Abstract
This study examines adaptation strategies to mitigate the risks posed by Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) in the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) region, encompassing Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Afghanistan. GLOFs occur when water is suddenly released from glacial lakes and they present significant threats to communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems in high-altitude regions, particularly as climate change intensifies their frequencies and severity. While there are many studies on the changes in glacial lakes, studies on adaptation to GLOF risks are scant. Also, these studies tend to focus on case-specific scenarios, leaving a gap in comprehensive, region-wide analyses. This review article aims to fill that gap by synthesizing the adaptation strategies adopted across the HKH region. We conducted a literature review following several inclusion and exclusion criteria and reviewed 23 scholarly sources on GLOF adaptation. We qualitatively synthesized the data and categorized the adaptation strategies into two main types: structural and non-structural. Structural measures include engineering solutions such as lake-level control, channel modifications, and flood defense infrastructure, designed to reduce the physical damage caused by GLOFs. Non-structural measures include community-based practices, economic diversification, awareness programs, and improvements in institutional governance, addressing social and economic vulnerabilities. We found that Afghanistan remains underrepresented in GLOF-related studies, with only one article that specifically focuses on GLOFs, while Nepal and Pakistan receive greater attention in research. The findings underscore the need for a holistic, context-specific approach that integrates both structural and non-structural measures to enhance resilience across the HKH region. Policy-makers should prioritize the development of sustainable mechanisms to support long-term adaptation efforts, foster cross-border collaborations for data sharing and coordinated risk management, and ensure that adaptation strategies are inclusive of vulnerable communities. Practitioners should focus on strengthening early warning systems, expanding community-based adaptation initiatives, and integrating traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches to enhance local resilience. By adopting a collaborative and regionally coordinated approach, stakeholders can improve GLOF risk preparedness, mitigate socioeconomic impacts, and build long-term resilience in South Asia’s high-altitude regions.
1. Introduction
With the rising temperature, the melting of glaciers is accelerated in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan (HKH) region. This melting of glaciers contributes to the formation of glacial lakes and increases the risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) [1,2,3]. Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) occur when the natural moraine dams of glacial lakes fail to contain the immense volume of water they hold. Events like earthquakes, cloudbursts, avalanches, and slope failures can trigger GLOFs by breaching these dams [4,5]. These events can lead to the sudden discharge of massive volumes of water and debris, causing catastrophic flooding downstream [6]. By releasing substantial volumes of water in a short timeframe and causing flash floods and debris flows with high peak discharges, GLOFs pose a grave threat to communities residing within and downstream of the HKH [7,8,9]. Over the past century, the HKH region has witnessed a 0.10 °C increase in mean temperatures per decade, with projections indicating a 1–2 °C temperature rise by 2050 [10]. Currently, across the HKH region, 24 glacial lakes in Bhutan, 20 in Nepal, 16 in India, and 52 in Pakistan are identified as potentially dangerous for GLOFs [11]. More than five million people are exposed to GLOFs in these countries [8]. Chen et al. (2021) found that between 2008 and 2017, the area coverage of glacial lakes increased by 6.90%, and on average, 306 new glacial lakes were formed every year in High Mountain Asia, including the HKH region [12].
The impacts of GLOFs in the HKH region are severe. GLOFs damage infrastructures and economic prospects of geographically remote communities as well as create public health crises. Historically, multiple devastating GLOFs have occurred across the region. In Nepal, the 1985 Dig Tsho GLOF caused extensive infrastructure damage, particularly destroying the Namche Small Hydel Project [13]. In Bhutan, the 1994 Luggye Tsho GLOF resulted in 21 fatalities and the economic losses were estimated at USD 7 million [14]. Similarly, in India, the 1926 GLOF event in Jammu and Kashmir caused massive flooding, destroying villages and farmlands [15]. Bhutan also experienced GLOFs, a 1994 event that resulted in millions of US dollar [16]. In the HKH region, Pakistan also faced severe GLOF events, such as the 1929 Shimshal GLOF, which led to widespread destruction in the Hunza Valley [17]. Afghanistan, although less studied in the context of GLOFs, experienced the 1953 Wakhan Corridor GLOF, which resulted in severe damage to agricultural land and displacement of communities [18]. Since 2000, several catastrophic GLOF events further underscored the region’s vulnerability. In June 2013, a GLOF event in the Kedarnath region of Uttarakhand, India, triggered devastating floods that claimed over 6000 lives and caused approximately USD 1 billion in damages [19]. More recently, in July 2016, a GLOF originating in Tibet led to severe flooding in Nepal’s Bhotekoshi River, causing extensive damage to hydropower infrastructure and resulting in prolonged power outages [20]. In Bhutan, the Thorthormi Lake has been closely monitored due to its increasing risk of a GLOF event, and mitigation efforts have been ongoing since 2008 to prevent an outburst [21]. Pakistan experienced a major GLOF event in July 2018, when the Ishkoman Valley in Gilgit-Baltistan was hit by glacial flooding, displacing over 40 families and submerging agricultural land [22]. The 2010 GLOF in Pakistan’s Hunza Valley led to substantial economic losses as it blocked the vital Karakoram Highway (13). In Afghanistan, recent climate change assessments have warned of an increasing GLOF risk in the Wakhan region, where glacial lakes such as the Bozai Gumbaz Lake have been expanding rapidly [23]. Most of these GLOF events are associated with numerous deaths and displacements. These events emphasize the increasing threats posed by GLOFs in the HKH region and the need for robust adaptation strategies to protect vulnerable communities and infrastructure. These examples underscore the significance of adaptation measures that are vital to addressing the risks posed by these glacial lakes in the face of ongoing climate change. The accelerated retreat of glaciers and the increasing formation of these lakes emphasize the pressing need for proactive mitigation measures and adaptation strategies to safeguard the communities and ecosystems in this GLOF vulnerable region [24,25,26,27].
