Abstract
In the vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) state of tiltrotor aircraft, the inlet entrance encounters the incoming airflow at a 90° attack angle, resulting in highly complex internal flow characteristics that are extremely susceptible to gusts. Meanwhile, the flow quality at the inlet exit directly affects the performance of the aircraft’s engine. This work made use of an unsteady numerical simulation method based on sliding meshes to investigate the internal flow characteristics of the inlet during the hover state of a typical tiltrotor aircraft and the effects of head-on gusts on the inlet’s aerodynamic characteristics. The results show that during the hover state, the tiltrotor aircraft inlet features three pairs of transverse vortices and one streamwise vortex at the aerodynamic interface plane (AIP). The transverse vortices generated due to the rotational motion of the air have the largest scale and exert the strongest influence on the inlet’s performance, which is characterized by pronounced unsteady features. Additionally, strong unsteady characteristics are present within the inlet. Head-on gusts mainly affect the mechanical energy and non-uniformity of the air sucked into the inlet by influencing the direction of the rotor’s induced slipstream, thereby impacting the performance of the inlet. The larger head-on gusts have beneficial effects on the performance of the inlet. When the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, there is a 1.01% increase in the total pressure recovery (σ) of the inlet, a 25.72% decrease in the circumferential distortion index (DC60), and a reduction of 62.84% in the area where the swirl angle |α| exceeds 15°. Conversely, when the gust velocity of head-on gusts reaches 12 m/s in the opposite direction, the inlet’s total pressure recovery decreases by 1.13%, the circumferential distortion index increases by 14.57%, and the area where the swirl angle exceeds 15° increases by 69.59%, adversely affecting the performance of the inlet. Additionally, the presence of gusts alters the unsteady characteristics within the inlet.
1. Introduction
Tiltrotor aircraft are a distinctive type of aircraft that combines the high-speed cruising capabilities of fixed-wing airplanes with the vertical takeoff and landing capabilities of helicopters. Such aircraft have a higher flight speed and larger payload than a helicopter and a wider speed envelope than a fixed-wing aircraft. Because of these features, tiltrotor aircraft are anticipated to be useful in both military and civil applications [1,2,3,4,5]. However, current research on tiltrotor aircraft primarily focuses on the aerodynamic interference between rotors and wings [6,7,8], the aerodynamic interference between rotors and the fuselage [9,10], the ground effect [11,12,13], and other related topics. There is a notable scarcity of studies exploring the influence of environmental factors on tiltrotor aircraft.
Gusts are a common weather phenomenon encountered by aircraft during operation and have a significant impact on both the aircraft and its engine [14,15]. Over the past few decades, there have been hundreds of flight safety incidents attributed to gusts [16]. As early as 1915, Hunsaker and Wilson noted the effects of gusts on aircraft flight [17]. Subsequently, researchers began to focus on the effects of gusts on various components of the aircraft, primarily in the area of external airflow around aircraft. Relevant research has shown that gusts not only affect lift components such as wings and horizontal stabilizers but also increase aerodynamic and structural loads, ultimately impacting the structural lifespan of the aircraft [18]. Since tiltrotor aircraft often operate in various complex environments, including gusty conditions, it is essential to consider the influence of gusts on these aircraft during their development and flight operation.
The inlet serves as the foremost component of an aircraft’s propulsion system and significantly affects engine performance through the quality of its exhaust airflow. Research indicates that a 1% decrease in the total pressure recovery coefficient at the inlet exit typically yields about a 1.25% loss in engine thrust. Moreover, non-uniform pressure distribution at the inlet exit directly affects the flow conditions at the compressor inlet, thereby narrowing the compressor’s operating range and limiting the aircraft’s operational and flight envelopes [19]. Several researchers have conducted relevant studies on the tiltrotor aircraft inlet. Paynter, G.C. [20] described the design methodology of an inlet for the V-22 “Osprey” tiltrotor aircraft and evaluated it through testing, effectively demonstrating the validity of the design approach. A. Garavello [21] conducted simulation calculations on the ERICA tiltrotor aircraft under cruising conditions. G. Gibertini [22] provided a detailed overview of establishing a wind tunnel test platform to evaluate the effectiveness of optimizing an inlet for the ERICA tiltrotor aircraft using CFD methods. Experiments assessed the inlet of the ERICA tiltrotor aircraft under 0.15 Ma inflow conditions, showing significant improvements in performance in both cruising and transition states after optimization [23]. Remco Habing [24] designed and manufactured a full-scale inlet duct model for wind tunnel experiments, simulating variations in parameters under full flight conditions for the NGTRC tiltrotor aircraft. The results indicated the presence of two low-pressure areas at the top of the AIP at the exit of the inlet, with significant values of observed in this region. The velocity field contained two recirculation regions caused by a pair of opposing vortices. As the inlet serves as the foremost component of the propulsion system for tiltrotor aircraft, any changes in incoming airflow can potentially alter engine performance. Gusts can easily degrade the quality of airflow entering the inlet, potentially affecting the performance of the entire aircraft.
However, no scholarly research has explored the effects of gusts on the tiltrotor aircraft inlet, and only a few researchers have more generally considered the effects of gusts on inlets. Sun [25] conducted a comprehensive study on the flow field and aerodynamic characteristics of a serpentine duct under horizontal periodic gust conditions. The study revealed that gusts not only significantly altered the internal flow structure of the serpentine inlet duct but also had an adverse effect on the total pressure distortion of the inlet. The authors found that the presence of gusts had a strong influence on the flow characteristics inside the inlet and its performance. However, tiltrotor aircraft often operate in complex environments, making their inlets more susceptible to the effects of gusts, resulting in a more complex internal flow field. Therefore, it is necessary to study the flow properties inside the inlet of a tiltrotor under gusty environments.
The present study investigates the internal flow of the tiltrotor aircraft inlet under the influence of gusts during hovering and aims to evaluate the effect of gusts on the inlet. The results of this work will provide support for the design and development of tiltrotor aircraft inlets, thereby facilitating their safety and stability.
2. Theory and Methodology
2.1. Model Introduction
Figure 1 shows the model investigated in the present study. This model consists of three parts: the rotor, the nacelle, and the inlet. The rotor selected for the research model employs a XV-15 rotor blade profile, which has been publicly disclosed [5,26]. The relevant parameters are provided in Table 1. The nacelle has a streamlined design to reduce aerodynamic drag and enhance flight efficiency. The inlet is a single-scoop type whose main parameters are listed in Table 2. The inlet is smoothly connected to the nacelle via a lip. Due to the vertical offset between the turbo-prop engine inlet and inlet entrance, the inlet is forced to connect to the aerodynamic interface plane (AIP) in an “S” shape. Additionally, since tiltrotor aircraft frequently operate in dusty environments, the inlet is equipped with a scavenge duct to expel foreign objects. The lip is characterized by a sharp profile to optimize aerodynamic performance and reduce flight drag at cruise conditions.
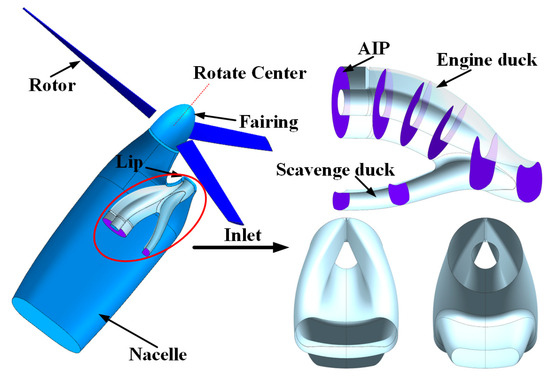
Figure 1.
