Virtual Dynamic Vibration Absorber Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Based on Inertial Actuators for Large Flexible Space Trusses
Abstract
1. Introduction
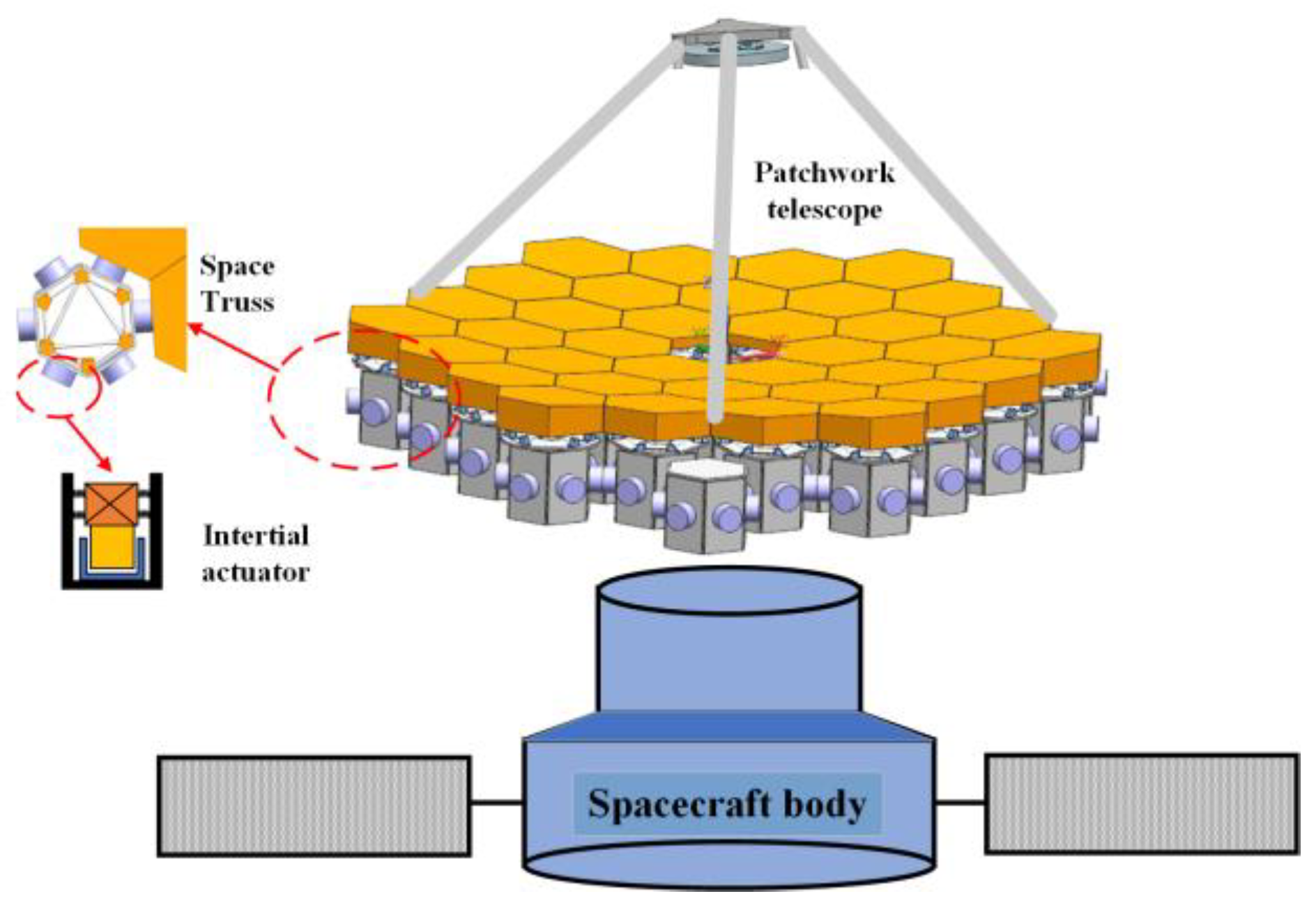
2. Mathematical Modeling of Space Truss and Inertial Actuators
2.1. Dynamic Modeling of Space Truss Structures
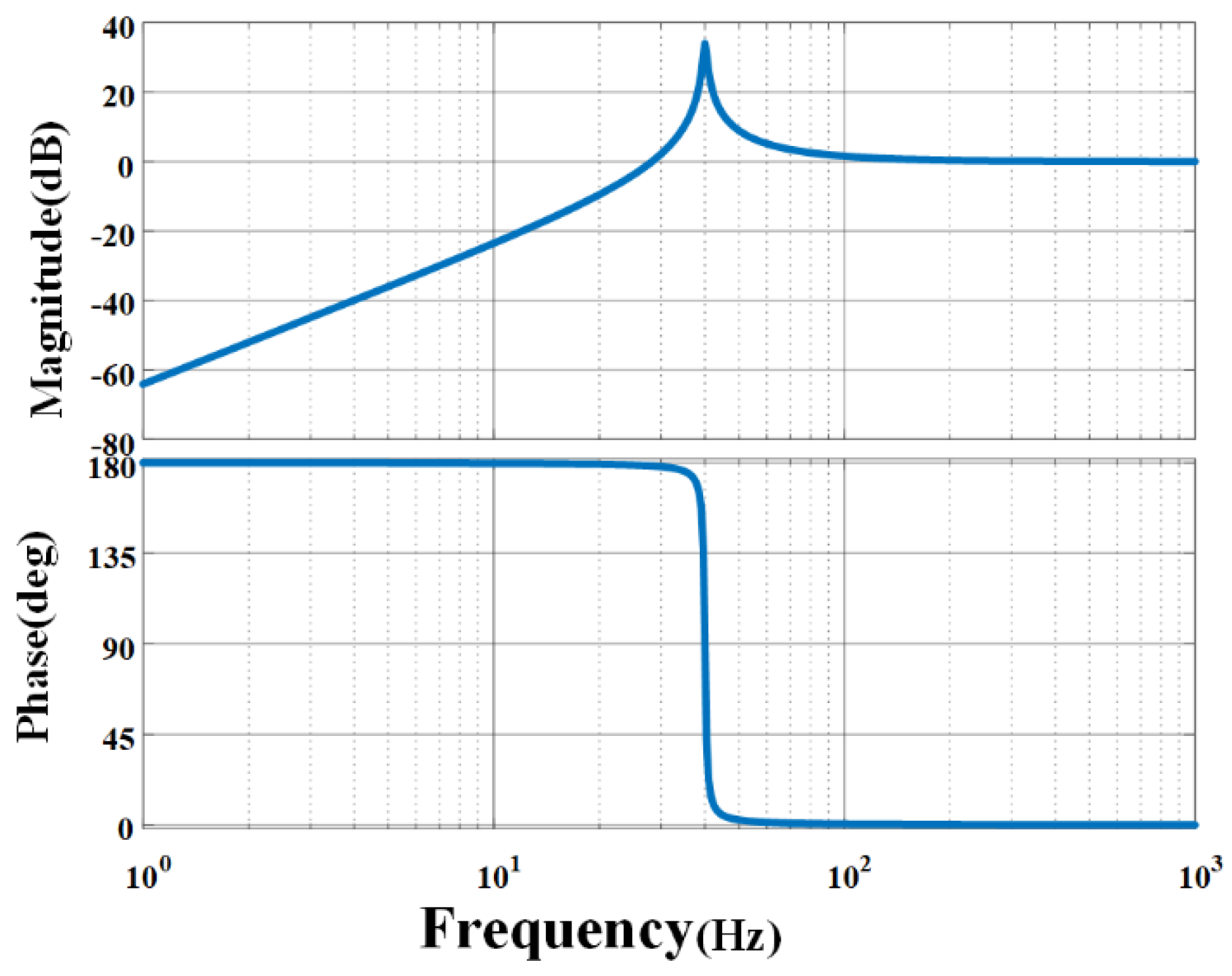
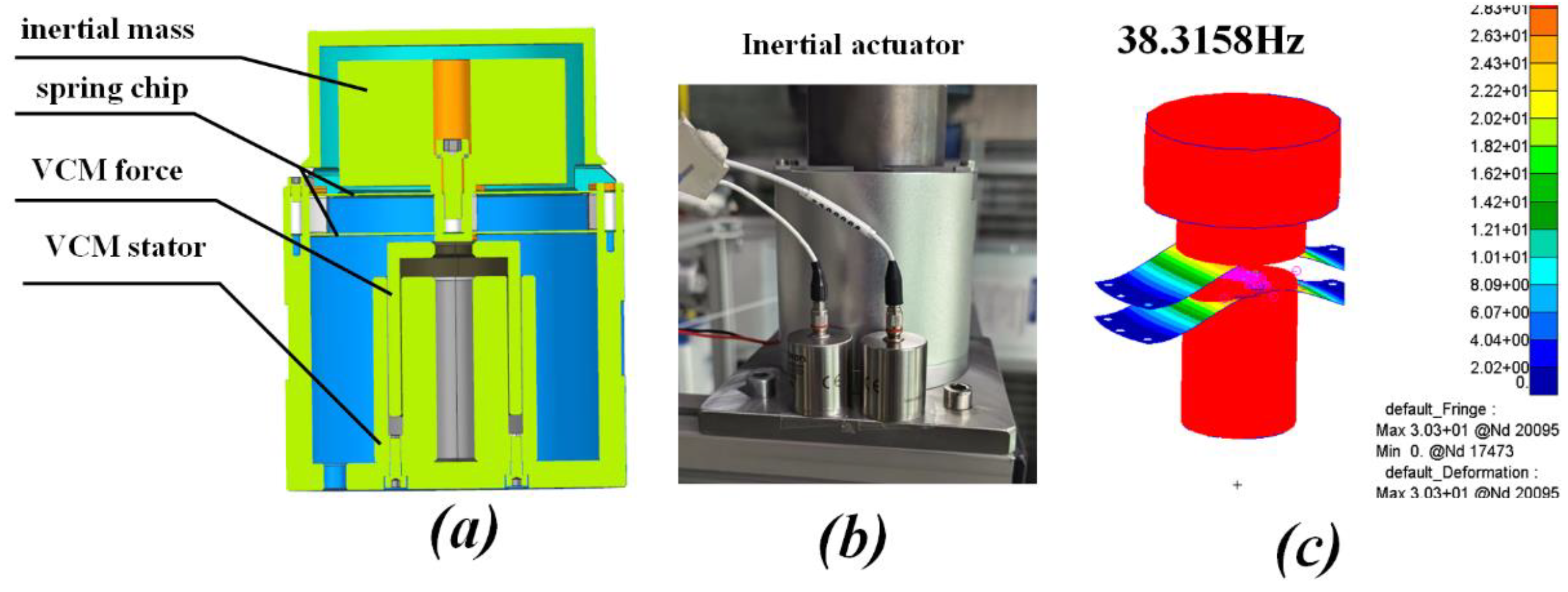
2.2. Mathematical Modeling of Inertial Actuators
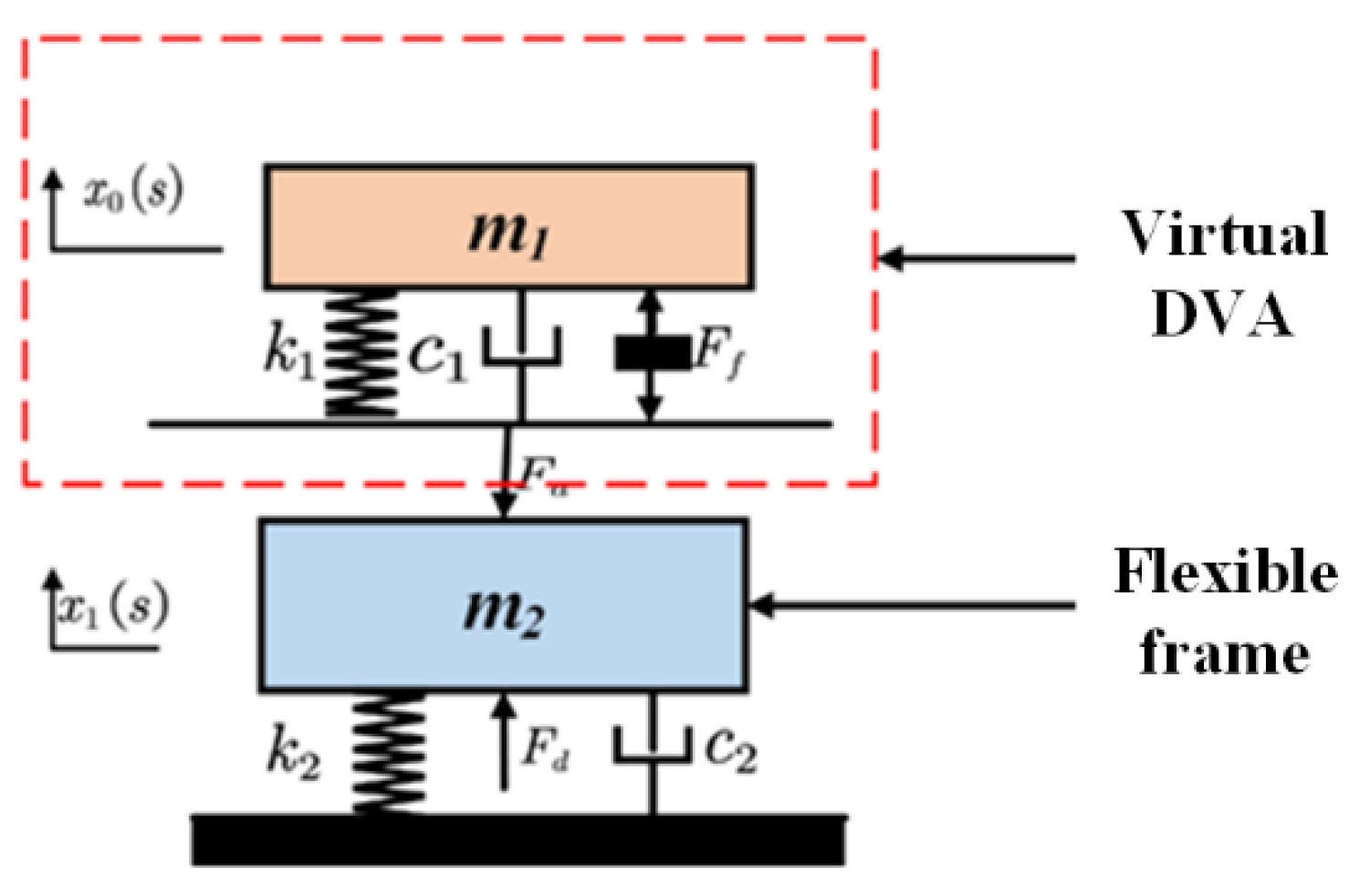
3. Virtual DVA Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Design
3.1. Virtual DVA and Traps
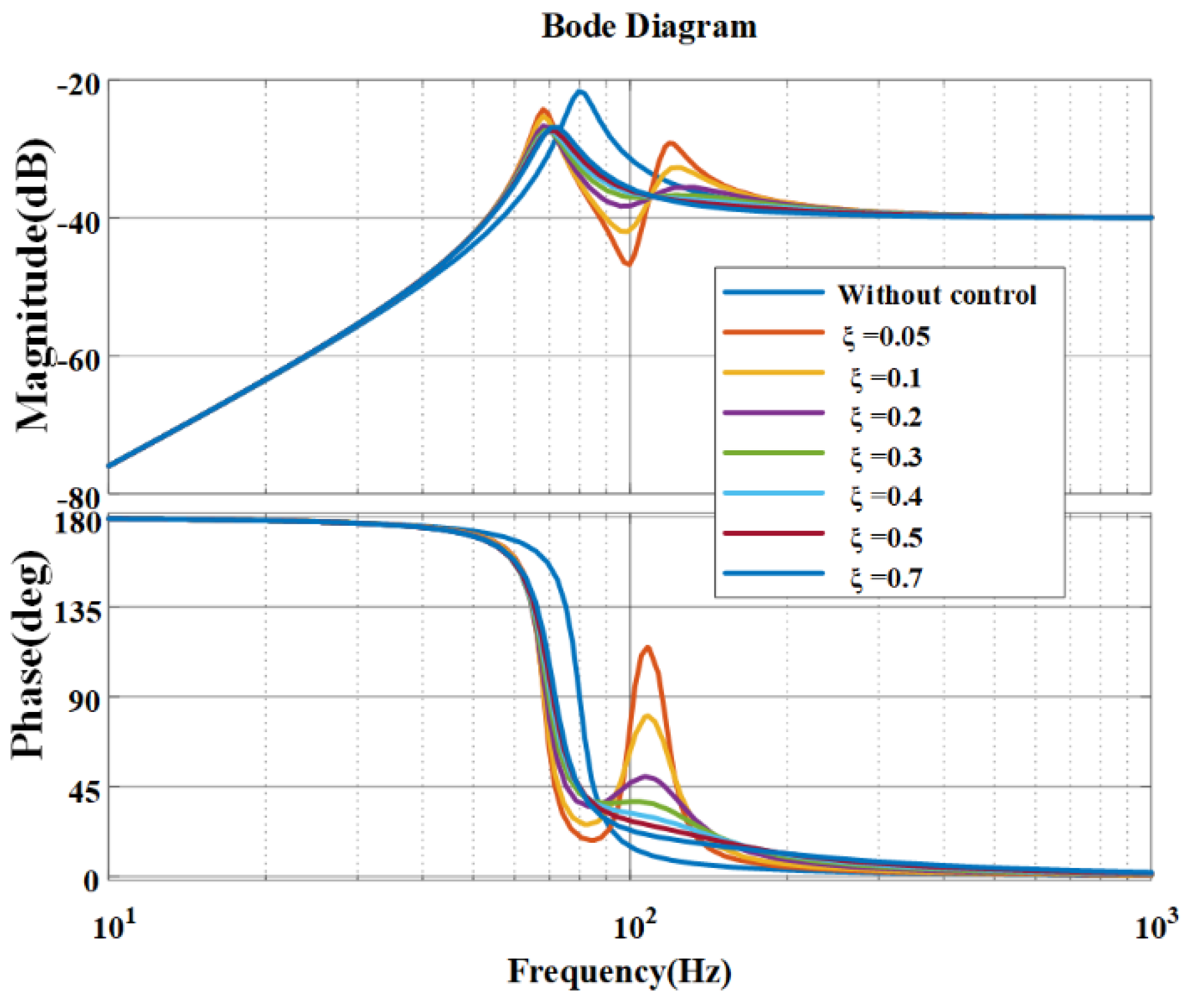
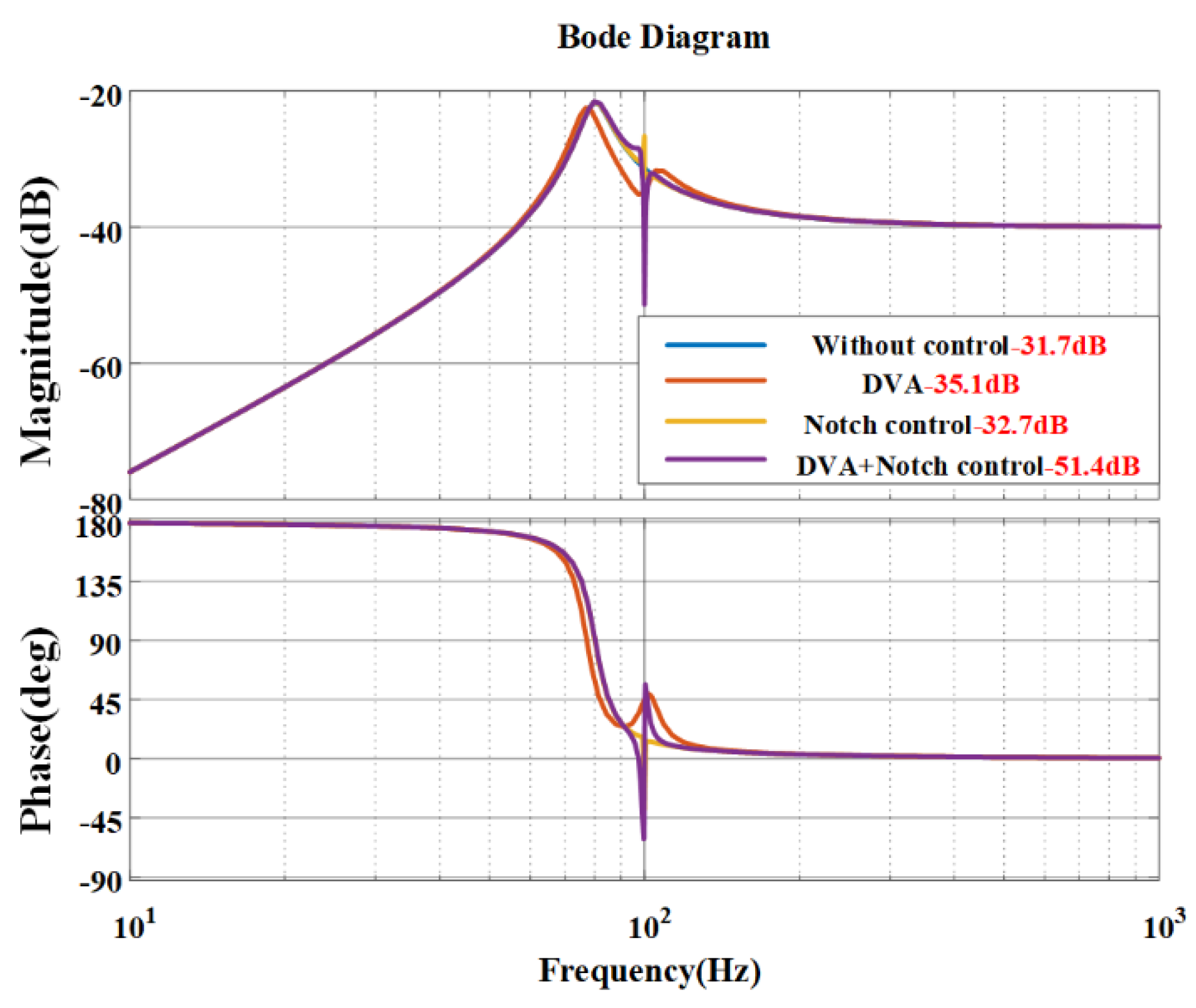
3.2. Parameter Analysis
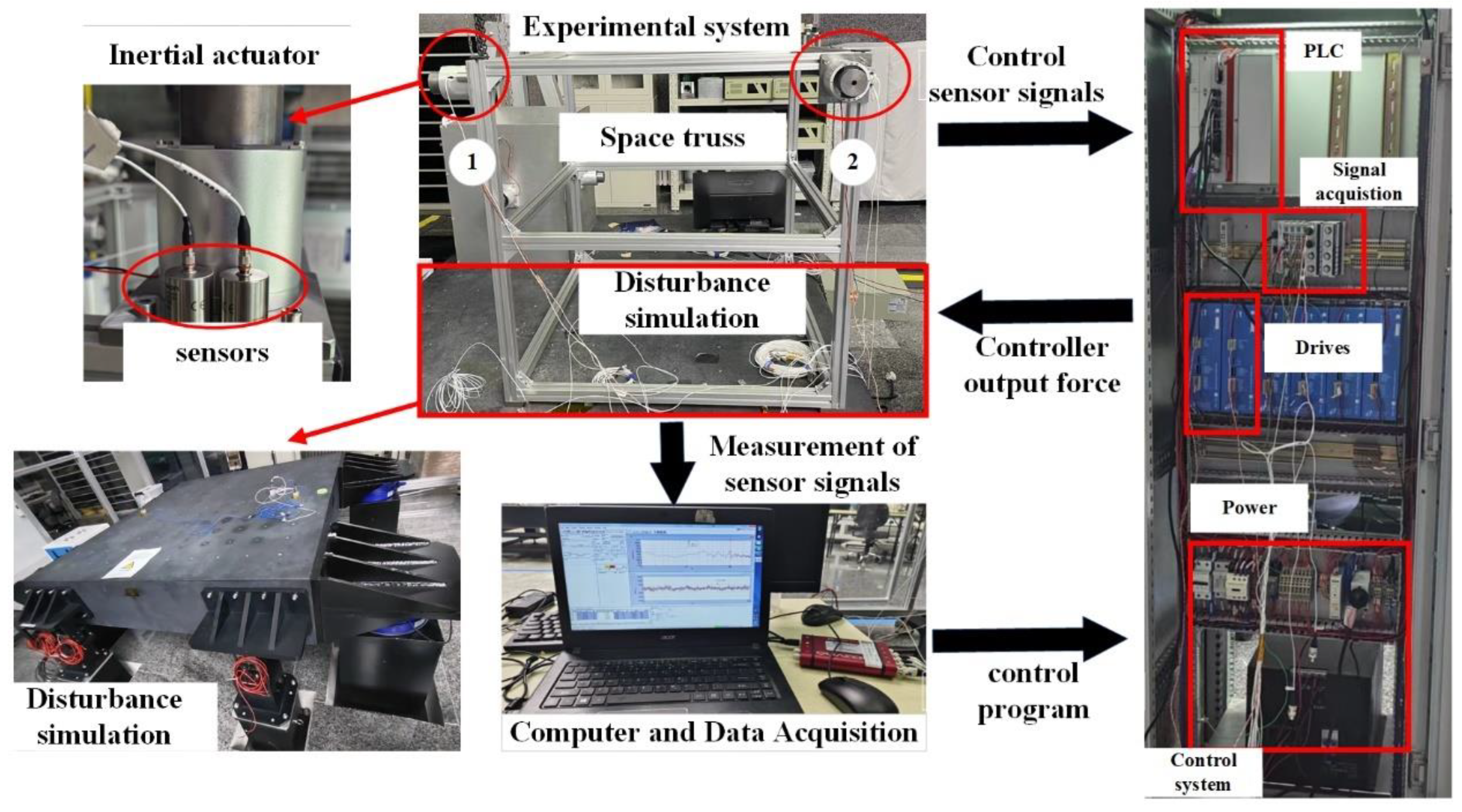
4. Experimental Methods
4.1. The Experimental Equipment Contains the Physical Inertial Exciter
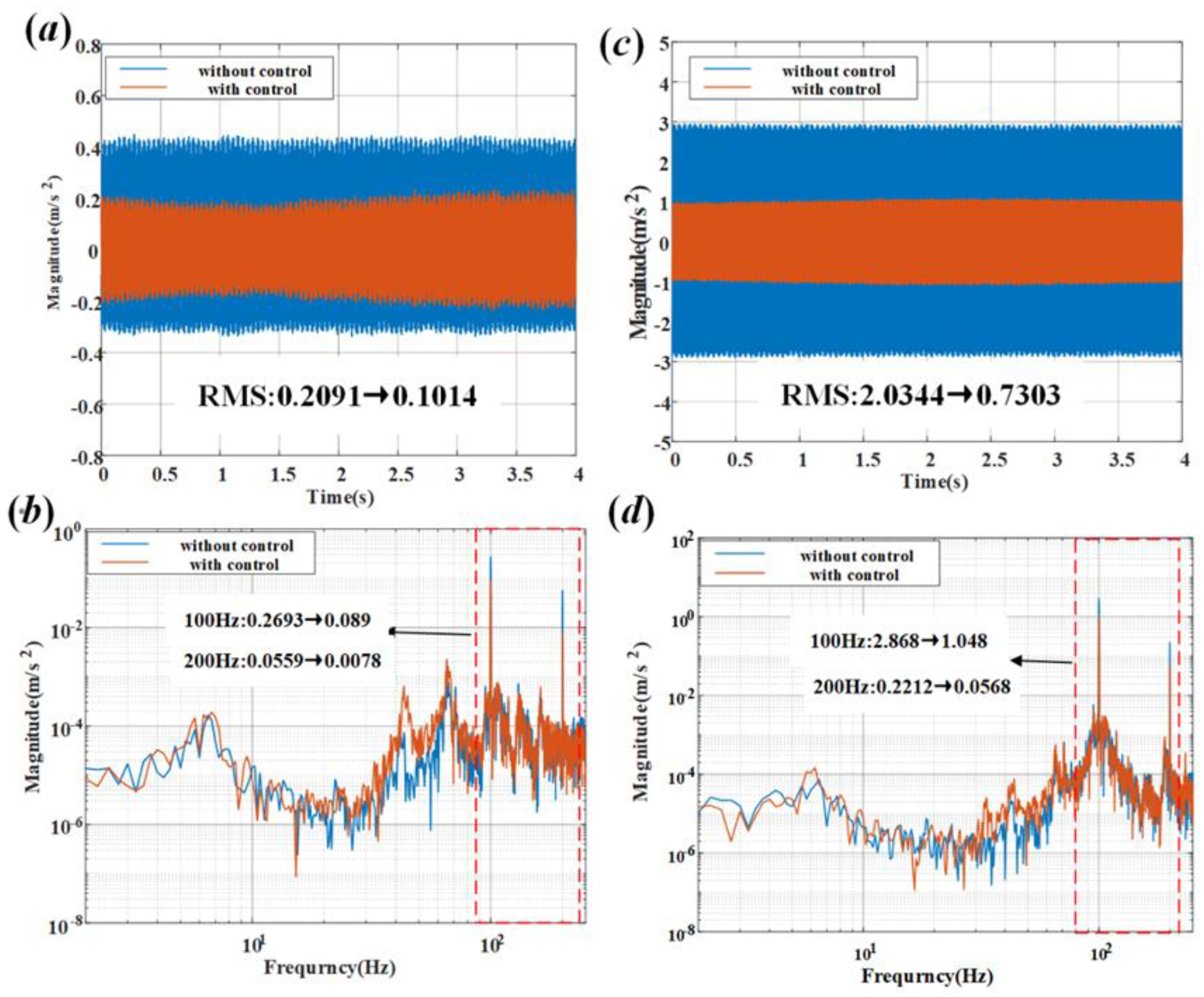
4.2. Truss Vibration Single-Degree-of-Freedom Control Algorithm Realization
4.3. Truss Vibration Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Control Algorithm Realization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, S. Design and Preliminary Ground Experiment for Deployable Sunshade Structures of a Modular Space Telescope. Sensors 2024, 24, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Sai, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z. Modular robotic manipulator and ground assembly system