Uncovering Engagement Networks for Adaptation in Three Regional Communities: Empirical Examples from New South Wales, Australia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
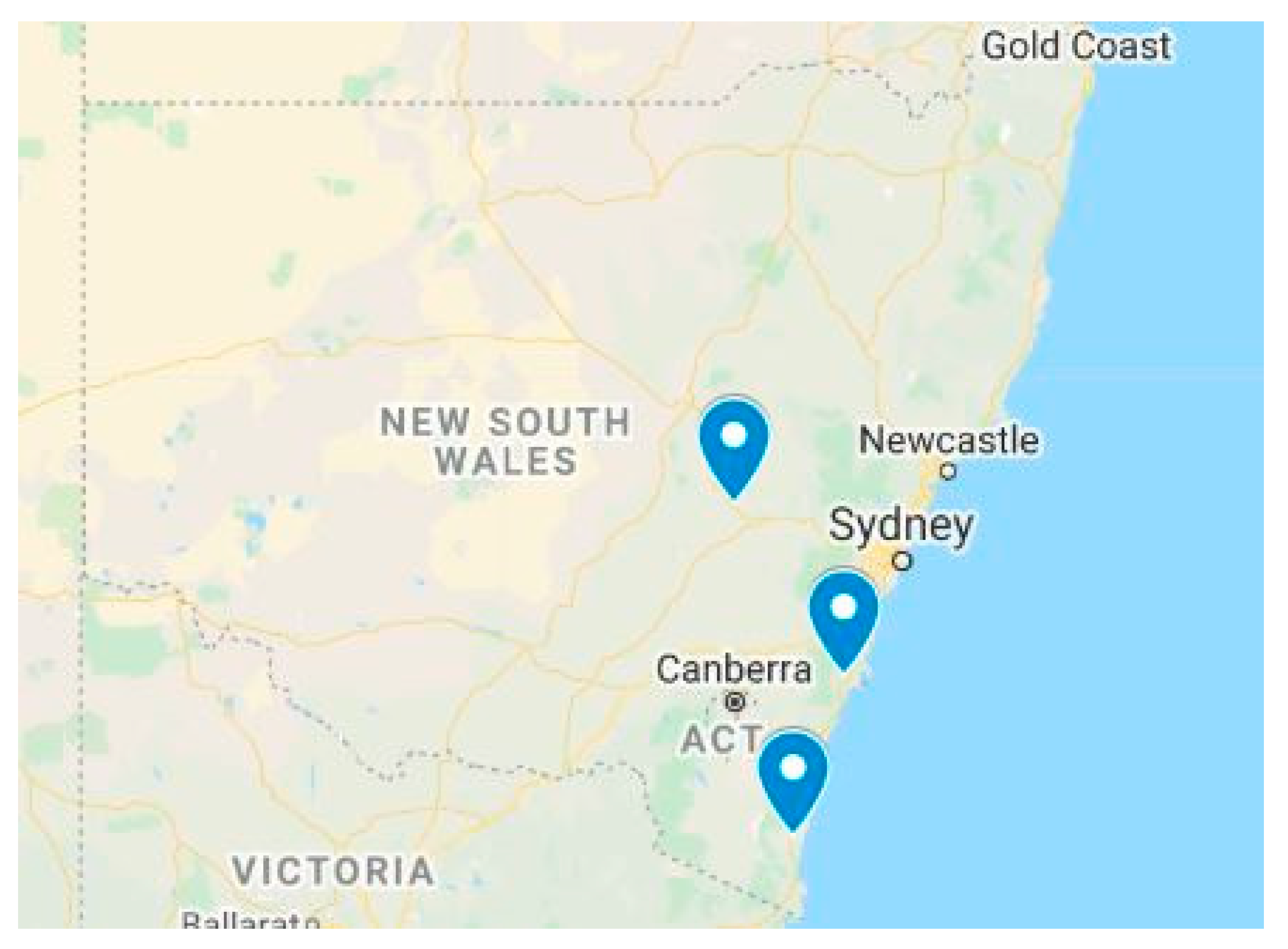
2.1. Case Study Sites and Context
2.1.1. Shoalhaven Region
2.1.2. Bega
2.1.3. Orange
2.2. Projected Climate Changes for SE NSW
2.3. A Mixed Method Approach
3. Results
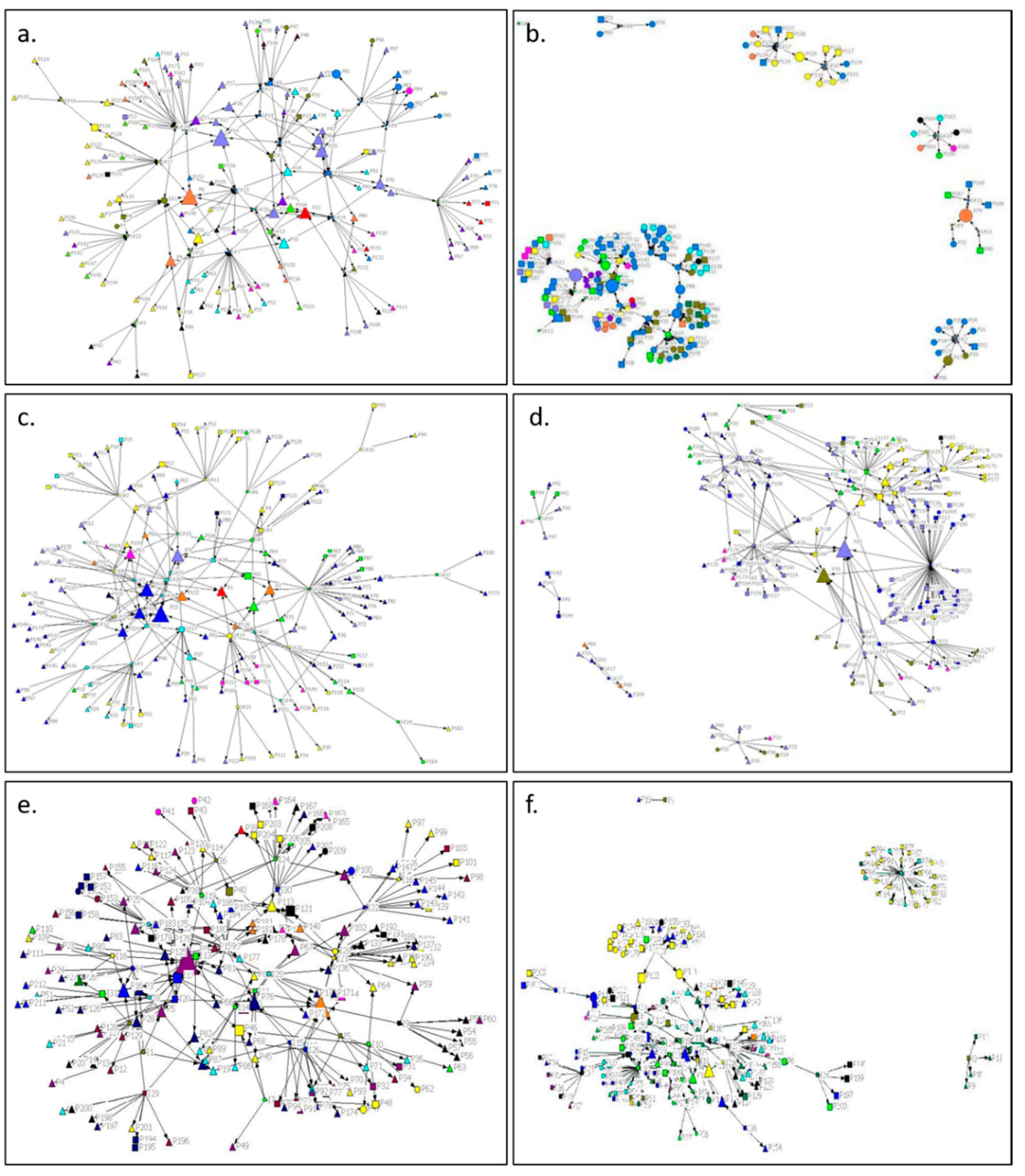
3.1. Access Information Results
3.1.1. Shoalhaven
3.1.2. Bega
3.1.3. Orange
3.2. Disseminating Climate Information
3.2.1. Shoalhaven
3.2.2. Bega
3.2.3. Orange
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pidgeon, N.; Demski, C.; Butler, C.; Parkhill, K.; Spence, A. Creating a national citizen engagement process for energy policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111 (Suppl. 4), 13606–13613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao-Neumann, S.; Schuch, G.; Harman, B.; Crick, F.; Sano, M.; Sahin, O.; van Stadin, R.; Baum, S.; Low Choy, D. One human settlement: A transdisciplinary approach to climate change adaptation research. Futures 2015, 65, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, M.; Fatorelli, L.; Paavola, J.; Locatelli, B.; Pramova, E.; Nurrochmat, D.R.; May, P.H.; Brockhaus, M.; Sari, I.M.; Kusumadewi, S.D. Multi-level governance and power in climate change policy networks. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 54, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, M.D.; Heller, N.E.; Root, T.L.; Schneider, S.H. Bridging the gap: Linking climate-impacts research with adaptation planning and management. Clim. Chang. 2010, 100, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodman, D.; Mitlin, D. Challenges for Community-based Adaptation: Discovering the potential for transformation. J. Int. Dev. 2013, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, B.; Pilifosova, O. From Adaptation to Adaptive Capacity and Vulnerability Reduction. In Climate Change, Adaptive Capacity and Development; World Scientific: Singapore, 2003; pp. 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; King, U.; Morrison, J. Disproportionate burdens: The multidimensional impacts of climate change on the health of Indigenous Australians. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 190, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adger, W.N. Social Capital, Collective Action, and Adaptation to Climate Change. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 79, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, S. Attributes of good governance for effective adaptation action and regional transitions. In Proceedings of the 4th Practical Responses to Climate Change Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 8–10 May 2018; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, D. All the Ships that Never Sailed: A General Model of Illicit Market Suppression; Georgetown University, Georgetown University-Graduate School of Arts & Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, R.; Cvitanovic, C.; Measham, T.; Jacobs, B.; Dowd, A.-M.; Harmq, B. Engaging communities in climate adaptation: The potential of social networks. Clim. Policy 2016, 16, 894–906. [Google Scholar]
