Additive Manufacturing of 17-4PH Alloy: Tailoring the Printing Orientation for Enhanced Aerospace Application Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
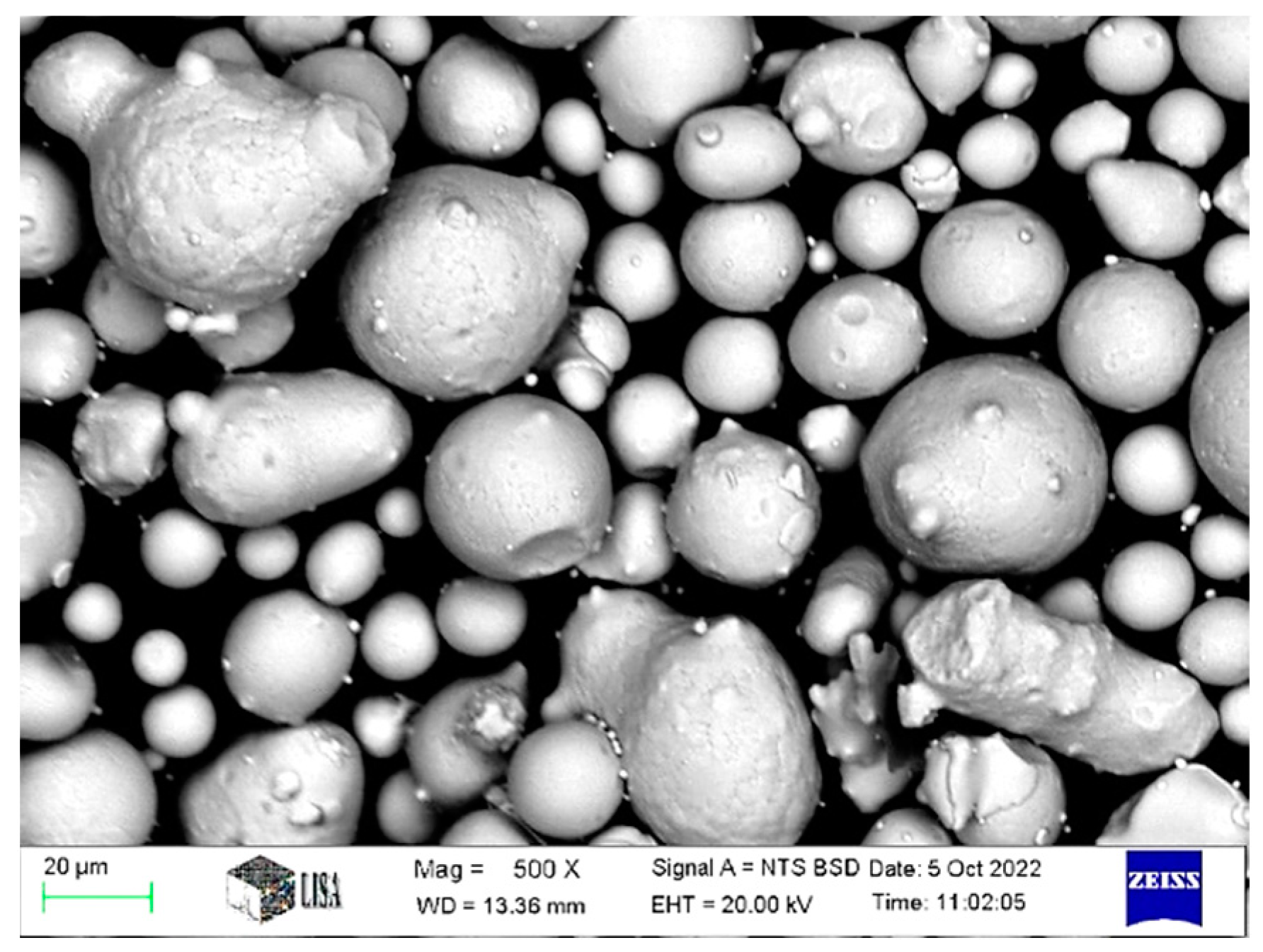
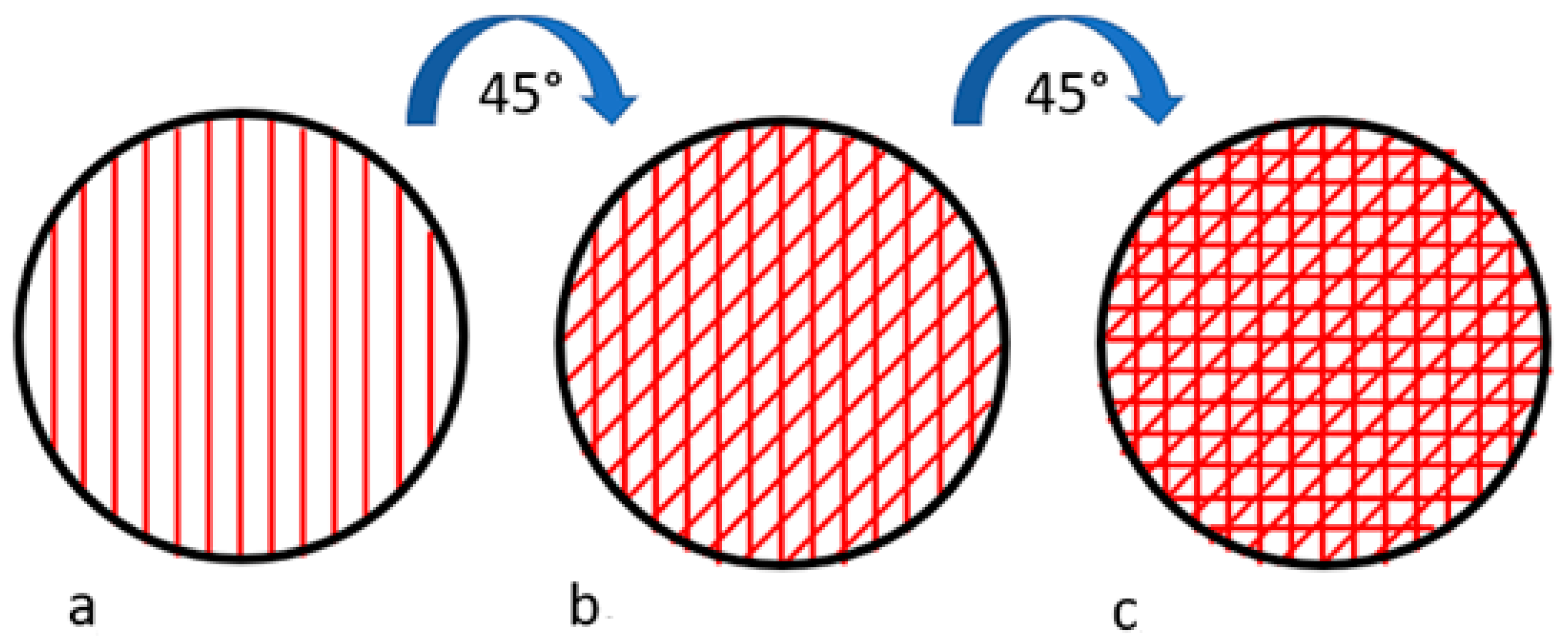
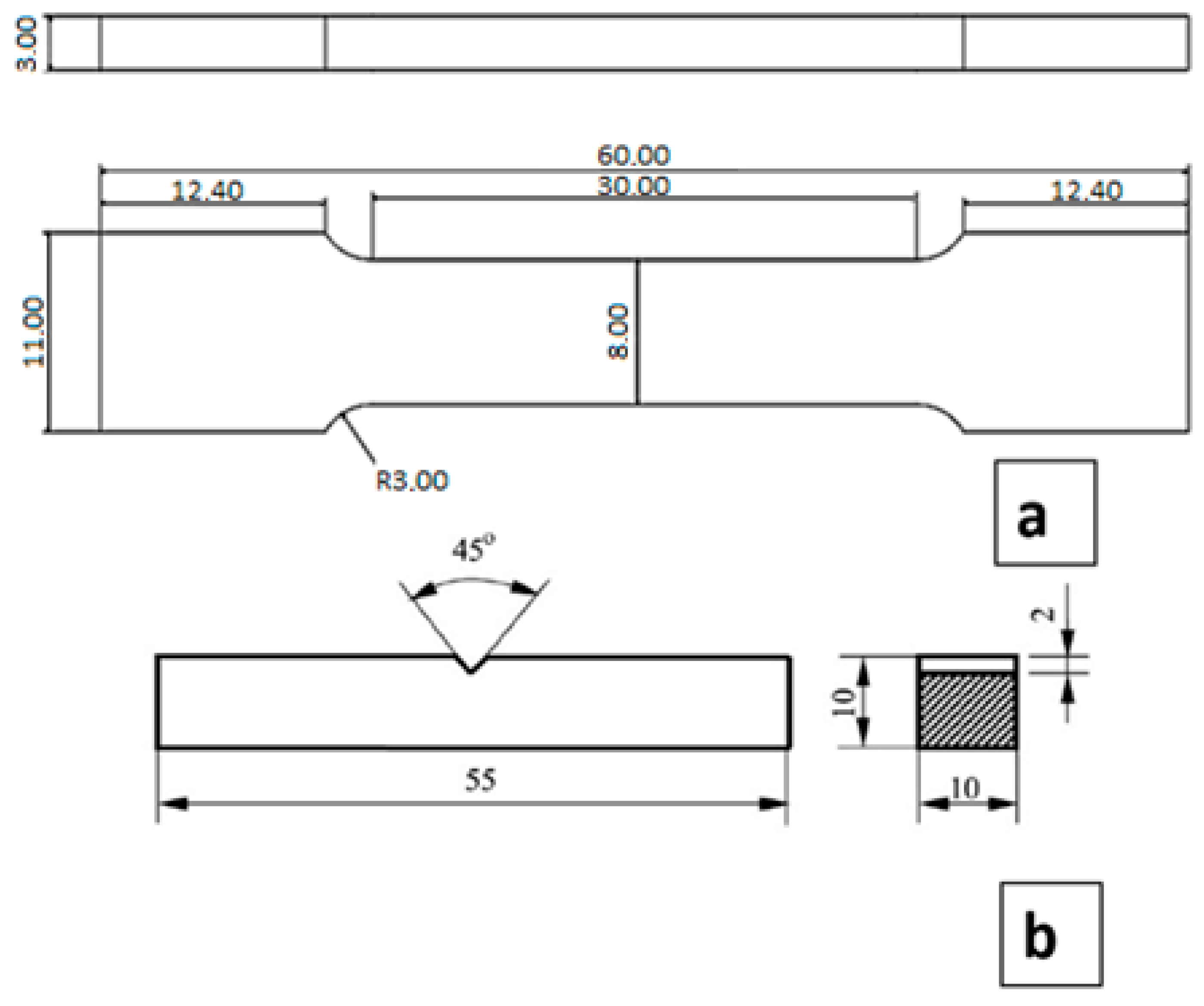
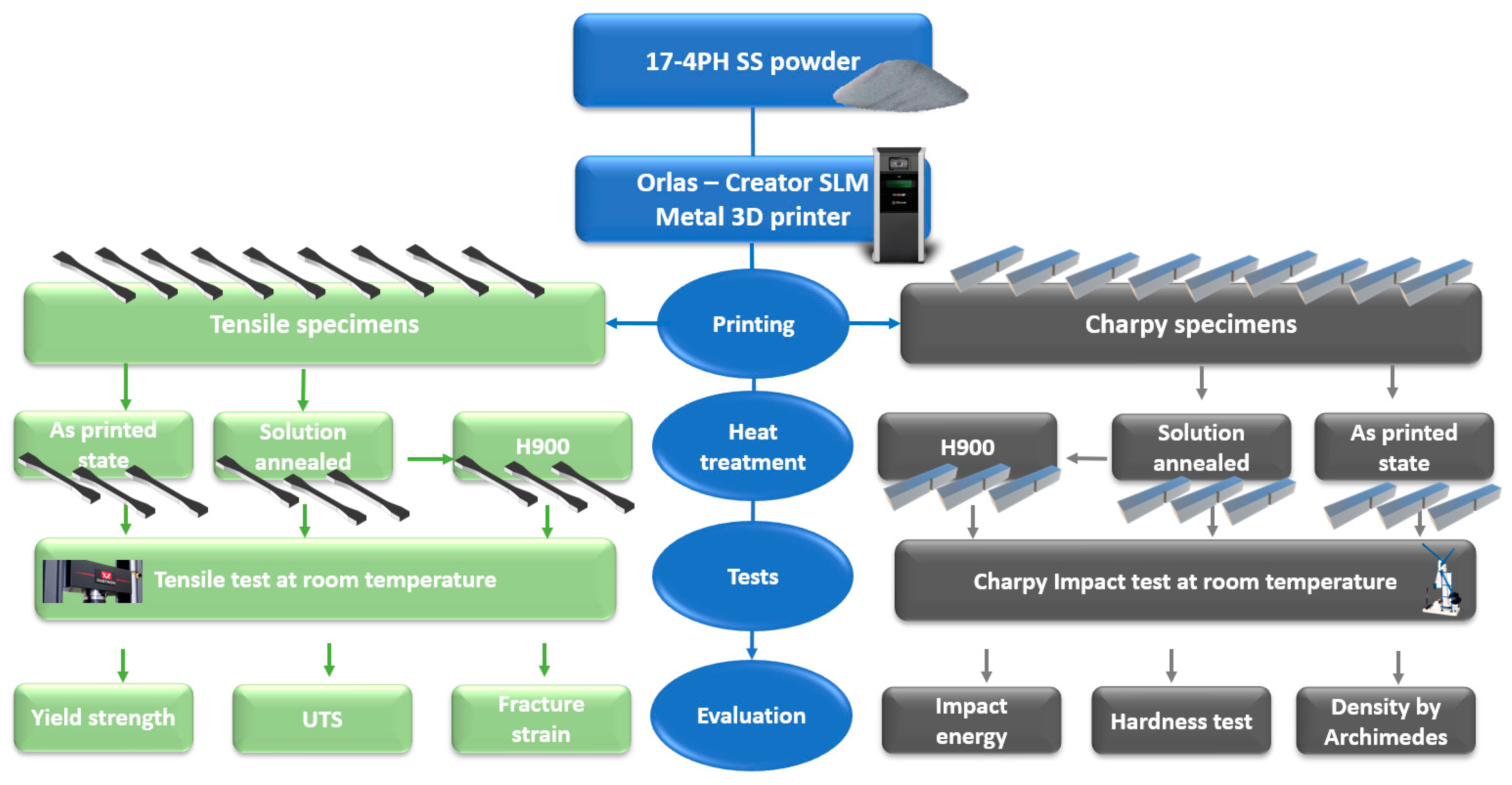
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Density and Microstructure
3.2. Hardness and Toughness
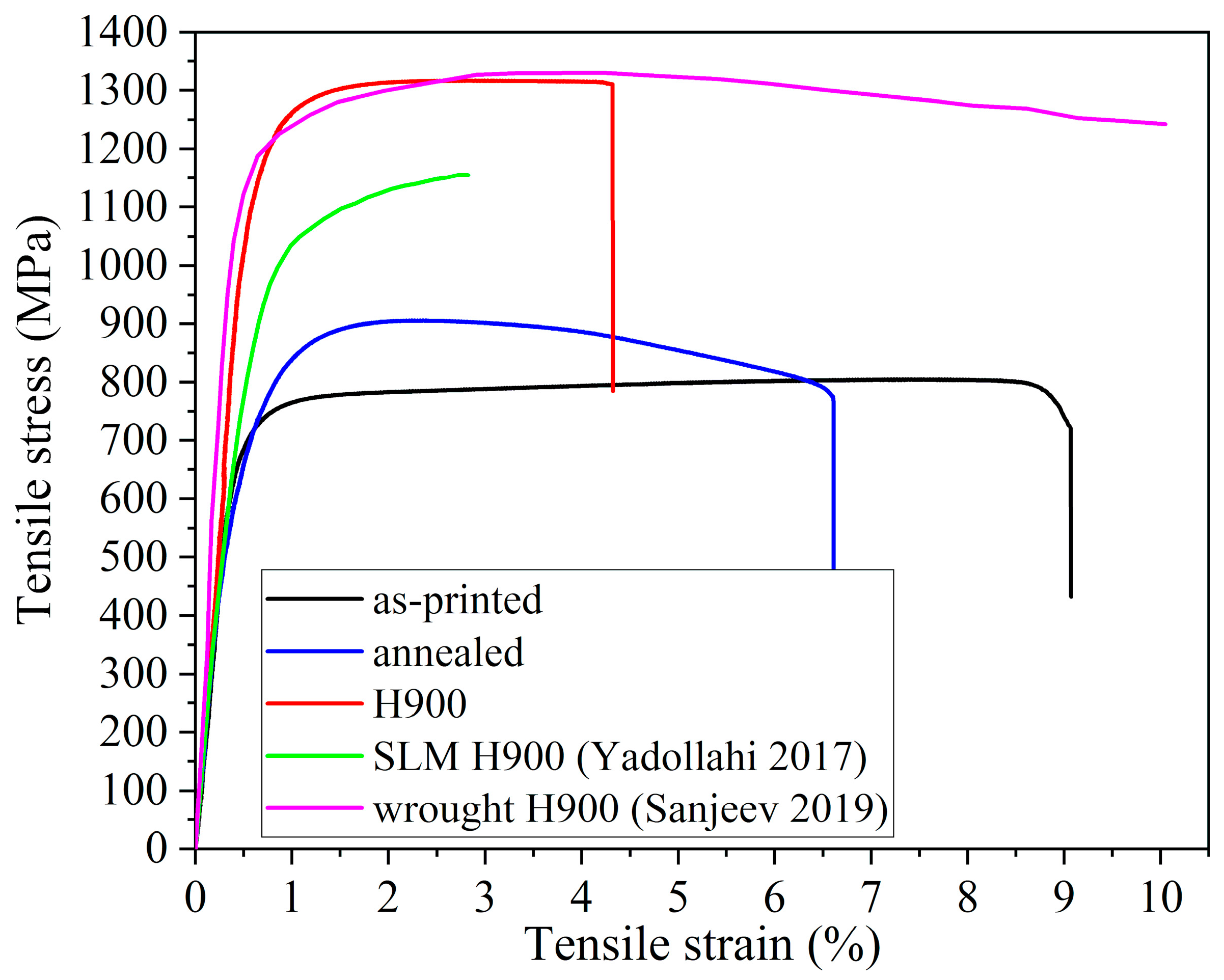
3.3. Tensile Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nickels, L. AM and aerospace: An ideal combination. Met. Powder Rep. 2015, 70, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, L.; Fernández, R.; González, S. Topology optimization and additive manufacturing for aerospace components. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 4, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.W.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing. In Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Sparks, T.; Liou, F.; Newkirk, J. Aerospace applications of laser additive manufacturing. In Laser Additive Manufacturing; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USAF Structures Bulletin EZ-SB-19-01, Durability and Damage Tolerance Certification for Additive Manufacturing of Aircraft Structural Metallic Parts, Wright Patterson Air Force Base, OH, USA, 10 June 2019. Available online: https://daytonaero.com/wp-content/uploads/EZ-SB-19-01.