Neural Network Modelling of Temperature and Salinity in the Venice Lagoon
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Rationale for a Data-Driven Modeling Approach
1.2. Convolutional Neural Networks as a Novel Tool for Coastal Hydrodynamics
1.3. Model Architecture and Study Outline
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Model Architecture and Training Protocol
2.2. Experimental Design and Climate Change Assessment
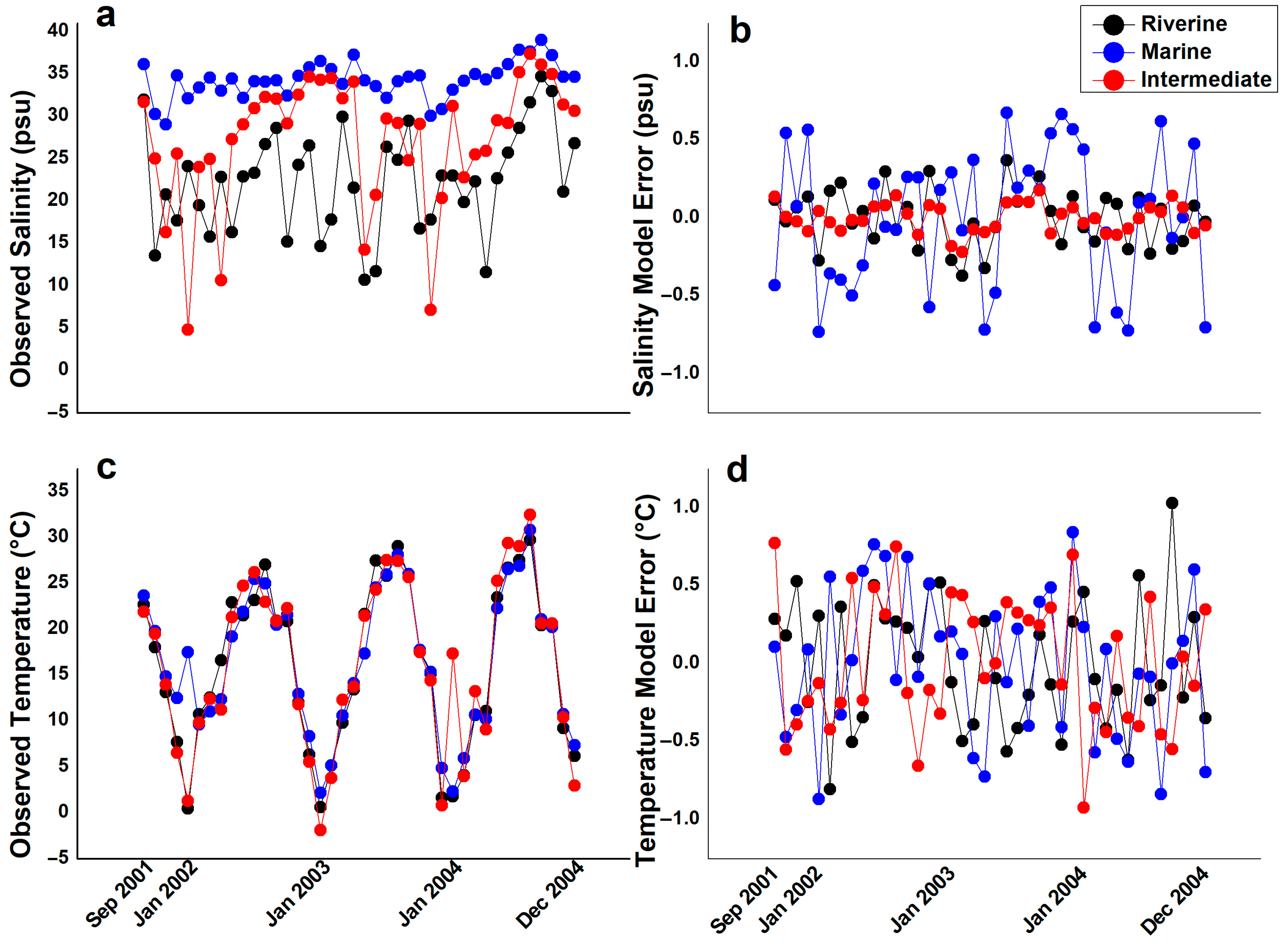
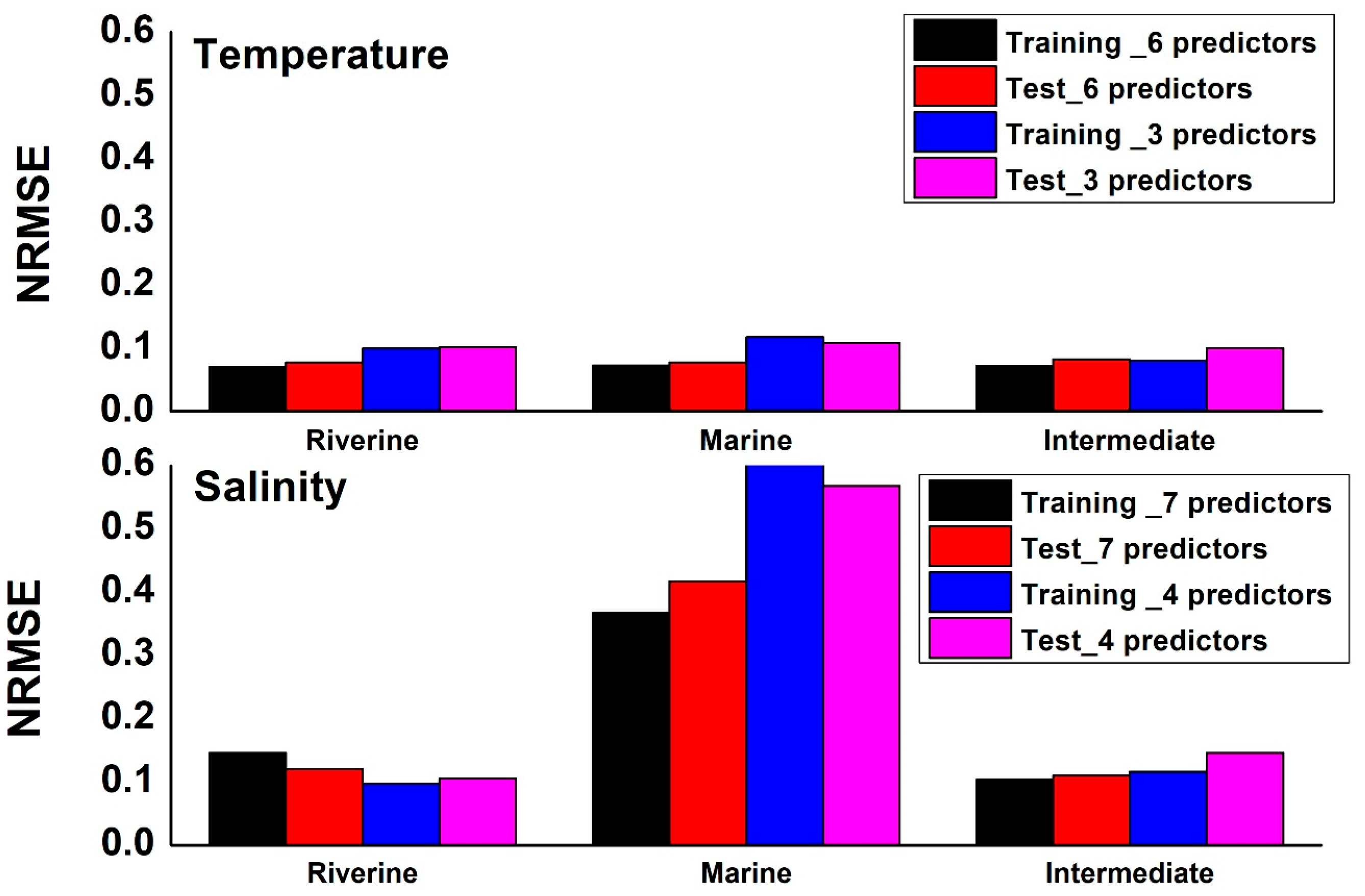
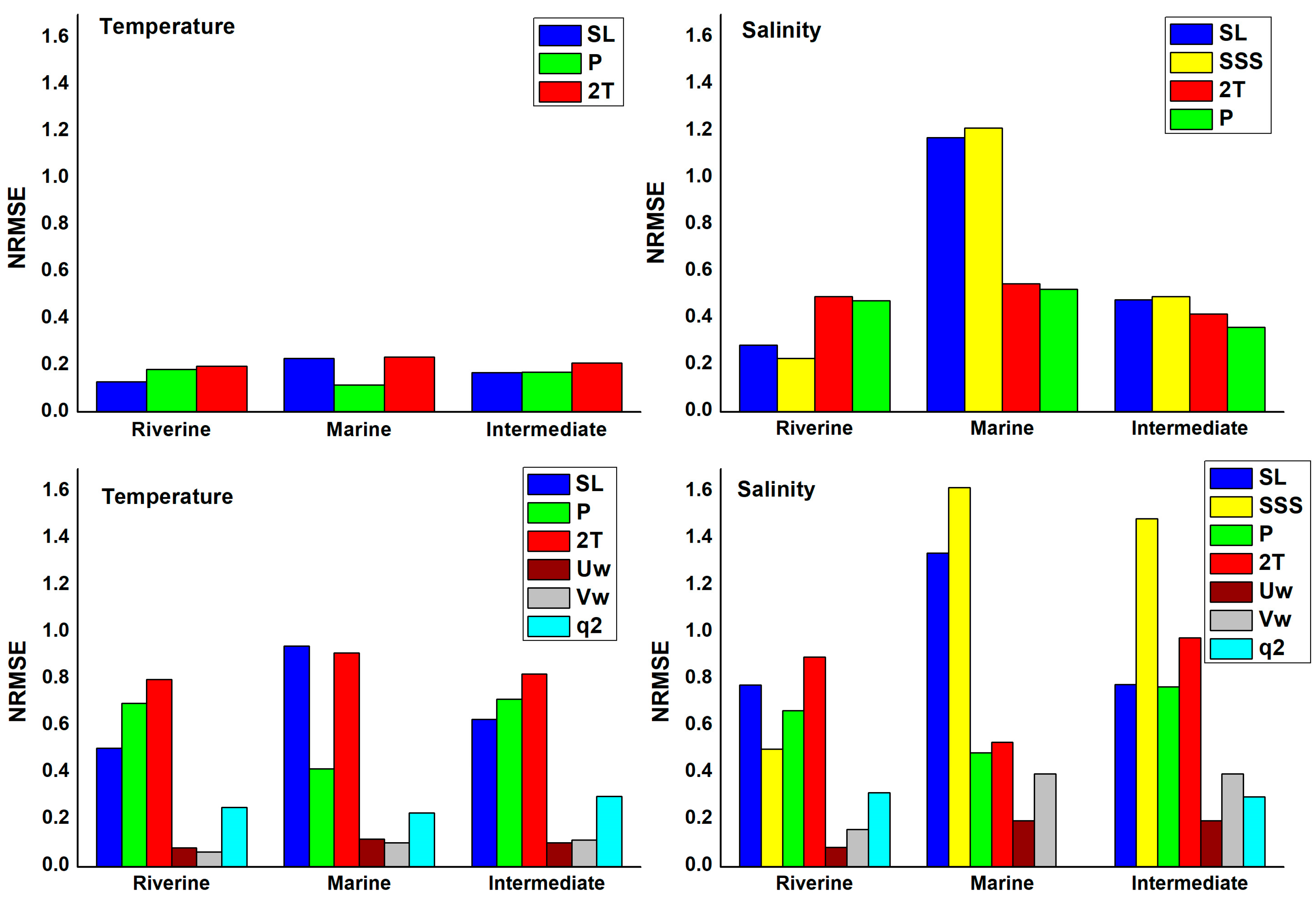
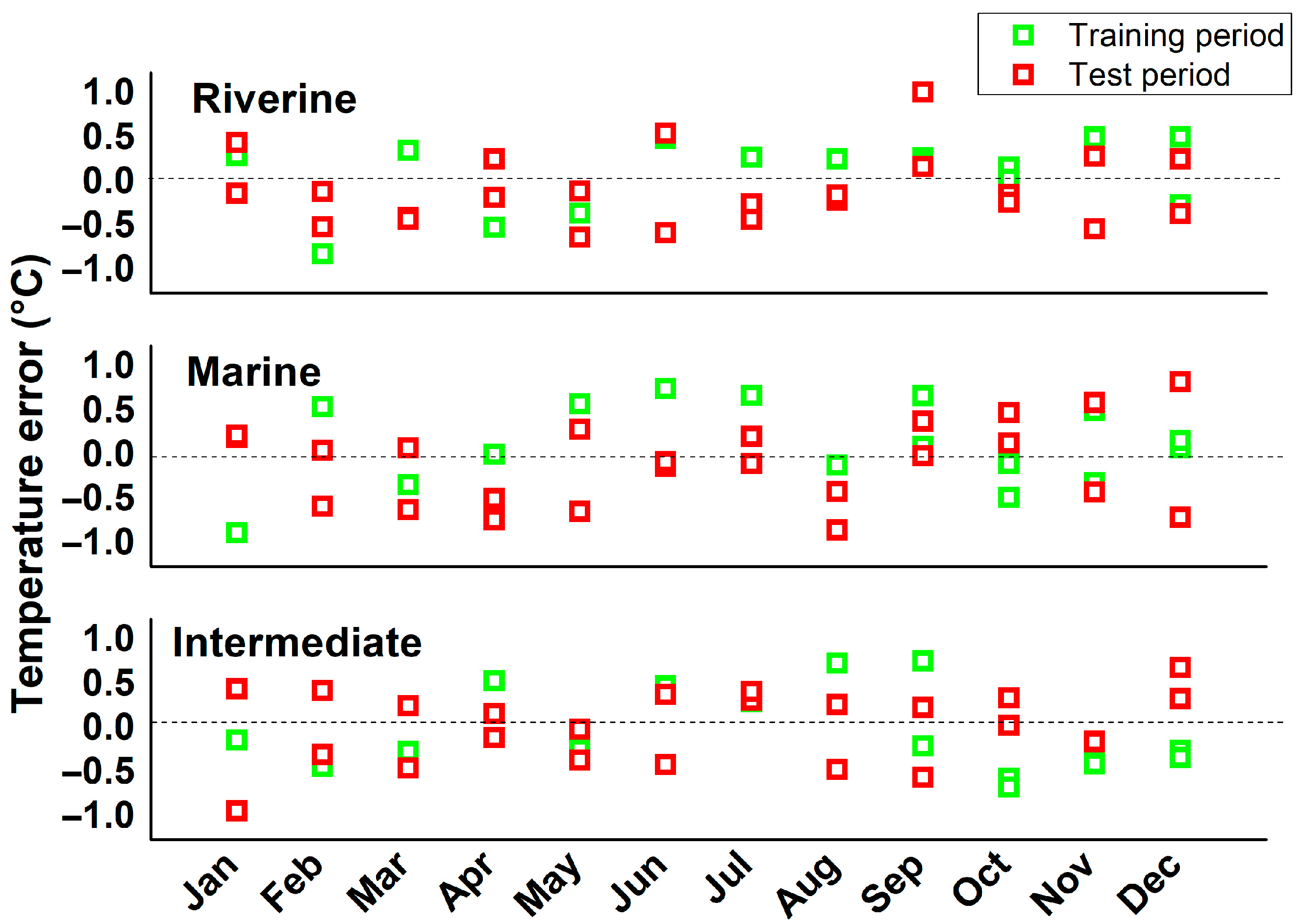
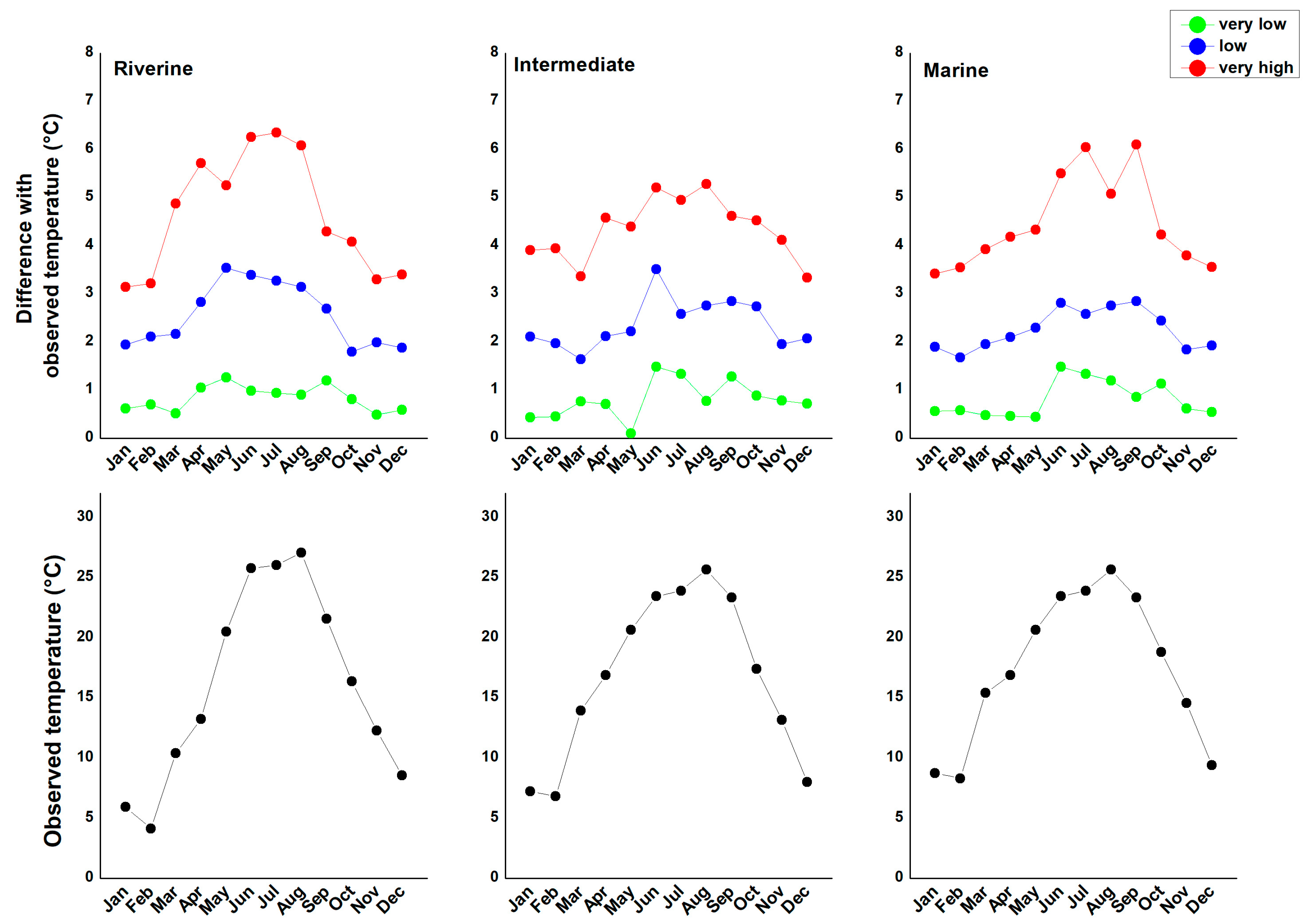
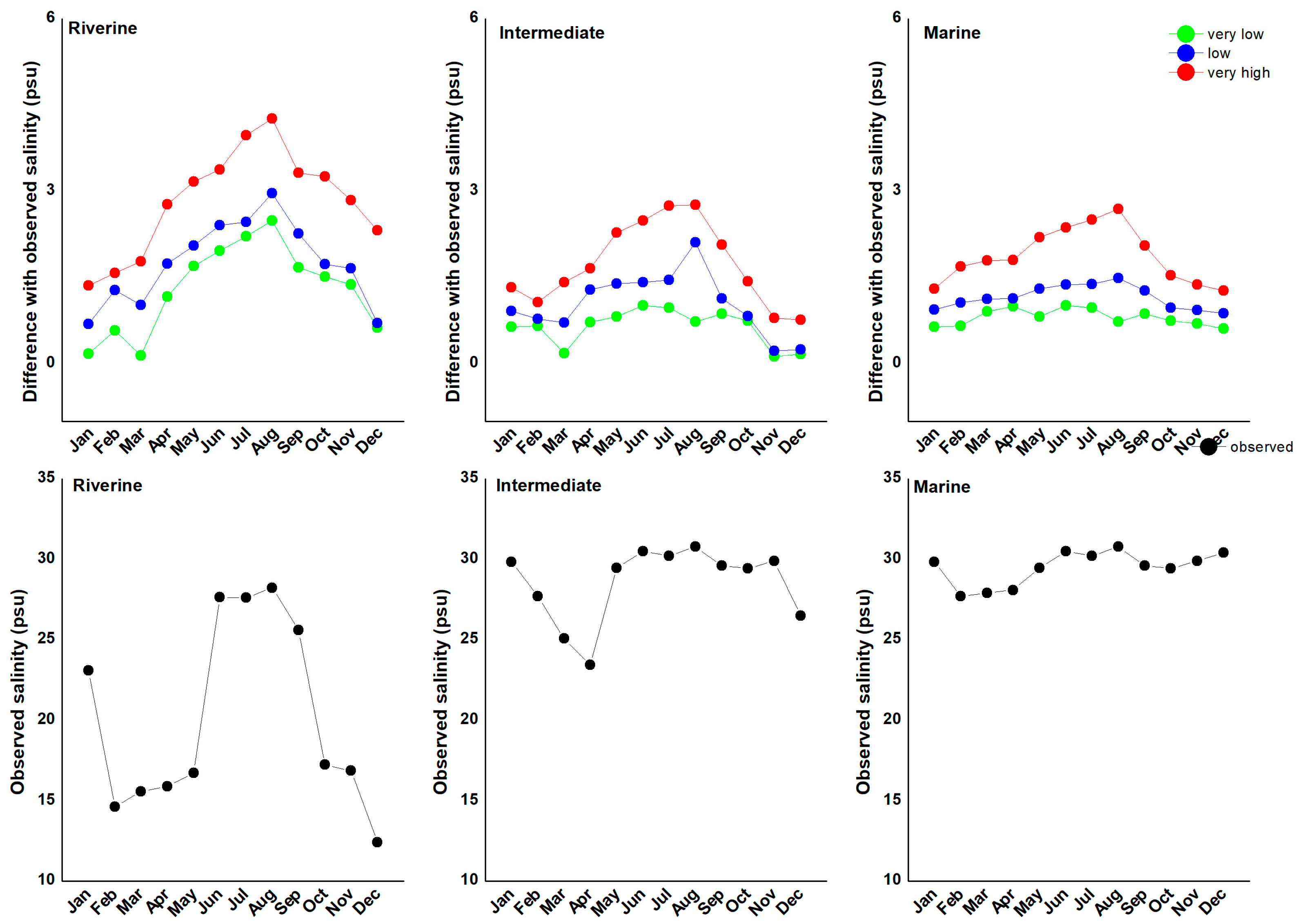
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performance and Projections of Climate-Driven Impacts
4.2. Study Limitations and Methodological Context
4.3. Methodological Rationale, Interpretability, and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GCM | General Circulation Model |
| GWL | Global Warming Level |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
| P | Precipitation |
| RCM | Regional Climate Model |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| SL | Sea Level |
| SSS | Sea Surface Salinity |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
| T2 | Air Temperature at 2 m |
| q2 | Specific Humidity at 2 m |
| Uw, Vw | Zonal and Meridional Wind Components |
References
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Brito, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Colijn, F.; Riva, S.D.; Gertz, F.; Hansen, J.W.; Holmer, M.; et al. An overview of ecological status, vulnerability and future perspectives of European large shallow, semi-enclosed coastal systems, lagoons and transitional waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solidoro, C.; Bandelj, V.; Aubry, F.B. Response of the Venice Lagoon ecosystem to natural and anthropogenic pressures over the last 50 years. In Coastal Lagoons: Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 8, pp. 483–511. