Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Periyar River Basin, Kerala, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
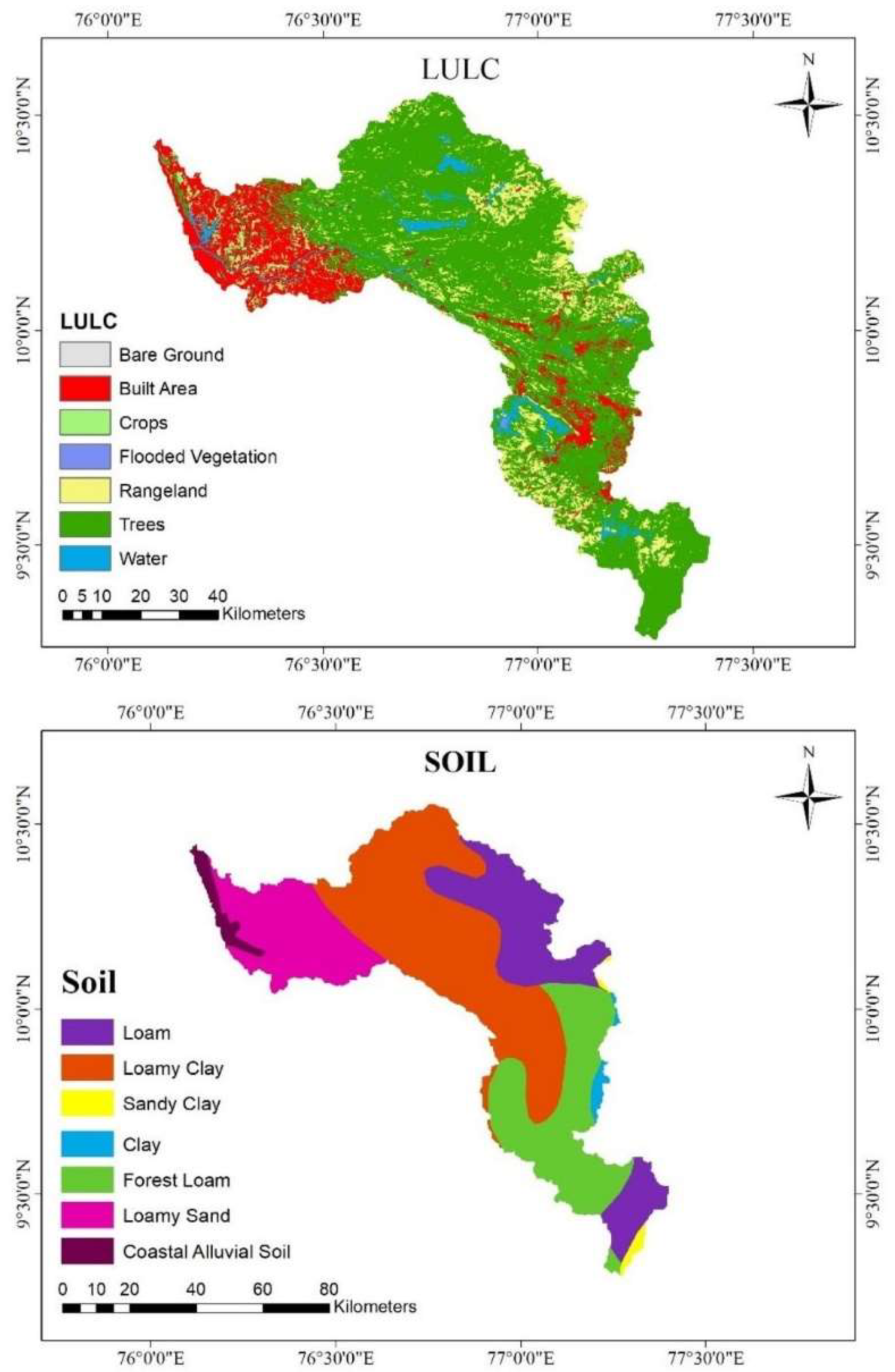
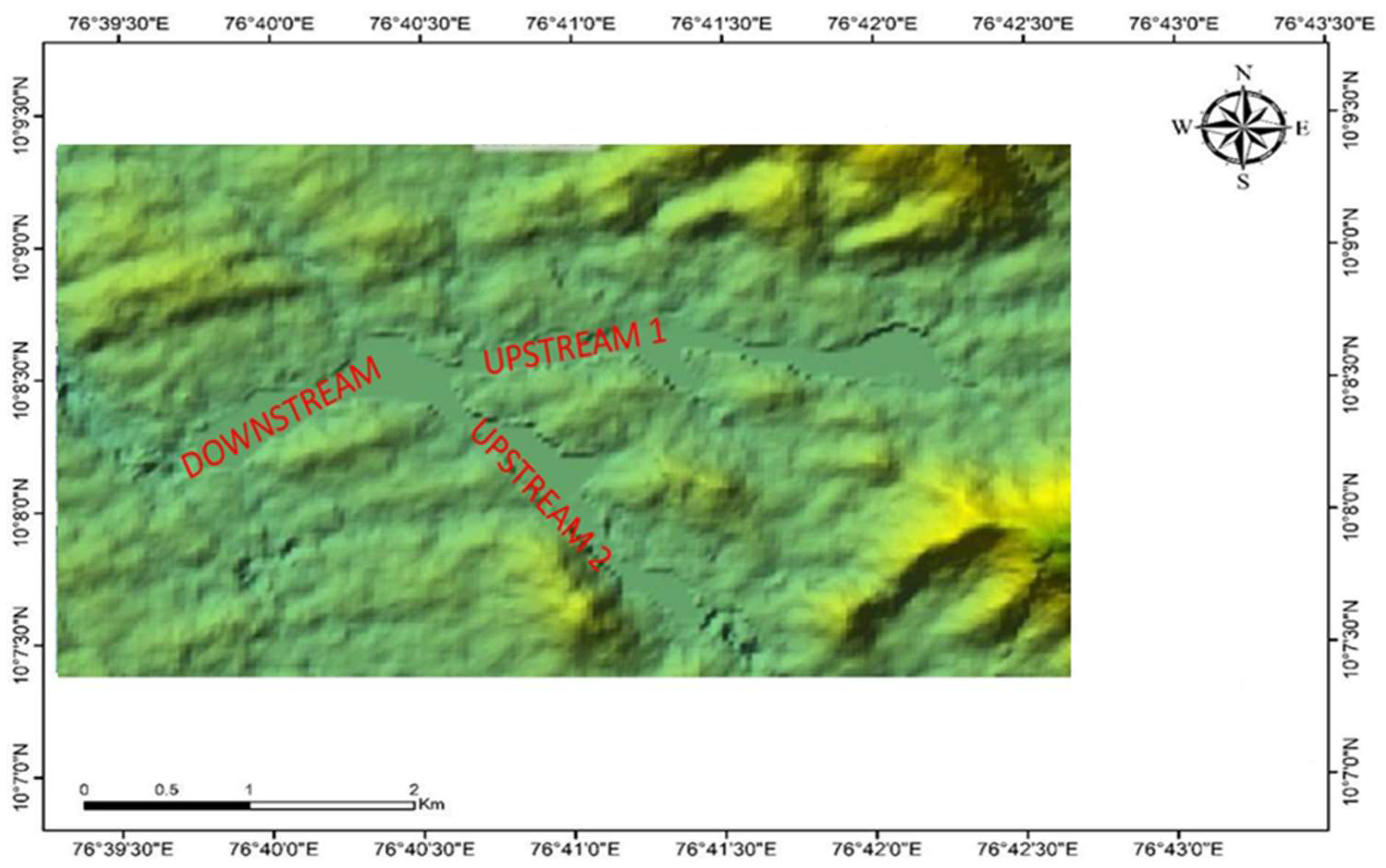
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Database
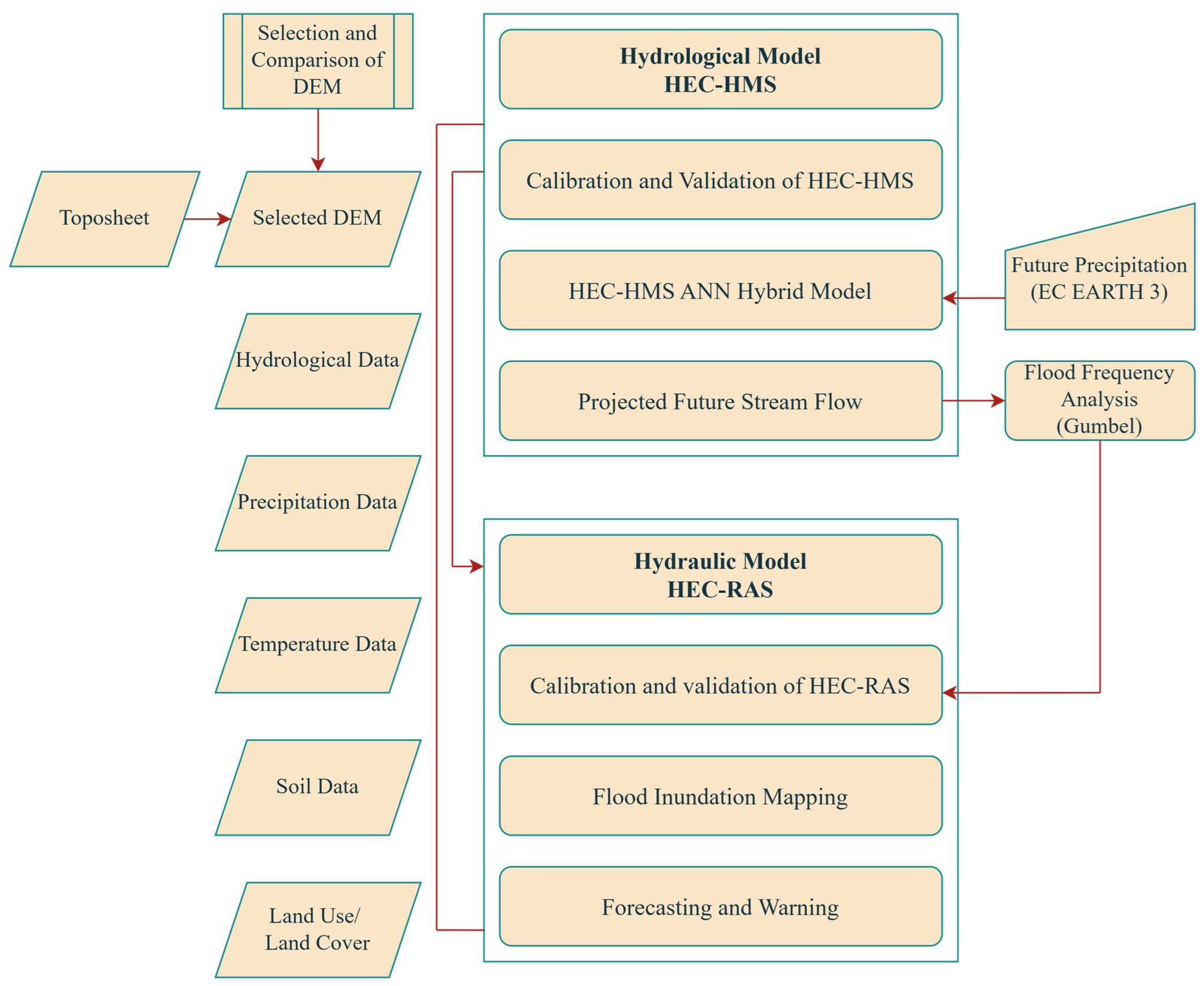
2.3. Methodology
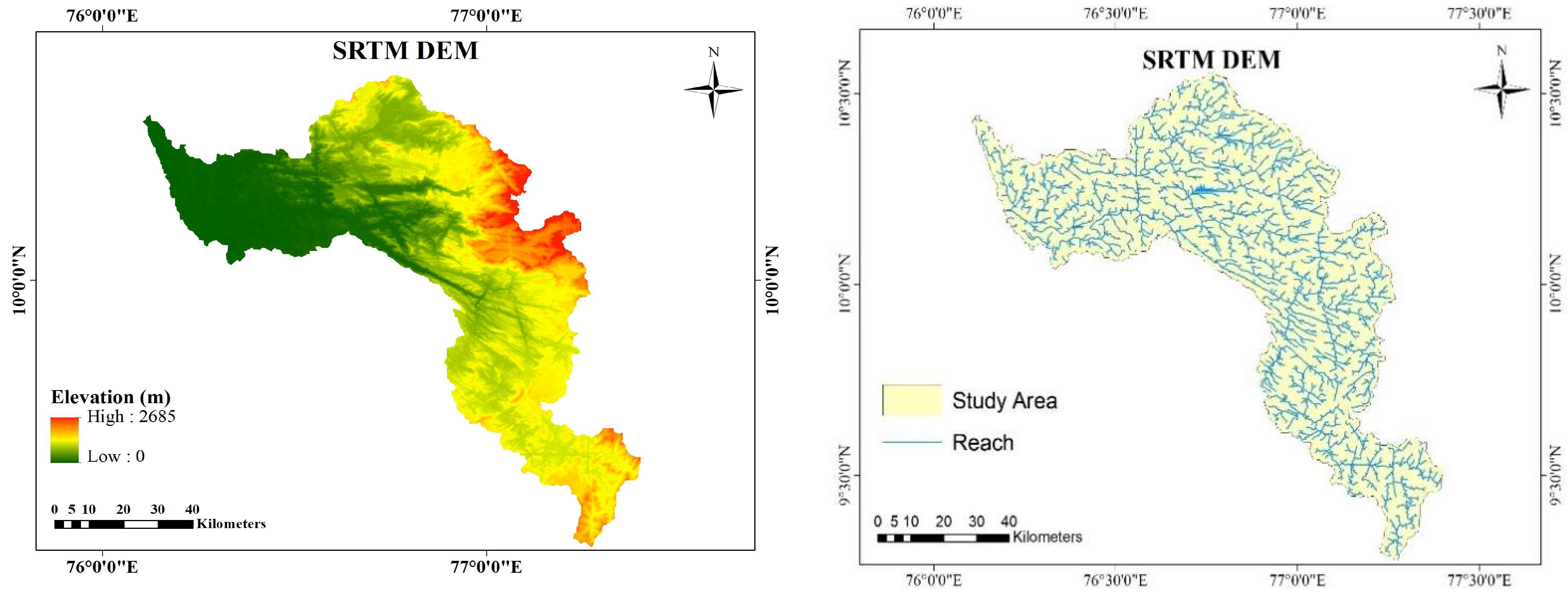
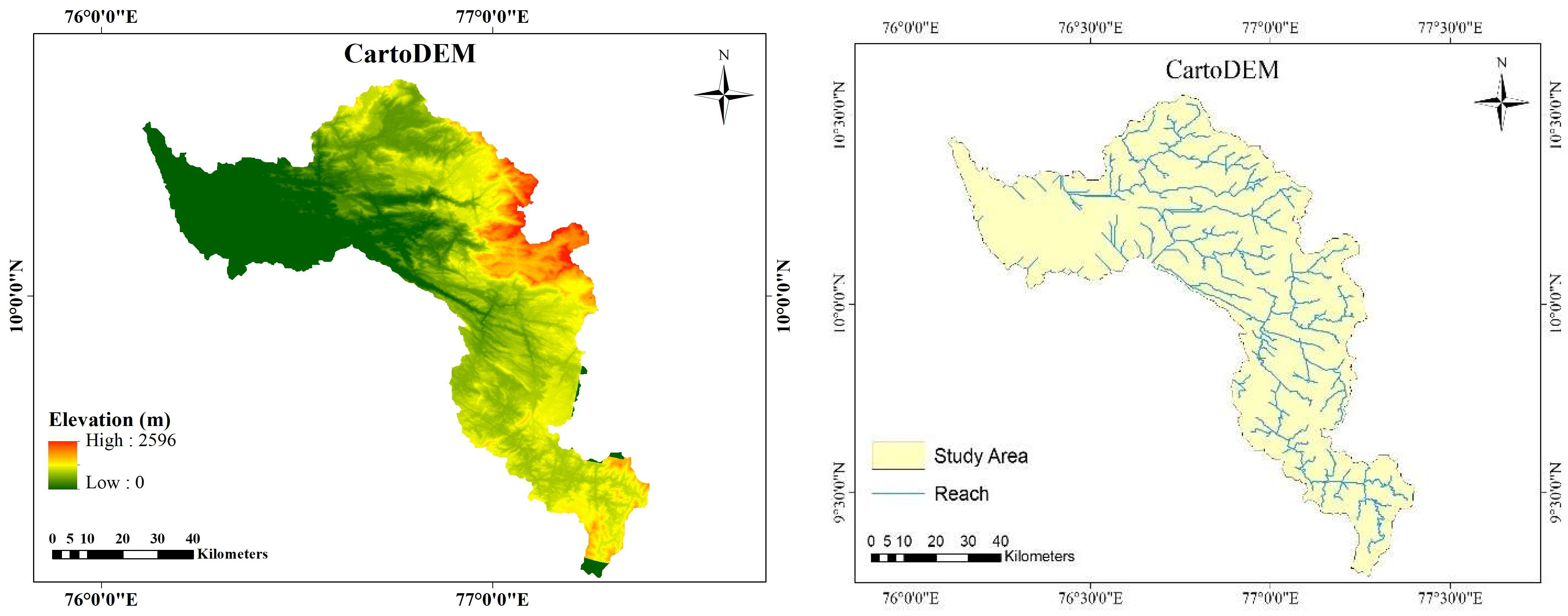
2.3.1. Comparison and Selection of DEM
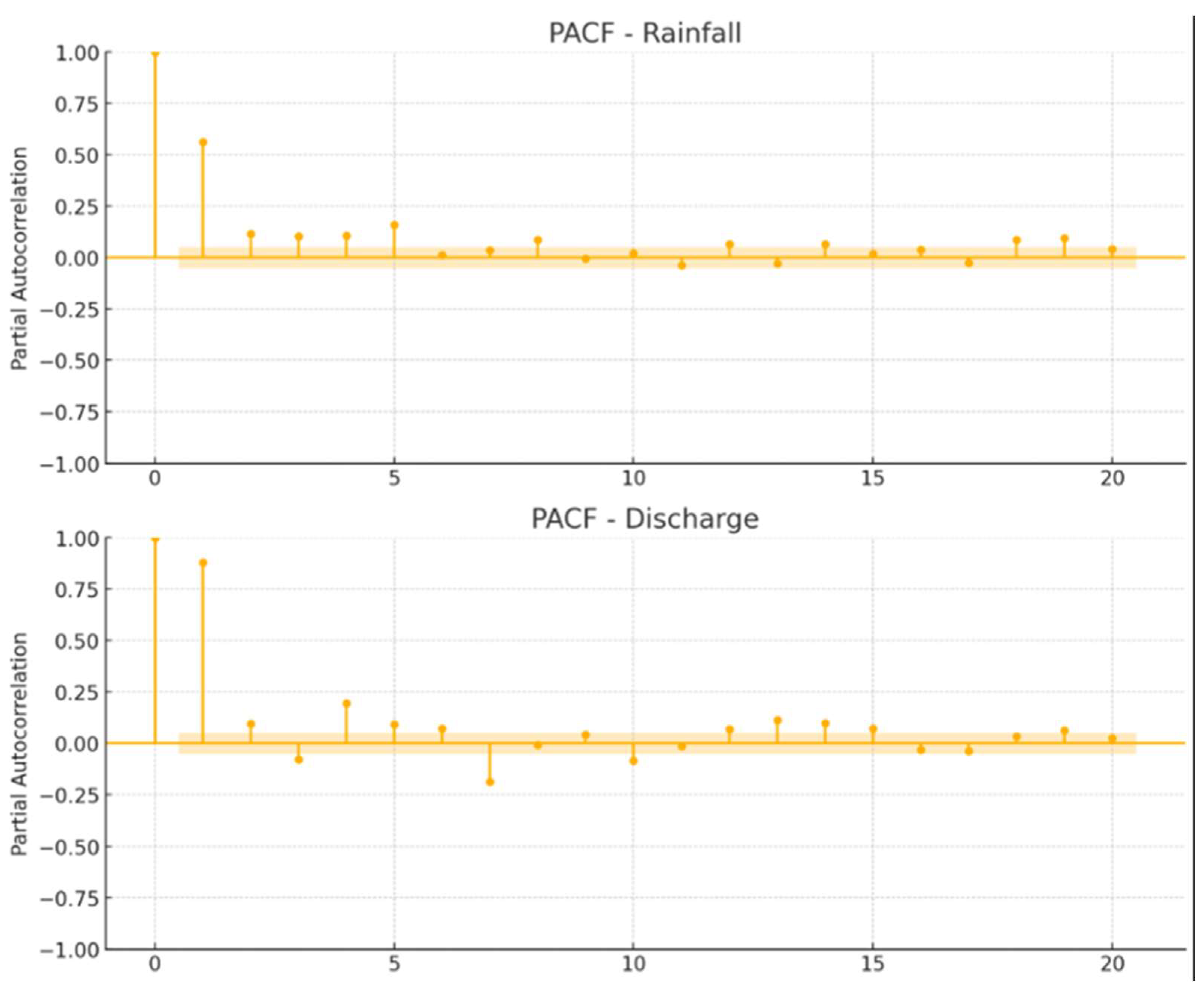
2.3.2. Rainfall–Runoff Modeling
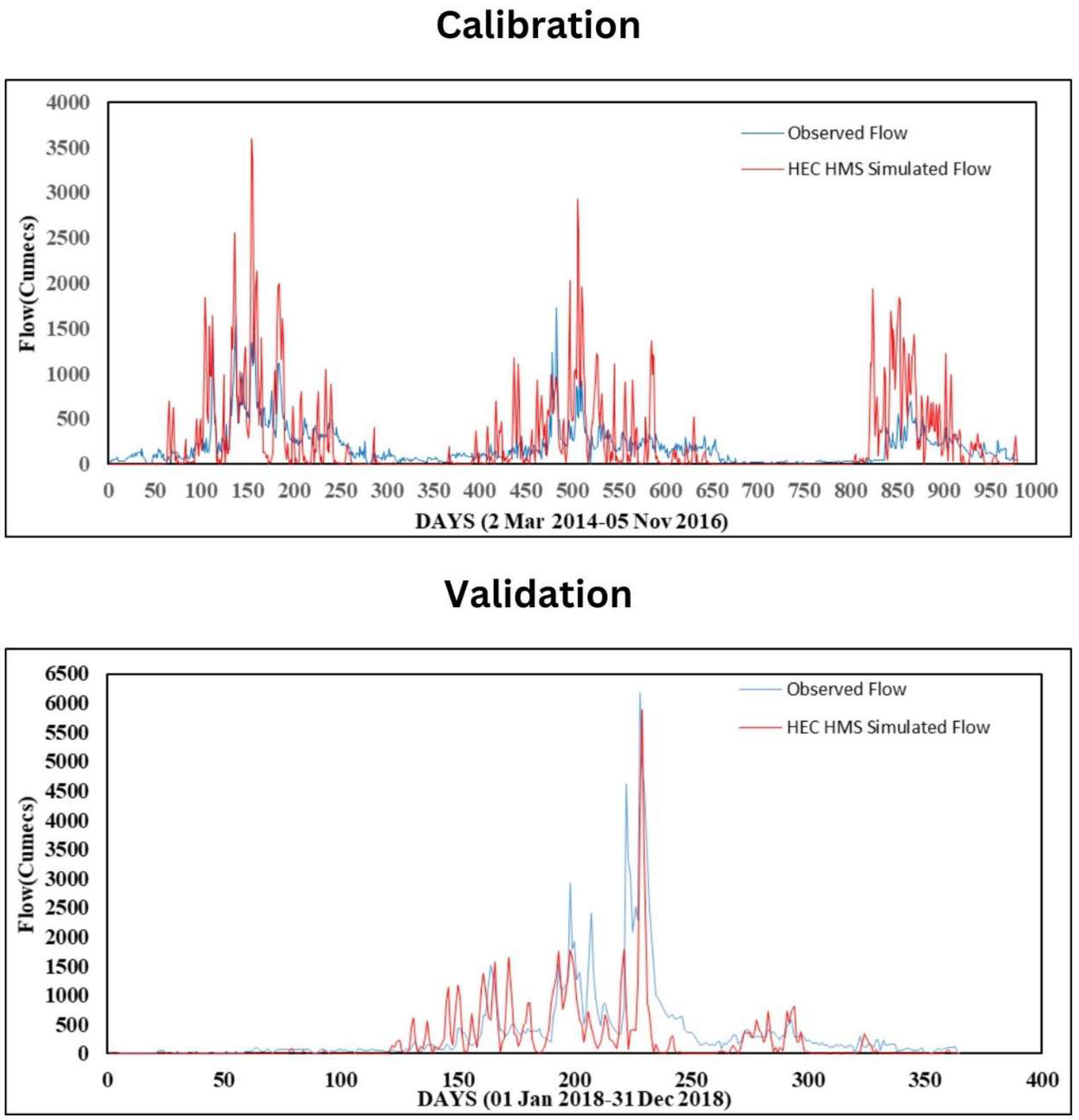
2.3.3. Calibration and Validation of the HEC-HMS Model
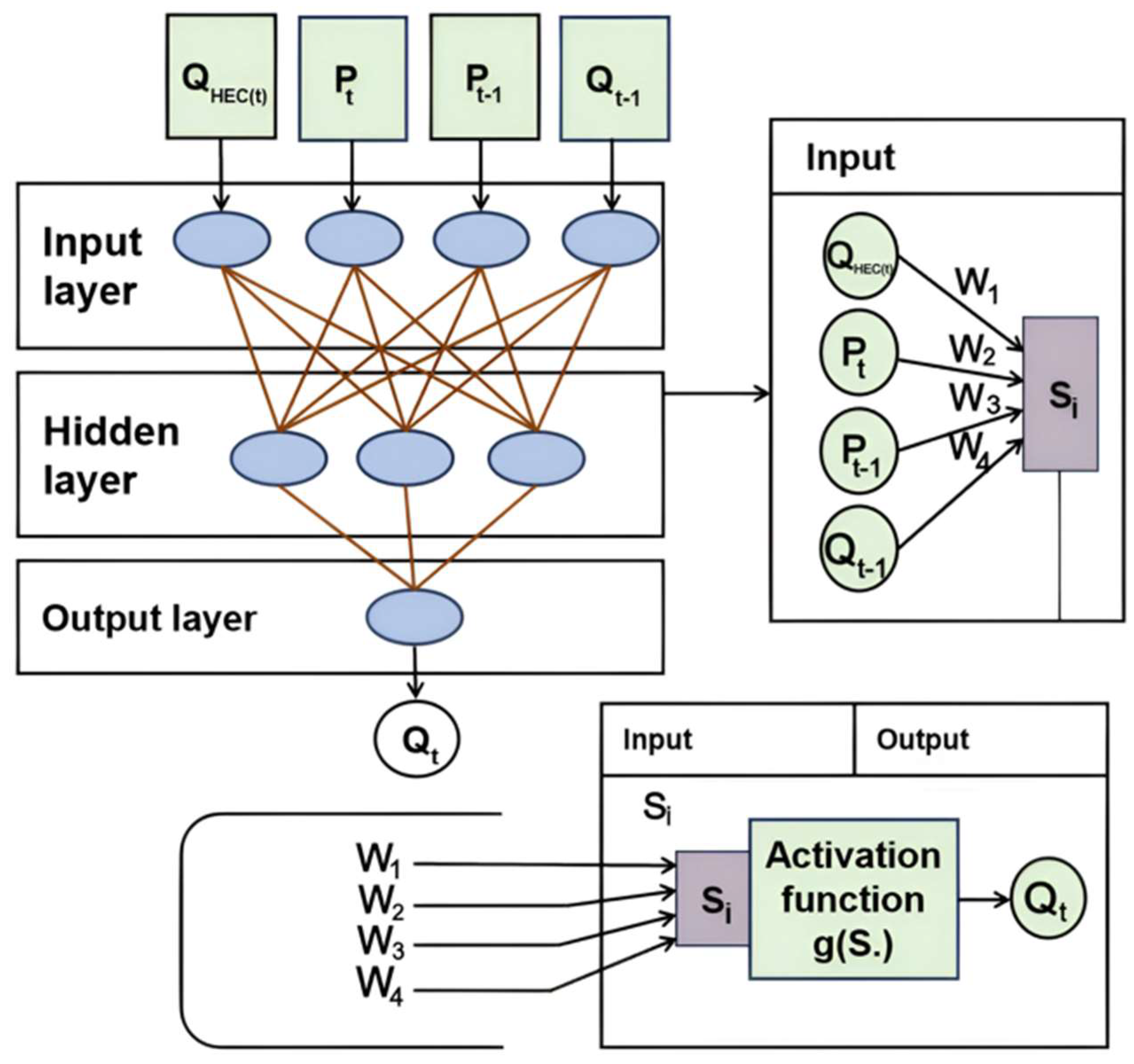
2.3.4. HEC-HMS-ANN Hybrid Model
2.3.5. Flood Inundation Modeling
2.3.6. Future Flood Inundation Map
3. Results and Discussions
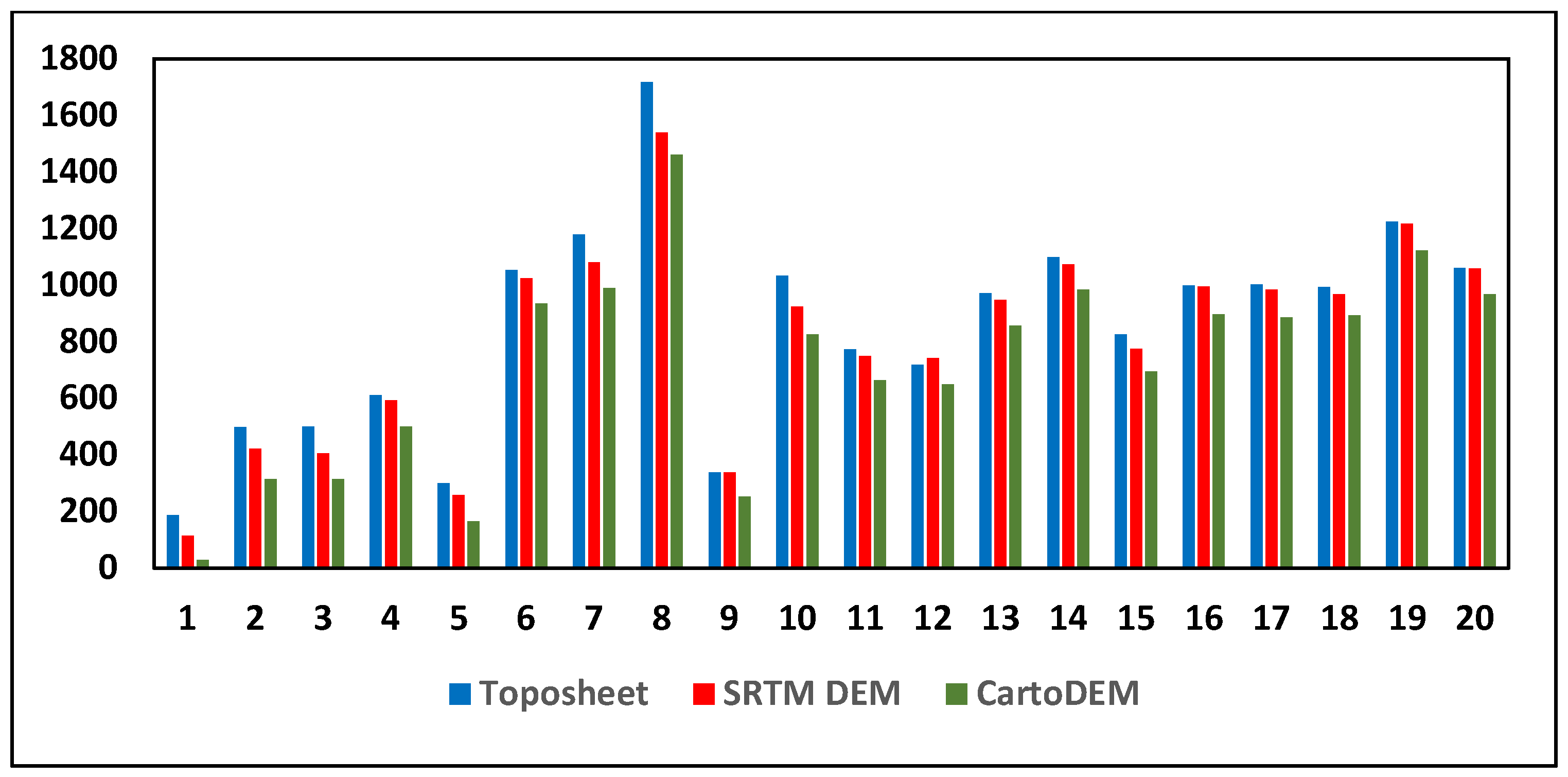
3.1. Comparison and Selection of DEM
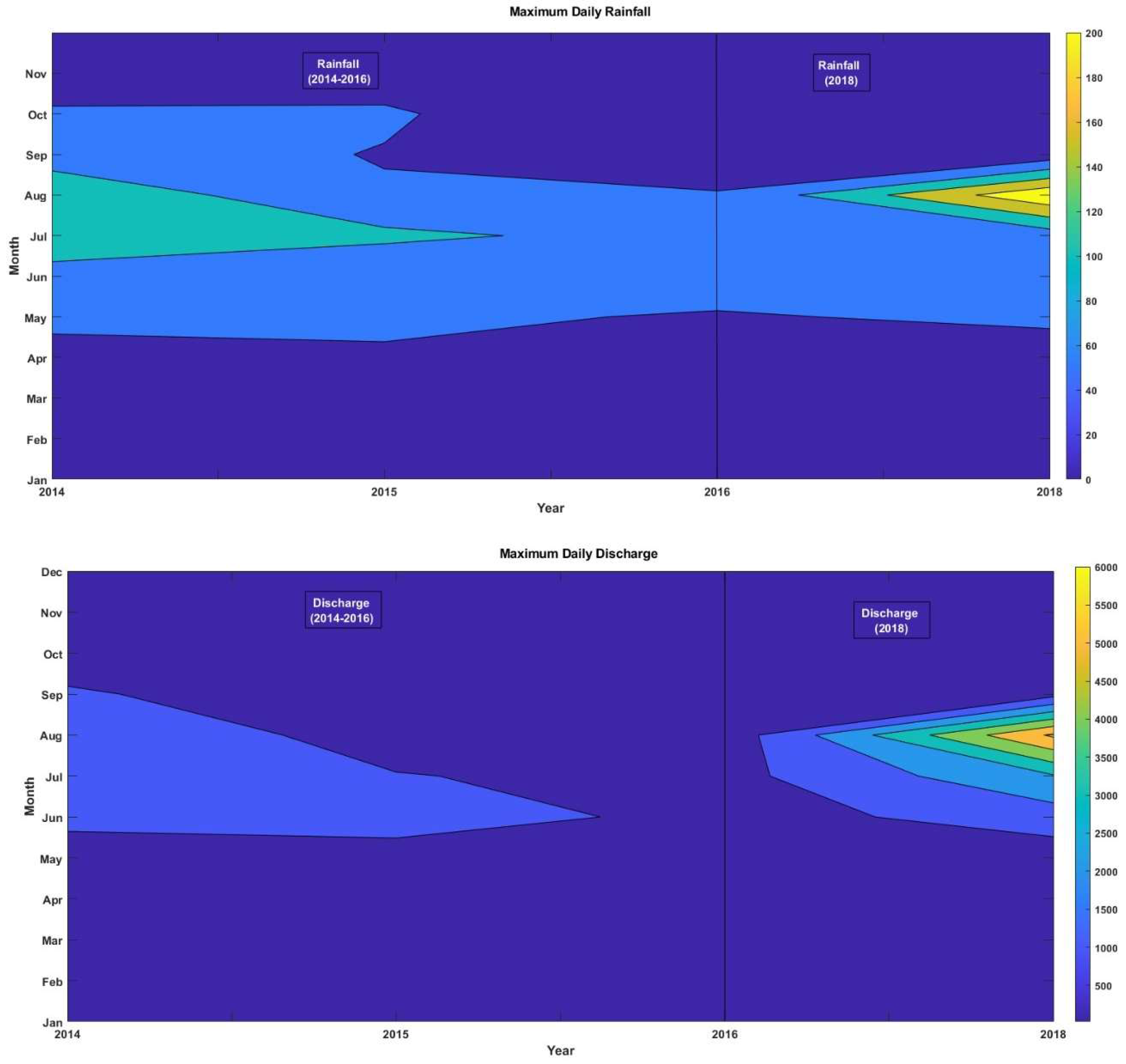
3.2. Comparison of Rainfall and Discharge
3.3. Rainfall–Runoff Modeling
3.3.1. Calibration and Validation
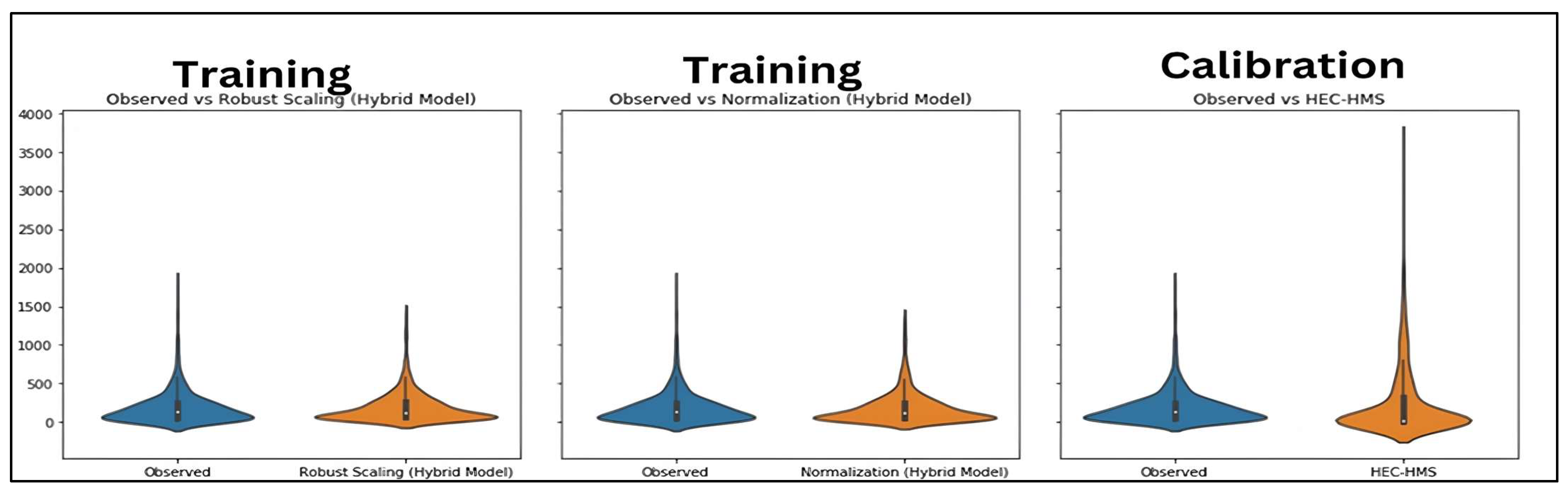
3.3.2. HEC-HMS-ANN Hybrid Model
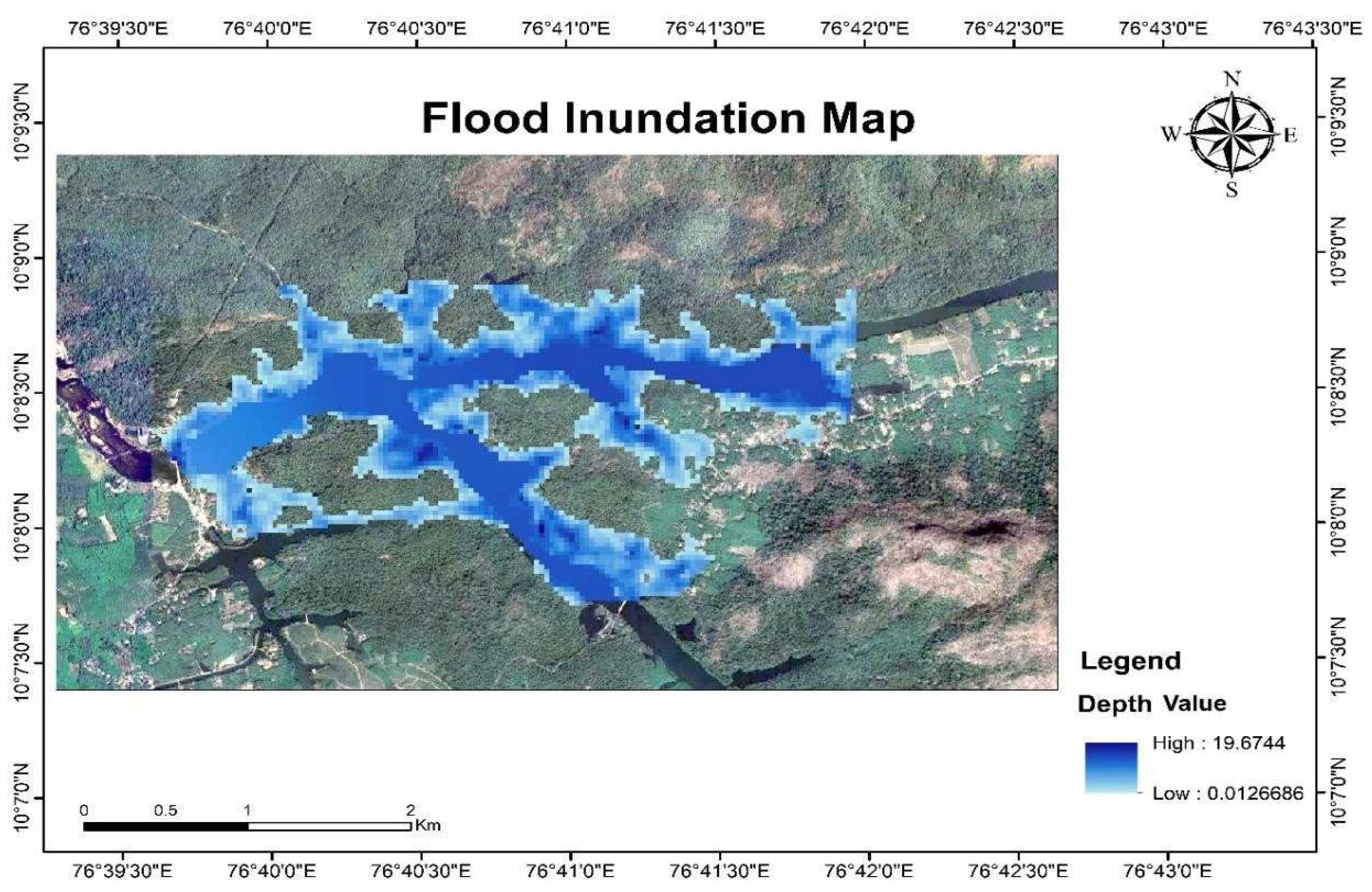
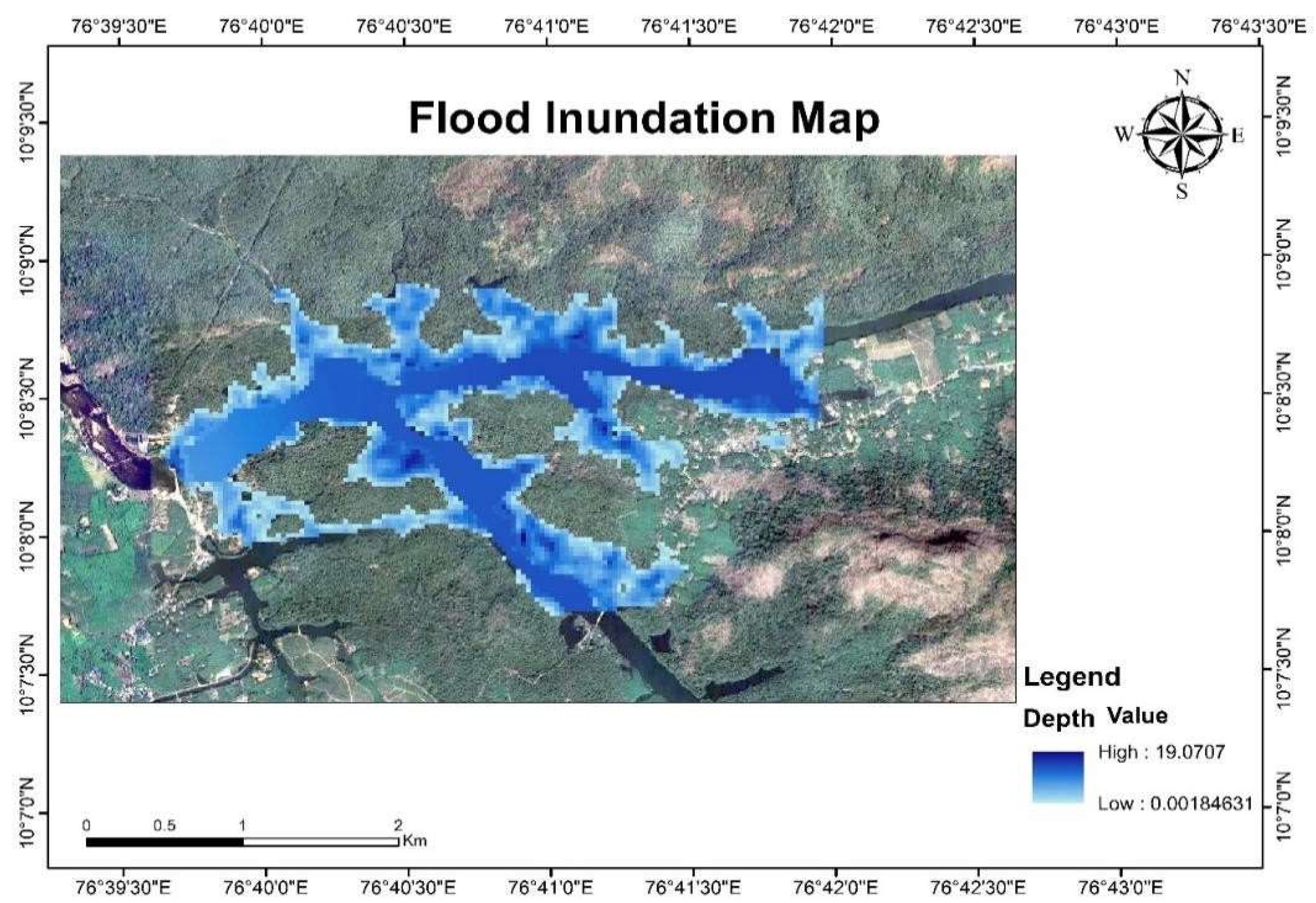
3.4. Flood Inundation Modeling and Mapping
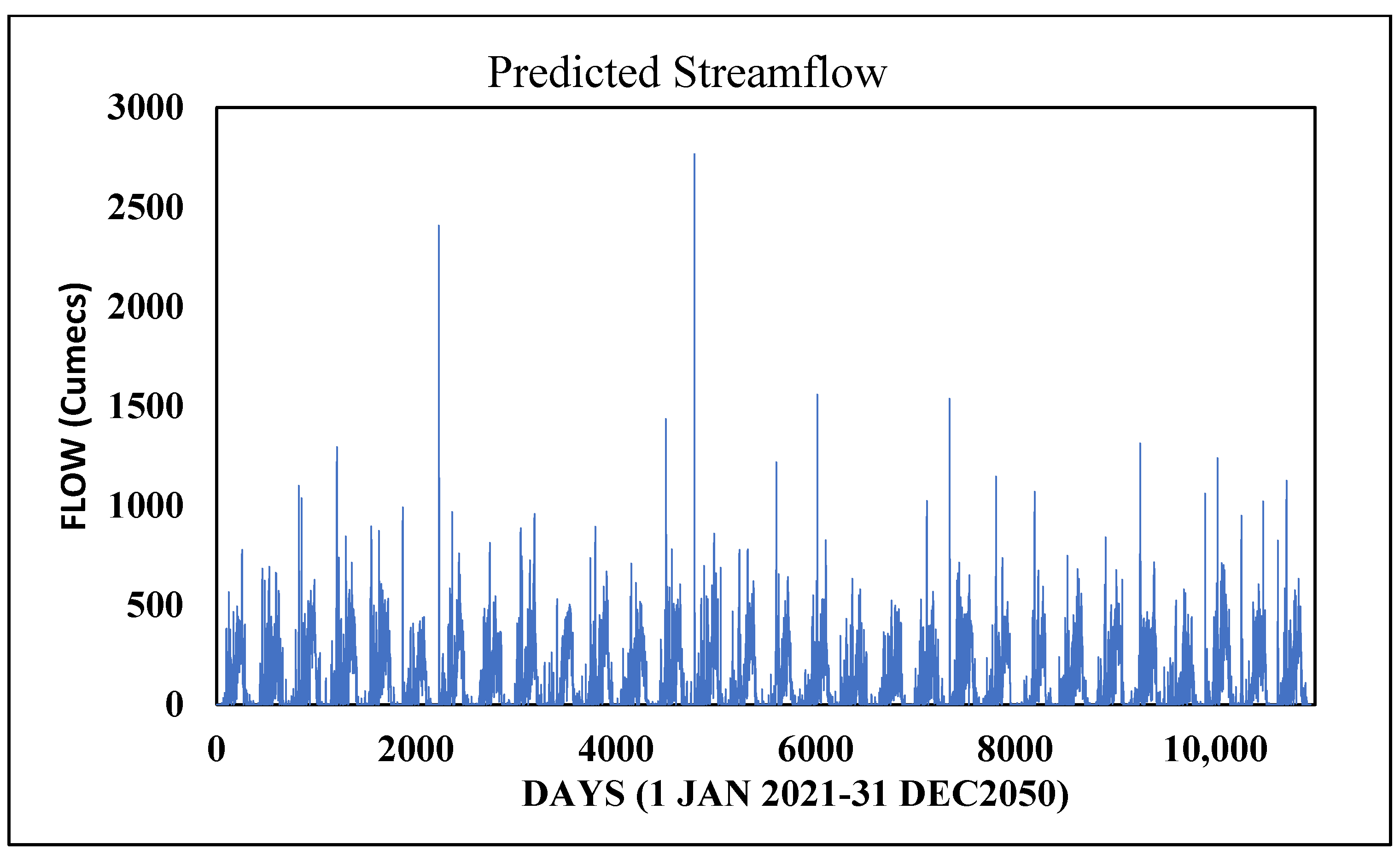
3.5. Future Flood Map Under Climate Change Scenarios
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.; Lei, H.; Shah, A.A.; Khan, I.; Muhammad, I. Climate change impact assessment, flood management, and mitigation strategies in Pakistan for sustainable future. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 29720–29731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashhar, M.; Keesara, V.R.; Sridhar, V. Flood inundation mapping of a river Stretch using machine learning algorithms in the Google Earth Engine environment. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2025, 18, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Crespo, P.; Aledo, A.; Melgarejo-Moreno, J.; Vallejos-Romero, A. Adapting social impact assessment to flood risk management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Modi, P.; Billah, M.M.; Valayamkunnath, P.; Goodall, J. Precipitation Extremes and Flood Frequency in a Changing Climate in Southeastern Virginia. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 55, 780–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Rao, G.; Keesara, V.R.; Sridhar, V.; Srinivasan, R.; Umamahesh, N.V.; Pratap, D. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Rainfall Extremes in the Flood-prone Nagavali and Vamsadhara Basins in Eastern India. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 29, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrike, T.; Keesara, V.R.; Sridhar, V. Analysis of the Causes of Extreme Precipitation in Major Cities of Peninsular India Using Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 33, 101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Wei, W.; Fang, G.; Duan, W. The increase in extreme precipitation and its proportion over global land. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, Y.; Tahara, R.; Meza, J. A methodology to estimate Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP) under climate change using a numerical weather model. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Garajeh, M.; Haji, F.; Tohidfar, M.; Sadeqi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Kariminejad, N. Spatiotemporal monitoring of climate change impacts on water resources using an integrated approach of remote sensing and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Bandala, E.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Anouzla, A.; Chew, K.W.; Aziz, F.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Nisa’ul Khoir, A. Implications of climate change on water quality and sanitation in climate hotspot locations: A case study in Indonesia. Water Supply 2024, 24, 517–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, F.; Sedighifar, Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Kisekka, I.; Li, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of the Impact of Land Use Dynamics and Climate Change Scenarios on Hydrological Processes. J. Environ. Inform. 2025, 45, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillard, U.; Sridhar, V.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; McDonald, K.C. Assessing snow melt dynamics with NASA Scatterometer (NSCAT) data and a hydrologic process model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Rao, G.; Keesara, V.R.; Sridhar, V.; Srinivasan, R.; Umamahesh, N.V.; Pratap, D. Real-Time Flood Forecasting Using an Integrated Hydrologic and Hydraulic Model for the Vamsadhara and Nagavali Basins, Eastern India, Natural Hazards. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 6011–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P.; Arunkumar, K.S. Sensitivity of digital elevation models: The scenario from two tropical mountain river basins of the Western Ghats, India. Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chymyrov, A. Comparison of different DEMs for hydrological studies in the mountainous areas. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhila, R.; Pramada, S.K. Suitability of different Digital Elevation Models in the estimation of LS factor and soil loss. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Prasannakumar, V. Comparison of basin morphometry derived from topographic maps, ASTER and SRTM DEMs: An example from Kerala, India. GeocartoInternational 2015, 30, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Jaksa, W.; Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Hubbard, K.; Jin, X. Evaluating bias corrected AMSR-E soil moisture using in-situ observations and model estimates. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.S.; Kanashiro, E.A.; Valverde, R.; Sridhar, V. Dynamic framework for intelligent control of river flooding—Case study. ASCE J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehurst, D.; Friedman, B.; Kochersberger, K.; Sridhar, V.; Weeks, J. Drone-based community assessment, planning, and disaster risk management for sustainable development. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.N.; Pramada, S.K. A hybrid artificial intelligence and semi-distributed model for runoff prediction. Water Supply 2022, 22, 6181–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, A.; Nisha, M.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Sridhar, V. A novel insight on input variable and time lag selection in daily streamflow forecasting using deep learning models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 179, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalegn, H.; Mulu, A. Mapping flood inundation areas using GIS and HEC-RAS model at Fetam River, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.A.; Ali, S.; Nazeer, A.; Khan, M.I.; Waqas, M.M.; Aslam, R.A.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Nadeem, M.; Saddique, N.; Muzammil, M.; et al. Flood Inundation Modeling by Integrating HEC–RAS and Satellite Imagery: A Case Study of the Indus River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namara, W.G.; Damisse, T.A.; Tufa, F.G. Application of HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS model for flood inundation mapping, the case of Awash bello flood plain, upper Awash River Basin, oromiya regional state, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Wasimi, S.A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Nasrin Baby, S. Recent trends and long-range forecasts of water resources of northeast Iraq and climate change adaptation measures. Water 2018, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Kwon, H.G.; Yang, D.S.; Kim, Y.S. Assessing environmental flows of coordinated operation of dams and weirs in the Geum River basin under climate change scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessamed, D.; Abderrazak, B. Coupling HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS in rainfall–runoff modeling and evaluating floodplain inundation maps in arid environments: Case study of Ain Sefra city, Ksour Mountain. SW of Algeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasimha Reddy, N.V.; Arunkumar, R. Development of flood inundation maps for the Chaliyar Basin, Kerala under climate change scenarios. Water Pract. Technol. 2023, 18, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, S.D.; Pramada, S.K. Spatiotemporal analysis of historic and future drought characteristics over a monsoon dominated humid region (Kerala) in India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu, S.; Pramada, S.K. Use of grace and in-situ data to characterize groundwater status along the coast of Kerala. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 132, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu, S.; Pramada, S.K.; Yadav, B.K. Seawater intrusion susceptibility and modeling: A case study of Kerala, India. Acta Geophys. 2024, 73, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, K.P.; Murty Bhallamudi, S.; Narasimhan, B.; Thomas, J.; Bindhu, V.M.; Vema, V.; Kurian, C. Role of dams on the floods of August 2018 in Periyar River Basin, Kerala. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitha, V.; Pramada, S.K.; Praseed, N.S.; Sridhar, V. Performance Evaluation of Numerical Weather Prediction Models in Forecasting Rainfall Events in Kerala, India. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.N.A.; Almuktar, S.; Scholz, M. Rainfall-runoff modeling using the hec-hms model for the al-adhaim river catchment, northern iraq. Hydrology 2021, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Joshi, N.; Baral, S.; Pradhan, S.N.; Mambepa, M.; Paudel, S.; Xia, C.; Gupta, R. Coupled 1D and 2D HEC-RAS floodplain modeling of pecos river in New Mexico. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2021: Planning a Resilient Future along America’s Freshwaters—Selected Papers from the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, virtually, 7–11 June 2021; pp. 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fang, F.; Pain, C.C.; Navon, I.M. Rapid spatio-temporal flood prediction and uncertainty quantification using a deep learning method. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish Kumar, K.; AnandRaj, P.; Sreelatha, K.; Bisht, D.S.; Sridhar, V. Monthly and seasonal drought characterization using GRACE-based groundwater drought index and its link to teleconnections across South Indian river basins. Climate 2021, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, S.; Morin, E.; Gerzi Rosenthal, A.; Metzger, A.; Barshai, C.; Weitzner, D.; Voloshin, D.; Kratzert, F.; Elidan, G.; Dror, G.; et al. Flood forecasting with machine learning models in an operational framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4013–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruq, A.; Marto, A.; Abdullah, S.S. Flood forecasting of Malaysia Kelantan River using support vector regression technique. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2021, 39, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Unit | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Observation Period. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | M | 30 m × 30 m | - | - | ISRO, USGS |
| Soil Data | - | - | - | 2018 | FAO |
| Land Use/Land Cover | km2 | 10 m | Yearly | 2015 | ESRI |
| Precipitation | mm | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily | 2014–2019 | IMD |
| Stream Flow | m3/s | Point | Daily | 2000–2019 | India WRIS |
| Precipitation (EC Earth 3) Future | kg m−2 s−1 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily | 2021–2050 | NCCS |
| Area (m2) | Perimeter (m) | Length of Reach(m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRTM | 4,489,682,074 | 526,202,920 | 225,049 |
| CartoDEM | 6,352,370,322 | 755,228,570 | 224,013 |
| R2 | ME | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRTM | 0.983 | 43.81 | 63.98 |
| CartoDEM | 0.983 | 134.11 | 141.86 |
| R | NSE | PBIAS | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.82 | 0.398 | 24.28 | 0.95 |
| Validation | 0.66 | 0.193 | 9.80 | 0.9 |
| Robust Scaling | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| R | NSE | PBIAS | |
