Abstract
The high-precision attitude estimation technique for non-cooperative targets in space, based on monocular cameras, has important application value in missions such as space debris removal, autonomous rendezvous and docking, and on-orbit services. However, due to the inherent missing information problem of monocular vision systems and the high complexity of target geometry, existing monocular pose estimation methods find it difficult to realize an effective balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. Current solutions commonly adopt deep neural network architectures to improve estimation accuracy; but, this method is often accompanied by the problems of a dramatic expansion of the number of model parameters and a significant increase in computational complexity, which limits its deployment and real-time inference capabilities in real spatial tasks. To address the above problems, this paper proposes a spacecraft pose estimation network, called Balance-URSONet, which weighs the trade-off between accuracy and the number of parameters, and makes the pose estimation model have a stronger feature extraction capability by innovatively using RepVGG as the feature extraction network. In order to effectively improve the performance and inference speed of the model, this paper proposes the feature excitation unit (FEU), which is able to flexibly adjust the feature representation of the network and thus optimize the utilization efficiency of spatial and channel information. The experimental results show that the Balance-URSONet proposed in this paper has excellent performance in the spacecraft pose estimation task, with an ESA score of 0.13 and a parameter count 13 times lower than that of URSONet.
1. Introduction
Spacecraft pose control technology is a core component of spaceflight technology and is widely used in complex space missions such as rendezvous and approach missions, on-orbit maintenance, space exploration, and debris removal [1,2]. With the increased utilization of near-Earth orbit, the forms of orbital operations are increasingly diversified, and the operation difficulty increases [3,4]. Pose estimation can effectively reduce human intervention by inputting images and extracting key features (e.g., corner points, edges, and textures) from them [5]. The pose information of the target object is calculated by matching the key features of the satellite with a known 3D model [6].
Traditional spacecraft attitude estimation techniques have reached a high level of maturity and have been successfully applied to numerous space manipulation missions. Common approaches include geometry-based methods (such as point, line, and surface matching and reconstruction) [7,8], which offer good geometric consistency and interpretability but suffer from limited performance when textures are absent or features are insufficient; multi-feature fusion methods [9,10] enhance robustness by combining multiple geometric elements, yet accuracy still degrades under complex lighting and background interference; appearance-based methods [11] rely on template or full-image matching, exhibiting sensitivity to attitude angles and environmental variations; model-based methods [11] typically utilise CAD models and geometric constraints, offering strong interpretability but performing poorly in complex backgrounds and strong illumination conditions. Overall, while these traditional approaches have achieved some progress, they exhibit insufficient robustness in scenarios involving complex lighting, low illumination, or overexposure, failing to meet multi-task and intelligent requirements [6,12]. Significant limitations persist in their adaptability and generalization capabilities, necessitating more efficient and adaptive technologies to address these problems [5].
Deploying position estimation models on edge devices for applications on a starboard computer is a central goal of spacecraft position estimation research [13]. In recent years, with the rapid advancement of deep learning technologies, neural network-based approaches have emerged as effective means for addressing such problems. This study focuses primarily on the application of neural network methods, particularly the performance of CNNs in spacecraft attitude estimation. The Surrey Space Center (UK) [14], NASA, European Space Agency (ESA) [15,16], National University of Defense Technology (NUDT) [17], Shanghai Jiaotong University (SJTU) [18], and Fudan University (FDU) [19] have carried out research on the deep learning-based six-degrees-of-freedom position estimation of spacecraft for scenarios of in-orbit spacecraft maintenance, space debris removal, and other scenarios. Deep learning-based pose estimation methods bypass the traditional feature extraction process and directly establish a pseudo-inverse mapping relationship between the input image and the output pose [20,21]. Currently, the deep learning-based spacecraft position estimation method, employing an end-to-end approach, has a simple structure and a more lightweight advantage compared to other methods [19,22,23] and can be deployed on edge devices [5,13]. Sharma [24] used AlexNet as the backbone network for pose prediction through classification. Proença [14] directly regressed the position and pose vectors of the space target based on ResNet as the backbone network. In addition, Sharma [25] proposed a spacecraft pose network (SPN) with a five-layer CNN as its backbone to estimate orientation and position through three branches. Some researchers [26] extended this idea by employing two ResNet sub-networks for orientation and position estimation, respectively. Although these methods have made a breakthrough in accuracy, most of them rely on structures such as AlexNet and ResNet, which have relatively large computational resources, and do not fully consider lightweight design.
Posso [13] used MobileNet-v2 as the backbone network instead of ResNet-101 for lightweighting. Ref. [27] proposes a lightweight end-to-end non-cooperative target bit-position estimation network based on GoogleNet using two branches for position and pose estimation, respectively. However, the above lightweight approach saves computational resources but does not achieve as accurate bit-position estimation as other approaches. Since there are fewer studies on end-to-end methods and lightweight methods, and most of the current models are biased towards high performance and large scale, it is difficult to meet the demands of resource-constrained environments, such as on-board computers. Therefore, future research needs to achieve an effective trade-off between large-scale, high-performance models and small-scale, deployable models to ensure efficient and accurate bit-position estimation with limited computational resources. Inspired by URSONet [14] and Mobile-URSONet [13], we propose Balance-URSONet for the trade-off problem between computational resources and high-precision bit-position estimation, and the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- In this paper, we propose a spacecraft pose estimation network, Balance-URSONet, that balances the accuracy and number of parameters. We make the pose estimation model more capable of feature extraction by innovatively using RepVGG as the feature extraction network. The inference stage significantly improves inference speed using structural reparameterization, while ensuring model accuracy.
- (2)
- This paper proposes a feature excitation unit (FEU) consisting of an encoder and decoder. The encoder compresses spatial redundancy, reinforces spatial features, and improves spatial semantic expression. The decoder further enhances channel feature expression and adds a skip connection between the encoder and decoder to enhance the model’s ability to capture the detailed contours of the spacecraft. The model inference stage only requires a 1 × 1 convolution to achieve dual-domain feature interaction, which greatly improves the accuracy of pose estimation without significantly increasing the number of model parameters.
- (3)
- In this paper, evaluation experiments are conducted on the spacecraft pose estimation dataset (SPEED). The experimental results show that the Balance-URSONet proposed in this paper exhibits excellent performance on the spacecraft pose estimation task, with an ESA score of 0.13 and 13 times fewer parameters than URSONet.
