Abstract
Models of particle acceleration in solar eruptive events suggest that roughly equal energy may go into accelerating electrons and ions. However, while previous solar X-ray spectroscopic imagers have transformed our understanding of electron acceleration, only one resolved image of γ-ray emission from solar accelerated ions has ever been produced. This paper outlines a new satellite instrument concept—the large imaging spectrometer for solar accelerated nuclei (LISSAN)—with the capability not only to observe hundreds of events over its lifetime, but also to capture multiple images per event, thereby imaging the dynamics of solar accelerated ions for the first time. LISSAN provides spectroscopic imaging at photon energies of 40 keV–100 MeV on timescales of ≲10 s with greater sensitivity and imaging capability than its predecessors. This is achieved by deploying high-resolution scintillator detectors and indirect Fourier imaging techniques. LISSAN is suitable for inclusion in a multi-instrument platform such as an ESA M-class mission or as a smaller standalone mission. Without the observations that LISSAN can provide, our understanding of solar particle acceleration, and hence the space weather events with which it is often associated, cannot be complete.
1. Introduction
Particle acceleration is one of the earliest observable consequences of impulsive magnetic energy release, a process that drives many phenomena in the solar corona. Among these are solar eruptive events, the most geo-effective form of space weather. In the standard model of solar eruptive events (Figure 1; see also [1]), the coronal magnetic field becomes highly stressed due to turbulent motions at the “footpoints” below. Here, the magnetic field passes between the lower atmosphere, where the plasma dictates the motion of the field (high-β plasma), to the corona, where the field dictates the motion of the plasma (low-β plasma). Under certain conditions, the excess energy in the field can be suddenly released via magnetic reconnection, which rapidly rearranges the field into a lower stress configuration (transition from blue to green field lines in Figure 1). Depending on the magnetic configuration, the plasma, magnetic field and accelerated particles may escape into the heliosphere as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), “jets” or solar energetic particle (SEP) events. Charged particles accelerated downwards spiral along magnetic field lines towards the footpoints, depositing their energy via Coulomb collisions as they propagate. Because the ambient density in the chromospheric footpoints is orders of magnitude greater than in the corona, most of the particles’ energy is deposited there. This rapidly heats and ionises the chromospheric plasma, which ablates back into the corona along the magnetic field lines in a process known as chromospheric evaporation. This produces coronal loops that glow at several million kelvin. The intense broadband radiation produced throughout this process is known as a solar flare.
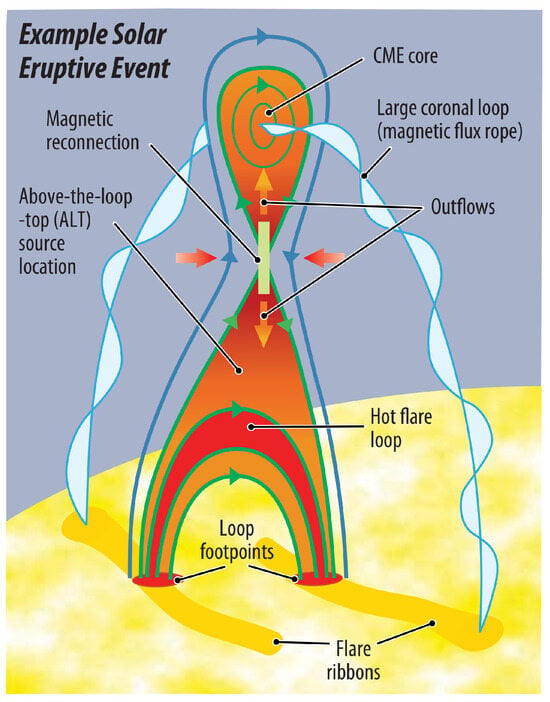
Figure 1.
Standard model of a solar eruptive event. Magnetic reconnection releases stored energy in the coronal magnetic field which accelerates charged particles and heats local plasma, causes the growth of flare loop arcades, and can result in the ejection of plasma and the magnetic field into the heliosphere (coronal mass ejection, CME). Figure courtesy of [2,3].
Particles in solar eruptive events can be divided into three populations: accelerated ions, accelerated electrons and hot plasmas. Accelerated ions in the range of 1–100 MeV/nucleon can be detected via various lines in the γ-ray range 1–10 MeV due to nuclear de-excitation, neutron capture, and positron annihilation [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Accelerated ions with energies greater than 100 MeV/nucleon can be detected via the decay of secondary pions via nuclear reactions with the ambient medium. As the pions decay, the decay products produce a broad-band continuum at photon energies above 10 MeV, with a broad peak around 70 MeV from neutral pion radiation [12,13]. Hot plasmas (≳5 MK) and non-thermally accelerated electrons can be characterised via the hard X-ray (HXR; ≳5 keV) bremsstrahlung emission, which is produced as they scatter in the ambient medium. The bremsstrahlung spectrum reflects the velocity distribution of the particles that produced it and can be inverted to calculate the spectrum of the emitting electrons [14,15]. Hot plasmas can therefore be distinguished by their Maxwellian-shaped (thermal) spectrum, which dominates at lower energies (≲20 keV), and accelerated electrons can be distinguished by their power-law-shaped (non-thermal) spectrum, which tends to dominate at higher energies (≳15 keV) (e.g., [16,17,18]). Moreover, unlike other signatures (e.g., radio emission), X-rays can provide measurements of the numbers and energies of accelerated electrons, and hence provide a unique insight into the underlying acceleration process.
The Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI; [19]) was the first instrument to simultaneously produce images and spectra of solar eruptive events in HXR on timescales of several seconds. Consequently, its observations have transformed our understanding of electron acceleration and the evolution of solar eruptive events. The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX; [20]) onboard Solar Orbiter is furthering this understanding by producing similar diagnostics at a higher time cadence from different viewing angles than that of Earth. Despite this, neither RHESSI nor STIX provide sufficient sensitivity and imaging capability in the γ-ray regime to reliably observe ion acceleration. An image of solar γ-ray line emission has only been produced for one solar flare, and the emission centroid has been localised in an additional four [21,22]. Moreover, solar γ-ray imaging has never been performed on timescales sufficient to reveal the spatio-temporal evolution of accelerated ions during a flare. Hence, the role of ion acceleration in solar eruptive events remains largely unknown. This is despite evidence that flare-accelerated ions may carry comparable energy to that of electrons (e.g., [23,24,25]). Thus, our understanding of solar particle acceleration and the space weather events with which it is often associated cannot be complete until we can reliably observe this missing half of the picture.
In this paper, we outline the large imaging spectrometer for solar accelerated nuclei (LISSAN) satellite instrument concept. LISSAN was originally conceived as part of a suite of instruments for an ESA M-class mission concept (SPARK; [26]). It provides reliable imaging and the spectral characterisation of both electron and ion acceleration in solar eruptive events for the first time. This will enable it to answer several important open questions regarding solar particle acceleration and the initiation of space weather events. We discuss some of the most pressing of these in Section 2 and define the instrument performance required to address them in Section 3. We also lay out LISSAN’s expected performance based on its design, which we describe in Section 4. Finally, in Section 5, we summarise the LISSAN instrument concept and its capabilities for revealing new science concerning ion acceleration in solar eruptive events.
