Towards a Balanced Design of a Grid Fin with Lightweight Aerodynamics and Structural Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modeling Approach
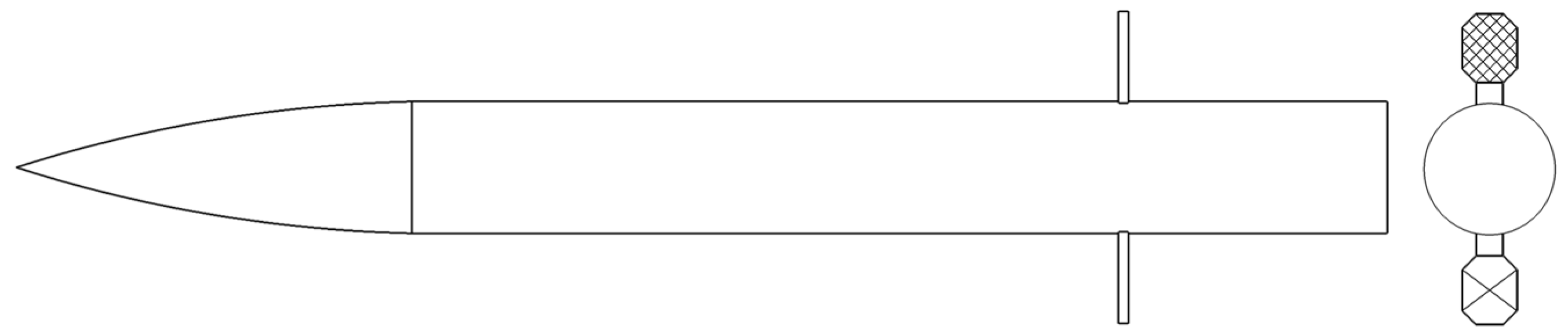
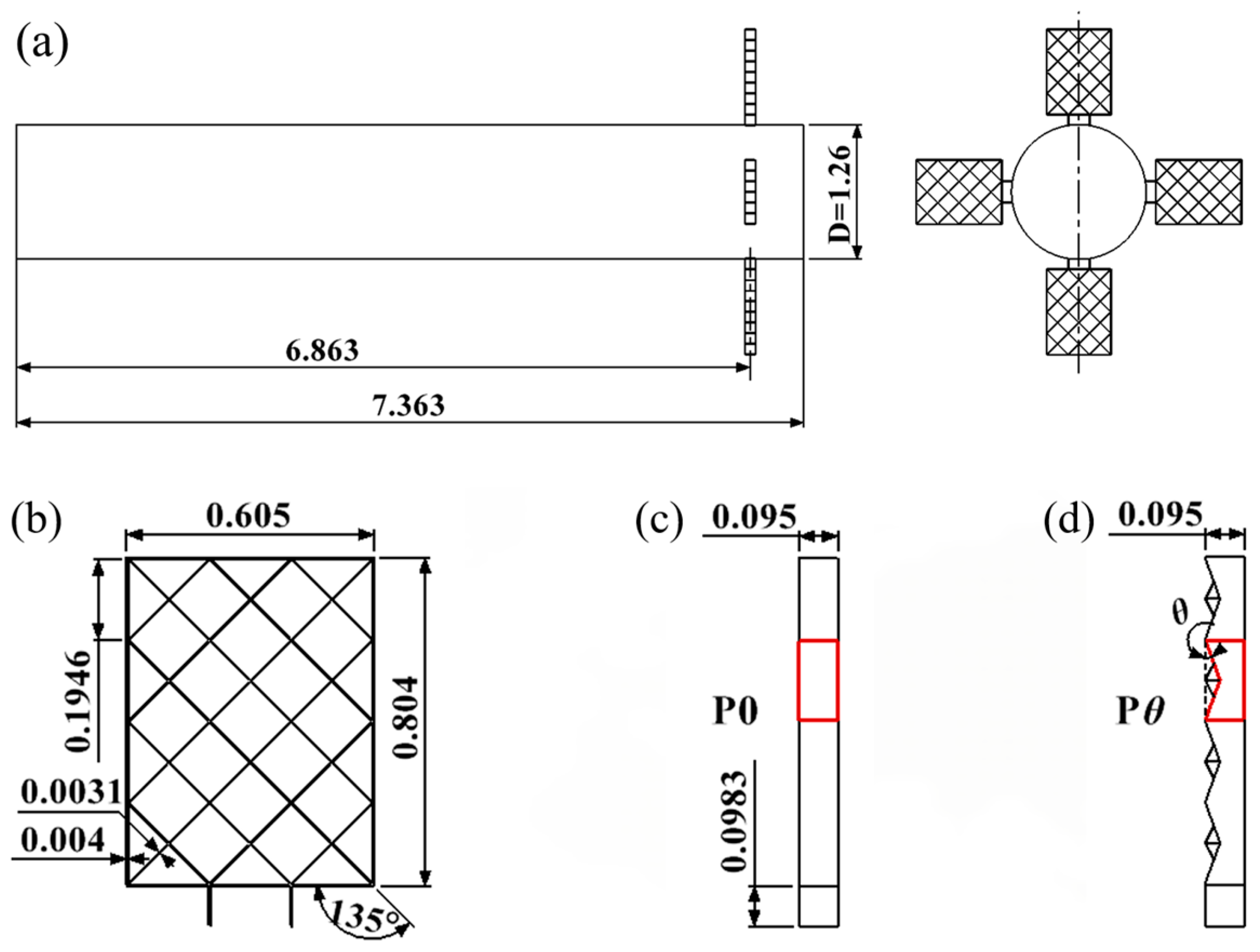
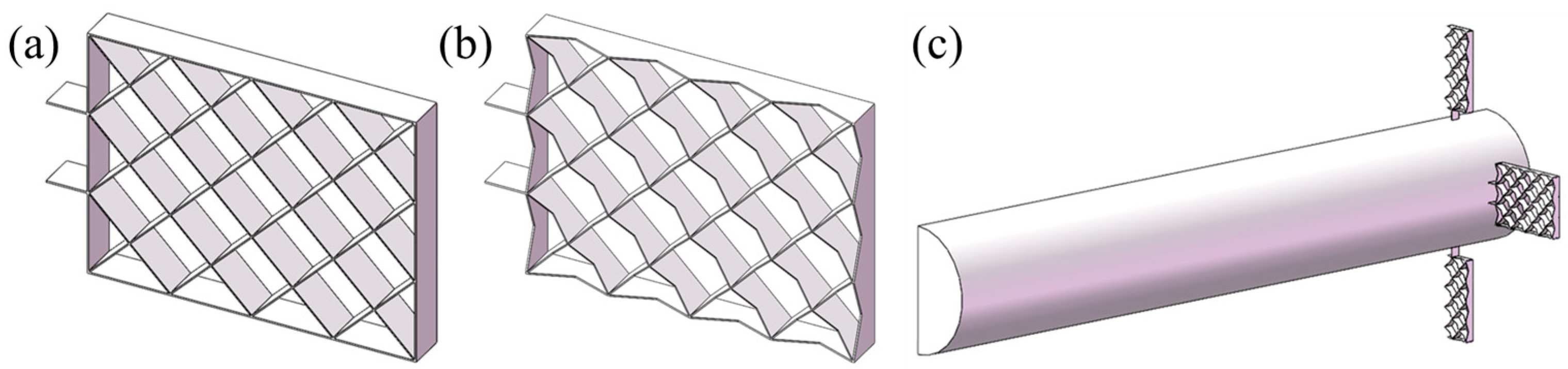
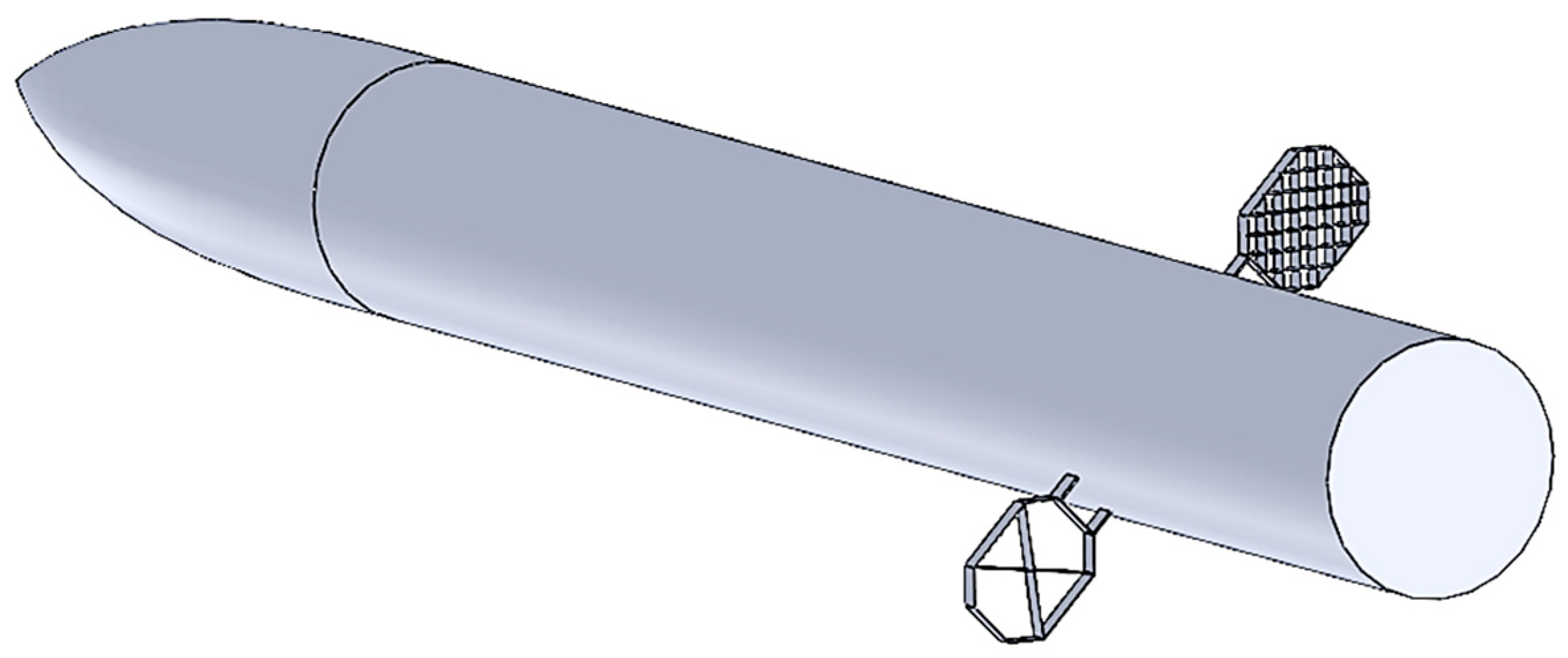
2.1. Geometry Model
2.2. Numerical Method
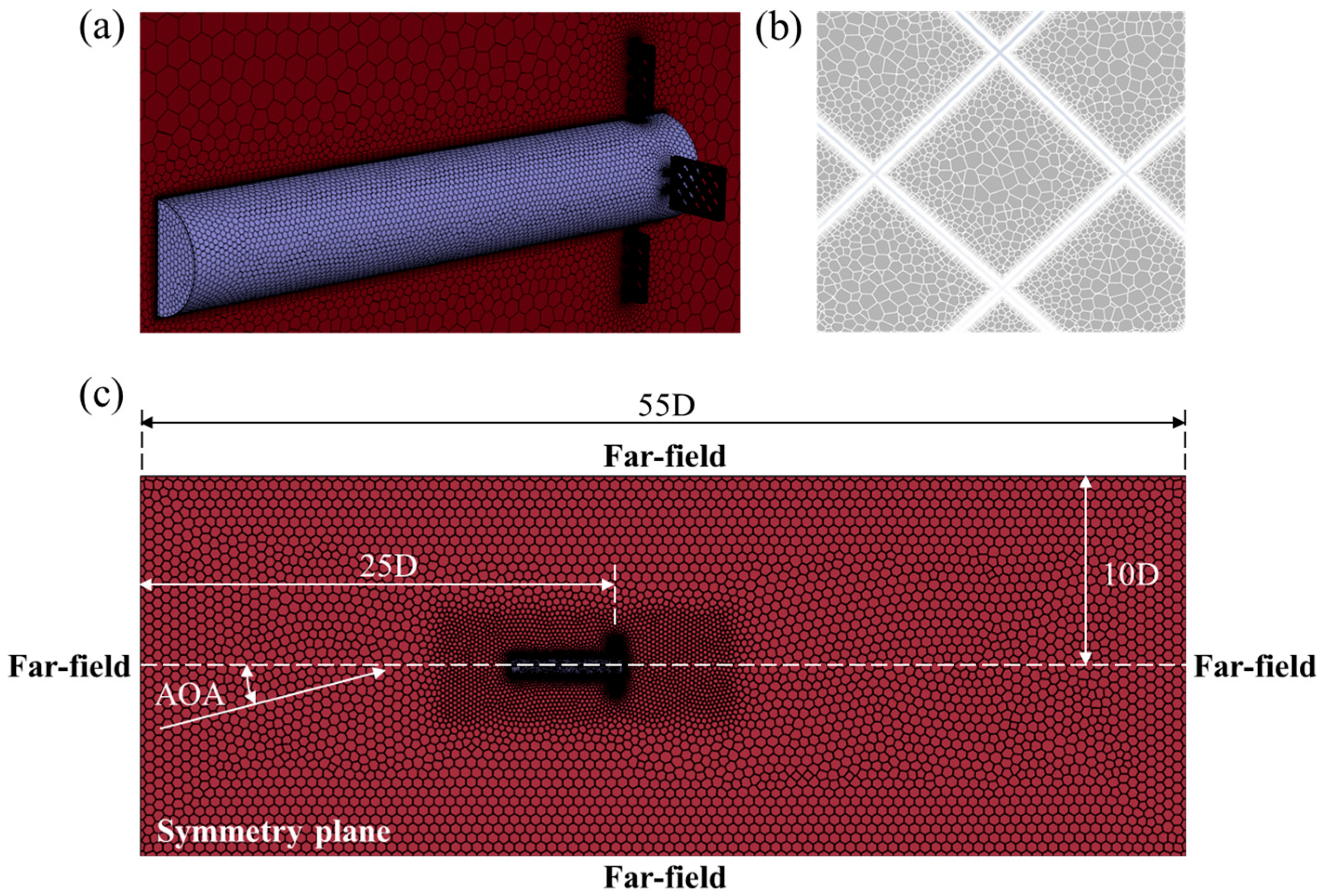
2.3. Computational Mesh
2.4. Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
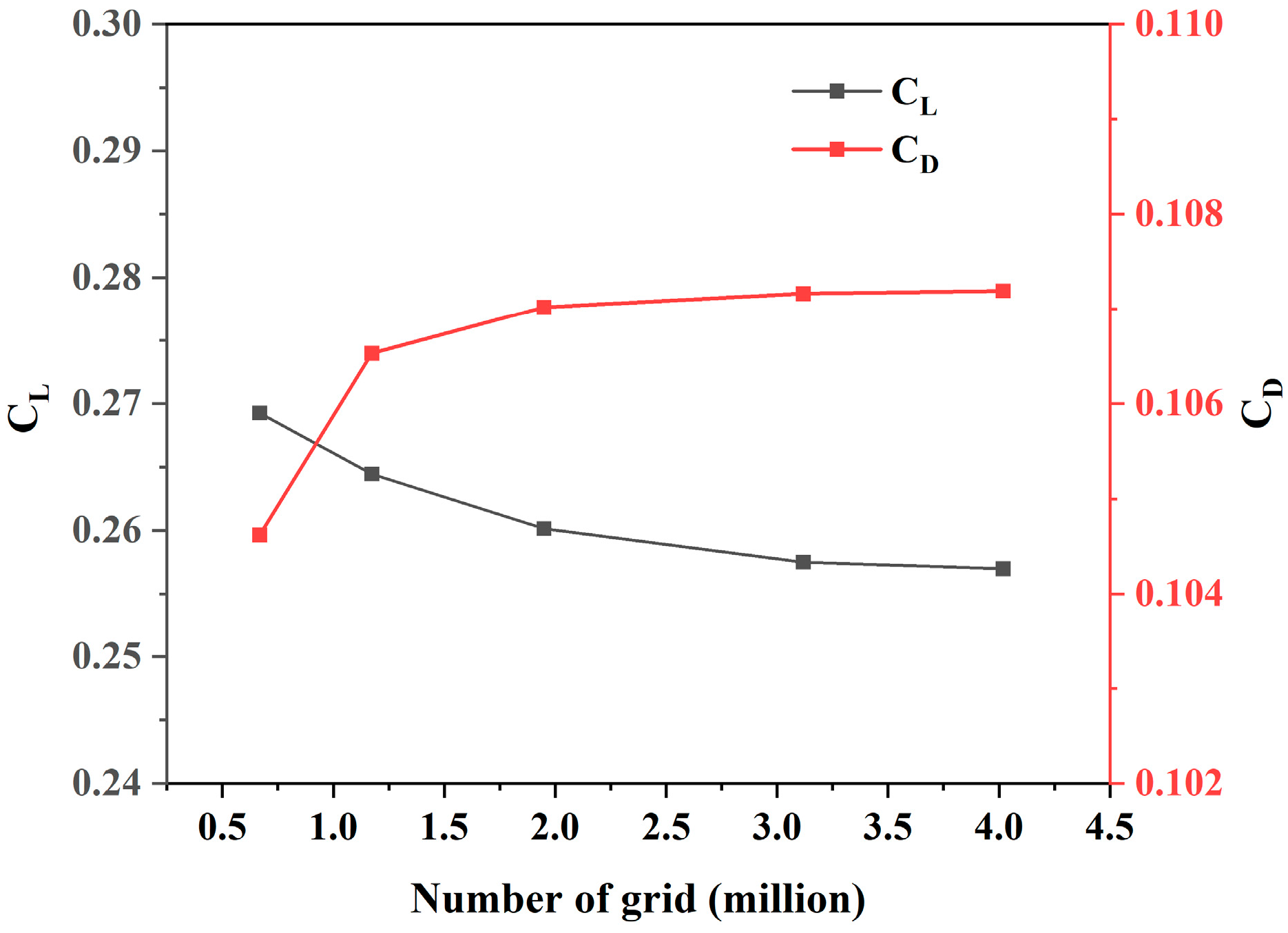
3.1. Grid Independence Test
3.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics Validation
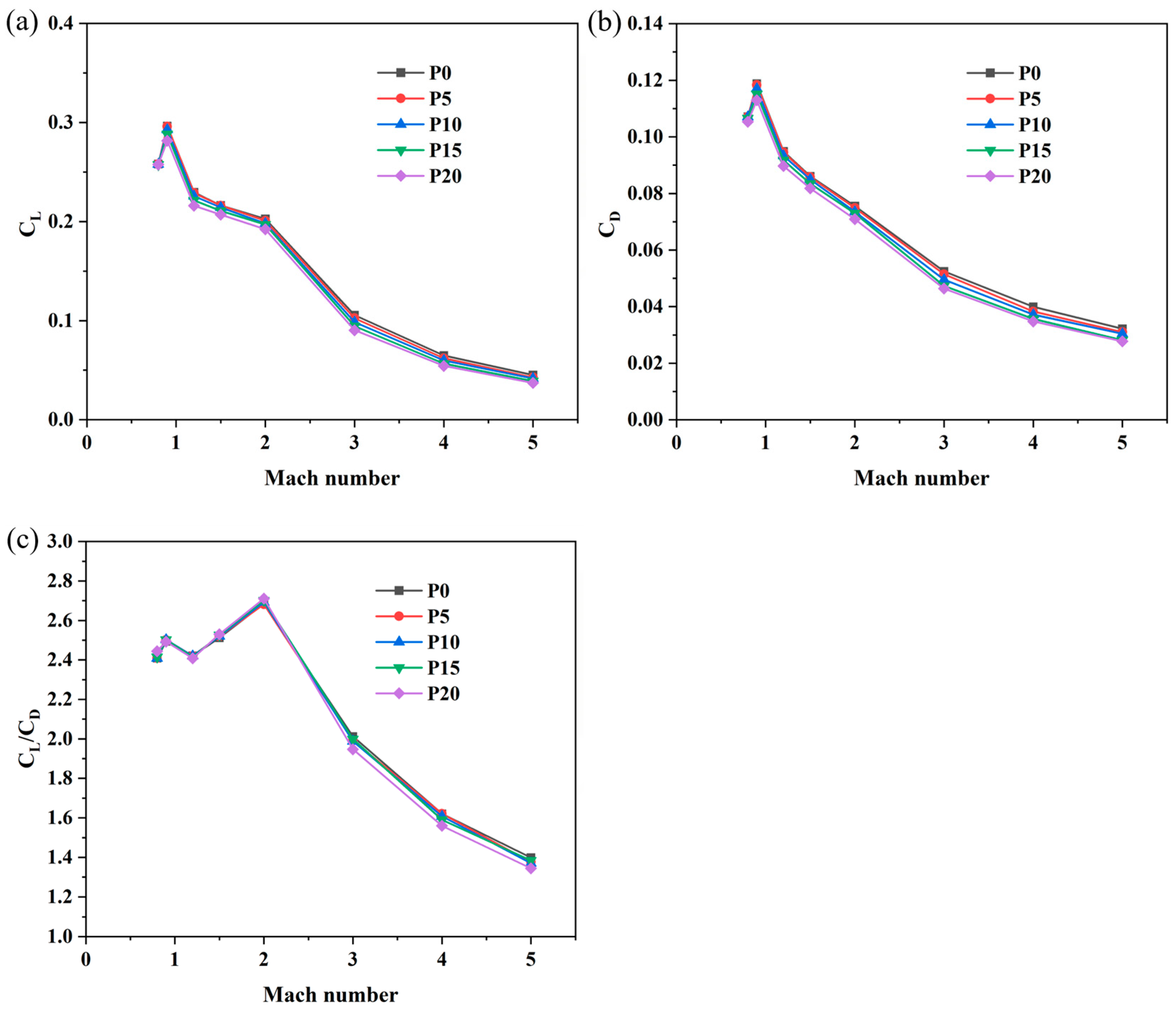
3.3. Effects of θ on Aerodynamic Coefficients
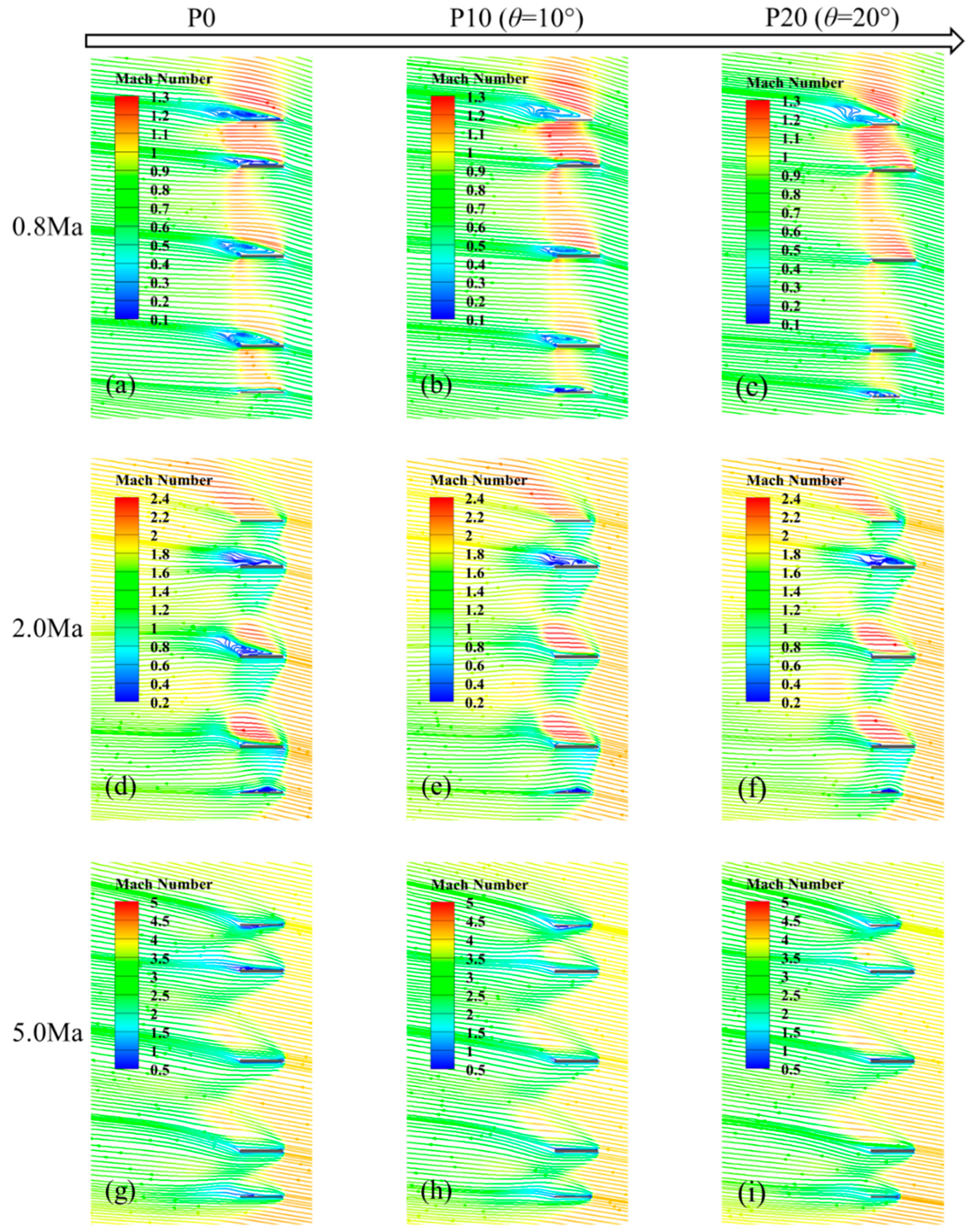
3.4. Effects of θ on Flow Characteristics
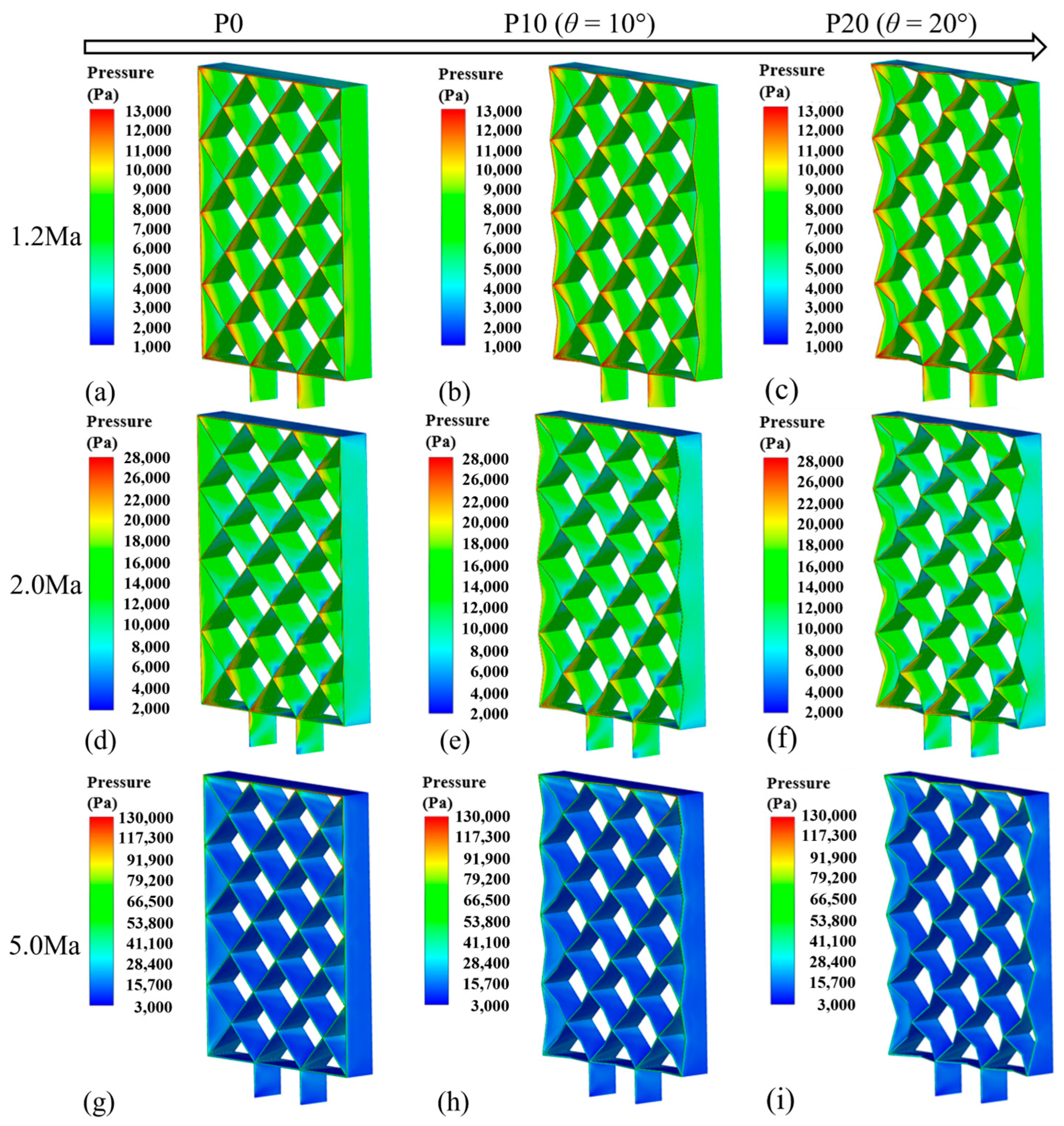
3.5. Effects of θ on Aerodynamic Loads
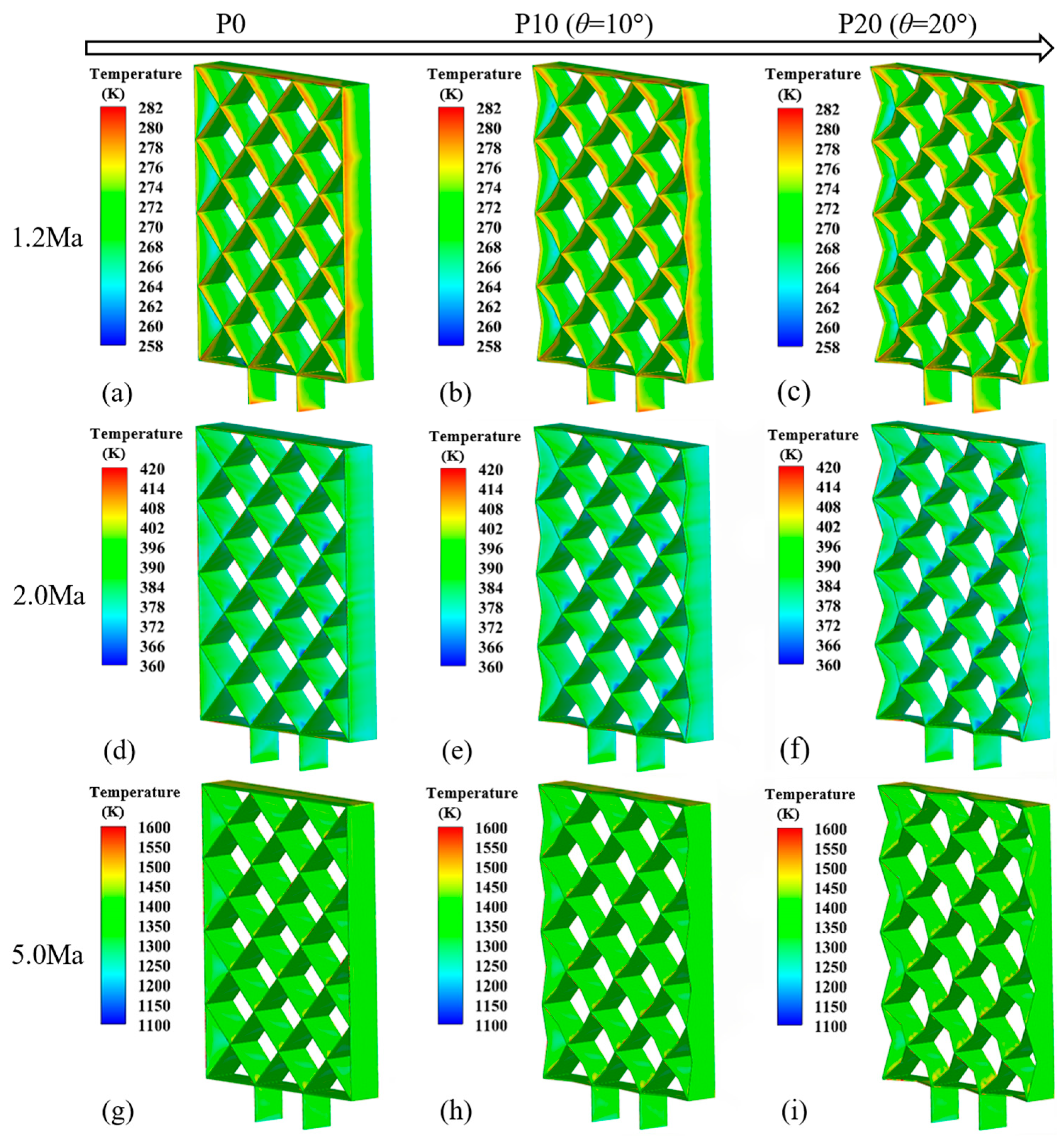
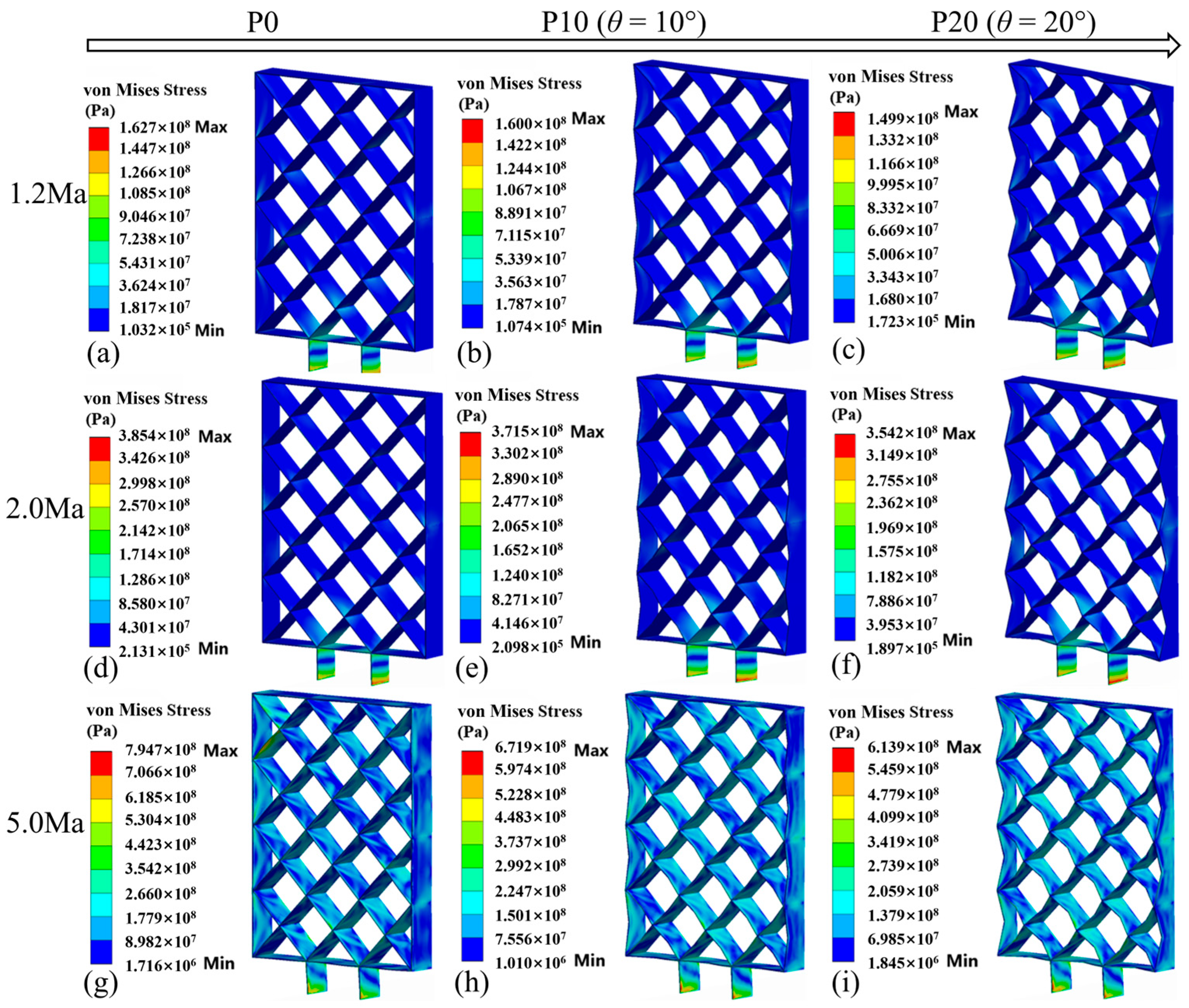
3.6. Effects of θ on Structural Responses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adilov, N.; Alexander, P.; Cunningham, B.; Albertson, N. An analysis of launch cost reductions for low earth orbit