2. Related Work
2.1. End-to-End Pose Estimation Methods
Sharma [24] proposed a bit-posture estimation method that discretizes the pose space along four degrees of freedom for pose prediction by means of classification. This approach learns the image features of the discretized categories by training the CNN. However, the increase in the number of categories after discretization also leads to a surge in the number of neurons in the softmax layer, which increases the number of parameters and computational overhead of the model. To solve the problem of predicting pose accuracy, Sharma [25] further proposed the spacecraft pose network (SPN), which estimates the orientation and position of the spacecraft through three branches and combines the Gauss–Newton algorithm and geometrical constraints to optimize the accuracy of the bit-pose estimation by detecting the 2D bounding box to derive the relative position. However, the network architecture of SPN is complex, with relatively low inference efficiency, making it difficult to meet the real-time requirements of embedded platforms. Proença [14] proposed the URSONet attitude estimation model, which is based on ResNet as the backbone network and directly regresses the position and attitude vectors of space targets. In order to deal with the position ambiguity problem, URSONet successfully copes with the uncertainty in position estimation by defining the position classification as soft classification based on a Gaussian mixture model. Although URSONet demonstrates advantages in handling uncertainty, its reliance on ResNet results in relatively high computational complexity and parameter counts, rendering it less suitable for deployment on in-vehicle platforms. The literature [26] further extends this idea by using two sub-networks of the ResNet architecture for orientation and position estimation. The pose prediction sub-network uses soft classification and error quadratic regression to estimate the orientation, while the position regression sub-network directly regresses to predict the position. This method achieves further improvements in accuracy, but the twin network architecture is more complex, thereby increasing computational demands. However, existing pose estimation networks based on AlexNet [28], GoogleNet [29], and ResNet [30], among other backbones, have high computational overheads and still find it difficult to adapt to resource-constrained application scenarios. These networks exhibit an insufficient capability to capture and model the fine-grained features of spacecraft surfaces, whilst also lacking in representing global contextual semantic relationships. Under conditions of complex lighting, background interference, or texture deficiency, they are prone to diminished accuracy in pose estimation. The Balance-URSONet proposed in this paper innovatively adopts RepVGG as the feature extraction network, which dramatically reduces the computational overheads through structural reparameterization. RepVGG significantly improves the computational efficiency of orientation and position estimation while maintaining high accuracy, and significantly improves the inference efficiency, making it suitable for spacecraft position estimation tasks with high real-time requirements.
2.2. Attitude Estimation Network Lightweighting
In terms of achieving a lightweight design, Posso [13] proposed Mobile-URSONet, a lightweight convolutional neural network suitable for on-board computers. By using MobileNet-v2 as the backbone network instead of the heavier ResNet-101, Mobile-URSONet reduces the number of parameters of URSONet by 178 times, and the loss in accuracy is less than four times that of URSONet, which significantly improves the computational efficiency and deployment adaptability of the model. In addition, the literature [27] proposes LSPENet, a lightweight end-to-end non-cooperative target position estimation network based on depth-separable convolution and the efficient channel attention (ECA) mechanism. LSPENet employs two branches for position and attitude estimation, respectively, and uses direct regression for position estimation, whereas soft-allocation coding is introduced for attitude estimation to improve the attitude estimation accuracy. Although Posso [13] made significant progress in reducing the number of parameters and computational complexity, it still suffers from a certain loss in accuracy, especially when facing more complex tasks, where accuracy degradation is more obvious. By combining depth-separable convolution and the efficient channel attention (ECA) mechanism, LSPENet does not achieve accurate bit-posture estimation, although it takes into account a lightweight design.
In order to solve these problems, this paper proposes a real-time spacecraft attitude estimation network, referred to as Balance-URSONet. This network is capable of accurately completing spacecraft attitude estimation tasks in a short period of time under resource-constrained environments.
3. Proposed Method
In Section 3.1, this paper describes the overall architecture of Balance-URSONet. Next, in Section 3.2, this paper describes the feature extraction network in detail. Section 3.3 discusses the feature excitation unit, and Section 3.4 describes the loss function used in this paper.
3.1. Overall Architectural Design of Balance-URSONet
The proposed Balance-URSONet architecture, as illustrated in Figure 1, comprises a backbone network and two branch networks. RGB images containing the target spacecraft are input into the backbone network RepVGG to capture contextual information and the global structure of the spacecraft’s multi-scale features. However, as RepVGG is not specifically optimized for detail enhancement or local information, the spacecraft features extracted by the backbone network may lack sufficient detail representation under certain complex lighting conditions or when textures are missing. This can lead to reduced accuracy in spacecraft attitude estimation within such scenarios. Therefore, within the FEU, we employ an encoder to strengthen the detailed features of the spacecraft’s local geometric structure. Subsequently, the decoder enhances the semantic information of key channels. By introducing skip connections, we bolster the model’s perception of boundary contour information, thereby improving its robustness in complex space backgrounds. By cascading 1 × 1 convolutional blocks, we combine RepVGG’s global feature extraction capability with FEU’s detail enhancement capability, thereby fully leveraging their complementary strengths. This cascaded structure effectively adjusts the number of feature map channels, enhances feature expressiveness, and avoids substantial increases in computational resources. Processed image features undergo global adaptive pooling to compress feature space dimensions, culminating in a fully connected layer for regressing the spacecraft’s three-dimensional position coordinates. For orientation attitude estimation, the quaternions are discretized by a quantization step with a continuous prediction method that employs soft classification and probabilistic coding to construct a 3D histogram output space, where each bin corresponds to a set of discrete orientation combinations. The true direction label is modeled as a Gaussian distribution centered around the target bin, whose variance is adaptively determined by the quantization step, enabling the network to learn the uncertainty of direction prediction and generate a smooth probability mass function (PMF). The network outputs a 3D histogram of probability distributions that decode the final direction by weighted aggregation of neighboring bins.
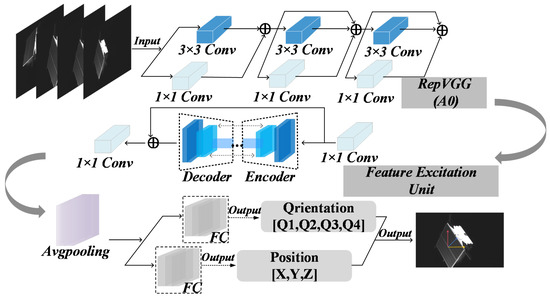
Figure 1.
Balance-URSONet architecture.
3.2. Feature Extraction Network
In this paper, RepVGG is innovatively introduced as the backbone network for the pose estimation task, which maintains high pose estimation accuracy while taking into account the number of model parameters by combining a multi-branch structure in the training phase and transforming it into a single path structure in the inference phase. In the training phase, this paper designs a multi-branch structure consisting of 3 × 3 convolutional branches, 1 × 1 convolutional branches, and constant mapping branches. Among these, 3 × 3 convolution is used to focus on the local contextual structure of the spacecraft, enabling the capture of complex relationships among its various components within their spatial neighborhoods; 1 × 1 convolution is used to achieve information interaction between channels in the feature map, effectively enhancing the collaborative representation capabilities between different regions on the spacecraft’s surface and improving feature compression and reconstruction efficiency; the identity mapping branch ensures smooth gradient propagation in the deep network, enhancing the overall network’s training stability and convergence. Each branch separately performs feature transformations of different scales and dimensions on the input feature maps, which are subsequently fused by a batch normalization layer () to enhance the network’s ability to perceive key pose features (spatial position and pose rotation).