for on-orbit assembly of space telescopes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2024, 238, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Photonics Scanning Pentaprism System for the Integrated Inspection of Large-Aperture Telescopes. Sensors 2023, 23, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R.; Reich, B.J.; Shaby, B.A. Modeling extremal streamflow using deep learning approximations and a flexible spatial process. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2024, 18, 1519–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Pan, C.; Xu, F. The Spatial Structure and Influencing Factors of the Tourism Economic Network in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Tour. Hosp. 2024, 5, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, D.; Luo, Q.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J. Microvibration suppression of space truss structures using viscoelastic dampers with design parameter optimization. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 230, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.A.; Striz, A.G. On using genetic algorithms for optimum damper placement in space trusses. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2004, 28, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, J.; Sano, T.; Minesugi, K. Passive damping of truss vibration using preloaded joint backlash. AIAA J. 1995, 33, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, S.; Matsagar, V. Research developments in vibration control of structures using passive tuned mass dampers. Annu. Rev. Control. 2017, 44, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.T. Numerical investigation of an MR damper-based smart passive control system for mitigating vibration of stay cables. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2011, 37, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramendiz, J.; Fidlin, A. On the vibration control of semi-active friction dampers with piecewise defined contact geometries. Acta Mech. 2023, 234, 6297–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Z.; Hua, X.; Chen, Z. Investigation on vibration mitigation methodology with synergistic friction and electromagnetic damping energy dissipation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 18885–18910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, H.R.; Mirtaheri, M.; Zandi, A.P. The study of frictional damper with various control algorithms. Earthq. Struct. 2017, 12, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Djojodihardjo, H.; Jafari, M.; Wiriadidjaja, S.; Ahmad, K.A. Active vibration suppression of an elastic piezoelectric sensor and actuator fitted cantilevered beam configurations as a generic smart composite structure. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, H.; Ichikawa, H. Robust pole assignment for vibration control of flexible structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2001, 12, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, K.; Ganguli, R. Shape and vibration control of a smart composite plate with matrix cracks. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 18, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Schmidt, S.P.; Agrawal, B.N. Experimental robustness study of positive position feedback control for active vibration suppression. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2002, 25, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Xu, M.; Fu, K.; Ye, L. Active vibration control of a hoop truss structure with piezoelectric bending actuators based on a fuzzy logic algorithm. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 085030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, J. Optimization of actuator placement in a truss-cored sandwich plate with independent modal space control. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Nonprobabilistic reliable LQR design method for active vibration control of structures with uncertainties. AIAA J. 2018, 56, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tian, D.; Huang, H.; Guo, Z.; Feng, Z. Optimal Placements of Actuators and Robust ADP-Based Vibration Control for Large Flexible Space Structures. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.M. Reinforcement learning vibration control of a multi-flexible beam coupling system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Tan, S.; Wu, Z. Distributed cooperative control for vibration suppression of a flexible satellite. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tian, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Optimized placement of piezoelectric actuator for multichannel adaptive vibration control of a stiffened plate. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2022, 35, 04021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Bishop, R.; Agrawal, B. Payload pointing and active vibration isolation using hexapod platforms. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Norfolk, VA, USA, 7–10 April 2003; p. 1643. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Micropositioning and microvibration isolation of a novel hybrid active–passive platform with two-axis actuator for optical payloads. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 204, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliacano, D.; Viscardi, M.; Ciminello, M.; Dimino, I. Feasibility study for a tonal vibration control system of a mounting bracket for automotive gearboxes. Int. J. Mech. 2016, 10, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Magliacano, D.; Viscardi, M.; Dimino, I. Active vibration control by piezoceramic