Recent Increasing Trend in Fire Activity over Southern India Inferred from Two Decades of MODIS Satellite Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. MODIS Active Fire Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
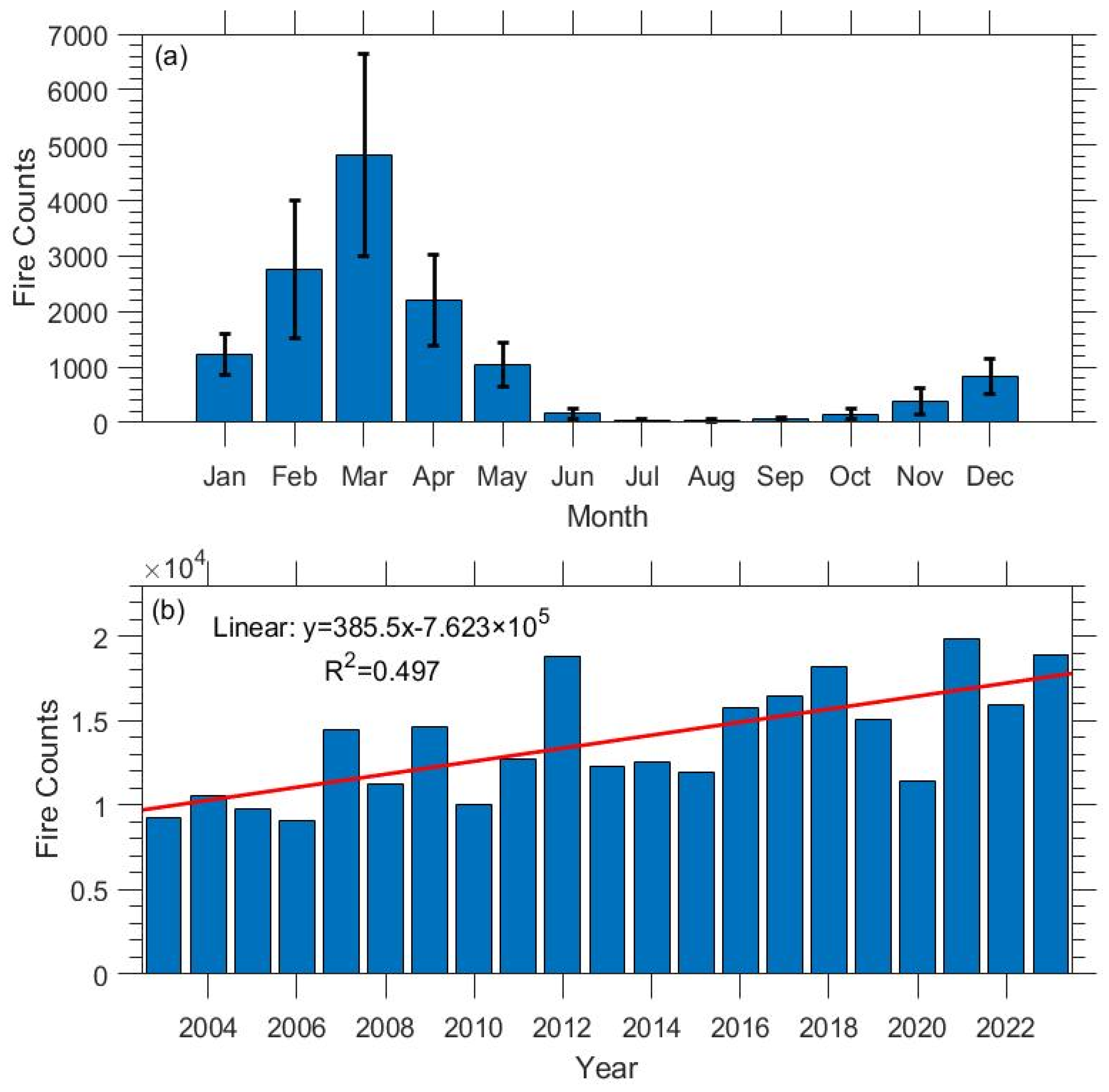
3.1. Long-Term Mean Pattern of Fire Activity over India
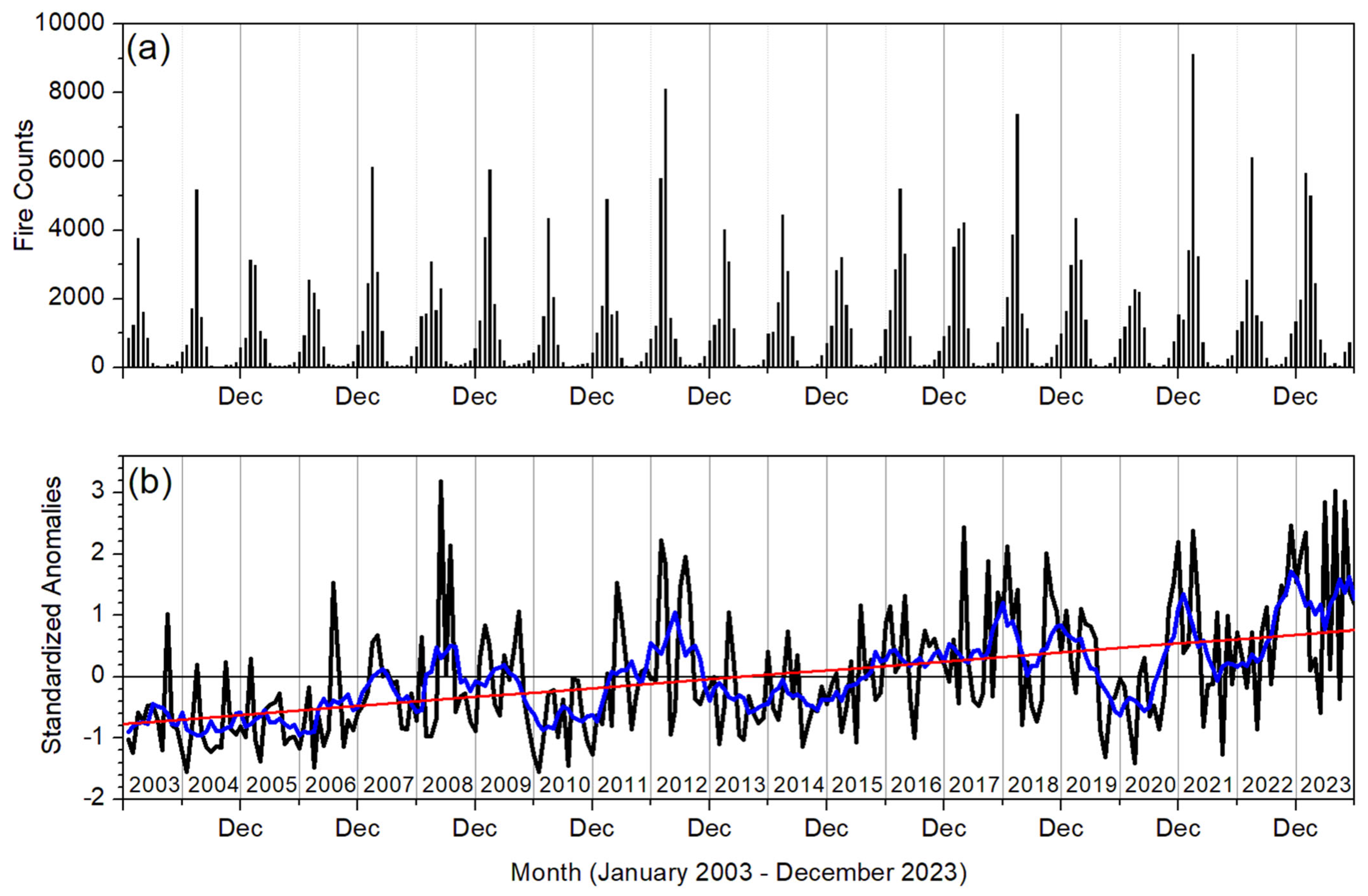
3.2. Fire Activity over Southern India
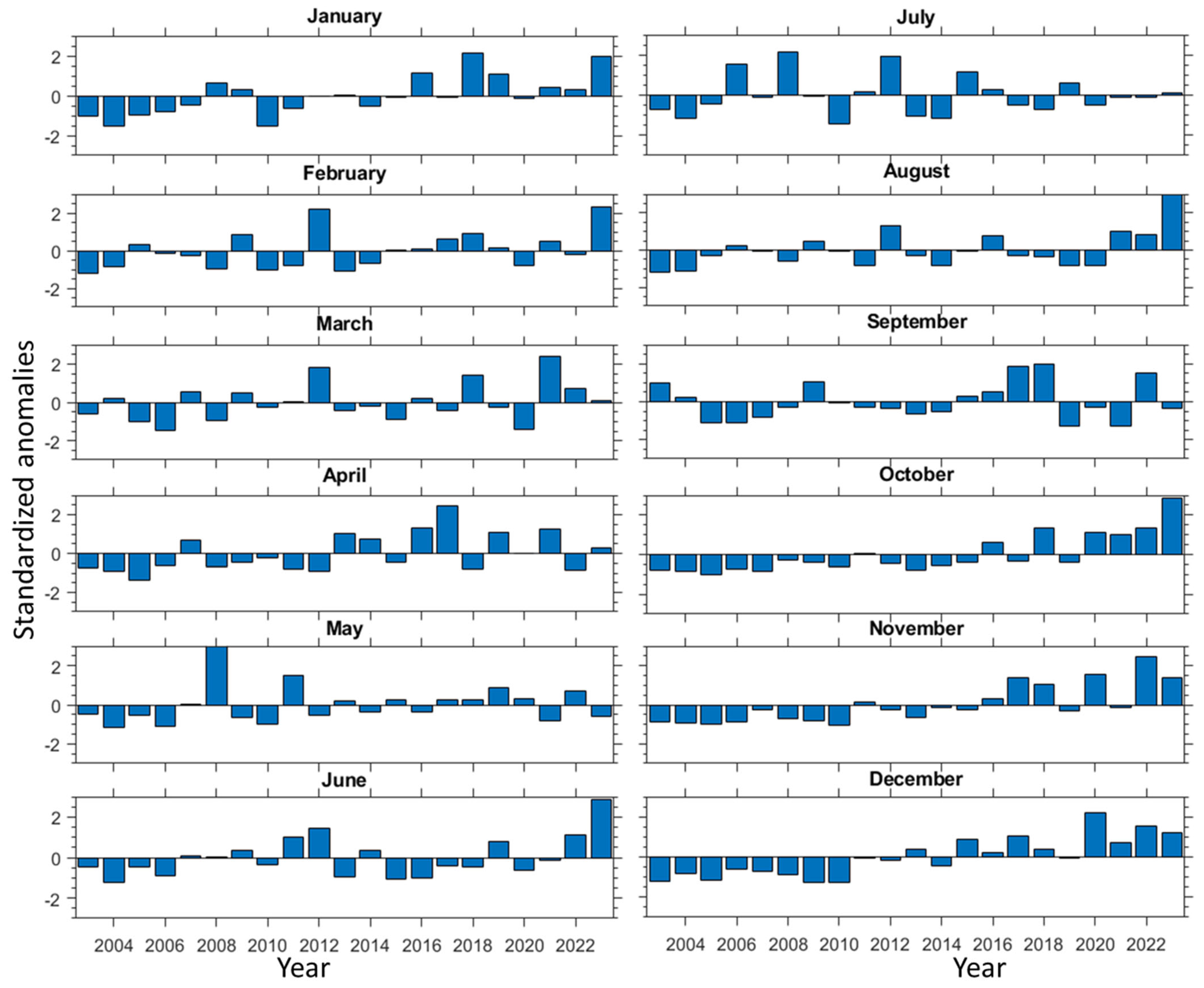
3.3. Long-Term Trends in Fire Activity over Southern India
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowman, D.M.J.S.; Balch, J.K.; Artaxo, P.; Bond, W.J.; Carlson, J.M.; Cochrane, M.A.; D’Antonio, C.M.; DeFries, R.S.; Doyle, J.C.; Harrison, S.P.; et al. Fire in the Earth System. Science 2009, 324, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, D.M.J.S.; Kolden, C.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Johnston, F.H.; van der Werf, G.R.; Flannigan, M. Vegetation fires in the Anthropocene. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Summary for Policy makers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Lasko, K.; Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Biswas, S.; Justice, C. Trends in Vegetation fires in South and Southeast Asian Countries. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forest Survey of India (FSI). Rapid Assessment of Fire Affected Forest Areas in the Country Based on MODIS-Detections Following a Sampling Approach; FSI Technical Information Series; Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change; Govt. of India: New Delhi, India, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 1–20. Available online: http://webline.co.in/fsi-result/technical-information-series-vol2-no2-2020.