- Hens, R.; Wilk, B.; Persson, Å.; Uittenbroek, C.; Wamsler, C. Mainstreaming climate adaptation: Taking stock about “what works” from empirical research worldwide. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccione, V.; Huggel, C.; Bresch, D.N.; Jurt, C.; Walliamann-Helmer, I.; Mehra, M.K.; Caicedo, J.D.P. Joint knolwedge production in climate change adapatation networks. Curr. Opin. Envrion. Sustain. 2019, 39, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelling, M. Adaptation to Climate Change: From Resilience to Transformation; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Borgatti, S.P.; Everett, M.G.; Johnson, J.C. Analyzing Social Networks; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bodin, O.; Prell, C. Social Networks and Natural Resource Management: Uncovering the Social Fabric of Environmental Governance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, J.C.; Knierim, A.; Knuth, U. Policy-induced innovations networks on climate change adaptation–An ex-post analysis of collaboration success and its influencing factors. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 56, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz-Sisitka, H.; Ali, M.B.; Mphepo, G.; Chaves, M.; Macintyre, T.; Pesanayi, T.; Wals, A.; Mukute, M.; Kronlid, D.; Tran, D.T.; et al. Co-designing research on transgressive learning in times of climate change. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of New South Wales. Adapt NSW: Climate Projections for Your Region. Available online: https://climatechange.environment.nsw.gov.au/Climate-projections-for-NSW/Climate-projections-for-your-region (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Shoalhaven City Council. Available online: https://www.shoalhaven.com/visitor-information (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Bega Valley Shire Council. About the Bega Valley Shire. Available online: https://www.begavalley.nsw.gov.au/cp_themes/default/page.asp?p=DOC-KWS-62-56-27 (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Bega Valey Shire Council. History of the Shire. Available online: https://www.begavalley.nsw.gov.au/cp_themes/default/page.asp?p=DOC-KWS-62-56-27 (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Harman, B.; Rylance, K.; Brown, P.; Cunningham, R.; Jacobs, B.; Measham, T. Engaging Local Communities in Climate Adaptation: A Social Network Perspective from Orange Valley, New South Wales, Australia; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Orange Regional Museum. A Short History of Orange. Available online: http://www.orange.nsw.gov.au/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Short-History-of-Orange.