Across the HKH region, various adaptation strategies have been undertaken to reduce the vulnerability of GLOFs including the establishment of early warning systems [28], emergency preparedness initiatives [29], household and community-level adaptations [30], resilient infrastructure development [31], and land-use planning [32]. To date, several studies have examined specific adaptation measures undertaken to deal with GLOF vulnerability. However, the majority of these studies used case study approaches focused on a particular region. For instance, Ref. [33] analyzed the indigenous adaptations in the Hunza Valley in Pakistan, while Ref. [34] examined the early warning system for the Dudh-Koshi basin in Nepal (see also Refs. [35,36,37]. With mostly case- or location-specific studies, there remains a critical gap in synthesizing the adaptation actions undertaken across the HKH region to deal with GLOF vulnerability. Due to the fragmented nature of the existing studies, it is essential to examine the diverse range of measures implemented across the five HKH countries (i.e., Afghanistan, Bhutan, Nepal, India, and Pakistan) to address their shared vulnerabilities and challenges effectively. In this review paper, we aim to map out the existing GLOF adaptation measures undertaken in the HKH region, highlighting the best practices, and identifying the shortcomings to enhance resilience and mitigate the impacts of GLOFs in the HKH region. The findings of this review would provide an overview of adaptation approaches and offer practical insights for practitioners and policy-makers about successful adaptations. Furthermore, the outcome of our findings will serve to guide and focus future research efforts by addressing knowledge gaps or facilitating more in-depth reviews of narrower selections of studies.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) region, covering parts of Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, and Bhutan, is home to numerous glaciers that pose significant risks of Glacial Lake Outburst Flooding (GLOF). This study focuses on these five countries, each facing similar GLOF hazards. In Afghanistan and Pakistan, the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges are particularly vulnerable, while India’s eastern Himalayan regions, Nepal’s Sagarmatha and Annapurna ranges, and Bhutan’s high-altitude areas are also experiencing GLOF threats. The research examines the adaptation strategies implemented in these countries to mitigate the risks, highlighting efforts from governments, local communities, and international organizations [37]. Figure 1 shows the GLOF-prone HKH region in South Asia.
Figure 1.
The GLOF-prone HKH region in South Asia.
2.2. Methods
To examine Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) adaptation strategies in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region of South Asia, we conducted a rigorous search on the Google Scholar platform. We identified articles using a combination of keywords including ‘glacial lake outburst flooding’, GLOF’, adaptation’, risk’, ‘risk reduction’, ‘vulnerability’, ‘glaciers’, ‘floods’, ‘mountains’ as well as the name of the countries. Additionally, we collected reports from environmental and development organizations (e.g., ICIMOD, UNDP) and national disaster management agencies. During the review process, to identify the articles and reports that include adaptation to GLOF, we not only emphasized adaptation strategies, but also included articles and documents that focus on GLOF risk reduction approaches.
Our review process involves three steps (see Table 1). First, we selected a subset of articles by evaluating titles, keywords, and abstracts. We conducted this search in April 2024. In this process, we removed the articles and other materials that are not related to GLOFs or our study area. We selected 61 articles for full-text review. In the next stage, we removed articles that addressed only the physical dimension of GLOFs (e.g., areal changes in glacial lakes) but did not discuss adaptation or risk reduction approaches elaborately. It is important to note that many articles may not focus on GLOF adaptation or risk reduction approaches directly; rather, they briefly mention them as a part of the discussion. We removed such articles or reports at this stage as these studies do not directly contribute to understanding how communities manage and mitigate GLOF risks. At the end of the second stage, we identified 28 articles, 5 reports, 2 symposium reports, and 1 doctoral dissertation for full-text review. In the critical appraisal stage, we conducted a full-text review and removed the articles or reports that did not provide sufficient details of GLOF adaptation or risk reduction strategies. This step generates 17 articles, 4 reports, 1 symposium report, and 1 dissertation (total = 23) for final review. We reviewed these materials in-depth and qualitatively synthesized the key adaptation or risk reduction approaches.

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
3. Results
We found that most of the studies on GLOF in South Asia addressed the biophysical dimensions of GLOF hazard, such as glacial lake-level monitoring, changes in glacial lake extent, and movements of glaciers. Limited emphasis has been given to adaptation to GLOF hazards in the HKH region. Out of the 23 scholarly materials we reviewed, 1 focused on Bhutan, 6 on Nepal, 5 on India, 7 on Pakistan, and 1 on Afghanistan, and there were three articles and reports that focused on more than one country (Figure 2a). Despite having communities exposed to GLOF hazards, studies from Afghanistan are scant, perhaps due to geographic remoteness and geopolitical instabilities. These scholarly materials were published in different years since 2002, but we observed that the number increased in recent years, particularly since 2020 (Figure 2b).
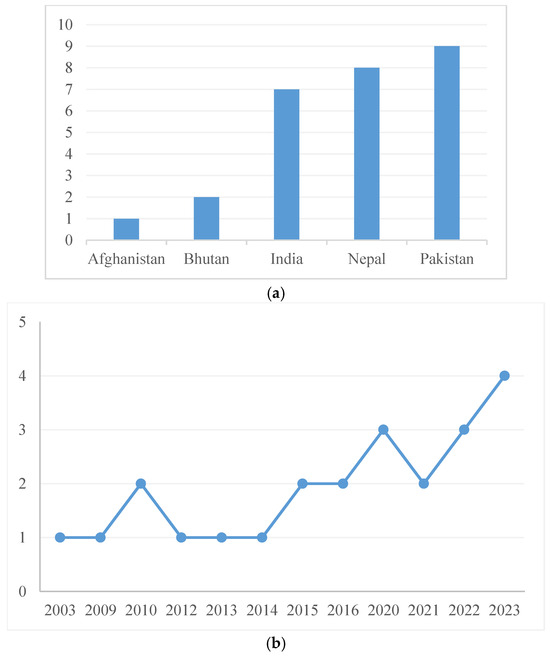
Figure 2.
