Investigation of Combustion Performance of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid Fuels Through Injector Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
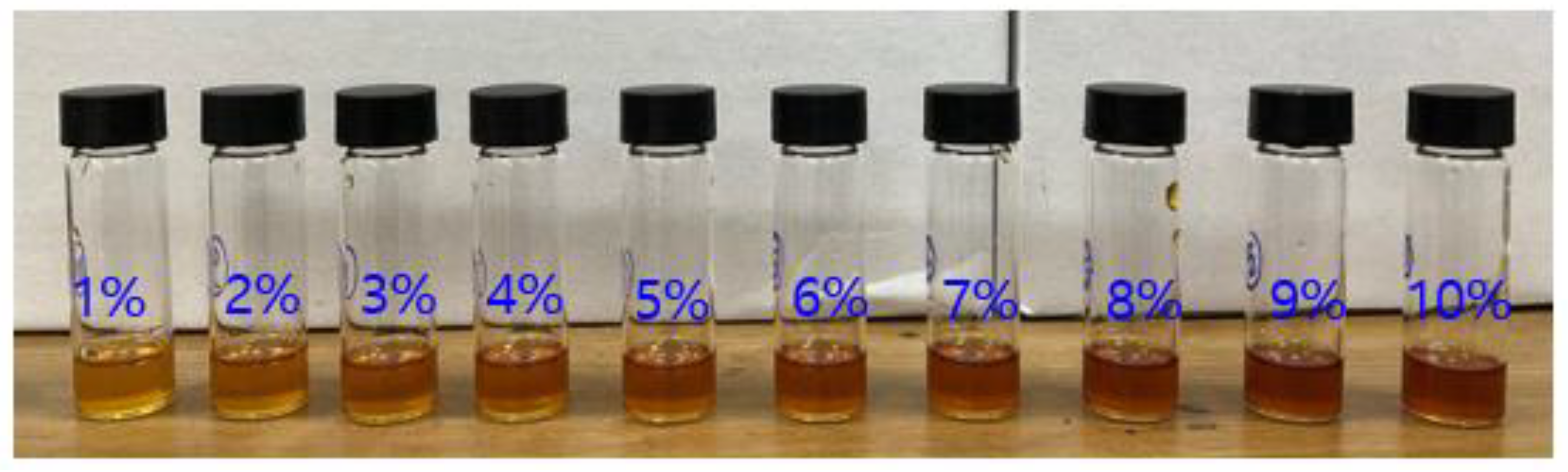
3.1. Hypergolic Drop Test
3.2. Physicochemcial Properties of Fuel
3.3. Theoretical Performance
3.4. Hot Fire Test Results
3.4.1. Mass Flow Rate Calibration
3.4.2. Thruster Behavior During Firing Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | Ionic liquid |
| [EMIM][SCN] | 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium thiocyanate |
| IDT | Ignition Delay Time |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| DLR | Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt |
| WSST | Wavelet Synchrosqueezed Transform |
| DM1/10 bar | Development Model 1 Injector (DM1)/Designed chamber pressure (10 bar) |
| DM1/15 bar | Development Model 1 Injector (DM1)/Designed chamber pressure (15 bar) |
| DM2/10 bar | Development Model 2 Injector (DM2)/Designed chamber pressure (10 bar) |
| MMH | Monomethyl Hydrazine |
| NTO | Nitrogen Tetroxide |
| DSC-TGA | Differential Scanning Calorimetry- Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| HTP | High-Test Peroxide |
| SST | Synchrosqueezing Transform |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| D/V | Diameter/Velocity |
References
- Rarata, G.; Florczuk, W. Novel Liquid Compounds As Hypergolic Propellants With HTP. J. KONES Powertrain Transp. 2016, 23, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J. IGNITION! An Informal Histroy of Liquid Propellants; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1972; ISBN 0813507251. [Google Scholar]
- Rusek, J.J.; Minthorn, M.K.; Purcell, N.L.; Pavia, T.C.; Grote, J.R.; Hudson, G.C.; Mckinney, B. Non-Toxic Homogeneous Fuel (NHMF) Development for Hypergolic Bipropellant Engines; Naval Air Warfare Center Weapons Division China Lake: Lake, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.L.; Heister, S.D. Characterization of Pintle Engine Performance for Nontoxic Hypergolic Bipropellants. In Proceedings of the 38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Indianapolis, Indiana, 7–10 July 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Lee, K.; Yoon, H.; Kwon, S. Green Bipropellant: Performance Evaluation of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid-Biofuel with Hydrogen Peroxide. Fuel 2024, 376, 132688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jang, D.; Kwon, S. Demonstration of 500 N Scale Bipropellant Thruster Using Non-Toxic Hypergolic Fuel and Hydrogen Peroxide. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, E.; Kwon, S. Suppression of Hard Start for Nontoxic Hypergolic Thruster Using H2O2 Oxidizer. J. Propuls. Power 2017, 33, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, L.J.; de Araújo, E.P.; Pereira, L.G.F.; Gouvêa, L.H.; Vieira, R. Assessing the Performance of a Green Liquid Fuel Hypergolic with Hydrogen Peroxide in a 50 n Bipropellant Thruster. Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2021, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarritzu, A.; Pasini, A.; Merz, F.; Werling, L.; Lauck, F. Experimental Investigation of Combustion Performance of a Green Hypergolic Bipropellant Based on Hydrogen Peroxide. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 219, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, M.; Lauck, F. Hot Firing Tests of a Novel Green Hypergolic Propellant in a Thruster. J. Propuls. Power 2022, 38, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasiewicz—Institute of Aviation. New Green Hypergolic Propellant—Potential Gamechnager for in-Space Propulsion. 2023. Available online: https://ilot.lukasiewicz.gov.pl/en/green-hypergolic-propellant/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Seo, M.; Bhosale, V.K.; Im, H.; Kwon, S. Performance Improvement of Triglyme-Based Fuels Using an Ionic Liquid with Hydrogen Peroxide. Combust. Flame 2024, 270, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Gwak, J.; Kim, K.S.; Churchill, D.G.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S. Rapid Ignition of “Green” Bipropellants Enlisting Hypergolic Copper (II) Promoter-in-Fuel. Fuel 2021, 297, 120734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, V.K.; Kulkarni, P.S. Ultrafast Igniting, Imidazolium Based Hypergolic Ionic Liquids with Enhanced Hydrophobicity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.H.; Huzel, D.K. Modern Engineering for Design of Liquid-Propellant Rocket Engines; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; ISBN 1563470136. [Google Scholar]