Geometric models and detailed inlet features.

Table 1.
Geometrical parameters of the tiltrotor aircraft rotor.

Table 2.
Geometrical parameters of the tiltrotor aircraft inlet.
A boundary layer diverter is installed between the rotating system and the inlet lip, preventing the inlet from ingesting the nacelle boundary layer disturbed by the rotor.
2.2. Performance Parameter Definitions
We evaluated the exit performance of the inlet using three common parameters: total pressure recovery coefficient (), circumferential distortion index (), and swirl angle ().
- (1)
- is defined aswhere is the total pressure of the freestream, and is the mass flow weighted average total pressure at the AIP.
- (2)
- is defined aswhere is the minimum value of the mass flow weighted average total pressure over any 60° sector around the center of the AIP, and is the mass flow weighted average dynamic pressure at the AIP.
- (3)
- The swirl angle used in this study follows the definition and swirl index system specified in the AUR5686 standard [27] for swirl distortion parameters. The expression is given as follows:where is the circumferential velocity at the measurement point on the AIP, and is the axial velocity at the same point. To better quantify the swirl intensity at the AIP, the absolute value of the swirl angle is integrated over the section to obtain the swirl angle flux , which quantifies the degree of swirl distortion at the AIP [28]. Additionally, since engineering applications are primarily concerned with areas and proportions where the swirl angle exceeds ±15° [29], we employed ηα15 to characterize the proportion of the area where || exceeds 15° to the AIP. The formula is as follows:
In addition, the pressure coefficient Cp is used to represent the pressure distribution along the inlet and is defined as
where is the static pressure of the wall surface, is the static pressure of the freestream air, and is the dynamic pressure of the freestream air.
2.3. Numerical Methods
To obtain the internal flow characteristics of the tiltrotor aircraft inlet, we applied the finite volume method to discretize the three-dimensional Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations using the Unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (URANS) approach. Due to the low velocities of the tiltrotor aircraft while hovering and the surrounding air, a pressure-based solver was employed for flow field computations. Discretization of the Navier–Stokes equations was performed using a second-order upwind scheme, and the velocity and pressure fields were corrected using the SIMPLEC algorithm. The turbulent viscosity was calculated using the SST k-w model proposed by Menter [30], which was shown to effectively predict three-dimensional complex flow structures with adverse pressure gradients in the inlet duct [31,32,33]. In addition, we selected a rotor speed of 589 RPM and transient time step sizes of 2.83 × 10−4 s based on the time needed for the rotor to rotate by 1°. In addition, the height from the propeller to the ground was 2.2 R. The details of the computational domain are depicted in Figure 2. To mitigate the boundary effects on the CFD results, the width of the computational domain was 40 times the length of the inlet, and the height was 13 times the length of the inlet. Moreover, a straight section was added at the exit of the inlet, corresponding to 1.5 times the diameter of the inlet exit diameter.
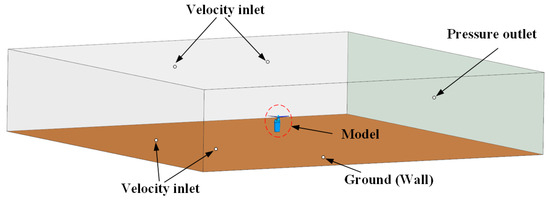
Figure 2.
Computational domain and boundary condition.
Here, the entire computational domain was filled with hexahedral and polyhedral cells using the Fluent Meshing 2021R1 software for mesh generation. The computational domain features stationary and rotating regions, with data exchange between the two regions occurring through interface boundaries. To meet the turbulence model’s requirement for a y+ value of approximately 1, mesh refinement was applied near the wall surfaces. Additionally, to validate mesh independence, three sets of meshes with varying levels of density—coarse, medium, and fine—were established. The mesh height of the first layer was the same across all three sets of meshes. The mesh sizes for each set were as follows: 7.21 million, 10.20 million, and 14.31 million. The medium grid, as shown in Figure 3, consisted of 10.20 million cells, with the rotational region containing 4.11 million cells, the inlet region containing 2.16 million cells, and the far-field region containing 3.93 million cells. Using these three sets of meshes, we can simulate the flow field inside the inlet of the hovering tiltrotor aircraft at a flow velocity of 0 m/s. The time-averaged pressure distribution along the inlet wall at the 9th rotation of the rotor is illustrated in Figure 4. Notably, the results obtained from the three sets of grids exhibit consistent trends. However, the results obtained from the coarse grid are significantly higher than those obtained from the medium and fine meshes, whose results almost overlap. Considering computational efficiency and accuracy, the medium mesh was ultimately used for further investigations.
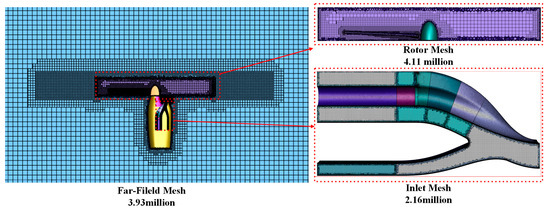
Figure 3.
Details of the medium meshes.
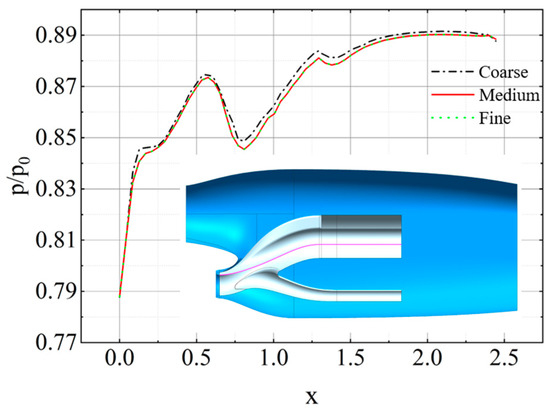
Figure 4.
Surface time-averaged pressure distribution obtained with different meshes.
2.4. Numerical Validation
Since this study employed the sliding mesh method to simulate the rotor’s rotation process, the research methodology’s accuracy was validated using a Caradonna–Tung experimental rotor from NASA [34,35]. This rotor is one of the standard cases in the field of rotor Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and its publicly available data are frequently referenced by researchers in rotor CFD studies. Table 3 presents this rotor’s parameters, while the experimental setup is shown in Figure 5.

Table 3.
Geometric parameters of the Caradonna–Tung rotor.
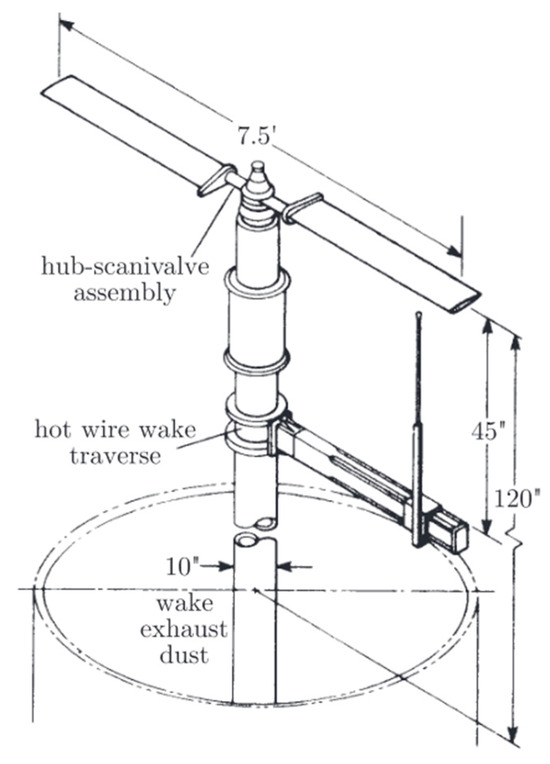
Figure 5.