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- MIL-STD-1530D; Department of Defense Standard Practice Aircraft Structural Integrity Program (ASIP). Military and Government Specs & Standards (Naval Publications and Form Center) (NPFC): New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Kundu, S.; Jones, R.; Peng, D.; Matthews, N.; Alankar, A.; Raman, S.R.K.; Huang, P. Review of Requirements for the Durability and Damage Tolerance Certification of Additively Manufactured Aircraft Structural Parts and AM Repairs. Materials 2020, 13, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbst, U.; Bruno, G.; Buffiere, J.Y.; Wegener, T.; Niendorf, T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Kashaev, N.; Meneghetti, G.; Hrabe, N.; et al. Damage tolerant design of additively manufactured metallic components subjected to cyclic loading: State of the art and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 121, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Leary, M.; Downing, D.; Gibson, I.; Sharabian, E.G.; Veetil, J.K.; Brandt, M.; Bateman, S.; Rolfe, B. Benchmark models for conduction and keyhole modes in laser-based powder bed fusion of Inconel 718. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 109509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavecchia, F.; Pellegrini, A.; Galantucci, L.M. Comparative study on the properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel parts made by metal fused filament fabrication process and atomic diffusion additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giganto, S.; Martínez-Pellitero, S.; Barreiro, J.; Leo, P.; Ángeles