satellites. Econ. Bull. 2022, 42, 1561–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi Paniagua, K.; García-Fogeda, P.; Arévalo, F. Aeroelastic stability of an aerial refueling hose–drogue system with aer-odynamic grid fins. Aerospace 2023, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunescu, I.; Hothazie, M.V.; Stoican, M.G.; Pricop, M.V.; Onel, A.I.; Afilipoae, T.P. Numerical Study of the Basic Finner Model in Rolling Motion. Aerospace 2025, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSpirit, J.; Milton, V.; Washington, W.D. CFD investigation of canard-controlled missile with planar and grid fins in supersonic flow. In Proceedings of the AIAA Atmospheric Flight Mechanics Conference and Exhibit, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 August 2002. AIAA 2002-4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Y.; Mi, B.G.; Liu, H.Y.; Yu, J.Y. A grid fusion lifting surface and its flow control mechanism at high angles of attack. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7788011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisz, T.S.; Taylor, J.C.; Gibson, D.; Kennerly, S.; Osei-Wusu, K.; Scriven, G.; Pottebaum, T.; Horvath, T.J.; Schwartz, R.; Tack, S.; et al. Processing infrared imagery of the SpaceX Falcon first stage reentry during CRS-4 mission. In Proceedings of the AIAA Space and Astronautics Forum and Exposition, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-O. An analysis of launch vehicle development strategy of SpaceX. J. Korean Soc. Propuls. Eng. 2019, 23, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.; Mun, H.; Nam, S.; Cha, J.; Ko, S. A survey on recovery technology for reusable space launch vehicle. J. Korean Soc. Propuls. Eng. 2018, 22, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.S.; Washington, W.D. An experimental investigation of grid fin drag reduction techniques. In Proceedings of the 12th Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–23 June 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sucheendran, M.M.; Misra, A. Experimental analysis of cell pattern on grid fin aerodynamics in subsonic flow. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 234, 537–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sucheendran, M.M.; Misra, A. Effect of aspect ratio variation on