(a) Country-wise number of GLOF adaptation studies; (b) year-wise number of GLOF adaptation studies.
Based on our review, we can categorize the adaptation strategies to GLOFs into two broad categories: structural and non-structural adaptations, each offering a distinct approach to addressing the risk. Structural interventions take a proactive stance by harnessing technology and engineering solutions, including sophisticated monitoring systems, controlled breaches of moraine dams, construction of outlet control structures, and even the creation of tunnels through moraine barriers. We further classify these structural adaptation actions into two types: infrastructure-based and technology-based adaptations. However, these measures, while effective, present resource and technical challenges, especially in remote and inaccessible areas. On the other hand, non-structural measures, such as land-use planning, community education, ecosystem-based approaches, and livelihood adaptation strategies, complement the structural efforts and enhance community resilience. Based on the types of adaptation actions, we categorize these non-structural adaptations into three types. Table 2 summarizes our findings of adaptation strategies under different categories. In the following sections, we will detail the structural and non-structural adaptation strategies.

Table 2.
GLOF adaptation strategies in the HKH region.
3.1. Structural Adaptations to GLOFs
3.1.1. Channel Modification and Flood Defense
Channel modification involves draining or controlled lowering of glacial lakes through the excavation of artificial channels in natural dams and the construction of outlet channels. In this process, the reinforcement of dams with concrete is implemented to bolster stability, emphasizing the need to avert potential disasters [38]. Channel modification plays a pivotal role in mitigating GLOF risks in the HKH region. For instance, in the upper Hunza region of Pakistan, channel excavation and spillway development were performed to mitigate GLOF risks [37]. Similarly, in Bhutan, the controlled opening of the moraine dam in Raphstreng Tsho Lake was carried out by manually widening the outlet channel [37]. More widescale-controlled lowering of glacial lakes was observed in the Tsho Rolpa and Imja lakes in Nepal [39,40].
In addition to channel modifications, flood defense measures are crucial to protect GLOF-vulnerable communities. Flood defense measures are often community-driven, with the construction of floodwalls along the stream banks. This proactive measure is essential for minimizing flood risks and reducing the potential impact on life and property in the region [32]. For instance, in Hundur Valley in Pakistan, after the 2010 flood, a local women’s organization raised money to build a protection wall [32]. Another vital aspect of flood defense includes the preparation of check dams in areas dependent on glacier meltwater. These check dams act as filters to ensure clean water flow for crop irrigation. In Shishper, Pakistan, for instance, community members have established check dams to filter sediments from the increased streamflow during the summer season, ensuring clean water for crop irrigation [32]. However, financial constraints hinder farmers from acquiring necessary irrigation equipment, negating limiting the significance of this action. This example underscores the critical role of check dams as adaptation strategies in regions vulnerable to climate change, emphasizing the need for financial support to bolster agricultural resilience in such areas.
3.1.2. Lake-Level Control
Controlling or reducing the lake level is a key adaptation strategy in the HKH region. This can be achieved through various methods such as controlled and safe breaching, excavation of channels, siphon systems, artificial spillways, or drainage projects [7,28,37]. Controlled breaching of moraine dams represents a key strategy employed in India and Pakistan to mitigate the risks of GLOFs. In the Indian Himalayas, controlled breaching of moraine-dammed lakes is used to prevent GLOFs [37]. This measure involves creating a controlled opening in the dam to gradually release water, reducing the risk of an unplanned breach. This measure has lowered the risk of floods and protected downstream areas. Similarly, in Pakistan’s Karakoram region, managing GLOF risks involves strategies like controlled drainage and the construction of spillways. An example of this can be found in the Bagrot Valley, where controlled drainage techniques have been applied to manage water levels in glacial lakes, effectively reducing the risk of catastrophic floods [7]. These proactive measures are crucial for protecting downstream communities from potential hazards associated with glacial lakes.
Safe breaching of potentially hazardous glacial lakes has also been observed in Nepal. Here, this strategy involves the construction of canals and earthen dams downstream to effectively manage water resources and mitigate the hazards associated with GLOFs [28]. As an example, the water level of Tsho Rolpa Lake was successfully reduced through the construction of a spillway, demonstrating the feasibility and effectiveness of such measures in managing GLOF risks in the Nepal part of the HKH region [41].
3.1.3. The Early Warning System
An early GLOF warning system detects and alerts communities about potential GLOFs, integrating meteorological data and community engagement for timely evacuation and mitigation, reducing the impact of flooding [42]. In the HKH region, the establishment of Early Warning Systems (EWS) is imperative to managing GLOF risks [43]. In [44], EWS continuously monitors water level changes, swiftly detects GLOF events, and issues timely warnings to downstream communities. This ensures that the community and authorities are alerted in advance, facilitating prompt and effective actions to mitigate potential impacts [37]. Recently, in May 2024, India initiated an early warning system for 188 critical glacial lakes in its territory [45].
In the HKH region, Nepal made a significant stride in establishing EWS for GLOFs [36]. Nepal employed EWS as a part of the risk reduction activities for GLOFs. Nepal used hydrodynamic modeling and simulation tools in predicting and planning for the extent and impact of GLOFs. Emphasis is placed on developing and implementing effective EWS, providing timely alerts to downstream communities, and facilitating protective measures and evacuations during imminent GLOFs. Nepal further advanced its commitment to EWS by focusing on near real-time monitoring of glacial lakes [28]. This involves leveraging remote sensing, microwave technology, geo-ICT tools, and web-based platforms to monitor changes, enabling timely risk assessments [29]. In the future, other factors will be involved, such as changes in the lake, movement of the moraine dam, and earthquakes. In EWS, water-level thresholds are particularly important weather thresholds acting as additional alerts. The system automatically sends a warning when any threshold is exceeded, allowing observers to check the situation and inform authorities. These advancements significantly contribute to planning and preparedness for potential GLOFs in the region.