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Reddy, C.S.; Jha, C.S.; Diwakar, P.G.; Dadhwal, V.K. Nationwide classification of forest types of India using remote sensing and GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Roy, A.; Prasad, P.R. Forest Fire Risk Modeling in Uttarakhand Himalaya Using TERRA Satellite Datasets. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Eaturu, A.; Badarinath, K.V.S. Spatial Distribution of Forest Fires and Controlling Factors in Andhra Pradesh, India Using Spot Satellite Datasets. Envrion. Monit Assess. 2006, 123, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Csiszar, I.; Ellicott, E.; Giglio, L.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Vermote, E.; Justice, C. Hotspot analysis of vegetation fires and intensity in the Indian region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, L.K.; Sheel, V.; Pandey, K.; Yadav, R.; Saxena, P.; Gunthe, S. Regional biomass burning trends in India: Analysis of satellite fire data. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Naja, M.; Kumar, R.; Chandola, H.C. Seasonal, Interannual, and Long-Term Variabilities in Biomass Burning Activity over South Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4397–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Pandey, A.C. MODIS based forest fire hotspot analysis and its relationship with climatic variables. Spat. Inf. Res. 2020, 28, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Dar, J.A.; Malasiya, D.; Khare, P.K.; Dayanandan, S.; Khan, M.L. A MODIS-based spatiotemporal assessment of agricultural residue burning in Madhya Pradesh, India. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Saxena, P.; Sharma, S.; Sonwani, S. Investigation of forest fire activity changes over the Central India domain using satellite observations During 2001–2020. Geohealth 2021, 5, e2021GH000528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttippurath, J.; Singh, A.; Dash, S.; Mallick, N.; Clerbaux, C.; VanDamme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Coheur, P.-F.; Raj, S.; Abbhishek, K. Record high levels of atmospheric ammonia over India: Spatial and temporal analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, N.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, M.; Girach, I.; Ansari, T.U.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, N.; Pozzer, A.; Gunthe, S.S. On the wide spread enhancement in fine particulate matter across the Indo-Gangetic Plain towards winter. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Sonwani, S.; Srivastava, A.; Jain, M.; Srivastava, A.; Bharti, A.; Rangra, D.; Mongia, N.; Tejan, S.; Bhardwaj, S. Impact of Crop Residue Burning in Haryana on the Air Quality of Delhi, India. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, D.S.; Kant, Y.; Mitra, D.; Singh, A.; Chandola, H.C.; Sateesh, M.; Babu, S.S.; Chauhan, P. Impact of biomass burning on regional aerosol optical properties: A case study over northern India. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RavindraBabu, S.; Ou-Yang, C.-F.; Griffith, S.M.; Pani, S.K.; Kong, S.S.-K.; Lin, N.-H. Transport pathways of carbon monoxide from Indonesian fire pollution to a sub tropical high-altitude mountain site in the western North Pacific. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 4727–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Mor, S. Emissions of air pollutants from primary crop residue burning in India and the mitigation strategies for cleaner emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Eastham, S.D.; Liu, T.; Norford, L.K.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air quality impacts of crop residue burning in India and mitigation alternatives. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Humber, M.L.; Justice, C.O. The Collection 6 MODIS burned area mapping algorithm and product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, C.A.; Thirumalai, K.; Kearney, K.A.; Delgado, J.M.; Schwanghart, W.; Wolfenbarger, N.S.; Thyng, K.M.; Gwyther, D.E.; Gardner, A.S.; Blankenship, D.D. The Climate Data Toolbox for MATLAB. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 3774–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.; Rana, D.; Khan, M.L. Forest fires in the Western Himalayan region of India: Areview. Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 48, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Singh, R.P.; Chauhan, A. Crop residue burning in Northern India: Increasing threat to Greater India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6920–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.; Ayantika, D.C.; Girach, I.; Chakrabarty, C. Intense biomass burning over northern India and its impact on air quality, chemistry and climate. In Extremes in Atmospheric Processes and Phenomenon: Assessment, Impacts and Mitigation; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 169–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, T.; Malasiya, D.; Rajpoot, R.; Verma, S.; Dar, J.A.; Dayanandan, A.; Raha, D.; Lone, P.; Pandey, P.; Khare, P.K.; et al. Impact of Forest Fire Frequency on Tree Diversity and Species Regeneration in Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest of Panna Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh, India. J. Sustain. For. 2020, 40, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgohain, A.; Gogoi, M.; Barman, N.; Kundu, A.; Banik, T.; Kundu, S.S.; Aggarwal, S.P. Impact of Biomass Burning on Black Carbon and NO2 over North Eastern Region of India using multi-satellite observations. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2023, 51, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Hot spot and Trend Analysis of Forest Fires and its Relation to Climatic in the Western Himalayas. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 3529–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Habib, G.; Kadamba, D.; Shrivastava, M.; Leon, J.F.; Crouzille, B.; Streets, D. Emissions from open biomass burning in India: Integrating the inventory approach with high-resolution Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro radiometer(MODIS) active-fire and land cover data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.; Suresh, K.P.; Naveesh, Y.B.; Archana, C.A.; Hemadri, D.; Patil, S.S.; Chethan, A.J. Forest fire dynamics in India (2005–2022):Unveiling climatic Impacts, spatial patterns, and interface with anthrax incidence. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India Meteorological Department (IMD). Statement on Climate of India During 2020; Press Release; Government of India, Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES): New Delhi, India, 2021; pp. 1–5.
- Earl, N.; Simmonds, I. Spatial and temporal variability and trends in 2001–2016 global fire activity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2524–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

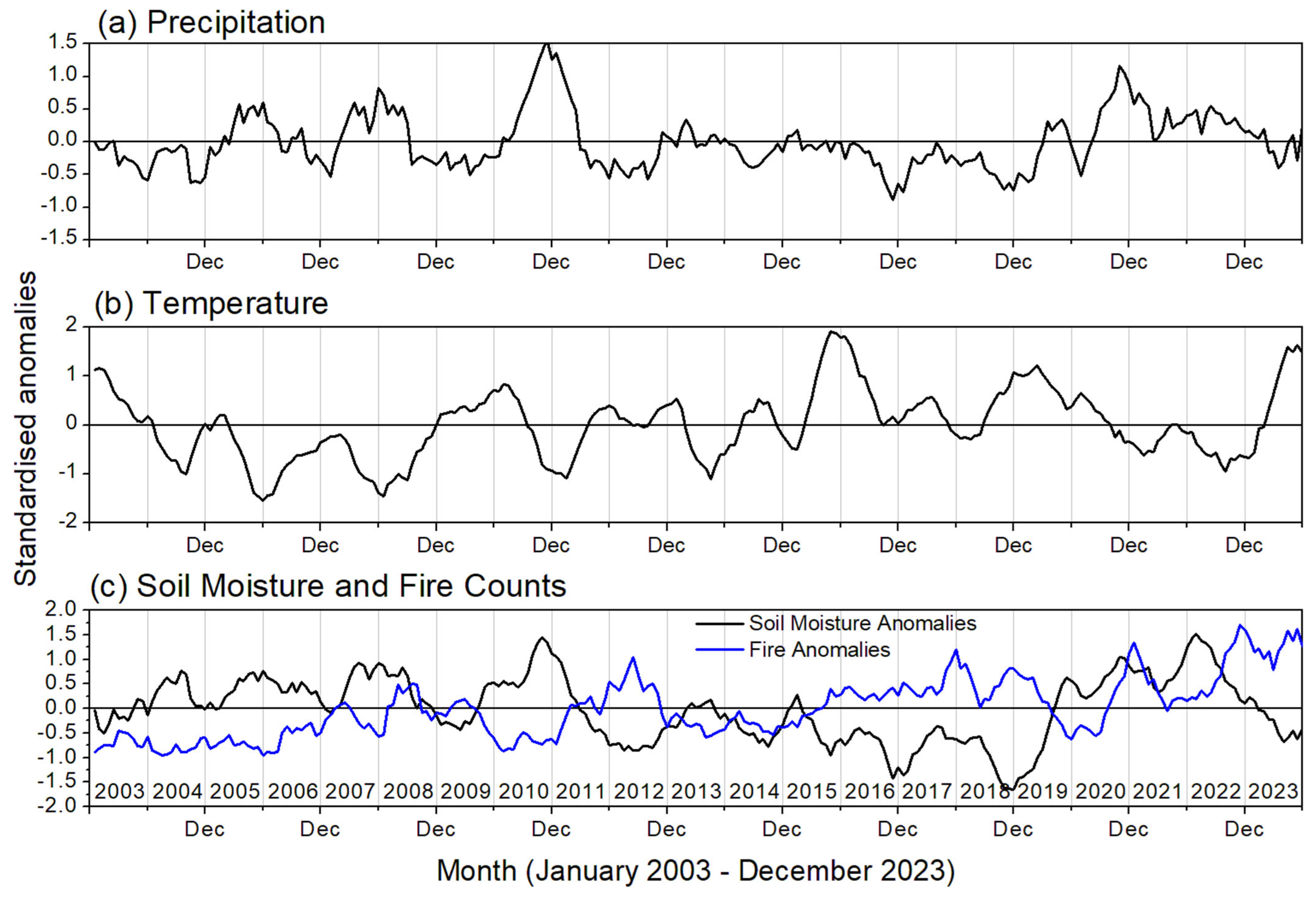
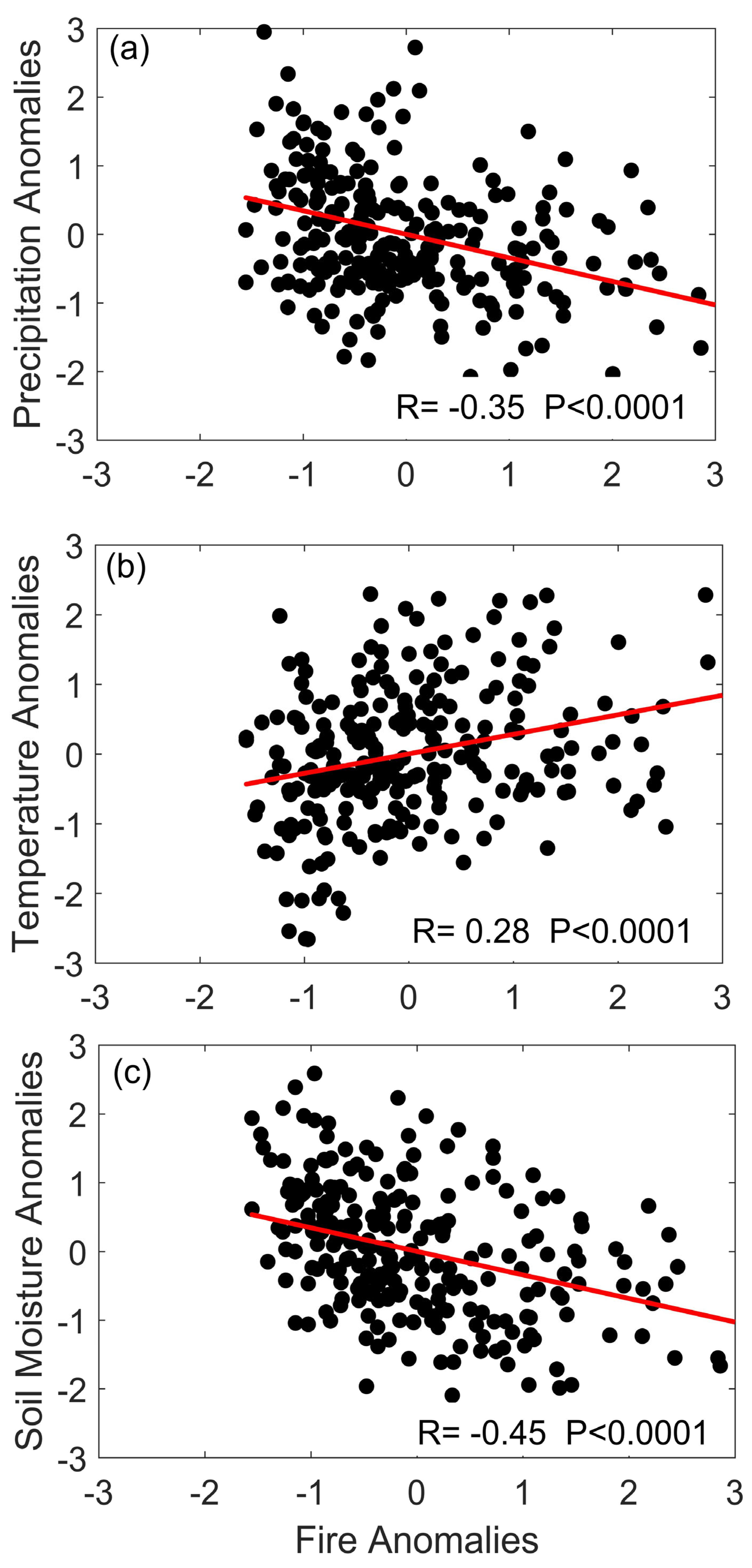
| Month | Soil Moisture | Temperature | Precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | −0.35 | −0.13 | −0.09 |
| February | −0.47 | −0.09 | −0.31 |
| March | −0.37 | 0.12 | −0.25 |
| April | −0.72 | 0.49 | −0.65 |
| May | −0.42 | 0.16 | −0.53 |
| June | −0.67 | 0.63 | −0.48 |
| July | −0.44 | 0.37 | −0.36 |
| August | −0.46 | 0.47 | −0.49 |
| September | −0.56 | 0.52 | −0.57 |
| October | −0.43 | 0.34 | −0.49 |
| November | −0.46 | 0.19 | −0.13 |
| December | −0.07 | 0.34 | 0.18 |
| Month | Trend (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| January | 3.41 | <0.001 |