- Suttan, G.P.; Biblarz, O. Rocket Propulsion Elements, 7th ed.; Suttan, G.P., Biblarz, O., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0471326429. [Google Scholar]
- Lauck, F.; Balkenhohl, J.; Negri, M.; Freudenmann, D.; Schlechtriem, S. Green Bipropellant Development—A Study on the Hypergolicity of Imidazole Thiocyanate Ionic Liquids with Hydrogen Peroxide in an Automated Drop Test Setup. Combust. Flame 2021, 226, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcbride, B.J.; Gordon, S. Computer Program for Calculation of Complex Chemical Equilibrium Composition and Applications II. User Manual and Pogram Description. In NASA Reference Publication 1311; NASA Lewis Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.; McBride, B.J. Computer Program for Calculation Complex Chemical Equilibrium Compositions and Applications, I. Analysis; NASA Lewis Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1994; ISBN 1995001376. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, A.H.; McDonell, V.G. Atomization and Sprays; Taylor & Francis Group; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781498736251. [Google Scholar]
- Kyu-seop, K. Ignition and Reactive Spray Characteristics of High Test Peroxide-Based Rapid Hypergol. PhD Thesis, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huzel, D.K.; Huang, D.H. Design of Liquid-Propellant Rocket Engines; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, M.W., Jr. NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 4th ed.; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 1998; pp. 1–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_peroxide (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Zaitsau, D.H.; Emel’yanenko, V.N.; Verevkin, S.P.; Heintz, A. Sulfur-Containing Ionic Liquids. Rotating-Bomb Combustion Calorimetry and First-Principles Calculations for 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Thiocyanate. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 5896–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Order Threshold, ppm | Exposure Limit, ppm | Vapor Pressure, Psia at 25 °C | Viscosity, cP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrazine | 2–3 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.97 at 298 K |
| MMH | 1–3 | 0.01 | 3.23 | 0.855 at 293 K |
| N2O4 | 1–3 | 3.0 | 17.4 | 0.47 at 293 K |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhosale, V.K.; Lee, K.; Ugolini, V.M.P.; Yoon, H. Investigation of Combustion Performance of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid Fuels Through Injector Design. Aerospace 2025, 12, 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090759
Bhosale VK, Lee K, Ugolini VMP, Yoon H. Investigation of Combustion Performance of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid Fuels Through Injector Design. Aerospace. 2025; 12(9):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090759
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhosale, Vikas Khandu, Keonwoong Lee, Vincent Mario Pierre Ugolini, and Hosung Yoon. 2025. "Investigation of Combustion Performance of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid Fuels Through Injector Design" Aerospace 12, no. 9: 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090759
APA StyleBhosale, V. K., Lee, K., Ugolini, V. M. P., & Yoon, H. (2025). Investigation of Combustion Performance of Hypergolic Ionic Liquid Fuels Through Injector Design. Aerospace, 12(9), 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090759