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues-Filho, J.L.; Macêdo, R.L.; Sarmento, H.; Pimenta, V.R.A.; Alonso, C.; Teixeira, C.R.; Pagliosa, P.R.; Netto, S.A.; Santos, N.C.L.; Daura-Jorge, F.G.; et al. From ecological functions to ecosystem services: Linking coastal lagoons biodiversity with human well-being. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2611–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guild, R.; Wang, X.; Quijón, A.P. Climate change impacts on coastal ecosystems. Environ. Res. Clim. 2025, 3, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennish, M.J.; Paerl, H.W. Coastal Lagoons: Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Roelvink, D. Coastal lagoons and rising sea level: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmaraki, S.; Somot, S.; Sevault, F.; Nabat, P. Past Variability of Mediterranean Sea Marine Heatwaves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 9813–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.E.; Burrows, M.T.; Hobday, A.J.; King, N.G.; Moore, P.J.; Gupta, A.S.; Thomsen, M.S.; Wernberg, T.; Smale, D.A. Biological Impacts of Marine Heatwaves. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2023, 15, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benthuysen, J.A.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Chen, K.; Wernberg, T. Editorial: Advances in Understanding Marine Heatwaves and Their Impacts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Turicchia, E.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; et al. Marine heatwaves drive recurrent mass mortalities in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivetti, I.; Fraschetti, S.; Lionello, P.; Zambianchi, E.; Boero, F.; Mazzuca, S. Global Warming and Mass Mortalities of Benthic Invertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, A.K.; Oppenheimer, M.; Garschagen, M.; Buchanan, M.K.; Duvat, V.K.E.; Forbes, D.L.; Ford, J.D.; Lambert, E.; Petzold, J.; Renaud, F.G.; et al. Sea level rise risks and societal adaptation benefits in low-lying coastal areas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochier, F.; Ramieri, E. Climate Change Impacts on the Mediterranean Coastal Zones; Nota di Lavoro No. 27.2001; Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei: Milano, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchettin, D.; Bruni, S.; Raicich, F.; Lionello, P.; Adloff, F.; Androsov, A.; Antonioli, F.; Artale, V.; Carminati, E.; Ferrarin, C.; et al. Sea-level rise in Venice: Historic and future trends. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 2643–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Navarro, I.C.; López-Ballesteros, A.; Mesman, J.P.; Trolle, D.; Pierson, D.; Senent-Aparicio, J. Modeling climate impacts on ecosystem services in an anthropized coastal lagoon for effective planning and adaptation. Clim. Change 2025, 178, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaletto, G.; Barletta, I.; Mocavero, S.; Federico, I.; Epicoco, I.; Verri, G.; Coppini, G.; Schiano, P.; Aloisio, G.; Pinardi, N. Parallel implementation of the SHYFEM (System of HydrodYnamic Finite Element Modules) model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 6025–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Downscaling daily rainfall using artificial neural networks and stochastic weather generators. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer and Communication Technologies in Agriculture Engineering, Chengdu, China, 12–13 June 2010; Volume 1, pp. 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rasp, S.; Scher, S.; Weyn, J.A.; Mouatadid, S.; Thuerey, N. WeatherBench: A benchmark dataset for data-driven weather forecasting. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, R.; Allen, D. Between the land and the sea: The ecological functioning of salt marsh estuaries. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 200, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Edinger, J.E.; Duttweiler, D.W.; Geyer, J.C. The heat exchange of a water surface. Water Resour. Res. 1968, 4, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Rogers, D.P.; Edson, J.B.; Young, G.S. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere Coupled-Ocean Atmosphere Response Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 3747–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Shen, J.; Hong, H. The influence of sea-level rise on the tidal circulation and flushing of the Jiulong River Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Kjerfve, B. Comparative oceanography of coastal lagoons. In Estuarine Variability; Wolfe, D.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kjerfve, B. Coastal lagoons. In Coastal Lagoon Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Umgiesser, G. The Venice Lagoon: A model for the past, a challenge for the future. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S1–S5. [Google Scholar]
- Vandal, T.; Kodra, E.; Ganguly, S.; Michaelis, A.; Nemani, R.; Ganguly, A.R. DeepSD: Generating high-resolution climate change projections through single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; pp. 1663–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Baño-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Configuration and evaluation of a statistical downscaling method based on convolutional neural networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031905. [Google Scholar]
- Doury, A.; Somot, S.; Gadat, S.; Ribes, A.; Corre, L. Regional climate model emulator based on deep learning: Concept and first evaluation of a novel hybrid downscaling approach. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 1751–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.G.; Kim, J.H.; Luo, J.J. Stochastic-Deep-U-Net for probabilistic precipitation downscaling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2020MS002409. [Google Scholar]
- Narejo, S.; Jawaid, M.M.; Talpur, S.; Baloch, R.; Pasero, E.G.A. Multi-step rainfall forecasting using deep learning approach. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alpaos, C.; D’alpaos, A. The Valuation of Ecosystem Services in the Venice Lagoon: A Multicriteria Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’aLpaos, L.; Defina, A. Mathematical modeling of tidal hydrodynamics in shallow lagoons: A review of open issues and applications to the Venice lagoon. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, D.; Umgiesser, G.; Cucco, A. Modeling the water exchanges between the Venice Lagoon and the Adriatic Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2008, 58, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation between climate change in the Mediterranean region and global warming. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.P. Water, Salt and Heat Balance of Coastal Lagoons; Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 69–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Monthly climate prediction using deep convolutional neural network and long short-term memory. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.A.; Cirillo, M.C. On the use of the normalized mean square error in evaluating dispersion model performance. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Han, D.; Jang, E.; Im, J.; Sung, T. Remote sensing of sea surface salinity: Challenges and research directions. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2166377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. A long short-term memory neural network-based model for sea surface temperature prediction. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Abiy, A.Z.; Wiederholt, R.P.; Lagerwall, G.L.; Melesse, A.M.; Davis, S.E. Multilayer Feedforward Artificial Neural Network Model to Forecast Florida Bay Salinity with Climate Change. Water 2022, 14, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, T.; Shi, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Prospective scenarios of the saltwater intrusion in an estuary under climate change context using Bayesian neural networks. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.S.; Hutton, P.H.; Chen, L.; Roy, S.B. A hybrid empirical-Bayesian artificial neural network model of salinity in the San Francisco Bay-Delta estuary. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.M.; Maier, H.R.; Gibbs, M.S.; Foale, E.R.; Grosvenor, N.A.; Harders, N.P.; Kikuchi-Miller, T.C. Framework for developing hybrid process-driven, artificial neural network and regression models for salinity prediction in river systems. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2987–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Ishida, K.; Baba, D. Surface Water Temperature Predictions at a Mid-Latitude Reservoir under Long-Term Climate Change Impacts Using a Deep Neural Network Coupled with a Transfer Learning Approach. Water 2021, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Qiu, W.; Wu, J.; Tao, Y. Water temperature forecasting based on modified artificial neural network methods: Two cases of the Yangtze River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Wang, Y.; Rhoads, B.; Wang, D.; Qiu, W.; Tao, Y.; Wu, J. River water temperature forecasting using a deep learning method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Zennaro, F.; Furlan, E.; Critto, A. Recurrent neural networks for water quality assessment in complex coastal lagoon environments: A case study on the Venice Lagoon. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 154, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunno, F.; De Marinis, G.; Gargano, R.; Granata, F. Tide Prediction in the Venice Lagoon Using Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous (NARX) Neural Network. Water 2021, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaldo, D.; Sanchez-Arcilla, A.; Samaras, A.G.; Snoussi, M. Climate change impacts on Mediterranean coastal and transitional areas: Assessment, projection, and adaptation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1341637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Prabhat. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Reinforcement learning for intelligent water resource management: A review. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128362. [Google Scholar]
- Umgiesser, G. The impact of the MOSE system in Venice. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2020, 31, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzo, M.; Guerzoni, S.; Umgiesser, G. Consequences of the MOSE barriers on the Venice lagoon hydrodynamics and sediment transport. In The Venice Lagoon in the New Millennium; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]




| Variables | SSS | SL | SST | T2 | P | Uw | Vv | q2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSS | −0.041 | −0.693 | −0.735 | −0.037 | −0.498 | −0.041 | 0.336 | |
| SL | 1 | 0.391 | 0.325 | 0.413 | 0.017 | −0.063 | 0.181 | |
| SST | 1 | 0.989 | 0.197 | 0.423 | 0.060 | −0.153 | ||
| T2 | 1 | 0.170 | 0.497 | 0.075 | −0.196 | |||
| P | 1 | 0.057 | 0.159 | 0.561 | ||||
| Uw | 1 | 0.577 | −0.053 | |||||
| Vw | 1 | 0.367 | ||||||
| q2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bozzeda, F.; Sigovini, M.; Lionello, P. Neural Network Modelling of Temperature and Salinity in the Venice Lagoon. Climate 2025, 13, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13090189
Bozzeda F, Sigovini M, Lionello P. Neural Network Modelling of Temperature and Salinity in the Venice Lagoon. Climate. 2025; 13(9):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13090189
Chicago/Turabian StyleBozzeda, Fabio, Marco Sigovini, and Piero Lionello. 2025. "Neural Network Modelling of Temperature and Salinity in the Venice Lagoon" Climate 13, no. 9: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13090189
APA StyleBozzeda, F., Sigovini, M., & Lionello, P. (2025). Neural Network Modelling of Temperature and Salinity in the Venice Lagoon. Climate, 13(9), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13090189