2. Unresolved Questions Regarding Ion Acceleration in Solar Eruptive Events
While our understanding of electron acceleration in solar eruptive events has been greatly enhanced in recent decades by instruments like RHESSI and STIX, our understanding of ion acceleration is poorly constrained due to the tiny number of γ-ray spectroscopic imaging observations available. In this section, we discuss three major outstanding questions regarding solar ion acceleration and the observations required to resolve them (Figure 2).
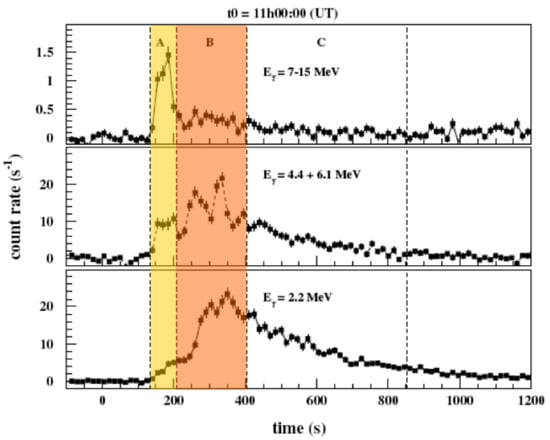
Figure 2.
Time histories of the -ray emission during the 28 October 2003 X17-class flare due to electron bremsstrahlung (upper panel) and the nuclear line emission (prompt lines: h = 4.4 and 6.1 MeV; delayed neutron capture line 2.223 MeV; INTEGRAL). The dashed lines and shading denote different phases of the flare. Initially (phase A, yellow), impulsive non-thermal bremsstrahlung emission from accelerated electrons dominates. As this ceases, increases in prompt line and delayed neutron capture emission is seen (phase B, orange) before it slowly decays (phase C, white). Figure taken from [27]. For more details, see that study.
2.1. Do Ion and Electron Acceleration in Solar Eruptive Events Share a Close Physical Relationship?
It is still unclear whether there is a close physical link between ion and electron acceleration in solar eruptive events, or whether different mechanisms dominate for the different species at different energies. For example, first-order Fermi acceleration in magnetic islands is expected to operate similarly for both ions and electrons [28], resulting in comparable spectral indices [29]. However, efficient energisation requires pre-heating, for which the responsible mechanisms likely differ between electrons and ions [30,31]. If ion and electron acceleration do share a close physical relationship, we might expect their emission to be well correlated in space and time. However, the few observations to date appear to paint an inconclusive and contradictory picture.
One study [32] examined event-integrated fluences in many events of bremsstrahlung emission above 300 keV from accelerated electrons and 2.223 MeV line emission indirectly produced by protons accelerated above 30 MeV. It found that these signatures correlate well over three orders of magnitude, suggesting that there is a close physical relationship between electron and ion acceleration. However, a detailed study of the 28 October 2003 X17 event showed differences in the spatially integrated time evolution of accelerated electrons and ions during the course of a flare [27]. This found that the emission from accelerated electrons initially dominated (Figure 2, top panel, phase A, yellow) while the γ-ray line emission from accelerated ions became prominent later (Figure 2, middle and lower panels, phase B, orange). Other studies [11,21] have observed differences in the relative locations of electron HXR and ion 2.2 MeV γ-ray line emission in three of the five flares for which γ-ray emission could be localised. Note that “localised” is not the same as “imaged”. A single γ-ray image was produced for only one of these events (28 October 2003; Figure 3). For the others, only the emission centroid could be inferred via localisation techniques, but not its size or morphology. Moreover, the spatial uncertainty associated with localisation is greater than when a resolved image can be produced. Nonetheless, the statistically significant separations determined with localisation techniques between electron HXR and ion γ-ray sources may suggest different acceleration mechanisms and/or paths taken by electrons and ions as they precipitate through the solar atmosphere.
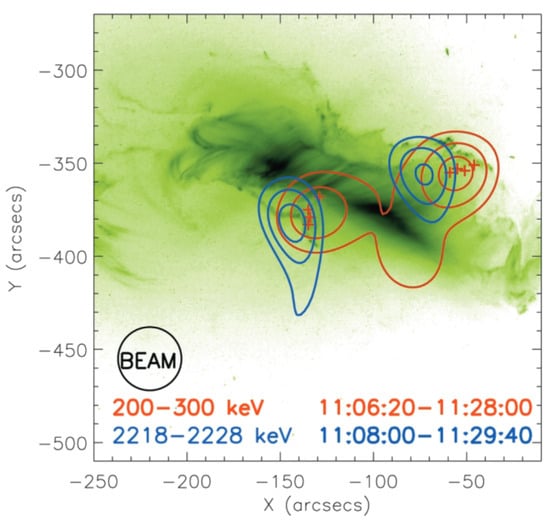
Figure 3.
The 50%, 70%, and 90% contours of γ-ray (blue) and HXR (red) images made with RHESSI were overlaid on a TRACE 195 Å image of the 28 October 2003 X17-class flare. The red plus signs indicate the 200–300 keV HXR footpoint locations for successive adjacent intervals of 100, 120, 180, and 240 s. This figure was taken from [22].
To reveal the temporal and spatial connections between accelerated electrons and ions, γ-ray and HXR emission must be imaged simultaneously for a significant number of solar eruptive events. Moreover, they must be imaged on timescales that reveal their evolution during the impulsive phase of flares when electron acceleration is known to be prominent. The one HXR-γ-ray flare image produced to date (Figure 3) is insufficient to achieve these goals.
2.2. How Efficient Is Ion Acceleration in Solar Eruptive Events?
The fraction of particles accelerated out of the ambient Maxwellian velocity distribution and the total energy they contain are essential constraints on acceleration models. Acceleration by magnetic islands [33] and super-Dreicer electric fields in a reconnecting current sheet [34] can accelerate a large fraction of the available electrons and perhaps ions, while mechanisms relying on large-scale sub-Dreicer electric fields cannot [35]. In the few extreme cases where RHESSI observed non-thermal HXR sources near the believed acceleration site above flaring loops, the interpretation of their spectra suggested that, essentially, all electrons in the acceleration region were accelerated in a bulk-energisation process [36,37]. It is unknown how such a process can be sustained given the limited number of electrons available in the acceleration region, although return currents repopulating the region is a possibility [38,39,40,41,42].