Castro-Sastre, M. Impact of the laser scanning strategy on the quality of 17-4PH stainless steel parts manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 2734–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, P.; Sharma, B.; Masood, S.H.; Rahman Rashid, R.A.; Rashid, R.; Palanisamy, S.; Ruan, D. A study of tensile behavior of SLM processed 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4531–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, E.; Lutey, A.; Ascari, A.; Fortunato, A. The effects of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) and solubilization heat treatment on the density, mechanical properties, and microstructure of austenitic stainless steel parts produced by selective laser melting (SLM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreacola, F.R.; Capasso, I.; Pilotti, L.; Brando, G. Influence of 3D-printing parameters on the mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel produced through Selective Laser Melting. Frat. Ed Integrità Strutt. 2021, 58, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Ghosn, L.; Lerch, B.; Hebsur, M.; Cosgriff, L.; Fedor, J. Mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel foam panels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, P.; Masood, S.H.; Palanisamy, S.; Rahman Rashid, R.A.; Ruan, D. Characterization of 17-4PH alloy processed by selective laser melting. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 8498–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Tong, J.D.; Jiang, M.G.; Chen, Z.W.; Xu, G.; Liao, H.B.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.Y.; Xu, M.; Lao, C.S. Effect of scanning strategy on microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aripin, M.A.; Sajuri, Z.; Jamadon, N.H.; Baghdadi, A.H.; Syarif, J.; Mohamed, I.F.; Aziz, A.M. Effects of Build Orientations on Microstructure Evolution, Porosity Formation, and Mechanical Performance of Selective Laser Melted 17-4 PH Stainless Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E 92; Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM E23-16b; Standard Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM A693-16(2022); Standard Specification for Precipitation-Hardening Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Simchi, A.; Rota, A.; Imgrund, P. An investigation on the sintering behavious of 316L and 17-4ph stainless steel powders for graded composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 424, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk-Nykiel, A.; Gadek, S.; Hebda, M.; Nykiel, M.; Pieczonka, T.; Kazior, J. Influence of Sintering Atmosphere on Densification Development of 17-4PH stainless steel powder. Materials 2023, 16, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Blaine, D.; Marx, B.; Schlaefer, C.; German, R.M. Sintering Densification and Microstructural Evolution of Injection Molting Grade 17-4 PH Stainless steel Powder. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, P.; Smarslok, B.P.; German, R.M. Impact properties of sintered and wrought 17-4 PH stainless steel. Powder Metall. 