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Visit NSW. Visit NSW-Welcome to Orange. Available online: https://www.visitnsw.com/destinations/country-nsw/orange-area (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Newcrest Mines Limited. Our Assets-Cadia. Available online: https://www.newcrest.com/our-assets/cadia (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- NSW Government, Office of Environment and Heritage. Central West and Orana Climate Change Snapshot; Office of Environment and Heritage: Sydney, Australia, 2014; p. 16.
- NSW Government, Office of Environment and Heritage. South East and Tableands Climate Change Snapshot; Office of Environment and Heritage: Sydney, Australia, 2014; p. 16.
- NSW Government, Office of Environment and Heritage. Illawarra Climate Change Snapshot; Office of Environment and Heritage: Sydney, Australia, 2014; p. 16.
- Prell, C. Social Network Analysis: History, Theory & Methodology; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, R.; Cvitanovic, C.; Measham, T.; Jacobs, B.; Dowd, A.; Harman, B. A preliminary Assessment into the Utility of Social Networks for Engaging Local Communities in Climate Adaptation Policy: Working Paper Prepared for NSW Office of Environment & Heritage; Institute for Sustainable Futures: Sydney, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, R.; Jacobs, B.; Measham, T.; Harman, B.; Cvitanovic, C. Social Network Analysis: A Primer on Engaging Communities on Climate Adaptation in New South Wales, Australia; University of Technology Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, B.; Cunningham, R.; Cvitanovic, C.; Jacobs, B.; Measham, T. Community Based Perspectives on Climate Change and Adaptation in the Shoalhaven Region; CSIRO: New South Wales, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, B.; Cunningham, R.; Jacobs, B.; Measham, T.; Cvitanovic, C. Engaging Local Communities in Climate Adaptation: A Social Netework Perspective from Bega Valley, New South Wales; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Borgatti, S.P. Identifying sets of key players in a social network. Comput. Math Organ. Theory 2006, 12, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, C.; Heidl, R.; Wadhwa, A. Knowledge, Networks, and Knowledge Networks: A Review and Research Agenda. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 1115–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, S.; Delaney, C.; Cunningham, R. Forced Innovation: Business Preparedness and Recovery after Extreme Weather Events; University of Technology Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dowd, A.; Marshall, N.A.; Fleming, A.; Jakku, E.; Gauillard, E.; Howden, M. The role of networks in trans- forming Australian agriculture. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogglin, C.L.; Cunningham, R.; Summerell, G.; Leys, J.; Barrett, T.; Auld, T.D.; Oliver, I.; Littleboy, M. Exploring the networks of government scientists using Social Network Analysis: A scoping study. In Proceedings of the 21st International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Gold Coast, Australia, 29 November–4 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, R.; Gogglin, C.L. Changes in Social Connection in a Government Research Network; University of Technology Sydney & NSW Government: Sydney, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cvitanovic, C.; Cunningham, R.; Dowd, A.-M.; Howden, S.M.; Putten, E.I.V. Using Social Network Analysis to Monitor and Assess the Effectiveness of Knowledge Brokers at Connecting Scientists and Decision-Makers: An Australian case study. Environ. Policy Gov. 2017, 27, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, N. Father of Shoalhaven’s oyster industry left strong legacy. In South Coast Register; South Coast Register: Nowra, New South Wales, Australia, 2018; Available online: https://www.southcoastregister.com.au/story/5170578/father-of-shoalhavens-oyster-industry-left-strong-legacy/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Huntsdale, J. The Oyster is Jilm Wild’s World as He Celebrates a Life Growing Seafood on the Shoalhaven Rivers; ABC Illawarra: Illawarra, New South Wales, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leith, P.B.; Haward, M. Climate Change Adaptation in the Australian Edible Oyster Industry: An Analysis of Policy and Practice; University of Tasmania: Hobart, Tasmania, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Food Agility CRC. Food Safety in the NSW Oyster Industry; Food Agility CRC: Sydney, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheese, B. ACCC Inquiry into the Australian Dairy Industry; Bega Cheese: Bega Town, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, M.T.; Cullen, B.R.; Rawnsley, R.P. Modelling the sensitivity of agricultural systems to climate change and extreme climatic events. Agric. Syst. 2016, 148, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.B.; Whetton, P.H.; Barlow, E.W.R. Climate change and winegrape quality in Australia. Clim. Res. 2008, 36, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government, Wine Australia. Available online: https://www.wineaustralia.com/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Goodrich, K.A.; Sjostrom, K.D.; Vaughan, C.; Nichols, L.; Bednarek, A.; Lemos, M.C. Who are boundary spanners and how can we support them in making knowledge more actionable in sustainability fields? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 42, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buys, L.; Aird, R.; van Megen, K.; Miller, E.; Sommerfeld, J. Perceptions of climate change and trust in information providers in rural Australia. Public Underst. Sci. 2014, 23, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šūmane, S.; Kunda, I.; Knickel, K.; Strauss, A.; Tisenkopfs, T.; Rios, I.D.I.; Rivera, M.; Chebach, T.; Ashkenazy, A. Local and farmers’ knowledge matters! How integrating informal and formal knowledge enhances sustainable and resilient agriculture. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 59, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.C.; Alderson, D.L.; Li, L.; Low, S.; Roughan, M.; Shalunov, S.; Tanaka, R.; Willinger, W. The “robust yet fragile” nature of the Internet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, S.A.; Lehmann, S.; Maier, A. Design process robustness: A bipartite network analysis reveals the central importance of people. Des. Sci. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Shoalhaven | Bega Valley | Orange | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First people | Wodi Wodi and Wandandian Aboriginal people | Yuin-Monaro Aboriginal people | Wiradjuri Aboriginal people |
| Population | ~98,000 | ~35,000 | ~40,000 |
| Local Industries | Dairy farming | Dairy farming | State and federal government administration |
| Beef farming | Beef farming | Mining and services to mining | |
| Nurseries | Timber | Hospitality | |
| Manufacturing | Fishing | Tourism | |
| Tourism | Oyster harvesting | Retail | |
| Oyster harvesting | Tourism | Service Sector | |
| Most significant climate impacts | Coastal storms Riverine flooding Bushfires | Coastal storms Riverine flooding Bushfires | Loss of cold nights Variable rainfall Rising temperatures |
| Case Study | Number of Formal Network Participants | Number of Informal Network Participants | Total Number of Participants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoalhaven | 12 | 12 | 24 |
| Bega | 9 | 22 | 31 |
| Orange | 15 | 16 | 31 |
| Common Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| Node | Any entity within the network. This includes all participants and all nominated information sources |
| Tie | Every connection between nodes is represented by a tie |
| In-degree | The number of incoming ties |
| Out-degree | The number of outgoing ties |
| Network cohesion measure | Brief description |
| Average degree | The average number of ties attributed to each node |
| Average distance | The average geodesic distance amongst reachable pairs |
| Closure | Measure of the completeness of relational triads |
| Components | The number of cliques |
| Density | The number of ties divided by the maximum number possible |
| Diameter | The length of the longest geodesic across the network |
| Fragmentation | The proportion of pairs of nodes that are unreachable |
| Shoalhaven | Bega | Orange | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research Undertaken | Mar.–Apr. 2014 | Oct.–Nov. 2014 | Nov.–Dec. 2015 | |||
| Sample Size | N = 24 | N = 31 (29 participated in SNA) | N = 31 | |||
| Access | Share | Access | Share | Access | Share | |
| Network size | 165 | 194 | 175 | 209 | 212 | 205 |
| Node types | ||||||
