Inversion of Space Debris Material by Synthetic Light Curves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Brightness Simulation Model and Result Analysis
2.1. Brightness Simulation Model
2.2. The Analysis of the Simulation Model
- (1)
- The identical shape, attitude, reflection condition(, , , ), and various orbit.
- (2)
- The identical shape, orbit, reflection condition(, , , ), and various attitude.
- (3)
- The identical shape, orbit, attitude, and various reflection condition(, , , ).
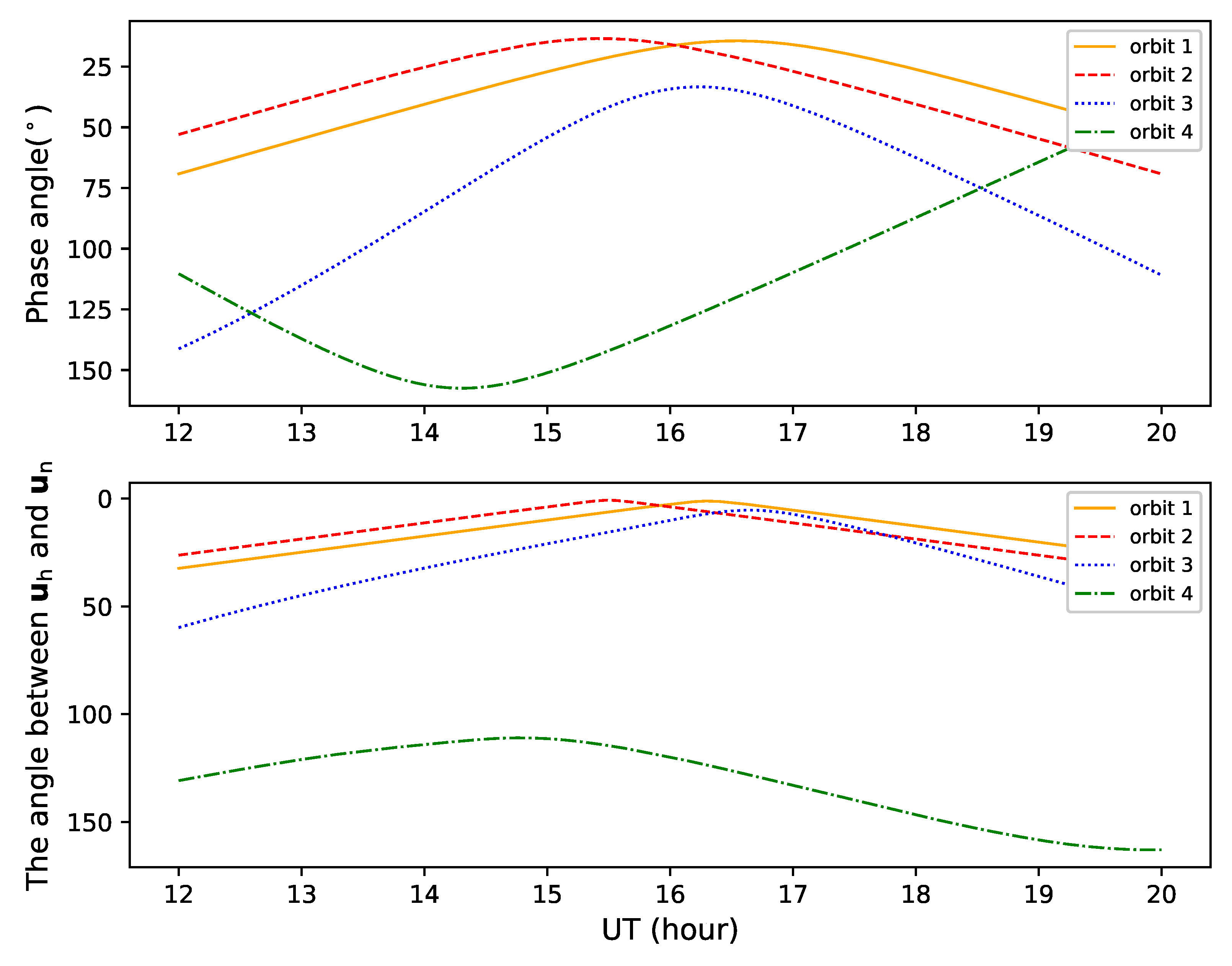
2.2.1. Effect of Orbit Parameters on Light Curves
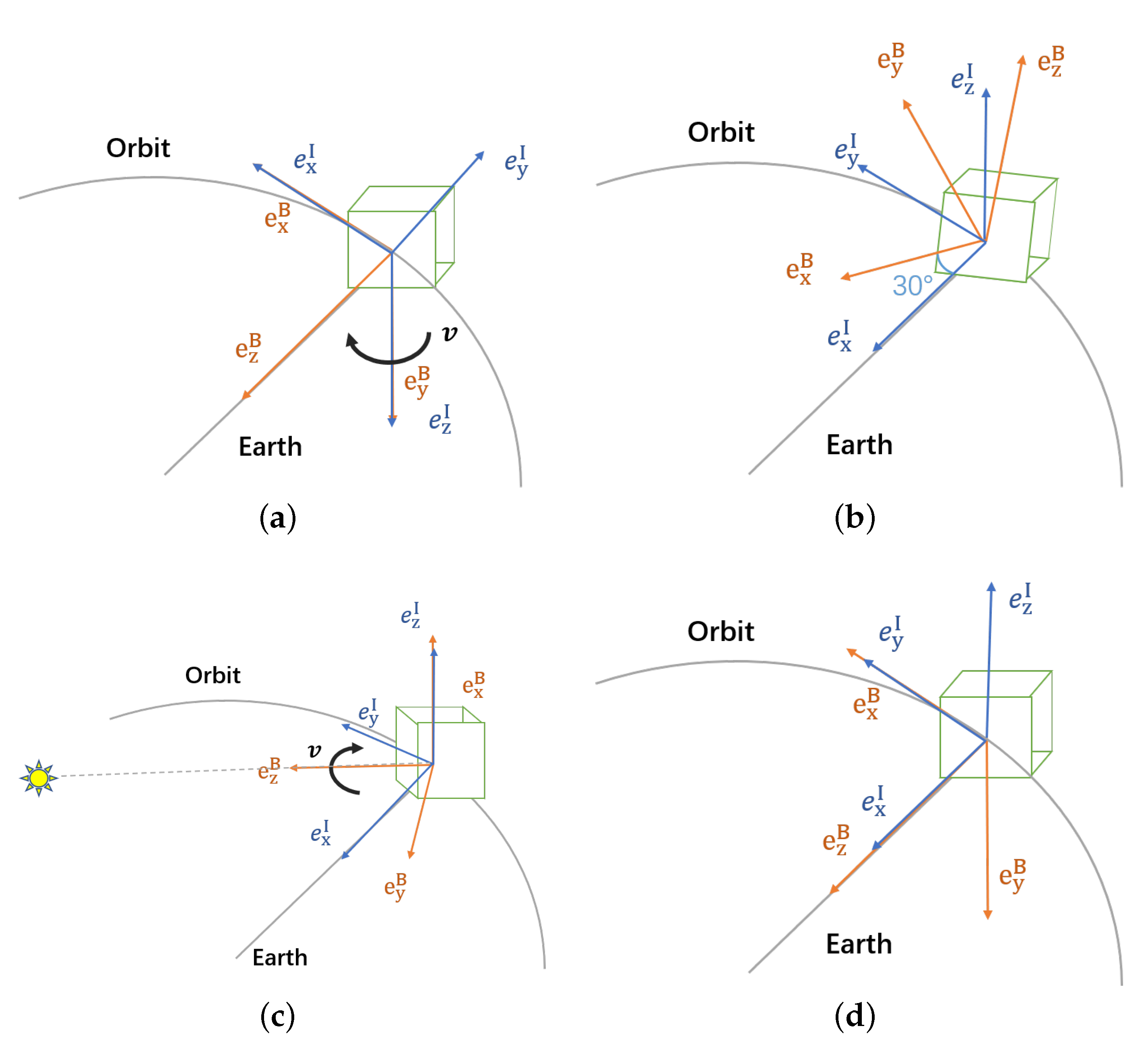
2.2.2. Effect of Attitude Parameters on Light Curves
- The Z axis of the body points to the nadir and spins around the Y axis of the body at the rate of 1 ;
- The Z axis of the body is aligned with the inertial Z axis, and the angle between the X axis of the body and the inertial X axis is 30;
- The Z axis of the body points to the Object-to-Sun vector, and the object spins around it at the rate of 1 ;
- The Z axis of the body points to the nadir, and the X axis of the body points to the velocity direction.
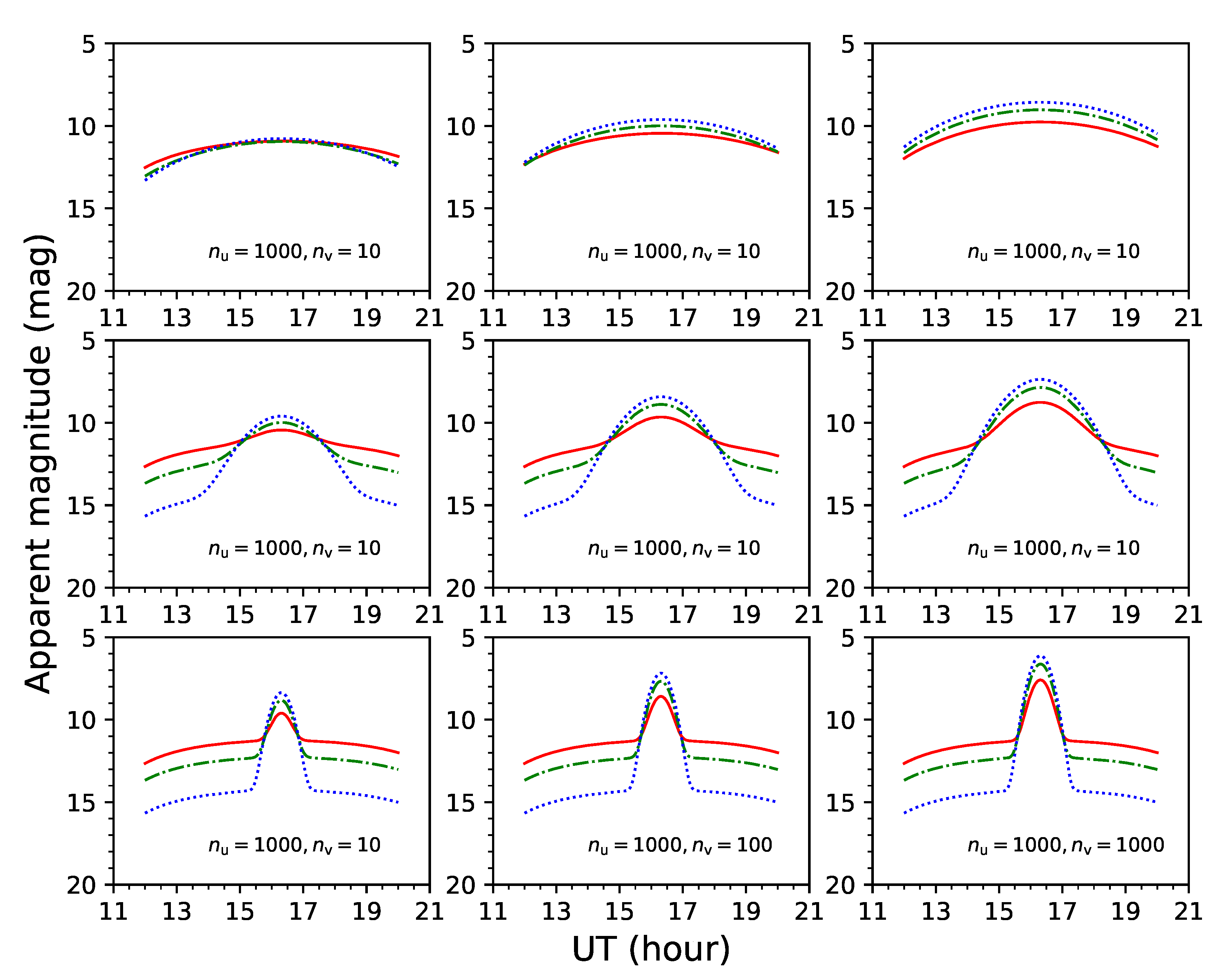
2.2.3. Effect of the Parameters of the BRDF Model on Light Curves
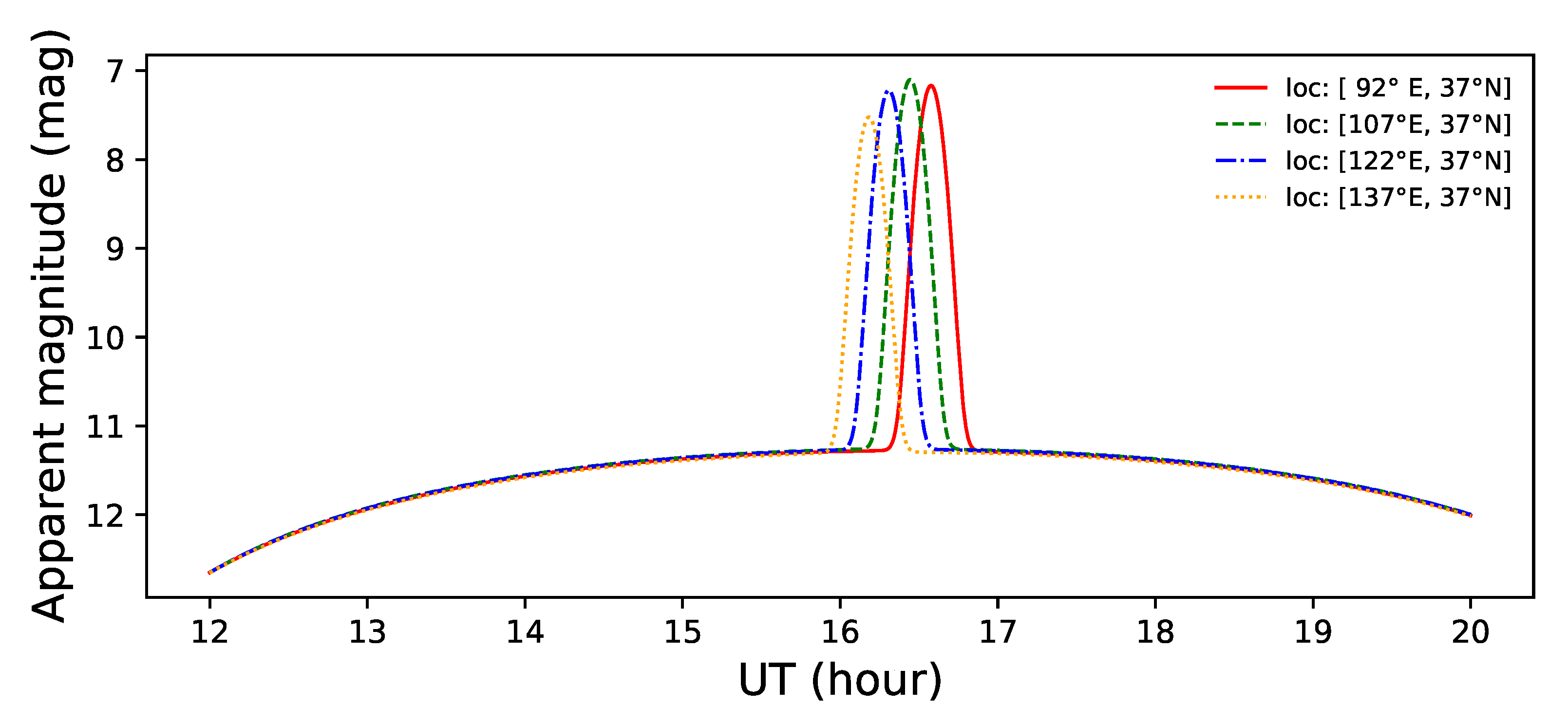
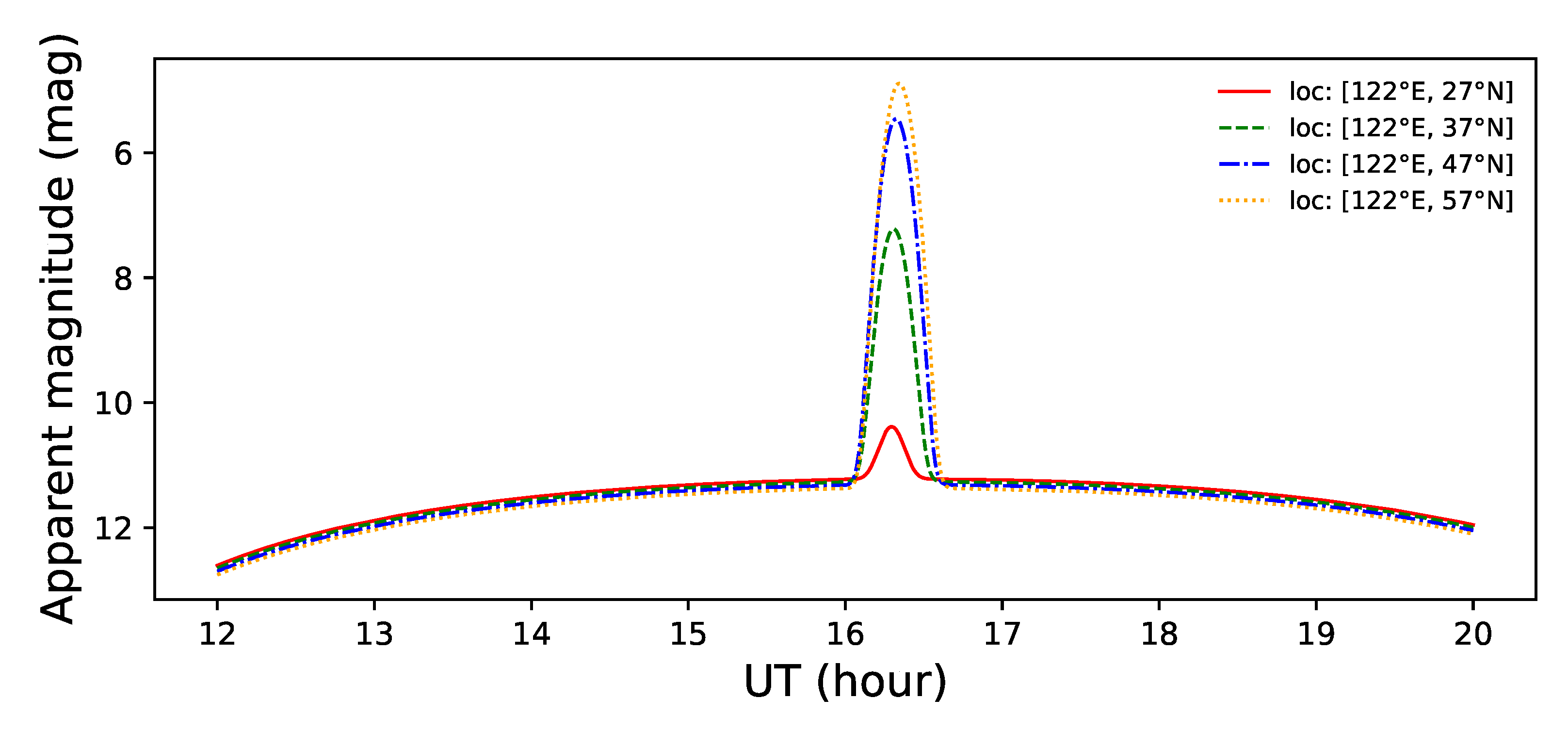
2.2.4. Effect of the Position of the Observation Station on the Light Curves
2.2.5. Summary of the Brightness Simulation Model
3. Material Inversion