In contrast, even less is known about the efficiency of the ion acceleration process. The relative number of accelerated particles of different ion species can be constrained by the shapes and fluences of various γ-ray lines (e.g., alpha/proton ratio; [27]). The relative abundances of heavier accelerated ions can be determined from the relative fluences of broad de-excitation lines produced when heavy energetic ions interact with ambient H and He. Because these lines are broad, they are difficult to distinguish from the underlying continua formed by electrons and nuclei. One study computed both narrow and broad γ-ray line spectra for the most abundant elements and accelerated ions in the solar atmosphere [43]. It compared elemental abundances of a single flare observed with SMM/GRS with similar abundances measured in space for large proton flares and impulsive 3He events. Although the uncertainties were large for most elements, Ref. [43] found that Mg and Fe were significantly enhanced (>3–4σ) relative to C and O, similarly to impulsive 3He-rich events. However, since this study only examined one event, it is unclear whether this result is representative of ion acceleration in flares. Observations of a behind the limb flare with GRANAT/PHEBUS showed that enhancements of heavy ions (Ne-Fe) increased with time over the course of the flare, before finally reaching the highest values observed in solar energetic particle events by in situ measurements [44].
The relative importance as a function of time of the narrow (proton and alpha-particle) and broad (heavier accelerated species) lines would be key evidence for the progress of the energisation process. However, observations to date have not been able to support sufficiently comprehensive studies to determine this.
2.3. How Are the Most Energetic Particles in the Solar Atmosphere Accelerated?
Studies of small numbers of events examining the γ-ray lines (1–10 MeV) and pion continuum (>10 MeV) suggest that the accelerated ion spectrum is not a simple power law extending from the non-relativistic (1–100 MeV/nucleon) to relativistic (>few hundred MeV/nucleon) regimes [45,46,47,48,49]. These studies were performed with observations from different instruments, and so uncertainties in cross-calibration mean that their results are not conclusive. They nonetheless raise the question of whether the most energetic particles are accelerated via a different mechanism.
The longevity of some pion emission presents another major challenge to our understanding of how most energetic solar particles are accelerated (e.g., [50]). Once again, the limited observations to date paint an inconclusive and contradictory picture. Fermi-LAT observed emission for more than two hours in 21 solar flares, almost half of the pion-producing flares observed in the first 13 years of the mission. This raises the question of why such high-energy particles are present in the solar atmosphere, despite the apparent absence of other flare signatures [51]. The fact that most accelerated electrons are seen within the first several minutes of a flare suggests that the long-duration pion emission is caused by an acceleration mechanism with no close physical link to that of the electrons. The often quoted alternative is acceleration at a CME-driven shock. One study [52] analysed 30 solar eruptive events with long-duration γ-ray emission and their associations with CMEs and relativistic ions observed near Earth. They concluded that the γ-ray emission is most likely due to back-precipitation from a CME-driven shock. However, another analysis of 14 events [53] found no correlation between the observed interplanetary ions and the numbers required to produce the observed γ-ray emission, casting doubt on the CME scenario. In addition, it has been shown that, due to strong magnetic mirroring, the fraction of ions accelerated at a CME that would back-precipitate to the chromosphere should be in the order of 0.5–1% [54], significantly smaller than that derived from observations [53]. The 20 January 2005 flare demonstrated the possibility that very high-energy ions are accelerated in the flare process, rather than in the interplanetary medium [55,56,57]. Meanwhile, the Fermi-LAT observations of the 7 March 2012 flare suggest that the emission above 100 MeV migrated from the active region towards the western limb during the first 10 h. This supports the idea that particle acceleration could be occurring at an extended source [58,59]. However, Fermi-LAT’s angular resolution is too coarse to resolve the γ-ray sources and the inferred source locations are associated with large uncertainties.
Unravelling the relative roles of flare and interplanetary processes in accelerating high-energy ions is crucial to understanding long-duration events and their potential space weather consequences. However, it is clear that higher sensitivity observations in the HXR and γ-ray regimes are required to sufficiently examine the timing and spectra of electron bremsstrahlung and pion decay radiation. Moreover, this must be performed for a significant number of events, as flare and interplanetary processes may dominate in different scenarios.
3. LISSAN Instrument Requirements
To address the scientific questions outlined in Section 2, LISSAN must meet the performance requirements listed in the middle column of Table 1. A lower energy limit of 40 keV is required to observe the HXR emission from accelerated electrons. A higher energy limit of 80 MeV is required to measure the broadly peaked pion decay emission, which peaks at 70 MeV. To distinguish emission in different parts of the coronal structure, a spatial resolution of 10″ is required. To detect γ-ray line emission in an active region, and possibly pion decay sources away from the main site of energy release, a field of view with a diameter of ≥10′ is required. To follow the spatio-temporal evolution of the γ-ray line emission, an imaging cadence of 10 s is required. To characterise the alpha/proton ratio via the shapes of the C and O nuclear lines 4.4 and 6.1 MeV (∼1.5–4% FWHM; [60]), an energy resolution of 1.5% FWHM is required at 6.1 MeV. To detect the γ-ray emission from M-class flares, and characterise the temporal evolution of the γ-ray emission during intense events, effective area for imaging of 75 cm2 and an effective area for spectroscopy of 400 cm2 are required at 2.2 MeV.

The right column of Table 1 gives LISSAN’s expected performance based on its design (Section 4) which meets or exceeds the requirements in all categories. LISSAN represents a significant advance over any previous satellite-based solar γ-ray spectroscopic imager. For example, LISSAN’s imaging effective area is 25 times greater than RHESSI’s at 2.2 MeV and its effective area for spectroscopy at 2.2 MeV is 20 times greater. This will enable hundreds of solar γ-ray events to be imaged and for multiple images to be produced during individual flares. This is a drastic improvement over the single resolved γ-ray flare image produced to date. LISSAN’s improved imaging time cadence will help reveal how accelerated ions evolve in space and time, and how their importance relative to electrons changes during flares. The greater number of events observed will include a range of flare magnitudes, which will help reveal the different conditions that affect the ion acceleration process(es). Despite being crucial to understanding how solar eruptive events occur and evolve, such observations have never before been possible.
4. LISSAN Design
In this section, we first provide a high-level overview of LISSAN’s design that enables it to provide the observational capabilities described in Section 3. We then describe LISSAN’s indirect imaging system in more detail before moving onto a more technical discussion of LISSAN’s main components. We finish with a brief discussion of LISSAN’s spacecraft interface requirements and environmental constraints.
4.1. Instrument Concept
LISSAN reveals the dynamics of accelerated ions and electrons via spectroscopic imaging on timescales of 10 s in a photon energy range of 40 keV–100 MeV. Its basic design is outlined in Figure 4. LISSAN employs an indirect Fourier imaging technique which is valid across its entire spectral range (Section 4.2). Spatial information is encoded into 15 moiré patterns by 15 pairs of slightly offset grids (bigrids) separated by a fixed distance. The moiré patterns each represent a “spatial frequency” at a certain orientation on the sky and can be combined on the ground into images via various Fourier reconstruction techniques. Each bigrid is aligned with a pixelated GAGG crystal scintillator detector which records the time, location, and energy of each incoming photon. This enables both the moiré pattern and spectrum to be reproduced via the same imaging system, hence providing simultaneous imaging and spectroscopy. This imaging concept was pioneered and successfully employed by STIX [20,61]. In addition to its 15 imaging subcollimators (bigrids plus detector), LISSAN has an additional five gridless subcollimators. Four are used for enhanced sensitivity spectroscopy, as the absence of bigrids amplifies the photon throughput to the detector by a factor of 4 at the cost of imaging information. The fifth is used for monitoring background.