In Bhutan, efforts have been made to enhance adaptive capacity and resilience by implementing automated EWS [46]. Wireless sets and satellite phones are used to regularly monitor and report lake water levels, ensuring that timely warnings can be issued to downstream communities. Several gauges have been installed along the main river and lakes, with monitoring conducted at various stations. The frequency of monitoring depends on the station’s proximity to the base camp. The station maintains consistent communication with other wireless stations downstream along the Puna Tsang Chu, including in the villages and towns of Punakha, Wangduephodrang, Sunkosh, Khalikhola, and Thimphu [28]. Similarly, in Pakistan, UNDP started installing EWS in 24 GLOF vulnerable valleys in 2023 [45].
3.2. Non-Structural Adaptations to GLOFs
3.2.1. Agriculture and Livelihood Adaptations
Food Security and Livestock
In some GLOF vulnerable areas in the HKH region, communities focus on food security by preserving food that can help them in post-disaster recovery. For instance, in GLOF-vulnerable regions of Pakistan, farmers employ traditional methods of sun-drying to preserve fruits and vegetables, with a particular emphasis on apricots—a prominent crop in the Hunza Valley [32]. This centuries-old practice involves slicing ripe apricots and drying them on wooden slabs in the sun for about a week. The dried apricots serve both household and commercial purposes. Notably, rising temperatures over the last two decades have reduced the drying time for apricots from over two weeks to just one week. Apples are also sun-dried to produce a sweet and refreshing powder mixed with water for drinking and medicinal purposes during hot summer days. These traditional preservation methods play a crucial role in the local agricultural practices of the region, contributing to food security and preserving indigenous farming community practices.
Furthermore, to ensure food security under impending threats of GLOFs as well as climate change impacts, local farmers in India and Pakistan are implementing adaptive crop management strategies, as highlighted in a field study conducted in the upper Indus basin [47]. These strategies involve dynamic adjustments to the timing of crop sowing, aligning planting with evolving climate patterns. Additionally, farmers are adopting improved seed varieties chosen for their resilience to water stress and shorter maturity periods.
Also, both in India and Pakistan, GLOF-vulnerable communities are adapting to changing climate conditions by introducing improved breeds of livestock as part of their livelihood strategy to compensate for declining crop and forage productivity. This adaptation, as outlined by [47], addresses the challenges posed by climate change on traditional agricultural practices. However, it is essential to note that the introducing improved livestock breeds may lead to increased water and fodder requirements, presenting additional considerations in the pursuit of sustainable and resilient agricultural systems.
Economic Diversification
Economic diversification helps GLOF-vulnerable communities by reducing their reliance on climate-sensitive sectors which can be severely impacted by such disasters. Economic diversification can reduce post-disaster economic shocks and accelerate recovery. In pursuing economic diversification in the HKH region, India and Pakistan are adopting distinct approaches to enhance socioeconomic resilience and climate adaptation. Nevertheless, the focus remains on agricultural products.
In Pakistan, there is a concerted effort to develop value chains for yak and sea buckthorn, as highlighted by [48] in their study on mountain product value chain development. This strategic initiative aims to establish sustainable economic pathways and boost the adaptive capacity of local communities confronting climate challenges in mountainous regions. Sea buckthorn cultivation goes beyond ecological benefits. The shrub’s berries are rich in vitamins and antioxidants, contributing to medicinal uses. The extracted oil is utilized for its anti-inflammatory properties and skincare benefits. Additionally, sea buckthorn berries are processed into food items like juices and jams, diversifying the local culinary industry. Interestingly, the durable wood of sea buckthorn finds application in jewelry production, showcasing the versatility of this cultivation beyond traditional practices. Yak husbandry, a vital component of this initiative in Pakistan, involves the careful breeding and management of yaks, robust animals well adapted to the challenging mountain environment. Yaks serve as sources of milk, meat, fur, and transportation, contributing significantly to the livelihoods of local communities. This sustainable practice ensures the availability of essential resources and preserves traditional ways of life.
Conversely, in India, economic diversification focuses on value addition to agricultural products in flood-affected areas. Despite local awareness of the advantages of value addition, challenges such as limited marketing facilities and resources hinder the complete harnessing of farmers’ initiatives [37]. The evolving role of markets in livelihood improvement is acknowledged, but issues like poor market access, inadequate pricing for products, and middlemen exploiting profits remain significant challenges [49]. This underscores the need for comprehensive strategies addressing economic diversification and market challenges in the context of climate adaptation for India.
3.2.2. Community-Based and Social Adaptations
Indigenous Knowledge and Cultural Practices
Local knowledge and cultural practices play a significant role in adaptation strategies to address the challenges posed by GLOFs in the HKH region, particularly in countries like Pakistan and Nepal. These practices, deeply rooted in indigenous traditions and wisdom, offer valuable insights into sustainable living and environmental stewardship amidst evolving climatic conditions. For instance, in Pakistan, communities have a longstanding tradition of planting trees along riverbanks, utilizing native species with deep-rooted systems. This practice serves to mitigate floods and adapt to contemporary challenges such as GLOFs [32]. Similarly, Nepal’s Local Adaptation Plan for Action (LAPA) emphasizes context-specific strategies tailored to local needs. LAPA includes ecosystem-based adaptation (EbA) activities like forest conservation and agroforestry, as well as community-based adaptation (CBA) practices, such as tree planting and improved cooking stoves [50]. These cultural practices and indigenous knowledge contribute to enhancing resilience to GLOFs by promoting ecosystem services, such as flood mitigation through tree planting and by fostering community-level preparedness and adaptation measures. Additionally, efforts to blend indigenous knowledge with modern technological innovations, such as weather forecasting apps and hydrodynamic modeling, further enhance the potential effectiveness of adaptation strategies in addressing GLOF risks [28,50].