3.1. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method
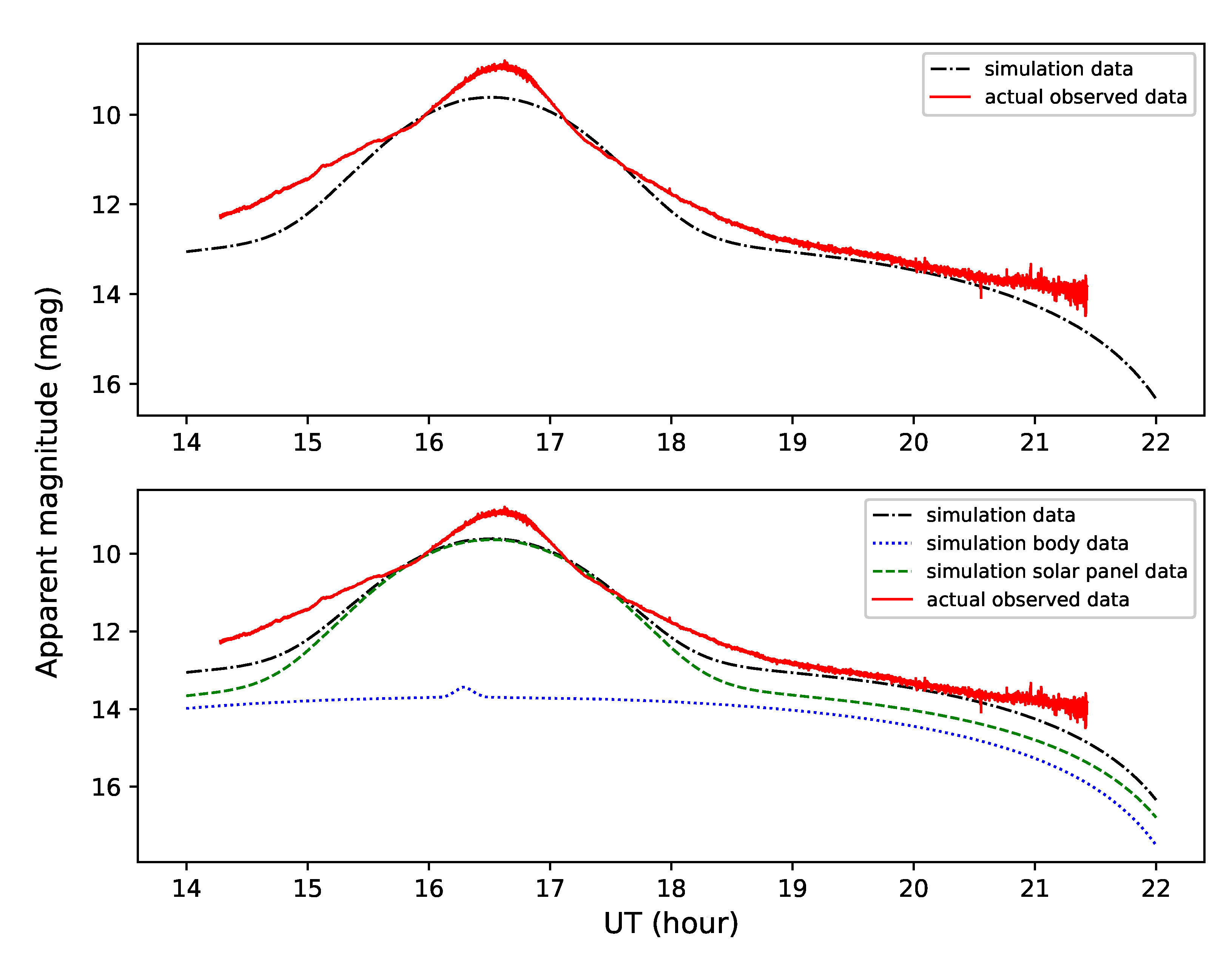
3.2. The Simulation of the Actual Objects
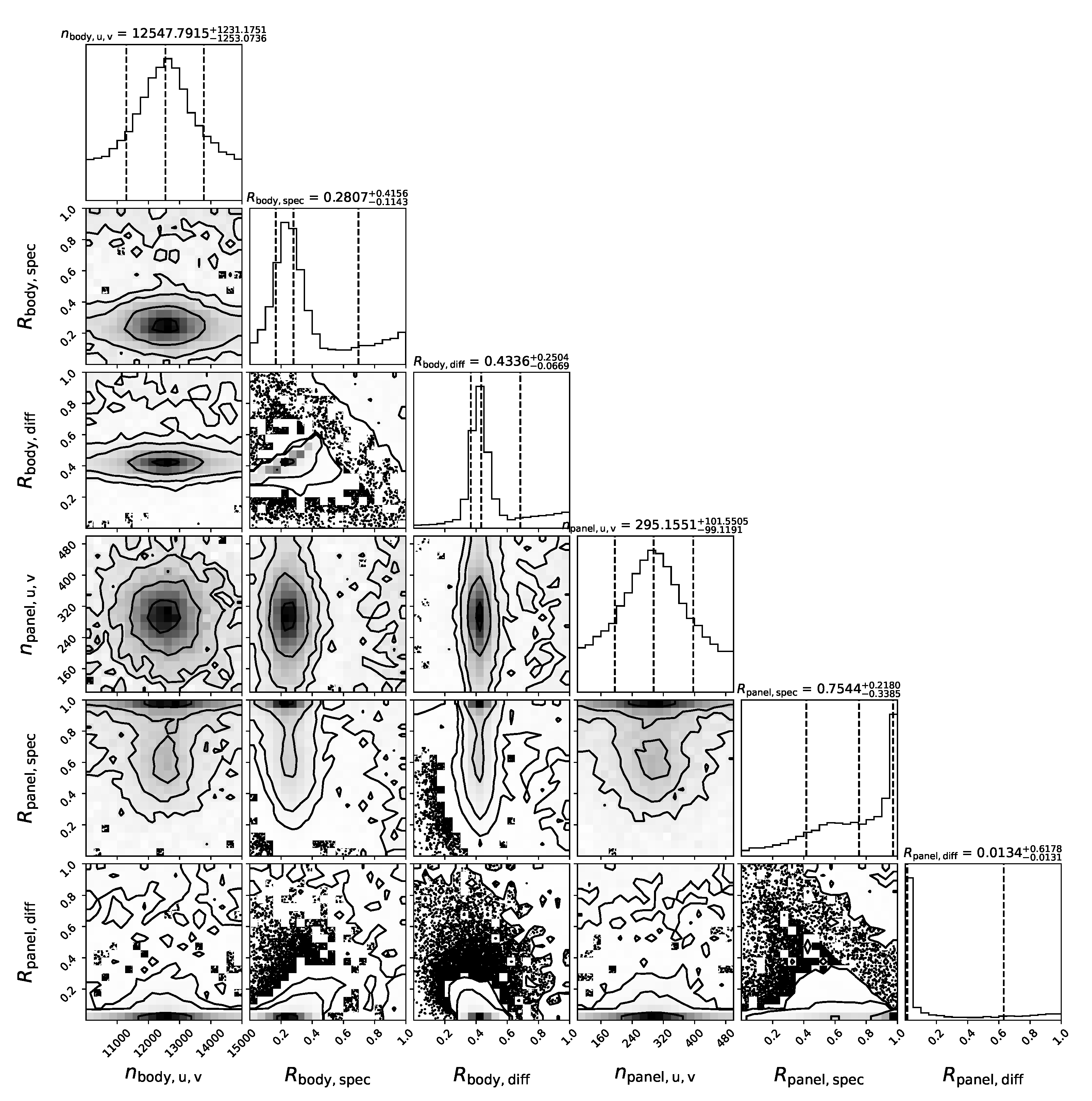
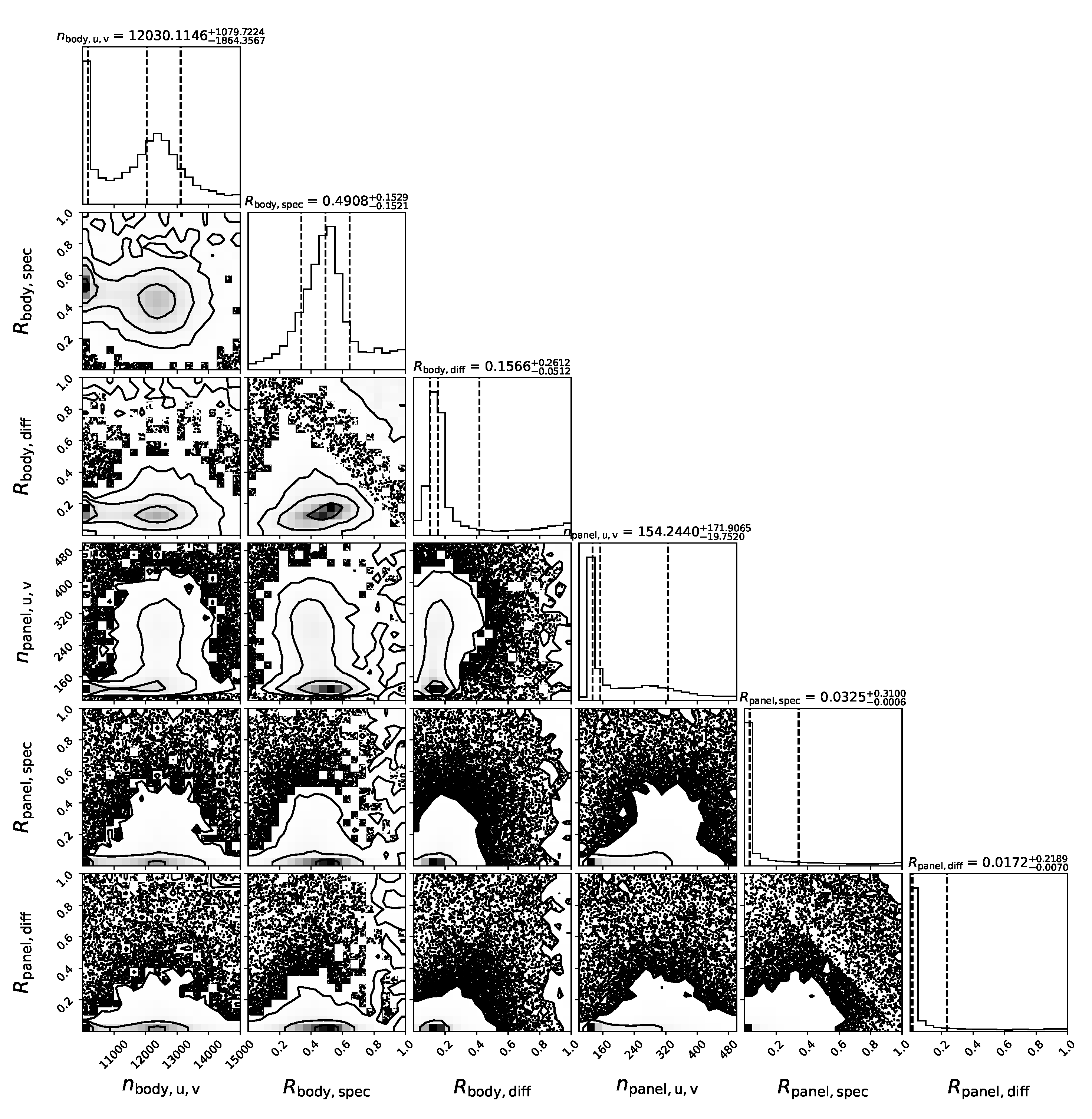
3.3. The Result of MCMC
3.4. Summary
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Payne, T.; Gregory, S.; Luu, K. SSA analysis of GEOS photometric signature classifications and solar panel offsets. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 10–14 September 2006; p. E73. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, L.S. Modeling, Estimation, and Analysis of Unresolved Space Object Tracking and Identification; The University of Texas at Arlington: Arlington, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jolley, A. Analysis of specular reflections off geostationary satellites. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 20–23 September 2016; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcoly, D.O.; Kalamaroff, K.I.; Chun, F.K. Determining basic satellite shape from photometric light curves. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2012, 49, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterer, C.J.; Jah, M. Attitude determination from light curves. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2009, 32, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.; Jah, M.K.; Crassidis, J.L. Space object area-to-mass ratio estimation using multiple model approaches. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 2012, 144, 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.; Calef, B.; Knox, K.; Bolden, M.; Kervin, P. Separating attitude and shape effects for non-resolved objects. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 12–15 September 2007; pp. 464–475. [Google Scholar]
- Bédard, D.; Lévesque, M. Analysis of the CanX-1 engineering model spectral reflectance measurements. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2014, 51, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauquy, M.A.A.; Roggemann, M.C.; Schulz, T.J. Approaches for processing spectral measurements of reflected sunlight for space situational awareness. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2004, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–15 April 2004; Volume 5428, pp. 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bédard, D.; Wade, G.A.; Abercromby, K. Laboratory characterization of homogeneous spacecraft materials. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2015, 52, 1038–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Birkemeier, C.; Gregory, S.; Payne, T.; Brown, J. Unmixing the materials and mechanics contributions in non-resolved object signatures. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 16–19 September 2008; p. E39. [Google Scholar]
- Cauquy, M.A.A. Approaches for Processing Spectral Measurements of Reflected Sunlight for Space Object Detection and Identification; Michigan Technological University: Houghton, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, P.; Dentamaro, A.; Ryan, B.; Ryan, E. Unmixing space object’s moderate resolution spectra. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 September 2013; p. E36. [Google Scholar]
- Cowardin, H.; Seitzer, P.; Abercromby, K.; Barker, E.; Schildknecht, T. Characterization of orbital debris photometric properties derived from Laboratory-Based Measurements. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 14–17 September 2010; pp. 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Krezan, J.; Inbody, W.; Dentamaro, A.; Gregory, S.; Dao, P.; Fulcoly, D. Algorithms for Automated Characterization of Three-Axis Stabilized GEOs using Non-Resolved Optical Observations. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 11–14 September 2012; pp. 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Vrba, F.J.; DiVittorio, M.E.; Hindsley, R.B.; Schmitt, H.R.; Armstrong, J.T.; Shankland, P.D.; Hutter, D.J.; Benson, J.A. A survey of geosynchronous satellite glints. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 1–4 September 2009; p. E28. [Google Scholar]
- Cognion, R.L. Observations and modeling of GEO satellites at large phase angles. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 September 2013; pp. 638–645. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, B.K.; Axelrad, P. Lightcurve inversion for shape estimation of geo objects from space-based sensors. In Proceedings of the International Space Symposium for Flight