Experimental set-up of the Caradonna–Tung two-bladed model rotor in hover [34,35].
In the numerical simulation conditions for the rotor, we selected a blade tip with a Mach number of 0.526 and collective pitch of 8°. Figure 6 compares the pressure coefficients at different locations along the rotor blade profiles. Overall, we observed excellent agreement between the simulation results and experimental values. This result effectively demonstrates that the simulation method utilized in this study accurately represents the flow field information around the rotor.
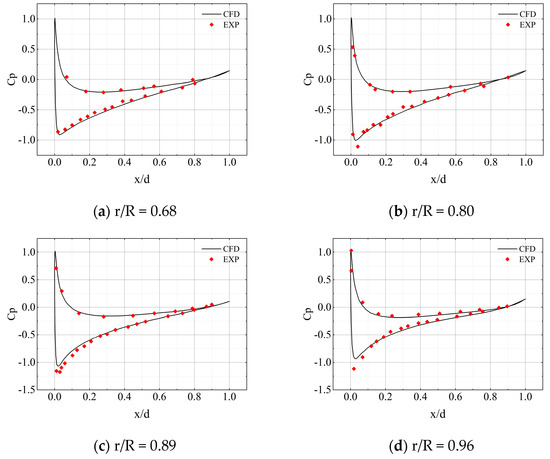
Figure 6.
Comparison of the pressure coefficient distributions between numerical and experimental results at different blade sections.
To further validate the predictive capabilities of the simulation method for the internal flow of the inlet, an S-shaped diffuser test case from NASA Lewis Research Center [36] was utilized for further verification. A comparison of the pressure distributions along the axial sections at circumferential angles of 90° and 170° is presented in Figure 7. The simulation results are also in a good agreement with the experimental results, further demonstrating the accuracy of the simulation method adopted in this study.
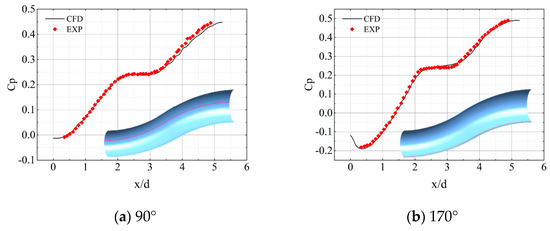
Figure 7.
Comparison of the pressure coefficient distributions between numerical and experimental results at various circumferential angles.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time-Averaged Internal Flow Field Analysis of Gust-Free Inlet
Firstly, we examined the internal flow dynamics within the inlet under the effects of the rotor in gust-free conditions. The time-averaged total pressure recovery distribution on the AIP is shown in Figure 8. The results indicate four primary regions of low total pressure on this plane, roughly ranging from 330° to 30°, 90° to 170°, 175° to 185°, and 210° to 270°. These regions are denoted as Zone 1, Zone 2, Zone 3, and Zone 4, respectively. The regions of Zone 2 and Zone 4 display larger areas and significantly lower pressures than other zones. The time-averaged contour plot of the Mach number and secondary streamlines on the AIP depicted in Figure 9 indicate that these areas contain large-scale transverse vortex pairs. The presence of these two vortices significantly increases viscous losses. Particularly, the region with a total pressure recovery coefficient below 0.9 covers 3.57% of the total area of the AIP, primarily concentrated in Zone 2. This factor significantly affects the total pressure recovery coefficient, reducing it to 0.9664, and also exacerbates the non-uniformity of the total pressure distribution on the AIP, resulting in a circumferential distortion index () of −0.572. To better characterize the vortex structures at the AIP, the Q-criterion is employed for vortex identification. The time-averaged vortex structures are depicted in Figure 10, where the arrows indicate the direction of rotation of the vortex. The presented vortex tubes correspond to regions , . The AIP features three pairs of transverse vortices and one streamwise vortex. These vortices are located at different positions on the AIP, with one at the top, another above the drive shaft, and one on each side directly beneath the plane. These vortices are designated transverse vortex pair 1, transverse vortex pair 2, transverse vortex pair 3, and streamwise vortex.
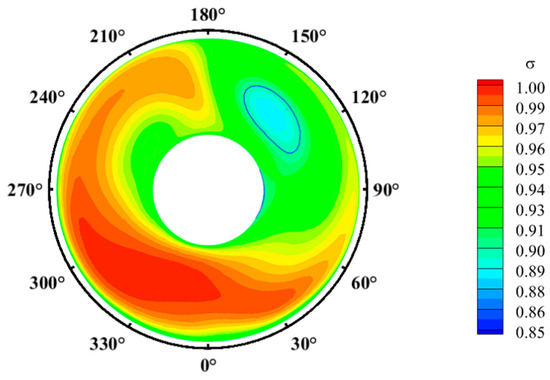
Figure 8.
Time-averaged total pressure recovery on the AIP.
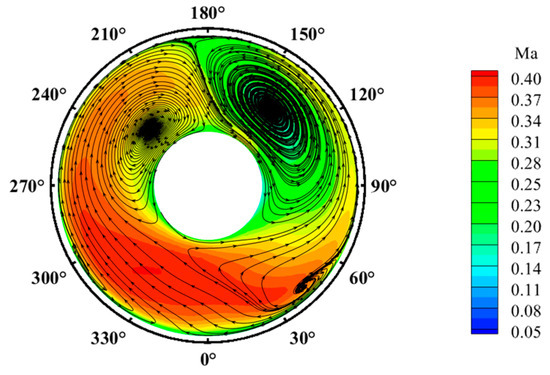
Figure 9.
Time-averaged velocity and secondary flow on the AIP.
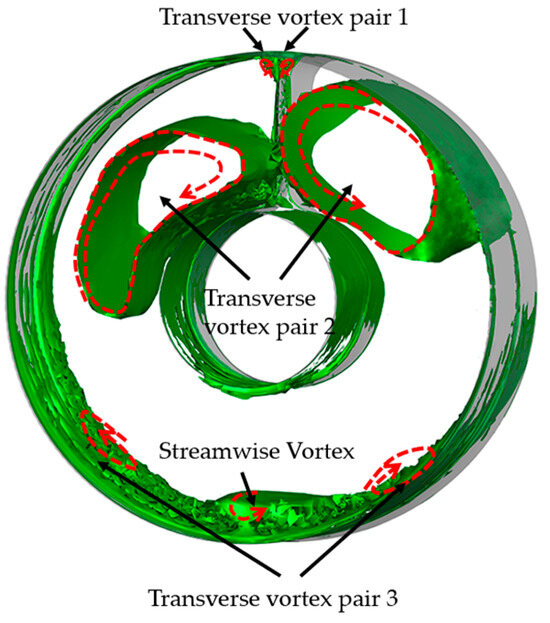
Figure 10.
Time-averaged vortex structures on the AIP.