actuators of a car floor panel. In Proceedings of the ICSV23: 23rd International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Athens, Greece, 10–14 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Li, S.; Tan, G.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L. Structural Vibration Suppression Using a Reduced-Order Extended State Observer-Based Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Controller with an Inertial Actuator. Machines 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Yuan, W.; Wu, J. Design and experimental study of a multiple-degree-of-freedom vibration absorber by using an inertial actuator. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024, 24, 2450006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Si, X.; Zhao, Z. A piezoelectric inertial actuator operating with elliptical drive and stick-slip drive modes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 373, 115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airimitoaie, T.-B.; Landau, I.D. Robust and Adaptive Active Vibration Control Using an Inertial Actuator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6482–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Diaz, I.M.; Hudson, E.J.; Reynolds, P. Optimal control-based methodology for active vibration control of pedestrian structures. Eng. Struct. 2014, 80, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Shi, X.; Jin, Y. Variable Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control for Seismic Vibration Suppression of Uncertain Building Structure. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, M.; Delavari, H. Experimental implementation of a novel model-free adaptive fractional-order sliding mode controller for a flexible-link manipulator. Int. J. Adapt. Control. Signal Process. 2021, 35, 1990–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Truss mass | m2 (kg) | 100 |
| Truss stiffness | k2 (N/m) | 2.5266 × 107 |
| Truss damping | c2 (N/(m/s)) | 1000 |
| Disturbed Working Condition | Control Methods | Response RMS (m/s2) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Hz | Without control | 2.9425 |
| 100 Hz | DVA | 0.4933 |
| 100 Hz | DVA + notch | 0.2261 |
| 100 Hz + 150 Hz | Without control | 2.3425 |
| 100 Hz + 150 Hz | DVA | 1.9560 |
| 100 Hz + 150 Hz | DVA + notch | 0.2612 |
| Virtual DVA 1 | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual mass | 5 | |
| Virtual natural frequency | 100 | |
| Virtual damping ratio | 0.05 | |
| Trap frequency | 100 | |
| Trap factor 1 | 0.005 | |
| Trap factor 2 | 0.01 |
| Virtual DVA 1 | Symbol | Value | Virtual DVA 2 | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual mass | 5 | Virtual mass | 5 | ||
| Virtual natural frequency | 100 | Virtual natural frequency | 200 | ||