Dynamics, Laurel, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasalainen, M.; Torppa, J. Optimization Methods for Asteroid Lightcurve Inversion: I. Shape Determination. Icarus 2001, 153, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbairn, M. Planetary Photometry: The Lommel-Seeliger Law. J. R. Astron. Soc. Can. 2005, 99, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasalainen, M.; Torppa, J.; Muinonen, K. Optimization Methods for Asteroid Lightcurve Inversion: II. The Complete Inverse Problem. Icarus 2001, 153, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelecy, T.; Hussein, I.I.; Miller, K.; Coughlin, J. Probabilistic Analysis of Light Curves. J. Astronaut. Sci. 2019, 66, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, B.T. Illumination for computer generated pictures. Commun. ACM 1975, 18, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn, J.F. Models of light reflection for computer synthesized pictures. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–22 July 1977; pp. 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, P.S. A realistic lighting model for computer animators. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2002, 10, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, M.; Nayar, S.K. Generalization of Lambert’s reflectance model. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–29 July 1994; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Torrance, K.E.; Sparrow, E.M. Theory for off-specular reflection from roughened surfaces. Josa 1967, 57, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.L.; Torrance, K.E. A reflectance model for computer graphics. ACM Trans. Graph. ToG 1982, 1, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, G.J. Measuring and modeling anisotropic reflection. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–31 July 1992; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ashikhmin, M.; Shirley, P. An anisotropic phong BRDF model. J. Graph. Tools 2000, 5, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, W. A data-driven reflectance model. ACM Trans. Graph. 2003, 22, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, T. Attitude Estimation of GEO Objects of Space-based Optical Observation Based on the Improved Phong Model. Acta Photonica Sin. 2020, 49, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelecy, T.; Gerber, E.; Akram, S.; Paffett, J. Characterization of Resident Space object States Using Functional Data Analysis. J. Astronaut. Sci. 2022, 69, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.; Crassidis, J.; Jah, M.; Kim, H. Astrometric and photometric data fusion for resident space object orbit, attitude, and shape determination via multiple-model adaptive estimation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 August 2010; p. 8341. [Google Scholar]
- Rush, K.A.; Yost, M.; Smith, L.; Zizzo, A. An application of the unscented Kalman filter for spacecraft attitude estimation on real and simulated light curve data. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 15–18 September 2020; pp. 198–217. [Google Scholar]