3.3. Feature Excitation Unit
Traditional methods rely on geometric features, such as points, lines, and surfaces, for pose estimation; however, they often perform poorly under complex backgrounds, varying lighting conditions, or when texture is absent. They struggle to adequately capture intricate details within images when processing targets with irregular geometries or dynamic changes, and are susceptible to background noise and illumination interference. Early neural networks (such as MLP) face significant challenges in handling complex scenes due to their lack of spatial information and optimization for local features, resulting in poor generalization. Achieving high-precision pose estimation hinges on accurately extracting the spacecraft’s local contours and detailed features. Given RepVGG’s limited capability in extracting image detail features, this paper proposes an enhanced feature excitation unit (FEU) based on SCConv [31]. The FEU framework is shown in Figure 2. Balance-URSONet first inputs the feature map extracted from the backbone network into the FEU for further feature reconstruction and semantic enhancement. This unit first performs global information fusion and initial reconstruction of channel dimensions by 1 × 1 convolution on the features, and the output features are shown in Equation (1):
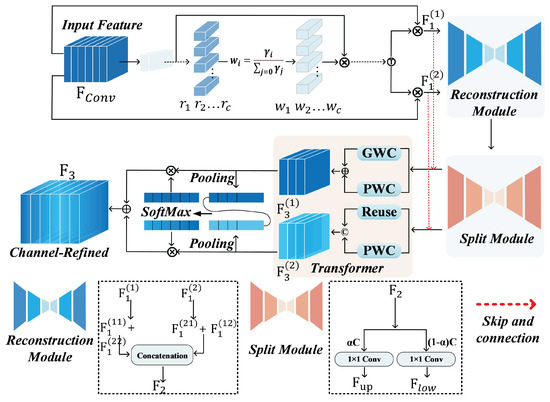
Figure 2.
Feature excitation unit structure.
This operation achieves fine feature adjustment in the channel dimension using small receptive fields, and the feature is fed into the encoder. Given that texture and lighting conditions may vary considerably across different images in spacecraft attitude estimation tasks, we must ensure consistent feature distribution across all levels, mitigate the impact of lighting and texture variations, enhance model training stability, and improve attitude estimation accuracy. Encoder performs group normalization () on the input feature to obtain the normalized feature , as shown in Equation (2):
The importance of each channel in the spatial dimension is measured through group normalization, and the information weight W is calculated by assigning weights to each channel C based on the scaling factors obtained from the separate module. Local features are more sensitive and crucial for pose estimation. By dynamically weighting spatial features, the model’s focus on critical local details of the spacecraft is enhanced, reducing interference from irrelevant background information and optimizing detail features in pose estimation. This weighting mechanism assigns higher weights to more distinctive and expressive spatial features. The information weight calculation formula is shown in Equation (3):
Information-rich features and more redundant features are classified by the computed information weights [31]. In order to retain the information expression and fuse the redundant structures, the spatial optimization feature is obtained by fusing and using cross reconstruction in the Reconstruct module [31]. provides the attitude estimation model with a more precise spatial representation of the spacecraft, enabling the model to focus more intently on the most distinctive local details (such as the spacecraft’s boundary contours and surface features). This suppresses interference from background or redundant features in pose estimation. The construction method for the final spatially optimized features is as shown in Equation (4):
The decoder splits the spatially optimized feature output from the encoder into two parts along the channel dimension with the ratio of and to obtain the upper branch and the lower branch , respectively, where is used as the main path to provide rich texture information, and is used as a complementary path to capture localized low-frequency, detailed contour information. In the Transformer module, we connect , which represents spatial high information density in the encoder, with for skip connection, which is used to take up the main semantic extraction task of the model, and , which represents high spatial redundancy, with for skip connection to go for extracting detailed features. This assists the model in accurately capturing key features such as the spacecraft’s local geometric contours and boundary shapes. At the same time, in order to avoid the problems of high information density, feature overfitting, and large gradient perturbation after skip connection, we automatically learn the optimal information flow allocation strategy during training by introducing learnable parameters, i.e., and , to adjust the fusion ratio of information and redundant features in upper and lower branches of the Transformer module so as to balance model expressiveness and redundancy compression. The connection process is shown in Equation (5):
where and are learnable parameters, and , , and are learnable weight matrices of GWC and PWC, respectively [31]. In spacecraft pose estimation, local geometric details, texture information, and background noise all impact model performance. By optimizing channel features, the network learns more critical features for pose estimation based on each channel’s weighting, thereby enhancing estimation accuracy. The decoder performs global average pooling on the outputs of both paths to obtain channel description vectors. Channel attention weights are derived via softmax, and these are finally fused into channel optimization features . This approach ensures that critical features are amplified and redundant information is compressed, thereby enhancing the precision and robustness of spacecraft pose estimation. The process is shown in Equation (6):
The feature excitation unit finally outputs the fusion-optimized feature, . In order to improve the information mobility of the network and enhance the gradient propagation capability, Balance-URSONet introduces a residual connection structure based on which is mapped by a 1 × 1 convolution and then subjected to an element-by-element summing operation with the input original feature, , to form the final output feature, as shown in Equation (7):
After fusing the enhanced feature, , Balance-URSONet uses a two-branch regression module to predict the orientation and position of the target. First, is compressed in the spatial dimension using a global average pooling operation to extract (global semantic features), as shown in Equation (8):
is fed in parallel into two fully connected (FC) branches to predict the target’s rotational quaternions(, , , and ) and 3D position coordinates (X, Y, and Z), respectively, which ensures the continuity of the feature expression through FEU, and enhances the network’s nonlinear modeling capability and stability without introducing additional parameter complexity. End-to-end regression for attitude estimation in the spacecraft on-orbit service mission is realized, which is applicable to the attitude estimation scenario of on-orbit service.
3.4. Loss Function
In spacecraft attitude estimation, the loss function consists of two parts: the position loss and the orientation loss. For orientation estimation, we borrow the approach of Proença [14]. First, we encode the real quaternion as a Gaussian random variable in discrete space. Then, we learn how to output the probability mass function (PMF) corresponding to this Gaussian random variable by training the neural network. Finally, we optimize the network by using the least-squares method [32] to obtain the final predicted quaternion. For the position loss, we choose as the loss function, see Equation (9):
The derivative of the loss function is a constant in the later stages of model training. When the difference between and the estimate is small, the gradient value is still large, causing the loss to fluctuate around a stable value and making it difficult to converge further. The derivative of the loss changes dynamically, so an increase in the estimate will also increase the loss, especially in the early stages of training when the difference between and the estimate is large, which leads to a large gradient and unstable training. When the loss is large, the gradient remains constant, solving the problem of large gradients in and destroying the training parameters. When the estimation is small, the gradient is dynamically reduced, solving the problem of difficult convergence in loss.
4. Experimentation and Analysis
4.1. Dataset
This paper evaluates the model using SPEED [15], which was constructed jointly by the European Space Agency (ESA) and Stanford University. The dataset is based on the physical characteristics of the Tango satellite from the PRISMA satellite formation mission, and the target spacecraft is constructed using a 1:2 scale-down model. The dataset contains a total of 15,303 high-resolution images (1920 × 1200 pixels), divided into a training set and a test set. The training set covers 12,000 synthesized images and 5 images of real space scenes, while the test set contains 2998 synthesized images and 300 real in-orbit images. The synthetic data are generated by a physical simulation engine to simulate the relative motion of the spacecraft in the range of 3.0–40.5 m. The real images are collected from the ground test environment, and the target distance is strictly controlled in the range of 2.8–4.7 m, covering complex lighting, occlusion, and multiple background interference conditions.
