Initial-Condition-Aware Polynomial Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
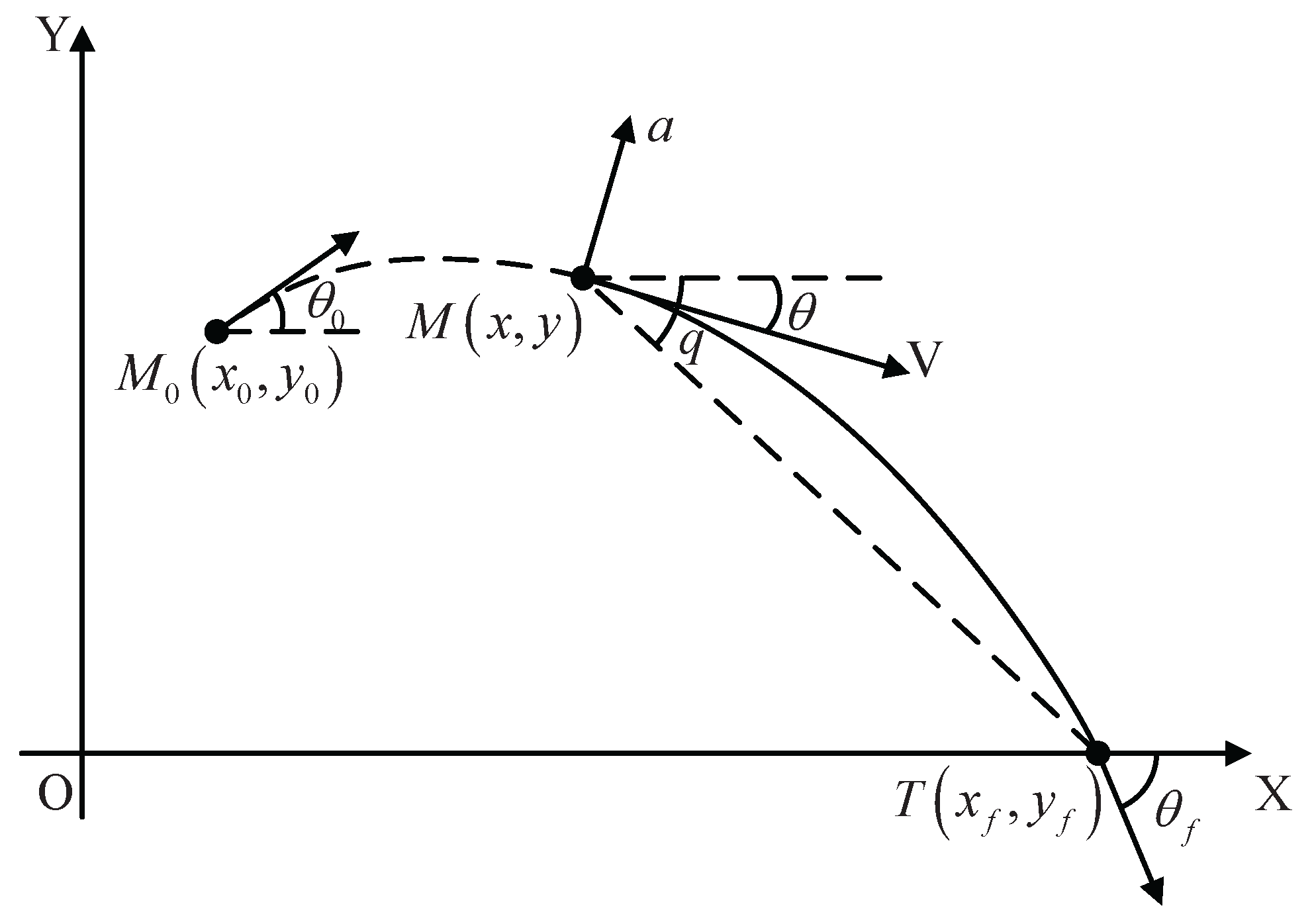
2. Problem Statement
3. Derivation of the Polynomial Guidance Law
3.1. Polynomial with Impact Angle and Time Control
3.2. Guidance Law Derivation
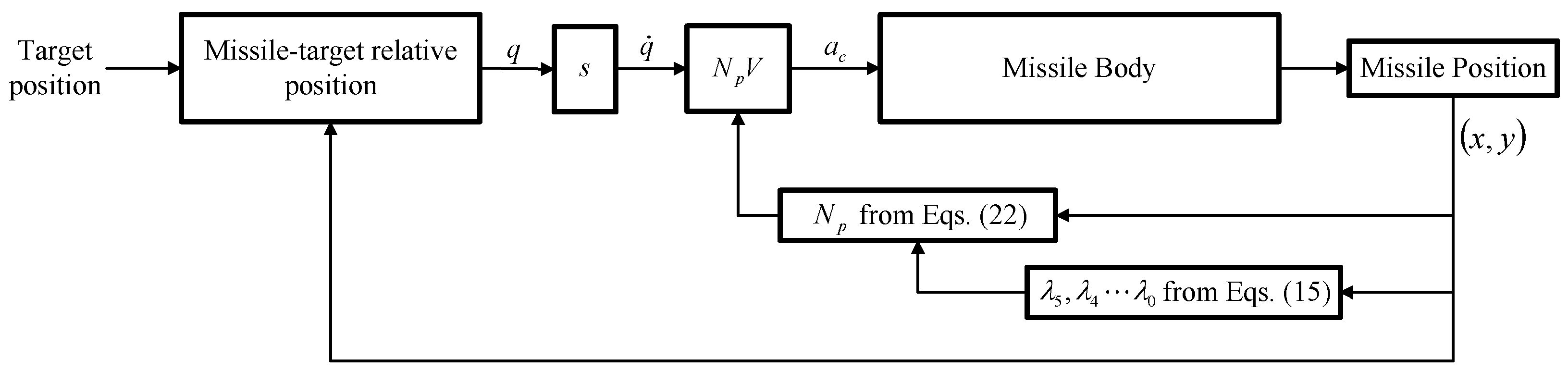
4. Closed-Loop Implementation
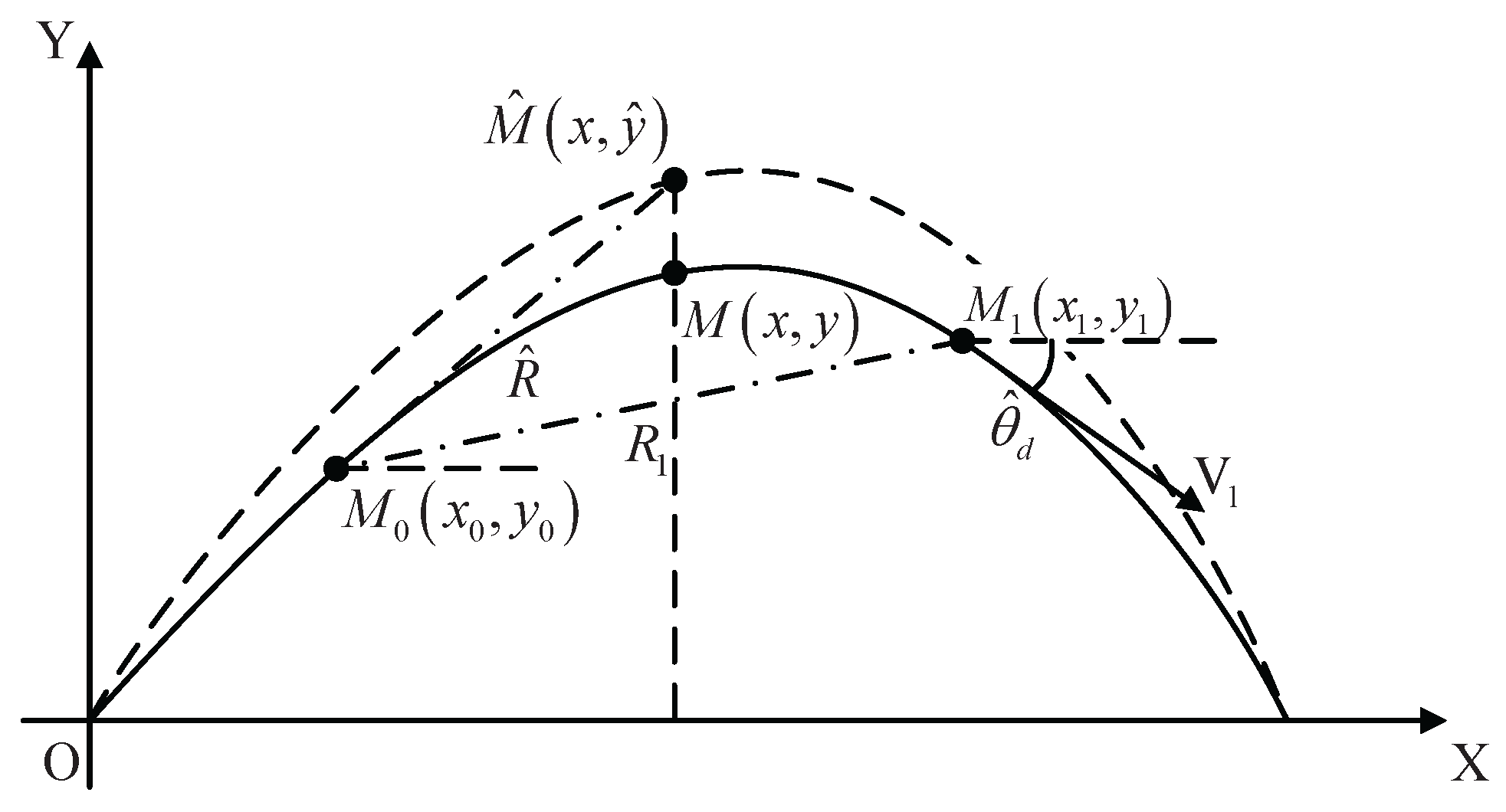
4.1. Compensation for the Small-Angle Assumption
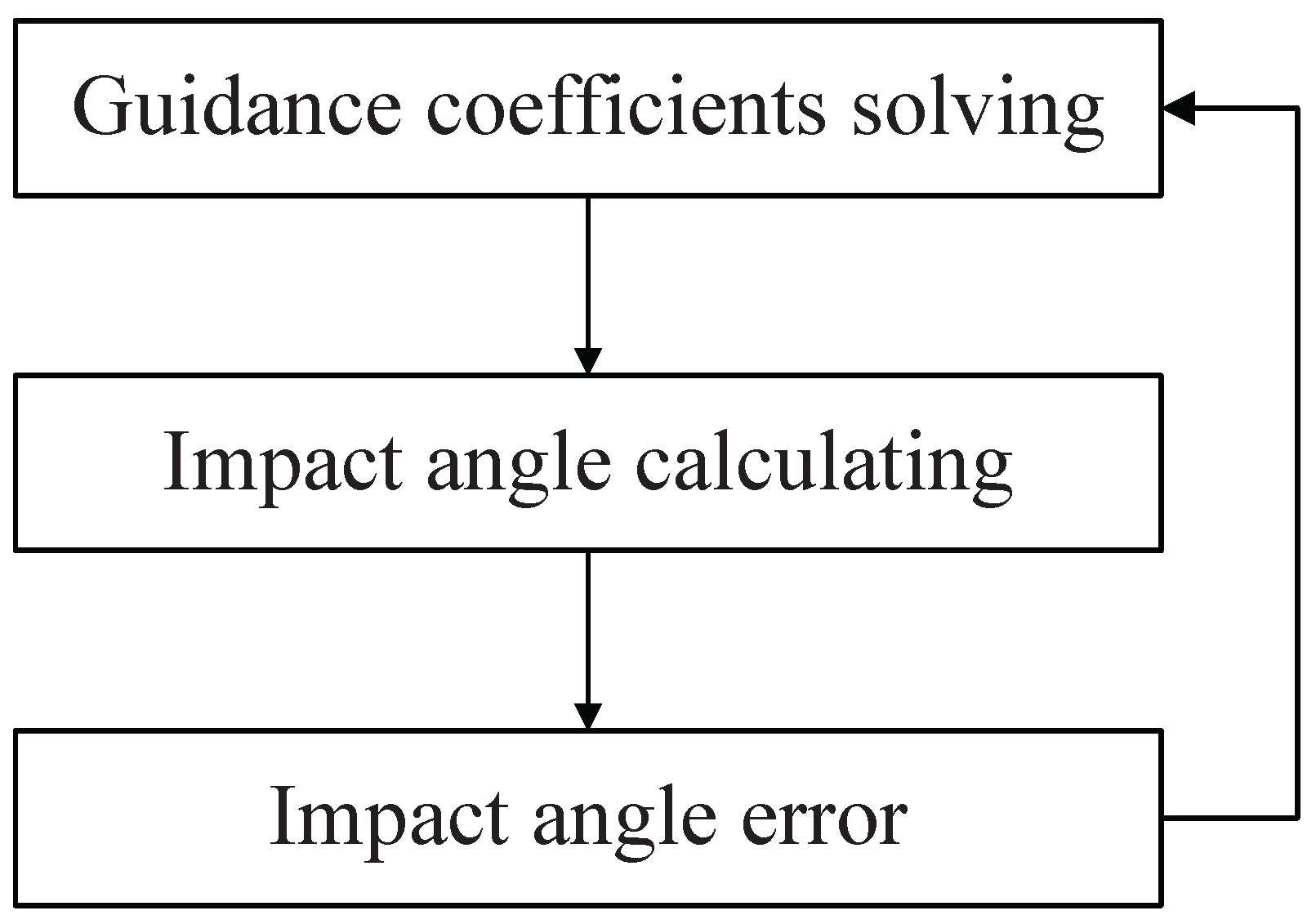
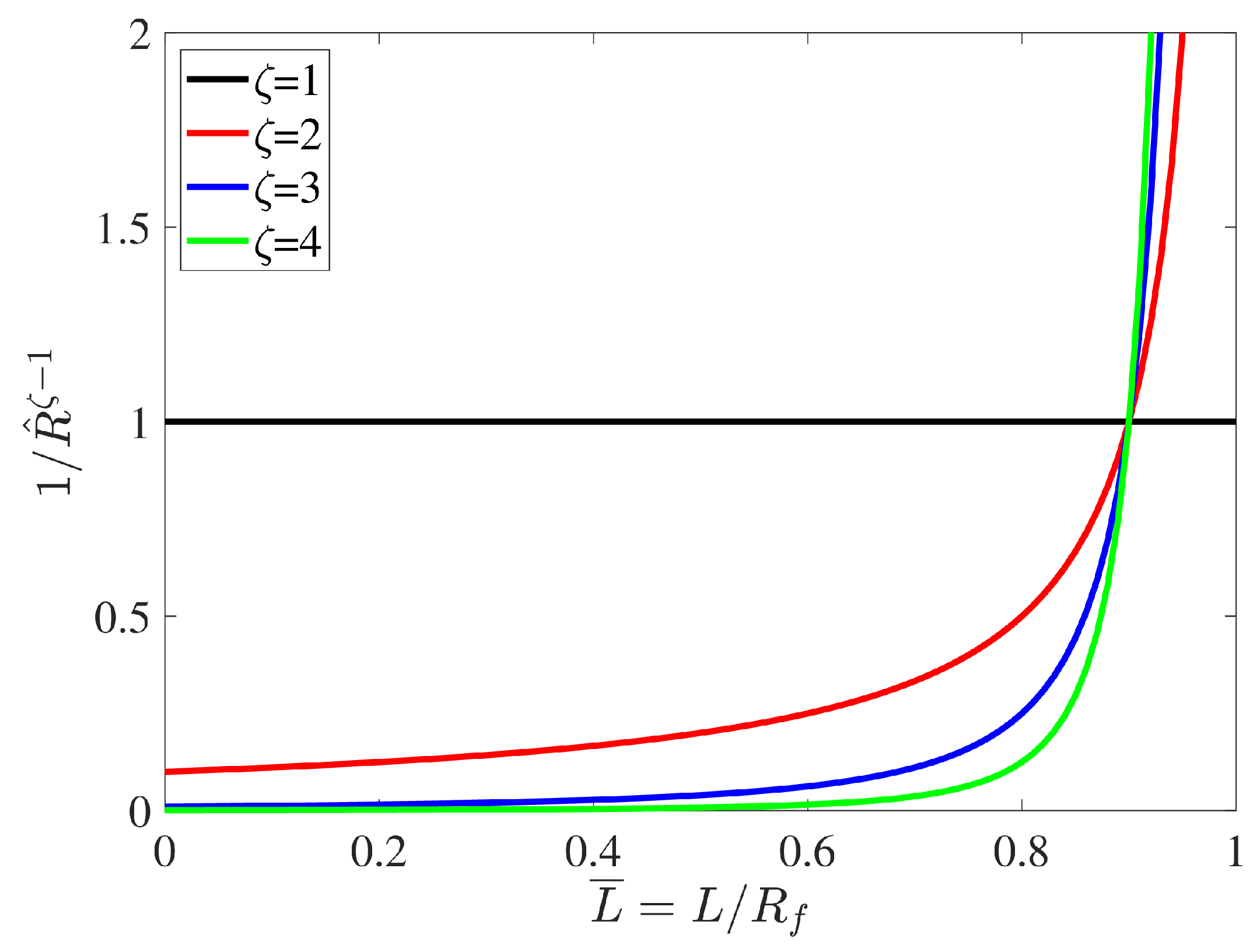
4.2. The the Polynomial Coefficients Replanning
4.3. Positional Error Elimination
5. Numerical Simulation
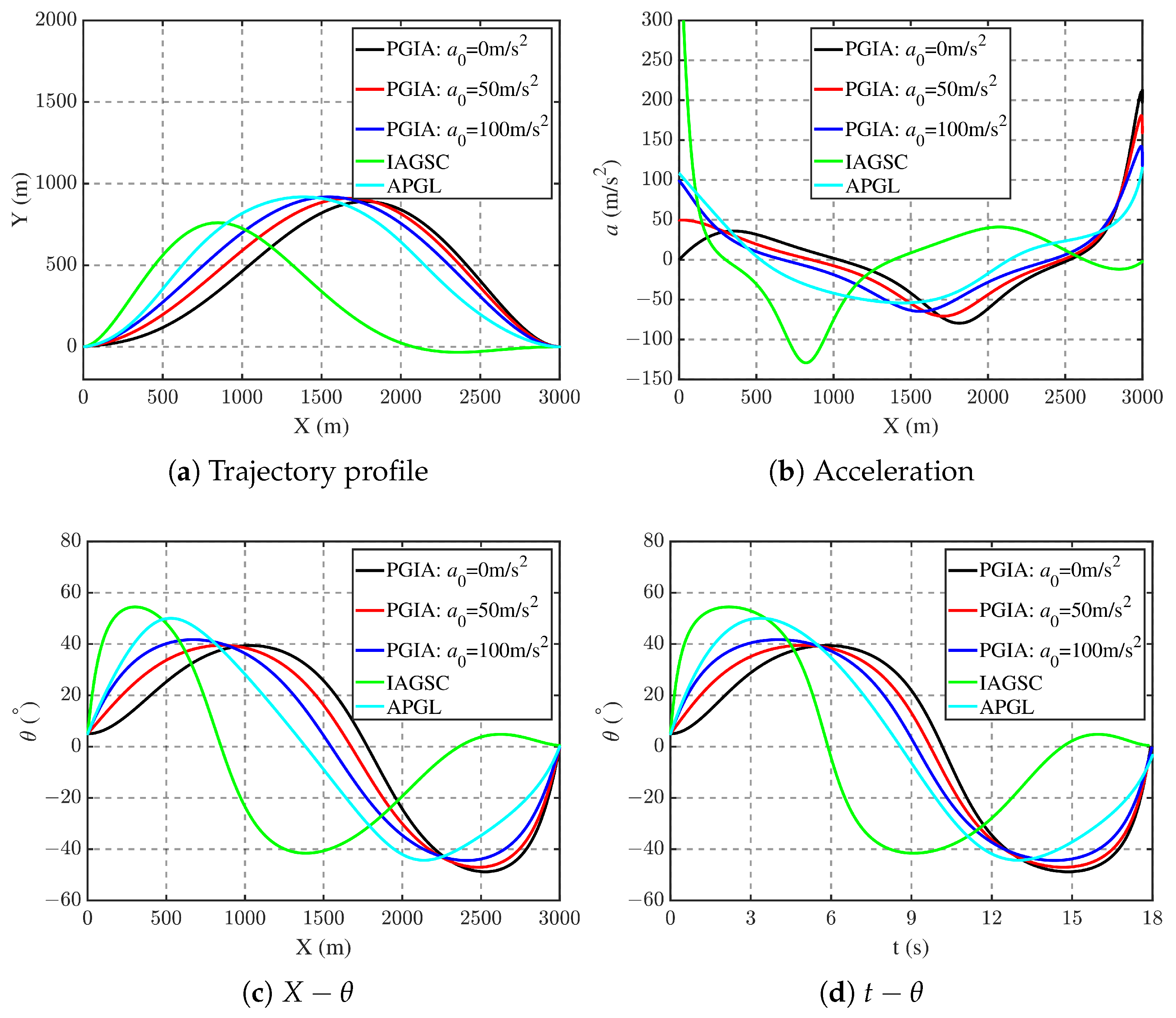
5.1. Guidance Law Performance
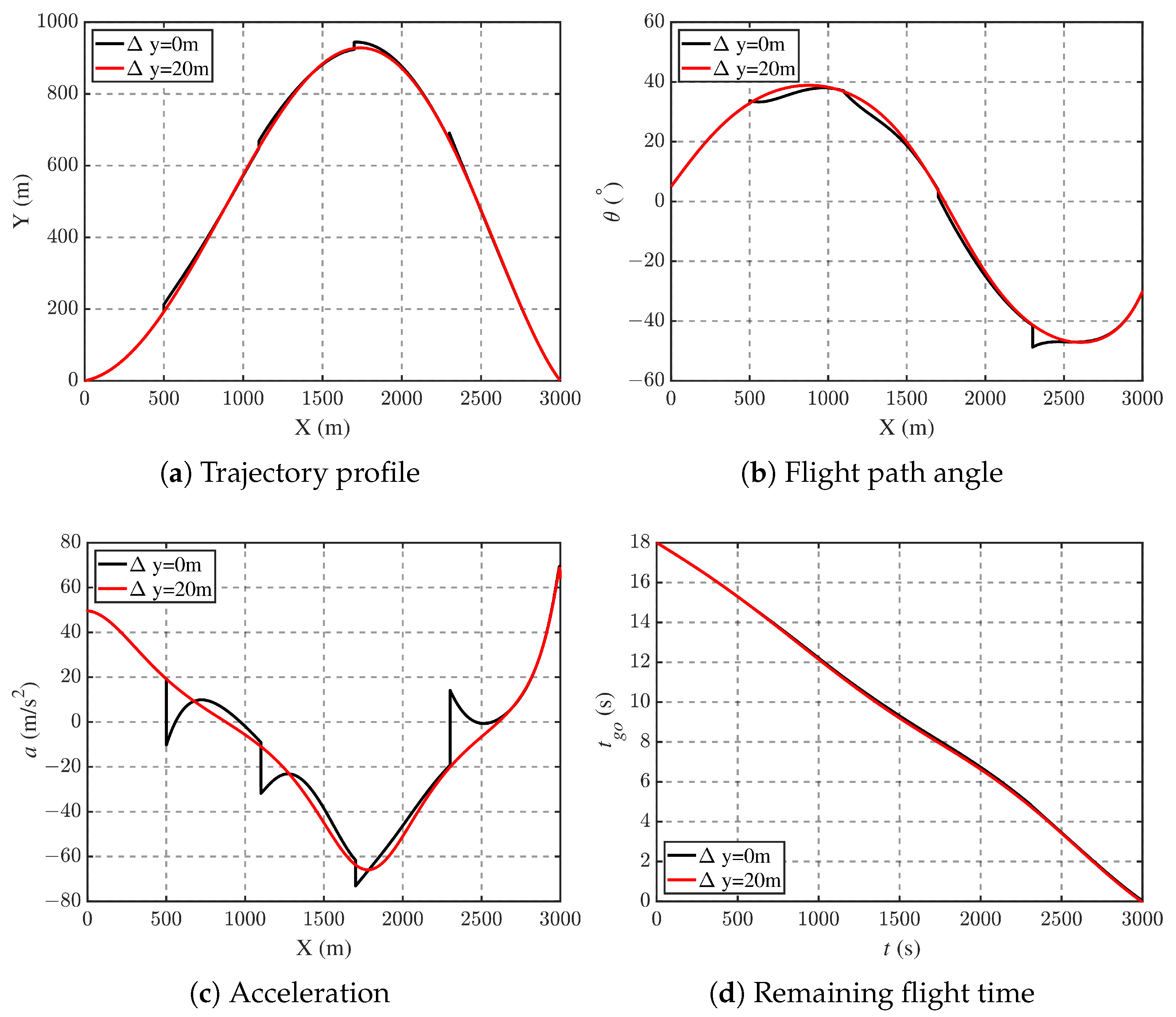
5.2. Performance with Positional Error
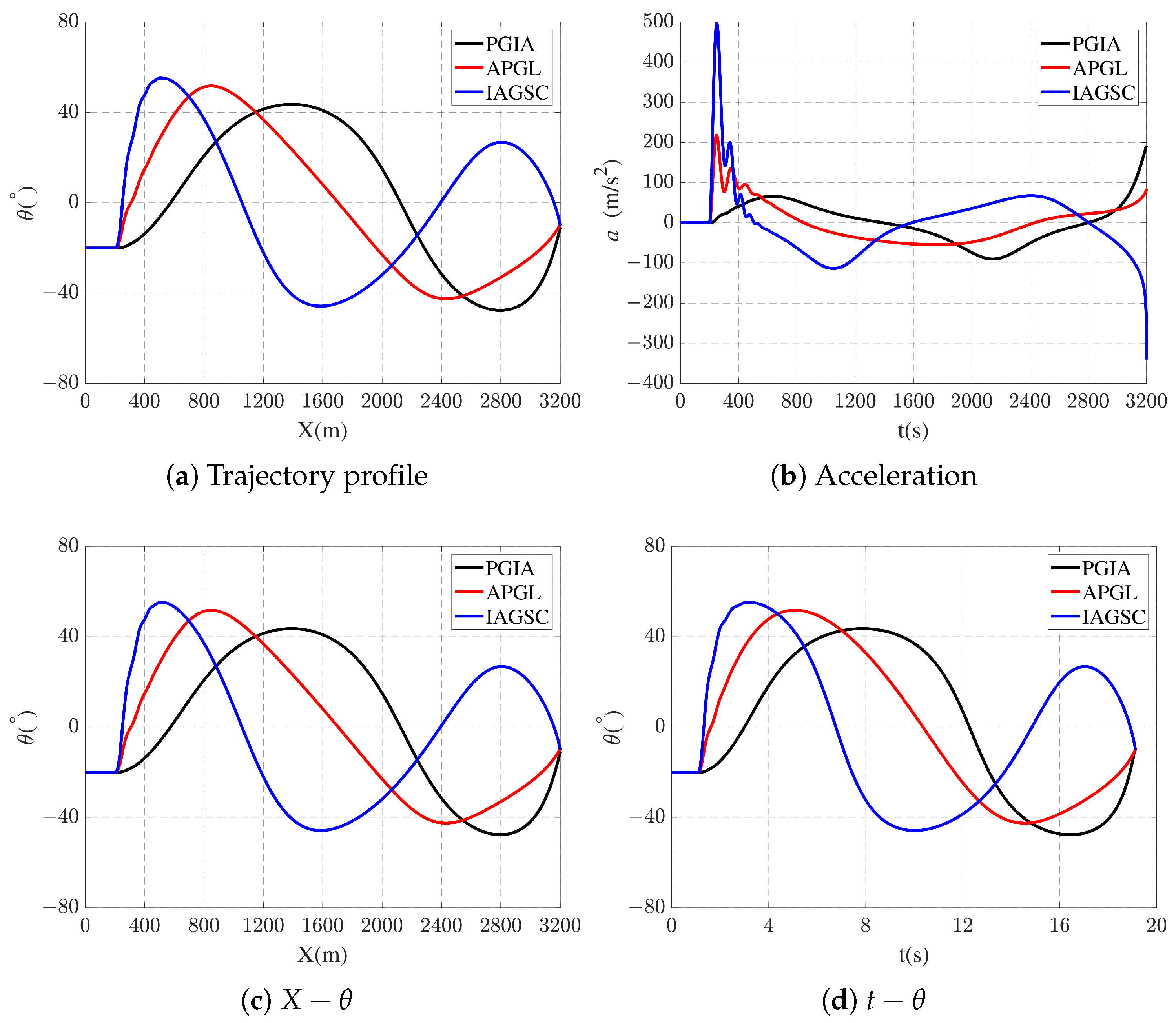
5.3. Comparison Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, I.S.; Lee, J.I.; Tahk, M.J. Impact-time-control guidance law for anti-ship