,37] |
| Tethers Unlimited, Bothell, WA, USA | HYDROS | 250–600 | 256 | Liquid water | - | [9,38] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (N) | I (s) | Propellant | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Corporation, El Segundo, CA, USA | I 30 s | 37 | 187 | - | - | [39] |
| Orbital ATK, Dulles, VA, USA | STAR 4G | 13 | 269.4 | Al and Ammonium perchlorate | - | [46] |
| DSSP, Reno, NV, USA | CAPS-3 | - | 245–260 | HIPEP-501A | flown on SPINSAT (57 kg) | [44,47] |
| DSSP, Reno, NV, USA | CDM-1 | 76 | 226 | AP/HTPB | - | [9] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Power (W) | Propellant | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSTL, Guildford, UK | LPR | 18 | 48 | 30 | Xe | flown on NovaSAR-S (100 kg) | [59,60] |
| CU Aerospace, Champaign, IL, USA and VACCO Industries Inc., Huntsville, AL, USA | PUC | 5.4 | 65 | 15 | SO | - | [30,61] |
| CU Aerospace, Champaign, IL, USA and VACCO Industries Inc., Huntsville, AL, USA | CHIPS | 30 | 82 | 30 | R134a, R236fa | - | [58,62] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | AMR | 10 | 150 | 15 | R134a, R236fa | - | [9,30,49] |
| University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA | FMMR | 0.129 | 79.2 | - | Water | - | [56] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Power (W) | Propellant | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BIT-1 | 0.1–0.18 | 2150–3200 | 28 | Xe, Iodine | - | [9,71] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BIT-3 | 1.15 | 2500 | 75 | Iodine | will fly on Lunar IceCube (6U) | [71,72] |
| Airbus, Lampoldshausen, Germany | RIT-X | 0.05–0.5 | 300–3000 | <50 | Xe | - | [73] |
| Airbus, Lampoldshausen, Germany | RIT 10 EVO | 5, 15, 25 | >1900, >3000, >3200 | 145 | Xe | available in 3 designs | [73] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Power (W) | Propellant | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BHT-200 | 12.8 | 1390 | 200 | Xe, I, Kr | flown TacSat-2 (370 kg) and FalconSat-5 (180 kg) | [46,85,89] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BHT-600 | 39.1 | 1530 | 600 | Xe, I, Kr | - | [85] |
| Sitael Aerospace, Mola di Bari, Italy | HT 100 | 10 | 1100 | 100 | Xe, Kr | - | [90,91] |
| Sitael Aerospace, Mola di Bari, Italy | HT 400 | 50 | 1750 | 100 | Xe | - | [92] |
| MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA | MHT-9 | 20–50 | 300–1500 | 30–200 | - | - | [46] |
| UTIAS-SFL, Toronto, ON, Canada | CHT | 1–10 | 1139 | <200 | Xe, Ar | - | [79] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Power (W) | Propellant | Heritage | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA | S-iEPS | 0.1 | 1200 | 1.5 | ionic liquid | Aero-Cube-8 (1.5U) | also called IMPACT | [9,94,106] |
| Accion Systems, Boston, MA, USA | TILE 5000 | 1.5 | 1800 | 30 | ionic liquid | - | - | [30] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BET-1mN | 0.7 | 800 | <9 | ionic liquid | - | flown on LISA Pathfinder (476.3 kg) | [107,108,109] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BET-100 | 0.005–0.1 | 1800 | 5.5 | ionic liquid | - | - | [9] |
| Company/Institution with Location | Engine | Thrust (mN) | I (s) | Power (W) | Propellant | Heritage | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mars Space Ltd., Southampton, UK | PPT | - | 578–727 | 2–10 | PTFE | - | PPT | [122] |
| Primex Aerospace Company Redmond, WA, USA | EO-1 PPT | 0.14 | 1150 | 12.5 | Teflon | - | PPT; flown on Dawgstar (13 kg) | [123,124] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | MPACS | 0.144 | 830 | <10 | PTFE (Teflon) | - | PPT; flown on FalconSat-3 (54.3 kg) | [46,125] |
| Busek, Natick, MA, USA | BmP-220 | 0.14 | 536 | 7.5 | Teflon | - | PPT | [9,30] |
| GWU, Washington, DC, USA | CAT | 0.001–0.02 | 3000 | <10 | Nickel | BRICSat-P (1.5U) | VAT | [126] |
| University of Illinois, Champaign, IL, USA | BLT | 0.054 | - | 4 | Aluminum | - | VAT | [9] |
| Wrzburg University, Wrzburg, Germany | UWE4 Arc Thruster | 0.002–0.01 | 900–1100 | 0.5–2 | Titanium, Tungsten | - | VAT | [127] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tummala, A.R.; Dutta, A. An Overview of Cube-Satellite Propulsion Technologies and Trends. Aerospace 2017, 4, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4040058
Tummala AR, Dutta A. An Overview of Cube-Satellite Propulsion Technologies and Trends. Aerospace. 2017; 4(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleTummala, Akshay Reddy, and Atri Dutta. 2017. "An Overview of Cube-Satellite Propulsion Technologies and Trends" Aerospace 4, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4040058
APA StyleTummala, A. R., & Dutta, A. (2017). An Overview of Cube-Satellite Propulsion Technologies and Trends. Aerospace, 4(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4040058