4.2. Implementation Details
The experimental environment configuration for the proposed method in this paper is based on Ubuntu16.04.1 (Linux 4.15.0-142-generic). We use an NVIDIA GPU (GeForce RTX 3090, NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with 24 GB of video memory and 256 GB of system memory. The batch size for training is set to 16, with a total of 100,000 iterations. During inference, the actual resource consumption of Balance-URSONet is relatively lightweight: the GPU memory usage is approximately 2383 MB, the system memory (RAM) usage is about 5.116 GB, and the average CPU utilization is around 6.84 cores.
4.3. Evaluation Indicators
For the evaluation metrics, we use the ESA score proposed and generalized by the ESA competition to quantitatively evaluate the model performance [33]. To compute the ESA score of an image, we require two steps: first, we compute the position score and orientation score of each image () based on the accuracy of the position of the target frame in space and the accuracy of the prediction of the target’s orientation, respectively; then, we combine these two scores into the final pose score. Specifically, the position score of is the position error (i.e., estimating the difference between the target’s predicted position and the true position) to obtain the score, and the difference between the two positions is measured and normalized using the two-norm (Euclidean distance), see Equation (10):
Orientation scoring is evaluated based on the difference between the predicted and true orientation of the target. The angle of rotation is calculated by means of the unit quaternion form, as shown in Equation (11):
The final ESA score is the sum of the position score and the orientation score, which is used to comprehensively evaluate the accuracy of target detection, as shown in Equation (12):
According to research results, most pose estimation models perform much worse on real images than on synthetic images. We are committed to applying this technique in practice [13]. The generalization factor () shows the ability of the model to generalize over the dataset; therefore, we further introduce the (as shown in Equation (13)) to quantify the difference between the performance of the model on real images and the performance of the model on synthetic images. The denotes the ratio of the average ESA scores obtained from the real and the synthetic test sets; the smaller it is, the better.
4.4. Comparative Experiment
In response to the above innovations, we conduct qualitative and quantitative experiments on the proposed method. Table 1 shows the results of our comparison with URSONet, which achieves excellent results in the ESA competition, relying on its high-precision bit-pose estimation capability and demonstrating strong generalization abilities across several test sets. However, this excellent performance comes at the cost of high computational complexity and a large number of parameters. In the bottleneck layer experiments of URSONet, increasing the number of feature map channels in the bottleneck layer reduces the orientation error, but the computational growth is exponential. Specifically, when the number of channels is increased from 8 to 512, the orientation error decreases from 10.22° to 7.20°, but the number of parameters sharply increases from 40 M to 240 M, which suggests that although increasing the number of channels in the feature map can optimize the model’s orientation estimation capability, it is not an optimal solution in an environment with limited computational resources.

Table 1.
Comparison results of the number of parameters, Ori error, and Pos error metrics of URSONet using different feature maps with the method in this paper.
In contrast, Balance-URSONet, proposed in this paper, reduces the computational complexity while still maintaining better attitude estimation accuracy than URSONet. The experimental data show that Balance-URSONet uses only 18.6 M parameters (1/13 of URSONet), but the orientation error is reduced to 5.61° (7.20° for URSONet), and the position error is reduced to 0.339 m (0.483 m for URSONet). This shows that Balance-URSONet can still provide better attitude estimation capabilities with significantly lower computational resources than URSONet. This improvement is not simply relying on increasing the computational volume in exchange for accuracy, but by optimizing the network structure and improving the efficiency of feature extraction, the problem of high computational complexity is fundamentally solved.
In addition, the generalization ability of URSONet on real-world datasets still has some limitations. Although it performs well on synthetic datasets in the ESA competition, its performance on real-world datasets is still affected by light variations, background complexity, etc., due to the deviation in the statistical distribution of the training data. This problem is partly due to the fact that URSONet relies on the complex network structure of ResNet-101, which performs well on synthetic data, but is prone to overfitting, resulting in a decrease in the generalization ability. Balance-URSONet improves the model’s adaptability to factors such as light changes, background complexity, and so on by optimizing the feature extraction method, and performs more stably on the real dataset, thereby reducing the performance caused by the deviation of data distribution. The estimation error due to data distribution bias is reduced.
Table 2 shows a comparison of our results with those of other models using soft classification coding for orientation estimation. In the spacecraft attitude estimation task, LSPENet adopts soft classification for direction estimation, which avoids the optimization instability that may be caused by the direct regression of direction quaternions by discretizing the continuous direction angle into multiple bins and classifying them for prediction. The core idea of soft classification coding is to convert the direction estimation problem into a discrete probabilistic prediction task by adjusting the classification granularity at different numbers of bins, allowing the network to trade off between accuracy and computational complexity. However, LSPENet provides only partial experimental results, especially in 12-bin and 16-bin settings; only partial direction error data are provided, and a complete position error evaluation is lacking, which limits the comprehensive analysis of the overall performance of the model. Taking the 16-bin results as an example, LSPENet achieves a directional error of 5.78° and a positional error of 0.54 m, which represents a significant improvement compared to lower bin numbers (e.g., eight bins with an error of 10.01°), but its accuracy can still be further optimized. Balance-URSONet, proposed in this paper, adopts RepVGG as a feature extraction backbone, proposes a FEU reconfiguration space to crop the redundant channel reconfiguration unit, and introduces a skip connection to provide rich boundary texture information for the model as a whole, which effectively enhances the feature expression capability, and the orientation error is reduced to 5.61°, which is improved by 0.17° compared with LSPENet. The direction error is reduced to 5.61°, which is 0.17° better than LSPENet, and the position error is reduced to 0.339 m, which is 0.201 m better than LSPENet, indicating that the method in this paper is advantageous in the prediction of target orientation and position. Too large a bin number will lead to an exponential increase in the number of parameters and computational complexity, potentially resulting in overfitting problems due to sparse data distribution. For example, the orientation error of LSPENet is as high as 10.01° at eight bins, whereas the orientation error of Balance-URSONet is only 8.69° in the same eight-bin setting, which indicates that the method in this paper maintains better orientation prediction performance at a low bin number setting.

Table 2.
Comparison results of parameter count, Ori error, and Pos error metrics of different models under the soft classification coding approach.
When compared with the 45.5 M parametric model proposed by Torteeka [34], LSPENet significantly reduces the computational effort; but, Balance-URSONet is still able to further improve the accuracy of orientation and position estimation at lower parameter counts, achieving a better balance between computation and accuracy. Thanks to improvements in feature extraction, spatial information expression, and channel information optimization, Balance-URSONet still has a strong attitude prediction ability even under a low bin number setting, without relying on an extremely high bin number setting for accuracy improvement.
Table 3 shows the comparison results of our method with Mobile-URSONet and SESPnet. Balance-URSONet strikes an ideal balance between attitude estimation accuracy and computational complexity, which has significant advantages, especially in embedded systems. By using RepVGG as the backbone network and combining it with the FEU, Balance-URSONet not only enhances the feature extraction capability but also effectively reduces the computational burden. On this basis, Balance-URSONet reduces the orientation error to 5.61° (compared with Mobile-URSONet and SESPnet, by 0.97° and 3.1°, respectively) in the 16-bin setting, and the position error reduces to 0.339 m (compared with Mobile-URSONet and SESPnet, by 0.231 m and 0.125 m), which significantly improves the accuracy of orientation and position prediction while maintaining a low computational complexity.