2006, 49, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasebani, S.; Ghayoor, M.; Badwe, S.; Irrinki, H.; Atre, S.V. Effects of atomizing media and post processing on mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel manufactured via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M. Thermal Processing Optimization of Injection Molded Stainless Steel Powders. Mater. Manuf. Process. 1997, 12, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbauer, B.M.; Yanase, K.; Endo, M. The influence of various types of small defects on the fatigue limit of precipitation-hardened 17-4PH stainless steel. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 87, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, J.D.; Daros, D.P.; Sokolwski, A.; Mesquita, R.A.; Barbosa, C.A. Influence of hardness on the wear resistance of 17-4 PHstainless steel evaluated by the pin-on-disc testing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 205, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeev, K.C.; Nezhadfar, P.D.; Phillips, C.; Kennedy, M.S.; Shamsei, N.; Jackson, R.L. Tribological behavior of 17–4 PH stainless steel fabricated by traditional manufacturing and laser-based additive manufacturing methods. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203100. [Google Scholar]
- Yadollahi, A.; Shamsaei, N.; Thompson, S.M.; Elwany, A.; Bian, L. Effects of building orientation and heat treatment on fatigue behavior of selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, H.R.; Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Kong, C.; Molina-Luna, L.; Li, S. Heat treatment response of additively manufactured 17-4PH stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Hono, K.; Katayama, Y. Microstructural evolution in a 17-4 PH stainless steel after aging at 400 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.; Jalalahmadi, B.; Ashtekar, A.; Jiang, Y. Cyclic deformation and fatigue behavior of additively manufactured 17-4 PH stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambroo, R.; Roychowdhury, S.; Kain, V.; Raja, V.S. Effect of reverted austenite on mechanical properties of precipitation hardenable 17-4 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 568, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balajaddeh, B.M.; Naffakh-Moosavy, H. Pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of 17-4 PH stainless steel: Microstructure, mechanical properties, and weldability investigation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 119, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. Experimental investigation on selective laser melting of 17-4PH stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 87, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Army Directive 2019-29, Enabling Readiness and Modernization Through Advanced Manufacturing, Secretary of The Army, Pentagon, Washington DC, 18 September 2019. Available online: https://armypubs.army.mil/epubs/DR_pubs/DR_a/pdf/web/ARN19451_AD2019-29_Web_Final.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023).