Figure 11 shows the time-averaged Mach number distribution on the symmetry plane of the inlet. External airflow is drawn into the inlet via suction at the entrance. At the bifurcation, the airflow divides into two streams. The majority of the fluid flows into the engine duct to power the engine, while a small portion passes through the scavenge duct to expel foreign objects from the engine. Combined with the wall-limited streamlines on the inlet wall shown in Figure 12, it is further observed that upon entering the inlet, some of the air initially attaches to both sides of the bifurcation, creating a high-pressure zone and reattachment line. Subsequently, the fluid within the boundary layer at the bifurcation converges towards the center under the influence of favorable pressure gradients. Eventually, the fluid meets at the central position, forming a saddle point. Subsequently, the boundary layer initiates detachment from the wall, leading to an interaction with the mainstream flow, inducing flow separation and the formation of a separation line. Eventually, a vortex emerges along the flow direction, depicted as the streamwise vortex in Figure 9. The air within the vortex is then replenished by low-pressure air from the interior of the boundary layer, culminating in the establishment of a low-pressure zone, Zone 1, on the AIP.
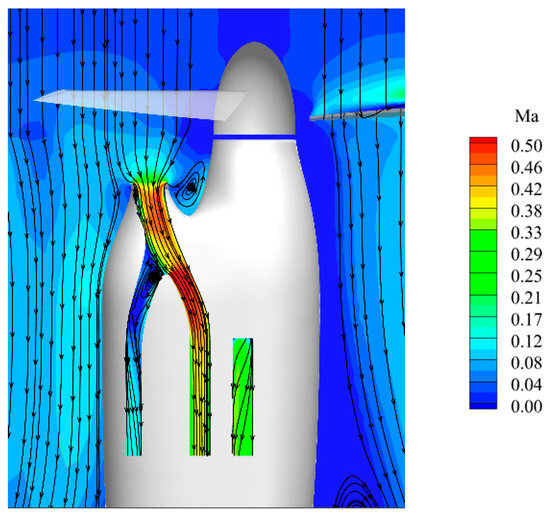
Figure 11.
Time-averaged Mach number distribution on the symmetry plane of the inlet.
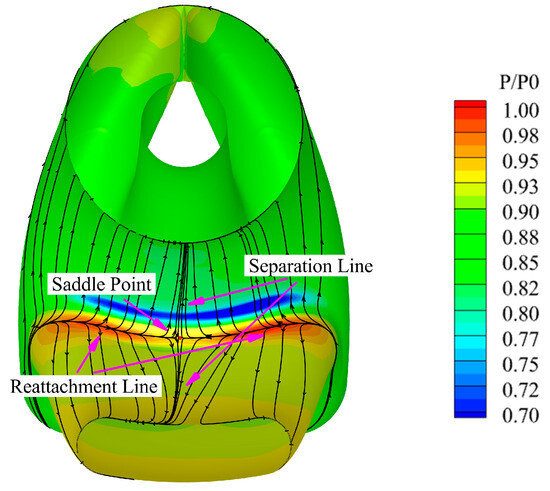
Figure 12.
Time-averaged wall-limited streamlines and pressure.
Figure 13 presents the time-averaged Mach number and secondary flow streamlines along the inlet cross-section. It can be observed that air in the engine duct must flow around both sides of the driving shaft. According to the theory of flow around slender bodies [37], this type of airflow will result in the formation of a stable pair of vortices behind the shaft, named transverse vortex pair 2. After vortex pair 2 forms, it continues to develop along the direction of the fluid flow and eventually converges as the airflow transitions to a circular cross-section at the inlet. Subsequently, a saddle point forms above the cross-section, where the air flows both above and below the saddle point. As the air flows upward and contacts the upper wall, it begins to induce the migration of air near the boundary layer to both sides. Eventually, transverse vortex pair 1 forms under the influence of adverse pressure gradients. Since the fluid within transverse vortex pair 1 mainly consists of fluid near the boundary layer, its total pressure is relatively low. However, due to its small scale, the fluid’s effect on the performance of the inlet is minimal.
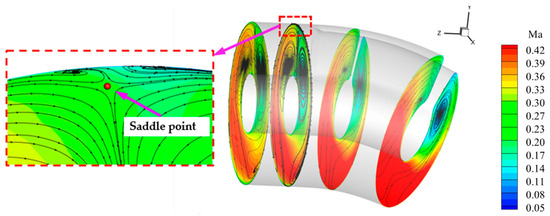
Figure 13.
Time-averaged Mach number along the inlet cross-section.
Transverse vortex pair 2’s area of effect gradually expands during its development. Combined with the time-averaged pressure distribution shown on the AIP wall in Figure 14, this result demonstrates that when the fluid near the boundary of transverse vortex pair 2 flows close to the outer wall of the inlet, it encounters adverse pressure gradients in both the 0° to 330° and 30° to 60° directions. Ultimately, transverse vortex pair 3 forms under the driving force of adverse pressure gradients.
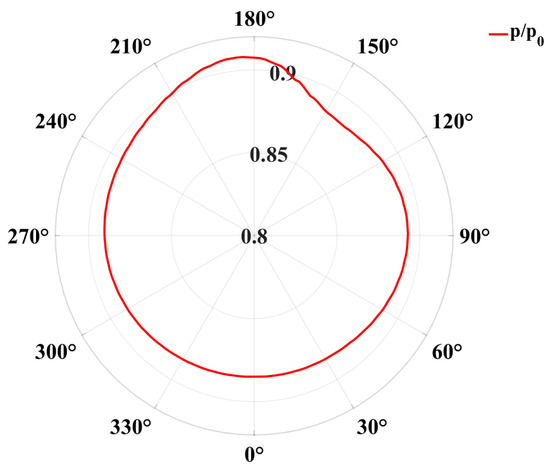
Figure 14.
Time-averaged pressure distribution on the AIP wall.
To further investigate the influence of vortices on the performance of the inlet, an analysis of the swirl angle distribution on the AIP was conducted, as shown in Figure 15. Here, regions where || = 15° are marked in purple solid lines. In these regions, areas with larger swirl angles are distributed on both sides above the shaft and on the right side of the inlet wall. Combined with the analysis of secondary streamlines, it can be inferred that these results are due to the presence of transverse vortex pair 2, which induces the rotation of the mainstream fluid, resulting in higher tangential velocities in this region, and, consequently, larger swirl angles.
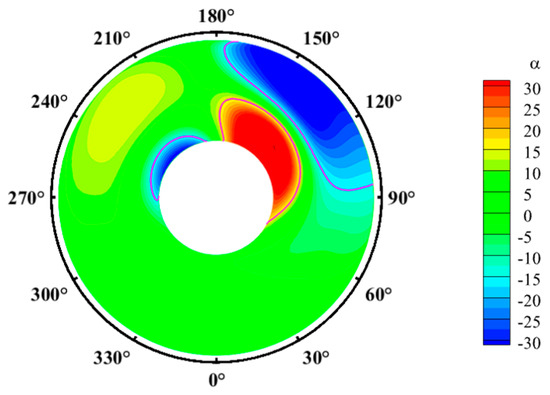
Figure 15.
Time-averaged swirl angle on the AIP.
Subsequently, an analysis was conducted to examine the dynamic evolution characteristics of the flow field during the rotation of the rotor. Figure 16 illustrates the total pressure recovery distribution on the AIP and its secondary streamlines at four moments within one period of the rotor’s rotation. Under the effect of the rotor, the pressure distribution on the AIP exhibits pronounced unsteady features. The location and magnitude of low-pressure regions oscillate within a certain range due to the effects of vortices, but the overall trend of the pressure distribution remains similar.