| Virtual damping ratio | 0.05 | Virtual damping ratio | 0.05 | ||
| Trap frequency | 100 | Trap frequency | 200 | ||
| Trap factor 1 | 0.005 | Trap factor 1 | 0.005 | ||
| Trap factor 2 | 0.01 | Trap factor 2 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, C.; Xu, A.; He, S.; Han, C.; Xu, Z. Virtual Dynamic Vibration Absorber Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Based on Inertial Actuators for Large Flexible Space Trusses. Aerospace 2024, 11, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090764
Qin C, Xu A, He S, Han C, Xu Z. Virtual Dynamic Vibration Absorber Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Based on Inertial Actuators for Large Flexible Space Trusses. Aerospace. 2024; 11(9):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090764
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Chao, Anpeng Xu, Shuai He, Chunyang Han, and Zhenbang Xu. 2024. "Virtual Dynamic Vibration Absorber Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Based on Inertial Actuators for Large Flexible Space Trusses" Aerospace 11, no. 9: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090764
APA StyleQin, C., Xu, A., He, S., Han, C., & Xu, Z. (2024). Virtual Dynamic Vibration Absorber Trap Fusion Active Vibration Suppression Algorithm Based on Inertial Actuators for Large Flexible Space Trusses. Aerospace, 11(9), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090764