| February | 3.04 | 0.05 |
| March | 1.94 | 0.15 |
| April | 2.75 | 0.03 |
| May | 0.83 | 0.55 |
| June | 3.66 | 0.06 |
| July | −0.07 | 0.95 |
| August | 3.48 | 0.03 |
| September | 0.83 | 0.55 |
| October | 8.25 | <0.001 |
| November | 8.08 | <0.001 |
| December | 5.3 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.V.; Babu, S.R.; Raman, M.R.; Sunilkumar, K.; Rao, N.N.; Ravisankar, M. Recent Increasing Trend in Fire Activity over Southern India Inferred from Two Decades of MODIS Satellite Measurements. Climate 2025, 13, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13050103
Kumar SV, Babu SR, Raman MR, Sunilkumar K, Rao NN, Ravisankar M. Recent Increasing Trend in Fire Activity over Southern India Inferred from Two Decades of MODIS Satellite Measurements. Climate. 2025; 13(5):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13050103
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, S. Vijaya, S. Ravindra Babu, M. Roja Raman, K. Sunilkumar, N. Narasimha Rao, and M. Ravisankar. 2025. "Recent Increasing Trend in Fire Activity over Southern India Inferred from Two Decades of MODIS Satellite Measurements" Climate 13, no. 5: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13050103
APA StyleKumar, S. V., Babu, S. R., Raman, M. R., Sunilkumar, K., Rao, N. N., & Ravisankar, M. (2025). Recent Increasing Trend in Fire Activity over Southern India Inferred from Two Decades of MODIS Satellite Measurements. Climate, 13(5), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13050103