Table 3.
Comparison of this paper’s method with Mobile-URSONet and SESPnet in terms of common performance metrics.
Although SESPnet introduces the SE attention mechanism and smooth L1 loss function to improve the feature extraction capability and position estimation accuracy, it improves the bit-position estimation accuracy with a lower number of parameters. However, the position prediction error increases from 0.397 m to 0.467 m when the direction encoding it is changed from 12 bins to 16 bins, and the overall prediction accuracy is not significantly improved. On the other hand, Balance-URSONet balances the number of parameters and the accuracy, and its performance index is better than SESPnet. Especially in the low bin setting (e.g., eight bins), the directional error of Balance-URSONet is 8.69°, which is significantly better than that of Mobile-URSONet (11.24°), and is close to the performance of SESPnet with 16 bins. It is also close to the performance of SESPnet with 16 bins, which shows that Balance-URSONet is more capable of predicting the direction in low-bin-number settings. Therefore, Balance-URSONet not only achieves a significant improvement in accuracy but also outperforms Mobile-URSONet and SESPnet in terms of the balance between the number of parameters and accuracy, which is especially suitable for embedded environments with limited computing resources.
In Figure 3, we normalize each indicator to the range of 0–1 using a proportional scaling method, allowing for a more intuitive comparison of the orientation error (), position error (), generalization ability (), real dataset error (), and synthetic dataset error () between Mobile-URSONet and Balance-URSONet under different bin settings in the radar chart. Overall, Balance-URSONet outperforms Mobile-URSONet in key metrics, especially in terms of the direction error, position error, and generalization ability, where it demonstrates more stable performance. Mobile-URSONet reduces the computational complexity by focusing on a lightweight design, but it exhibits larger direction errors, poorer generalization ability, and unstable performance on real datasets under high bin settings. In contrast, Balance-URSONet achieves more precise and stable attitude estimation by leveraging better feature extraction methods and computational optimization strategies, offering improved performance while reducing the computational burden, making it suitable for high-precision, low-computation-resource satellite missions.
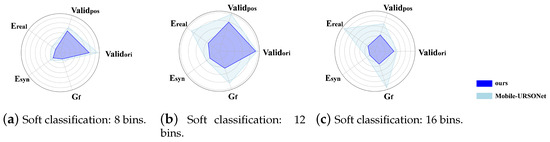
Figure 3.
Comparison with Mobile-URSONet under equal scaling reduction (lower values indicate better performance).
Table 4 shows the generalization factors of this paper’s method compared to other methods. When compared with the models proposed by Proença et al., Balance-URSONet demonstrates a significant improvement in accuracy while keeping the computational effort low. Especially in the comparison between and , Balance-URSONet shows its superiority in different bin settings, and the model is still effective in improving the accuracy of orientation and position estimation at lower bin numbers. By comparing the , it can be seen that Balance-URSONet achieves better performance at 8 bins, 12 bins, and 16 bins. In particular, at eight bins, its is close to , which further proves the model’s superiority in different datasets with respect to the of other models. The improvement in the compared to other models further proves the advantage of the model on different datasets. This shows that Balance-URSONet, through its innovation in feature extraction and channel information optimization, is able to maintain high accuracy with low computational overhead, and provides a better balance between computation and accuracy with lower bin numbers.

Table 4.
ESA scores and corresponding generalization measures for this paper’s method and other methods on the test set.
4.5. Computational Efficiency and Real-Time Performance
To further validate the real-time performance and lightweight characteristics of Balance-URSONet, we conduct experiments on a workstation running Ubuntu 16.04.1, equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 GPU (24 GB VRAM) and 256 GB system memory. We evaluate the computational complexity and inference latency of Balance-URSONet under different bin settings. Experiments are conducted with a single-image input (batch size = 1) to simulate single-frame inference in real-world orbital scenarios. The results are presented in Table 5. With 8, 12, and 16 bins, the computational load remains stable at approximately 4.094 GFLOPS, with single-frame inference latencies of 30.53 ms, 31.46 ms, and 32.71 ms, respectively. Corresponding frame rates exceed 30 FPS. The results demonstrate that Balance-URSONet maintains a stable real-time inference capability while preserving high attitude estimation accuracy. Benefiting from the RepVGG structure’s reparameterization design and FEU’s ability to extract fine-grained features, it reduces computational overhead without compromising the precision of spacecraft pose estimation.

Table 5.
Performance of Balance-URSONet under different bin settings.
4.6. Genuine Performance
The performance of Balance-URSONet under different complex conditions in the experiments on the SPEED real test set further validates its robustness and practical application capability.
The following figures show the cases in the real test set, where Figure 4a–e shows the success cases under the real test set, and Figure 4f shows the failure cases, while the predicted and real directions are shown in polar coordinate plots in the form of Euler angles. Figure 4a presents the attitude estimation under good conditions: under the ideal environmental conditions, the Balance-URSONet performs stably, and the prediction result is close to the actual observations. In this case, the system is able to accurately estimate the satellite’s attitude, indicating that the model is able to maximize its performance under normal operating conditions. Figure 4b presents pose estimation under poor illumination: when the illumination conditions are poor, the image quality and data acquisition accuracy of the satellite sensor may be degraded. At this time, Balance-URSONet is still able to effectively process information in low-light environments, and the results are more stable. This indicates that the model is robust to illumination changes and can extract useful information from incomplete or undesirable data. Figure 4c presents attitude estimation when the background is complex: when the background contains more complex elements (e.g., noise or interference sources), traditional attitude estimation algorithms may be affected, leading to a decrease in estimation accuracy. However, Balance-URSONet still performs well in such complex backgrounds, effectively separating useful signals and suppressing noise to ensure the accuracy of the pose estimation results. Figure 4d presents the pose estimation of a distant spacecraft with a distinct silhouette against a complex background: despite the target’s considerable distance within a complex background environment, Balance-URSONet accurately estimates its pose owing to the spacecraft’s well-defined silhouette. This demonstrates that even amidst intricate backgrounds, Balance-URSONet effectively separates the spacecraft from its surroundings to perform precise position estimation. Figure 4e presents performance under dim lighting with slightly blurred contour editing: in low-light conditions, although some areas appear dim, the spacecraft’s body does not vanish entirely into darkness. Balance-URSONet remains capable of sensitively capturing edge features. Even under conditions of certain light deficiency, the model can still identify and estimate the spacecraft’s pose. Figure 4f presents performance in the absence of a complex background and detailed information: in extremely complex background environments, feature extraction is affected by extreme conditions, the model’s prediction of the direction is shifted, and the distribution of the direction in the polar plot is unstable, which shows that the model needs to be improved further in the extreme conditions. Overall, the performance of Balance-URSONet in the real test set verifies its potential for application in diverse environments, with both high accuracy and good stability, which can meet the needs of actual on-orbit pose estimation tasks.