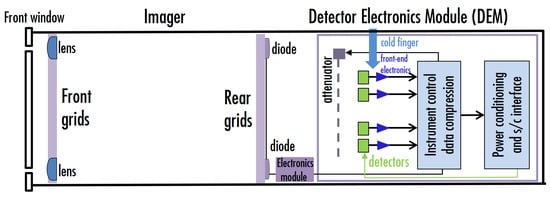
Figure 4.
Block diagram showing the main components of LISSAN’s design.
Incident photon flux can be moderated by a moveable attenuator that automatically responds to count rate thresholds. This avoids issues that corrupt the measured spectrum such as pile-up, which occurs when the rate at which photons are detected approaches the maximum rate at which the detector system can count. Due to the higher penetrating power of more energetic photons, the attenuator preferentially blocks lower energy X-rays. Thus, lower count rates can be achieved without impacting LISSAN’s ability to observe γ-rays from accelerated ions. Moreover, since solar X-ray spectra increase exponentially at lower energies, enough X-rays can still be observed to characterise electron acceleration.
The data processing unit (DPU) performs low-level processing and the compression of data received from the detector system’s electronics. It also performs instrument control functions and interfaces with the spacecraft.
Detection of faint solar X-ray and γ-ray signals requires a low background flux. This depends on many factors, including the satellite orbit and phase of the solar cycle. For an orbit at L1 during solar maximum, approximately 2 protons cm−2 s−1 are expected to be incident on the satellite due to isotropic cosmic rays. These will be shielded from LISSAN’s detectors by the surrounding spacecraft, as well as by tungsten passive shielding around the detector plane. A more reliable background estimate can be computed via a Monte Carlo Geant4 simulation of the whole system. A plastic scintillator can also be placed below the detectors to tag high-energy particles (GeV cosmic rays), and produce an anti-coincidence signal to the main detectors. Calculations for previous missions, including INTEGRAL, suggest that active shielding may enable a reduction in the background by a factor of 5–10.
LISSAN’s imaging axis is defined by the position of the front grids relative to the rear ones. LISSAN’s solar aspect system monitors this orientation relative to the Sun, thereby enabling the coordinates of the reconstructed images to be determined.
LISSAN’s design enables it to achieve 40 times greater sensitivity than RHESSI at 6.1 MeV (5 counts/cm2) and at the 2.2 MeV neutron capture line (50 counts/cm2). This will enable it to detect, image, and characterise emission from accelerated ions in a significant number of flares for the first time. Moreover, LISSAN’s design is scalable. Therefore, if mass, volume, and power budgets allow, LISSAN can be augmented with additional subcollimators. These can be used to enhance LISSAN’s imaging capabilities by producing more moiré patterns, and/or further boost sensitivity for spectroscopy. Alternatively, if mass and funding budgets are tight, thinner grids could be used that are partially or fully transparent to the highest energy γ-rays. This would reduce LISSAN’s imaging capability at these energies (e.g., the C and O lines), but spectroscopic sensitivity would be enhanced by the greater transmission through the grids. Thinner grids would affect lower energy imaging far less—e.g., the Ne, Mg, Fe, and Si lines—and so still provide valuable information on the locations of accelerated ions. LISSAN would therefore still be able to address many of the science questions outlined in Section 2.
4.2. Indirect Imaging System
Photons cannot be focused easily at the energies observed by LISSAN, and so an indirect imaging technique is required [62]. LISSAN’s imaging system is composed of 15 imaging subcollimators, each composed of a detector and a pair of grids (bigrids) of parallel slits and slats. Each pair of grids is separated by 3 m and have slightly mismatched pitches (slit/slat size). This casts a moiré pattern onto the detector as photons pass through the slits and are absorbed by the slats (Figure 5). The moiré pattern represents a Fourier imaging component, also known as a complex visibility. This is a spatial sampling on the plane of the sky whose angular resolution is determined by the grid pitch and its direction by the bigrid orientation. The visibility’s phase (shift of the moiré pattern’s peak across the detector) and amplitude (difference between the moiré pattern’s peak and trough intensities) are sensitive to both the extent and position of the source. For instance, any source located off-axis will result in a shifted pattern. The visibilities can be recombined into images using reconstruction algorithms similar to a 2D Fourier transform.
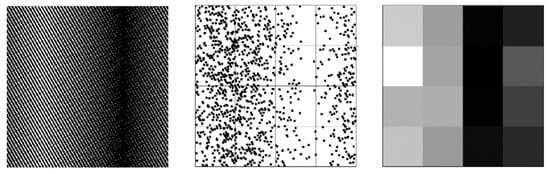
Figure 5.
Left: moiré pattern created by the transmission through the grids in one of the LISSAN collimators by a point source on the Sun 100″ from the line of sight (black areas mark areas where the transmission is blocked by the grids). Middle: corresponding counts reaching the LISSAN detector. Right: relative flux registered in each GAGG crystal of the detector array: the highest flux is in white and the lower flux in black. Differences between pixels in a single column are due to counting statistics.
The minimum angular resolution is dictated by the subcollimator with the finest bigrid pitch. However, coarser pitches are also needed to capture the larger scale structure of the source. Moreover, since each subcollimator produces a visibility sensitive in only one direction, it is desirable to have multiple subcollimators with the same or similar resolutions at different orientations to better capture the asymmetric structure. The LISSAN design proposed in this paper therefore includes 5 different bigrid pitches, each arranged at 3 different orientations, resulting in the previously quoted 15 imaging subcollimators. The finest bigrid pitch is 230 µm (115 µm slit width) corresponding to a minimum angular resolution of 8″ FWHM. The distribution of subcollimator resolutions and orientations can be visualised by plotting their corresponding visibilities in Fourier space, known as the (u,v) plane. Altering the pitch and orientation of the bigrids causes the (u,v) points to shift. One possible visibility distribution is shown in the left panel of Figure 6. The resultant point spread function (PSF) is shown in the middle panel. The right panel shows the 50–84 keV image that LISSAN would have produced with this visibility distribution for the M9.7 flare observed by STIX on 31 March 2022. Two flare footpoints produced by HXR bremsstrahlung from precipitating accelerated electrons are clearly visible. While Figure 6 clearly shows that this visibility distribution can produce scientifically useful images, a more optimal distribution may exist. This can be determined by a trade study during the design phase of a LISSAN mission.
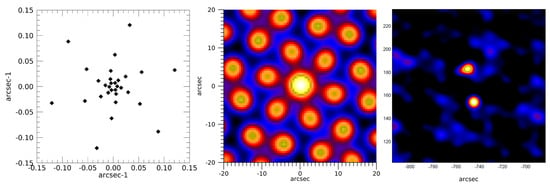
Figure 6.
Left: One possible (u,v) plane coverage for LISSAN; Middle: associated point spread function (dirty map of a point source on-axis: this image contains both the X-ray source and instrumental artefacts to be removed with the adequate cleaning algorithms); Right: simulation of a LISSAN image of the 50–84 keV emission from the two hard X-ray footpoints during the M9.7 flare on 31 March 2022, which was observed by STIX on Solar Orbiter. This image was obtained by running the CLEAN image reconstruction algorithm (e.g., [63] and Section 2.5 in [61]) on the dirty image.
