Effect of Temperature on the Spread of Contagious Diseases: Evidence from over 2000 Years of Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Description
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO COVID Dashboard. Available online: https://COVID19.who.int/ (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Cirillo, P.; Taleb, N.N. Tail risk of contagious diseases. Nat. Phys. 2020, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.R.; Allen, R.J.; Evan, A.T.; Zelinka, M.D.; O’dell, C.W.; Klein, S.A. Evidence for climate change in the satellite cloud record. Nature 2016, 536, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; 2391p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, A. Climate change hastens disease spread across the globe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200481119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorris, M.E.; Treseder, K.K.; Zender, C.S.; Randerson, J.T. Expansion of coccidioidomycosis endemic regions in the United States in response to climate change. GeoHealth 2019, 3, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, C.; McKenzie, T.; Gaw, I.M.; Dean, J.M.; von Hammerstein, H.; Knudson, T.A.; Setter, R.O.; Smith, C.Z.; Webster, K.M.; Patz, J.A.; et al. Over half of known human pathogenic diseases can be aggravated by climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminade, C.; McIntyre, K.M.; Jones, A.E. Climate change and vector-borne diseases: Where are we next heading? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e302–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siraj, A.S.; Santos-Vega, M.; Bouma, M.J.; Yadeta, D.; Ruiz Carrascal, D.; Pascual, M. Altitudinal changes in malaria incidence in Colombia and Ethiopia due to warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, M.C.; Stanberry, L.R. Climate Change and Vectorborne Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.M.; Sauer, E.L.; Santiago, O.; Spencer, S.; Rohr, J.R. Divergent impacts of warming weather on wildlife disease risk across climates. Science 2020, 370, eabb1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.M.; Venesky, M.D.; Sauer, E.L.; Civitello, D.J.; Taegan, A.M.; Roznik, E.A.; Rohr, J.R. The thermal mismatch hypothesis explains host susceptibility to an emerging infectious disease. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Fauci, A.S. A Centenary Tale of Two Pandemics: The 1918 Influenza Pandemic and COVID-19, Part I. Am. J. Public Health 2021, 111, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dias, J.G.; Vermunt, J.K.; Ramos, S. Clustering financial time series: New insights from an extended hidden Markov model. Eur J. Oper Res. 2015, 243, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamon, R.S.; Elliott, R.J. Hidden Markov Models in Finance; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genon-Catalot, V.; Jeantheau, T.; Laredo, C. Stochastic volatility models as hidden Markov models and statistical applications. Bernoulli 2000, 6, 1051–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.L.; James, G.M.; Sugar, C.A. Hidden Markov Models for Longitudinal Comparisons. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2005, 100, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, H.J.; Young, S.J. Modelling asynchrony in automatic speech recognition using loosely coupled hidden Markov models. Cog Sci. 2002, 3, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; Gershman, S. Memory as a Computational Resource. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2021, 25, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.L.; Chong, Y.W. Optimized access point selection with mobility prediction using hidden Markov Model for wireless network. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, M.O.; Sarwar, H.; Chowdhury, M.R. Prediction of State of Wireless Network Using Markov and Hidden Markov Model. J. Netw. 2009, 4, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchini, W.; Guttorp, P. A hidden Markov model for space-time precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.M.; Robertson, A.W.; Smyth, P.; Triglia, S. Downscaling projections of Indian monsoon rainfall using a non-homogeneous hidden Markov model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Haines, A.; Cox, J.; Corvalán, C.; Anker, M. Using Climate to Predict Infectious Disease Epidemics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Wu, P.-C.; Lung, S.-C.; Su, H.-J. Effects of Extreme Precipitation to the Distribution of Infectious Diseases in Taiwan, 1994–2008. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, L.; Dragicevic, S. An agent-based approach for modeling dynamics of contagious disease spread. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Richmond, P.; Roehner, B.M. Effect of population density on epidemics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 510, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiderud, C.-J. How urbanization affects the epidemiology of emerging infectious diseases. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 27060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinasih, S.E.; Devy, S.R.; Koesbardiati, T.; Romadhona, M.K. Human migration, infectious diseases, plague, global health crisis–historical evidence. Cogent Arts Humanit. 2024, 11, 2392399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Garcia, D. Residential segregation and the epidemiology of infectious diseases. Soc. Sci. Med. 2000, 51, 1143–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Moreno, J.M.; Alegre-Martinez, A.; Martin-Gorgojo, V.; Alfonso-Sanchez, J.L.; Torres, F.; Pallares-Carratala, V. Predictive Models for Forecasting Public Health Scenarios: Practical Experiences Applied during the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, A.J.; Sampson, K.M.; Steinhoff, D.F.; Ernst, K.C.; Ebi, K.L.; Jones, B.; Hayden, M.H. The potential impacts of 21st century climatic and population changes on human exposure to the virus vector Aedes aegypti. Clim. Change 2015, 131, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.N.; Gage, K.L.; Khan, A.S. Potential influence of climate change on vector-borne and zoonotic diseases: A review and proposed research plan. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trærup, S.; Ortiz, R.A.; Markandya, A. The health impacts of climate change: A study of cholera in Tanzania. Glob. Environ. Change 2011, 21, 392–403. [Google Scholar]