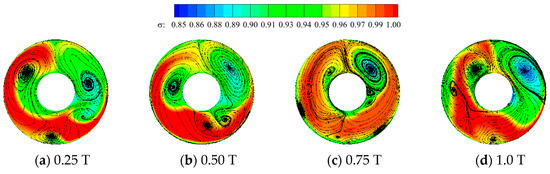
Figure 16.
Total pressure recovery and secondary flow on the AIP at different times.
We next employ the unsteady intensity Su [38] to better illustrate the unsteady characteristics of the inlet’s internal flow and quantitatively characterize the unsteady fluctuation intensity of the total pressure field on the AIP. The unsteady intensity Su is determined as follows:
where is the total pressure at each moment within one period on the AIP, and is the time-averaged total pressure within one period. Figure 17 illustrates the distribution of Su on the AIP. Significant pressure pulsations are clearly present within the inlet, with larger fluctuations concentrated primarily on both sides of transverse vortex pair 2. These fluctuations can be attributed to the larger scale of the inlet and the stronger swirling effects induced by the rotor. Under the influence of the rotor, transverse vortex pair 2 undergoes periodic changes in size and position on both sides of the shaft, resulting in intense interactions between its fluid and the mainstream. Subsequently, this interaction causes strong unsteady disturbances at the edges of transverse vortex pair 2. This interaction significantly affects variations in the size of transverse vortex pair 3 due to continuous changes in transverse vortex pair 2, resulting in larger total pressure fluctuations near the wall within the range of 240° to 270°. Additionally, strong pressure pulsations exist in the boundary layer from 15° to 90° on the AIP and in some mainstream regions. This result is attributed to the movement of streamwise vortices under the rotor’s effects continuously traversing the bottom surface of the inlet and interacting with air inside the boundary layer. This interaction becomes further intensified by the presence of transverse vortex pair 2 in the range of 30° to 60°, leading to relatively higher total pressure fluctuations from 15° to 90° near the boundary layer on the AIP.
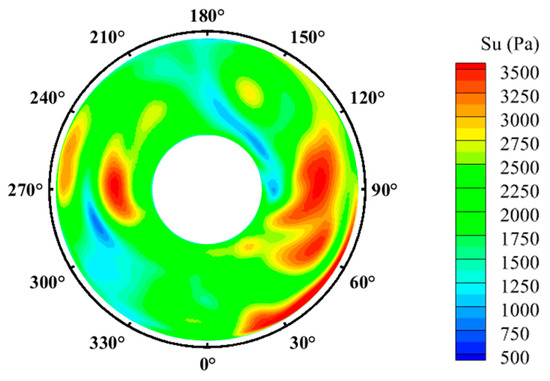
Figure 17.
Unsteady intensity Su on the AIP.
The above findings also indicate that the flow structure within the inlet of a hovering tiltrotor aircraft is highly intricate and features significant transient characteristics. However, when the tiltrotor aircraft operates in gusty environments, additional changes in its internal flow structure will occur, thereby affecting the operational status of the downstream engines.
3.2. Gust Model and Simulation Condition
There are three types of gust directionality: vertical, lateral, and head-on. These types of gust are conventionally understood to have effects akin to altering the angle of attack, side-slip angle, and dynamic pressure of the aircraft, respectively. The head-on linear discrete gust model is utilized in this study, the shape of which is illustrated in Figure 18. The velocity profile of the gust can be represented by the following equation:
where represents the instantaneous wind velocity, represents the mean wind velocity, represents the gust velocity, and represents the maximum gust velocity. Following the standards outlined in the Civil Aviation Manual (CAM 04) issued in 1941 [39], this study uses a maximum gust speed of 12 m/s. The gust profile was discretized into five key velocity points for analysis, as depicted in Figure 19. The simulation conditions are shown in Table 4.
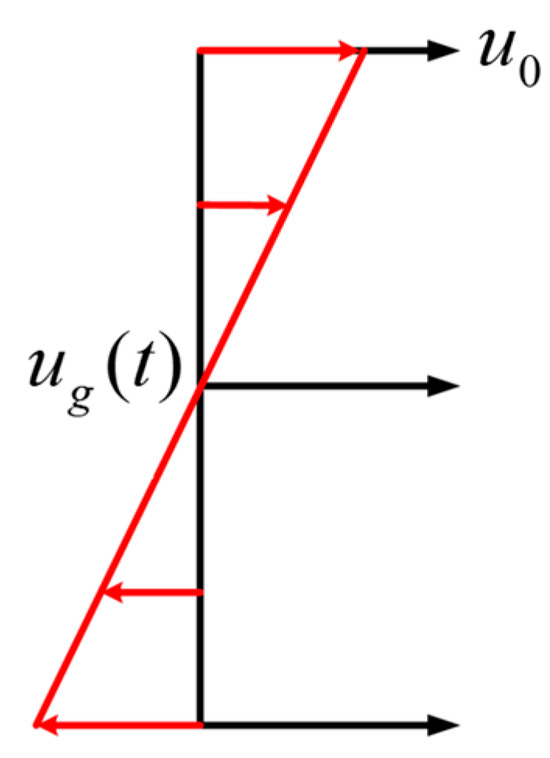
Figure 18.
Illustration of the gust model.
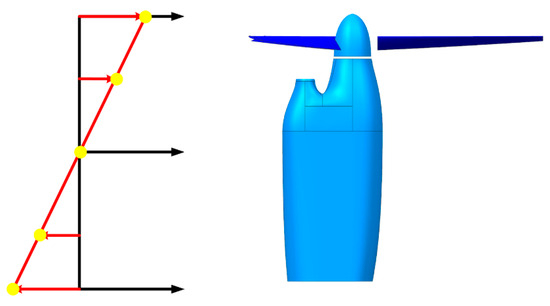
Figure 19.
The gust encountered by the tiltrotor aircraft.

Table 4.
Simulation conditions of the gust.
3.3. Effect of Head-On Gusts on the Time-Averaged Performance of the Inlet
Figure 20 presents the performance variation curve of the tiltrotor aircraft’s inlet under the influence of head-on gusts. Head-on gusts significantly influence the performance of the inlet, causing related performance parameters to exhibit similar trends. As the gust velocity positively increases, the total pressure recovery of the inlet gradually increases by 1.01% when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, and the circumferential distortion at the exit decreases by 25.72% when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s. However, the swirl intensity and area ratio with a swirl angle || greater than 15° initially experience a slow increase before rapidly declining, demonstrating an overall decreasing trend. Ultimately, when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, ηα15 decreases by 62.84%, which has a relatively strong effect on the performance of the inlet. However, when the gust velocity increases negatively, the performance parameters exhibit opposite trends. As the gust velocity reverses its increase, the total pressure recovery coefficient of the inlet gradually decreases by 1.13%% when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s. Then, the circumferential distortion index increases, and η increases by 14.57% when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s. Both the swirl intensity and the area ratio with a swirl angle || greater than 15° indicate an overall increasing trend. Ultimately, when the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, ηα15 increases by 69.59%, thereby decreasing inlet performance.
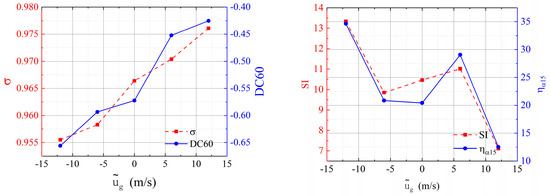
Figure 20.
The time-averaged performance parameters of the inlet under various gust velocities.