Migration
Migration is increasingly recognized as a key adaptation strategy to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region. Migration involves people moving within countries, temporarily or permanently, to mitigate the impacts of GLOFs. [51] emphasized its importance in response to GLOF risks, particularly in regions like Pakistan’s Karakoram, where temporary migration to urban centers is common. This strategy allows households to access resources and services in safer areas, diversify livelihoods, decrease dependency on GLOF vulnerable sectors (e.g., agriculture), and increase resilience to GLOF hazards.
3.2.3. Institutional and Governance Adaptations
Institutional- and governance-related adaptation to GLOFs include capacity building, planning, and multilateral collaboration. These adaptations entail enhancing skills, resources, and partnerships to effectively address challenges and achieve common goals. In the pursuit of climate resilience, India, Nepal, and Pakistan are engaging in collaborative efforts with local organizations and NGOs to enhance preparedness and response capacities [50]. This cooperative approach underscores the importance of shared knowledge and resources in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change.
Within Nepal, the Local Adaptation Plans of Action (LAPA) initiative plays a pivotal role in building local capacity and fostering collaboration. LAPA goes beyond theoretical approaches, incorporating practical measures such as training in agriculture, animal husbandry, water resource management, and forest conservation. This comprehensive capacity-building initiative equips local communities with the necessary skills to effectively navigate the impacts of climate change, including GLOF. Moreover, Ghimire and Chhetri (2023) highlighted the participatory and collaborative nature of LAPA, involving local communities, women’s groups, indigenous communities, governments, and NGOs [50]. This collaborative framework ensures the holistic and inclusive implementation of adaptation strategies, acknowledging the interconnected nature of climate challenges [51]. Furthermore, Nepal conducts rigorous vulnerability assessments to pinpoint areas at heightened risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs). This knowledge is then applied in strategic development planning, promoting activities in safer regions and discouraging construction in high-risk zones. Such proactive measures align with the broader goal of safeguarding infrastructure and human well-being from the impacts of climate change, particularly GLOFs [28].
In Bhutan, the National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) represents a significant effort in climate change adaptation. The NAPA emphasizes the importance of integrating climate risk assessments into national development planning. It focuses on improving early warning systems and infrastructure resilience to GLOFs and other climate-induced hazards. For example, Bhutan has implemented a network of monitoring stations equipped with wireless sets and satellite telephones to report lake water levels and issue warnings to downstream communities. This proactive approach helps safeguard towns such as Punakha and Thimphu from potential GLOF impacts [52].
In Pakistan, managing the risks of GLOFs involves a multifaceted approach that includes monitoring, early warning systems, and community preparedness. Various international agencies, including the United Nations Development Program and several local agencies, have been actively working on enhancing their capacities to handle GLOF events through research and the implementation of technical measures. Efforts also focus on building resilience in high-risk areas through infrastructure improvements and community-based adaptation initiatives [53]. Similarly, India has developed comprehensive guidelines for managing GLOF risks through its National Disaster Management Authority. These guidelines include early warning systems, community preparedness, and infrastructure protection. Risk maps based on extensive research highlight vulnerable areas and guide land-use planning to avoid high-risk zones. India also emphasizes cross-border cooperation, acknowledging that GLOF risks often span national boundaries [54]. Afghanistan has been actively involved in addressing the risks posed by Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) through collaborative initiatives and capacity-building efforts. The SERVIR-HKH program, in partnership with Afghanistan’s National Water Affairs Regulation Authority (NWARA), focused on establishing a comprehensive glacier and glacial lake database to enhance GLOF monitoring and response. The co-development approach, where Afghan professionals were trained in remote sensing (RS) and GIS techniques, enabled them to independently monitor and assess glacial hazards. This capacity-building initiative led to the successful development of a glacier database, which was launched in 2018, followed by a glacial lake database in 2020. These efforts aim to provide data-driven insights for mitigating GLOF risks and strengthening resilience in vulnerable regions [55].
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Adaptation strategies for GLOF have been pivotal in mitigating risks and enhancing community resilience in glacial regions. Structural adaptations, including lake-level control, channel modification, and flood defense systems, have delivered immediate protection against potential outburst events. These measures have been particularly beneficial in high-risk areas, where they effectively reduce the threat to human lives and infrastructure by physically altering the landscape and controlling water levels [39]. Non-structural adaptations, such as agricultural diversification, community-based practices, and institutional governance strategies, have also played a crucial role. These strategies help communities build resilience by promoting alternative income sources, enhancing local knowledge, and improving preparedness. For instance, community-based adaptations leverage traditional knowledge to adapt to environmental changes, thus aiding in the maintenance of livelihoods despite GLOF risks [56].
Across Afghanistan, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Pakistan, structural and non-structural adaptations to GLOFs exhibit varying success and challenges. Nepal and Bhutan have made significant strides in early warning systems and lake-level control, with Bhutan implementing automated monitoring stations and Nepal employing hydrodynamic modeling for real-time assessments [28,36,46]. However, financial and infrastructural limitations remain a challenge in scaling these measures [28,46]. India has developed a robust institutional framework for disaster management, integrating risk mapping and cross-border cooperation, yet resource constraints and governance complexities hinder the effectiveness of these strategies [37,54]. Pakistan has focused on both community-driven flood defenses and institutional collaborations, but financial limitations and technological gaps restrict broader implementation [32,45,53]. For instance, the 2010 GLOF in Pakistan’s Hunza Valley led to substantial economic losses by blocking the vital Karakoram Highway, highlighting the need for enhanced structural defenses and early warning systems to mitigate such disruptions [33] Afghanistan, despite its strides in capacity building through the SERVIR-HKH program and glacial lake monitoring initiatives, continues to face institutional and technical limitations in fully addressing GLOF risks [44]. Recent climate change assessments have warned of increasing GLOF risk in the Wakhan region, where glacial lakes such as the Bozai Gumbaz Lake have been expanding rapidly, emphasizing the urgency for proactive adaptation strategies [22]. Notably, the adoption and effectiveness of structural and non-structural adaptation strategies vary across regions, influenced by factors such as geographic conditions, economic resources, and institutional support. In some areas, structural measures like embankments and check dams are more widely implemented due to higher government and NGO investments, whereas in other regions, community-led non-structural strategies such as early warning systems and livelihood diversification play a more prominent role. Regions with frequent GLOF events but limited financial resources tend to rely more on non-structural measures, which, while cost-effective, may not provide the same level of long-term protection as well-maintained structural interventions. For example, Nepal’s Bhotekoshi River flooding in 2016, caused by a GLOF from Tibet, severely damaged hydropower infrastructure and led to prolonged power outages, demonstrating the necessity of integrating structural mitigation with non-structural resilience-building measures [19].