- Revich, B.; Podolnaya, M.A.; Popova, E.Y. Thawing of permafrost may disturb historic cattle burial grounds in East Siberia. Glob. Health Action 2011, 4, 8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ListFist List of Epidemics Compared to Coronavirus (COVID-19). Available online: https://listfist.com/list-of-epidemics-compared-to-coronavirus-COVID-19 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Wikipedia List of Epidemics and Pandemics. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_epidemics_and_pandemics#cite_note-38 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- World History Encyclopedia. Available online: https://www.worldhistory.org/article/1532/plagues-of-the-near-east-562-1486-ce/ (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Hawkins, E. Climate Lab Book. 2020. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20200202220240/https://www.climate-lab-book.ac.uk/2020/2019-years/ (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- National Centers for Environmental Information NOAA. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/global-temperature-anomalies#:~:text=The%20term%20temperature%20anomaly%20means,cooler%20than%20the%20reference%20value (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Wood, S. Thin plate regression splines. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2003, 65, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C. An Introduction to Discrete-Valued Time Series; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yan, C.; Xu, L.; Büntgen, U.; Stenseth, N.C.; Zhang, Z. Scale-dependent climatic drivers of human epidemics in ancient China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12970–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book; Wiley: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]

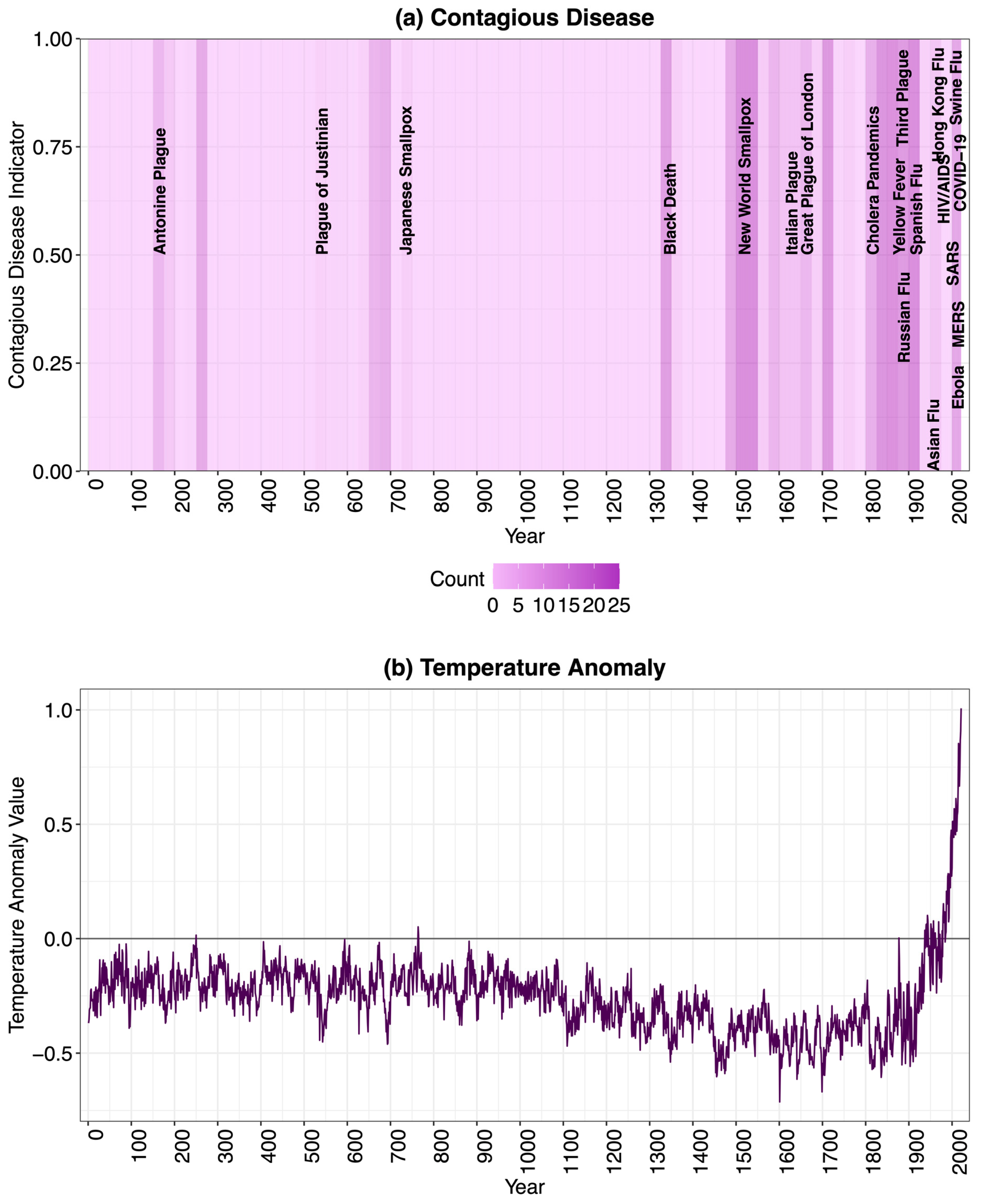










| Event | Start Year | End Year | Location | Estimated Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plague of Athens | −429 | −426 | Greece, Libya, Egypt, Ethiopia | 75,000–100,000 |
| Antonine Plague | 165 | 180 | Roman Empire | 5–10 million |
| Plague of Cyprian | 250 | 266 | Europe | 310,000 |
| Plague of Justinian | 541 | 542 | Europe, West Asia | 15–100 million |
| Plague of Amida | 562 | 562 | Mesopotamia (modern day Turkey) | 30,000 |
| Roman Plague of 590 | 590 | 590 | Rome, Byzantine Empire | Unknown |
| Plague of Sheroe | 627 | 628 | Bilad al-Sham | 25,000+ |
| Plague of the British Isles | 664 | 689 | British Isles | Unknown |
| Plague of Basra | 688 | 689 | Basra (southeast Turkey) | 200,000 |
| Japanese Smallpox Epidemic | 735 | 737 | Japan | 2 million |
| Black Death | 1331 | 1353 | Eurasia and North Africa | 75–200 million |
| Sweating Sickness | 1485 | 1551 | Britain | 10,000+ |
| Smallpox Epidemic in Mexico | 1520 | 1520 | Mexico | 5–8 million |
| Cocoliztli Epidemic of 1545–1548 | 1545 | 1548 | Mexico | 5–15 million |
| 1563 London Plague | 1562 | 1564 | London, England | 20,100 |
| Malta Plague Epidemic | 1592 | 1593 | Malta | 3000 |
| Plague in Spain | 1596 | 1602 | Spain | 600,000–700,000 |
| New England Epidemic | 1616 | 1620 | New England | Unknown |
| Italian Plague of 1629–1631 | 1629 | 1631 | Italy | 1 million |
| Great Plague of Sevilla | 1647 | 1652 | Spain | 500,000 |
