CMAG: A Mission to Study and Monitor the Inner Corona Magnetic Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. State-of-the-Art in Coronal Science
1.2. Observing the Inner Solar Corona
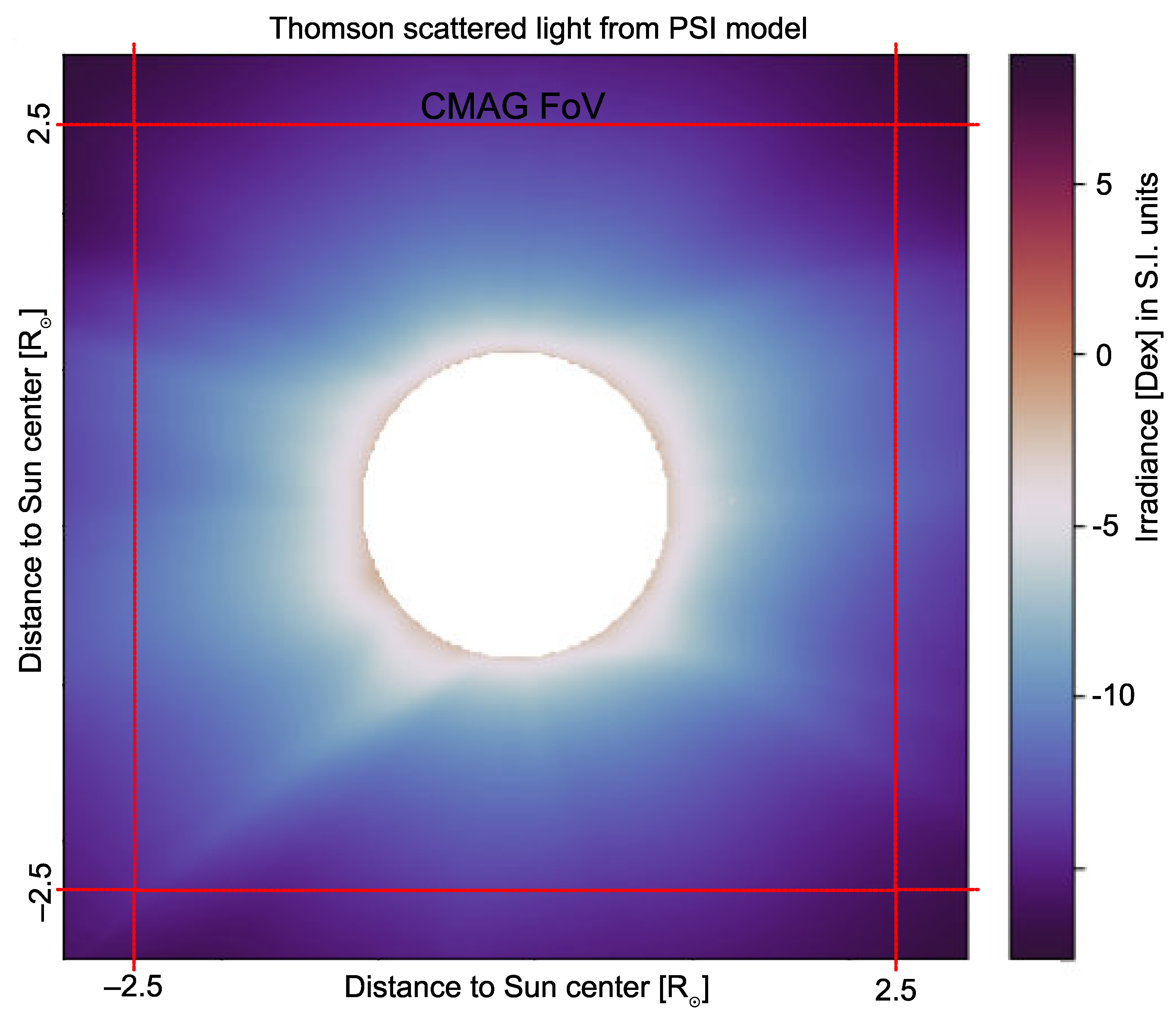
1.3. Solar Corona Polarimetry
1.4. Scientific Goals of the CMAG Mission
- What is the structure of the inner coronal magnetic field? Understanding the magnetic field’s structuring in coronal loops and streamers and its evolution and relationship with photospheric fields is crucial. CMAG’s high spatial resolution (2.5″) and cadence (≈1 min) will determine the strength and direction of the vector magnetic field from close to the surface to the higher layers for providing an empirical basis that help validate and refine current extrapolations and improve coronal magnetic models.