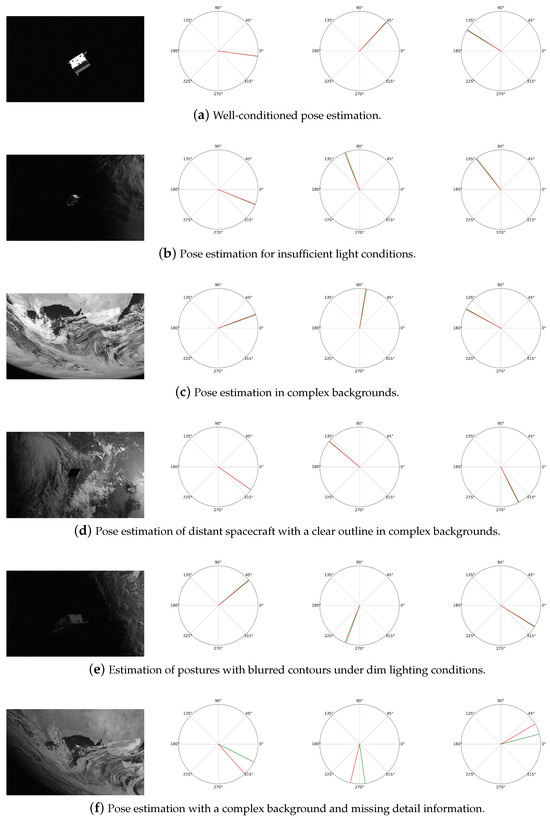
Figure 4.
Visualization on the SPEED real test set. The red curve is the ground truth; the green curve is the prediction.
Additionally, to test the model’s generalizability and robustness while clarifying its performance and limitations across diverse scenarios, we conduct extensive evaluations on the URSO [14] and SPEED+ datasets [16]. The URSO dataset, constructed using the unreal engine (UE4), incorporates multiple spacecraft models (such as Soyuz and Dragon) and is widely applied in spacecraft pose estimation tasks. The URSO dataset provides a large number of synthetic images that can simulate different space environment conditions and covers images of Soyuz and Dragon spacecraft within different operational ranges (e.g., 10–20 m and 10–40 m). The SPEED+ dataset aims to bridge the domain gap between synthetic images and real space images, containing 60,000 synthetic images and 9531 hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) images from the TRON robotics test platform. The TRON platform precisely simulates lighting variations, shadows, and scattering effects in space environments through two light source configurations: lightbox and sunlamp. We conduct experiments on both datasets to test the model’s generalization capabilities and performance under inconsistent lighting and background conditions, thereby validating the robustness of our pose estimation model when confronting the uncertainties and complexities of real space environments. Our model’s performance on the SPEED+ and URSO datasets is illustrated in Figure 5.
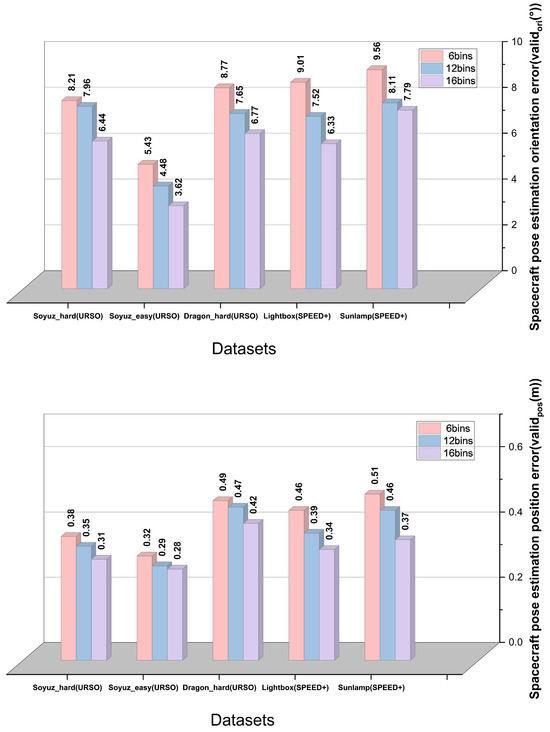
Figure 5.
Orientation and position errors of spacecraft under different bin settings on the URSO and SPEED+ datasets.
Our model’s results under sunlamp illumination are shown in Figure 6. Under appropriate lighting conditions depicted in Figure 6a, where the spacecraft’s contour details are clearly discernible, the Balance-URSONet model demonstrates robust stability, reliably identifying and accurately predicting its pose. Under the intense illumination conditions depicted in Figure 6b, despite some variation in lighting, the spacecraft’s outline and detailed features remain sufficiently discernible for Balance-URSONet to accurately predict its pose. In this scenario, excessive brightness exerts a limited influence on the model, with prediction results closely matching the actual pose. This indicates that the model possesses good stability and a degree of resistance to stray light under strong illumination. Under the overexposed conditions depicted in Figure 6c, the spacecraft’s details are almost entirely obscured by bright regions, resulting in a severe lack of usable features in the image. Consequently, pose prediction exhibits a significant deviation, with results that markedly differ from the actual pose. This demonstrates that overexposure severely limits the model’s feature extraction capability, thereby reducing the accuracy of pose estimation. Under the underexposed conditions depicted in Figure 6d, the overall image brightness is excessively low, causing the spacecraft to blend into the background almost completely. The model struggles to capture effective geometric and textural information, resulting in a marked deterioration in pose estimation performance. Our experimental results demonstrate that under appropriate illumination conditions, Balance-URSONet achieves stable and accurate pose estimation. However, in overexposed scenarios, excessive illumination and bright regions impair the model’s feature extraction capability, leading to increased estimation bias. Both overexposed and underexposed lighting conditions adversely affect the performance of our pose estimation network.
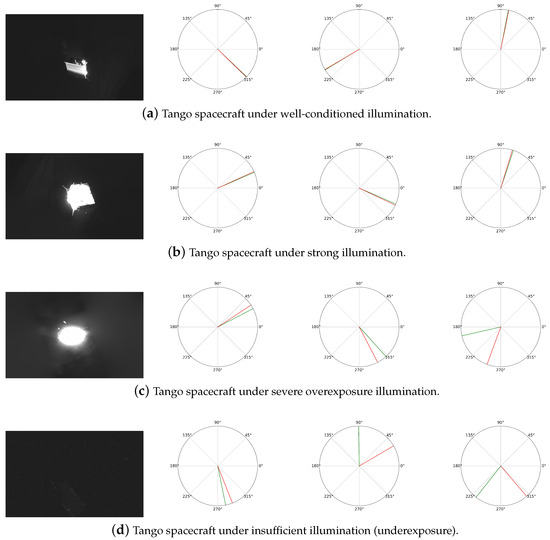
Figure 6.
Tango spacecraft pose estimation under sunlamp illumination. The red curve is the ground truth; the green curve is the prediction.
In the lightbox experiment, Figure 7 illustrates the environment in which the spacecraft operates, set against a complex terrestrial backdrop with varying illumination conditions. Despite these challenges, Balance-URSONet continues to demonstrate robust pose estimation performance. Under the well-lit conditions depicted in Figure 7a, the spacecraft’s geometric contours and details remain clearly discernible. The model reliably extracts effective features, enabling accurate pose prediction. In the low-light environment of Figure 7b, the spacecraft image exhibits pronounced alternating light and dark features, with some areas being excessively dark while others retain brightness. This complex illumination distribution can interfere with feature extraction. Nevertheless, experimental results demonstrate that Balance-URSONet remains capable of effective estimation using limited geometric and contour information. The model maintains robust performance and stability under complex backgrounds and varying illumination conditions, including alternating light and shadow scenarios.