missiles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.; Kim, Y. Modified pure proportional navigation guidance law for impact time control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2016, 39, 852–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Shan, J.; Xin, M. Cooperative guidance for multiple powered missiles with constrained impact and bounded speed. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2021, 44, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H. Impact time control guidance law with field of view constraint. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Xin, M. Varying-gain proportional navigation guidance for precise impact time control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2023, 46, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulov, G.; Weiss, M.; Shima, T.Y. Minimum-Effort Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints Using Quadratic Kinematics Approximation. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 January 2022; p. 2040. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.G.; Cho, D.; Kim, H.J. Sliding mode guidance law for impact time control without explicit time-to-go estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 55, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Nanavati, R.V.; Ranjan Kumar, S. Three-Dimensional nonlinear impact time guidance using predicted interception point. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2023, 46, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Jeon, I.S.; Tahk, M.J. Guidance law to control impact time and angle. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, A. Guidance law with impact time and impact angle constraints. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H. Impact time and angle control guidance with rendezvous concept. In Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018; p. 1322. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Lee, C.H. Optimality of error dynamics in missile guidance problems. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2018, 41, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lin, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, S. Guidance law to control impact angle and time based on optimality of error dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 233, 3577–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S. Two-stage cooperative guidance strategy with impact-angle and field-of-view constraints. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2023, 46, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lv, Y.; Wen, G.; Wu, X.; Cai, M. Three-dimensional cooperative guidance law design for simultaneous attack with multiple missiles against a maneuvering target. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Xiamen, China, 10–12 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, G.; Zhang, H. Multiple missiles cooperative guidance with simultaneous attack requirement under directed topologies. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, S.; Wang, J.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Near-optimal midcourse guidance for velocity maximization with constrained arrival angle. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2021, 44, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.; Kikukawa, Y.; Takano, H.; Yamaguchi, I. Terminal Impact Angle Control Guidance Taking Account of Field-of-View Constraint Using a Time-Shifting Sliding Surface. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024; p. 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.R.; Ghose, D. Impact time and angle control guidance. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 5–9 January 2015; p. 0616. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, R.; Erer, K.S.; Holzapfel, F. Polynomial shaping of the look angle for impact-time control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2017, 40, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harl, N.; Balakrishnan, S.N. Impact time and angle guidance with sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 20, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, R.; Erer, K.S.; Holzapfel, F. Quartic range shaping for impact time control. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Valletta, Malta, 3–6 July 2017; pp. 1213–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, R.; Erer, K.S. Impact time and angle control against moving targets with look angle shaping. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2020, 43, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, R.; Erer, K.S.; Holzapfel, F. Impact time control with generalized-polynomial range formulation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2018, 41, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Liang, Y. Polynomial Guidance for Impact-Time Control Against Maneuvering Targets. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2023, 46, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, I.S.; Tahk, M.J. Augmented polynomial guidance with impact time and angle constraints. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 2806–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, T.H.; Tahk, M.J.; Whang, I.H. Polynomial guidance laws considering terminal impact angle and acceleration constraints. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarchan, P. Tactical and Strategic Missile Guidance; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Initial interceptor-target distance R | 3000 m |
| Missile Velocity V | 200 m/s |
| Initial position (,) | (0, 0) |
| Target position (,) | (3000, 0) |
| Cases | Impact Angle (°) | Impact Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | −20 | 16 |
| 2 | −20 | 17 |
| 3 | −20 | 18 |
| 4 | −40 | 16 |
| 5 | −40 | 17 |
| 6 | −40 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S. Initial-Condition-Aware Polynomial Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints. Aerospace 2025, 12, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060484
Duan X, Wang J, Wang Y, Fan S. Initial-Condition-Aware Polynomial Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints. Aerospace. 2025; 12(6):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060484
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Xinyao, Jiang Wang, Yadong Wang, and Shipeng Fan. 2025. "Initial-Condition-Aware Polynomial Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints" Aerospace 12, no. 6: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060484
APA StyleDuan, X., Wang, J., Wang, Y., & Fan, S. (2025). Initial-Condition-Aware Polynomial Guidance with Impact Time and Angle Constraints. Aerospace, 12(6), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060484