3.4. Effect of Head-On Gusts on the Time-Averaged Flow Field Characteristics of the Inlet
Figure 21 presents the Mach number distribution on the symmetry plane of the inlet under different gust velocities. When the gust velocity is positive, the interaction between the incoming flow and the downwash generated by the rotor causes the downwash flow to shift towards the inlet side of the inlet. As the gust velocity increases, this phenomenon becomes more pronounced. Consequently, a greater downwash flow with higher mechanical energy, located further away from the blade root, is drawn into the inlet under its suction effect. This phenomenon leads to an increase in the total mechanical energy entering the inlet, which is one of the main reasons why the total pressure recovery coefficient increases under positive gust velocities. However, when the gust velocity is negative, a majority of the air entering the intake duct originates from the blade root, with low-energy fluid from the boundary layer diverter also being drawn into the inlet. Consequently, the air drawn into the inlet possesses lower mechanical energy, thereby reducing the total pressure recovery coefficient compared to that under conditions without gusts.
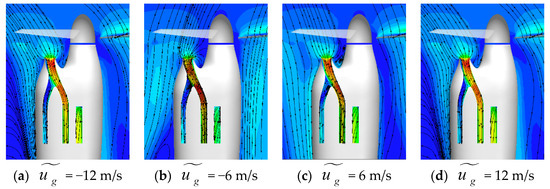
Figure 21.
Time-averaged Mach number distribution on the symmetry plane of the inlet under different gust velocities.
Figure 22 exhibits the total pressure recovery on the AIP under the various gust velocities to better understand how gusts affect the pressure and circumferential distortion on the AIP. The boundaries of areas where the total pressure recovery coefficient equals 0.9 are delineated with solid blue lines. Additionally, Figure 23 illustrates the proportion of the total AIP area with total pressure recovery below 0.9. Clearly, as the gust velocity gradually increases from the positive direction, areas where the total pressure recovery is less than 0.9 are primarily concentrated in Zone 2, which contains the low-pressure region influenced by transverse vortex pair 2. Moreover, as the gust velocity increases positively, the areas with total pressure recovery less than 0.9 gradually decrease. These areas eventually only remain in Zone 2, despite initially being distributed in both Zone 2 and Zone 4. By the time the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, the areas with total pressure recovery less than 0.9 completely disappear, and pressure distribution across the section becomes increasingly uniform. However, as the gust velocity increases in the negative direction, the areas with total pressure recovery values below 0.9 gradually expand. When the negative gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, Zone 4, which is influenced by transverse vortex pair 2, also presents a significant area with total pressure recovery coefficients below 0.9. This result indicates that head-on gusts primarily influence the total pressure recovery and circumferential distortion index of the inlet by modifying the intensity of transverse vortex pair 2 and the pressure values of the air contained within.
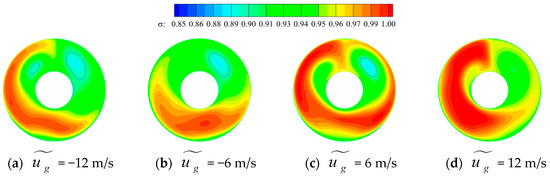
Figure 22.
The time-averaged total pressure recovery distribution on the AIP under various gust velocities.
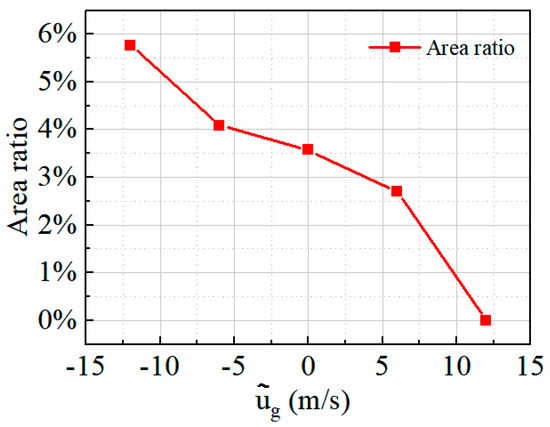
Figure 23.
The proportion of the area where the time-averaged total pressure recovery is less than 0.9.
Figure 24 and Figure 25, respectively, present the distribution of secondary streamlines and swirl angles on the AIP of the inlet under different gust velocities. The regions where || = 15° are marked by solid purple lines in Figure 25. Here, gusts also have a significant effect on the swirl angle at the exit of the inlet. In all four gust velocity cases, areas with large swirl angles on the AIP of the inlet are distributed on both sides above the shaft and upper wall of the inlet. Combined with the secondary streamlines, this phenomenon can be analyzed as being induced by the presence of transverse vortex pair 2. Transverse vortex pair 2 redirects the airflow towards the center of the section, resulting in higher tangential velocities in this region, leading to a larger distribution of swirl angles. Due to the influence of gusts, the swirl angle of the AIP continuously changes. Both parameters undergo significant changes as the gust velocity varies. When the gust velocity is positive, the distribution of swirl intensity and the area with swirl angle || > 15° initially increases before decreasing with an increase in wind velocity. However, when the gust velocity is in the opposite direction, the proportion of the area with swirl angle||> 15° increases as the wind velocity increases. The swirl intensity shows a trend of decreasing first and then increasing. Notably, throughout this process, the change in swirl angle is most pronounced in the top left corner. The fundamental reason for this phenomena is that gusts cause significant variations in the size and intensity of transverse vortex pair 2 within the intake duct and alter the magnitude and distribution of the secondary swirl, ultimately leading to changes in the swirl angle.
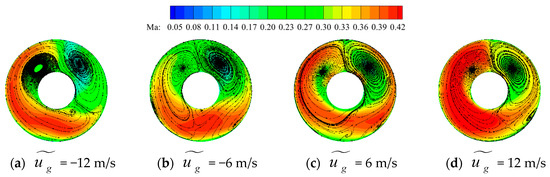
Figure 24.
Time-averaged secondary streamlines on the AIP under different gust velocities.
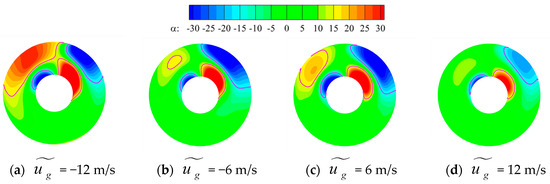
Figure 25.
Time-averaged swirl angle on the AIP under different gust velocities.
3.5. Effect of Head-On Gusts on the Unsteady Characteristics of the Flow Field within the Inlet
Figure 26 presents pressure and secondary streamline contour maps in four instances within one period for the AIP of the tiltrotor aircraft inlet under various gust velocities. Here, the combined influence of rotor motion and gusts yields significant unsteady characteristics in pressure distribution and vortices on the AIP. When the gust velocity is positive, the largest scale lateral transverse vortex pair on the AIP surface of the intake duct (vortex pair 2) induces a relatively stable low-pressure area. Consequently, the pressure distribution on the AIP exhibits a similar trend. However, the low-pressure area caused by the streamwise vortex undergoes continuous oscillation at the bottom of the AIP surface due to the rotation of the rotor. Thus, regions with significant total pressure fluctuations, as depicted in Figure 27, are mainly concentrated at the bottom of the AIP surface. When the gust velocity is positive, the largest scale transverse vortex pair on the AIP of the inlet (vortex pair 2) induces a relatively stable low-pressure area. Consequently, the pressure distribution on the AIP surface exhibits a similar trend. However, the low-pressure area caused by the streamwise vortex undergoes continuous oscillation at the bottom of the AIP due to the rotation of the rotor. As a result, regions with significant total pressure fluctuations, as depicted in Figure 27, are mainly concentrated at the bottom of the AIP. The proportion of areas with significant total pressure fluctuations near transverse vortex pair 2 is relatively small. Furthermore, as the gust velocity increases, the total pressure on the left side of the AIP becomes more stable. This observation suggests that head-on gusts exert a certain promoting effect on the stability of vortices inside the inlet. Conversely, when the gust velocity is negative, the vortices on the AIP of the inlet undergo violent oscillations under the combined effect of the rotor and gusts, primarily concentrating in the region influenced by lateral transverse vortex pair 2. This phenomenon produces significant total pressure fluctuations on both sides of the shaft, as shown in Figure 27. When the negative gust velocity reaches 12 m/s, the streamwise vortex at the bottom also undergoes violent oscillations, ultimately resulting in areas with significant total pressure fluctuations at the bottom.