Despite their effectiveness, these adaptation strategies face several limitations. Structural adaptations are often resource-intensive and technically challenging, especially in remote, high-altitude regions. The implementation and maintenance of such measures require specialized equipment, materials, and expertise, which can be financially unsustainable, particularly for low-income regions [5,39]. Innovations in water management, such as artificial glaciers, also encounter sustainability issues. These technologies require continuous support and maintenance, and their long-term effectiveness remains uncertain as they may not fully address the underlying drivers of GLOF risk, such as climate change [31,38]. Non-structural strategies face their own set of challenges. Economic diversification through agriculture may be limited by market access and infrastructure constraints. Unpredictable climate patterns complicate adaptive crop management, necessitating ongoing adjustments that strain resources [38,48]. Community-based adaptations, while valuable, are vulnerable to rapid societal changes and cultural shifts. Preserving traditional knowledge and community cohesion is critical but can be undermined by external influences [56,57]. Institutional and governance adaptations are crucial for coordinated efforts but often face difficulties related to inter-governmental cooperation and coordination. Fragmented efforts across multiple jurisdictions can diminish the overall effectiveness of GLOF risk management strategies. Additionally, ensuring equitable distribution of adaptation benefits remains a challenge, as disparities in resource access can exacerbate vulnerabilities [50].
In the short term, structural adaptations are more effective in providing immediate protection against GLOF events. They offer tangible solutions that can be quickly implemented to reduce the risk of catastrophic events. However, their long-term sustainability is questionable, requiring ongoing maintenance, funding, and technical expertise [58]. Non-structural adaptations, while potentially less effective immediately, provide more sustainable long-term resilience. By focusing on community capacity building, economic diversification, and institutional strengthening, these strategies address the root causes of 4vulnerability and enhance adaptive capacity over time. Their success, however, depends on continued support and adaptation to evolving conditions [57,59].
To enhance the effectiveness of GLOF adaptation strategies, a holistic and context-specific approach is needed. Structural adaptations should be complemented by investments in local capacity building and the development of sustainable financing mechanisms. This could involve training local communities in the maintenance and operation of structural defenses, as well as exploring innovative funding models that ensure the long-term viability of these interventions [5]. Non-structural strategies should integrate traditional knowledge with modern scientific understanding, ensuring that adaptation measures are culturally appropriate and context-specific. For instance, indigenous knowledge of seasonal patterns and water flow can inform the design and placement of engineering structures or incorporating indigenous practices such as agricultural diversification and land conservation into larger engineering projects further strengthens the region’s resilience. Strengthening market linkages and infrastructure for agricultural diversification, as well as enhancing climate forecasting and early warning systems, can help communities better cope with climate variability [57,59]. Institutional coordination and governance frameworks must be streamlined to ensure effective collaboration across different levels of government and stakeholders. Developing multi-jurisdictional task forces or standardized protocols for GLOF risk management can improve coordination. Additionally, efforts should focus on ensuring equitable distribution of adaptation benefits, particularly for vulnerable and marginalized populations [50].
Successful adaptation initiatives, such as the Tsho Rolpa risk mitigation project in Nepal and local flood defense measures in Pakistan, provide valuable lessons for GLOF risk management in less-studied areas. The Tsho Rolpa project, which involved lake-level lowering and the establishment of an early warning system, serves as a model for proactive risk reduction through structural intervention and technological integration. This approach could be replicated in regions where glacial lakes pose a similar threat but lack systematic risk assessments. Likewise, Pakistan’s community-based flood defenses demonstrate how localized, low-cost strategies can enhance resilience even in resource-limited settings [28,53]. Bhutan’s success in integrating automated monitoring stations highlights the role of technological advancements in risk mitigation [15,20]. India’s institutional disaster management framework exemplifies the benefits of coordinated governance and cross-border collaboration [35,57]. Afghanistan’s engagement in regional monitoring programs, despite challenges, reflects the importance of capacity building and international partnerships [55]. These experiences highlight the importance of combining structural measures with community participation, policy support, and sustained investment.
Actionable recommendations for policy-makers, researchers, and local communities involve a comprehensive and collaborative approach to adaptation. Policy-makers should implement region-specific adaptation frameworks that combine structural and non-structural strategies, establish cross-border collaborations to improve early warning systems and data sharing, and secure long-term funding mechanisms to sustain adaptation projects. Researchers should focus on localized risk assessments to identify the most effective adaptation measures for different regions, enhance monitoring technologies, and improve GLOF forecasting and intervention planning. Local communities should strengthen traditional knowledge systems by integrating them with scientific approaches and actively participate in community-based adaptation projects to ensure that risk reduction measures align with local needs and capacities. By coordinating efforts across these key stakeholders, the overall resilience to GLOF risks can be significantly improved.
