Study on the Improvement of Theoretical and Electric Field Simulation Methods for the Accurate Prediction of FEEP Thruster Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
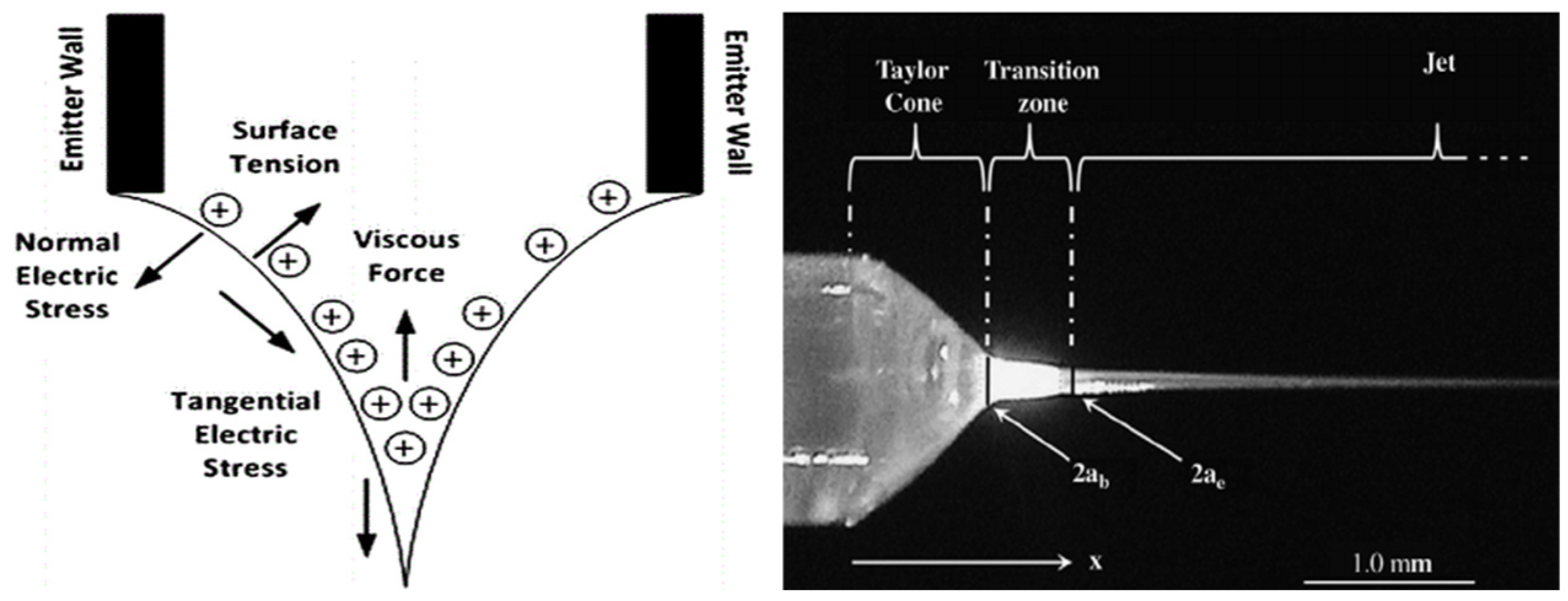
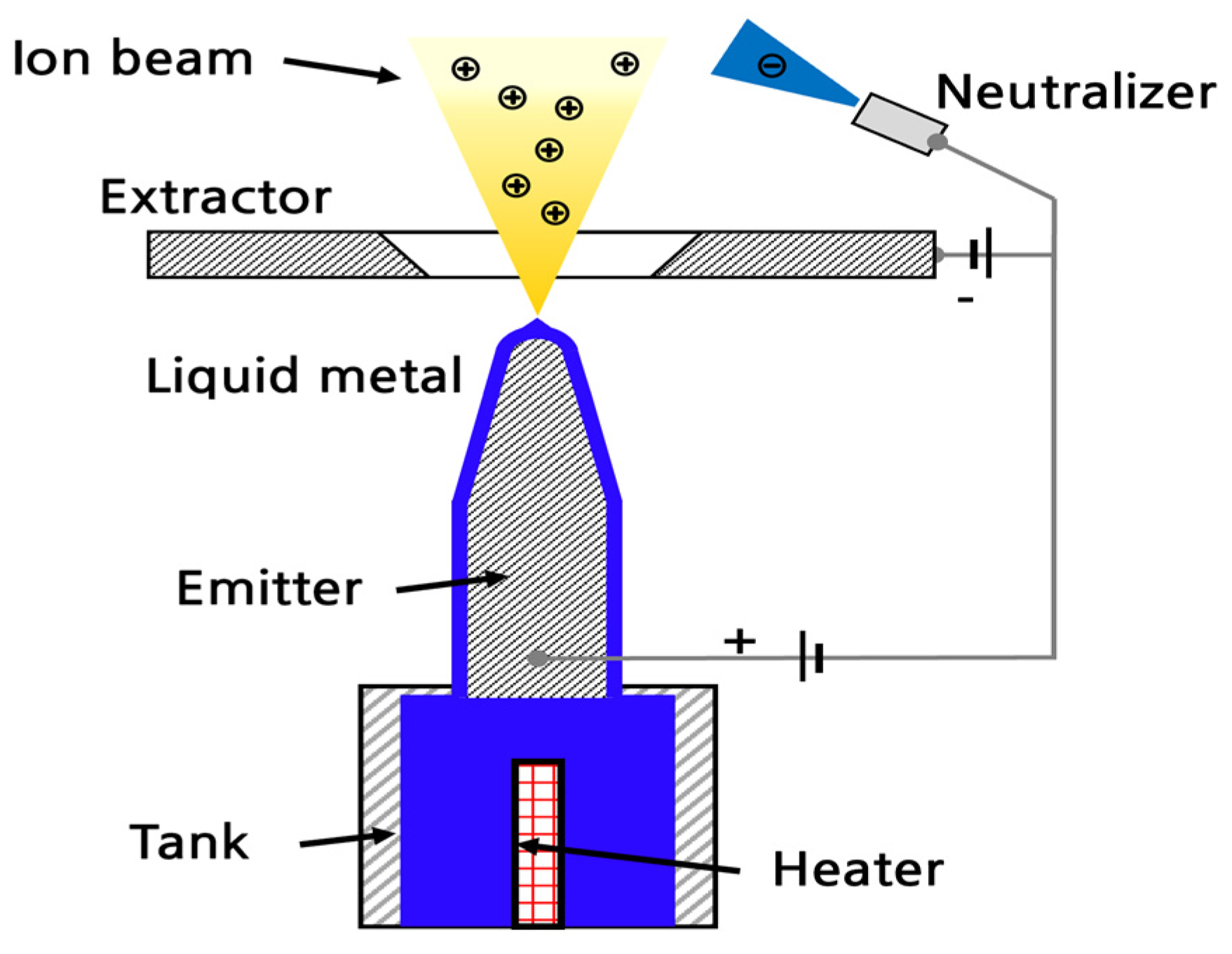
2. Principle and Theoretical Methods of FEEP Thruster
2.1. Working Principle
2.2. Previous Theoretical Methods
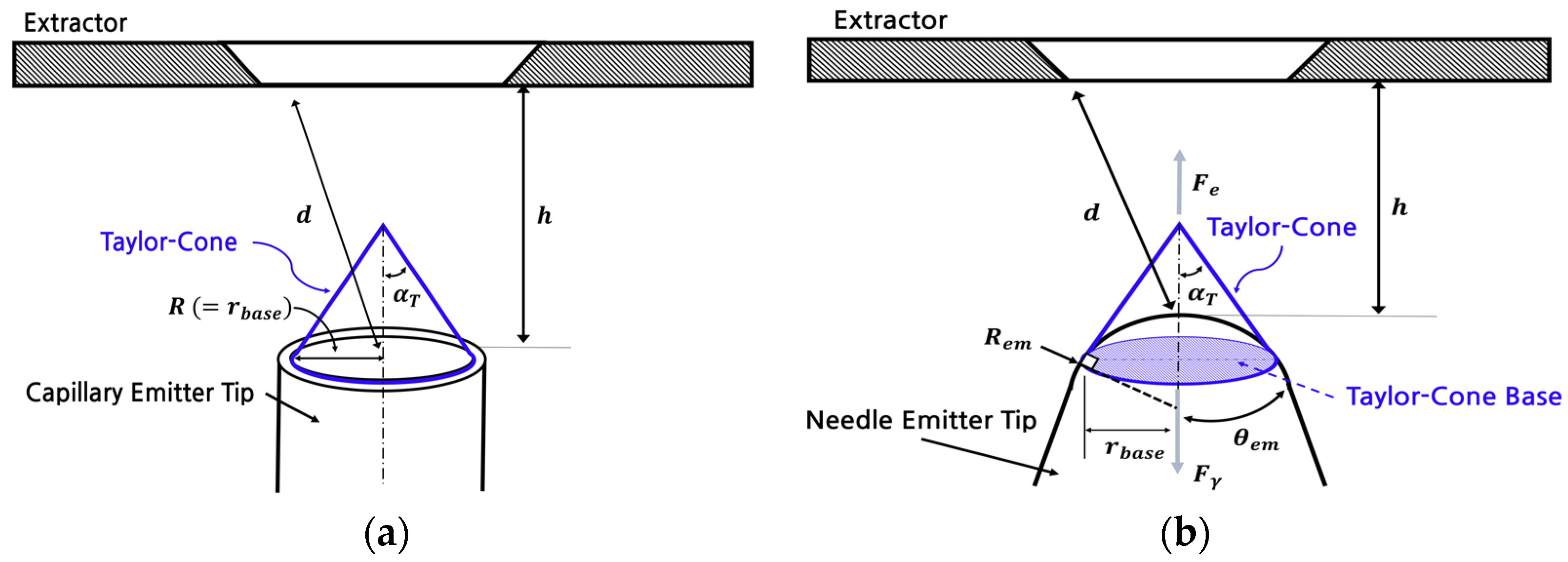
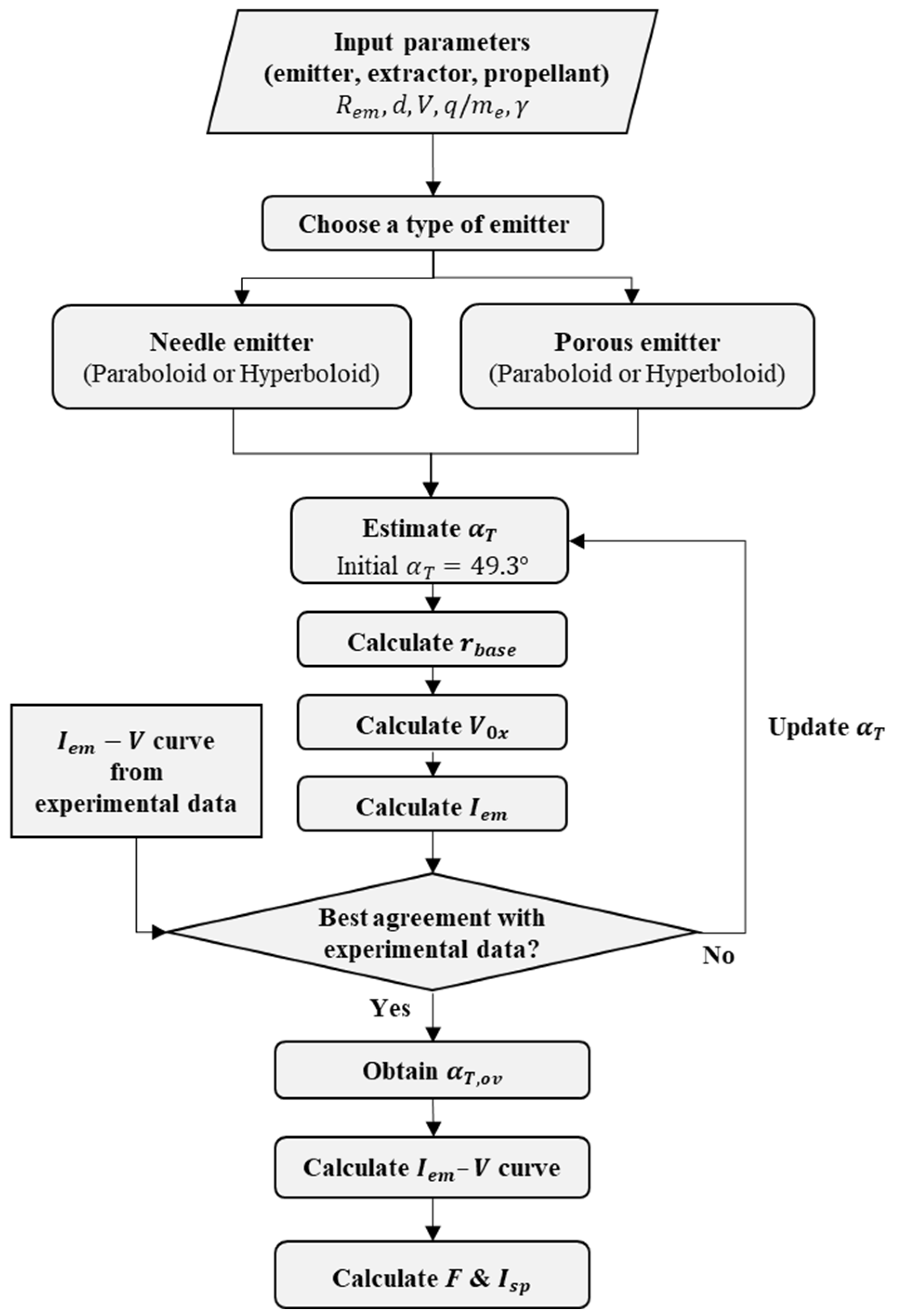
3. Improved Theoretical Method
3.1. Overview and Method
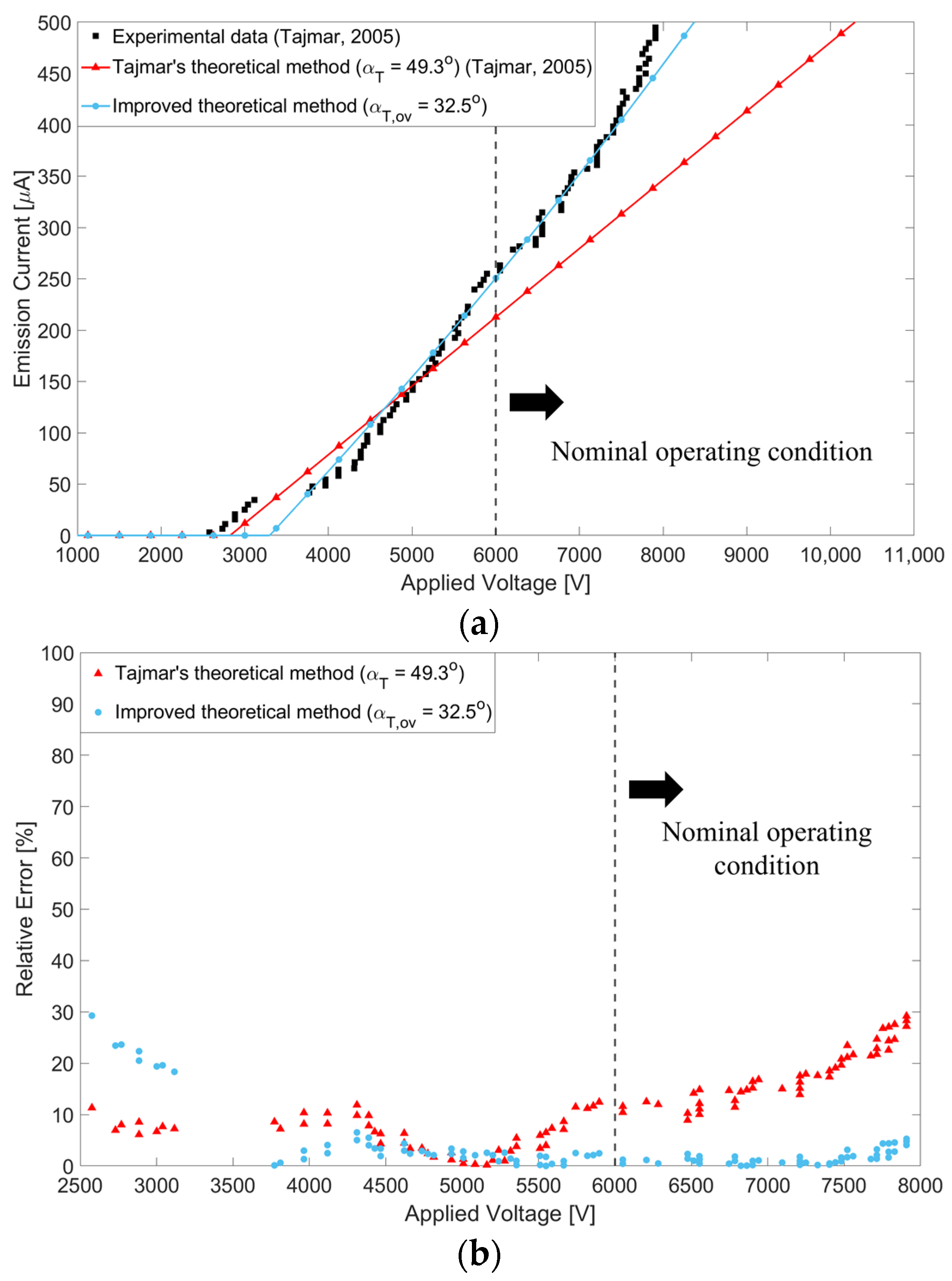
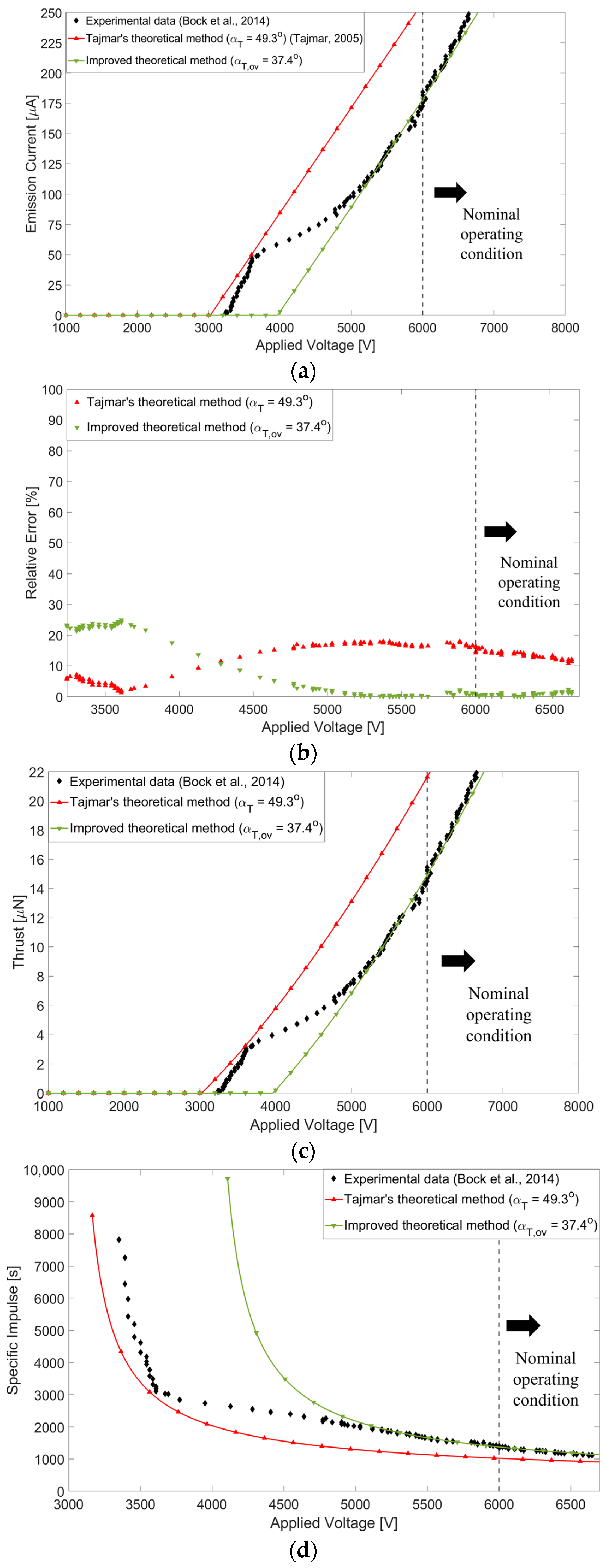
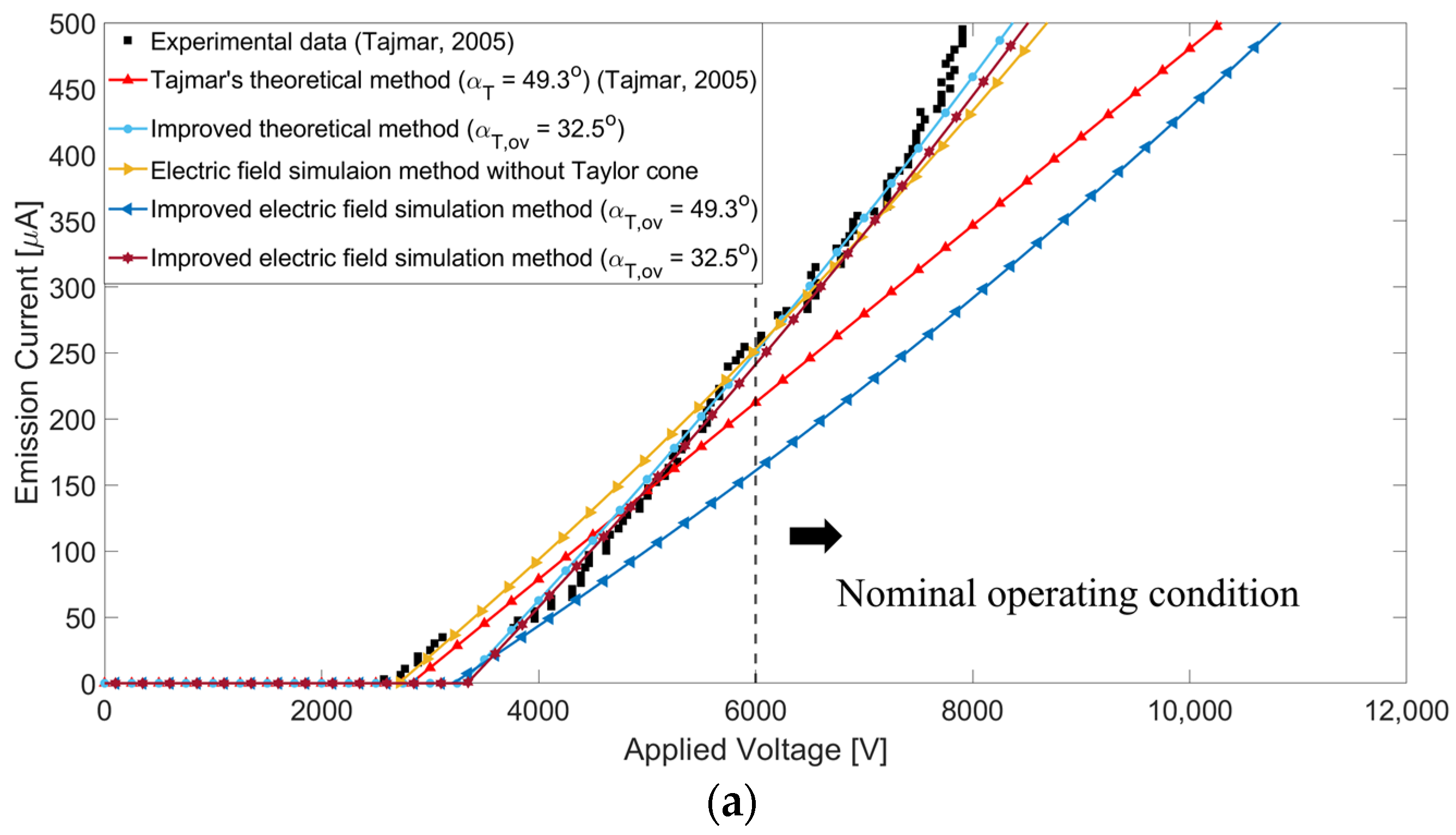
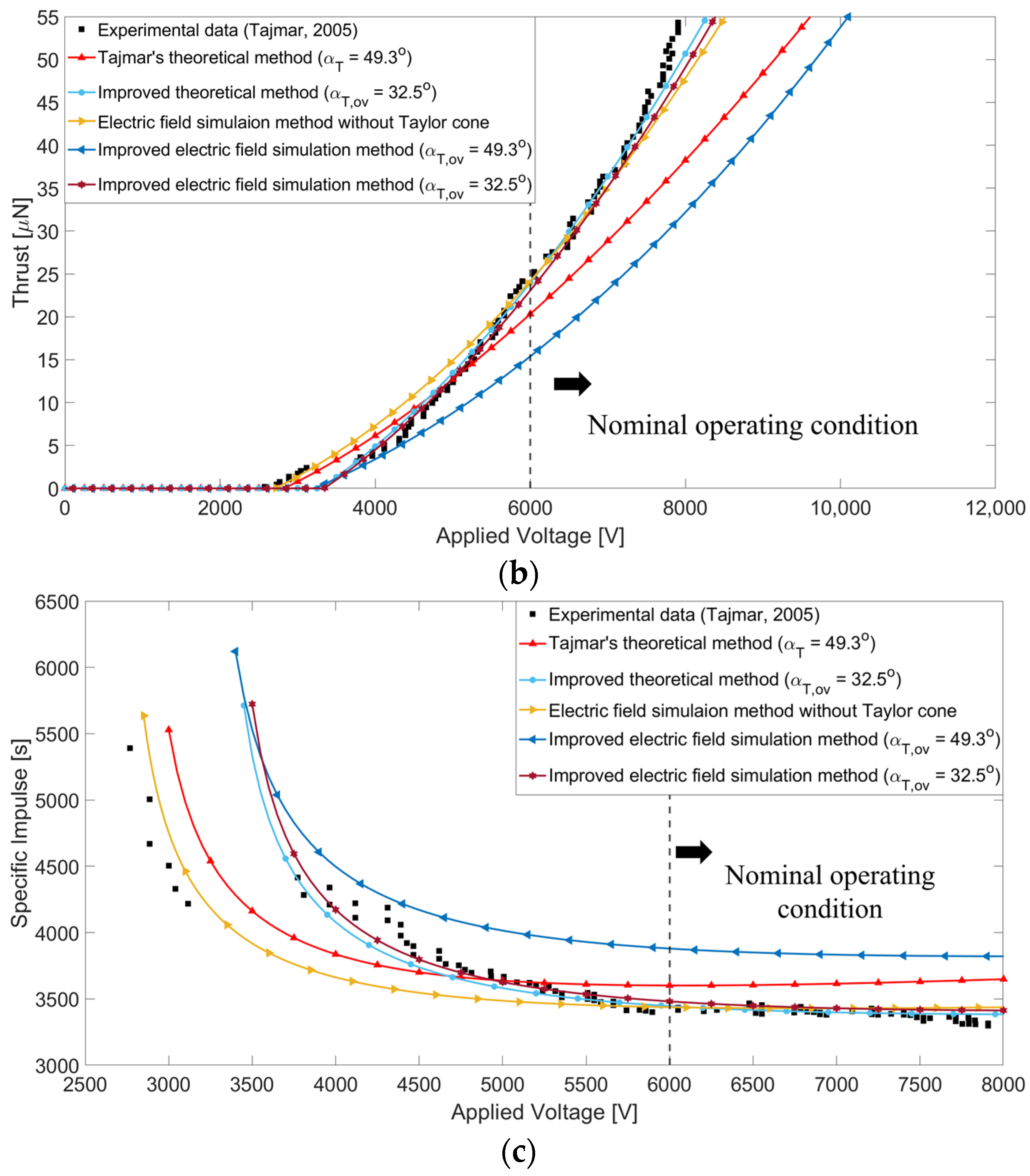
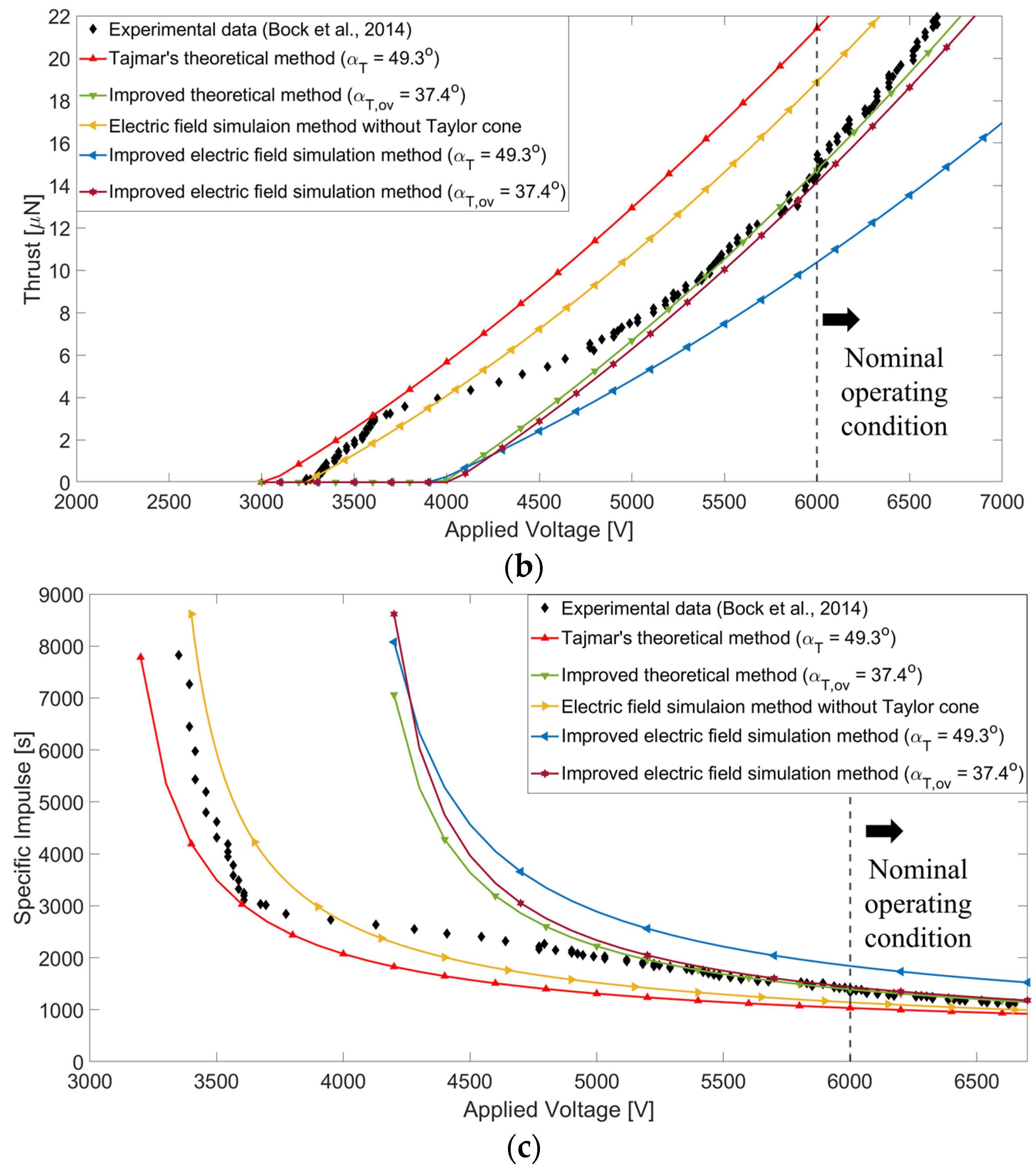
3.2. Results
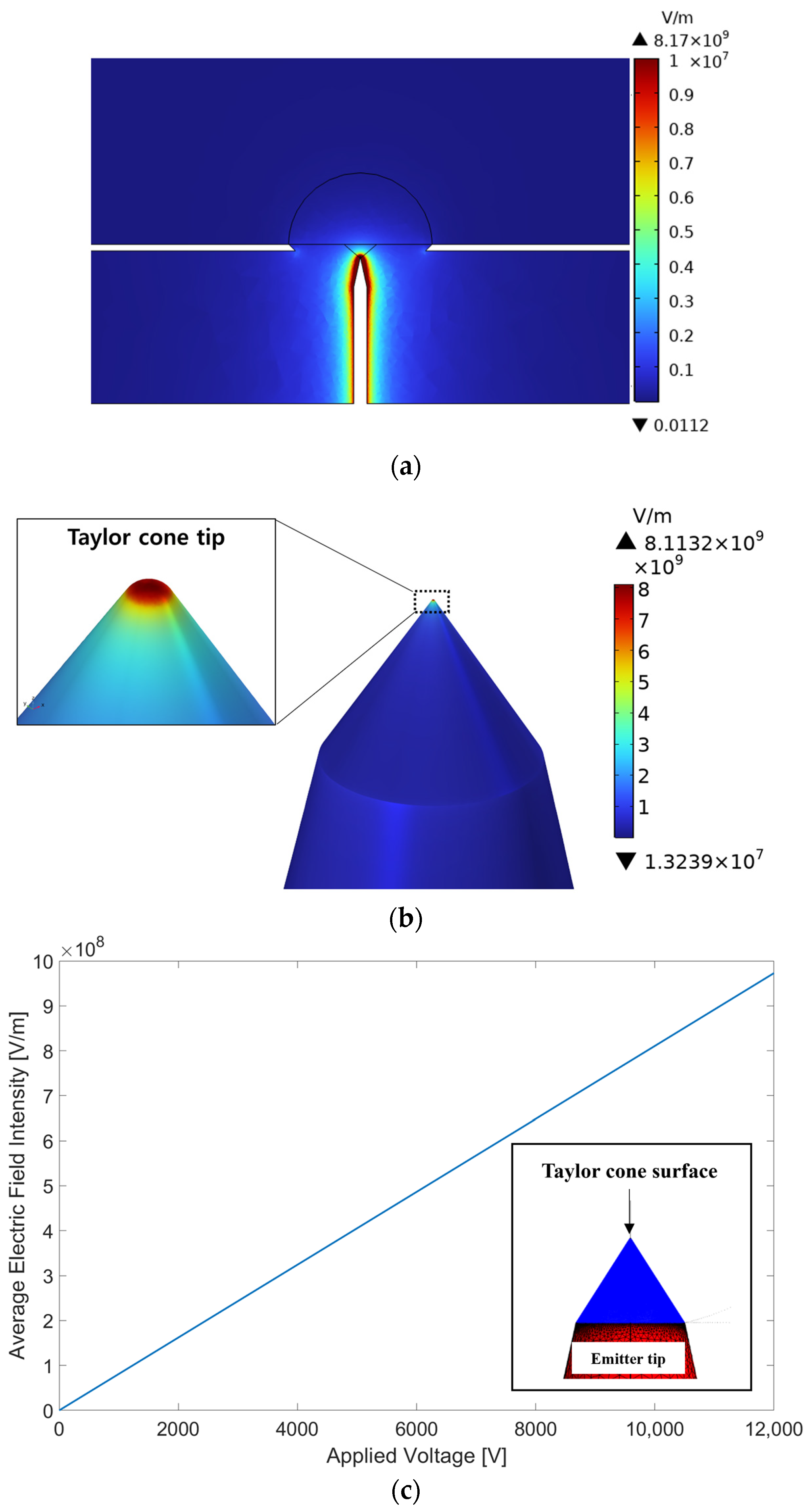
4. Improved Electric Field Simulation Method
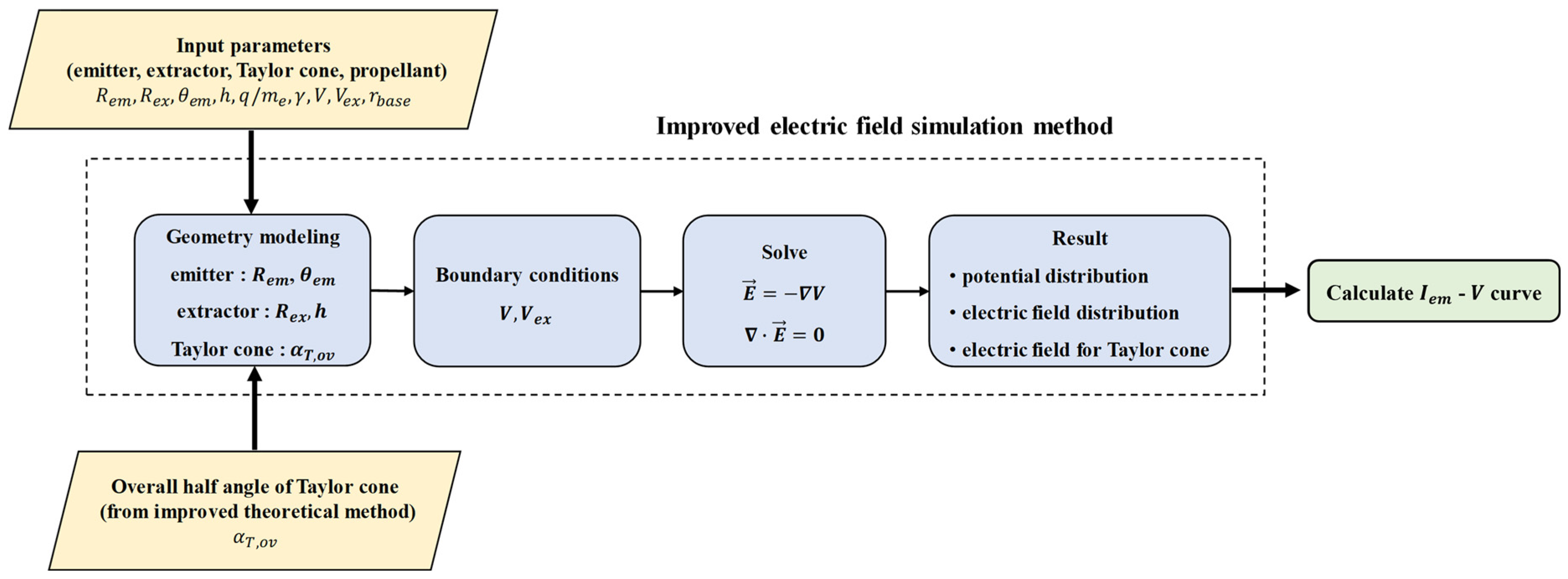
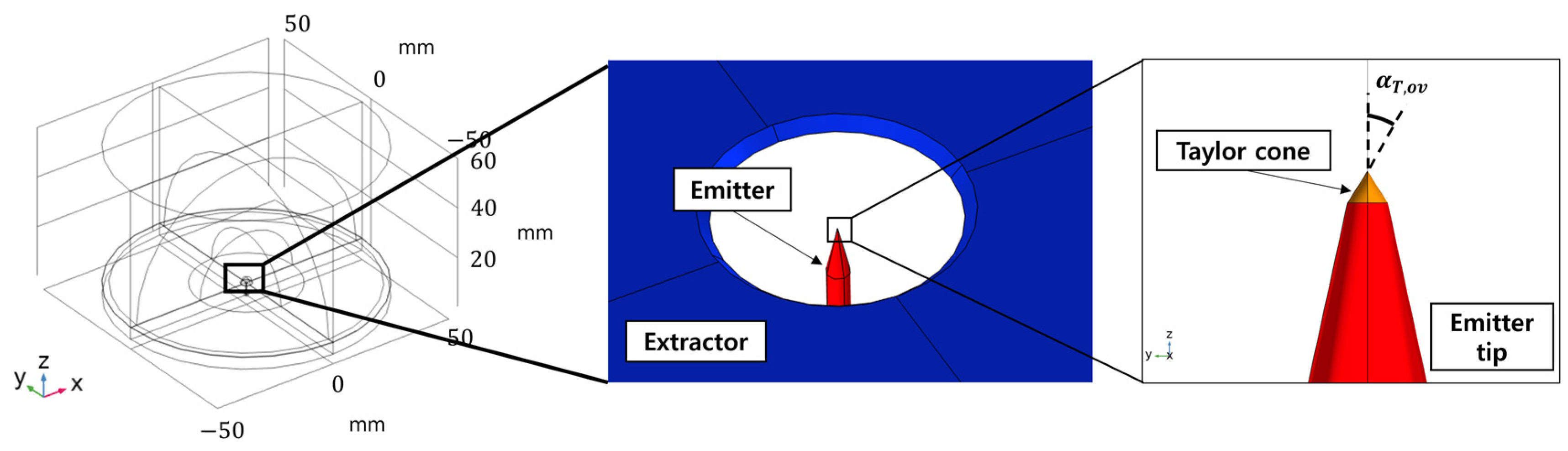
4.1. Overview and Method
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| amu | atomic mass unit, 1.66054 × 10−27 kg |
| d | straight distance between an emitter tip and an extractor, m |
| E | electric field, V/m |