| International | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Federal, state and local government | 45 | 47 | 44 | 47 | 48 | 84 |
| Non-government organisations | 14 | 15 | 24 | 51 | 17 | 28 |
| Community-based organisations | 25 | 79 | 22 | 77 | 27 | 42 |
| Mass media channels (e.g., tv, newspaper) | 23 | 6 | 28 | 9 | 33 | 5 |
| Mass communication channels (e.g., internet) | 12 | 7 | 19 | 1 | 22 | 3 |
| Social media | 5 | 5 | 26 | 8 | 9 | 1 |
| Research organisations | 6 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 30 | 18 |
| Total formal nodes | 77 | 65 | 77 | 99 | 96 | 130 |
| Total informal nodes | 82 | 129 | 98 | 111 | 116 | 75 |
| ACCESS | SHARE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoalhaven | Bega | Orange | Shoalhaven | Bega | Orange | |
| Average degree | 2.558 | 1.320 | 1.316 | 1.99 | 1.257 | 1.185 |
| Density | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| Components | 1 | 175 | 212 | 7 | 209 | 198 |
| Component ratio | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.031 | 0.995 | 0.966 |
| Fragmentation | 0 | 0.989 | 0.990 | 0.449 | 0.991 | 0.978 |
| Closure | 0.015 | 0.063 | 0.106 | 0.007 | 0.213 | 0.107 |
| Average distance | 4.417 | 1.392 | 1.513 | 4.249 | 1.398 | 2.664 |
| Diameter | 9 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 8 |
| Density | 2.558 | 1.320 | 1.316 | 1.99 | 1.257 | 1.185 |
| SHOALHAVEN | BEGA | ORANGE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACCESS | Bureau of Meteorology | CSIRO | Ind CBO |
| ABC Radio | Internet | Ind state gov | |
| Sydney Morning Herald | ABC News | Ind state gov | |
| % nodes reached in the network | 84.2% | 77.7% | 34.93% |
| SHARE | 2ST Radio | Friends | Individual state government |
| Interviewee CBO | Interviewee CBO | Individual NGO | |
| Interviewee local government | Interviewee LLS | Individual CBO | |
| % nodes reached in the network | 70.1% | 79.5% | 49.01% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cunningham, R.; Jacobs, B.; Measham, T.G. Uncovering Engagement Networks for Adaptation in Three Regional Communities: Empirical Examples from New South Wales, Australia. Climate 2021, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9020021
Cunningham R, Jacobs B, Measham TG. Uncovering Engagement Networks for Adaptation in Three Regional Communities: Empirical Examples from New South Wales, Australia. Climate. 2021; 9(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleCunningham, Rebecca, Brent Jacobs, and Thomas G. Measham. 2021. "Uncovering Engagement Networks for Adaptation in Three Regional Communities: Empirical Examples from New South Wales, Australia" Climate 9, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9020021
APA StyleCunningham, R., Jacobs, B., & Measham, T. G. (2021). Uncovering Engagement Networks for Adaptation in Three Regional Communities: Empirical Examples from New South Wales, Australia. Climate, 9(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9020021