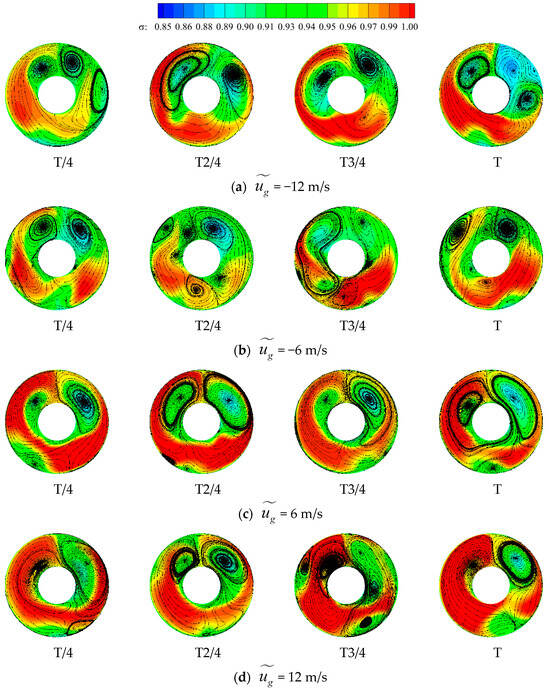
Figure 26.
Total pressure recovery on the AIP under different gust velocities.
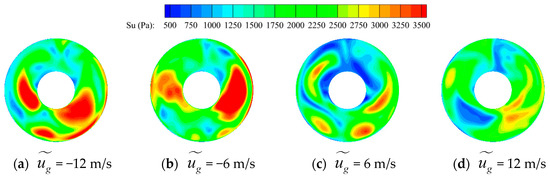
Figure 27.
Su on the AIP under different gust velocities.
To better quantify the total pressure fluctuations on the AIP of the tiltrotor aircraft’s inlet caused by gusts, the unsteady intensity Su across the AIP is integrated and normalized to obtain the dimensionless parameter , which represents the flux of unsteady intensity. This parameter serves to measure the effects of head-on gusts on the pressure fluctuations of the inlet AIP:
Figure 28 shows the variation trend of under different gust velocities. When the gust velocity is positive, the fluctuation of the inlet AIP significantly decreases, which improves the stability of inlet performance. Although the overall amplitude of the total pressure fluctuation of the inlet AIP does not change significantly when the gust velocity is negative, Figure 27 shows the presence of localized regions with significant total pressure fluctuations, which have a relatively adverse effect on the performance of the inlet.
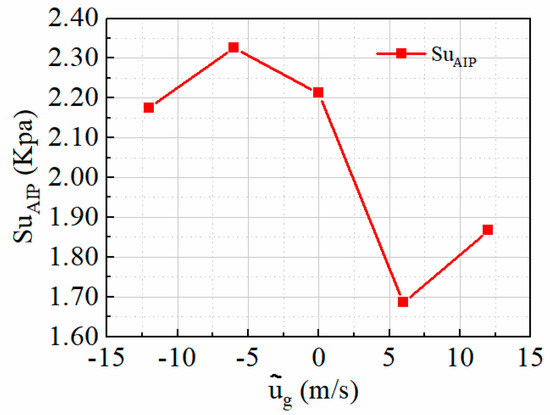
Figure 28.
on the AIP at different gust velocities.
4. Conclusions
This work utilized an unsteady numerical simulation method based on a slip mesh to conduct a series of studies on inlet internal flow characteristics and the effects of head-on gusts on the aerodynamic characteristics of the inlet during the tiltrotor aircraft’s hovering state. The primary conclusions are as follows.
In the hovering state of the tiltrotor aircraft, there are three pairs of transverse vortices and one streamwise vortex in the inlet AIP. The transverse vortices generated by the airflow around the shaft have the largest scale, the lowest fluid pressure inside, and the greatest effect on the performance of the inlet. Moreover, due to the presence of the rotor, there are strong unsteady characteristics inside the inlet. The region with the largest total pressure pulsation at the AIP of the inlet is mainly distributed on both sides of the shaft and the bottom of its AIP.
Head-on gusts mainly affect the mechanical energy and non-uniformity of the air sucked into the inlet by influencing the direction of the rotor’s induced slipstream, thereby impacting the performance of the inlet. When the gust velocity reaches 12 m/s (), the total pressure recovery of the inlet increases by 1.01%, the circumferential distortion index decreases to 25.72%, and the region with || greater than 15° decreases by 62.84%. However, when the gust velocity of the head-on gust reverses and reaches 12 m/s (), the total pressure recovery of the inlet decreases by 1.13%, the circumferential distortion index increases by 14.57%, and the region with || greater than 15° increases by 69.59%, which has a relatively adverse effect on the performance of the inlet.
Head-on gusts also have a significant effect on the unsteadiness inside the inlet. When encountering head-on gusts in the forward direction, the internal vortex structure is relatively stable, and the unsteady pulsation of the total pressure is small. Although head-on gusts in the reverse direction have a relatively small effect on the overall pressure pulsation of the AIP, they enhance the pressure pulsation in local areas, which has a relatively adverse effect on the performance of the inlet.
Ultimately, this research determined the flow characteristics inside the inlet of a hovering tiltrotor aircraft, as well as the effects of gusts on the total pressure recovery coefficient, the distortion index, and the swirl angle of the tiltrotor aircraft inlet. These results will provide guidance for designing tiltrotor aircraft inlets and studying the effects of gusts on the power systems of these aircraft.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and Y.Z.; methodology, Y.Z., D.C. and H.Z.; software, H.Z. and X.H.; validation, H.Z., Z.W. and H.T.; formal analysis, H.Z., X.H. and Y.Z.; investigation, H.Z. and Y.H.; resources, H.T. and X.H.; data curation, Z.W. and X.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and D.C.; visualization, H.T. and Y.H.; supervision, Y.Z. and D.C.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project, grant number J2019-II-0014-0035; the Science Center for Gas Turbine Project, grant number P2022-C-II-002-001; and the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF, grant number GZB20230970.