| Eavg | average value of electric field, V/m |
| F | thrust, N |
| f | thrust factor |
| Fe | electric field force at the Taylor cone base, N |
| Fγ | surface tension force at the Taylor cone base, N |
| h | vertical distance between an emitter tip and an extractor, m |
| Iem | emission current, A |
| Isp | specific impulse, s |
| k | numerical constant |
| me | ion mass of liquid metal propellant, kg |
| g | gravitational acceleration, 9.81 m/s2 |
| q | electric charge of ion, 1.60218 × 10−19 C |
| R | inner radius of capillary emitter, m |
| Rem | radius of emitter tip, m |
| Rex | radius of extractor, m |
| rbase | radius of Taylor cone base, m |
| V | applied voltage, V |
| V0 | onset or starting voltage, V |
| V0x | extinction voltage, V |
| Vex | extractor voltage, V |
| Greek symbols | |
| αT | Taylor cone half angle |
| αT,ov | overall Taylor cone half angle |
| ε0 | vacuum permittivity, 8.85419 × 10−12 F/m |
| γ | surface tension, N/m2 |
| emitter tip half angle, ° | |
References
- Alnaqbi, S.; Darfilal, D.; Swei, S.S.M. Propulsion technologies for CubeSats: Review. Aerospace 2024, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrenucci, M.; Marcuccio, S.; Spagli, L.; Genovese, A.; Repola, F. Experimental study of FEEP emitter starting characteristics. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Electric Propulsion Conference, Viareggio, Italy, 14–17 October 1991; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuccio, S.; Giannelli, S.; Andrenucci, M. Attitude and orbit control of small satellites and constellations with feep thrusters. In Proceedings of the 25th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 24–28 August 1997; pp. 1152–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuccio, S.; Genovese, A.; Andrenucci, M. Experimental performance of field emission microthrusters. J. Propuls. Power 1998, 14, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, D.; Chesta, E.; Gonzalez del Amo, J.; Saccoccia, G.; Hughes, E.B.; Oldfield, S. FEEP-5 thrust validation in the 10–100 µN range with a simple nulled-pendulum thrust stand: Integration procedures. In Proceedings of the 27th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Pasadena, CA, USA, 15–19 October 