- Akenine-Moller, T.; Haines, E.; Hoffman, N. Real-Time Rendering, 3rd ed.; AK PETERS: Natick, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
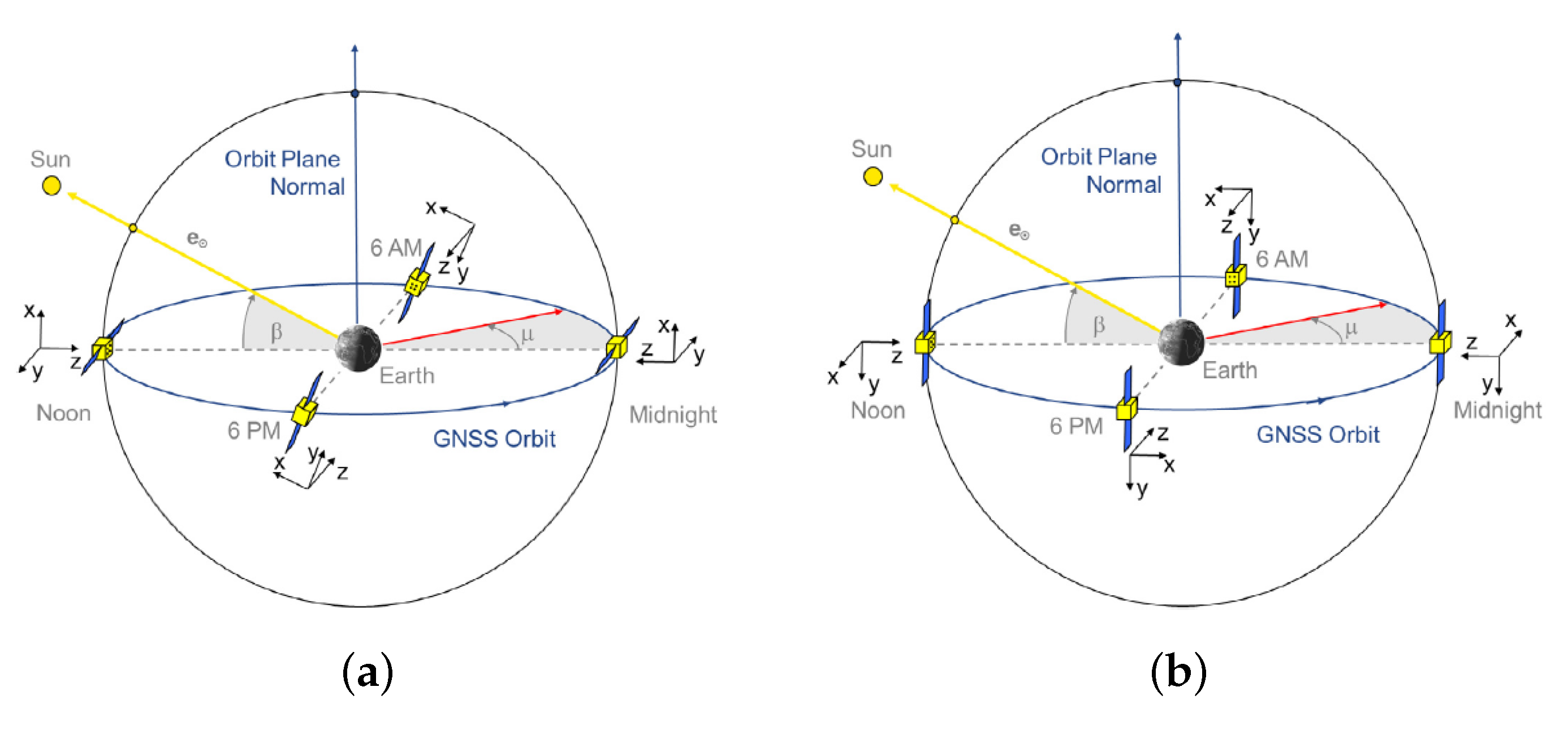
- Montenbruck, O.; Schmid, R.; Mercier, F.; Steigenberger, P.; Noll, C.; Fatkulin, R.; Kogure, S.; Ganeshan, A.S. GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Orbit | TLE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| orbit 1 | 1 | xxxxxU | 16,037 A | 20,284.07341138 | −0.00000354 | 00000-0 | 00000+0 | 0 | 9996 |
| 2 | xxxxx | 1.7237 | 67.2351 | 0007471 | 0.1818 | 88.7233 | 1.00273124 | 15,969 | |
| orbit 2 | 1 | xxxxxU | 19,097 A | 20,284.25674796 | −0.00000355 | +00000-0 | +00000-0 | 0 | 9990 |
| 2 | xxxxx | 000.4814 | 094.5914 | 0028139 | 151.0334 | 350.7694 | 01.0027179300 | 2881 | |
| orbit 3 | 1 | xxxxxU | 14,026 A | 20,284.37504348 | −0.00000027 | +00000-0 | +00000-0 | 0 | 9997 |
| 2 | xxxxx | 056.2287 | 052.2835 | 0020597 | 291.4800 | 068.3069 | 02.005690530 | 46,909 | |
| orbit 4 | 1 | xxxxxU | 18,109 A | 20,284.07190081 | +0.00000009 | +00000-0 | +00000-0 | 0 | 9995 |
| 2 | xxxxx | 055.0110 | 174.1807 | 0009159 | 205.9132 | 258.7572 | 02.005692580 | 13,471 |
| Object | Component 1 | Facet 2 | Area () |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object 1 | body | 3.748 | |
| body | 4.4 | ||
| body | 3.44 | ||
| solar panel | 11.352 × 2 | ||
| Object 2 | body | 4 | |
| body | 4 | ||
| body | 4 | ||