The field of view (FOV) of the imaging system is defined by the grid pitch and thickness. The finest pitch of 230 µm and 3 cm grid thickness proposed here results in an FOV with a diameter of 13 arcmin. This is greater than the 10 arcmin required to image the γ-ray line emission in an active region and possible pion decay source away from the main flare site (middle column, Table 1). The thickness of the bigrids is determined by the highest energy at which imaging is required. This is because grids of a certain thickness become transparent to γ-rays above a certain energy, and so moiré patterns are no longer formed.
4.3. Main Instrument Components
4.3.1. Grids
The LISSAN grids are square, with lengths of 15 cm for the front grids and 11 cm for the rear ones. The pitches range from 230 µm to 3720 µm (slit widths 115–1860 µm) and their thickness is 3 cm. The grids can be made of tungsten or a tungsten–copper alloy. Manufacturing grids with such an extreme thickness-to-pitch aspect ratio is challenging, and all conventional manufacturing techniques have drawbacks. Machining can fail due to the length of the channels compared to the thin wall thickness of the grids. Laser ablation is often only suitable for relatively shallow depths, while electrochemical machining usually requires a tool that is expensive to manufacture. A feasible alternative is modern 3D printing. We identified two options:
- Laser powder bed fusion (cf. [64]): for tungsten, the components for nuclear fusion, medical imaging, and space applications have been manufactured with this technique by the Fraunhofer Institute for Casting, Composite and Processing Technology (IGCV).
- Three-dimensional screen printing (cf. [65]): Anti-scatter grids with fine pitches and large-aspect ratios for medical imaging were developed in tungsten–copper by the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials (IFAM).
Examples of grids manufactured with these techniques are shown in Figure 7. While the manufacturing technologies are mature, grids with such fine pitches have not yet been developed for space applications at the time of writing. Issues currently remain with microcracks in the laser-based printing technique that are susceptible to vibrations during launch. Therefore, further development is required to bring these components to TRL 6. However, mitigation strategies such as switching to a tungsten–copper alloy are already known. The only performance penalty associated with this measure would be a reduction in the field of view from 13″ to 10″, as the material’s lower density would require thicker grids to achieve the same absorption. However, this still fulfils the field of view requirement in Table 1.
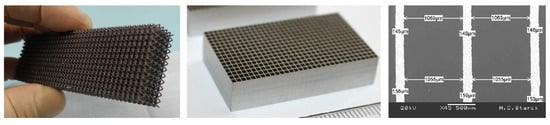
Figure 7.
Examples of 3D-printed tungsten components developed by Fraunhofer institutes. (Left): tungsten grid structure for nuclear fusion applications, manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (IGCV). (Middle): tungsten anti-scatter grid for medical imaging manufactured by screen printing (IFAM). (Right): Measured dimensions of anti-scatter grid (IFAM).
4.3.2. Detectors
The LISSAN detectors provide a spectral resolution that is better than 1.5% FWHM at 6.1 MeV which is sufficient to measure the Doppler profiles of the C and O lines at 4.4 and 6.1 MeV (Table 1). Each detector is composed of a 4 × 4 array of gadolinium aluminium gallium garnet (GAGG) crystal pixels, which provide a total active area of 100 cm2. GAGG:Ce are new crystals which are fast (50–100 ns), bright (30–50 photons/keV), and non-hygroscopic. They perform at moderate cooling temperatures compared to Germanium-based detectors and have a high quantum efficiency in the γ-ray regime. The detection chain is composed of:
- GAGG crystals that scintillate when X-rays and γ-rays are absorbed;
- Silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) and their front-end electronics (FEE; analog/digital front–end ASIC and voltage regulation) that record the scintillation;
- Fully digital back-end electronics (BEEs).
A single pixel is composed of a 2.5 × 2.5 cm2 GAGG crystal with a thickness of 10 cm for good high-energy photon absorption. They are surrounded by a 3 M Vikuiti reflecting foil. Each pixel is readout at both ends by SiPM matrices, each composed of 4 × 4 pixels (6 mm), resulting in a total matrix size comparable to the ends of the GAGG pixel. The analog signals from each 16-pixel matrix are combined before being sent to the FEE, which are cooled to 0 °C.
The LISSAN detector units are covered by a Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) cover, transparent to γ-rays, to shield the detectors against visible photons. Each GAGG pixel produces two SiPM signals (giving a total of 32 analog signals) which are readout by two IDEAS/APOCAT fast 16-channel ASICs. The APOCAT ASIC, conceived by the IDEAS company and inherited from SIPHRA ASIC, is radiation-hardened and optimised for SiPM readout and has been used by several space missions. The two APOCAT ASICs provide digital information on the detected events, SiPM HV voltage (∼50 V), temperature probes to monitor SiPM temperatures, and voltage and current probes to verify the health of the detection unit. The APOCAT ASIC also enables high-voltage fine-tuning to optimise the detector performance and uniformity between detector units.
The detector plane is composed of 20 LISSAN detection units, each associated with a subcollimator (15 imaging and 5 gridless). The total detection area is 2000 cm2. After full functional and performance validation, these detection units are mounted in a main structure of aluminium alloy or AlBemet. All the detection units’ information is sent to the BEE card, which is based on two nanoExplore NG-LARGE FPGA hardened components. The FPGA then produces photon event lists, which are sent to the data processing unit (DPU). The FPGA can produce higher-level products such as spectra, light curves, and images, instead of, or as well as, the event lists depending on the telemetry budget.
APC and LESIA are currently developing a new detector system funded by CNES known as the fast gamma-ray spectrometer (FGS) which is similar to that required by LISSAN. It is also based on new GAGG scintillators readout by SiPMs and controlled by the IDEAS/APOCAT fast ASIC (Figure 8). FGS differs from the LISSAN detection unit design only in its crystal size: 2 × 2 × 1 cm3 for FGS compared to 2.5 × 2.5 × 10 cm3 for LISSAN. LISSAN can therefore leverage the FGS development, which is expected to bring this technology to TRL 6 in 2024. It is important to note that, although the FGS system will soon be space-qualified, its main components, i.e., GAGG crystals, SiPMs, and the IDEAS APOCAT ASIC have already flown in space. Although SiPM dark current has been observed in space missions to increase with the radiation dose, this effect is not expected to be significant for LISSAN as the SiPMs are shielded by their surroundings. We anticipate a fluence of less than 109 protons cm−2 (67 MeV equivalent) during a three-year mission. Radiation measurements made with CNES at the Louvain-la-Neuve cyclotron have shown that the Hamamatsu SiPM will operate sufficiently with this dosage.