| Condition | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness, Vickers | YS/UTS | Charpy Impact Energy (Joule) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | 1171 | 1309 | 10 | 410 | 0.89 | 22 |
| H1025 | 999 | 1068 | 12 | 349 | 0.94 | 54 |
| H1075 | 861 | 999 | 13 | 328 | 0.86 | 61 |
| H1150 | 723 | 930 | 16 | 292 | 0.78 | 75 |
| C | Cr | Cu | Ni | Nb | Ta | Mn | Si | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured | 0.01 | 17.1 | 3.03 | 4.46 | 0.27 | <0.01 | - | - | Bal. |
| Certification | 0.02 | 16.52 | 3.94 | 4.47 | 0.30 | - | 0.04 | 0.43 | Bal. |
| State | Sample | ρ Measured (g/cm3) | ρ Relative (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| as printed | 1. | 7.54 | 97.30 |
| 2. | 7.63 | 98.46 | |
| 3. | 7.52 | 96.98 | |
| annealed | 4. | 7.58 | 97.76 |
| 5. | 7.56 | 97.61 | |
| 6. | 7.56 | 97.58 | |
| H900 | 7. | 7.55 | 97.40 |
| 8. | 7.54 | 97.27 | |
| 9. | 7.57 | 97.70 |
| CONDITION | YS (MPA) | UTS (MPA) | EL (%) | YS/UTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS PRINTED | 712 ± 6 | 796 ± 8 | 9.4 ± 0.6 | 0.89 |
| ANNEALED | 714 ± 5 | 904 ± 6 | 6.1 ± 0.4 | 0.79 |
| H900 (AGED) | 1190 ± 16 | 1309 ± 13 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacs, S.E.; Miko, T.; Troiani, E.; Markatos, D.; Petho, D.; Gergely, G.; Varga, L.; Gacsi, Z. Additive Manufacturing of 17-4PH Alloy: Tailoring the Printing Orientation for Enhanced Aerospace Application Performance. Aerospace 2023, 10, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10070619
Kovacs SE, Miko T, Troiani E, Markatos D, Petho D, Gergely G, Varga L, Gacsi Z. Additive Manufacturing of 17-4PH Alloy: Tailoring the Printing Orientation for Enhanced Aerospace Application Performance. Aerospace. 2023; 10(7):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10070619
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacs, Sandor Endre, Tamas Miko, Enrico Troiani, Dionysios Markatos, Daniel Petho, Greta Gergely, Laszlo Varga, and Zoltan Gacsi. 2023. "Additive Manufacturing of 17-4PH Alloy: Tailoring the Printing Orientation for Enhanced Aerospace Application Performance" Aerospace 10, no. 7: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10070619
APA StyleKovacs, S. E., Miko, T., Troiani, E., Markatos, D., Petho, D., Gergely, G., Varga, L., & Gacsi, Z. (2023). Additive Manufacturing of 17-4PH Alloy: Tailoring the Printing Orientation for Enhanced Aerospace Application Performance. Aerospace, 10(7), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10070619