| Plague in Kingdom of Naples | 1656 | 1658 | Italy | 1,250,000 |
| Plague in the Netherlands | 1663 | 1664 | Amsterdam, Netherlands | 24,148 |
| Great Plague of London | 1665 | 1666 | England | 100,000 |
| Plague in France | 1668 | 1668 | France | 40,000 |
| Malta Plague Epidemic | 1675 | 1676 | Malta | 11,300 |
| Great Plague of Vienna | 1679 | 1679 | Vienna, Austria | 76,000 |
| Great Northern War plague Outbreak | 1700 | 1721 | Denmark, Sweden, Lithuania | 164,000 |
| Great Smallpox Epidemic in Iceland | 1707 | 1709 | Iceland | 18,000+ |
| Great Plague of Marseille | 1720 | 1722 | France | 100,000 |
| Great Plague of 1738 | 1738 | 1738 | Balkans | 50,000 |
| Russian Plague of 1770–1772 | 1770 | 1772 | Russia | 50,000 |
| Ottoman Plague Epidemic | 1812 | 1819 | Ottoman Empire | 300,000+ |
| Caragea’s Plague | 1813 | 1813 | Romania | 60,000 |
| Malta Plague Epidemic | 1813 | 1814 | Malta | 4500 |
| First Cholera Pandemic | 1816 | 1826 | Asia, Europe | 100,000+ |
| Second Cholera Pandemic | 1829 | 1851 | Asia, Europe, North America | 100,000+ |
| Typhus Epidemic in Canada | 1847 | 1848 | Canada | 20,000+ |
| Third Cholera Pandemic | 1852 | 1860 | Worldwide | 1 million+ |
| Cholera Epidemic of Copenhagen | 1853 | 1853 | Copenhagen, Denmark | 4737 |
| Third Plague Pandemic | 1855 | 1960 | Worldwide (India, China) | 12–15 million |
| Smallpox in British Columbia | 1862 | 1863 | Pacific Northwest, Canada, US | 20,000+ |
| Fourth Cholera Pandemic | 1863 | 1875 | Middle East | 600,000 |
| Fiji Measles outbreak | 1875 | 1875 | Fiji | 40,000 |
| Yellow Fever | 1880 | 1900 | Mississippi, New Orleans, US | 17,000+ |
| Fifth Cholera Pandemic | 1881 | 1896 | Asia, Africa, Europe, South America | 298,600 |
| Smallpox in Montreal | 1885 | 1885 | Montreal, Canada | 3164 |
| Russian Flu | 1889 | 1890 | Russia, Worldwide | 1 million |
| Sixth Cholera Pandemic | 1899 | 1923 | Europe, Asia, Africa | 800,000 |
| China Plague | 1910 | 1912 | China | 40,000 |
| Encephalitis Lethargica Pandemic | 1915 | 1926 | Worldwide | 500,000 |
| American Polio Epidemic | 1916 | 1916 | United States | 7130 |
| Spanish Flu | 1918 | 1920 | Worldwide | 17–100 million |
| HIV/AIDS Pandemic | 1981 | 2023 | Worldwide | 42 million |
| Poliomyelitis in USA | 1946 | 1946 | United States | 9000 |
| Asian Flu | 1957 | 1958 | Worldwide | 1–4 million |
| Hong Kong Flu | 1968 | 1969 | Worldwide | 1–4 million |
| London Flu | 1972 | 1973 | United States | 1027 |
| Smallpox Epidemic of India | 1974 | 1974 | India | 15,000 |
| Zimbabwean Cholera Outbreak | 2008 | 2009 | Zimbabwe | 4293 |
| Swine Flu | 2009 | 2009 | Worldwide | 151,700–575,400 |
| Haiti Cholera Outbreak | 2010 | 2020 | Haiti | 10,075 |
| Measles in D.R. Congo | 2010 | 2014 | Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) | 4500 |
| Ebola in West Africa | 2013 | 2016 | Worldwide (Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone) | 11,323+ |
| Indian Swine Flu Outbreak | 2015 | 2015 | India | 2035 |
| Yemen Cholera Outbreak | 2016 | 2020 | Yemen | 3981 |
| 2018-2019 Kivu Ebola Epidemic | 2018 | 2020 | DRC and Uganda | 2280 |
| Measles in D.R. Congo | 2019 | 2020 | DRC | 7018 |
| Dengue Fever | 2019 | 2020 | Asia-Pacific, Latin America | 3930 |
| COVID-19 Pandemic | 2019 | To date | Worldwide | 7–29.3 million |