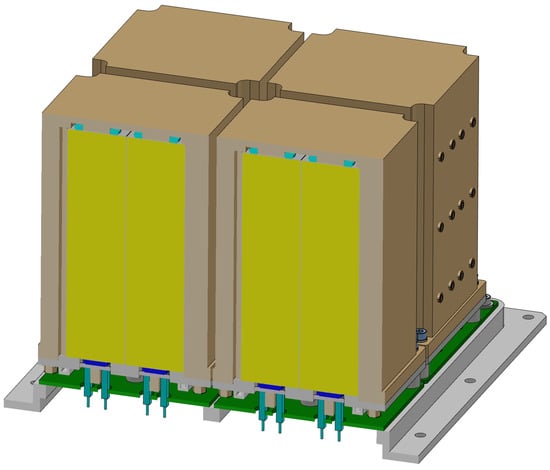
Figure 8.
CAD drawing of LISSAN’s detector system design arranged in four 2 × 2 pixel arrays (4 × 4 pixels in total). The artificial cutaways in the two nearest arrays reveal the yellow GAGG:Ce crystals (pixels) surrounded by 3M Vikuiti reflecting foil. Each pixel is read out by SiPMs at their top and bottom and are connected to the APOCAT ASICs below.
4.3.3. Solar Aspect and Twist Monitoring System
LISSAN’s solar aspect system determines the imaging axis by monitoring the relative position of the front and rear grids, including their shift and twist, in relation to the Sun. This will be achieved by mounting two aspect system units in two corners of the instrument, as shown in Figure 4. Each unit is composed of a small optical lens in the front collimator assembly and a photodetector in the rear. The position of Sun-centre can then be determined from the image produced. This system provides an absolute pointing precision to better than 4″. A similar system is currently being successfully used by STIX. An alternative is to directly image the Sun with a CCD or CMOS detector. The pros and cons of each system can be determined by a trade study during the initial design phases of a LISSAN mission, but both are viable.
4.3.4. Data Processing Unit (DPU)
Figure 9 shows the main components of the DPU subsystem. The central element is an Aeroflex GR712RC chip implementing a Leon3FT processor. The CPU is clocked by the 20 MHz oscillator in order to minimise the power consumption. The DPU is equipped with 8 MBytes of Aeroflex SRAM operating memory and a further 2 MBytes of Aeroflex MRAM memory for storing the application software. The MRAM has very good radiation immunity. The size of the SRAM and MRAM can be increased depending on LISSAN’s requirements. The DPU’s start-up (boot) software is stored in PROM memory from Aeroflex. This also has good radiation immunity and is supplied by a 3.3 V voltage source. Communication with the spacecraft is achieved via SpaceWire using Aeroflex drivers and receivers UT54LVDS031LVUCC and UT54LVDS032LVUCC. The Leon3FT processor is widely used by ESA space projects and several space-qualified real-time operating systems can run on it, e.g., RTEMS OS.
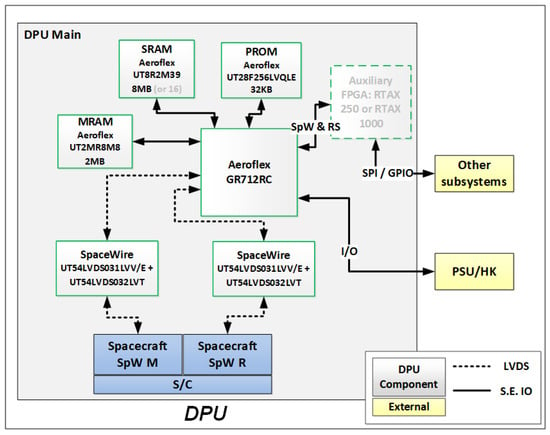
Figure 9.
LISSAN DPU subsystem.
The LISSAN DPU is based on GR712RC, which is used in different space applications. A similar design concept was used by the SWI instrument onboard JUICE, and a similar architecture was used in PROBA3. An alternative concept is based on RTAX2000S/SL, which was used by STIX.
4.4. Spacecraft Interface Requirements and Environmental Constraints
The resources required by LISSAN are summarised in Table 2. The mass is driven by the mass of the individual grids (∼3 kg each) and detector units (∼6 kg each). The dimensions are 350 cm × 75 cm × 75 cm to accommodate the grids and the separation between them needed to achieve the described imaging performance. The data rate will be highly dependent on the solar activity. Each photon count in each detector segment is individually recorded as a 4-byte data record. During the largest flare (>X10), the data volume transmitted from the DPU to the onboard storage could reach 10 GB in ∼10 min. Such events are rare, and the average data rate is expected to be at least 2 orders of magnitude lower. Onboard storage will be used to store large data volumes if needed. Binning the data in energy and time on request, as is performed for STIX, can also be considered if the telemetry is limited. The strongest thermal requirement is driven by the FEE operating temperature (∼0 °C). This can be achieved with a cold finger and radiators. To locate solar targets in its FOV, LISSAN requires an absolute pointing accuracy of 30″. To maintain the angular resolution of the instrument, a pointing stability of 0.2″ over a second is required. L1 and LEO equatorial orbits both provide an environment with sufficiently low background radiation for LISSAN to achieve its required sensitivity.

Table 2.
Resources required for LISSAN.
5. Summary
LISSAN provides solar X-ray and γ-ray imaging spectroscopy in the range of 40 keV–100 MeV on timescales in the order of 10 s. Its observations will answer many open scientific questions regarding electron and ion acceleration in the solar corona, whose underlying physical processes also drive many other phenomena throughout the universe. Its ability to unveil the acceleration of ions is particularly valuable because of their anticipated energetic importance in solar eruptive events and the fact that the spatio-temporal regime has largely been unexplored. Only one resolved γ-ray image of a solar flare has previously been achieved. Most of the technology required by LISSAN is already TRL 6 or greater, while other technologies are currently being brought to this level by ongoing funded efforts. LISSAN is appropriate for deployment on a multi-instrument ESA M-class mission or as a smaller standalone mission. See [26] for one such multi-instrument mission concept.