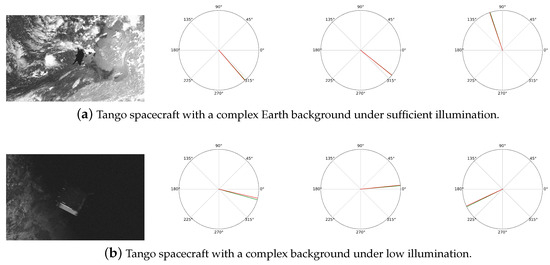
Figure 7.
Pose estimation of Tango spacecraft under different illumination and background conditions. The red curve is the ground truth; the green curve is the prediction.
Figure 8 presents the pose estimation results of Balance-URSONet across different spacecraft types (Dragon and Soyuz) and diverse experimental scenarios. These scenarios encompass complex backgrounds, such as the Earth’s cloud layers and atmospheric edges, as well as simple backgrounds in deep space environments. They also involve varied illumination conditions, including ample lighting, intense illumination, and point-light source illumination. The experimental results further demonstrate that Balance-URSONet is not only effective for the Tango spacecraft but also exhibits excellent adaptability across different spacecraft such as Dragon and Soyuz, reflecting strong generalization capabilities. Whether in complex or simple backgrounds, the model consistently extracts spacecraft contours and geometric features to achieve accurate pose estimation. It maintains robust performance even under lighting perturbations and dynamic pose changes. This demonstrates Balance-URSONet’s strong cross-spacecraft universality and robustness, indicating significant application potential.
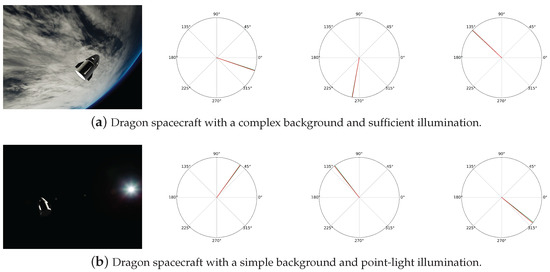
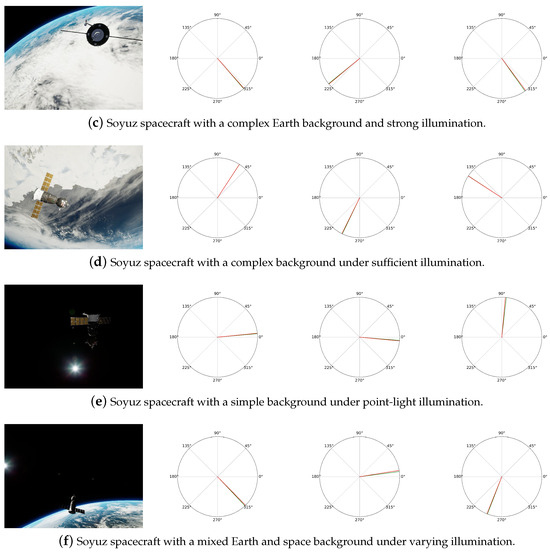
Figure 8.
Pose estimation of Dragon and Soyuz spacecraft under diverse conditions. The red curve is the ground truth; the green curve is the prediction.
4.7. Ablation Study
In the ablation experiment section, we evaluate the impact of the following modular design on the results of this paper: we evaluate the importance of the FEU to the backbone network RepVGG, as shown in Table 6. We first remove the FEU from the architecture and estimate the spacecraft pose directly using the original RepVGG (A0) (called Network 1). This network has 8.3 million parameters and has an orientation error of 10.97, a position error of 0.697, and an of 1.23 on the real dataset. Next, we add the FEU to RepVGG (A0) and retrain the model. We also explore the effect of the loss function on position estimation by replacing the loss function in the base model with a loss function, and the model becomes Net.3. The model still has 8.3 million parameters, and the positional error improves to 0.471, but it still underperforms when compared to the model incorporating the FEU. Finally, we propose the Balance-URSONet model, which combines the loss function and the FEU. The Balance-URSONet model has 11.2 million parameters, with an orientation error of 8.69, a position error of 0.459, and an of 0.28 on the real dataset. Following these two improvements, the model demonstrates enhanced accuracy and computational efficiency.

Table 6.
Ablation experiments on the SPEED dataset.
Also, in the ablation experiments, we verify the convergence of the model during training. The convergence of the model is illustrated in Figure 9, where Figure 9a shows the variation in the different metrics (orientation error, position error, and ESA score) with the number of training rounds. It can be seen that the model gradually stabilizes in all three metrics as training progresses, indicating that the model’s performance continues to improve and converge. Figure 9b shows the variation in training and validation losses. The training loss decreases rapidly in the early stage and then gradually stabilizes, while the validation loss shows a similar trend, indicating that the model not only converges on the training set but also generalizes well on the validation set. These convergence trends further demonstrate that the proposed model works stably under a variety of training conditions without overfitting. The model is able to effectively converge and stabilize at lower loss values and higher accuracy with proper training through these experimental results.
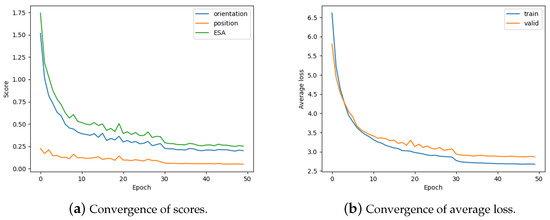
Figure 9.
Convergence of model metrics with 8 bins during training.
To validate the statistical stability of the experimental results, we conduct 10 independent runs of the Balance-URSONet model under different bin configurations and calculate the mean and standard deviation for each metric (see Table 7). The results show minimal variation between experiments (as illustrated in Figure 10), indicating that the model maintains stable performance across multiple trials. Specifically, the standard deviations for under 8 bins, 12 bins, and 16 bins are 0.30°, 0.40°, and 0.10°, respectively, while those for are 0.05 m, 0.02 m, and 0.03 m. These experiments demonstrate that the performance improvements in the Balance-URSONet model are consistent and reliable, rather than coincidental.

Table 7.
Mean and standard deviation of Balance-URSONet over multiple runs under different bins.
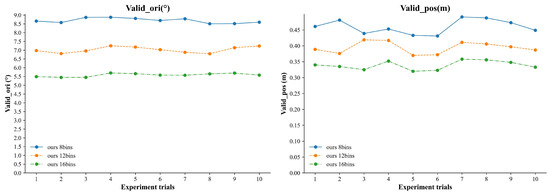
Figure 10.
Performance variation of Balance-URSONet over multiple runs under different bins.