| (1) Temperature Anomaly: Full Sample | (2) Temperature Anomaly: Nondisease Periods | (3) Temperature Anomaly: Disease Periods | (4) Low Temperature Anomaly: Disease Periods | (5) High Temperature Anomaly: Disease Periods | (6) Contagious Disease | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observations | 2021 | 1662 | 359 | 342 | 17 | 2021 |
| Mean | −0.2565 | −0.2439 | −0.3148 | −0.3630 | 0.6542 | 0.1776 |
| S.D. | 0.1626 | 0.1315 | 0.2544 | 0.1315 | 0.1789 | 0.3823 |
| Min | −0.7128 | −0.6688 | −0.7128 | −0.7128 | 0.4428 | 0.0000 |
| Max | 1.0071 | 0.5680 | 1.0071 | 0.0774 | 1.0071 | 1.0000 |
| Skewness | 1.8552 | 0.6627 | 2.8153 | 0.6760 | 0.4781 | 1.6856 |
| Kurtosis | 10.3064 | 4.2776 | 9.2488 | 0.4030 | −1.2498 | 0.8417 |
| JB | 10,128.7200 *** | 1394.1920 *** | 1776.7710 *** | 28.8250 *** | 1.5200 | 1018.6720 *** |
| Q(1) | 1608.9177 *** | 1218.9419 *** | 291.7578 *** | 208.1254 *** | 9.8364 *** | 1574.3151 *** |
| Q(4) | 5750.1233 *** | 4171.6226 *** | 981.4622 *** | 629.5901 *** | 17.7115 *** | 4927.1886 *** |
| ARCH(1) | 1844.5608 *** | 1297.6202 *** | 335.4321 *** | 136.2012 *** | 4.5872 ** | 1574.9812 *** |
| ARCH(4) | 1876.8272 *** | 1346.6727 *** | 337.1974 *** | 157.6724 *** | 4.6465 | 1585.6803 *** |
| Model: | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.102 *** (0.019) | −0.101 *** (0.019) | −0.100 *** (0.018) | −0.099 *** (0.018) | −0.098 *** (0.018) | −0.098 *** (0.018) | 0.077 *** (0.016) |
| −0.080 (0.121) | −0.108 (0.115) | −0.185 *** (0.050) | −0.393 *** (0.052) | ||||
| −0.034 (0.138) | −0.084 (0.115) | −0.087 (0.117) | −0.186 *** (0.051) | ||||
| −0.089 (0.123) | −0.115 (0.117) | −0.192 *** (0.052) | |||||
| 0.00022 *** (0.00001) | 0.00022 *** (0.00001) | 0.00023 *** (0.00001) | 0.00022 *** (0.00001) | 0.00023 *** (0.00001) | 0.00023 *** (0.00001) | ||
| R-squared | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.028 |
| Log L | −772.311 | −772.532 | −772.573 | −773.186 | −773.021 | −772.851 | −895.195 |
| AIC | 1556.622 | 1555.064 | 1555.146 | 1554.372 | 1554.042 | 1553.703 | 1796.389 |
| BIC | 1590.284 | 1583.116 | 1583.198 | 1584.421 | 1576.483 | 1576.144 | 1813.220 |
| Model: | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.254 *** (0.217) | −4.247 *** (0.217) | −4.247 *** (0.217) | −4.237 *** (0.216) | −4.234 *** (0.216) | −4.237 *** (0.216) | −2.518 *** (0.149) |
| −0.609 (0.902) | −0.767 (0.859) | −1.237 *** (0.334) | −3.501 *** (0.451) | ||||
| −0.191 (1.045) | −0.592 (0.860) | −0.518 (0.875) | −1.240 *** (0.339) | ||||
| −0.527 (0.919) | −0.717 (0.875) | −1.271 *** (0.345) | |||||
| 0.002 *** (0.0001) | 0.002 *** (0.0001) | 0.002 *** (0.0001) | 0.002 *** (0.00001) | 0.002 *** (0.0001) | 0.002 *** (0.000) | ||
| R-squared | 0.164 | 0.163 | 0.164 | 0.163 | 0.163 | 0.163 | 0.036 |
| Log L | −790.317 | −790.545 | −790.481 | −790.782 | −790.881 | −790.657 | −911.140 |
| AIC | 1590.634 | 1589.090 | 1588.963 | 1587.564 | 1587.763 | 1587.315 | 1826.280 |
| BIC | 1618.686 | 1611.532 | 1611.404 | 1604.395 | 1604.594 | 1604.146 | 1837.501 |
| Model: | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.739 *** (0.750) | −4.767 *** (0.755) | −4.753 *** (0.754) | −4.829 *** (0.764) | −4.784 *** (0.760) | −4.791 *** (0.760) | −1.822 *** (0.075) |