Author Contributions
The writing of this paper was led by D.F.R. and S.K. The LISSAN concept was developed as part of the SPARK mission concept which was coordinated by H.A.S.R., S.M. and D.F.R. All other authors contributed by providing scientific or instrumentation expertise on the development of the LISSAN concept and/or the paper itself. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Parts of the science case for LISSAN builds upon those developed for the FOXSI SMEX [2] and FIERCE MIDEX [3] mission proposals. We acknowledge the work by those teams that helped make this paper possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| APC | Laboratoire Astroparticule & Cosmologie |
| ASIC | Application-specific integrated circuit |
| BEE | (Detector unit) back-end electronics |
| CCD | Charge-coupled device |
| CME | Coronal mass ejection |
| CMOS | Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor |
| CNES | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique |
| CPU | Central processing unit |
| DPU | Data processing unit |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| EUV | Extreme ultraviolet |
| FEE | (Detector unit) front-end electronics |
| Fermi-LAT | Fermi large-area telescope |
| FGS | Fast Gamma-ray spectrometer |
| FOV | Field of view |
| FPGA | Field-programmable gate array |
| FWHM | Full-width half-maximum |
| GAGG(CE) | Gadolinium aluminium gallium garnet (Cerium) |
| HXR | Hard X-rays (≳5 keV) |
| IGCV | Fraunhofer Institute for Casting, Composite and Processing Technology |
| IFAM | Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing 294 Technology and Advanced Materials |
| L1 | Lagrange point 1 |
| LEO | Low Earth orbit |
| LESIA | Laboratoire d’études spatiales et d’instrumentation en astrophysique |
| LISSAN | Large Imaging Spectrometer for Solar Accelerated Nuclei |
| MRAM | Magnetoresistive random-access memory |
| PEEK | Polyether ether ketone |
| PROM | Programmable read-only memory |
| PSF | Point spread function |
| RHESSI | Reuven Ramaty high-energy solar spectroscopic Imager |
| SEPs | Solar energetic particles |
| SiPM | Silicon photomultiplier |
| SMM/GRS | Solar maximum mission/gamma-ray spectrometer |
| SRAM | Static random-access memory |
| STIX | Spectrometer/telescope for imaging X-rays |
| TRL | Technology readiness level |
References
- Shibata, K. New observational facts about solar flares from YOHKOH studies—Evidence of magnetic reconnection and a unified model of flares. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 17, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.; Alaoui, M.; Allred, J.; Battaglia, M.; Baumgartner, W.; Buitrago-Casas, J.C.; Chen, B.; Chen, T.; Dennis, B.; Drake, J.; et al. The Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager (FOXSI). Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 55, 065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.Y.; Glesener, L.; Krucker, S.; Guidoni, S.; Christe, S.; Reeves, K.; Gburek, S.; Caspi, A.; Alaoui, M.; Allred, J.; et al. Combined Next-Generation X-ray and EUV Observations with the FIERCE Mission Concept. In Proceedings of the American Meteorological Society 100th Annual Meeting (AMS), Boston, MA, USA, 12–16 January 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, E.L. High-Energy Neutral Radiations from the Sun. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 22, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaty, R. Nuclear processes in solar flares. Phys. Sun 1986, 2, 291–323. [Google Scholar]
- Chupp, E.L. Evolution of our understanding of solar flare particle acceleration: (1942–1995). AIP Conf. Proc. 1996, 374, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottet, G.; Vilmer, N. The Production of Flare-Accelerated Particles at the Sun. In European Meeting on Solar Physics; Simnett, G.M., Alissandrakis, C.E., Vlahos, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 489, p. 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, G.H.; Murphy, R.J. Gamma Ray Spectroscopy in the Pre-HESSI Era. High Energy Sol. Phys. Workshop 2000, 206, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer, N.; MacKinnon, A.L.; Trottet, G.; Barat, C. High energy particles accelerated during the large solar flare of 1990 May 24: X/γ-rayobservations. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 412, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, G.H.; Murphy, R.J. Gamma Radiation from Flare-Accelerated Particles Impacting the Sun. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2006, 165, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmer, N.; MacKinnon, A.L.; Hurford, G.J. Properties of Energetic Ions in the Solar Atmosphere from γ-ray and Neutron Observations. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 167–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. The Cosmic γ-Ray Spectrum from Secondary Particle Production in Cosmic-Ray Interactions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1970, 6, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Dermer, C.D.; Ramaty, R. High-Energy Processes in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1987, 63, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C. The Deduction of Energy Spectra of Non-Thermal Electrons in Flares from the Observed Dynamic Spectra of Hard X-ray Bursts. Sol. Phys. 1971, 18, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, M.; Massone, A.M.; Kontar, E.P.; Emslie, A.G.; Brown, J.C.; Schwartz, R.A. Regularized Electron Flux Spectra in the 23 July 2002 Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 595, L127–L130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, G.D.; Aschwanden, M.J.; Aurass, H.; Battaglia, M.; Grigis, P.C.; Kontar, E.P.; Liu, W.; Saint-Hilaire, P.; Zharkova, V.V. Implications of X-ray Observations for Electron Acceleration and Propagation in Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 107–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontar, E.P.; Brown, J.C.; Emslie, A.G.; Hajdas, W.; Holman, G.D.; Hurford, G.J.; Kašparová, J.; Mallik, P.C.V.; Massone, A.M.; McConnell, M.L.; et al. Deducing Electron Properties from Hard X-ray Observations. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 301–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Flare Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.P.; Dennis, B.R.; Hurford, G.J.; Smith, D.M.; Zehnder, A.; Harvey, P.R.; Curtis, D.W.; Pankow, D.; Turin, P.; Bester, M.; et al. The Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). Sol. Phys. 2002, 210, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucker, S.; Hurford, G.J.; Grimm, O.; Kögl, S.; Gröbelbauer, H.P.; Etesi, L.; Casadei, D.; Csillaghy, A.; Benz, A.O.; Arnold, N.G.; et al. The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX). Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J.; Schwartz, R.A.; Krucker, S.; Lin, R.P.; Smith, D.M.; Vilmer, N. First Gamma-Ray Images of a Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 595, L77–L80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J.; Krucker, S.; Lin, R.P.; Schwartz, R.A.; Share, G.H.; Smith, D.M. Gamma-Ray Imaging of the 2003 October/November Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 644, L93–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaty, R.; Mandzhavidze, N. High energy processes in solar flares. AIP Conf. Proc. 2000, 522, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Dennis, B.R.; Shih, A.Y.; Chamberlin, P.C.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Moore, C.S.; Share, G.H.; Vourlidas, A.; Welsch, B.T. Global Energetics of Thirty-eight Large Solar Eruptive Events. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschwanden, M.J.; Caspi, A.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Holman, G.; Jing, J.; Kretzschmar, M.; Kontar, E.P.; McTiernan, J.M.; Mewaldt, R.A.; O’Flannagain, A.; et al. Global Energetics of Solar Flares. V. Energy Closure in Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.A.S.; Musset, S.; Ryan, D.F.; Calcines Rosario, A.; Dudík, J.; Auchère, F.; Dahlin, J.; Hayes, L.A.; Kerr, G.S.; Nakariakov, V.M.; et al. The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) mission concept. Aerospace 2023. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Kiener, J.; Gros, M.; Tatischeff, V.; Weidenspointner, G. Properties of the energetic particle distributions during the 28 October 2003 solar flare from INTEGRAL/SPI observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 445, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, J.T.; Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M. The mechanisms of electron heating and acceleration during magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 2014, 21, 092304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M.; Cassak, P.A.; Phan, T.D. On the 3-D structure and dissipation of reconnection-driven flow bursts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3710–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, J.T.; Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M. Parallel electric fields are inefficient drivers of energetic electrons in magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, J.T.; Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M. The role of three-dimensional transport in driving enhanced electron acceleration during magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 092110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.Y.; Lin, R.P.; Smith, D.M. RHESSI Observations of the Proportional Acceleration of Relativistic >0.3 MeV Electrons and >30 MeV Protons in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 698, L152–L157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M.; Che, H.; Shay, M.A. Electron acceleration from contracting magnetic islands during reconnection. Nature 2006, 443, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinenko, Y.E.; Craig, I.J.D. Flare Energy Release by Flux Pile-up Magnetic Reconnection in a Turbulent Current Sheet. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Holman, G.D.; Benka, S.G. A Hybrid Thermal/Nonthermal Model for the Energetic Emissions from Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 400, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucker, S.; Hudson, H.S.; Glesener, L.; White, S.M.; Masuda, S.; Wuelser, J.P.; Lin, R.P. Measurements of the Coronal Acceleration Region of a Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. 2010, 714, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, M.; Krucker, S.; Hudson, H.S.; Saint-Hilaire, P. Electron Energy Partition in the Above-the-looptop Solar Hard X-ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.W.; Sturrock, P.A. Reverse current in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 1977, 218, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G. The effect of reverse currents on the dynamics of nonthermal electron beams in solar flares and on their emitted X-ray bremsstrahlung. Astrophys. J. 1980, 235, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oord, G.H.J. The electrodynamics of beam/return current systems in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 234, 496–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zharkova, V.V.; Gordovskyy, M. The Effect of the Electric Field Induced by Precipitating Electron Beams on Hard X-ray Photon and Mean Electron Spectra. Astrophys. J. 2006, 651, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaoui, M.; Holman, G.D. Understanding Breaks in Flare X-ray Spectra: Evaluation of a Cospatial Collisional Return-current Model. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Ramaty, R.; Kozlovsky, B.; Reames, D.V. Solar Abundances from Gamma-ray Spectroscopy: Comparisons with Energetic Particle, Photospheric, and Coronal Abundances. Astrophys. J. 1991, 371, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottet, G.; Barat, C.; Ramaty, R.; Vilmer, N.; Dezalay, J.P.; Kuznetsov, A.; Mandzhavidze, N.; Sunyaev, R.; Talon, R.; Terekhov, O. Thin target γ-ray line production during the 1991 June 1 flare. AIP Conf. Proc. 1996, 374, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, W.M.; Tanner, W.G.; McDonald, R.A.; Schaub, G.E.; Stephenson, S.L.; McDonnell, J.A.M.; Maag, C.R. The Status of Measurement Technologies Concerning Micrometer and Submicrometer Space Articulate Matter Capture, Recovery, Velocity, and Trajectory. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Particle Capture, Recovery and Velocity/Trajectory Measurement Technologies, Houston, TX, USA, 27–28 September 1993; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy, P.P.; Chupp, E.L.; Bertsch, D.L.; Schneid, E.J.; Gottesman, S.R.; Kanbach, G. Gamma-Rays and Neutrons as a Probe of Flare Proton Spectra: The Solar Flare of 11 June 1991. Sol. Phys. 1999, 187, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharov, L.G.; Lee, J.W.; Zirin, H.; Kovaltsov, G.A.; Usoskin, I.G.; Pyle, K.R.; Shea, M.A.; Smart, D.F. Neutron and electromagnetic emissions during the 24 May 1990 solar flare. Sol. Phys. 1994, 155, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharov, L.; Debrunner, H.; Kovaltsov, G.; Lockwood, J.; McConnell, M.; Nieminen, P.; Rank, G.; Ryan, J.; Schoenfelder, V. Deduced spectrum of interacting protons accelerated after the impulsive phase of the 15 June 1991 solar flare. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 340, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer, N.; Krucker, S.; Trottet, G.; Lin, R.P. Hard X-ray and metric/decimetric spatially resolved observations of the 10 April 2002 solar flare. Adv. Space Res. 2003, 32, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbach, G.; Bertsch, D.L.; Fichtel, C.E.; Hartman, R.C.; Hunter, S.D.; Kniffen, D.A.; Kwok, P.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Mattox, J.R.; Mayer-Hasselwander, H.A. Detection of a long-duration solar gamma-ray flare on 11 June 1991 with EGRET on COMPTON-GRO. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1993, 97, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.M.; Lockwood, J.A.; Debrunner, H. Solar Energetic Particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 93, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, G.H.; Murphy, R.J.; White, S.M.; Tolbert, A.K.; Dennis, B.R.; Schwartz, R.A.; Smart, D.F.; Shea, M.A. Characteristics of Late-phase >100 MeV Gamma-Ray Emission in Solar Eruptive Events. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nolfo, G.A.; Bruno, A.; Ryan, J.M.; Dalla, S.; Giacalone, J.; Richardson, I.G.; Christian, E.R.; Stochaj, S.J.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Boezio, M.; et al. Comparing Long-duration Gamma-Ray Flares and High-energy Solar Energetic Particles. Astrophys. J. 2019, 879, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.; Dalla, S.; Laitinen, T.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Bruno, A.; Ryan, J.M.; Waterfall, C.O.G. Energetic proton back-precipitation onto the solar atmosphere in relation to long-duration gamma-ray flares. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 658, A23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechnev, V.V.; Kurt, V.G.; Chertok, I.M.; Uralov, A.M.; Nakajima, H.; Altyntsev, A.T.; Belov, A.V.; Yushkov, B.Y.; Kuznetsov, S.N.; Kashapova, L.K.; et al. An Extreme Solar Event of 20 January 2005: Properties of the Flare and the Origin of Energetic Particles. Sol. Phys. 2008, 252, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, K.G.; Moraal, H.; Stoker, P.H. Investigation of the multiple-component structure of the 20 January 2005 cosmic ray ground level enhancement. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, A12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Pariat, E.; Aulanier, G.; Schrijver, C.J. The Nature of Flare Ribbons in Coronal Null-Point Topology. Astrophys. J. 2009, 700, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Allafort, A.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; Bonamente, E.; Brandt, T.J.; et al. Impulsive and Long Duration High-energy Gamma-ray Emission from the Very Bright 7 March 2012 Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajello, M.; Baldini, L.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Berretta, A.; Bissaldi, E.; Blandford, R.D.; Bonino, R.; Bruel, P.; Buson, S.; et al. First Fermi-LAT Solar Flare Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2021, 252, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gan, W.Q. A Spectroscopic Method Based on the Shapes of Nuclear Deexcitation γ-ray Lines in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2020, 895, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, P.; Battaglia, A.F.; Volpara, A.; Collier, H.; Hurford, G.J.; Kuhar, M.; Perracchione, E.; Garbarino, S.; Massone, A.M.; Benvenuto, F.; et al. First Hard X-ray Imaging Results by Solar Orbiter STIX. Sol. Phys. 2022, 297, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J. X-ray imaging with collimators, masks and grids. ISSI Sci. Rep. Ser. 2010, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Högbom, J.A. Aperture Synthesis with a Non-Regular Distribution of Interferometer Baselines. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1974, 15, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.v.; Dorow-Gerspach, D.; Balden, M.; Binder, M.; Buschmann, B.; Curzadd, B.; Loewenhoff, T.; Neu, R.; Schlick, G.; You, J.H. Progress in additive manufacturing of pure tungsten for plasma-facing component applications. J. Nucl. Mater. 2022, 566, 153760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studnitzky, T.; Reuter, K.; Stiebritz, G.; Wirth, S. 3D Screen Printing of Anti-Scatter Grids—Part Development and Industrialization. In Proceedings of the EuroPM 2019, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 14–16 October 2019. Euro Powder Metallurgy Conference Series. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).