Future research on GLOF adaptation should prioritize analyzing how social, economic, and governance factors shape adaptation strategies and community resilience. While current research largely focuses on structural adaptations and case-specific studies, there is a need for a comparative analysis of adaptation effectiveness across different geographic and socioeconomic contexts. Future studies should explore the long-term sustainability of structural measures, particularly in the face of climate change-driven glacial melt and evolving hydrological patterns. Additionally, research should delve deeper into community-led and hybrid adaptation approaches, assessing how traditional knowledge can be effectively combined with technological innovations for more resilient adaptation strategies. Studies should explore how marginalized and vulnerable groups, including Indigenous communities, women, and low-income households, experience and respond to GLOF threats, ensuring that adaptation strategies are inclusive and equitable. There is a critical need to investigate policy coherence across national and regional governance frameworks, examining how cross-border collaborations can be strengthened for better GLOF risk management. Addressing knowledge gaps in underrepresented regions, such as Afghanistan and parts of India, through localized studies will also be crucial for a comprehensive understanding of adaptation needs. In short, future research needs to contribute to more socially responsive and sustainable GLOF adaptation strategies that empower communities and strengthen resilience in the HKH region.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I.; methodology, A.I.; formal analysis, S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.; writing—review and editing, A.I.; visualization, S.S. and A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors declare that they have no known or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ahmed, R.; Wani, G.F.; Ahmad, S.T.; Sahana, M.; Singh, H.; Ahmed, P. A review of glacial lake expansion and associated glacial lake outburst floods in the Himalayan region. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Allen, S.K.; Bao, A.; Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A.; Huss, M.; Zhang, G.; Stoffel, M. Increasing risk of glacial lake outburst floods from future Third Pole deglaciation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Hassan, J.; Liu, D.; Jin, W. Increasing glacial lake outburst flood hazard in response to surge glaciers in the Karakoram. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, M. Glacial lake inventory and lake outburst flood/debris flow hazard assessment after the Gorkha earthquake in the Bhote Koshi Basin. Water 2020, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.B.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K.; Baba, Y.; Zhang, H. Glacial hazards in the Rolwaling Valley of Nepal and numerical flood to predict potential outburst flood from glacial lake. Landslides 2013, 10, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Nüsser, M.; Baghel, R.; Dame, J. Cryosphere hazards in Ladakh: The 2014 Gya glacial lake outburst flood and its implications for risk assessment. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 2071–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, K. The Karakoram Anomaly? Glacier Expansion and the ‘Elevation Effect,’ Karakoram Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 2005, 25, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Robinson, T.R.; Dunning, S.; Rachel Carr, J.; Westoby, M. Glacial lake outburst floods threaten millions globally. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Goyal, M.K. Glacial lake outburst flood hazard, downstream impact, and risk over the Indian Himalayas. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.Y.; Ren, G.Y.; Sun, X.B.; Shrestha, A.B.; You, Q.L.; Zhan, Y.J.; Rajbhandari, R.; Zhang, P.F.; Wen, K.M. Observed changes in surface air temperature and precipitation in the Hindu Kush Himalayan region during 1901–2014. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 8, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICIMOD. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Allen, S.; Kargel, J.S.; Haritashya, U.K.; Watson, C.S. Annual 30 m dataset for glacial lakes in High Mountain Asia from 2008 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, J.D. Glacial Lake Outburst Floods and Risk Engineering in the Himalaya; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): Kathmandu, Nepal, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, S.D.; Reynolds, J.M. An overview of glacial hazards in the Himalayas. Quat. Int. 2000, 65–66, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, R.; Hewitt, K.; Kawishwar, P.; Pratap, B. Surge-type and non-surge-type glaciers in Jammu and Kashmir, India. Geosciences 2020, 10, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Gurung, D.R.; Khanal, N.R.; Bajracharya, S.R.; Tsering, K.; Joshi, S.; Tshering, P.; Chhetri, L.K.; Lotay, Y.; Penjor, T. Lemthang Tsho glacial Lake outburst flood (GLOF) in Bhutan: Cause and impact. Geoenviron. Disasters 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturrizaga, L. New observations on present and prehistorical glacier-dammed lakes in the Shimshal Valley (Karakoram Mountains). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2005, 25, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, K. Natural dams and outburst floods of the Karakoram Himalaya. IAHS Publ. 1982, 138, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Dobhal, D.P.; Gupta, A.K.; Mehta, M.; Khandelwal, D.D. Kedarnath disaster: Facts and plausible causes. Curr. Sci. 2013, 105, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kathmandu Post. Bhotekoshi Flood Damages Hydropower Project. 2023. Available online: www.kathmandupost.com (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Komori, J. Recent expansions of glacial lakes in the Bhutan Himalayas. Quat. Int. 2008, 184, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP Pakistan. Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in Gilgit-Baltistan. 2019. Available online: www.pk.undp.org (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Azizi, F.; Lane, S. Impacts and Downstream Propagation of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) in Afghanistan: A Case Study of the 2018 and 2021 Outbursts in Peshghor, Panjshir Valley. Abstract Presented at the 25th International Mountain Cartography Conference (IMC2025). 2025. Available online: https://imc2025.info/imc25/abstract/impacts-and-downstream-propagation-of-glacial-lake-outburst-floods-glofs-in-afghanistan-a-case-study-of-the-2018-and-2021-outbursts-in-peshghor-panjshir-valley/ (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Shroder, J.F.; Bishop, M.P. Climate change and glacier hazards in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 14, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2014, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.; Babel, M.S.; Sharma, D. Coping with changing water resources: The case of the Ganges Basin in South Asia. Water Int. 2014, 39, 186–200. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.K.; Rastner, P.; Arora, M.; Huggel, C.; Stoffel, M. Lake outburst and debris flow disaster at Kedarnath, June 2013: Hydrometeorological triggering and topographic predisposition. Landslides 2016, 13, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Sakai, A.; Tshering, P. Impact of glacial lake outburst floods in the Bhutan Himalaya. Ann. Glaciol. 2007, 45, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Mool, P.K.; Shrestha, B.R. Impact of Climate Change on Himalayan Glaciers and Glacial Lakes: Case Studies on GLOF and Associated Hazards in Nepal and Bhutan; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2007; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yao, T.; An, B. Monitoring and early warning system of Cirenmaco glacial lake in the central Himalayas. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 73, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.K.; Rastner, P.; Arora, M.; Huggel, C.; Stoffel, M. Lake outburst and debris flow hazard assessment of the Shimshal Valley, Karakoram Mountains, Pakistan: Implications for climate change impacts. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 1805–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, N.R.; Aryal, K.; Sharma, R.; Adhikari, K. The role of artificial glaciers in improving water security in the Himalayas: A review. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 256–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, W.; Khan, M.A. Climate change-induced Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in Hunza Valley of Pakistan: An assessment of indigenous farming community perceptions and adaptation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 11515–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Joshi, S.D.; Parajuli, B. Overview of an early warning system for Glacial Lake outburst flood risk mitigation in Dudh-Koshi Basin, Nepal. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2021, 13, 206–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.; Iqbal, M.B.; Mustafa, N.; Naz, R.; Ahmad, B. Prevalent risk of glacial lake outburst flood hazard in the Hindu Kush–Karakoram–Himalaya region of Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, S.; Sethi, N. Social vulnerability assessment of Glacial Lake Outburst Flood in a Northeastern state in India. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 74, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.; Shrestha, M.; Chhetri, N.; Agusdinata, D.B. An institutional analysis of glacial floods and disaster risk management in the Nepal Himalaya. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, J.D.; Shrestha, R.B.; Mool, P.K. Formation of Glacial Lakes in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas and GLOF Risk Assessment; ICIMOD: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2010; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Akhtar, R.; Hussain, J. Unveiling High Mountain Communities’ Perception of Climate Change Impact on Lives and Livelihoods in Gilgit-Baltistan: Evidence from People-Centric Approach. Environ. Commun. 2023, 17, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mool, P.K.; Maskey, P.R.; Koirala, A.; Joshi, S.P.; Lizong, W.; Shrestha, A.B.; Shrestha, R.B. Glacial Lakes and Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in Nepal; GFDRR: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khadka, N.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. The state of six dangerous glacial lakes in the Nepalese Himalaya. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 30, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattelmann, R. Glacial lake outburst floods in the Nepal Himalaya: A manageable hazard? Nat. Hazards 2003, 28, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsering, K.; Shakya, K.; Matin, M.A.; Nelson, J.; Bajracharya, B. Enhancing Flood Early Warning System in the HKH Region. In Earth Observation Science and Applications for Risk Reduction and Enhanced Resilience in Hindu Kush Himalaya Region: A Decade of Experience from SERVIR; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Global Survey of Early Warning Systems. A Report Prepared by UNISDR at the Request of the Secretary General of the United Nations; UNISDR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.unisdr.org/2006/ppew/info-resources/ewc3/Global-Survey-of-Early-Warning-Systems.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- UNDP. Capacity building for disaster risk reduction of regional glacial lake outburst floods (GLOF): Preparatory assessment study report—Sutlej Basin, Himachal Pradesh, India. In Proceedings of the DIPECHO Interagency Coordination Meeting, New Delhi, India, 23 September 2008; UNDP and European Commission Humanitarian Aid: New Delhi, India, 2008. Available online: https://chimalaya.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/india-preparatory-assessment-report-glof-initiative.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- The Economic Times. GLOF Early Warning System Takes Off; Centre Targets 188 Critical Glacial Lakes. Available online: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/GLOF-early-warning-system-takes-off-centre-targets-188-critical-glacial-lake/articleshow/109780863.cms (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Meenawat, H.; Sovacool, B.K. Improving adaptive capacity and resilience in Bhutan. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2011, 16, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, S.; Hussain, A.; Baig, S.; Ali, A.; Soheb, M.; Angchuk, T.; Shrestha, A.B. Climate change, water and agriculture linkages in the upper Indus basin: A field study from Gilgit-Baltistan and Leh-Ladakh. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 6, 1012363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.M.; Khan, A.A.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Ahmed, S.; Shah, G.M.; Ali, G. Enhancing socioeconomic resilience and climate adaptation through value chain development of mountain products in Hindu Kush Himalayas. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 8451–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Nair, S.S. (Eds.) Ecosystem Approach to Disaster Risk Reduction; National Institute of Disaster Management: New Delhi, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire, R.; Chhetri, N. Coproduction imaginaries for climate change adaptation: A case of adaptation initiatives in the Gandaki River Basin, Western Nepal. Prof. Geogr. 2023, 75, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioli, G.; Khan, T.; Scheffran, J. Climatic and environmental change in the Karakoram: Making sense of community perceptions and adaptation strategies. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environment Commission. National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) to Climate Change (Report No. BTN01). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). 2009. Available online: https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/napa/btn01.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Rijal, A.; Ali, J. Reducing Risks and Vulnerabilities from Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in Northern Pakistan; UNDP: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, E.; Molden, D.; Rahman, A.; Khatiwada, Y.R.; Zhang, L.; Singh, S.P.; Yao, T.; Wester, P. Introduction to the Hindu Kush Himalaya assessment. In The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment; Wester, P., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A., Shrestha, A.B., Eds.; Springer AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Maharjan, S.B.; Shrestha, F.; Azizi, F.; Joya, E.; Bajracharya, B.; Bromand, M.T.; Rahimi, M.M. Monitoring of glaciers and glacial lakes in Afghanistan. In Earth Observation Science and Applications for Risk Reduction and Enhanced Resilience in Hindu Kush Himalaya Region: A Decade of Experience from SERVIR; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 211–230. [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale, A.J. Beyond the Local: Indigenous Knowledge and Global Adaptation. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 44, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, N.; Narama, C.; Gyalson, S. Knowledge sharing for disaster risk reduction: Insights from a glacier lake workshop in the Ladakh region, Indian Himalayas. Mt. Res. Dev. 2016, 36, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.V.; Harasawa, H.; Lal, M.; Wu, S.; Anokhin, Y.; Peñalba, O. Asia. In Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; pp. 469–506.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).