| 12.337 ** (3.933) | 13.788 ** (3.964) | 73.866 *** (5.246) | 251.475 *** (6.633) | ||||
| 9.124 (4.186) | 29.620 *** (5.257) | 10.414 * (4.145) | 70.326 *** (5.429) | ||||
| 0.499 (1.243) | 3.048 (2.053) | 64.645 *** (4.986) | |||||
| 207.781 *** (12.176) | 208.388 *** (12.188) | 208.685 *** (12.182) | 209.577 *** (12.214) | 210.482 *** (12.196) | 209.530 *** (12.199) | ||
| R-squared | 0.393 | 0.390 | 0.393 | 0.384 | 0.389 | 0.388 | 0.167 |
| Log L | −544.991 | −549.450 | −545.648 | −556.882 | −551.469 | −550.085 | −789.674 |
| AIC | 1141.834 | 1145.625 | 1138.606 | 1151.717 | 1141.915 | 1138.542 | 1595.723 |
| BIC | 1287.286 | 1276.693 | 1271.321 | 1258.182 | 1251.255 | 1246.180 | 1641.660 |
| UBRE | 595.411 | 598.140 | 595.064 | 603.269 | 598.528 | 596.767 | 803.486 |
| Model: | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.682 *** (0.697) | −4.683 *** (0.697) | −4.695 *** (0.701) | −4.729 *** (0.705) | −4.713 *** (0.705) | −4.719 *** (0.705) | −1.823 *** (0.074) |
| 11.569 ** (3.546) | 13.269 *** (3.595) | 75.069 *** (4.931) | 250.085 *** (6.239) | ||||
| 9.393 ** (3.832) | 67.878 *** (5.178) | 9.887 ** (3.713) | 69.784 *** (5.051) | ||||
| 0.862 (1.000) | 2.127 (1.000) | 67.738 *** (4.676) | |||||
| 192.115 *** (12.023) | 192.891 *** (12.029) | 193.256 *** (12.030) | 195.289 *** (12.056) | 195.721 *** (12.043) | 195.017 *** (12.045) | ||
| 0.891 | 0.858 | 0.858 | 0.854 | 0.858 | 0.885 | 0.878 | |
| R-squared | 0.393 | 0.389 | 0.393 | 0.383 | 0.388 | 0.388 | 0.167 |
| Log L | −599.653 | −602.125 | −600.074 | −607.753 | −603.168 | −601.435 | −802.978 |
| AIC | 1217.306 | 1218.251 | 1214.148 | 1225.505 | 1216.337 | 1212.870 | 1611.955 |
| BIC | 1267.799 | 1257.523 | 1253.421 | 1253.557 | 1244.389 | 1240.922 | 1628.786 |
| Parameter | Estimate | Probabilities at Zero Values of the Covariates | |
|---|---|---|---|
| −6.9516 *** (0.7727) | |||
| −0.8445 (0.9618) | 0.9990 | ||
| 0.0023 *** (0.0004) | 0.0010 | ||
| 2.3465 *** (0.0016) | 0.0010 | ||
| −0.0184 (0.1223) | 0.9990 | ||
| 0.00002 *** (0.000002) | |||
| −683.0342 (23.2476) | |||
| 17.7412 (18.0686) | |||
| 0.4651 *** (0.0155) | |||
| Log L | −262.0879 | ||
| AIC | 542.1758 | ||
| BIC | 592.6779 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balcilar, M.; Mukherjee, Z.; Gupta, R.; Das, S. Effect of Temperature on the Spread of Contagious Diseases: Evidence from over 2000 Years of Data. Climate 2024, 12, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12120225
Balcilar M, Mukherjee Z, Gupta R, Das S. Effect of Temperature on the Spread of Contagious Diseases: Evidence from over 2000 Years of Data. Climate. 2024; 12(12):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12120225
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalcilar, Mehmet, Zinnia Mukherjee, Rangan Gupta, and Sonali Das. 2024. "Effect of Temperature on the Spread of Contagious Diseases: Evidence from over 2000 Years of Data" Climate 12, no. 12: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12120225
APA StyleBalcilar, M., Mukherjee, Z., Gupta, R., & Das, S. (2024). Effect of Temperature on the Spread of Contagious Diseases: Evidence from over 2000 Years of Data. Climate, 12(12), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli12120225