| Calibration | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.224 |
| Validation | 0.88 | 0.64 | 23.590 |
| Normalization Scaling | |||
| R | NSE | PBIAS | |
| Calibration | 0.90 | 0.80 | 3.884 |
| Validation | 0.87 | 0.63 | 25.442 |
| Scenario | Upstream 1 (m3/s) | Upstream 2 (m3/s) | Downstream |
|---|---|---|---|
| Historical (2018) | 1243 | 1015 | Normal Depth (0.001 slope) |
| Future (SSP2–4.5) | 1325 | 1087 | Normal Depth (0.001 slope) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renu, S.; Reddy, B.S.N.; Santhosh, S.; Sreelekshmi; Lekshmi, V.; Pramada, S.K.; Sridhar, V. Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Periyar River Basin, Kerala, India. Climate 2025, 13, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13060129
Renu S, Reddy BSN, Santhosh S, Sreelekshmi, Lekshmi V, Pramada SK, Sridhar V. Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Periyar River Basin, Kerala, India. Climate. 2025; 13(6):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13060129
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenu, S., Beeram Satya Narayana Reddy, Sanjana Santhosh, Sreelekshmi, V. Lekshmi, S. K. Pramada, and Venkataramana Sridhar. 2025. "Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Periyar River Basin, Kerala, India" Climate 13, no. 6: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13060129
APA StyleRenu, S., Reddy, B. S. N., Santhosh, S., Sreelekshmi, Lekshmi, V., Pramada, S. K., & Sridhar, V. (2025). Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling for Flood Risk Assessment: A Case Study of Periyar River Basin, Kerala, India. Climate, 13(6), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13060129