Data Availability Statement
The data within the article can be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Nomenclature
| VTOL | vertical take-off and landing |
| AIP | aerodynamic interface plane |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| total pressure of the freestream | |
| mass flow weighted average total pressure at the AIP | |
| total pressure recovery coefficient | |
| minimum value of the mass flow weighted average total pressure over any 60° sector around the center AIP | |
| mass flow weighted average dynamic pressure at the AIP | |
| circumferential distortion index | |
| swirl angle | |
| circumferential velocity at the measurement point on the AIP | |
| axial velocity at the measurement point on the AIP | |
| SI | swirl angle flux |
| proportion of the area where || exceeds 15° to the AIP | |
| Cp | pressure coefficient |
| RPM | revolutions per minute |
| instantaneous wind velocity | |
| mean wind velocity | |
| gust velocity | |
| maximum gust velocity | |
| Su | unsteady intensity |
| flux of unsteady intensity |
References
- Zanotti, A.; Savino, A.; Palazzi, M.; Tugnoli, M.; Muscarello, V. Assessment of a Mid-Fidelity Numerical Approach for the Investigation of Tiltrotor Aerodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Yang, C. Hybrid Adaptive Control for Tiltrotor Aircraft Flight Control Law Reconfiguration. Aerospace 2023, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.J.; Barakos, G.N. Numerical Simulations on the ERICA Tiltrotor. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, V. Test and Evaluation of an Inlet Barrier Filter to Increase Engine Time-on-Wing for the Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey Tiltrotor; The University of Texas at Arlington: Arlington, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Maisel, M.D.; Giulianetti, D.J.; Dugan, D.C. The History of the XV-15 Tilt Rotor Research Aircraft: From Concept to Flight, The NASA History; Series No. 17; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Office of Policy and Plans, NASA History Division: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Droandi, G.; Zanotti, A.; Gibertini, G.; Grassi, D.; Campanardi, G. Experimental Investigation of the Rotor-Wing Aerodynamic Interaction in a Tiltwing Aircraft in Hover. Aeronaut. J. 2015, 119, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Z.L.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.H. Numerical Simulation of Rotor–Wing Transient Interaction for a Tiltrotor in the Transition Mode. Mathematics 2019, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meakin, R. Unsteady Simulation of the Viscous Flow about a V-22 Rotor and Wing in Hover. In Proceedings of the 20th Atmospheric Flight Mechanics Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–15 August 1995; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q. Numerical Analyses of Aeroacoustic Characteristics of Tiltrotor Considering the Aerodynamic Interaction by the Fuselage in Hover. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Dong, J. Numerical Simulation of Aerodynamic Interaction for a Tilt Rotor Aircraft in Helicopter Mode. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narducci, R.P.; Liu, J.; Wells, A.J.; Mobley, F.J.; Mayer, R.J. CFD Simulations of a Hovering Tiltrotor in Ground Effect. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Desopper, A.; Routhieau, V.; Roth, G. Study of the low speed characteristics of a tiltrotor. In Proceedings of the 28th European Rotorcraft Forum, Bristol, UK, 17–20 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshminarayan, V.K.; Kalra, T.S.; Baeder, J.D. Detailed Computational Investigation of a Hovering Microscale Rotor in Ground Effect. AIAA J. 2013, 51, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbolt, J.C. Atmospheric Turbulence. AIAA J. 1973, 11, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, B. Turbulent Wind and Its Effect on Flight. J. Aircr. 1981, 18, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Qiu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Z. Review of Aircraft Gust Alleviation Technology. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2022, 43, 527350. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hunsaker, J.C.; Wilson, E.B. Report on Behavior of Aeroplanes in Gusts; NACA-TR-1: Washington, DC, USA, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ismail, M. Gust Loads on Aircraft. Aeronaut. J. 2019, 123, 1216–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.; Goldsmith, E.L. Intake Aerodynamics: An Account of the Mechanics of Flow in and around the Air Intake of Turbine-Engined and Ramjet Aircraft and Missiles; Collins Professional and Technical: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Paynter, G.; Koncsek, J.; Turczeniuk, B.; Dvorak, F.A. Extension of CFD Technology Used to Design the JVX Inlet. In Proceedings of the 21st Joint Propulsion Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 8–10 July 1985.
- Garavello, A.; Benini, E.; Ponza, R.; Scandroglio, A.; Saporiti, A. Aerodynamic Optimization of the ERICA Tilt-Rotor Intake and Exhaust System. In Proceedings of the 37th European Rotorcraft Forum, Ticino Park, Italy, 13–15 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gibertini, G.; Auteri, F.; Colaiuda, L.; Ermacora, M.; Grassi, D.; Zanotti, A. Optimized ERICA Engine Intake Wind Tunnel Test. In Proceedings of the 41st European Rotorcraft Forum, Munich, Germany, 1–4 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gibertini, G.; Zanotti, A.; Campanardi, G.; Auteri, F.; Zagaglia, D.; Crosta, G. Wind-tunnel tests of the ERICA tiltrotor optimised air-intake. Aeronaut. J. 2018, 122, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soemarwoto, B.; Habing, R.; Pecoraro, M. Adaptive Design Method for a Tilt-Rotor Engine Inlet Duct Optimization. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2022 Forum, Virtual, 27 June 2022; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Chicago, IL, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, H.; Bangga, G.; Tan, H. Aerodynamic Response of a Serpentine Inlet to Horizontal Periodic Gusts. Aerospace 2022, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, F.F.; Betzina, M.D.; Signor, D.B. Performance and Loads Data from a Hover Test of a Full-Scale XV-15 Rotor; Technical Report; NASA Ames Research Center: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Turbine Engine Inlet Flow Distortion Committee. A Methodology for Assessing Inlet Swirl Distortion; Report No. AIR5686; Society of Automotive Engineers: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.J.; He, X.M.; Li, D.P.; Tan, H.J.; Wang, K.; Wu, Z.L.; Wang, D.P. Double 90-Degree Deflection Inlet/Volute Coupling Flow Characteristics of Tail Powered UAV. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2023, 44, 128782. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L.; Da, X.Y.; Fang, Z.L. Assessment of Swirl Distortion of Serpentine Inlet Based on Five-Hole Probe. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2017, 37, 121342. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-Equation Eddy-Viscosity Turbulence Models for Engineering Applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Tan, H.J.; Lin, Z.K.; Li, Z.J.; Sun, S.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Z.X. Flowfield of a Helicopter Submerged Inlet with Power Output Shaft. Acta Mech. Sin. 2021, 37, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.S.; Tan, H.J.; Sun, S.; Tong, Y. Computational Study of a High-Performance Submerged Inlet with Bleeding Vortex. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.J.; Wu, Z.L.; Tan, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. Design and Examination of a Turboprop Inlet with Scavenge Duct. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 36, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonna, F.X.; Tung, C.; Caradonna, F.X.; Tung, C. Experimental and Analytical Studies of a Model Helicopter Rotor in Hover. In Proceedings of the European Rotorcraft and Powered Lift Aircraft Forum, Bristol, UK, 16 September 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Doerffer, P.; Szulc, O.; Doerffer, P.; Szulc, O. Numerical Simulation of Model Helicopter Rotor in Hover. Sci. Bull. Acad. Comput. Cent. Gdan. 2008, 12, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, R.W.; Theodore, H.O. A Study of the Compressible Flow through a Diffusing S-Duct; NASA Technical Memorandum: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 106411. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, R.M.; Forsythe, J.R.; Morton, S.A.; Squires, K.D. Computational Challenges in High Angle of Attack Flow Prediction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2003, 39, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xi, G.; Zhou, L. Experimental and Computational Investigation of Flows in a Vaned Diffuser Under Stage Environment. Acta Mech. Sin. 2005, 37, 110–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Civil Aeronautics Manual 0434: Airplane Airworthiness; United States Civil Aeronautics Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1941.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).