subsonic aerodynamics of cascade type grid fin at different gap-to-chord ratios. Aeronaut. J. 2020, 124, 472–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sucheendran, M.M.; Misra, A. Effect of chord variation on subsonic aerodynamics of grid fins. In Design and Development of Aerospace Vehicles and Propulsion Systems, Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Misra, A.; Sucheendran, M.M. Effect of planar member cross-section on cascade fin aerodynamics. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2019, 56, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.-S.; Dinh, C.-T.; Pham, V.-S. Numerical study on aerodynamic characteristics of the grid fins with different grid patterns. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 123117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cai, J.S.; Debiasi, M.; Chng, T.L. Numerical study on drag reduction for grid-fin configurations. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. Drag reduction for sweptback grid fin with blunt and sharp leading edges. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.S. Numerical study on choked flow over grid-fin configurations. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2009, 46, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiasi, M.; Yan, Z.; Loon, C.T. Swept-back grid fins for transonic drag reduction. In Proceedings of the 28th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiasi, M. Measurements of the forces and moments generated by swept-back grid fins. In Proceedings of the 30th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schülein, E.; Guyot, D. Novel high-performance grid fins for missile control at high speeds: Preliminary numerical and experimental investigations. In Proceedings of the RTO Applied Vehicle Technology Panel (AVT) Business Meeting Week, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–18 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guyot, D.; Schülein, E. Novel locally swept lattice wings for missile control at high speeds. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Joshi, G.N.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, M. Effect on aerodynamic efficiency of cascade fin due to presence of locally swept planar members at subsonic speed. In Recent Advancements