5. Conclusions
Balance-URSONet, proposed in this paper, while retaining high-precision pose estimation performance, enhances feature semantic expression through the structural reparameterization of the RepVGG backbone network with FEU to trim redundancy in the space and channel, effectively reduces the number of bins and the amount of inference computation, and makes it more suitable for on-board computing platforms. The experimental results show that Balance-URSONet exhibits excellent pose estimation accuracy and strong generalization ability on both SPEED synthesis and real test sets, and the model still maintains excellent performance at lower bin counts, avoiding over-reliance on the computational overhead associated with high bin counts, and providing a feasible solution for embedded deployment.
Future work will be carried out in the following aspects: (1) Balance-URSONet has demonstrated commendable performance in small-to-medium spacecraft missions, but it remains constrained by hardware limitations and environmental factors when addressing complex spacecraft and extreme conditions. Future enhancements may be achieved through network optimization and hardware acceleration. (2) The Transformer and self-attention mechanisms can be introduced to further improve the model’s adaptability to complex backgrounds and illumination variations. (3) A multi-source data training system should be constructed, combining synthetic data, real orbit data, and high-fidelity simulation data to improve the model’s adaptive capability. High-fidelity simulation data will improve the robustness of the model in real complex scenes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.B.; methodology, Z.B.; software, Z.B.; validation, Z.B., M.C., G.D., S.H., H.Y., Z.L. and R.M.; formal analysis, Z.B.; investigation, Z.B., M.C. and G.D.; resources, G.D.; data curation, Z.B.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.B. and G.D.; writing—review and editing, M.C., G.D., S.H. and H.Y.; visualization, Z.B.; supervision, M.C. and G.D.; project administration, M.C. and G.D.; funding acquisition, G.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out on a computer platform provided by the Shanghai Ocean University and the Key Laboratory of Satellite Digitization Technology (Chinese Academy of Sciences), and it was supported by Autonomous Navigation Technology and Validation Based on Deep Space Dynamic Optical Measurements (2024YFB3909400).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available at https://kelvins.esa.int/satellite-pose-estimation-challenge/ [33] (accessed on 2 August 2025).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the support of Shanghai Ocean University and the Key Laboratory of Satellite Digitization Technology (Chinese Academy of Sciences) for providing the computer platform. We also appreciate the administrative and technical support provided during the research process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zhang, P.; Wu, D.; Baoyin, H. Real-time hybrid method for maneuver detection and estimation of non-cooperative space targets. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechini, M.; Lavagna, M. Robust and efficient single-CNN-based spacecraft relative pose estimation from monocular images. Acta Astronaut. 2025, 233, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjangud, A.; Blacker, P.C.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Gao, Y. Robotics and AI-enabled on-orbit operations with future generation of small satellites. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, G.S.; Taylor, B.; Fellowes, S.; Salmon, T.; Retat, I.; Hall, A.; Chabot, T.; Pisseloup, A.; Cox, C.; Mafficini, A.; et al. The active space debris removal mission RemoveDebris. Part 2: In orbit operations. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 168, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jing, Z.; Pan, H.; Dun, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, H.; Cao, S. SESPnet: A lightweight network with attention mechanism for spacecraft pose estimation. Aerosp. Syst. 2024, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C. Learning-based pose estimation of non-cooperative spacecrafts with uncertainty prediction. Aerospace 2022, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H. A new approach for the estimation of non-cooperative satellites based on circular feature extraction. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 129, 103532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liang, B.; Xu, W. Attitude determination of large non-cooperative spacecrafts in final approach. In Proceedings of the 2010 11th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision, Singapore, 7–10 December 2010; pp. 1571–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Yuan, D.; Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Satellite pose estimation via single perspective circle and line. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Hu, Q. Monocular-vision-based relative pose estimation of noncooperative spacecraft using multicircular features. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 5403–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinis, L.P.; Fonod, R.; Gill, E. Review of the robustness and applicability of monocular pose estimation systems for relative navigation with an uncooperative spacecraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 110, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yao, M.; Xiong, Y.; Cui, H.; Fu, Y. PVSPE: A pyramid vision multitask transformer network for spacecraft pose estimation. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posso, J.; Bois, G.; Savaria, Y. Mobile-ursonet: An embeddable neural network for onboard spacecraft pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 27 May–1 June 2022; pp. 794–798. [Google Scholar]
- Proença, P.F.; Gao, Y. Deep learning for spacecraft pose estimation from photorealistic rendering. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 6007–6013. [Google Scholar]
- Kisantal, M.; Sharma, S.; Park, T.H.; Izzo, D.; Märtens, M.; D’Amico, S. Satellite pose estimation challenge: Dataset, competition design, and results. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4083–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Märtens, M.; Lecuyer, G.; Izzo, D.; D’Amico, S. SPEED+: Next-generation dataset for spacecraft pose estimation across domain gap. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q. Revisiting monocular satellite pose estimation with transformer. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 4279–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Duan, Y.; Schilling, K.; Wu, S. Monocular 6-DoF Pose Estimation for Non-cooperative Spacecrafts Using Riemannian Regression Network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 186–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Jiao, B.; Yang, D.; Su, L.; Zhai, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L. Ca-spacenet: Counterfactual analysis for 6d pose estimation in space. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 10627–10634. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.H.; Sharma, S.; D’Amico, S. Towards Robust Learning-Based Pose Estimation of Noncooperative Spacecraft. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.00392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cao, J.; Parra, A.; Chin, T.J. Satellite pose estimation with deep landmark regression and nonlinear pose refinement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.; Detry, R.; De Vleeschouwer, C. End-to-end neural estimation of spacecraft pose with intermediate detection of keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 154–169. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Villar, J.I.B.; García-Martín, Á.; Bescós, J.; SanMiguel, J.C. Test-Time Adaptation for Keypoint-Based Spacecraft Pose Estimation Based on Predicted-View Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 6752–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Beierle, C.; D’Amico, S. Pose estimation for non-cooperative spacecraft rendezvous using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 3–10 March 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; D’Amico, S. Neural network-based pose estimation for noncooperative spacecraft rendezvous. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4638–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, G.; Gu, D.; Bo, Y. Non-model-based monocular pose estimation network for uncooperative spacecraft using convolutional neural network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 24579–24590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Lightweight Network-Based End-to-End Pose Estimation for Noncooperative Targets. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2024, 61, 1437010. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25 (NIPS 2012), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2015; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. Scconv: Spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Markley, F.L.; Cheng, Y.; Crassidis, J.L.; Oshman, Y. Averaging quaternions. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelvins Pose Estimation Challenge 2019. 2019. Available online: https://kelvins.esa.int/satellite-pose-estimation-challenge/ (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Phisannupawong, T.; Kamsing, P.; Torteeka, P.; Channumsin, S.; Sawangwit, U.; Hematulin, W.; Jarawan, T.; Somjit, T.; Yooyen, S.; Delahaye, D.; et al. Vision-based spacecraft pose estimation via a deep convolutional neural network for noncooperative docking operations. Aerospace 2020, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.; Shankar, S.; Fonseka, D.; Deutsch, J.; Dhir, A.; Akella, M.R. Real-Time, Flight-Ready, Non-Cooperative Spacecraft Pose Estimation Using Monocular Imagery. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.09553. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; D’Amico, S. Pose Estimation for Non-Cooperative Rendezvous Using Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.09868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).