2001; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Paita, L.; Ceccanti, F.; Spurio, M.; Cesari, U.; Priami, L.; Nania, F.; Rossodivita, A.; Andrenucci, M. Alta’s FT-150 FEEP microthruster: Development and qualification status. In Proceedings of the 31st International Electric Propulsion Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tajmar, M.; Scharlemann, C.; Genovese, A.; Buldrini, N.; Steiger, W.; Vasiljevich, I. Liquid-metal-ion source development for space propulsion at ARC. Ultramicroscopy 2009, 109, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljevich, I.; Tajmar, M.; Grienauer, W.; Plesescu, F.; Buldrini, N.; Gonzalez del Amo, J.; Carnicero Domunguez, B.; Betto, M. Development of an indium mN FEEP thruster. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Hartford, CT, USA, 21–23 July 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Krejci, D.; Reissner, A.; Schönherr, T.; Koch, Q.; Hugonnaud, V.; Grimaud, L.; Vogel, T.; Seifert, B. Informing FEEP thruster design utilizing the flight heritage from 167 thrusters in LEO and GEO. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tajmar, M.; Genovese, A.; Steiger, W. Indium field emission electric propulsion microthruster experimental characterization. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmar, M. Influence of Taylor cone size on droplet generation in an indium liquid metal ion source. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 81, 1447–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmar, M. Development of a lifetime prediction model for indium FEEP thrusters. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, D.; Bethge, M.; Tajmar, M. Highly miniaturized FEEP thrusters for CubeSat applications. In Proceedings of the 4th Spacecraft Propulsion Conferences, Cologne, Germany, 19–22 May 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Oleschuk, R.D.; Cann, N.M. Characterization of microstructured fibre emitters: In pursuit of improved nano electrospray ionization performance. Analyst 2012, 137, 4150–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R.; Khraisheh, M. Electrospun metallic nanowires: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 171301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelem, D.; Seifert, B.; Sypniewski, R.; Buldrini, N.; Reissner, A. Performance mapping and qualification of the IFM Nano thruster FM for in orbit demonstration. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, B.S.; Dressler, R.A.; Chiu, Y.-h.; Fedkiw, T. Electrospray Propulsion Engineering Toolkit (ESPET). Aerospace 2020, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, G.L.R. Theoretical determination of current-voltage curves for liquid metal ion sources. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1984, 17, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, R.A.; Peter, B.S. Electrospray Propulsion Engineering Toolkit, ESPET 1.0; Spectral Sciences, Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Disintegration of water drop in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math Phys. Sci. 1964, 280, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Driesel, W.; Dietzsch, C.; Möser, M. In situ HV TEM observation of the tip shape of lead liquid metal ion sources. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENPULSION GmbH. ENPULSION NANO Thruster Product Data Sheet; ENPULSION GmbH.: Wien-Flughafen, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]




| Emitter Type | Rem [μm] | d [mm] | Liquid Metal Propellant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | me [kg] | γ [N/m] | |||
| Needle emitter [11] | 3.4504 | 2 | Indium | 1.9066 × 10−25 | 0.5607 |
| Porous emitter [13] | 3 | 1.9 | Gallium | 1.1578 × 10−25 | 0.7226 |
| Emitter Type | Geometry | Boundary Condition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rem [μm] | Rex [mm] | αT,ov [°] | θem [°] | h [mm] | V [kV] | Vex [kV] | |
| Needle emitter [11] | 3.4504 | 2 | 32.5 | 12.5 | 0.2 | 0–12 | 0 |
| Porous emitter [13] | 3 | 1.9 | 37.4 | 16 | 0.5 | 3–7 | |
| Emitter Type | Average Relative Errors of Iem − V Relations with Experiments [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tajmar’s Theoretical Method | Improved Theoretical Method | Electric Field Simulation Without Taylor Cone | Electric Field Simulation with Taylor Cone (αT = 49.3°) | Improved Electric Field Simulation (αT,ov = 32.5°/37.4°) | |
| Needle emitter | 12.273 | 1.940 | 5.325 | 21.539 | 2.320 |
| Porous emitter | 15.267 | 0.752 | 9.064 | 11.212 | 2.068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Lee, K.H.; Kuk, J.; Ko, H.S. Study on the Improvement of Theoretical and Electric Field Simulation Methods for the Accurate Prediction of FEEP Thruster Performance. Aerospace 2024, 11, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090716
Shin J, Lee KH, Kuk J, Ko HS. Study on the Improvement of Theoretical and Electric Field Simulation Methods for the Accurate Prediction of FEEP Thruster Performance. Aerospace. 2024; 11(9):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090716
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jeongsik, Kyun Ho Lee, Jungwon Kuk, and Han Seo Ko. 2024. "Study on the Improvement of Theoretical and Electric Field Simulation Methods for the Accurate Prediction of FEEP Thruster Performance" Aerospace 11, no. 9: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090716
APA StyleShin, J., Lee, K. H., Kuk, J., & Ko, H. S. (2024). Study on the Improvement of Theoretical and Electric Field Simulation Methods for the Accurate Prediction of FEEP Thruster Performance. Aerospace, 11(9), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11090716