in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Misra, A.; Joshi, G.N.; Tripathi, M. Effect of complex internal grid pattern variations on the subsonic aerodynamic characteristics of grid-fins. Aeronaut. J. 2025, 129, 2712–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Experimental study on aerodynamic characteristics of generic missile configuration with grid fin in transonic flow. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2025, 26, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Ye, Z.Y.; Li, C.N.; Wu, J. Effects of the aerothermoelastic deformation on the performance of the three-dimensional hypersonic inlet. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.D.; Liu, W.; Yang, G.W. Numerical studies of static aeroelastic effects on grid fin aerodynamic performances. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Han, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Song, W.P.; Gui, F.; Tang, J.B. Surrogate-based aerodynamic shape optimization of hypersonic flows considering transonic performance. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, W.D.; Miller, M.S. Grid fins—A new concept for missile stability and control. In Proceedings of the 31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 11–14 January 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kumar, R. Missile grid fins analysis using computational fluid dynamics: A systematic review. INCAS Bull. 2019, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Temperature K | Density kg/m3 | Elasticity Modulus GPa | Poisson Ratio | Thermal Conductivity W/(m·K) | Specific Heat J/(kg·K) | Linear Expansion Coefficient ×10−6 (K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2293.15~1273.15 | 8240 | 204~104 | 0.3~0.33 | 13.4~30.4 | 427~707.4 | 11.8~18.7 |
| θ (°) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPθ (%) | 0.8 Ma | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.27 | 1.49 |
| 0.9 Ma | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.34 | −0.03 | |
| 1.2 Ma | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.26 | −0.54 | |
| 1.5 Ma | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.57 | 0.71 | |
| 2.0 Ma | −0.13 | 0.24 | 0.57 | 0.94 | |
| 3.0 Ma | −1.01 | −1.17 | −0.65 | −3.20 | |
| 4.0 Ma | 0.00 | −0.75 | −1.89 | −3.75 | |
| 5.0 Ma | −1.59 | −2.04 | −1.04 | −3.91 | |
| RPθavg (%) | −0.26 | −0.39 | −0.26 | −1.04 | |
| θ (°) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WSθ (%) | 3.35 | 6.67 | 9.95 | 13.20 |
| LWθavg (%) | 7.83 | 5.84 | 2.63 | 7.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xuan, F. Towards a Balanced Design of a Grid Fin with Lightweight Aerodynamics and Structural Integrity. Aerospace 2025, 12, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100899
Liu Y, Zhu M, Xuan F. Towards a Balanced Design of a Grid Fin with Lightweight Aerodynamics and Structural Integrity. Aerospace. 2025; 12(10):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100899
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuxin, Mingliang Zhu, and Fuzhen Xuan. 2025. "Towards a Balanced Design of a Grid Fin with Lightweight Aerodynamics and Structural Integrity" Aerospace 12, no. 10: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100899
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhu, M., & Xuan, F. (2025). Towards a Balanced Design of a Grid Fin with Lightweight Aerodynamics and Structural Integrity. Aerospace, 12(10), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100899