- What is the coronal origin of the solar wind? The solar wind has distinct components: slow and fast, related to coronal streamers, coronal hole boundaries, and the solar network. CMAG will investigate the magnetic connection between coronal holes, streamers, and the solar wind, aiding the understanding of how the solar wind propagates through the heliosphere and its relationship with coronal waves.
- How are flares and CMEs generated? Flares and CMEs are phenomena with different effects on the heliosphere and the Earth’s environment. CMAG will reveal the inner corona’s internal structure and evolution and follow the magnetic field vector during the CME onset and the generation of associated waves. At a resolution of 2.5″, it could also provide a glimpse of the evolution of the magnetic field structure at the reconnection sites.
- What is the origin of solar coronal heating? Measurements of magnetic field strength will provide a quantitative basis for assessing the origin of non-thermal heat observed in the Sun’s inner coronal layers.
- What is the role of the inner corona in space weather? CMAG’s measurements of inner coronal magnetic fields at L5, provided in almost real time, will greatly enhance space weather nowcasting and forecasting capabilities, crucial for predicting radiation and energetic particle impacts on Earth as a consequence of flares and CMEs.
1.5. Top Science Requirements
2. Mission Concept
2.1. Mission Profile
2.2. Mission Operations Baseline and Spacecraft Concept
2.3. Payload Concept Design
2.4. CMAG Data Products
3. A Mission Opportunity
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMAG | Coronal magnetograph |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| CME | Coronal mass ejection |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamic |
| LASCO | Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph |
| UVCS | Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer |
| SOHO | Solar and Heliospheric Observatory |
| STEREO | Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory |
| SECCHI | Sun–Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation |
| METIS | The multiwavelength coronagraph for the Solar Orbiter mission |
| SoloHI | Solar Orbiter Heliospheric Imager |
| ASPIICS | Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the |
| Corona of the Sun | |
| CRYO-NIRSP | Cryogenic Near-IR Spectropolarimeter |
| DKIST | Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope |
| SPARK | Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics |
| PDE | Performance Drift Error |
| COSMO | COronal Solar Magnetism Observatory |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| PUNCH | Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere |
| AOCS | Attitude and Orbit Control Subsystem |
| PHI | Polarimetric and Helioseismic Imager |
| TuMAG | Tunable Magnetograph |
References
- Reale, F. Coronal Loops: Observations and Modeling of Confined Plasma. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2014, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmer, M. Space weather: The solar perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdélyi, R.; Fedun, V. Are There Alfvén Waves in the Solar Atmosphere? Science 2007, 318, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathioudakis, M.; Jess, D.B.; Erdélyi, R. Alfvén Waves in the Solar Atmosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 175, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschwanden, M.J. Physics of the Solar Corona. An Introduction with Problems and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Library of Congress Control Number: 2005937065; Aschwanden, M.J., Ed.; Praxis Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin, Germany, 2005; 892p, ISBN 3-540-30765-6. [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner, G.E.; Howard, R.A.; Koomen, M.J.; Korendyke, C.M.; Michels, D.J.; Moses, J.D.; Socker, D.G.; Dere, K.P.; Lamy, P.L.; Llebaria, A.; et al. The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, J.L.; Esser, R.; Gardner, L.D.; Habbal, S.; Daigneau, P.S.; Dennis, E.F.; Nystrom, G.U.; Panasyuk, A.; Raymond, J.C.; Smith, P.L.; et al. The Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer for the solar and heliospheric observatory. Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, V.; Fleck, B.; Poland, A.I. The scientific payload of the space-based Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO). Space Sci. Rev. 1994, 70, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.A.; Moses, J.D.; Vourlidas, A.; Newmark, J.S.; Socker, D.G.; Plunkett, S.P.; Korendyke, C.M.; Cook, J.W.; Hurley, A.; Davila, J.M.; et al. Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 136, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, E.; Romoli, M.; Andretta, V.; Fineschi, S.; Heinzel, P.; Moses, J.D.; Naletto, G.; Nicolini, G.; Spadaro, D.; Teriaca, L.; et al. Metis: The Solar Orbiter visible light and ultraviolet coronal imager. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.A.; Vourlidas, A.; Colaninno, R.C.; Korendyke, C.M.; Plunkett, S.P.; Carter, M.T.; Wang, D.; Rich, N.; Lynch, S.; Thurn, A.; et al. The Solar Orbiter Heliospheric Imager (SoloHI). Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; St Cyr, O.C.; Zouganelis, I.; Gilbert, H.R.; Marsden, R.; Nieves-Chinchilla, T.; Antonucci, E.; Auchère, F.; Berghmans, D.; Horbury, T.S.; et al. The Solar Orbiter mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourlidas, A.; Howard, R.A.; Plunkett, S.P.; Korendyke, C.M.; Thernisien, A.F.R.; Wang, D.; Rich, N.; Carter, M.T.; Chua, D.H.; Socker, D.G.; et al. The Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe Plus (WISPR). Space Sci. Rev. 2016, 204, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouafi, N.E.; Matteini, L.; Squire, J.; Badman, S.T.; Velli, M.; Klein, K.G.; Chen, C.H.K.; Matthaeus, W.H.; Szabo, A.; Linton, M.; et al. Parker Solar Probe: Four Years of Discoveries at Solar Cycle Minimum. Space Sci. Rev. 2023, 219, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, D.; Bemporad, A.; Buckley, S.; Cernica, I.; Dániel, V.; Denis, F.; de Vos, L.; Fineschi, S.; Galy, C.; Graczyk, R.; et al. Development of ASPIICS: A coronagraph based on Proba-3 formation flying mission. Proc. SPIE 2018, 10698, 106982Y. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; Card, G.L.; Darnell, T.; Elmore, D.F.; Lull, R.; Nelson, P.G.; Streander, K.V.; Burkepile, J.; Casini, R.; Judge, P.G. An Instrument to Measure Coronal Emission Line Polarization. Sol. Phys. 2008, 247, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; Landi, E. Solar Heliospheric and INterplanetary Environment (SHINE 2019). Available online: https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2022/nsf22570/nsf22570.htm (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Fehlmann, A.; Kuhn, J.R.; Schad, T.A.; Scholl, I.F.; Williams, R.; Agdinaoay, R.; Berst, D.C.; Craig, S.C.; Giebink, C.; Goodrich, B.; et al. The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) Cryogenic Near-Infrared Spectro-Polarimeter. Sol. Phys. 2023, 298, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmele, T.R.; Warner, M.; Keil, S.L.; Goode, P.R.; Knölker, M.; Kuhn, J.R.; Rosner, R.R.; McMullin, J.P.; Casini, R.; Lin, H.; et al. The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope—Observatory Overview. Sol. Phys. 2020, 295, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Grumer, J.; Yang, Y.; Brage, T.; Yao, K.; Chen, C.; Watanabe, T.; Jönsson, P.; Lundstedt, H.; Hutton, R.; et al. A Novel Method to Determine Magnetic Fields in Low-Density Plasma Facilitated through Accidental Degeneracy of Quantum States in Fe9+. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Tu, B.; Xiao, J.; Grumer, J.; Brage, T.; Watanabe, T.; Hutton, R.; Zou, Y. Atomic-Level Pseudo-Degeneracy of Atomic Levels Giving Transitions Induced by Magnetic Fields, of Importance for Determining the Field Strengths in the Solar Corona. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, P.G.; Hutton, R.; Li, W.; Brage, T. On the Fine Structure Splitting of the 3p43d4D5/2 and 3p43d4D7/2 Levels of Fex. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.H.; Warren, H.P.; Landi, E. Measurements of Coronal Magnetic Field Strengths in Solar Active Region Loops. Astrophys. J. 2021, 915, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Sakao, T.; Shimizu, T.; Sone, Y.; Tachikawa, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Minesugi, K.; Ohnishi, A.; Yamada, T.; et al. The Hinode (Solar-B) Mission: An Overview. Sol. Phys. 2007, 243, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culhane, J.L.; Harra, L.K.; James, A.M.; Al-Janabi, K.; Bradley, L.J.; Chaudry, R.A.; Rees, K.; Tandy, J.A.; Thomas, P.; Whillock, M.C.R.; et al. The EUV Imaging Spectrometer for Hinode. Sol. Phys. 2007, 243, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bethge, C.; Tian, H.; Tomczyk, S.; Morton, R.; Del Zanna, G.; McIntosh, S.W.; Karak, B.B.; Gibson, S.; Samanta, T.; et al. Global maps of the magnetic field in the solar corona. Science 2020, 369, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.A.S. The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept; University College London: London, UK, 2024; [Manuscript in preparation]. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo Bueno, J.; del Pino Alemán, T. Magnetic Field Diagnostics in the Solar Upper Atmosphere. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 60, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissandrakis, C.E.; Gary, D.E. Radio Measurements of the Magnetic Field in the Solar Chromosphere and the Corona. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computation of the Thomson Scattering of the K-Corona. Available online: https://github.com/aliciavr/thomsonpy (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Judge, P.G.; Casini, R.; Tomczyk, S.; Edwards, D.P.; Francis, E. Technical Report, PB2002-102493; NCAR/TN-466-STR, 02. 2001. Available online: https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/technotes:304 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Schad, T.; Dima, G. Forward Synthesis of Polarized Emission in Target DKIST Coronal Lines Applied to 3D MURaM Coronal Simulations. Sol. Phys. 2020, 295, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi Degl’Innocenti, E.; Landolfi, M. Polarization in Spectral Lines; Degl’innocenti, E.L., Landolfi, M., Eds.; University of Fierenze: Firenze, Italy; Arcetri Observatory: Firenze, Italy; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2004; Volume 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo Bueno, J. Atomic Polarization and the Hanle Effect. Adv. Sol.-Polarim.—Theory Obs. Instrum. 2001, 236, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, P.G. Spectral Lines for Polarization Measurements of the Coronal Magnetic Field. I. Theoretical Intensities. Astrophys. J. 1998, 500, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, P.G.; Casini, R. Advanced Solar Polarimetry: Theory, Observation, and Instrumentation. Adv. Sol.-Polarim.—Theory Obs. Instrum. 2001, 236, 503. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Kuhn, J.R.; Coulter, R. Coronal Magnetic Field Measurements. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, L177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuridze, D.; Mathioudakis, M.; Morgan, H.; Oliver, R.; Kleint, L.; Zaqarashvili, T.V.; Reid, A.; Koza, J.; Löfdahl, M.G.; Hillberg, T.; et al. Mapping the Magnetic Field of Flare Coronal Loops. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Abbo, L.; Andretta, V.; Auchère, F.; Bemporad, A.; Berrilli, F.; Bommier, V.; Braukhane, A.; Casini, R.; Curdt, W.; et al. Solar magnetism eXplorer (SolmeX). Exp. Astron. 2012, 33, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Ballester, E.A.; Andretta, V.; Auchère, F.; Belluzzi, L.; Bemporad, A.; Berghmans, D.; Buchlin, E.; Calcines, A.; Chitta, L.P.; et al. Magnetic imaging of the outer solar atmosphere (MImOSA). Exp. Astron. 2022, 54, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; Burkepile, J.; Casini, R.; Corchado-Albelo, M.; DeLuca, E.; de Toma, G.; de Wijn, A.; Dikpati, M.; Fan, Y.; Farid, S.; et al. COSMO: The COronal Solar Magnetism Observatory. Bull. AAS 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougeot, R.; Flamary, R.; Galano, D.; Aime, C. Performance of the hybrid externally occulted Lyot solar coronagraph. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 599, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deforest, C.; Killough, R.; Gibson, S.; Henry, A.; Case, T.; Beasley, M.; Laurent, G.; Colaninno, R.; Waltham, N. Polarimeter to UNify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH): Science, Status, and Path to Flight. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; p. 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Pillet, V.; Tritschler, A.; Harra, L.; Andretta, V.; Vourlidas, A.; Raouafi, N.; Alterman, B.L.; Bellot Rubio, L.; Cauzzi, G.; Cranmer, S.R.; et al. Solar Physics in the 2020s: DKIST, Parker Solar Probe, and Solar Orbiter as a Multi-Messenger Constellation. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2020, 18, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.W.; Williams, D.R.; O’Kane, J. Evolution of the critical torus instability height and coronal mass ejection likelihood in solar active regions. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 665, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.K.; del Toro, Iniesta, J.C.; Woch, J.; Gandorfer, A.; Hirzberger, J.; Alvarez-Herrero, A.; Appourchaux, T.; Martínez Pillet, V.; Pérez-Grande, I.; Sanchis Kilders, E.; et al. The Polarimetric and Helioseismic Imager on Solar Orbiter. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Toro Iniesta, J.C.; Orozco Suárez, D.; Álvarez-Herrero, A. Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, Granada, Spain. 2024; [Manuscript in preparation]. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, S.K. Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Göttingen, Germany. 2024; [Manuscript in preparation]. [Google Scholar]
- Casini, R.; White, S.M.; Judge, P.G. Magnetic Diagnostics of the Solar Corona: Synthesizing Optical and Radio Techniques. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 210, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.; Fernandez-Rico, G.; Gandorfer, A.; Gizon, L.; Hirzberger, J.; Kraft, S.; Lagg, A.; Schou, J.; Solanki, S.K.; del Toro Iniesta, J.C.; et al. PMI: The Photospheric Magnetic Field Imager. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spatial resolution | 2.5″ at 750 nm |
| Aperture | 10 cm |
| Cadence | ≈1 min for S/N = 1000 in Stokes Q, U, and V |
| Field of view (FoV) | ≈2400″ (≈0.66 = 2.5 R⊙) |
| Targets spectral lines | Fe XIV 530 nm; Fe XI 789 nm; Fe XIII 1074 nm |
| Spectral resolution | 20 pm; 30 pm; 40 pm |
| Maximum spectral shift over the FoV | 25 pm; 30 pm; 50 pm |
| Detector dimensions | 4 k × 4 k pixels |
| Etalon max. incidence angle 1 | 1.28° |
| Etalon diameter | ≈60 mm |
| Polarization modulator interm. image diameter | ≈55 mm |
| dimensions | <1 m |
| stray light requirements | <0.1% @ 1.02 R⊙ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orozco Suárez, D.; del Toro Iniesta, J.C.; Bailén Martínez, F.J.; Balaguer Jiménez, M.; Álvarez García, D.; Serrano, D.; Peñin, L.F.; Vázquez-Ramos, A.; Bellot Rubio, L.R.; Atienzar, J.; et al. CMAG: A Mission to Study and Monitor the Inner Corona Magnetic Field. Aerospace 2023, 10, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10120987
Orozco Suárez D, del Toro Iniesta JC, Bailén Martínez FJ, Balaguer Jiménez M, Álvarez García D, Serrano D, Peñin LF, Vázquez-Ramos A, Bellot Rubio LR, Atienzar J, et al. CMAG: A Mission to Study and Monitor the Inner Corona Magnetic Field. Aerospace. 2023; 10(12):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10120987
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrozco Suárez, David, Jose Carlos del Toro Iniesta, Francisco Javier Bailén Martínez, María Balaguer Jiménez, Daniel Álvarez García, Daniel Serrano, Luis F. Peñin, Alicia Vázquez-Ramos, Luis Ramón Bellot Rubio, Julia Atienzar, and et al. 2023. "CMAG: A Mission to Study and Monitor the Inner Corona Magnetic Field" Aerospace 10, no. 12: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10120987
APA StyleOrozco Suárez, D., del Toro Iniesta, J. C., Bailén Martínez, F. J., Balaguer Jiménez, M., Álvarez García, D., Serrano, D., Peñin, L. F., Vázquez-Ramos, A., Bellot Rubio, L. R., Atienzar, J., Pérez Grande, I., Torralbo Gimeno, I., Sanchis Kilders, E., Gasent Blesa, J. L., Hernández Expósito, D., Ruiz Cobo, B., Trujillo Bueno, J., Erdélyi, R., Davies, J. A., ... Scullion, E. (2023). CMAG: A Mission to Study and Monitor the Inner Corona Magnetic Field. Aerospace, 10(12), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10120987