| solar panel | 11 × 2 |
| Simulation Object | Component | Parameter | Best-Fitted Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object 1 | body | 12,030.1146 | |
| 0.4908 | |||
| 0.1566 | |||
| panel | 154.2440 | ||
| 0.0325 | |||
| 0.0172 | |||
| Object 2 | body | 12,547.791 | |
| 0.2807 | |||
| 0.4336 | |||
| panel | 295.1551 | ||
| 0.7544 | |||
| 0.0134 |
| Material | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kapton | 0.1418 | 0.8234 | 12,455.8892 |
| Lambert-plate | 0.6350 | 0.0220 | 0.0719 |
| GaAs | 0.2746 | 0.6427 | 2233.3101 |
| Al | 0.3685 | 0.5746 | 596.9783 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Hu, S.; Du, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, H.; Liu, S.; Feng, S. Inversion of Space Debris Material by Synthetic Light Curves. Aerospace 2023, 10, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10010041
Jiang Y, Hu S, Du J, Chen X, Cao H, Liu S, Feng S. Inversion of Space Debris Material by Synthetic Light Curves. Aerospace. 2023; 10(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yuchen, Shaoming Hu, Junju Du, Xu Chen, Hai Cao, Shuqi Liu, and Shuai Feng. 2023. "Inversion of Space Debris Material by Synthetic Light Curves" Aerospace 10, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10010041
APA StyleJiang, Y., Hu, S., Du, J., Chen, X., Cao, H., Liu, S., & Feng, S. (2023). Inversion of Space Debris Material by Synthetic Light Curves. Aerospace, 10(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10010041






